amlodipine besylate- Amlodipine Besylate tablet
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Drug Details [pdf]
- N/A - Section Title Not Found In Database
- Prescribing Information
-
DESCRIPTION
Amlodipine besylate is a besylate salt of amlodipine, and is a long-acting calcium channel blocker.
Amlodipine besylate monohydrate is chemically described as 3-Ethyl-5-methyl (±)-2-[(2-aminoethoxy)methyl]-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-6-methyl-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate, monobenzenesulphonate monohydrate. Its molecular formula is C20H25ClN2O5C6H6SO3H2O and its structural formula is:
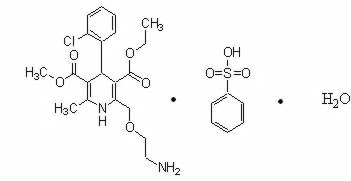
Amlodipine besylate monohydrate is a white crystalline powder with a molecular weight of 585.07. It is slightly soluble in water, ethanol, acetone and 2-propanol and soluble in N, N-dimethylformamide and dimethylsulfoxide. Amlodipine besylate tablets are formulated as white to off-white tablets equivalent to 2.5, 5 and 10 mg of amlodipine for oral administration. In addition to the active ingredient, amlodipine besylate, each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: microcrystalline cellulose, sodium starch glycolate, and magnesium stearate.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Amlodipine is a dihydropyridine calcium antagonist (calcium ion antagonist or slow-channel blocker) that inhibits the transmembrane influx of calcium ions into vascular smooth muscle and cardiac muscle. Experimental data suggest that amlodipine binds to both dihydropyridine and nondihydropyridine binding sites. The contractile processes of cardiac muscle and vascular smooth muscle are dependent upon the movement of extracellular calcium ions into these cells through specific ion channels. Amlodipine inhibits calcium ion influx across cell membranes selectively, with a greater effect on vascular smooth muscle cells than on cardiac muscle cells. Negative inotropic effects can be detected in vitro but such effects have not been seen in intact animals at therapeutic doses. Serum calcium concentration is not affected by amlodipine. Within the physiologic pH range, amlodipine is an ionized compound (pKa=8.6), and its kinetic interaction with the calcium channel receptor is characterized by a gradual rate of association and dissociation with the receptor binding site, resulting in a gradual onset of effect.
Amlodipine is a peripheral arterial vasodilator that acts directly on vascular smooth muscle to cause a reduction in peripheral vascular resistance and reduction in blood pressure.
The precise mechanisms by which amlodipine relieves angina have not been fully delineated, but are thought to include the following:
Exertional Angina: In patients with exertional angina, amlodipine reduces the total peripheral resistance (afterload) against which the heart works and reduces the rate pressure product, and thus myocardial oxygen demand, at any given level of exercise.
Vasospastic Angina: Amlodipine has been demonstrated to block constriction and restore blood flow in coronary arteries and arterioles in response to calcium, potassium epinephrine, serotonin, and thromboxane A2 analog in experimental animal models and in human coronary vessels in vitro. This inhibition of coronary spasm is responsible for the effectiveness of amlodipine in vasospastic (Prinzmetal's or variant) angina.
Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism
After oral administration of therapeutic doses of amlodipine, absorption produces peak plasma concentrations between 6 and 12 hours. Absolute bioavailability has been estimated to be between 64 and 90%. The bioavailability of amlodipine is not altered by the presence of food.
Amlodipine is extensively (about 90%) converted to inactive metabolites via hepatic metabolism with 10% of the parent compound and 60% of the metabolites excreted in the urine. Ex vivo studies have shown that approximately 93% of the circulating drug is bound to plasma proteins in hypertensive patients. Elimination from the plasma is biphasic with a terminal elimination half-life of about 30 to 50 hours. Steady-state plasma levels of amlodipine are reached after 7 to 8 days of consecutive daily dosing.
