sotalol- Sotalol tablet
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Drug Details [pdf]
- N/A - Section Title Not Found In Database
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
To minimize the risk of induced arrhythmia, patients initiated or re-initiated on sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) should be placed for a minimum of three days (on their maintenance dose) in a facility that can provide cardiac resuscitation, continuous electrocardiographic monitoring and calculations of creatinine clearance. For detailed instructions regarding dose selection and special cautions for people with renal impairment, see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION. Sotalol is also indicated for the treatment of documented life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias and is marketed under the brand name BETAPACE®. BETAPACE® however, should not be substituted for sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) because of significant differences in labeling (i.e. patient package insert, dosing administration and safety information).
-
DESCRIPTION
Sotalol hydrochloride, is an antiarrhythmic drug with Class II (beta-adrenoreceptor blocking) and Class III (cardiac action potential duration prolongation) properties. It is supplied as a white, capsule-shaped tablet for oral administration. Sotalol hydrochloride is a white, crystalline solid with a molecular weight of 308.8. It is hydrophilic, soluble in water, propylene glycol and ethanol, but is only slightly soluble in chloroform. Chemically, sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) is d,l-N-[4-[l-hydroxy-2-[(l-methylethyl) amino]ethyl]phenyl]methane-sulfonamide monohydrochloride. The molecular formula is C12H20N2O3SHCl and is represented by the following structural formula:
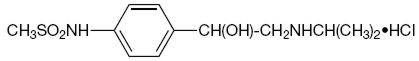
Each tablet contains 80 mg, 120 mg, or 160 mg of sotalol hydrochloride. In addition, each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: anhydrous lactose, colloidal silicon dioxide, corn starch, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, pregelatinized starch, sodium starch glycolate, stearic acid.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Sotalol hydrochloride has both beta-adrenoreceptor blocking (Vaughan Williams Class II) and cardiac action potential duration prolongation (Vaughan Williams Class III) antiarrhythmic properties. Sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) is a racemic mixture of d- and l-sotalol. Both isomers have similar Class III antiarrhythmic effects, while the l-isomer is responsible for virtually all of the beta-blocking activity. The beta-blocking effect of sotalol is non-cardioselective, half maximal at about 80 mg/day and maximal at doses between 320 and 640 mg/day. Sotalol does not have partial agonist or membrane stabilizing activity. Although significant beta-blockade occurs at oral doses as low as 25 mg, significant Class III effects are seen only at daily doses of 160 mg and above.
In children, a Class III electrophysiological effect can be seen at daily doses of 210 mg/m2 body surface area (BSA). A reduction of the resting heart rate due to the beta-blocking effect of sotalol is observed at daily doses ≥ 90 mg/m2 in children.
Electrophysiology
Sotalol hydrochloride prolongs the plateau phase of the cardiac action potential in the isolated myocyte, as well as in isolated tissue preparations of ventricular or atrial muscle (Class III activity). In intact animals it slows heart rate, decreases AV nodal conduction and increases the refractory periods of atrial and ventricular muscle and conduction tissue.
In man, the Class II (beta-blockade) electrophysiological effects of sotalol are manifested by increased sinus cycle length (slowed heart rate), decreased AV nodal conduction and increased AV nodal refractoriness. The Class III electrophysiological effects in man include prolongation of the atrial and ventricular monophasic action potentials, and effective refractory period prolongation of atrial muscle, ventricular muscle, and atrio-ventricular accessory pathways (where present) in both the anterograde and retrograde directions. With oral doses of 160 to 640 mg/day, the surface ECG shows dose-related mean increases of 40-100 msec in QT and 10-40 msec in QTc. In a study of patients with atrial fibrillation (AFIB)/flutter (AFIB/AFL) receiving three different oral doses of sotalol given q12h (or q24h in patients with a reduced creatinine clearance), mean increases in QT intervals measured from 12-lead ECGs of 25 msec, 40 msec and 54 msec were found in the 80 mg, 120 mg and 160 mg dose groups, respectively. (See WARNINGS for description of relationship between QTc and torsade de pointes type arrhythmias.) No significant alteration in QRS interval is observed.
In a small study (n=25) of patients with implanted defibrillators treated concurrently with sotalol the average defibrillatory threshold was 6 joules (range 2-15 joules) compared to a mean of 16 joules for a non-randomized comparative group primarily receiving amiodarone.
In a dose-response trial comparing three dose levels of sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF), 80 mg, 120 mg, and 160 mg with placebo given q12h (or q24h in patients with a reduced renal creatinine clearance) for the prevention of recurrence of symptomatic atrial fibrillation (AFIB)/flutter (AFL), the mean ventricular rate during recurrence of AFIB/AFL was 125, 107, 110 and 99 beats/min in the placebo, 80 mg, 120 mg and 160 mg dose groups, respectively (p < 0.017 for each sotalol dose group versus placebo). In another placebo controlled trial in which sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) was titrated to a dose between 160 and 320 mg/day in patients with chronic AFIB, the mean ventricular rate during recurrence of AFIB was 107 and 84 beats/min in the placebo and sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) groups, respectively (p< 0.001).
Twenty-five children in an unblended, multicenter trial with supraventricular (SVT) and/or ventricular (VT) tachyarrhythmias, aged between 3 days and 12 years (mostly neonates and infants), received an ascending titration regimen with daily doses of 30, 90 and 210 mg/m2 with dosing every 8 hours for a total of 9 doses. During steady-state, the respective average increases above baseline of the QTC interval, in msec (%), were 2 (+1%), 14 (+4%) and 29 (+7%) msec at the 3 dose levels. The respective mean maximum increases above baseline of the QTC interval, in msec (%) were 23 (+6%), 36 (+9%) and 55 (+14%) msec at the 3 dose levels. The steady-state percent increases in the RR interval were 3, 9 and 12%. The smallest children (BSA < 0.33 m2) showed a tendency for larger Class III effects (ΔQTC) and an increased frequency of prolongations of the QTC interval as compared with the larger children (BSA ≥ 0.33 m2). The beta-blocking effects also tended to be greater in the smaller children (BSA < 0.33m2). Both the Class III and beta-blocking effects of sotalol were linearly related with the plasma concentrations.
Hemodynamics
In a study of systemic hemodynamic function measured invasively in 12 patients with a mean LV ejection fraction of 37% and ventricular tachycardia (9 sustained and 3 non-sustained), a median dose of 160 mg twice daily of sotalol produced a 28% reduction in heart rate and a 24% decrease in cardiac index at 2 hours post dosing at steady-state. Concurrently, systemic vascular resistance and stroke volume showed non-significant increases of 25% and 8%, respectively. Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure increased significantly from 6.4 mmHg to 11.8 mmHg in the 11 patients who completed the study. One patient was discontinued because of worsening congestive heart failure. Mean arterial pressure, mean pulmonary artery pressure and stroke work index did not significantly change. Exercise and isoproterenol induced tachycardia are antagonized by sotalol, and total peripheral resistance increases by a small amount.
In hypertensive patients, sotalol produces significant reductions in both systolic and diastolic blood pressures. Although sotalol is usually well-tolerated hemodynamically, caution should be exercised in patients with marginal cardiac compensation as deterioration in cardiac performance may occur. (See WARNINGS: Congestive Heart Failure.).
Clinical Studies
Prolongation of Time to Recurrence of Symptomatic Atrial Fibrillation/Flutter
Sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) has been studied in patients with symptomatic AFIB/AFL in two principal studies, one in patients with primarily paroxysmal AFIB/AFL, the other in patients with primarily chronic AFIB.
In one study, a U.S. multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, dose-response trial of patients with symptomatic primarily paroxysmal AFIB/AFL, three fixed dose levels of sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) (80 mg, 120 mg and 160 mg) twice daily and placebo were compared in 253 patients. In patients with reduced creatinine clearance (40 to 60 mL/min) the same doses were given once daily. Patients were not randomized for the following reasons: QT > 450 msec; creatinine clearance < 40 mL/min; intolerance to beta-blockers; bradycardia-tachycardia syndrome in the absence of an implanted pacemaker; AFIB/AFL was asymptomatic or was associated with syncope, embolic CVA or TIA; acute myocardial infarction within the previous 2 months; congestive heart failure; bronchial asthma or other contraindications to beta-blocker therapy; receiving potassium losing diuretics without potassium replacement or without concurrent use of ACE-inhibitors; uncorrected hypokalemia (serum potassium < 3.5 meq/L) or hypomagnesemia (serum magnesium < 1.5 meq/L); received chronic oral amiodarone therapy for > 1 month within previous 12 weeks; congenital or acquired long QT syndromes; history of torsade de pointes with other antiarrhythmic agents which increase the duration of ventricular repolarization; sinus rate < 50 bpm during waking hours; unstable angina pectoris; receiving treatment with other drugs that prolong the QT interval; and AFIB/AFL associated with the Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome. If the QT interval increased to ≥ 520 msec (or JT ≥ 430 msec if QRS > 100 msec) the drug was discontinued. The patient population in this trial was 64% male, and the mean age was 62 years. No structural heart disease was present in 43% of the patients. Doses were administered once daily in 20% of the patients because of reduced creatinine clearance.
Sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) were shown to prolong the time to the first symptomatic, ECG-documented recurrence of AFIB/AFL, as well as to reduce the risk of such recurrence at both 6 and 12 months. The 120 mg dose was more effective than 80 mg, but 160 mg did not appear to have an added benefit. Note that these doses were given twice or once daily, depending on renal function. The results are shown in Figure 1 and Tables 1 and 2.
Figure 1
Study 1 - Time to First ECG-Documented Recurrence of Symptomatic AFIB/AFL Since Randomization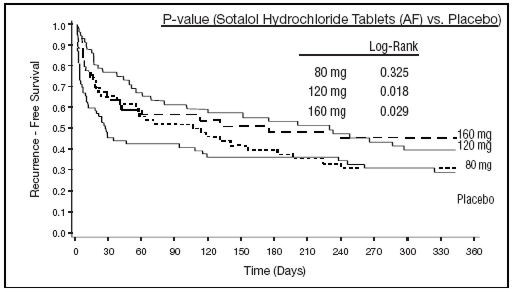
Table 1 Study 1 – Patient Status at 12 Months Sotalol Hydrochloride Tablets (AF) Dose Placebo 80 mg 120 mg 160 mg Please note that columns do not add up to 100% due to discontinuations (D/C) for "other" reasons. - * Symptomatic AFIB/AFL
- † Efficacy endpoint of Study 1; study treatment stopped
Randomized 69 59 63 62 On treatment in NSR at 12 months without recurrence* 23% 22% 29% 23% Recurrence *,† 67% 58% 49% 42% D/C for AEs 6% 12% 18% 29% Table 2 Study 1 – Median Time to Recurrence of Symptomatic Sotalol Hydrochloride Tablets (AF) Dose Placebo 80 mg 120 mg 160 mg AFIB/AFL and Relative Risk (vs. Placebo) at 12 Months p-value vs placebo p=0.325 p=0.018 p=0.029 Relative Risk (RR) to placebo 0.81 0.59 0.59 Median time to recurrence (days) 27 106 229 175 Discontinuation because of adverse events was dose related.
In a second multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study of 6 months duration in 232 patients with chronic AFIB, sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) was titrated over a dose range from 80 mg/day to 320 mg/day. The patient population of this trial was 70% male with a mean age of 65 years. Structural heart disease was present in 49% of the patients. All patients had chronic AFIB for > 2 weeks but < 1 year at entry with a mean duration of 4.1 months. Patients were excluded if they had significant electrolyte imbalance, QTc> 460 msec, QRS > 140 msec, any degree of AV block or functioning pacemaker, uncompensated cardiac failure, asthma, significant renal disease (estimated creatinine clearance < 50 mL/min), heart rate < 50 bpm, myocardial infarction or open heart surgery in past 2 months, unstable angina, infective endocarditis, active pericarditis or myocarditis, ≥ 3 DC cardioversions in the past, medications that prolonged QT interval, and previous amiodarone treatment. After successful cardioversion patients were randomized to receive placebo (n=114) or sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) (n=118) at a starting dose of 80 mg twice daily. If the initial dose was not tolerated it was decreased to 80 mg once daily, but if it was tolerated it was increased to 160 mg twice daily. During the maintenance period 67% of treated patients received a dose of 160 mg twice daily, and the remainder received doses of 80 mg once daily (17%) and 80 mg twice daily (16%).
Figure 2 and Tables 3 and 4 show the results of the trial. There was a longer time to ECG-documented recurrence of AFIB and a reduced risk of recurrence at 6 months compared to placebo.
Figure 2
Study 2 - Time to First ECG-Documented Recurrence of Symptomatic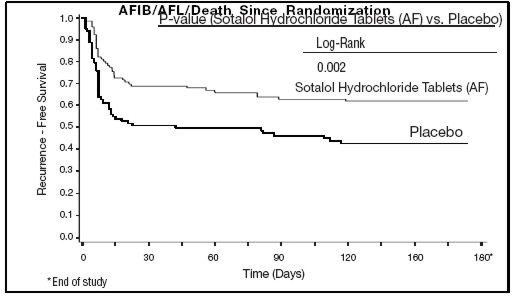
Table 3 Sotalol Hydrochloride Tablets (AF) Placebo Study 2 - Patient Status at 6 Months - * Symptomatic or asymptomatic AFIB/AFL
- † Efficacy endpoint of Study 2; study treatment stopped
Randomized 118 114 On treatment in NSR at 6 months without recurrence* 45% 29% Recurrence*,† 49% 67% D/C for AEs 6% 3% Death 1% Table 4 Study 2 – Median Time to Recurrence of Symptomatic AFIB/AFL/Death and Relative Risk (vs. Placebo) at 6 Months Sotalol Hydrochloride Tablets (AF) Placebo p-value vs placebo p=0.002 Relative Risk (RR) to placebo 0.55 Median time to recurrence (days) > 180 44 Safety in Patients with Structural Heart Disease
In a multicenter double-blind randomized study reported by D. Julian et al, the effect of sotalol 320 mg once daily was compared with that of placebo in 1456 patients (randomized 3:2, sotalol to placebo) surviving an acute myocardial infarction (MI). Treatment was started 5 to 14 days after infarction. Patients were followed for 12 months. The mortality rate was 7.3% in the sotalol group and 8.9% in the placebo group, not a statistically significant difference. Although the results do not show evidence of a benefit of sotalol in this population, they do not show an added risk in post MI patients receiving sotalol.
Pharmacokinetics
In healthy subjects, the oral bioavailability of sotalol is 90 to 100%. After oral administration, peak plasma concentrations are reached in 2.5 to 4 hours, and steady-state plasma concentrations are attained within 2 to 3 days (i.e., after 5 to 6 doses when administered twice daily). Over the dosage range 160 to 640 mg/day sotalol displays dose proportionality with respect to plasma concentrations. Distribution occurs to a central (plasma) and to a peripheral compartment, with a mean elimination half-life of 12 hours. Dosing every 12 hours results in trough plasma concentrations which are approximately one-half of those at peak.
Sotalol does not bind to plasma proteins and is not metabolized. Sotalol shows very little intersubject variability in plasma levels. The pharmacokinetics of the d and l enantiomers of sotalol are essentially identical. Sotalol crosses the blood brain barrier poorly. Excretion is predominantly via the kidney in the unchanged form, and therefore lower doses are necessary in conditions of renal impairment (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION). Age per se does not significantly alter the pharmacokinetics of sotalol, but impaired renal function in geriatric patients can increase the terminal elimination half-life, resulting in increased drug accumulation. The absorption of sotalol was reduced by approximately 20% compared to fasting when it was administered with a standard meal. Since sotalol is not subject to first-pass metabolism, patients with hepatic impairment show no alteration in clearance of sotalol.
The combined analyses of two unblended, multicenter trials (a single dose and a multiple dose study) with 59 children, aged between 3 days and 12 years, showed the pharmacokinetics of sotalol to be first order. A daily dose of 30 mg/m2 of sotalol was administered in the single dose study and daily doses of 30, 90 and 210 mg/m2 were administered q8h in the multi-dose study. After rapid absorption with peak levels occurring on average between 2 to 3 hours following administration, sotalol was eliminated with a mean half-life of 9.5 hours. Steady-state was reached after 1 to 2 days. The average peak to trough concentration ratio was 2. BSA was the most important covariate and more relevant than age for the pharmacokinetics of sotalol. The smallest children (BSA < 0.33 m2) exhibited a greater drug exposure (+59%) than the larger children who showed a uniform drug concentration profile. The intersubject variation for oral clearance was 22%.
