fluvoxamine maleate- Fluvoxamine maleate tablet, film coated
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Drug Details [pdf]
- N/A - Section Title Not Found In Database
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
Suicidality and Antidepressant Drugs
Antidepressants increased the risk compared to placebo of suicidal thinking and behavior (suicidality) in children, adolescents, and young adults in short-term studies of major depressive disorder (MDD) and other psychiatric disorders. Anyone considering the use of Fluvoxamine Maleate or any other antidepressant in a child, adolescent, or young adult must balance this risk with the clinical need. Short-term studies did not show an increase in the risk of suicidality with antidepressants compared to placebo in adults beyond age 24; there was a reduction in risk with antidepressants compared to placebo in adults aged 65 and older. Depression and certain other psychiatric disorders are themselves associated with increases in the risk of suicide. Patients of all ages who are started on antidepressant therapy should be monitored appropriately and observed closely for clinical worsening, suicidality, or unusual changes in behavior. Families and caregivers should be advised of the need for close observation and communication with the prescriber. Fluvoxamine is not approved for use in pediatric patients except for patients with obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD). (See Warnings and Precautions: Pediatric Use.) (See Warnings: Clinical Worsening and Suicide Risk, Precautions: Information for Patients, and Precautions: Pediatric Use)
-
DESCRIPTION
Fluvoxamine maleate is a selective serotonin (5-HT) reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) belonging to a new chemical series, the 2-aminoethyl oxime ethers of aralkylketones. It is chemically unrelated to other SSRIs and clomipramine. It is chemically designated as 5-methoxy-4'-(trifluoromethyl)valerophenone-(E)-O-(2-aminoethyl)oxime maleate (1:1) and has the empirical formula C15H21O2N2F3 C4H4O4. Its molecular weight is 434.4.
The structural formula is:
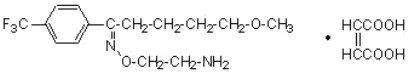
Fluvoxamine maleate is a white or off white, odorless, crystalline powder which is sparingly soluble in water, freely soluble in ethanol and chloroform and practically insoluble in diethyl ether.
Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets are available in 25 mg, 50 mg and 100 mg strengths for oral administration. In addition to the active ingredient, fluvoxamine maleate, each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: hypromellose, mannitol, polyethylene glycol, pregelatinized starch (corn), colloidal silicon dioxide, sodium stearyl fumarate, starch (corn), titanium dioxide and talc.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Pharmacodynamics
The mechanism of action of fluvoxamine maleate in Obsessive Compulsive Disorder is presumed to be linked to its specific serotonin reuptake inhibition in brain neurons. In preclinical studies, it was found that fluvoxamine inhibited neuronal uptake of serotonin.
In in vitro studies fluvoxamine maleate had no significant affinity for histaminergic, alpha or beta adrenergic, muscarinic, or dopaminergic receptors. Antagonism of some of these receptors is thought to be associated with various sedative, cardiovascular, anticholinergic, and extrapyramidal effects of some psychotic drugs.
Pharmacokinetics
Bioavailability
The absolute bioavailability of fluvoxamine maleate is 53%. Oral bioavailability is not significantly affected by food.
In a dose proportionality study involving fluvoxamine maleate at 100, 200 and 300 mg/day for 10 consecutive days in 30 normal volunteers, steady state was achieved after about a week of dosing. Maximum plasma concentrations at steady state occurred within 3-8 hours of dosing and reached concentrations averaging 88, 283 and 546 ng/mL, respectively.
Thus, fluvoxamine had nonlinear pharmacokinetics over this dose range, i.e., higher doses of fluvoxamine maleate produced disproportionately higher concentrations than predicted from the lower dose.
Distribution/Protein Binding
The mean apparent volume of distribution for fluvoxamine is approximately 25 L/kg, suggesting extensive tissue distribution.
Approximately 80% of fluvoxamine is bound to plasma protein, mostly albumin, over a concentration range of 20 to 2000 ng/mL.
Metabolism
Fluvoxamine maleate is extensively metabolized by the liver; the main metabolic routes are oxidative demethylation and deamination. Nine metabolites were identified following a 5 mg radiolabelled dose of fluvoxamine maleate, constituting approximately 85% of the urinary excretion products of fluvoxamine. The main human metabolite was fluvoxamine acid which, together with its N- acetylated analog, accounted for about 60% of the urinary excretion products. A third metabolite, fluvoxethanol, formed by oxidative deamination, accounted for about 10%.
Fluvoxamine acid and fluvoxethanol were tested in an in vitro assay of serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibition in rats; they were inactive except for a weak effect of the former metabolite on inhibition of serotonin uptake (1-2 orders of magnitude less potent than the parent compound). Approximately 2% of fluvoxamine was excreted in urine unchanged. (See PRECAUTIONS-Drug Interactions)
Elimination
Following a 14C-labelled oral dose of fluvoxamine maleate (5 mg), an average of 94% of drug-related products was recovered in the urine within 71 hours.
The mean plasma half-life of fluvoxamine at steady state after multiple oral doses of 100 mg/day in healthy, young volunteers was 15.6 hours.
Elderly Subjects
In a study of Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets at 50 and 100 mg comparing elderly (ages 66-73) and young subjects (ages 19-35), mean maximum plasma concentrations in the elderly were 40% higher. The multiple dose elimination half-life of fluvoxamine was 17.4 and 25.9 hours in the elderly compared to 13.6 and 15.6 hours in the young subjects at steady state for 50 and 100 mg doses, respectively.
In elderly patients, the clearance of fluvoxamine was reduced by about 50% and, therefore, Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets should be slowly titrated during initiation of therapy.
Pediatric Subjects
The multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of fluvoxamine were determined in male and female children (ages 6-11) and adolescents (ages 12-17). Steady-state plasma fluvoxamine concentrations were 2-3 fold higher in children than adolescents. AUC and Cmax in children were 1.5- to 2.7-fold higher than that in adolescents (see table below). As in adults, both children and adolescents exhibited nonlinear multiple-dose pharmacokinetics. Female children showed significantly higher AUC (0-12) and Cmax compared to male children and, therefore, lower doses of Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets may produce therapeutic benefit (see table below). No gender differences were observed in adolescents. Steady-state plasma fluvoxamine concentrations were similar in adults and adolescents at a dose of 300 mg/day, indicating that fluvoxamine exposure was similar in these two populations (see table below). Dose adjustment in adolescents (up to the adult maximum dose of 300 mg) may be indicated to achieve therapeutic benefit.
Comparison of Mean (SD) fluvoxamine pharmacokinetic parameters between children, adolescents and adults Pharmacokinetic Parameter
(Body weight corrected)Dose=200 mg/day (100 mg/day bid) Dose=300 mg/day (150 mg bid) Children
(n=10)Adolescent
(n=17)Adolescents
(n=13)Adults
(n=16)AUC0-12
(ng ∙ h/ml/kg)155.1 (160.9) 43.9 (27.9) 69.6 (46.6) 59.4 (40.9) Cmax (ng/ml/kg) 14.8 (14.9) 4.2 (2.6) 6.7 (4.2) 5.7 (3.9) Cmin (ng/ml/kg) 11.0 (11.9) 2.9 (2.0) 4.8 (3.8) 4.6 (3.2) Comparison of Mean (SD) fluvoxamine pharmacokinetic parameters between male and female children (6-11 years) Pharmacokinetic Parameter
(Body weight corrected)Dose =200 mg/day (100 mg bid) Male children (n=7) Female children (n=3) AUC0-12 (ng ∙ h/ml/kg) 95.8 (83.9) 293.5 (233.0) Cmax (ng/ml/kg) 9.1 (7.6) 28.1 (21.1) Cmin (ng/ml/kg) 6.6 (6.1) 21.2 (17.6) Hepatic and Renal Disease
A cross study comparison (healthy subjects vs. patients with hepatic dysfunction) suggested a 30% decrease in fluvoxamine clearance in association with hepatic dysfunction. The mean minimum plasma concentrations in renally impaired patients (creatinine clearance of 5 to 45 mL/min) after 4 and 6 weeks of treatment (50 mg bid, N=13) were comparable to each other, suggesting no accumulation of fluvoxamine in these patients. (See PRECAUTIONS-Use in Patients with Concomitant Illness)
Clinical Trials
Adult OCD Studies
The effectiveness of Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets for the treatment of Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD) was demonstrated in two 10-week multicenter, parallel group studies of adult outpatients. Patients in these trials were titrated to a total daily fluvoxamine maleate dose of 150 mg/day over the first two weeks of the trial, following which the dose was adjusted within a range of 100-300 mg/day (on a bid schedule), on the basis of response and tolerance. Patients in these studies had moderate to severe OCD (DSM-III-R), with mean baseline ratings on the Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale (Y-BOCS), total score of 23. Patients receiving fluvoxamine maleate experienced mean reductions of approximately 4 to 5 units on the Y-BOCS total score, compared to a 2 unit reduction for placebo patients.