The pharmacokinetics of amlodipine are not significantly influenced by renal impairment. Patients with renal failure may therefore receive the usual initial dose.
Elderly patients and patients with hepatic insufficiency have decreased clearance of amlodipine with a resulting increase in AUC of approximately 40 to 60%, and a lower initial dose may be required. A similar increase in AUC was observed in patients with moderate to severe heart failure.
Pediatric Patients
Sixty-two hypertensive patients aged 6 to 17 years received doses of amlodipine besylate between 1.25 mg and 20 mg. Weight-adjusted clearance and volume of distribution were similar to values in adults.
Pharmacodynamics
Hemodynamics
Following administration of therapeutic doses to patients with hypertension, amlodipine produces vasodilation resulting in a reduction of supine and standing blood pressures. These decreases in blood pressure are not accompanied by a significant change in heart rate or plasma catecholamine levels with chronic dosing. Although the acute intravenous administration of amlodipine decreases arterial blood pressure and increases heart rate in hemodynamic studies of patients with chronic stable angina, chronic oral administration of amlodipine in clinical trials did not lead to clinically significant changes in heart rate or blood pressures in normotensive patients with angina.
With chronic once daily oral administration, antihypertensive effectiveness is maintained for at least 24 hours. Plasma concentrations correlate with effect in both young and elderly patients. The magnitude of reduction in blood pressure with amlodipine is also correlated with the height of pretreatment elevation; thus, individuals with moderate hypertension (diastolic pressure 105 to 114 mmHg) had about a 50% greater response than patients with mild hypertension (diastolic pressure 90 to 104 mmHg). Normotensive subjects experienced no clinically significant change in blood pressures (+1/-2 mmHg).
In hypertensive patients with normal renal function, therapeutic doses of amlodipine resulted in a decrease in renal vascular resistance and an increase in glomerular filtration rate and effective renal plasma flow without change in filtration fraction or proteinuria
As with other calcium channel blockers, hemodynamic measurements of cardiac function at rest and during exercise (or pacing) in patients with normal ventricular function treated with amlodipine have generally demonstrated a small increase in cardiac index without significant influence on dP/dt or on left ventricular end diastolic pressure or volume. In hemodynamic studies, amlodipine has not been associated with a negative inotropic effect when administered in the therapeutic dose range to intact animals and man, even when coadministered with beta-blockers to man. Similar findings, however, have been observed in normals or well-compensated patients with heart failure with agents possessing significant negative inotropic effects.
Electrophysiologic Effects
Amlodipine does not change sinoatrial nodal function or atrioventricular conduction in intact animals or man. In patients with chronic stable angina, intravenous administration of 10 mg did not significantly alter A-H and H-V conduction and sinus node recovery time after pacing. Similar results were obtained in patients receiving amlodipine and concomitant beta blockers. In clinical studies in which amlodipine was administered in combination with beta-blockers to patients with either hypertension or angina, no adverse effects on electrocardiographic parameters were observed. In clinical trials with angina patients alone, amlodipine therapy did not alter electrocardiographic intervals or produce higher degrees of AV blocks.
Clinical Studies
Effects in Hypertension
Adult Patients: The antihypertensive efficacy of amlodipine has been demonstrated in a total of 15 double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized studies involving 800 patients on amlodipine and 538 on placebo. Once daily administration produced statistically significant placebo-corrected reductions in supine and standing blood pressures at 24 hours postdose, averaging about 12/6 mmHg in the standing position and 13/7 mmHg in the supine position in patients with mild to moderate hypertension. Maintenance of the blood pressure effect over the 24-hour dosing interval was observed, with little difference in peak and trough effect. Tolerance was not demonstrated in patients studied for up to 1 year. The 3 parallel, fixed dose, dose response studies showed that the reduction in supine and standing blood pressures was dose-related within the recommended dosing range. Effects on diastolic pressure were similar in young and older patients. The effect on systolic pressure was greater in older patients, perhaps because of greater baseline systolic pressure. Effects were similar in black patients and in white patients.