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) are indicated for the maintenance of normal sinus rhythm [delay in time to recurrence of atrial fibrillation/atrial flutter (AFIB/AFL)] in patients with symptomatic AFIB/AFL who are currently in sinus rhythm. Because sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) can cause life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias, it should be reserved for patients in whom AFIB/AFL is highly symptomatic. Patients with paroxysmal AFIB/AFL that is easily reversed (by Valsalva maneuver, for example) should usually not be given sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) (See WARNINGS).
In general, antiarrhythmic therapy for AFIB/AFL aims to prolong the time in normal sinus rhythm. Recurrence is expected in some patients (See CLINICAL STUDIES).
Sotalol is also indicated for the treatment of documented life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias and is marketed under the brand name BETAPACE® (sotalol hydrochloride). BETAPACE®, however, must not be substituted for sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) because of significant differences in labeling (i.e. patient package insert, dosing administration and safety information).
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Sotalol hydrochloride tablets is contraindicated in patients with sinus bradycardia (< 50 bpm during waking hours), sick sinus syndrome or second and third degree AV block (unless a functioning pacemaker is present), congenital or acquired long QT syndromes, baseline QT interval > 450 msec, cardiogenic shock, uncontrolled heart failure, hypokalemia (< 4 meq/L), creatinine clearance < 40 mL/min, bronchial asthma and previous evidence of hypersensitivity to sotalol.
-
WARNINGS
Ventricular Arrhythmia
Sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) can cause serious ventricular arrhythmias, primarily torsade de pointes (tdp) type ventricular tachycardia, a polymorphic ventricular tachycardia associated with QT interval prolongation. QT interval prolongation is directly related to the dose of sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF). Factors such as reduced creatinine clearance, gender (female) and larger doses increase the risk of tdp. The risk of tdp can be reduced by adjustment of the sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) dose according to creatinine clearance and by monitoring the ECG for excessive increases in the QT interval.
Treatment with sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) must therefore be started only in patients observed for a minimum of three days on their maintenance dose in a facility that can provide electrocardiographic monitoring and in the presence of personnel trained in the management of serious ventricular arrhythmias. Calculation of the creatinine clearance must precede administration of the first dose of sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF). For detailed instructions regarding dose selection, see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.
Proarrhythmia in Atrial Fibrillation/Atrial Flutter Patients
In eight controlled trials of patients with AFIB/AFL and other supraventricular arrhythmias (N=659) there were four cases of torsade de pointes reported (0.6%) during the controlled phase of treatment with sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF). The incidence of torsade de pointes was significantly lower in those patients receiving total daily doses of 320 mg or less (0.3%), as summarized in Table 5 below. Both patients who had torsade de pointes in the group receiving > 320 mg/day were receiving 640 mg/day. In the group receiving ≤ 320 mg daily, one case of tdp occurred at a daily dose of 320 mg on day 4 of treatment and one case occurred on a daily dose of 160 mg on day 1 of treatment.
Table 5 Incidence of Torsade de Pointes in Controlled Trials of AFIB and Other Supraventricular Arrhythmias SOTALOL HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS (AF) (DAILY DOSE) Any Dose
(N=659)> 320 mg/day
(N=62)≤ 320 mg/day
(N=597)≤ 240 mg/day
(N=340)Placebo
(N=358)n(%) n(%) n(%) n(%) n(%) Torsade de pointes 4 (0.6%) 2 (3.2%) 2 (0.3%) 1 (0.3%) 0 Prolongation of the QT interval is dose related, increasing from baseline an average of 25, 40, and 50 msec in the 80, 120, and 160 mg groups, respectively, in the clinical dose-response study. In this clinical trial sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) treatment was not initiated if the QT interval was greater than 450 msec and during therapy the dose was reduced or discontinued if the QT interval was ≥ 520 msec.
Experience in patients with ventricular arrhythmias is also pertinent to the risk of torsade de pointes in patients with AFIB/AFL (see below).
Proarrhythmia in Ventricular Arrhythmia Patients: [see Sotalol Hydrochloride Package Insert]
In patients with a history of sustained ventricular tachycardia, the incidence of torsade de pointes during sotalol treatment was 4% and worsened VT in about 1%; in patients with other less serious ventricular arrhythmias the incidence of torsade de pointes was 1% and new or worsened VT in about 0.7%. Additionally, in approximately 1% of patients, deaths were considered possibly drug related; such cases, although difficult to evaluate, may have been associated with proarrhythmic events.
Torsade de pointes arrhythmias in patients with VT/VF were dose related, as was the prolongation of QT (QTc) interval, as shown in Table 6 below.
Table 6 Percent Incidence of Torsade de Pointes and Mean QTc Interval by Dose For Patients With Sustained VT/VF Daily Dose (mg) Incidence of torsade de pointes Mean QTc*(msec) ( ) Number of patients assessed - * highest on-therapy value
80 0 (69) 463 (17) 160 0.5 (832) 467 (181) 320 1.6 (835) 473 (344) 480 4.4 (459) 483 (234) 640 3.7 (324) 490 (185) > 640 5.8 (103) 512 (62) Table 7 below relates the incidence of torsade de pointes to on-therapy QTc and change in QTc from baseline. It should be noted, however, that the highest on-therapy QTc was in many cases the one obtained at the time of the torsade de pointes event, so that the table overstates the predictive value of a high QTc.
Table 7 Relationship Between QTc Interval Prolongation and torsade de pointes On-Therapy QTc Interval (msec) Incidence of Torsade de Pointes Change in QTc Interval From Baseline (msec) Incidence of Torsade de Pointes ( ) Number of patients assessed less than 500 1.3% (1787) less than 65 1.6% (1516) 500-525 3.4% (236) 65-80 3.2% (158) 525-550 5.6% (125) 80-100 4.1% (146) > 550 10.8% (157) 100-130 5.2% (115) > 130 7.1% (99) In addition to dose and presence of sustained VT, other risk factors for torsade de pointes were gender (females had a higher incidence), excessive prolongation of the QTc interval and history of cardiomegaly or congestive heart failure. Patients with sustained ventricular tachycardia and a history of congestive heart failure appear to have the highest risk for serious proarrhythmia (7%). Of the ventricular arrhythmia patients experiencing torsade de pointes, approximately two-thirds spontaneously reverted to their baseline rhythm. The others were either converted electrically (D/C cardioversion or overdrive pacing) or treated with other drugs (see OVERDOSAGE). It is not possible to determine whether some sudden deaths represented episodes of torsade de pointes, but in some instances sudden death did follow a documented episode of torsade de pointes. Although sotalol therapy was discontinued in most patients experiencing torsade de pointes, 17% were continued on a lower dose.
Use with Drugs that Prolong QT Interval and Antiarrhythmic Agents
The use of sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) in conjunction with other drugs that prolong the QT interval has not been studied and is not recommended. Such drugs include many antiarrhythmics, some phenothiazines, bepridil, tricyclic antidepressants, and certain oral macrolides. Class I or Class III antiarrhythmic agents should be withheld for at least three half-lives prior to dosing with sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF). In clinical trials, sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) was not administered to patients previously treated with oral amiodarone for > 1 month in the previous three months. Class Ia antiarrhythmic drugs, such as disopyramide, quinidine and procainamide and other Class III drugs (e.g., amiodarone) are not recommended as concomitant therapy with sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF), because of their potential to prolong refractoriness (see WARNINGS). There is only limited experience with the concomitant use of Class Ib or Ic antiarrhythmics.
Congestive Heart Failure
Sympathetic stimulation is necessary in supporting circulatory function in congestive heart failure, and beta-blockade carries the potential hazard of further depressing myocardial contractility and precipitating more severe failure. In patients who have heart failure controlled by digitalis and/or diuretics, sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) should be administered cautiously. Both digitalis and sotalol slow AV conduction. As with all beta-blockers, caution is advised when initiating therapy in patients with any evidence of left ventricular dysfunction. In a pooled data base of four placebo-controlled AFIB/AFL and PSVT studies, new or worsening CHF occurred during therapy with sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) in 5 (1.2%) of 415 patients. In these studies patients with uncontrolled heart failure were excluded (i.e. NYHA Functional Classes III or IV). In other premarketing sotalol studies, new or worsened congestive heart failure (CHF) occurred in 3.3% (n=3257) of patients and led to discontinuation in approximately 1% of patients receiving sotalol. The incidence was higher in patients presenting with sustained ventricular tachycardia/fibrillation (4.6%, n=1363), or a prior history of heart failure (7.3%, n=696). Based on a life-table analysis, the one-year incidence of new or worsened CHF was 3% in patients without a prior history and 10% in patients with a prior history of CHF. NYHA Classification was also closely associated to the incidence of new or worsened heart failure while receiving sotalol (1.8% in 1395 Class I patients, 4.9% in 1254 Class II patients and 6.1% in 278 Class III or IV patients).