The following table provides the outcome classification by treatment group on the Global Improvement item of the Clinical Global Impressions (CGI) scale for both studies combined.
OUTCOME CLASSIFICATION (%) ON CGI-GLOBAL IMPROVEMENT ITEM FOR COMPLETERS IN POOL OF TWO ADULT OCD STUDIES Outcome Classification Fluvoxamine (N = 120) Placebo (N = 134) Very Much Improved 13% 2% Much Improved 30% 10% Minimally Improved 22% 32% No Change 31% 51% Worse 4% 6% Exploratory analyses for age and gender effects on outcomes did not suggest any differential responsiveness on the basis of age or sex.
Pediatric OCD Study
The effectiveness of Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets for the treatment of OCD was also demonstrated in a 10-week multicenter, parallel group study in a pediatric outpatient population (children and adolescents, ages 8-17). Patients in this study were titrated to a total daily fluvoxamine maleate dose of approximately 100 mg/day over the first two weeks of the trial, following which the dose was adjusted within a range of 50-200 mg/day (on a bid schedule) on the basis of response and tolerance. All patients had moderate-to-severe OCD (DSM-III-R) with mean baseline ratings on the Children's Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale (CY-BOCS), total score of 24. Patients receiving fluvoxamine maleate experienced mean reductions of approximately 6 units on the CY-BOCS total score, compared to a 3 unit reduction for placebo patients.
The following table provides the outcome classification by treatment group on the Global Improvement item of the Clinical Global Impression (CGI) scale for the pediatric study.
OUTCOME CLASSIFICATION (%) ON CGI-GLOBAL IMPROVEMENT ITEM FOR COMPLETERS IN PEDIATRIC STUDIES Outcome Classification Fluvoxamine (N = 38) Placebo (N = 36) Very Much Improved 21% 11% Much Improved 18% 17% Minimally Improved 37% 22% No Change 16% 44% Worse 8% 6% Post hoc exploratory analyses for gender effects on outcomes did not suggest any differential responsiveness on the basis of gender. Further exploratory analyses revealed a prominent treatment effect in the 8-11 age group and essentially no effect in the 12-17 age group. While the significance of these results is not clear, the 2-3 fold higher steady state plasma fluvoxamine concentrations in children compared to adolescents (see Pharmacokinetics) is suggestive that decreased exposure in adolescents may have been a factor, and dose adjustment in adolescents (up to the adult maximum of 300 mg) may be indicated to achieve therapeutic benefit.
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets are indicated for the treatment of obsessions and compulsions in patients with Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD), as defined in the DSM-III-R. The obsessions or compulsions cause marked distress, are time-consuming, or significantly interfere with social or occupational functioning.
The efficacy of Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets was established in three 10-week trials with obsessive compulsive outpatients with the diagnosis of Obsessive Compulsive Disorder as defined in DSM-III-R. (See Clinical Trials under CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY.)
Obsessive Compulsive Disorder is characterized by recurrent and persistent ideas, thoughts, impulses or images (obsessions) that are ego- dystonic and/or repetitive, purposeful, and intentional behaviors (compulsions) that are recognized by the person as excessive or unreasonable.
The effectiveness of Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets for long-term use, i.e., for more than 10 weeks, has not been systematically evaluated in placebo-controlled trials. Therefore, the physician who elects to use Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets for extended periods should periodically re-evaluate the long-term usefulness of the drug for the individual patient. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.)
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Co-administration of thioridazine, terfenadine, astemizole, cisapride, pimozide, alosetron or tizanidine with fluvoxamine maleate is contraindicated (see WARNINGS, PRECAUTIONS, and Lotronex™ (alosetron) package insert).
Fluvoxamine maleate tablets are contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to fluvoxamine maleate.
-
WARNINGS
Potential for Interaction with Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors
In patients receiving another serotonin reuptake inhibitor drug in combination with monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI), there have been reports of serious, sometimes fatal, reactions including hyperthermia, rigidity, myoclonus, autonomic instability with possible rapid fluctuations of vital signs, and mental status changes that include extreme agitation progressing to delirium and coma. These reactions have also been reported in patients who have discontinued that drug and have been started on a MAOI. Some cases presented with features resembling neuroleptic malignant syndrome. Therefore, it is recommended that Fluvoxamine MaleateTablets not be used in combination with a MAOI, or within 14 days of discontinuing treatment with a MAOI. After stopping Fluvoxamine MaleateTablets, at least 2 weeks should be allowed before starting a MAOI.
Potential Interaction with Thioridazine
The effect of fluvoxamine (25 mg bid for one week) on thioridazine steady-state concentrations was evaluated in 10 male inpatients with schizophrenia. Concentrations of thioridazine and its two active metabolites, mesoridazine and sulforidazine, increased threefold following co-administration of fluvoxamine.
Thioridazine administration produces a dose-related prolongation of the QTc interval, which is associated with serious ventricular arrhythmias, such as torsade de pointes-type arrhythmias, and sudden death. It is likely that this experience underestimates the degree of risk that might occur with higher doses of thioridazine. Moreover, the effect of fluvoxamine may be even more pronounced when it is administered at higher doses.
Therefore, fluvoxamine and thioridazine should not be co-administered (see CONTRAINDICATIONS and PRECAUTIONS).
Potential Terfenadine, Astemizole, Cisapride, and Pimozide Interactions
Terfenadine, astemizole, cisapride, and pimozide are all metabolized by the cytochrome P4503A4 isozyme, and it has been demonstrated that ketoconazole, a potent inhibitor of 3A4, blocks the metabolism of these drugs, resulting in increased plasma concentrations of parent drug. Increased plasma concentrations of terfenadine, astemizole, cisapride, and pimozide cause QT prolongation and have been associated with torsades de pointes-type ventricular tachycardia, sometimes fatal. As noted below, a substantial pharmacokinetic interaction has been observed for fluvoxamine in combination with alprazolam, a drug that is known to be metabolized by the 3A4 isozyme. Although, it has not been definitively demonstrated that fluvoxamine is a potent 3A4 inhibitor, it is likely to be, given the substantial interaction of fluvoxamine with alprazolam. Consequently, it is recommended that fluvoxamine not be used in combination with either terfenadine, astemizole, cisapride, or pimozide (see CONTRAINDICATIONS and PRECAUTIONS).
Potential Tizanidine Interaction
Fluvoxamine is a potent inhibitor of CYP1A2 and tizanidine is a CYP1A2 substrate. The effect of fluvoxamine (100 mg daily for 4 days) on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of a single 4 mg dose of tizanidine has been studied in 10 healthy subjects. Tizanidine Cmax was increased approximately 12-fold (range 5-fold to 32-fold), elimination half-life was increased by almost 3-fold, and AUC increased 33-fold (range 14-fold to 103-fold). The mean maximal effect on blood pressure was a 35 mm Hg decrease in systolic blood pressure, a 20 mm Hg decrease in diastolic blood pressure, and a 4 beat/min decrease in heart rate. Drowsiness was significantly increased and performance on a psychomotor task was significantly impaired. Fluvoxamine and tizanidine should not be used together. (See Contraindications and Precautions).
Potential Alosetron Interaction
Fluvoxamine, an inhibitor of several CYP isozymes, has been shown to increase mean alosetron plasma concentrations (AUC) approximately 6-fold and prolonged the half-life by approximately 3-fold. Consequently, it is recommended that fluvoxamine not be used in combination with alosetron (See Contraindications, Precautions, and Lotronex™ (alosetron) package insert).