Pediatric Patients
Two-hundred sixty-eight hypertensive patients aged 6 to 17 years were randomized first to amlodipine besylate 2.5 or 5 mg once daily for 4 weeks and then randomized again to the same dose or to placebo for another 4 weeks. Patients receiving 5 mg at the end of 8 weeks had lower blood pressure than those secondarily randomized to placebo. The magnitude of the treatment effect is difficult to interpret, but it is probably less than 5 mmHg systolic on the 5-mg dose. Adverse events were similar to those seen in adults.
Effects in Chronic Stable Angina
The effectiveness of 5 to 10 mg/day of amlodipine in exercise-induced angina has been evaluated in 8 placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trials of up to 6 weeks duration involving 1038 patients (684 amlodipine, 354 placebo) with chronic stable angina. In 5 of the 8 studies significant increases in exercise time (bicycle or treadmill) were seen with the 10 mg dose. Increases in symptom-limited exercise time averaged 12.8% (63 sec) for amlodipine 10 mg, and averaged 7.9% (38 sec) for amlodipine 5 mg. Amlodipine 10 mg also increased time to 1 mm ST segment deviation in several studies and decreased angina attack rate. The sustained efficacy of amlodipine in angina patients has been demonstrated over long-term dosing. In patients with angina there were no clinically significant reductions in blood pressures (4/1 mmHg) or changes in heart rate (+0.3 bpm).
Effects in Vasospastic Angina
In a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial of 4 weeks duration in 50 patients, amlodipine therapy decreased attacks by approximately 4/week compared with a placebo decrease of approximately 1/week (p <0.01). Two (2) of 23 amlodipine and 7 of 27 placebo patients discontinued from the study due to lack of clinical improvement.
Studies in Patients with Congestive Heart Failure
Amlodipine has been compared to placebo in four 8 to 12 week studies of patients with NYHA class II/III heart failure, involving a total of 697 patients. In these studies, there was no evidence of worsened heart failure based on measures of exercise tolerance, NYHA classification, symptoms, or left ventricular ejection fraction. In a long-term (follow-up at least 6 months, mean 13.8 months) placebo-controlled mortality/morbidity study of amlodipine 5 to 10 mg in 1153 patients with NYHA classes III (n=931) or IV (n=222) heart failure on stable doses of diuretics, digoxin, and ACE inhibitors, amlodipine had no effect on the primary endpoint of the study which was the combined endpoint of all-cause mortality and cardiac morbidity (as defined by life-threatening arrhythmia, acute myocardial infarction, or hospitalization for worsened heart failure), or on NYHA classification, or symptoms of heart failure. Total combined all-cause mortality and cardiac morbidity events were 222/571 (39%) for patients on amlodipine and 246/583 (42%) for patients on placebo; the cardiac morbid events represented about 25% of the endpoints in the study.
Another study (PRAISE-2) randomized patients with NYHA class III (80%) or IV (20%) heart failure without clinical symptoms or objective evidence of underlying ischemic disease, on stable doses of ACE inhibitor (99%), digitalis (99%) and diuretics (99%), to placebo (n=827) or amlodipine (n=827) and followed them for a mean of 33 months. There was no statistically significant difference between amlodipine and placebo in the primary endpoint of all-cause mortality (95% confidence limits from 8% reduction to 29% increase on amlodipine). With amlodipine there were more reports of pulmonary edema.
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Hypertension
Amlodipine besylate is indicated for the treatment of hypertension. It may be used alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents.
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
WARNINGS
Increased Angina and/or Myocardial Infarction
Rarely, patients, particularly those with severe obstructive coronary artery disease, have developed documented increased frequency, duration and/or severity of angina or acute myocardial infarction on starting calcium channel blocker therapy or at the time of dosage increase. The mechanism of this effect has not been elucidated.