Electrolyte Disturbances
Sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) should not be used in patients with hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia prior to correction of imbalance, as these conditions can exaggerate the degree of QT prolongation, and increase the potential for torsade de pointes. Special attention should be given to electrolyte and acid-base balance in patients experiencing severe or prolonged diarrhea or patients receiving concomitant diuretic drugs.
Bradycardia/Heart Block
The incidence of bradycardia (as determined by the investigators) in the supraventricular arrhythmia population treated with sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) (N = 415) was 13%, and led to discontinuation in 2.4% of patients. Bradycardia itself increases the risk of torsade de pointes.
Recent Acute MI
Sotalol has been used in a controlled trial following an acute myocardial infarction without evidence of increased mortality (see Safety in Patients with Structural Heart Disease). Although specific studies of its use in treating atrial arrhythmias after infarction have not been conducted, the usual precautions regarding heart failure, avoidance of hypokalemia, bradycardia or prolonged QT interval apply.
The following warnings are related to the beta-blocking activity of sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF).
Abrupt Withdrawal
Hypersensitivity to catecholamines has been observed in patients withdrawn from beta-blocker therapy. Occasional cases of exacerbation of angina pectoris, arrhythmias and, in some cases, myocardial infarction have been reported after abrupt discontinuation of beta-blocker therapy. Therefore, it is prudent when discontinuing chronically administered sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF), particularly in patients with ischemic heart disease, to carefully monitor the patient and consider the temporary use of an alternate beta-blocker if appropriate. If possible, the dosage of sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) should be gradually reduced over a period of one to two weeks. If angina or acute coronary insufficiency develops, appropriate therapy should be instituted promptly. Patients should be warned against interruption or discontinuation of therapy without the physician's advice. Because coronary artery disease is common and may be unrecognized in patients receiving sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF), abrupt discontinuation in patients with arrhythmias may unmask latent coronary insufficiency.
Non-Allergic Bronchospasm (e.g., chronic bronchitis and emphysema)
PATIENTS WITH BRONCHOSPASTIC DISEASES SHOULD IN GENERAL NOT RECEIVE BETA-BLOCKERS. It is prudent, if sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) is to be administered, to use the smallest effective dose, so that inhibition of bronchodilation produced by endogenous or exogenous catecholamine stimulation of beta2 receptors may be minimized.
Anaphylaxis
While taking beta-blockers, patients with a history of anaphylactic reaction to a variety of allergens may have a more severe reaction on repeated challenge, either accidental, diagnostic or therapeutic. Such patients may be unresponsive to the usual doses of epinephrine used to treat the allergic reaction.
Anesthesia
The management of patients undergoing major surgery who are being treated with beta-blockers is controversial. Protracted severe hypotension and difficulty in restoring and maintaining normal cardiac rhythm after anesthesia have been reported in patients receiving beta-blockers.
Diabetes
In patients with diabetes (especially labile diabetes) or with a history of episodes of spontaneous hypoglycemia, sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) should be given with caution since beta-blockade may mask some important premonitory signs of acute hypoglycemia; e.g., tachycardia.
Sick Sinus Syndrome
Sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) should be used only with extreme caution in patients with sick sinus syndrome associated with symptomatic arrhythmias, because it may cause sinus bradycardia, sinus pauses or sinus arrest. In patients with AFIB and sinus node dysfunction, the risk of torsade de pointes with sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) therapy is increased, especially after cardioversion. Bradycardia following cardioversion in these patients is associated with QTc interval prolongation which is augmented due to the reverse use dependence of the Class III effects of sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF). Patients with AFIB/AFL associated with the sick sinus syndrome may be treated with sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) if they have an implanted pacemaker for control of bradycardia symptoms.
Thyrotoxicosis
Beta-blockade may mask certain clinical signs (e.g., tachycardia) of hyperthyroidism. Patients suspected of developing thyrotoxicosis should be managed carefully to avoid abrupt withdrawal of beta-blockade which might be followed by an exacerbation of symptoms of hyperthyroidism, including thyroid storm. The beta-blocking effects of sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) may be useful in controlling heart rate in AFIB associated with thyrotoxicosis but no study has been conducted to evaluate this.
-
PRECAUTIONS
Renal Impairment
Sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) is eliminated principally via the kidneys through glomerular filtration and to a small degree by tubular secretion. There is a direct relationship between renal function, as measured by serum creatinine or creatinine clearance, and the elimination rate of sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF). Guidance for dosing in conditions of renal impairment can be found under "DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION."
Information for Patients
Please refer to the patient package insert.
Prior to initiation of sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) therapy, the patient should be advised to read the patient package insert and reread it each time therapy is renewed. The patient should be fully instructed on the need for compliance with the recommended dosing of sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF), the potential interactions with drugs that prolong the QT interval and other antiarrhythmics, and the need for periodic monitoring of QT and renal function to minimize the risk of serious abnormal rhythms.
Medications and Supplements
Assessment of patients' medication history should include all over-counter, prescription and herbal/natural preparations with emphasis on preparations that may affect the pharmacodynamics of sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) such as other cardiac antiarrhythmic drugs, some phenothiazines, bepridil, tricyclic antidepressants and oral macrolides (see WARNINGS and Use With Drugs That Prolong QT Interval and Antiarrhythmic Agents). Patients should be instructed to notify their health care providers of any change in over-the-counter, prescription or supplement use. If a patient is hospitalized or is prescribed a new medication for any condition, the patient must inform the health care provider of ongoing sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) therapy. Patients should also check with their health care provider and/or pharmacist prior to taking a new over-the-counter medicine.
Drug Interactions
Drugs undergoing CYP450 metabolism
Sotalol is primarily eliminated by renal excretion; therefore, drugs that are metabolized by CYP450 are not expected to alter the pharmacokinetics of sotalol.
Digoxin
Proarrhythmic events were more common in sotalol treated patients also receiving digoxin; it is not clear whether this represents an interaction or is related to the presence of CHF, a known risk factor for proarrhythmia, in the patients receiving digoxin.
Calcium blocking drugs
Sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) should be administered with caution in conjunction with calcium blocking drugs because of possible additive effects on atrioventricular conduction or ventricular function. Additionally, concomitant use of these drugs may have additive effects on blood pressure, possibly leading to hypotension.
Catecholamine-depleting agents
Concomitant use of catecholamine-depleting drugs, such as reserpine and guanethidine, with a beta-blocker may produce an excessive reduction of resting sympathetic nervous tone. Patients treated with sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) plus a catecholamine depletor should therefore be closely monitored for evidence of hypotension and/or marked bradycardia which may produce syncope.
Insulin and oral antidiabetics
Hyperglycemia may occur, and the dosage of insulin or antidiabetic drugs may require adjustment. Symptoms of hypoglycemia may be masked.
Beta-2-receptor stimulants
Beta-agonists such as salbutamol, terbutaline and isoprenaline may have to be administered in increased dosages when used concomitantly with sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF).
Clonidine
Beta-blocking drugs may potentiate the rebound hypertension sometimes observed after discontinuation of clonidine; therefore, caution is advised when discontinuing clonidine in patients receiving sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF).
Antacids
Administration of sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) within 2 hours of antacids containing aluminum oxide and magnesium hydroxide should be avoided because it may result in a reduction in Cmax and AUC of 26% and 20%, respectively and consequently in a 25% reduction in the bradycardic effect at rest. Administration of the antacid two hours after sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) has no effect on the pharmacokinetics or pharmacodynamics of sotalol.
Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
The presence of sotalol in the urine may result in falsely elevated levels of urinary metanephrine when measured by fluorimetric or photometric methods. In screening patients suspected of having a pheochromocytoma and being treated with sotalol, a specific method, such as a high performance liquid chromatographic assay with solid phase extraction (e.g., J. Chromatogr. 385:241, 1987) should be employed in determining levels of catecholamines.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No evidence of carcinogenic potential was observed in rats during a 24-month study at 137 to 275 mg/kg/day (approximately 30 times the maximum recommended human oral dose (MRHD) as mg/kg or 5 times the MRHD as mg/m2) or in mice, during a 24-month study at 4141 to 7122 mg/kg/day (approximately 450 to 750 times the MRHD as mg/kg or 36 to 63 times the MRHD as mg/m2).