Clinical Worsening and Suicide Risk
Patients with major depressive disorder (MDD), both adult and pediatric, may experience worsening of their depression and/or the emergence of suicidal ideation and behavior (suicidality) or unusual changes in behavior, whether or not they are taking antidepressant medications, and this risk may persist until significant remission occurs. Suicide is a known risk of depression and certain other psychiatric disorders, and these disorders themselves are the strongest predictors of suicide. There has been a long-standing concern, however, that antidepressants may have a role in inducing worsening of depression and the emergence of suicidality in certain patients during the early phases of treatment. Pooled analyses of short-term placebo-controlled trials of antidepressant drugs (SSRIs and others) showed that these drugs increase the risk of suicidal thinking and behavior (suicidality) in children, adolescents, and young adults (ages 18-24) with major depressive disorder (MDD) and other psychiatric disorders. Short-term studies did not show an increase in the risk of suicidality with antidepressants compared to placebo in adults beyond age 24; there was a reduction with antidepressants compared to placebo in adults aged 65 and older.
The pooled analyses of placebo-controlled trials in children and adolescents with MDD, obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD), or other psychiatric disorders included a total of 24 short-term trials of 9 antidepressant drugs in over 4400 patients. The pooled analyses of placebo-controlled trials in adults with MDD or other psychiatric disorders included a total of 295 short-term trials (median duration of 2 months) of 11 antidepressant drugs in over 77,000 patients. There was considerable variation in risk of suicidality among drugs, but a tendency toward an increase in the younger patients for almost all drugs studied. There were differences in absolute risk of suicidality across the different indications, with the highest incidence in MDD. The risk differences (drug vs placebo), however, were relatively stable within age strata and across indications. These risk differences (drug-placebo difference in the number of cases of suicidality per 1000 patients treated) are provided in Table 1.
Table 1 Age Range Drug-Placebo Difference in Number of Cases of Suicidality per 1000 Patients Treated Increases Compared to Placebo <18 14 additional cases 18-24 5 additional cases Decreases Compared to Placebo 25-64 1 fewer case ≥65 6 fewer cases No suicides occurred in any of the pediatric trials. There were suicides in the adult trials, but the number was not sufficient to reach any conclusion about drug effect on suicide.
It is unknown whether the suicidality risk extends to longer-term use, i.e., beyond several months. However, there is substantial evidence from placebo-controlled maintenance trials in adults with depression that the use of antidepressants can delay the recurrence of depression.
All patients being treated with antidepressants for any indication should be monitored appropriately and observed closely for clinical worsening, suicidality, and unusual changes in behavior, especially during the initial few months of a course of drug therapy, or at times of dose changes, either increases or decreases.
The following symptoms, anxiety, agitation, panic attacks, insomnia, irritability, hostility, aggressiveness, impulsivity, akathisia (psychomotor restlessness), hypomania, and mania, have been reported in adult and pediatric patients being treated with antidepressants for major depressive disorder as well as for other indications, both psychiatric and nonpsychiatric. Although a causal link between the emergence of such symptoms and either the worsening of depression and/or the emergence of suicidal impulses has not been established, there is concern that such symptoms may represent precursors to emerging suicidality.
Consideration should be given to changing the therapeutic regimen, including possibly discontinuing the medication, in patients whose depression is persistently worse, or who are experiencing emergent suicidality or symptoms that might be precursors to worsening depression or suicidality, especially if these symptoms are severe, abrupt in onset, or were not part of the patient's presenting symptoms.
If the decision has been made to discontinue treatment, medication should be tapered, as rapidly as is feasible, but with recognition that abrupt discontinuation can be associated with certain symptoms (see PRECAUTIONS and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION - Discontinuation of Treatment with Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets, for a description of the risks of discontinuation of Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets).
Families and caregivers of patients being treated with antidepressants for major depressive disorder or other indications, both psychiatric and nonpsychiatric, should be alerted about the need to monitor patients for the emergence of agitation, irritability, unusual changes in behavior, and the other symptoms described above, as well as the emergence of suicidality, and to report such symptoms immediately to health care providers. Such monitoring should include daily observation by families and caregivers. Prescriptions for Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets should be written for the smallest quantity of tablets consistent with good patient management, in order to reduce the risk of overdose.
Screening Patients for Bipolar Disorder
A major depressive episode may be the initial presentation of bipolar disorder. It is generally believed (though not established in controlled trials) that treating such an episode with an antidepressant alone may increase the likelihood of precipitation of a mixed/manic episode in patients at risk for bipolar disorder. Whether any of the symptoms described above represent such a conversion is unknown. However, prior to initiating treatment with an antidepressant, patients with depressive symptoms should be adequately screened to determine if they are at risk for bipolar disorder; such screening should include a detailed psychiatric history, including a family history of suicide, bipolar disorder, and depression. It should be noted that Fluvoxamine Maleate is not approved for use in treating bipolar depression.
Other Potentially Important Drug Interactions
(Also see PRECAUTIONS - Drug Interactions)
Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines metabolized by hepatic oxidation (e.g., alprazolam, midazolam, triazolam, etc.) should be used with caution because the clearance of these drugs is likely to be reduced by fluvoxamine. The clearance of benzodiazepines metabolized by glucuronidation (e.g., lorazepam, oxazepam, temazepam) is unlikely to be affected by fluvoxamine.
Alprazolam
When fluvoxamine maleate (100 mg qd) and alprazolam (1 mg qid) were co-administered to steady state, plasma concentrations and other pharmacokinetic parameters (AUC, Cmax, T1/2) of alprazolam were approximately twice those observed when alprazolam was administered alone; oral clearance was reduced by about 50%. The elevated plasma alprazolam concentrations resulted in decreased psychomotor performance and memory.
This interaction, which has not been investigated using higher doses of fluvoxamine, may be more pronounced if a 300 mg daily dose is co-administered, particularly since fluvoxamine exhibits non-linear pharmacokinetics over the dosage range 100-300 mg.
If alprazolam is co-administered with Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets, the initial alprazolam dosage should be at least halved and titration to the lowest effective dose is recommended. No dosage adjustment is required for Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets.
Diazepam
The co-administration of Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets and diazepam is generally not advisable. Because fluvoxamine reduces the clearance of both diazepam and its active metabolite, N-desmethyldiazepam, there is a strong likelihood of substantial accumulation of both species during chronic co-administration.
Evidence supporting the conclusion that it is inadvisable to co-administer fluvoxamine and diazepam is derived from a study in which healthy volunteers taking 150 mg/day of fluvoxamine were administered a single oral dose of 10 mg of diazepam. In these subjects (N=8), the clearance of diazepam was reduced by 65% and that of N-desmethyldiazepam to a level that was too low to measure over the course of the 2 week long study.
It is likely that this experience significantly underestimates the degree of accumulation that might occur with repeated diazepam administration. Moreover, as noted with alprazolam, the effect of fluvoxamine may even be more pronounced when it is administered at higher doses. Accordingly, diazepam and fluvoxamine should not ordinarily be co-administered.
Mexiletine
The effect of steady-state fluvoxamine (50 mg BID for 7 days) on the single dose pharmacokinetics of mexiletene (200 mg) was evaluated in 6 healthy Japanese males. The clearance of mexiletine was reduced by 38% following co-administration with fluvoxamine compared to mexiletene alone. If fluvoxamine and mexiletene are co-administered, serum mexiletene levels should be monitored.
Serotonin Syndrome
The development of a potentially life-threatening serotonin syndrome may occur with fluvoxamine treatment particularly with concomitant use of serotonergic drugs (including triptans) and with drugs which impair metabolism of serotonin (including MAOIs). Serotonin syndrome symptoms may include mental status changes (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, coma), autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, labile blood pressure, hyperthermia), neuromuscular aberrations (e.g., hyperreflexia, incoordination) and/or gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea).
The concomitant use of fluvoxamine with MAOIs intended to treat depression is contraindicated (see CONTRAINDICATIONS and WARNINGS – Potential for Interaction with Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors.)
If concomitant treatment of fluvoxamine with 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor agonist (triptan) is clinically warranted, careful observation of the patient is advised, particularly during treatment initiation and dose increases (see PRECAUTIONS – Drug Interactions).
The concomitant use of fluvoxamine with serotonin precursors (such a tryptophan) is not recommended (see PRECAUTIONS – Drug Interactions).