-
PRECAUTIONS
General
Since the vasodilation induced by amlodipine is gradual in onset, acute hypotension has rarely been reported after oral administration. Nonetheless, caution as with any other peripheral vasodilator, should be exercised when administering amlodipine, particularly in patients with severe aortic stenosis.
Use in Patients with Congestive Heart Failure
In general, calcium channel blockers should be used with caution in patients with heart failure. Amlodipine (5 to 10 mg/day) has been studied in a placebo-controlled trial of 1153 patients with NYHA Class III or IV heart failure (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY) on stable doses of ACE inhibitor, digoxin, and diuretics. Follow-up was at least 6 months, with a mean of about 14 months. There was no overall adverse effect on survival or cardiac morbidity (as defined by life-threatening arrhythmia, acute myocardial infarction, or hospitalization for worsened heart failure). Amlodipine has been compared to placebo in four 8 to 12 week studies of patients with NYHA class II/III heart failure, involving a total of 697 patients. In these studies, there was no evidence of worsened heart failure based on measures of exercise tolerance, NYHA classification, symptoms, or LVEF.
Beta-Blocker Withdrawal
Amlodipine is not a beta-blocker and therefore gives no protection against the dangers of abrupt beta-blocker withdrawal; any such withdrawal should be by gradual reduction of the dose of beta-blocker.
Patients with Hepatic Failure
Since amlodipine is extensively metabolized by the liver and the plasma elimination half-life (t½) is 56 hours in patients with impaired hepatic function, caution should be exercised when administering amlodipine to patients with severe hepatic impairment.
Drug Interactions
In vitro data indicate that amlodipine has no effect on the human plasma protein binding of digoxin, phenytoin, warfarin, and indomethacin.
Effect of other agents on amlodipine
CIMETIDINE: Coadministration of amlodipine with cimetidine did not alter the pharmacokinetics of amlodipine.
GRAPEFRUIT JUICE: Coadministration of 240 mL of grapefruit juice with a single oral dose of amlodipine 10 mg in 20 healthy volunteers had no significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of amlodipine.
MAALOX (antacid): Coadministration of the antacid Maalox with a single dose of amlodipine had no significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of amlodipine.
SILDENAFIL: A single 100 mg dose of sildenafil (Viagra®) in subjects with essential hypertension had no effect on the pharmacokinetic parameters of amlodipine. When amlodipine and sildenafil were used in combination, each agent independently exerted its own blood pressure lowering effect.
Effect of amlodipine on other agents
ATORVASTATIN: Coadministration of multiple 10 mg doses of amlodipine with 80 mg of atorvastatin resulted in no significant change in the steady state pharmacokinetic parameters of atorvastatin.
DIGOXIN: Coadministration of amlodipine with digoxin did not change serum digoxin levels or digoxin renal clearance in normal volunteers.
ETHANOL (alcohol): Single and multiple 10 mg doses of amlodipine had no significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of ethanol.
WARFARIN: Coadministration of amlodipine with warfarin did not change the warfarin prothrombin response time.
In clinical trials, amlodipine has been safely administered with thiazide diuretics, beta-blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, long-acting nitrates, sublingual nitroglycerin, digoxin, warfarin, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, and oral hypoglycemic drugs.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Rats and mice treated with amlodipine maleate in the diet for up to two years, at concentrations calculated to provide daily dosage levels of 0.5, 1.25, and 2.5 amlodipine mg/kg/day, showed no evidence of a carcinogenic effect of the drug. For the mouse, the highest dose was, on a mg/m2 basis, similar to the maximum recommended human dose of 10 mg amlodipine/day1. For the rat, the highest dose was, on a mg/m2 basis, about twice the maximum recommended human dose.1
Mutagenicity studies conducted with amlodipine maleate revealed no drug related effects at either the gene or chromosome level.