Sotalol has not been evaluated in any specific assay of mutagenicity or clastogenicity.
No significant reduction in fertility occurred in rats at oral doses of 1000 mg/kg/day (approximately 100 times the MRHD as mg/kg or 9 times the MRHD as mg/m2) prior to mating, except for a small reduction in the number of offspring per litter.
Pregnancy Category B
Reproduction studies in rats and rabbits during organogenesis at 100 and 22 times the MRHD as mg/kg (9 and 7 times the MRHD as mg/m2), respectively, did not reveal any teratogenic potential associated with sotalol HCl. In rabbits, a high dose of sotalol HCl (160 mg/kg/day) at 16 times the MRHD as mg/kg (6 times the MRHD as mg/m2) produced a slight increase in fetal death likely due to maternal toxicity. Eight times the maximum dose (80 mg/kg/day or 3 times the MRHD as mg/m2) did not result in an increased incidence of fetal deaths. In rats, 1000 mg/kg/day sotalol HCl, 100 times the MRHD (18 times the MRHD as mg/m2), increased the number of early resorptions, while at 14 times the maximum dose (2.5 times the MRHD as mg/m2), no increase in early resorptions was noted. However, animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response.
Although there are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women, sotalol HCl has been shown to cross the placenta, and is found in amniotic fluid. There has been a report of subnormal birth weight with sotalol. Therefore, sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit outweighs the potential risk.
Nursing Mothers
Sotalol is excreted in the milk of laboratory animals and has been reported to be present in human milk. Because of the potential for adverse reactions in nursing infants from sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF), a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Adverse events that are clearly related to sotalol are those which are typical of its Class II (beta-blocking) and Class III (cardiac action potential duration prolongation) effects. The common documented beta-blocking adverse events (bradycardia, dyspnea, and fatigue) and Class III effects (QT interval prolongation) are dose related.
In a pooled clinical trial population consisting of four placebo-controlled studies with 275 patients with AFIB/AFL treated with 160 to 320 mg doses of sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF), the following adverse events were reported at a rate of 2% or more in the 160 to 240 mg treated patients and greater than the rate in placebo patients (see Table 8). The data are presented by incidence of events in the sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) and placebo groups by body system and daily dose. No significant irreversible non-cardiac end-organ toxicity was observed.
Table 8 Incidence (%) of Common Adverse Events (≥ 2% in the 160 to 240 mg group and more frequent than on placebo) in Four Placebo-Controlled Studies of Patients with AFIB/AFL Placebo Sotalol HCl Tablets (AF)
Total Daily Dose(mg)Body System/ Adverse Event (Preferred Term) N=282 160 – 240
N=153> 240 – 320
N=122CARDIOVASCULAR Abnormality ECG 0.4 3.3 2.5 Angina Pectoris 1.1 2.0 1.6 Bradycardia 2.5 13.1 12.3 Chest pain Cardiac/Non-Anginal 4.6 4.6 2.5 Disturbance Rhythm Atrial 2.1 2.0 1.6 Disturbance Rhythm Subjective 9.9 9.8 7.4 GASTROINTESTINAL Appetite Decreased 0.4 2.0 1.6 Diarrhea 2.1 5.2 5.7 Distention Abdomen 0.4 0.7 2.5 Dyspepsia/Heartburn 1.8 2.0 2.5 Nausea/Vomiting 5.3 7.8 5.7 Pain Abdomen 2.5 3.9 2.5 GENERAL Fatigue 8.5 19.6 18.9 Fever 0.7 0.7 3.3 Hyperhidrosis 3.2 5.2 4.9 Influenza 0.4 2.0 0.8 Sensation Cold 0.7 2.0 2.5 Weakness 3.2 5.2 4.9 MUSCULOSKELETAL/CONNECTIVE TISSUE Pain Chest Musculoskeletal 1.4 2.0 2.5 Pain Musculoskeletal 2.8 2.6 4.1 NERVOUS SYSTEM Dizziness 12.4 16.3 13.1 Headache 5.3 3.3 11.5 Insomnia 1.1 2.6 4.1 RESPIRATORY Cough 2.5 3.3 2.5 Dyspnea 7.4 9.2 9.8 Infection Upper Respiratory 1.1 2.6 3.3 Tracheobronchitis 0.7 0.7 3.3 SPECIAL SENSES Disturbance Vision 0.7 2.6 0.8 Overall, discontinuation because of unacceptable adverse events was necessary in 17% of the patients, and occurred in 10% of patients less than two weeks after starting treatment. The most common adverse events leading to discontinuation of sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) were: fatigue 4.6%, bradycardia 2.4%, proarrhythmia 2.2%, dyspnea 2%, and QT interval prolongation 1.4%.
In clinical trials involving 1292 patients with sustained VT/VF, the common adverse events (occurring in ≥ 2% of patients) were similar to those described for the AFIB/AFL population.
Occasional reports of elevated serum liver enzymes have occurred with sotalol therapy but no cause and effect relationship has been established. One case of peripheral neuropathy, which resolved on discontinuation of sotalol and recurred when the patient was rechallenged with the drug, was reported in an early dose tolerance study. Elevated blood glucose levels and increased insulin requirements can occur in diabetic patients.
In an unblinded multicenter trial of 25 pediatric patients with SVT and/or VT receiving daily doses of 30, 90 and 210 mg/m2 with dosing every 8 hours for a total of 9 doses, no torsade de pointes or other serious new arrhythmias were observed. One (1) patient, receiving 30 mg/m2 daily, was discontinued because of increased frequency of sinus pauses/bradycardia. Additional cardiovascular AEs were seen at the 90 and 210 mg/m2 daily dose levels. They included QT prolongations (2 patients), sinus pauses/bradycardia (1 patient), increased severity of atrial flutter and reported chest pain (1 patient). Values for QTc≥ 525 msec were seen in 2 patients at the 210 mg/m2 daily dose level. Serious adverse events including death, torsades de pointe, other proarrhythmias, high-degree A-V blocks and bradycardia have been reported in infants and/or children.
Potential Adverse Effects
Foreign marketing experience with sotalol hydrochloride shows an adverse experience profile similar to that described above from clinical trials. Voluntary reports since introduction also include rare reports of: emotional lability, slightly clouded sensorium, incoordination, vertigo, paralysis, thrombocytopenia, eosinophilia, leukopenia, photosensitivity reaction, fever, pulmonary edema, hyperlipidemia, myalgia, pruritus, alopecia.
The oculomucocutaneous syndrome associated with the beta-blocker practolol has not been associated with sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) during investigational use and foreign marketing experience.
-
OVERDOSAGE
Intentional or accidental overdosage with sotalol has rarely resulted in death.
Symptoms and Treatment of Overdosage
The most common signs to be expected are bradycardia, congestive heart failure, hypotension, bronchospasm and hypoglycemia. In cases of massive intentional overdosage (2 to 16 grams) of sotalol the following clinical findings were seen: hypotension, bradycardia, cardiac asystole, prolongation of QT interval, torsade de pointes, ventricular tachycardia, and premature ventricular complexes. If overdosage occurs, therapy with sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) should be discontinued and the patient observed closely. Because of the lack of protein binding, hemodialysis is useful for reducing sotalol plasma concentrations. Patients should be carefully observed until QT intervals are normalized and the heart rate returns to levels > 50 bpm. The occurrence of hypotension following an overdose may be associated with an initial slow drug elimination phase (half life of 30 hours) thought to be due to a temporary reduction of renal function caused by the hypotension. In addition, if required, the following therapeutic measures are suggested:
Bradycardia or Cardiac Asystole: Atropine, another anticholinergic drug, a beta-adrenergic agonist or transvenous cardiac pacing. Heart Block: (second and third degree) transvenous cardiac pacemaker. Hypotension: (depending on associated factors) epinephrine rather than isoproterenol or norepinephrine may be useful. Bronchospasm: Aminophylline or aerosol beta-2-receptor stimulant. Torsade de Pointes: DC cardioversion, transvenous cardiac pacing, epinephrine, magnesium sulfate. -
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Dosing and Administration in Adults
- Therapy with sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) must be initiated (and, if necessary, titrated) in a setting that provides continuous electrocardiographic (ECG) monitoring and in the presence of personnel trained in the management of serious ventricular arrhythmias. Patients should continue to be monitored in this way for a minimum of 3 days on the maintenance dose. In addition, patients should not be discharged within 12 hours of electrical or pharmacological conversion to normal sinus rhythm.