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS) or NMS-Like Events
Rare instances of neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS) or NMS-like events have been reported in association with fluvoxamine treatment when co-administered with antipsychotic. Additionally, a small number of such cases have been reported with fluvoxamine treatment in the absence of antipsychotic co-administration. These serious and sometimes fatal events can include hyperthermia, muscle rigidity, autonomic instability with possible rapid fluctuations of vital signs, and mental status changes. As these events may result in potentially life-threatening conditions, patients receiving this combination of therapy should be monitored for the emergence of NMS-like signs and symptoms. Treatment with fluvoxamine and any concomitant antipsychotic agent should be discontinued immediately if such event occurs and supportive symptomatic treatment should be initiated.
Theophylline
The effect of steady-state fluvoxamine (50 mg bid) on the pharmacokinetics of a single dose of theophylline (375 mg as 442 mg aminophylline) was evaluated in 12 healthy non-smoking, male volunteers. The clearance of theophylline was decreased approximately 3-fold. Therefore, if theophylline is co-administered with fluvoxamine maleate, its dose should be reduced to one third of the usual daily maintenance dose and plasma concentrations of theophylline should be monitored. No dosage adjustment is required for Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets.
Warfarin
When fluvoxamine maleate (50 mg tid) was administered concomitantly with warfarin for two weeks, warfarin plasma concentrations increased by 98% and prothrombin times were prolonged.
Thus patients receiving oral anticoagulants and Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets should have their prothrombin time monitored and their anticoagulant dose adjusted accordingly. No dosage adjustment is required for Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets.
-
PRECAUTIONS
General
Discontinuation of Treatment with Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets
During marketing of fluvoxamine maleate tablets and other SSRIs and SNRIs (Serotonin and Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors), there have been spontaneous reports of adverse events occurring upon discontinuation of these drugs, particularly when abrupt, including the following: dysphoric mood, irritability, agitation, dizziness, sensory disturbances (e.g., paresthesias, such as electric shock sensations), anxiety, confusion, headache, lethargy, emotional lability, insomnia, and hypomania. While these events are generally self-limiting, there have been reports of serious discontinuation symptoms. Patients should be monitored for these symptoms when discontinuing treatment with Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets. A gradual reduction in the dose rather than abrupt cessation is recommended whenever possible. If intolerable symptoms occur following a decrease in the dose or upon discontinuation of treatment, then resuming the previously prescribed dose may be considered. Subsequently, the physician may continue decreasing the dose but at a more gradual rate (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Abnormal Bleeding
Published case reports have documented the occurrence of bleeding episodes in patients treated with psychotropic agents that interfere with serotonin reuptake. Subsequent epidemiological studies, both of the case-control and cohort design, have demonstrated an association between use of psychotropic drugs that interfere with serotonin reuptake and the occurrence of upper gastrointestinal bleeding. In two studies, concurrent use of a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) or aspirin potentiated the risk of bleeding (see Drug Interactions). Although these studies focused on upper gastrointestinal bleeding, there is reason to believe that bleeding at other sites may be similarly potentiated. Patients should be cautioned regarding the risk of bleeding associated with the concomitant use of fluvoxamine with NSAIDs, aspirin, or other drugs that affect coagulation.
Activation of Mania/Hypomania
During premarketing studies involving primarily depressed patients, hypomania or mania occurred in approximately 1% of patients treated with fluvoxamine. In a 10 week pediatric OCD study, 2 out of 57 patients (4%) treated with fluvoxamine experienced manic reactions compared to none of 63 placebo patients.
Activation of mania/hypomania has also been reported in a small proportion of patients with major affective disorder who were treated with other marketed antidepressants. As with all antidepressants, Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets should be used cautiously in patients with a history of mania.
Seizures
During premarketing studies, seizures were reported in 0.2% of fluvoxamine-treated patients. Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets should be used cautiously in patients with a history of seizures. It should be discontinued in any patient who develops seizures.
Hyponatremia
Hyponatremia may occur as a result of treatment with SSRIs and SNRIs, including fluvoxamine. In many cases, this hyponatremia appears to be the result of the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH). Cases with serum sodium lower than 110 mmol/L have been reported. Elderly patients may be at greater risk of developing hyponatremia with SSRIs and SNRIs. Also, patients taking diuretics or who are otherwise volume depleted may be at greater risk (see Geriatric Use). Discontinuation of fluvoxamine should be considered in patients with symptomatic hyponatremia and appropriate medical intervention should be instituted.
Signs and symptoms of hyponatremia include headache, difficulty concentrating, memory impairment, confusion, weakness, and unsteadiness, which may lead to falls. Signs and symptoms associated with more severe and/or acute cases have included hallucination, syncope, seizure, coma, respiratory arrest, and death.
Use in Patients with Concomitant Illness
Closely monitored clinical experience with Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets in patients with concomitant systemic illness is limited. Caution is advised in administering Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets to patients with diseases or conditions that could affect hemodynamic responses or metabolism.
Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets have not been evaluated or used to any appreciable extent in patients with a recent history of myocardial infarction or unstable heart disease. Patients with these diagnoses were systematically excluded from many clinical studies during the product's premarketing testing. Evaluation of the electrocardiograms for patients with depression or OCD who participated in premarketing studies revealed no differences between fluvoxamine and placebo in the emergence of clinically important ECG changes.
In patients with liver dysfunction, fluvoxamine clearance was decreased by approximately 30%. Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets should be slowly titrated in patients with liver dysfunction during the initiation of treatment.
Information for Patients
Prescribers or other health professionals should inform patients, their families, and their caregivers about the benefits and risks associated with treatment with Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets and should counsel them in its appropriate use. A patient Medication Guide about "Antidepressant Medicines, Depression and other Serious Mental Illness, and Suicidal Thoughts or Actions" is available for Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets. The prescriber or health professional should instruct patients, their families, and their caregivers to read the Medication Guide and should assist them in understanding its contents. Patients should be given the opportunity to discuss the contents of the Medication Guide and to obtain answers to any questions they may have. The complete text of the Medication Guide is reprinted at the end of this document.
Patients should be advised of the following issues and asked to alert their prescriber if these occur while taking Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets.
Patients should be cautioned about the risk of serotonin syndrome with the concomitant use of fluvoxamine and triptans, tramadol or other serotonergic agents.
Clinical Worsening and Suicidal Risk
Patients, their families, and their caregivers should be encouraged to be alert to the emergence of anxiety, agitation, panic attacks, insomnia, irritability, hostility, aggressiveness, impulsivity, akathisia (psychomotor restless), hypomania, mania, other unusual changes in behavior, worsening of depression, and suicidal ideation, especially early during antidepressant treatment and when the dose is adjusted up or down. Families and caregivers of patients should be advised to look for the emergence of such symptoms on a day-to-day basis, since changes may be abrupt. Such symptoms should be reported to the patient's prescriber or health professional, especially if they are severe, abrupt in onset, or were not part of the patient's presenting symptoms. Symptoms such as these may be associated with an increased risk for suicidal thinking and behavior and indicate a need for very close monitoring and possibly changes in the medication.
Interference with Cognitive or Motor Performance
Since any psychoactive drug may impair judgement, thinking, or motor skills, patients should be cautioned about operating hazardous machinery, including automobiles, until they are certain that fluvoxamine maleate tablet therapy does not adversely affect their ability to engage in such activities.
Pregnancy
Patients should be advised to notify their physicians if they become pregnant or intend to become pregnant during therapy with Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets.
Nursing
Patients receiving Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets should be advised to notify their physicians if they are breast feeding an infant. (See PRECAUTIONS - Nursing Mothers)
Concomitant Medication
Patients should be advised to notify their physicians if they are taking, or plan to take, any prescription or over-the-counter drugs, since there is a potential for clinically important interactions with Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets. Patients should be cautioned about the concomitant use of fluvoxamine and NSAIDs, aspirin, or other drugs that affect coagulation since the combined use of psychotropic drugs that interfere with serotonin reuptake and these agents has been associated with an increased risk of bleeding.
Because of the potential for the increased risk of serious adverse reactions including severe lowering of blood pressure and sedation when fluvoxamine and tizanidine are used together, fluvoxamine should not be used with tizanidine.
Because of the potential for the increased risk of serious adverse reactions when fluvoxamine and alosetron are used together, fluvoxamine should not be used with Lotronex™ (alosetron).
Drug interactions
Potential Interactions with Drugs that Inhibit or are Metabolized by Cytochrome P450 Isozymes
Multiple hepatic cytochrome P450 (CYP450) enzymes are involved in the oxidative biotransformation of a large number of structurally different drugs and endogenous compounds. The available knowledge concerning the relationship of fluvoxamine and the CYP450-enzyme system has been obtained mostly from pharmacokinetic interaction studies conducted in healthy volunteers, but some preliminary in vitro data are also available.