There was no effect on the fertility of rats treated orally with amlodipine maleate (males for 64 days and females for 14 days prior to mating) at doses up to 10 mg amlodipine/kg/day (8 times1 the maximum recommended human dose of 10 mg/day on a mg/m2 basis).
- 1 Based on patient weight of 50 kg.
Pregnancy Category C
No evidence of teratogenicity or other embryo/fetal toxicity was found when pregnant rats and rabbits were treated orally with amlodipine maleate at doses up to 10 mg amlodipine/kg/day (respectively 8 times1 and 23 times1 the maximum recommended human dose of 10 mg on a mg/m2 basis) during their respective periods of major organogenesis. However, litter size was significantly decreased (by about 50%) and the number of intrauterine deaths was significantly increased (about 5-fold) in rats receiving amlodipine maleate at a dose equivalent to 10 mg amlodipine/kg/day for 14 days before mating and throughout mating and gestation. Amlodipine maleate has been shown to prolong both the gestation period and the duration of labor in rats at this dose. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Amlodipine should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether amlodipine is excreted in human milk. In the absence of this information, it is recommended that nursing be discontinued while amlodipine is administered.
Pediatric Use
The effect of amlodipine on blood pressure in patients less than 6 years of age is not known.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of amlodipine did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy. Elderly patients have decreased clearance of amlodipine with a resulting increase of AUC of approximately 40 to 60%, and a lower initial dose may be required (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Amlodipine has been evaluated for safety in more than 11,000 patients in US and foreign clinical trials. In general, treatment with amlodipine was well-tolerated at doses up to 10 mg daily. Most adverse reactions reported during therapy with amlodipine were of mild or moderate severity. In controlled clinical trials directly comparing amlodipine (n=1730) in doses up to 10 mg to placebo (n=1250), discontinuation of amlodipine due to adverse reactions was required in only about 1.5% of patients and was not significantly different from placebo (about 1%). The most common side effects are headache and edema. The incidence (%) of side effects which occurred in a dose related manner are found as follows:
Adverse Event
2.5 mg
N=275
5 mg
N=296
10 mg
N=268
Placebo
N=520Edema 1.8 3.0 10.8 0.6 Dizziness 1.1 3.4 3.4 1.5 Flushing 0.7 1.4 2.6 0.0 Palpitation 0.7 1.4 4.5 0.6 Other adverse experiences which were not clearly dose related but which were reported with an incidence greater than 1.0% in placebo-controlled clinical trials include the following:
Placebo-Controlled Studies AMLODIPINE (%)
(N=1730)PLACEBO (%)
(N=1250)Headache 7.3 7.8 Fatigue 4.5 2.8 Nausea 2.9 1.9 Abdominal pain 1.6 0.3 Somnolence 1.4 0.6 For several adverse experiences that appear to be drug and dose related, there was a greater incidence in women than men associated with amlodipine treatment as shown in the following table:
Adverse Event AMLODIPINE PLACEBO Male=%
(N=1218)Female=%
(N=512)Male=%
(N=914)Female=%
(N=336)Edema 5.6 14.6 1.4 5.1 Flushing 1.5 4.5 0.3 0.9 Palpitations 1.4 3.3 0.9 0.9 Somnolence 1.3 1.6 0.8 0.3 The following events occurred in <1% but >0.1% of patients in controlled clinical trials or under conditions of open trials or marketing experience where a causal relationship is uncertain; they are listed to alert the physician to a possible relationship:
Cardiovascular: arrhythmia (including ventricular tachycardia and atrial fibrillation), bradycardia, chest pain, hypotension, peripheral ischemia, syncope, tachycardia, postural dizziness, postural hypotension, vasculitis.
Central and Peripheral Nervous System: hypoesthesia, neuropathy peripheral, paresthesia, tremor, vertigo.
Gastrointestinal: anorexia, constipation, dyspepsia,2 dysphagia, diarrhea, flatulence, pancreatitis, vomiting, gingival hyperplasia.