- The QT interval is used to determine patient eligibility for sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) treatment and for monitoring safety during treatment. The baseline QT interval must be ≤ 450 msec in order for a patient to be started on sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) therapy. During initiation and titration, the QT interval should be monitored 2 to 4 hours after each dose. If the QT interval prolongs to 500 msec or greater, the dose must be reduced or the drug discontinued.
- The dose of sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) must be individualized according to creatinine clearance. In patients with a creatinine clearance > 60 mL/min sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) is administered twice daily (QD) while in those with a creatinine clearance between 40 and 60 mL/min, the dose is administered once daily (QD) or half the dose is administered twice daily (BID). In patients with a creatinine clearance less than 40 mL/min sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) is contraindicated. The recommended initial dose of sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) is 80 mg and is initiated as shown in the dosing algorithm described below. The 80 mg dose can be titrated upward to 100mg or 120 mg during initial hospitalization or after discharge on 80 mg in the event of recurrence, by rehospitalization and repeating the same steps used during the initiation of therapy (see Upward Titration of Dose).
- Patients with atrial fibrillation should be anticoagulated according to usual medical practice. Hypokalemia should be corrected before initiation of sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) therapy (see WARNINGS, Ventricular Arrhythmia).
- In patients with a creatinine clearance between 40 and 60 mL/min the initial daily dose is 80mg. The initial daily dose of 80 mg can be administered once daily (QD) and can be titrated up to 100 or 120 mg once daily (QD) or can be administered as 40 mg twice daily (BID) and can be titrated up to 60 mg BID.
- Patients to be discharged on sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) therapy from an in-patient setting should have an adequate supply of sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) to allow uninterrupted therapy until the patient can fill a sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) prescription.
Initiation of Sotalol Hydrochloride Tablets (AF) Therapy
Step 1. Electrocardiographic assessment: Prior to administration of the first dose, the QT interval must be determined using an average of 5 beats. If the baseline QT is greater than 450 msec (JT ≥ 330 msec if QRS over 100 msec), sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) is contraindicated.
Step 2: Calculation of creatinine clearance: Prior to the administration of the first dose, the patient's creatinine clearance should be calculated using the following formula:
creatinine clearance (male) = (140-age) × body weight in kg
72 × serum creatinine (mg/dL)creatinine clearance (female) = (140-age) × body weight in kg × 0.85
72 × serum creatinine (mg/dL)When serum creatinine is given in µmol/L, divide the value by 88.4 (1 mg/dL = 88.4 µmol/L)
Step 3. Starting Dose: The starting dose of sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) is 80 mg twice daily (BID) if the creatinine clearance is > 60 mL/min, and 80 mg once daily (QD) or 40mg twice daily (BID) if the creatinine clearance is 40 to 60 mL/min. If the creatinine clearance is < 40 mL/min sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) are contraindicated.
Step 4. Administer the appropriate daily dose of sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) and begin continuous ECG monitoring with QT interval measurements 2 to 4 hours after each dose.
Step 5. In patients with a creatinine clearance > 60 mL/min, if the 80 mg dose level is tolerated and the QT interval remains < 500 msec after at least 3 days, the patient can be discharged. Alternatively, during hospitalization, the dose can be increased to 100 mg or 120 mg BID and the patient followed for 3 days on this dose.
In patients with a creatinine clearance of 40 to 60 mL/min, if the 80 mg daily dose (administered as 80 mg QD or 40 mg BID) is tolerated and the QT interval remains <500 msec after 5 or 6 days, the patient can be discharged. Alternatively, during hospitalization, the dose can be increased from 80 mg QD to 100 mg or 120 mg QD, or from 40 mg BID to 60 mg BID and the patient followed for 5 or 6 days on the dose.
The steps described above are summarized in the following diagram:
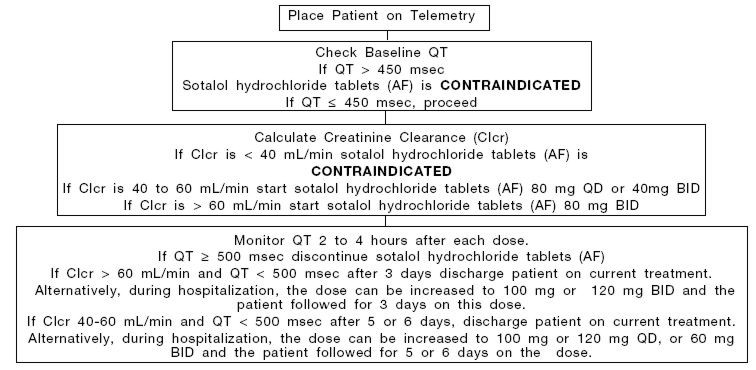
Upward Titration of Dose
In patients with Clcr > 60 mL/min, if the 80 mg dose level (given BID) does not reduce the frequency of relapses of AFIB/AFL and is tolerated without excessive QT interval prolongation (i.e. ≥ 520 msec), the dose level may be increased to 100 mg or 120 mg BID. In patients with Clcr 40-60 mL/min, if the daily dose of 80 mg (given as QD or 40 mg BID) does not reduce the frequency of relapses of AFIB/AFL and is tolerated without excessive QT prolongation (i.e. ≥ 520 msec), the dose level may be increased to 100 mg or 120 mg QD or 60 mg BID. As proarrhythmic events can occur not only at initiation of therapy, but also with each upward dosage adjustment, Steps 2 through 5 used during initiation of sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) therapy should be followed when increasing the dose level. In the U.S. multicenter dose-response study, the 120 mg dose (BID or QD) was found to be the most effective in prolonging the time to ECG documented symptomatic recurrence of AFIB/AFL. If, in patients with Clcr > 60 mL/min, the 120 mg BID dose does not reduce the frequency of early relapse of AFIB/AFL and is tolerated without excessive QT interval prolongation (≥520 msec), an increase to 160 mg BID can be considered. If, in patients with Clcr 40 – 60 mL/min, the 120 mg QD or 60 mg BID does not reduce the frequency of early relapse of AFIB/AFL and is tolerated without excessive QT interval prolongation (i.e. ≥ 520 msec), an increase to 160 mg QD or 80 mg BID can be considered. Steps 2 through 5 used during the initiation of therapy should be used again to introduce such an increase.
Maintenance of Sotalol Hydrochloride Tablets (AF) Therapy
Renal function and QT should be reevaluated regularly if medically warranted. If QT is 520 msec or greater (JT 430 msec or greater if QRS is > 100 msec), the dose of sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) therapy should be reduced and patients should be carefully monitored until QT returns to less than 520 msec. If the QT interval is ≥ 520 msec while on the lowest maintenance dose level (80 mg BID in patients with Clcr > 60 mL/min, 80 mg QD or 40 mg BID in patients with Clcr 40 – 60 mL/min) the drug should be discontinued. If renal function deteriorates, reduce the daily dose in half by administering the drug once daily at the same dose level or twice daily at half the dose as described in Initiation of Sotalol Hydrochloride Tablets (AF) Therapy, Step 3. If the creatinine clearance decreases to < 40 mL/min, treatment with sotalol hydrochloride (AF) should be discontinued.
Special Considerations
The maximum recommended dose in patients with a calculated creatinine clearance greater than 60 mL/min is 160 mg BID, doses greater than 160 mg BID have been associated with an increased incidence of torsade de pointes and are not recommended.
A patient who misses a dose should NOT double the next dose. The next dose should be taken at the usual time.
Dosing and Administration in Pediatric Patients
As in adults the following precautionary measures should be considered when initiating sotalol treatment in children: initiation of treatment in the hospital after appropriate clinical assessment: individualization regimen as appropriate: gradual increase of doses if required: careful assessment of therapeutic response and tolerability: and frequent monitoring of the QTc interval heart rate.
For children aged about 2 years and greater with normal renal function, doses normalized for body surface area are appropriate for both initial and incremental dosing. Since the Class III potency in children (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY) is not very different from that in adults, reaching plasma concentrations that occur within the adult dose range is an appropriate guide. From pediatric pharmacokinetic data the following is recommended.