Based on a finding of substantial interactions of fluvoxamine with certain of these drugs (see later parts of this section and also WARNINGS for details) and limited in vitro data for the 3A4 isozyme, it appears that fluvoxamine inhibits the following isozymes that are known to be involved in the metabolism of the listed drugs:
1A2 2C9 3A4 2C19 Warfarin Warfarin Alprazolam Omeprazole Theophylline Propranolol Tizanidine In vitro data suggest that fluvoxamine is a relatively weak inhibitor of the 2D6 isozyme.
Approximately 7% of the normal population has a genetic defect that leads to reduced levels of activity of the cytochrome P4502D6 isozyme. Such individuals have been referred to as "poor metabolizers" (PM) of drugs such as debrisoquin, dextromethorphan, and tricyclic antidepressants. While none of the drugs studied for drug interactions significantly affected the pharmacokinetics of fluvoxamine, an in vivo study of fluvoxamine single- dose pharmokinetics in 13 PM subjects demonstrated altered pharmokinetic properties compared to 16 "extensive metabolizers" (EM): mean Cmax, AUC, and half-life were increased by 52%, 200%, and 62%, respectively, in the PM compared to the EM group. This suggests that fluvoxamine is metabolized, at least in part, by the 2D6 isozyme. Caution is indicated in patients known to have reduced levels of P4502D6 activity and those receiving concomitant drugs known to inhibit this isozyme (e.g. quinidine).
The metabolism of fluvoxamine has not been fully characterized and the effects of potent P450 isozyme inhibition, such as the ketoconazole inhibition of 3A4, on fluvoxamine metabolism have not been studied.
A clinically significant fluvoxamine interaction is possible with drugs having a narrow therapeutic ratio such as terfenadine, astemizole, cisapride, or pimozide, warfarin, theophylline, certain benzodiazepines and phenytoin. If Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets are to be administered together with a drug that is eliminated via oxidative metabolism and has a narrow therapeutic window, plasma levels and/or pharmacodynamic effects of the latter drug should be monitored closely, at least until steady-state conditions are reached (See CONTRAINDICATIONS and WARNINGS).
CNS Active Drugs
Alcohol
Studies involving single 40 g doses of ethanol (oral administration in one study and intravenous in the other) and multiple dosing with fluvoxamine maleate (50 mg bid) revealed no effect of either drug on the pharmacokinetics or pharmacodynamics of the other.
Carbamazepine
Elevated carbamazepine levels and symptoms of toxicity have been reported with the co-administration of fluvoxamine maleate and carbamazepine.
Clozapine
Elevated serum levels of clozapine have been reported in patients taking fluvoxamine maleate and clozapine. Since clozapine related seizures and orthostatic hypotension appear to be dose related, the risk of these adverse events may be higher when fluvoxamine and clozapine are co-administered. Patients should be closely monitored when fluvoxamine maleate and clozapine are used concurrently.
Lithium
As with other serotonergic drugs, lithium may enhance the serotonergic effects of fluvoxamine and, therefore, the combination should be used with caution. Seizures have been reported with the co-administration of fluvoxamine maleate and lithium.
Lorazepam
A study of multiple doses of fluvoxamine maleate (50 mg bid) in healthy male volunteers (N=12) and a single dose of lorazepam (4 mg single dose) indicated no significant pharmacokinetic interaction. On average, both lorazepam alone and lorazepam with fluvoxamine produced substantial decrements in cognitive functioning; however, the co-administration of fluvoxamine and lorazepam did not produce larger mean decrements compared to lorazepam alone.
Methadone
Significantly increased methadone (plasma level:dose) ratios have been reported when fluvoxamine maleate was administered to patients receiving maintenance methadone treatment, with symptoms of opioid intoxication in one patient. Opioid withdrawal symptoms were reported following fluvoxamine maleate discontinuation in another patient.
Serotonergic Drugs
Based on the mechanism of action of fluvoxamine and the potential for serotonin syndrome, caution is advised when fluvoxamine is coadministered with other drugs that may affect the serotonergic neurotransmitter systems, such as triptans, linezolid (an antibiotic which is a reversible non-selective MAOI), lithium, tramadol, or St. John's Wort (see WARNINGS – Serotonin Syndrome). The concomitant use of fluvoxamine with other SSRIs, SNRIs or tryptophan is not recommended (see PRECAUTIONS – Drug Interactions).
Sumatriptan
There have been rare postmarketing reports describing patients with weakness, hyperreflexia, and incoordination following the use of a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) and sumatriptan. If concomitant treatment with sumatriptan and an SSRI (eg. fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine, sertraline) is clinically warranted, appropriate observation of the patient is advised.
Tacrine
In a study of 13 healthy, male volunteers, a single 40 mg dose of tacrine added to fluvoxamine 100 mg/day administered at steady-state was associated with five- and eight-fold increases in tacrine Cmax and AUC, respectively, compared to the administration of tacrine alone. Five subjects experienced nausea, vomiting, sweating, and diarrhea following co-administration, consistent with the cholinergic effects of tacrine.
Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs)
Significantly increased plasma TCA levels have been reported with the co-administration of fluvoxamine maleate and amitriptyline, clomipramine or imipramine. Caution is indicated with the co-administration of Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets and TCAs; plasma TCA concentrations may need to be monitored, and the dose of TCA may need to be reduced.
Triptans
There have been rare postmarketing reports of serotonin syndrome with use of an SSRI and a triptan. If concomitant treatment of fluvoxamine with a triptan is clinically warranted, careful observation of the patient is advised, particularly during treatment initiation and dose increases (see WARNINGS – Serotonin Syndrome).
Other Drugs
Drugs That Interfere With Hemostasis (NSAIDs, Aspirin, Warfarin, etc.)
Serotonin release by platelets plays an important role in hemostasis. Epidemiological studies of the case-control and cohort design that have demonstrated an association between use of psychotropic drugs that interfere with serotonin reuptake and the occurrence of upper gastrointestinal bleeding have also shown that concurrent use of an NSAID or aspirin potentiated the risk of bleeding. Thus, patients should be cautioned about the use of such drugs concurrently with fluvoxamine.
Alosetron
Because alosetron is metabolized by a variety of hepatic CYP drug-metabolizing enzymes, inducers or inhibitors of these enzymes may change the clearance of alosetron. Fluvoxamine is a known potent inhibitor of CYP1A2 and also inhibits CYP3A4, CYP2C9, and CYP2C19. In a pharmacokinetic study, 40 healthy female subjects received fluvoxamine in escalating doses from 50 to 200 mg a day for 16 days, with coadministration of alosetron 1 mg on the last day. Fluvoxamine increased mean alosetron plasma concentrations (AUC) approximately 6-fold and prolonged the half-life by approximately 3-fold. (See Contraindications, Precautions, and Lotronex™ (alosetron) package insert.)
Digoxin
Administration of fluvoxamine maleate 100 mg daily for 18 days (N=8) did not significantly affect the pharmacokinetics of a 1.25 mg single intravenous dose of digoxin.
Diltiazem
Bradycardia has been reported with the co-administration of fluvoxamine maleate and diltiazem.
Propranolol and Other Beta-Blockers
Co-administration of fluvoxamine maleate 100 mg per day and propranolol 160 mg per day in normal volunteers resulted in a mean five-fold increase (range 2 to 17) in minimum propranolol plasma concentrations. In this study, there was a slight potentiation of the propranolol-induced reduction in heart rate and reduction in the exercise diastolic pressure.
One case of bradycardia and hypotension and a second case of orthostatic hypotension have been reported with the co-administration of fluvoxamine and metoprolol.
If propranolol or metoprolol is co-administered with Fluvoxamine Maleate tablets, a reduction in the initial beta-blocker dose and more cautious dose titration is recommended. No dosage adjustment is required for Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets.
Co-administration of fluvoxamine maleate 100 mg per day with atenolol 100 mg per day (N=6) did not affect the plasma concentrations of atenolol. Unlike propranolol and metoprolol which undergo hepatic metabolism, atenolol is eliminated primarily by renal excretion.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, and Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
There is no evidence of carcinogenicity, mutagenicity or impairment of fertility with fluvoxamine maleate.