General: allergic reaction, asthenia,2 back pain, hot flushes, malaise, pain, rigors, weight gain, weight decrease.
Musculoskeletal System: arthralgia, arthrosis, muscle cramps,2 myalgia.
Psychiatric: sexual dysfunction (male2 and female), insomnia, nervousness, depression, abnormal dreams, anxiety, depersonalization.
Respiratory System: dyspnea,2 epistaxis.
Skin and Appendages: angioedema, erythema multiforme, pruritus,2 rash,2 rash erythematous, rash maculopapular.
Special Senses: abnormal vision, conjunctivitis, diplopia, eye pain, tinnitus.
Urinary System: micturition frequency, micturition disorder, nocturia.
Autonomic Nervous System: dry mouth, sweating increased.
Metabolic and Nutritional: hyperglycemia, thirst.
Hemopoietic: leukopenia, purpura, thrombocytopenia.
The following events occurred in <0.1% of patients: cardiac failure, pulse irregularity, extrasystoles, skin discoloration, urticaria, skin dryness, alopecia, dermatitis, muscle weakness, twitching, ataxia, hypertonia, migraine, cold and clammy skin, apathy, agitation, amnesia, gastritis, increased appetite, loose stools, coughing, rhinitis, dysuria, polyuria, parosmia, taste perversion, abnormal visual accommodation, and xerophthalmia.
Other reactions occurred sporadically and cannot be distinguished from medications or concurrent disease states such as myocardial infarction and angina.
Amlodipine therapy has not been associated with clinically significant changes in routine laboratory tests. No clinically relevant changes were noted in serum potassium, serum glucose, total triglycerides, total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, uric acid, blood urea nitrogen, or creatinine.
The following postmarketing event has been reported infrequently where a causal relationship is uncertain: gynecomastia. In postmarketing experience, jaundice and hepatic enzyme elevations (mostly consistent with cholestasis or hepatitis) in some cases severe enough to require hospitalization have been reported in association with use of amlodipine.
Amlodipine has been used safely in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, well-compensated congestive heart failure, peripheral vascular disease, diabetes mellitus, and abnormal lipid profiles.
- 2 These events occurred in less than 1% in placebo-controlled trials, but the incidence of these side effects was between 1% and 2% in all multiple dose studies.
-
OVERDOSAGE
Single oral doses of amlodipine maleate equivalent to 40 mg amlodipine/kg and 100 mg amlodipine/kg in mice and rats, respectively, caused deaths. Single oral amlodipine maleate doses equivalent to 4 or more mg amlodipine/kg or higher in dogs (11 or more times the maximum recommended human dose on a mg/m2 basis) caused a marked peripheral vasodilation and hypotension.
Overdosage might be expected to cause excessive peripheral vasodilation with marked hypotension and possibly a reflex tachycardia. In humans, experience with intentional overdosage of amlodipine is limited. Reports of intentional overdosage include a patient who ingested 250 mg and was asymptomatic and was not hospitalized; another (120 mg) was hospitalized, underwent gastric lavage and remained normotensive; the third (105 mg) was hospitalized and had hypotension (90/50 mmHg) which normalized following plasma expansion. A case of accidental drug overdose has been documented in a 19-month-old male who ingested 30 mg amlodipine (about 2 mg/kg). During the emergency room presentation, vital signs were stable with no evidence of hypotension, but a heart rate of 180 bpm. Ipecac was administered 3.5 hours after ingestion and on subsequent observation (overnight) no sequelae were noted.
If massive overdose should occur, active cardiac and respiratory monitoring should be instituted. Frequent blood pressure measurements are essential. Should hypotension occur, cardiovascular support including elevation of the extremities and the judicious administration of fluids should be initiated. If hypotension remains unresponsive to these conservative measures, administration of vasopressors (such as phenylephrine), should be considered with attention to circulating volume and urine output. Intravenous calcium gluconate may help to reverse the effects of calcium entry blockade. As amlodipine is highly protein bound, hemodialysis is not likely to be of benefit.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Adults
The usual initial antihypertensive oral dose of amlodipine is 5 mg once daily with a maximum dose of 10 mg once daily. Small, fragile, or elderly individuals, or patients with hepatic insufficiency may be started on 2.5 mg once daily and this dose may be used when adding amlodipine to other antihypertensive therapy.