For initiation of treatment, 30 mg/m2 three times a day (90 mg/m2 total daily dose) is approximately equivalent to the initial 160 mg total daily dose for adults. Subsequent titration to a maximum of 60 mg/m2 (approximately equivalent to the 360 mg total daily dose for adults) can then occur. Titration should be guided by clinical response, heart rate and QTc, with increased dosing being preferably carried out in-hospital. At least 36 hours should be allowed between dose increments to attain steady-state plasma concentrations of sotalol in patients with age-adjusted normal renal function.
For children aged about 2 years or younger the above pediatric dosage should be reduced by a factor that depends heavily upon age, as shown in the following graph, age plotted on a logarithmic scale in months.
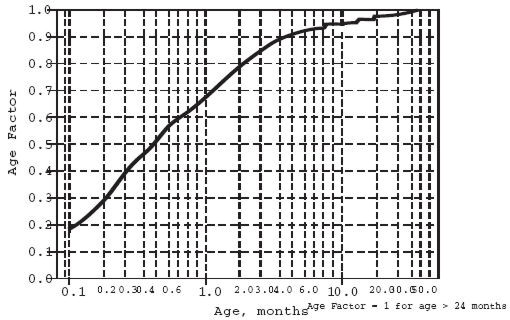
For a child aged 20 months, the dosing suggested for children with normal renal function aged 2 years or greater should be multiplied by about 0.97; the initial starting dose would be (30 × 0.97) =29.1 mg/m2, administered three times daily. For a child aged 1 month, the starting dose should be multiplied by 0.68; the initial starting dose would be (30 × 0.68) = 20 mg/m2, administered three times daily. For a child aged about 1 week, the initial starting dose should be multiplied by 0.3; the starting dose would be (30 × 0.3)=9 mg/m2. Similar calculations should be made for increased doses as titration proceeds. Since the half-life of sotalol decreases with decreasing age (below about 2 years), time to steady-state will also increase. Thus, in neonates the time to steady-state may be as long as a week or longer.
In all children, individualization of dosage is required. As in adults sotalol hydrochloride should be used with particular caution in children if the QTc is greater than 500 msec on therapy and serious consideration should be given to reducing the dose or discontinuing therapy when QTc, exceeds 550 msec.
The use of sotalol hydrochloride AF in children with renal impairment has not been investigated. Sotalol elimination is predominantly via the kidney in the unchanged form. Use of sotalol in any age group with decreased renal function should be at lower doses or at increased intervals between doses. Monitoring of heart rate and QTc is more important and it will take much longer to reach steady-state with any dose and/or frequency of administration.
Transfer to Sotalol Hydrochloride Tablets (AF) from Sotalol Hydrochloride
Patients with a history of symptomatic AFIB/AFL who are currently receiving sotalol hydrochloride for the maintenance of normal sinus should be transferred to sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) because of the significant differences in labeling (i.e., patient package insert, dosing administration, and safety information).
Transfer to Sotalol Hydrochloride Tablets (AF) from Other Antiarrhythmic Agents
Before starting sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF), previous antiarrhythmic therapy should generally be withdrawn under careful monitoring for a minimum of 2 to 3 plasma half-lives if the patient's clinical condition permits (see DRUG INTERACTIONS). Treatment has been initiated in some patients receiving I.V. lidocaine without ill effect. After discontinuation of amiodarone, sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) should not be initiated until the QT interval is normalized (see WARNINGS).
Preparation of Extemporaneous Oral Solution
Sotalol Hydrochloride Syrup 5 mg/mL can be compounded using Simple Syrup containing 0.1% sodium benzoate (Syrup, NF) available from Humco Laboratories as follows:
- Measure 120 mL of Simple Syrup
- Transfer the syrup to a 6-ounce amber plastic (polyethylene terephthalate [PET]) prescription bottle. NOTE: An oversized bottle is used to allow for a headspace so that there will be more effective mixing during shaking of the bottle.
- Add five (5) Sotalol Hydrochloride 120 mg tablets to the bottle. These tablets are added intact: it is not necessary to crush the tablets. NOTE: The addition of the tablets can also be done first. The tablets can also be crushed if preferred. If the tablets are crushed, care should be taken to transfer the entire quantity of tablet powder into the bottle containing the syrup.
- Shake the bottle to wet the entire surface of the tablets. If the tablets have been crushed, shake the bottle until the endpoint is achieved.
- Allow the tablets to hydrate for approximately two hours.
- After at least two hours have elapsed, shake the bottle intermittently over the course of at least another two hours until the tablets are completely disintegrated. NOTE: The tablets can be allowed to hydrate overnight to simplify the disintegration process.
The endpoint is achieved when a dispersion of fine particles in the syrup is obtained.
This compounding procedure results in a solution containing 5 mg/mL of sotalol HCl. The fine solid particles are the water-insoluble inactive ingredients of the tablets.
This extemporaneously prepared oral solution of sotalol HCl (with suspended inactive particles) must be shaken well prior to administration. This is to ensure that the amount of inactive solid particles per dose remains constant throughout the duration of use.
Stability studies indicate that the suspension is stable when stored at controlled room temperature (15°-30°C/59°-86°F) and ambient humidity for three (3) months.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF), 80 mg, oval white, scored, debossed MP 518 on one side, the other side plain.
Bottles of 30 unit of use NDC: 53489-503-07
Bottles of 60 unit of use NDC: 53489-503-06
Bottles of 100 NDC: 53489-503-01
Bottles of 250 NDC: 53489-503-03
Bottles of 500 NDC: 53489-503-05
Bottles of 1000 NDC: 53489-503-10Sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF), 120 mg, oval white, scored, debossed MP 519 on one side, the other side plain.
Bottles of 30 unit of use NDC: 53489-504-07
Bottles of 60 unit of use NDC: 53489-504-06
Bottles of 100 NDC: 53489-504-01
Bottles of 250 NDC: 53489-504-03
Bottles of 500 NDC: 53489-504-05
Bottles of 1000 NDC: 53489-504-10Sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF), 160 mg, oval white, scored, debossed MP 520 on one side, the other side plain.
Bottles of 30 unit of use NDC: 53489-505-07
Bottles of 60 unit of use NDC: 53489-505-06
Bottles of 100 NDC: 53489-505-01
Bottles of 250 NDC: 53489-505-03
Bottles of 500 NDC: 53489-505-05
Bottles of 1000 NDC: 53489-505-10 -
SUPPLEMENTAL PATIENT MATERIAL
PATIENT INFORMATION
WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT SOTALOL HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS (AF)
(generic name: sotalol hydrochloride) so-ta-lol hy-dro-chlor-ide
This summary contains important patient information that has been reviewed and approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. This summary is not meant to take the place of your doctor's instructions. Read this patient information carefully before you start taking sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF). Each time you get a refill, you will receive patient information. Be sure to read it because it may contain new information that you need to know.
What is the most important information I should know about sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF)?
Because you have irregular heartbeats (atrial fibrillation) that are troublesome to you, sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) has been prescribed to help your heart to beat in a more normal way. However, in some patients sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) can cause a different type of abnormal heartbeat that can be dangerous, and in rare instances can even cause death. You may feel this different type of abnormal heartbeat as a fast beating of the heart with lightheadedness and fainting. The possibility of this different type of abnormal heartbeat is the reason you and your doctor have discussed whether your symptoms are troublesome enough for you to start taking sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF).
Clinical studies using sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) have shown that the most important way to decrease your chance of getting this different type of dangerous abnormal heartbeat is for you to take the dose of sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) that is right for you. If this abnormal heartbeat occurs, it usually happens during the first few days of treatment. This is why you should be started on sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) in a hospital or another place where your heartbeat can be watched closely by health care professionals for the first few days. They can help you if problems occur. When sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) are started this way, this different type of abnormal heartbeat is rare and the hospital staff is there to treat it.
It is important that when you go home, you take the exact dose the doctor prescribed for you. At any time while you are taking sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF), watch for signs that you may be getting this different type of abnormal heartbeat and call your doctor if they occur. Call your doctor right away if you:
- faint,
- become dizzy, or
- have fast heartbeats.
If you cannot reach your doctor, go to the nearest hospital emergency room. Take your sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) with you and show them to the doctor or nurse.
Also, call your doctor right away if you have any of the following conditions:
- severe diarrhea
- unusual sweating
- vomiting
- less appetite than normal, or
- more thirst than normal.