There was no evidence of carcinogenicity in rats treated orally with fluvoxamine maleate for 30 months or hamsters treated orally with fluvoxamine maleate for 20 (females) or 26 (males) months. The daily doses in the high dose groups in these studies were increased over the course of the study from a minimum of 160 mg/kg to a maximum of 240 mg/kg in rats, and from a minimum of 135 mg/kg to a maximum of 240 mg/kg in hamsters. The maximum dose of 240 mg/kg is approximately 6 times the maximum human daily dose on a mg/m2 basis.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy Category C
In teratology studies in rats and rabbits, daily oral doses of fluvoxamine maleate of up to 80 and 40 mg/kg, respectively (approximately 2 times the maximum human daily dose on a mg/m2 basis) caused no fetal malformations. However, in other reproduction studies in which pregnant rats were dosed through weaning there was (1) an increase in pup mortality at birth (seen at 80 mg/kg and above but not at 20 mg/kg), and (2) decreases in postnatal pup weights (seen at 160 but not at 80 mg/kg) and survival (seen at all doses; lowest dose tested = 5 mg/kg). (Doses of 5, 20, 80, and 160 mg/kg are approximately 0.1, 0.5, 2, and 4 times the maximum human daily dose on a mg/m2 basis.) While the results of a cross-fostering study implied that at least some of these results likely occurred secondarily to maternal toxicity, the role of a direct drug effect on the fetuses or pups could not be ruled out. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Fluvoxamine maleate should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Nonteratogenic Effects
Neonates exposed to fluvoxamine and other SSRIs or serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), late in the third trimester have developed complications requiring prolonged hospitalization, respiratory support, and tube feeding. These findings are based on postmarketing reports. Such complications can arise immediately upon delivery. Reported clinical findings have included respiratory distress, cyanosis, apnea, seizures, temperature instability, feeding difficulty, vomiting, hypoglycemia, hypotonia, hypertonia, hyperreflexia, tremor, jitteriness, irritability, and constant crying. These features are consistent with either a direct toxic effect of SSRIs and SNRIs or, possibly, a drug discontinuation syndrome. It should be noted that, in some cases, the clinical picture is consistent with serotonin syndrome (see WARNINGS).
Infants exposed to SSRIs in late pregnancy may have an increased risk for persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn (PPHN). PPHN is associated with substantial neonatal morbidity and mortality. In a case-control study of 377 women whose infants were born with PPHN and 836 women whose infants were born healthy, the risk for developing PPHN was approximately six-fold higher for infants exposed to SSRIs after the 20th week of gestation compared to infants who had not been exposed to antidepressants during pregnancy. PPHN occurs in 1-2 per 1000 live births in the general population.
When treating a pregnant woman with fluvoxamine during the third trimester, the physician should carefully consider both the potential risks and benefits of treatment (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION). Physicians should note that in a prospective longitudinal study of 201 women with a history of major depression who were euthymic at the beginning of pregnancy, women who discontinued antidepressant medication during pregnancy were more likely to experience a relapse of major depression than women who continued antidepressant medication.
Nursing Mothers
As for many other drugs, fluvoxamine is secreted in human breast milk. The decision of whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug should take into account the potential for serious adverse effects from exposure to fluvoxamine in the nursing infant as well as the potential benefits of Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets therapy to the mother.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in the pediatric population other than pediatric patients with OCD have not been established (see BOX WARNING and WARNINGS – Clinical Worsening and Suicide Risk). Anyone considering the use of Fluvoxamine in a child or adolescent must balance the potential risks with the clinical need.
The efficacy of fluvoxamine maleate for the treatment of OCD was demonstrated in a 10-week multicenter placebo controlled study with 120 outpatients ages 8-17. In addition, 99 of these outpatients continued open-label fluvoxamine maleate treatment for up to another one to three years, equivalent to 94 patient years. The adverse event profile observed in that study was generally similar to that observed in adult studies with fluvoxamine (See WARNINGS – Clinical Worsening and Suicide Risk, ADVERSE REACTIONS, and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Decreased appetite and weight loss have been observed in association with the use of fluvoxamine as well as other SSRIs. Consequently, regular monitoring of weight and growth is recommended if treatment of a child with an SSRI is to be continued long term.
The risks, if any that may be associated with fluvoxamine's extended use in children and adolescents with OCD have not been systematically assessed. The prescriber should be mindful that the evidence relied upon to conclude that fluvoxamine is safe for use in children and adolescents derives from relatively short term clinical studies and from extrapolation of experience gained with adult patients. In particular, there are no studies that directly evaluate the effects of long term fluvoxamine use on growth, development, and maturation of children and adolescents. Although there is no affirmative finding to suggest that fluvoxamine possesses a capacity to adversely affect growth, development or maturation, the absence of such findings is not compelling evidence of the absence of the potential of fluvoxamine to have adverse effects in chronic use.
Geriatric Use
Approximately 230 patients participating in controlled premarketing studies with Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets were 65 years of age or over. No overall differences in safety were observed between these patients and younger patients. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in response between the elderly and younger patients. SSRIs and SNRIs, including fluvoxamine, have been associated with cases of clinically significant hyponatremia in elderly patients, who may be at greater risk for this adverse event (see PRECAUTIONS, Hyponatremia). Furthermore, the clearance of fluvoxamine is decreased by about 50% in elderly compared to younger patients (see Pharmacokinetics under CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY), and greater sensitivity of some older individuals also cannot be ruled out. Consequently, Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets should be slowly titrated during initiation of therapy.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Associated with Discontinuation of Treatment
Of the 1087 OCD and depressed patients treated with fluvoxamine maleate in controlled clinical trials conducted in North America, 22% discontinued treatment due to an adverse event. The most common events (≥1%) associated with discontinuation and considered to be drug related (i.e., those events associated with dropout at a rate at least twice that of placebo) included:
Table 2 ADVERSE EVENTS ASSOCIATED WITH DISCONTINUATION OF TREATMENT IN OCD AND DEPRESSION POPULATIONS BODY SYSTEM/
ADVERSE EVENTPERCENTAGE OF PATIENTS FLUVOXAMINE PLACEBO BODY AS A WHOLE Headache 3% 1% Asthenia 2% <1% Abdominal Pain 1% 0% DIGESTIVE Nausea 9% 1% Diarrhea 1% <1% Vomiting 2% <1% Anorexia 1% <1% Dyspepsia 1% <1% NERVOUS SYSTEM Insomnia 4% 1% Somnolence 4% <1% Nervousness 2% <1% Agitation 2% <1% Dizziness 2% <1% Anxiety 1% <1% Dry mouth 1% <1% Incidence in Controlled Trials
Commonly Observed Adverse Events in Controlled Clinical Trials
Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets have been studied in controlled trials of OCD (N=320) and depression (N=1350).
In general, adverse event rates were similar in the two data sets as well as in the pediatric OCD study. The most commonly observed adverse events associated with the use of Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets and likely to be drug-related (incidence of 5% or greater and at least twice that for placebo) derived from TABLE 2 were: somnolence, insomnia, nervousness, tremor, nausea, dyspepsia, anorexia, vomiting, abnormal ejaculation, asthenia, and sweating. In a pool of two studies involving only patients with OCD, the following additional events were identified using the above rule: dry mouth, decreased libido, urinary frequency, anorgasmia, rhinitis and taste perversion. In a study of pediatric patients with OCD, the following additional events were identified using the above rule: agitation, depression, dysmenorrhea, flatulence, hyperkinesia, and rash.
Adverse Events Occurring at an Incidence of 1%
Table 2 enumerates adverse events that occurred in adults at a frequency of 1% or more, and were more frequent than in the placebo group, among patients treated with Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets in two short-term placebo controlled OCD trials (10 week) and depression trials (6 week) in which patients were dosed in a range of generally 100 to 300 mg/day.
This table shows the percentage of patients in each group who had at least one occurrence of an event at some time during their treatment. Reported adverse events were classified using a standard COSTART-based Dictionary terminology.
The prescriber should be aware that these figures cannot be used to predict the incidence of side effects in the course of usual medical practice where patient characteristics and other factors may differ from those that prevailed in the clinical trials. Similarly, the cited frequencies cannot be compared with figures obtained from other clinical investigations involving different treatments, uses, and investigators. The cited figures, however, do provide the prescribing physician with some basis for estimating the relative contribution of drug and non-drug factors to the side-effect incidence rate in the population studied.