Dosage should be adjusted according to each patient's need. In general, titration should proceed over 7 to 14 days so that the physician can fully assess the patient's response to each dose level. Titration may proceed more rapidly, however, if clinically warranted, provided the patient is assessed frequently.
The recommended dose for chronic stable or vasospastic angina is 5 to 10 mg, with the lower dose suggested in the elderly and in patients with hepatic insufficiency. Most patients will require 10 mg for adequate effect. See ADVERSE REACTIONS section for information related to dosage and side effects.
Children
The effective antihypertensive oral dose in pediatric patients ages 6 to 17 years is 2.5 mg to 5 mg once daily. Doses in excess of 5 mg daily have not been studied in pediatric patients. See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Amlodipine besylate tablets, 2.5 mg, equivalent to 2.5 mg of amlodipine per tablet, are white to off-white, triangular, biconvex, unscored tablet, one side engraved "ADP bes" and the other side engraved with "2.5" and supplied as follows:
- NDC 63672-0044-3 Bottle of 90 tablets
Amlodipine besylate tablets, 5 mg, equivalent to 5 mg of amlodipine per tablet, are white to off-white, oblong, biconvex, unscored tablet, one side engraved with "ADP bes" and the other side engraved with "5" and supplied as follows:
- NDC 63672-0045-3 Bottle of 90 tablets
Amlodipine besylate tablets, 10 mg, equivalent to 10 mg of amlodipine per tablet, are white to off-white, round, biconvex, unscored tablet, one side engraved with "ADP bes" and the other side engraved with "10" and supplied as follows:
- NDC 63672-0046-3 Bottle of 90 tablets
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
SUMMARY OF INFORMATION ABOUT AMLODIPINE BESYLATE TABLETS
Read this information carefully before you start amlodipine besylate and each time you refill your prescription. There may be new information. This information does not replace talking with your doctor. If you have any questions about amlodipine besylate, ask your doctor. Your doctor will know if amlodipine besylate is right for you.
What is amlodipine besylate?
Amlodipine besylate is a type of medicine known as a calcium channel blocker (CCB). It is used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension) and a type of chest pain called angina. It can be used by itself or with other medicines to treat these conditions.
High Blood Pressure (hypertension)
High blood pressure comes from blood pushing too hard against your blood vessels. Amlodipine besylate relaxes your blood vessels which lets your blood flow more easily and helps lower your blood pressure. Drugs that lower blood pressure lower your risk of having a stroke or heart attack.
Angina
Angina is a pain or discomfort that keeps coming back when part of your heart does not get enough blood. Angina feels like a pressing or squeezing pain, usually in your chest under the breastbone. Sometimes you can feel it in your shoulders, arms, neck, jaws, or back. Amlodipine besylate can relieve this pain.
Who should not use amlodipine besylate?
Do not use amlodipine besylate if you are allergic to amlodipine (the active ingredient in amlodipine besylate), or to the inactive ingredients. Your doctor or pharmacist can give you a list of these ingredients.
What should I tell my doctor before taking amlodipine besylate?
Tell your doctor about any prescription and non-prescription medicines you are taking, including natural or herbal remedies.
Tell your doctor if you:
- ever had heart disease
- ever had liver problems
- are pregnant, or plan to become pregnant. Your doctor will decide if amlodipine besylate is the best treatment for you.
- are breastfeeding. Do not breastfeed while taking amlodipine besylate. You can stop breastfeeding or take a different medicine.
How should I take amlodipine besylate?
- Take amlodipine besylate once a day, with or without food. You can take amlodipine besylate with most drinks, including grapefruit juice.