These are conditions that will make you more likely to get the different type of abnormal heartbeat.
If you take sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) with certain other medicines, you will increase your chance of getting this different type of abnormal heartbeat. These medicines are listed below under "Who should not take sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF)?"
Once your doctor finds the right dose for you, always take that exact amount of sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF). Never take an extra dose and never skip a dose of sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF).
What are sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF)?
Sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) is a medicine that is given to patients with atrial fibrillation (irregular heartbeats). Atrial fibrillation happens when certain parts of the heart (the chambers known as atria) beat too fast or irregularly. When this happens, your heart cannot pump blood through your body as well as it should. This may make you feel weak and tired, or get out of breath easily. You may get an uncomfortable feeling in your chest and "fluttering" or "palpitations." Atrial fibrillation can be changed back (converted) to normal heart rhythm by an electric shock or by using certain medicines. However, atrial fibrillation can return. Sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) may help your heart stay beating regularly for a longer period of time.
This information about sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) was developed to ensure that you and your doctor get the right information about your type of irregular heartbeats. Consult your doctor before you accept any other sotalol product that does not provide this patient information.
Who should not take sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF)?
Sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) are not for everyone with irregular heartbeats (atrial fibrillation). This is why you and your doctor need to discuss the benefits and risks of sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) and whether your symptoms are troublesome enough for you to start taking sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF).
Do not take sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) if you:
- have serious kidney problems or are on kidney dialysis;
- have lung disease causing shortness of breath (such as asthma, chronic bronchitis or emphysema);
- have symptoms of heart failure (such as shortness of breath when you exercise or are physically active and swelling of the ankles or legs);
- have a very slow heart beat and do not have an implanted artificial pacemaker;
Taking certain other medicines with sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) can increase the chance that you will get the dangerous abnormal heartbeat discussed in "What is the most important information I should know about sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF)?" These include medicines used to treat abnormal heart rhythms and some other heart problems as well as medicines used to treat depression and other mental problems, night-time heartburn, asthma and infections. Therefore, you should be sure to tell your health care provider about all prescription and non-prescription medicines you are taking, as well as vitamins, dietary supplements, and any natural or herbal remedies. In addition, tell your doctor about any problems you have with your heart or kidneys.
If you are pregnant, you should know that there is no information about the safety of sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) in pregnant women. Some reports indicate that sotalol hydrochloride is passed into the breast milk. Women who are taking sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) should not breast feed a child.
How should I take sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF)?
Your doctor will start you on sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) in the hospital and will check your heart rhythm for the first 2 or more days of treatment. This will allow your doctor to find the right dose for you. Always take the exact amount your doctor prescribes. Never change your sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) dose unless your doctor tells you to. Your doctor will do regular tests to check that the amount you're taking is still right for you.
Keep taking your sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) until your doctor tells you to stop. Keep taking it even if you feel fine. However, never take an extra dose of sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) even if you do not feel well. When it is time to stop taking sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF), your doctor will give you instructions on how to gradually reduce your dose over a period of 1 to 2 weeks.
You may take sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) with or without food. However, it is important to take sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) at the same time every day. This gives your heart a steady supply of the medicine. It might be helpful to take sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) at the same time as something you regularly do every day.
If you are taking an antacid containing aluminum or magnesium to treat heartburn or upset stomach wait at least 2 hours after your dose of sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) before you take the antacid.
Never try to make up for a missed dose of sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF). You could increase your chance of getting the different type of abnormal heartbeat. If you miss taking a dose of sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF), just take your normal amount at the next scheduled time.
If you take more sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) than you should have, call your doctor right away. If you cannot reach your doctor, go to the nearest hospital emergency room. Take your sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) with you to show to the doctor or nurse.
What should I avoid while taking sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF)?
Certain other medicines taken with sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) may increase the chance that you will get the dangerous abnormal heartbeat (see "Who should not take sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF)?) Do not take sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) with these medicines. Before you start taking sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) tell your doctor about all prescription and non-prescription medicines you are taking (see also "Who should not take sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF)?"). Once you begin taking sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF), do not start taking any new medicines until you check with your doctor.
Carry a list of all the medicines and supplements you take. If you have to go to the hospital or are treated by new or different health care providers, tell them you are taking sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) and show them the list of other medicines you take. They need this information to make sure your medicines are safe to take at the same time.
Tell your doctor or dentist you are taking sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) before you have an operation or dental surgery. Sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) can affect how well some anesthetics work.
What are the possible side effects of sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF)?
Sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF's) most serious side effect, a different type of dangerous abnormal heartbeat, is discussed in "What is the most important information I should know about sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF)?" Dangerous abnormal heartbeats happen rarely. But they can be serious and, in rare instances, can even cause death.
Sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF's) most common side effects are tiredness, slow rate, shortness of breath, and dizziness. Sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) can also cause other side effects. If you are concerned about these or any other side effects, ask your doctor.
Important points about sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF)
Sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) can help you best if you take it as your doctor has prescribed it.
- Take your medicine every day as prescribed.
- Do not miss doses or take extra doses.
- Call your doctor right away if you feel new fast heartbeats with lightheadedness and fainting. These can be serious and in rare instances can even cause death.
- Do not take sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) if you have serious kidney problems, lung disease causing shortness of breath, symptoms of heart failure.
- Tell your doctor and pharmacist the name of all medications (prescription, non-prescription, and natural/herbal remedies) you are taking.
- Do not start taking any other medicines without telling your doctor.
- Go for all your regular checkups.
- Get your refills on time.
- Do not stop taking sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) until your doctor tells you to stop.
This leaflet provides a summary of information about sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF). Your doctor or pharmacist has a longer leaflet written for healthcare professionals that you can ask to read. Sotalol hydrochloride tablets (AF) was prescribed for your particular condition. Do not use it for another condition or give it to others.
"Betapace is a registered trademark of Berlex Laboratories"
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
SOTALOL
sotalol tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 53489-503 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength sotalol (UNII: A6D97U294I) (sotalol - UNII:A6D97U294I) 80 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Anhydrous lactose () colloidal silicon dioxide () corn starch () magnesium stearate (UNII: 70097M6I30) microcrystalline cellulose () pregelatinized starch () sodium starch glycolate () stearic acid (UNII: 4ELV7Z65AP) Product Characteristics Color WHITE Score 2 pieces Shape OVAL Size 11mm Flavor Imprint Code MP;518 Contains Coating false Symbol false Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 53489-503-07 30 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC 2 NDC: 53489-503-06 60 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC 3 NDC: 53489-503-01 100 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC 4 NDC: 53489-503-03 250 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC 5 NDC: 53489-503-05 500 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC 6 NDC: 53489-503-10 1000 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC SOTALOL
sotalol tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 53489-504 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength sotalol (UNII: A6D97U294I) (sotalol - UNII:A6D97U294I) 120 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Anhydrous lactose () colloidal silicon dioxide () corn starch () magnesium stearate (UNII: 70097M6I30) microcrystalline cellulose () pregelatinized starch () sodium starch glycolate () stearic acid (UNII: 4ELV7Z65AP) Product Characteristics Color WHITE Score 2 pieces Shape OVAL Size 12mm Flavor Imprint Code MP;519 Contains Coating false Symbol false Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 53489-504-07 30 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC 2 NDC: 53489-504-06 60 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC 3 NDC: 53489-504-01 100 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC 4 NDC: 53489-504-03 250 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC 5 NDC: 53489-504-05 500 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC 6 NDC: 53489-504-10 1000 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC SOTALOL
sotalol tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 53489-505 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength sotalol (UNII: A6D97U294I) (sotalol - UNII:A6D97U294I) 160 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Anhydrous lactose () colloidal silicon dioxide () corn starch () magnesium stearate (UNII: 70097M6I30) microcrystalline cellulose () pregelatinized starch () sodium starch glycolate () stearic acid (UNII: 4ELV7Z65AP) Product Characteristics Color WHITE Score 2 pieces Shape OVAL Size 14mm Flavor Imprint Code MP;520 Contains Coating false Symbol false Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 53489-505-07 30 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC 2 NDC: 53489-505-06 60 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC 3 NDC: 53489-505-01 100 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC 4 NDC: 53489-505-03 250 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC 5 NDC: 53489-505-05 500 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC 6 NDC: 53489-505-10 1000 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC Labeler - MUTUAL PHARMACEUTICAL
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.