Table 3 TREATMENT-EMERGENT ADVERSE EVENT INCIDENCE RATES BY BODY SYSTEM IN ADULT OCD AND DEPRESSION POPULATIONS COMBINED* Percentage Of Patients Reporting Event BODY SYSTEM/
ADVERSE EVENTFLUVOXAMINE PLACEBO N = 892 N = 778 - * Events for which fluvoxamine maleate incidence was equal to or less than placebo are not listed in the table above, but include the following: abdominal pain, abnormal dreams, appetite increase, back pain, chest pain, confusion, dysmenorrhea, fever, infection, leg cramps, migraine, myalgia, pain, paresthesia, pharyngitis, postural hypotension, pruritus, rash, rhinitis, thirst and tinnitus.
- † Includes "toothache," "tooth extraction and abscess," and "caries."
- ‡ Mostly feeling warm, hot, or flushed.
- § Mostly "blurred vision."
- ¶ Mostly "delayed ejaculation."
- # Incidence based on number of male patients.
BODY AS WHOLE Headache 22 20 Asthenia 14 6 Flu Syndrome 3 2 Chills 2 1 CARDIOVASCULAR Palpitations 3 2 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Nausea 40 14 Diarrhea 11 7 Constipation 10 8 Dyspepsia 10 5 Anorexia 6 2 Vomiting 5 2 Flatulence 4 3 Tooth Disorder† 3 1 Dysphagia 2 1 NERVOUS SYSTEM Somnolence 22 8 Insomnia 21 10 Dry Mouth 14 10 Nervousness 12 5 Dizziness 11 6 Tremor 5 1 Anxiety 5 3 Vasodilatation‡ 3 1 Hypertonia 2 1 Agitation 2 1 Decreased Libido 2 1 Depression 2 1 CNS Stimulation 2 1 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Upper Respiratory Infection 9 5 Dyspnea 2 1 Yawn 2 0 SKIN Sweating 7 3 SPECIAL SENSES Taste Perversion 3 1 Amblyopia§ 3 2 UROGENITAL Abnormal Ejaculation¶, # 8 1 Urinary Frequency 3 2 Impotence# 2 1 Anorgasmia 2 0 Urinary Retention 1 0 Adverse Events in OCD Placebo Controlled Studies Which are Markedly Different (defined as at least a two-fold difference) in rate from the Pooled Event Rates in OCD and Depression Placebo Controlled Studies
The events in OCD studies with a two-fold decrease in rate compared to event rates in OCD and depression studies were dysphagia and amblyopia (mostly blurred vision). Additionally, there was an approximate 25% decrease in nausea.
The events in OCD studies with a two-fold increase in rate compared to event rates in OCD and depression studies were: asthenia, abnormal ejaculation (mostly delayed ejaculation), anxiety, infection, rhinitis, anorgasmia (in males), depression, libido decreased, pharyngitis, agitation, impotence, myoclonus/twitch, thirst, weight loss, leg cramps, myalgia and urinary retention. These events are listed in order of decreasing rates in the OCD trials.
Other Adverse Events in OCD Pediatric Population
In pediatric patients (N=57) treated with Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets, the overall profile of adverse events was generally similar to that seen in adult studies, as shown in Table 2. However, the following adverse events, not appearing in Table 2, were reported in two or more of the pediatric patients and were more frequent with Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets than with placebo: abnormal thinking, cough increase, dysmenorrhea, ecchymosis, emotional lability, epistaxis, hyperkinesia, infection, manic reaction, rash, sinusitis, and weight decrease.
Male and Female Sexual Dysfunction with SSRIs
Although changes in sexual desire, sexual performance and sexual satisfaction often occur as manifestations of a psychiatric disorder and with aging, they may also be a consequence of pharmacologic treatment. In particular, some evidence suggests that selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) can cause such untoward sexual experiences.
Reliable estimates of the incidence and severity of untoward experiences involving sexual desire, performance and satisfaction are difficult to obtain, however, in part because patients and physicians may be reluctant to discuss them. Accordingly, estimates of the incidence of untoward sexual experience and performance cited in product labeling are likely to underestimate their actual incidence.
The table below displays the incidence of sexual side effects reported by at least 2% of patients taking Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets in placebo controlled trials in depression and OCD.
Table 4 PERCENTAGE OF PATIENTS REPORTING SEXUAL ADVERSE EVENTS IN ADULT PLACEBO-CONTROLLED TRIALS IN OCD AND DEPRESSION Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets N=892 Placebo
N=778- * Based on the number of male patients.
Abnormal Ejaculation* 8% 1% Impotence* 2% 1% Decreased Libido 2% 1% Anorgasmia 2% 0% There are no adequate and well-controlled studies examining sexual dysfunction associated with fluvoxamine treatment.
Fluvoxamine treatment has been associated with several cases of priapism. In those cases with a known outcome, patients recovered without sequelae and upon discontinuation of fluvoxamine.
While it is difficult to know the precise risk of sexual dysfunction associated with the use of SSRIs, physicians should routinely inquire about such possible side effects.
Vital Sign Changes
Comparisons of fluvoxamine maleate and placebo groups in separate pools of short-term OCD and depression trials on (1) median change from baseline on various vital signs variables and on (2) incidence of patients meeting criteria for potentially important changes from baseline on various vital signs variables revealed no important differences between fluvoxamine maleate and placebo.
Laboratory Changes
Comparisons of fluvoxamine maleate and placebo groups in separate pools of short-term OCD and depression trials on (1) median change from baseline on various serum chemistry, hematology, and urinalysis variables and on (2) incidence of patients meeting criteria for potentially important changes from baseline on various serum chemistry, hematology, and urinalysis variables revealed no important differences between fluvoxamine maleate and placebo.
ECG Changes
Comparisons of fluvoxamine maleate and placebo groups in separate pools of short-term OCD and depression trials on (1) mean change from baseline on various ECG variables and on (2) incidence of patients meeting criteria for potentially important changes from baseline on various ECG variables revealed no important differences between fluvoxamine maleate and placebo.
Other Events Observed During the Premarketing Evaluation of Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets
During premarketing clinical trials conducted in North America and Europe, multiple doses of fluvoxamine maleate were administered for a combined total of 2737 patient exposures in patients suffering OCD or Major Depressive Disorder. Untoward events associated with this exposure were recorded by clinical investigators using descriptive terminology of their own choosing. Consequently, it is not possible to provide a meaningful estimate of the proportion of individuals experiencing adverse events without first grouping similar types of untoward events into a limited (i.e., reduced) number of standard event categories.
In the tabulations which follow, a standard COSTART-based Dictionary terminology has been used to classify reported adverse events. If the COSTART term for an event was so general as to be uninformative, it was replaced with a more informative term. The frequencies presented, therefore, represent the proportion of the 2737 patient exposures to multiple doses of fluvoxamine maleate who experienced an event of the type cited on at least one occasion while receiving fluvoxamine maleate. All reported events are included in the list below, with the following exceptions: 1) those events already listed in Table 2, which tabulates incidence rates of common adverse experiences in placebo-controlled OCD and depression clinical trials, are excluded; 2) those events for which a drug cause was considered remote (i.e., neoplasia, gastrointestinal carcinoma, herpes simplex, herpes zoster, application site reaction, and unintended pregnancy) are omitted; and 3) events which were reported in only one patient and judged to not be potentially serious are not included. It is important to emphasize that, although the events reported did occur during treatment with fluvoxamine maleate, a causal relationship to fluvoxamine maleate has not been established.
Events are further classified within body system categories and enumerated in order of decreasing frequency using the following definitions: frequent adverse events are defined as those occurring on one or more occasions in at least 1/100 patients; infrequent adverse events are those occurring between 1/100 and 1/1000 patients; and rare adverse events are those occurring in less than 1/1000 patients.
Body as a Whole: Frequent: accidental injury, malaise; Infrequent: allergic reaction, neck pain, neck rigidity, overdose, photosensitivity reaction, suicide attempt; Rare: cyst, pelvic pain, sudden death.
Cardiovascular System: Frequent: hypertension, hypotension, syncope, tachycardia; Infrequent: angina pectoris, bradycardia, cardiomyopathy, cardiovascular disease, cold extremities, conduction delay, heart failure, myocardial infarction, pallor, pulse irregular, ST segment changes; Rare: AV block, cerebrovascular accident, coronary artery disease, embolus, pericarditis, phlebitis, pulmonary infarction, supraventricular extrasystoles.