- It may be easier to take your dose if you do it at the same time every day, such as with breakfast, dinner, or at bedtime. Do not take more than one dose of amlodipine besylate at a time.
- If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. Do not take amlodipine besylate if it has been more than 12 hours since you missed your last dose. Wait and take the next dose at your regular time.
- Other medicines: You can use nitroglycerin and amlodipine besylate together. If you take nitroglycerin for angina, dont stop taking it while you are taking amlodipine besylate.
- While you are taking amlodipine besylate, do not stop taking your other prescription medicines, including any other blood pressure medicines, without talking to your doctor.
- If you took too much amlodipine besylate, call your doctor or Poison Control Center, or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
What should I avoid while taking amlodipine besylate?
- Do not breastfeed. It is not known if amlodipine besylate will pass through your milk.
- Do not start any new prescription or non-prescription medicines or supplements, unless you check with your doctor first.
What are the possible side effects of amlodipine besylate?
Amlodipine besylate may cause the following side effects. Most side effects are mild or moderate:
- headache
- swelling of your legs or ankles
- tiredness, extreme sleepiness
- stomach pain, nausea
- dizziness
- flushing (hot or warm feeling in your face)
- arrhythmia (irregular heartbeat)
- heart palpitations (very fast heartbeat)
It is rare, but when you first start amlodipine besylate or increase your dose, you may have a heart attack or your angina may get worse. If that happens, call your doctor right away or go directly to a hospital emergency room.
Tell your doctor if you are concerned about any side effects you experience. These are not all the possible side effects of amlodipine besylate. For a complete list, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
How do I store amlodipine besylate?
Keep amlodipine besylate away from children. Store amlodipine besylate at room temperature (between 59 and 86 degrees Fahrenheit). Keep amlodipine besylate out of the light. Do not store in the bathroom. Keep amlodipine besylate in a dry place.
General advice about amlodipine besylate
Sometimes, doctors will prescribe a medicine for a condition that is not written in the patient information leaflets. Only use amlodipine besylate the way your doctor told you to. Do not give amlodipine besylate to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
You can ask your pharmacist or doctor for information about amlodipine besylate, or you can call 1-919-493-6006.
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
AMLODIPINE BESYLATE
amlodipine besylate tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 63672-0044 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Amlodipine besylate (UNII: 864V2Q084H) (Amlodipine - UNII:1J444QC288) 2.5 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength microcrystalline cellulose () sodium starch glycolate () magnesium stearate (UNII: 70097M6I30) Product Characteristics Color WHITE (White) Score no score Shape TRIANGLE (Biconvex and triangular) Size 7mm Flavor Imprint Code ADP;bes;2.5 Contains Coating false Symbol false Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 63672-0044-3 90 in 1 BOTTLE AMLODIPINE BESYLATE
amlodipine besylate tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 63672-0045 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Amlodipine besylate (UNII: 864V2Q084H) (Amlodipine - UNII:1J444QC288) 5 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength microcrystalline cellulose () sodium starch glycolate () magnesium stearate (UNII: 70097M6I30) Product Characteristics Color WHITE (White) Score no score Shape OVAL (OVAL) Size 5mm Flavor Imprint Code ADP;bes;5 Contains Coating false Symbol false Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 63672-0045-3 90 in 1 BOTTLE AMLODIPINE BESYLATE
amlodipine besylate tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 63672-0046 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Amlodipine besylate (UNII: 864V2Q084H) (Amlodipine - UNII:1J444QC288) 10 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength microcrystalline cellulose () sodium starch glycolate () magnesium stearate (UNII: 70097M6I30) Product Characteristics Color WHITE (White) Score no score Shape ROUND (Biconvex and round) Size 5mm Flavor Imprint Code ADP;bes;10 Contains Coating false Symbol false Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 63672-0046-3 90 in 1 BOTTLE Labeler - Synthon Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.