Digestive System: Frequent: elevated liver transaminases; Infrequent: colitis, eructation, esophagitis, gastritis, gastroenteritis, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, gastrointestinal ulcer, gingivitis, glossitis, hemorrhoids, melena, rectal hemorrhage, stomatitis; Rare: biliary pain, cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, fecal incontinence, hematemesis, intestinal obstruction, jaundice.
Endocrine System: Infrequent: hypothyroidism; Rare: goiter
Hemic and Lymphatic Systems: Infrequent: anemia, ecchymosis, leukocytosis, lymphadenopathy, thrombocytopenia; Rare: leukopenia, purpura.
Metabolic and Nutritional Systems: Frequent: edema, weight gain, weight loss; Infrequent: dehydration, hypercholesterolemia; Rare: diabetes mellitus, hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, hypoglycemia, hypokalemia, lactate dehydrogenase increased.
Musculoskeletal System: Infrequent: arthralgia, arthritis, bursitis, generalized muscle spasm, myasthenia, tendinous contracture, tenosynovitis; Rare: arthrosis, myopathy, pathological fracture.
Nervous System: Frequent: amnesia, apathy, hyperkinesia, hypokinesia, manic reaction, myoclonus, psychotic reaction; Infrequent: agoraphobia, akathisia, ataxia, CNS depression, convulsion, delirium, delusion, depersonalization, drug dependence, dyskinesia, dystonia, emotional lability, euphoria, extrapyramidal syndrome, gait unsteady, hallucinations, hemiplegia, hostility, hypersomnia, hypochondriasis, hypotonia, hysteria, incoordination, increased salivation, increased libido, neuralgia, paralysis, paranoid reaction, phobia, psychosis, sleep disorder, stupor, twitching, vertigo; Rare: akinesia, coma, fibrillations, mutism, obsessions, reflexes decreased, slurred speech, tardive dyskinesia, torticollis, trismus, withdrawal syndrome.
Respiratory System: Frequent: cough increased, sinusitis; Infrequent: asthma, bronchitis, epistaxis, hoarseness, hyperventilation; Rare: apnea, congestion of upper airway, hemoptysis, hiccups, laryngismus, obstructive pulmonary disease, pneumonia.
Skin: Infrequent: acne, alopecia, dry skin, eczema, exfoliative dermatitis, furunculosis, seborrhea, skin discoloration, urticaria.
Special Senses: Infrequent: accommodation abnormal, conjunctivitis, deafness, diplopia, dry eyes, ear pain, eye pain, mydriasis, otitis media, parosmia, photophobia, taste loss, visual field defect; Rare: corneal ulcer, retinal detachment.
Urogenital System: Infrequent: anuria, breast pain, cystitis, delayed menstruation1, dysuria, female lactation1, hematuria, menopause1, menorrhagia1, metrorrhagia1, nocturia, polyuria, premenstrual syndrome1, urinary incontinence, urinary tract infection, urinary urgency, urination impaired, vaginal hemorrhage1, vaginitis1; Rare: kidney calculus, hematospermia2, oliguria.
- 1 Based on the number of females.
- 2 Based on the number of males.
Postmarketing Reports
Voluntary reports of adverse events in patients taking Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets that have been received since market introduction and are of unknown causal relationship to Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets use include: ventricular tachycardia (including torsades de pointes), porphyria, toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, Henoch-Schoenlein purpura, bullous eruption, priapism, agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, anaphylactic reaction, angioedema, vasculitis, hyponatremia, acute renal failure, hepatitis, pancreatitis, ileus, serotonin syndrome, neuropathy, laryngismus and severe akinesia with fever when fluvoxamine was co- administered with antipsychotic medication.
-
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
Physical and Psychological Dependence
The potential for abuse, tolerance and physical dependence with fluvoxamine maleate has been studied in a nonhuman primate model. No evidence of dependency phenomena was found. The discontinuation effects of Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets were not systematically evaluated in controlled clinical trials. Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets were not systematically studied in clinical trials for potential for abuse, but there was no indication of drug-seeking behavior in clinical trials. It should be noted, however, that patients at risk for drug dependency were systematically excluded from investigational studies of fluvoxamine maleate. Generally, it is not possible to predict on the basis of preclinical or premarketing clinical experience the extent to which a CNS active drug will be misused, diverted, and/or abused once marketed.
Consequently, physicians should carefully evaluate patients for a history of drug abuse and follow such patients closely, observing them for signs of fluvoxamine maleate misuse or abuse (i.e., development of tolerance, incrementation of dose, drug-seeking behavior).
-
OVERDOSAGE
Human Experience
Worldwide exposure to fluvoxamine maleate includes over 45,000 patients treated in clinical trials and an estimated exposure of 23,000,000 patients treated during worldwide marketing experience (circa 1999). Of the 462 cases of deliberate or accidental overdose involving fluvoxamine maleate reported from this population, there were 44 deaths. Of these, six were in patients taking fluvoxamine maleate alone and the remaining 38 were in patients taking fluvoxamine maleate along with other drugs. Among non-fatal overdose cases, 373 patients had complete recovery, four patients experienced adverse sequelae of overdosage, to include persistent mydriasis, unsteady gait, kidney complications (from trauma associated with overdose), and bowel infarction requiring a hemicolectomy. In the remaining 41 patients, the outcome was unknown. The largest known ingestion of fluvoxamine maleate involved 12,000 mg (equivalent of 2-3 months' dosage). The patient fully recovered. However, ingestions as low as 1,400 mg have been associated with lethal outcome, indicating considerable prognostic variability.
Commonly (≥5%) observed adverse events associated with fluvoxamine maleate overdose include coma, hypokalemia, hypotension, nausea, respiratory difficulties, somnolence, tachycardia, and vomiting. Other notable signs and symptoms seen with fluvoxamine maleate overdose (single or mixed drugs) included bradycardia, ECG abnormalities (such as heart arrest, QT interval prolongation, first degree atrioventricular block, bundle branch block, and junctional rhythm), convulsions, tremor, diarrhea, and increased reflexes.
Management of Overdose
Treatment should consist of those general measures employed in the management of overdosage with any antidepressant.
Ensure an adequate airway, oxygenation, and ventilation. Monitor cardiac rhythm and vital signs. General supportive and symptomatic measures are also recommended. Induction of emesis is not recommended. Gastric lavage with large-bore orogastric tube with appropriate airway protection, if needed, may be indicated if performed soon after ingestion, or in symptomatic patients.
Activated charcoal should be administered. Due to the large volume of distribution of this drug, forced diuresis, dialysis, hemoperfusion, and exchange transfusion are unlikely to be of benefit. No specific antidotes for fluvoxamine are known.
A specific caution involves patients taking, or recently having taken, fluvoxamine who might ingest excessive quantities of a tricyclic antidepressant. In such a case, accumulation of the parent tricyclic and/or an active metabolite may increase the possibility of clinically significant sequelae and extend the time needed for close medical observation (see Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs) under PRECAUTIONS).
In managing overdosage, consider the possibility of multiple drug involvement. The physician should consider contacting a poison control center for additional information on the treatment of any overdose. Telephone numbers for certified poison control centers are listed in the Physicians' Desk Reference (PDR).
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Dosage for Adults
The recommended starting dose for Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets in adult patients is 50 mg, administered as a single daily dose at bedtime. In the controlled clinical trials establishing the effectiveness of Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets in OCD, patients were titrated within a dose range of 100 to 300 mg/day. Consequently, the dose should be increased in 50 mg increments every 4 to 7 days, as tolerated, until maximum therapeutic benefit is achieved, not to exceed 300 mg per day. It is advisable that a total daily dose of more than 100 mg should be given in two divided doses. If the doses are not equal, the larger dose should be given at bedtime.
Dosage for Pediatric Population (children and adolescents)
The recommended starting dose for Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets in pediatric populations (age 8-17 years) is 25 mg, administered as a single daily dose at bedtime. In a controlled clinical trial establishing the effectiveness of Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets in OCD, pediatric patients (ages 8-17) were titrated within a dose range of 50 to 200 mg/day. Physicians should consider age and gender differences when dosing pediatric patients. The maximum dose in children up to age 11 should not exceed 200 mg/day. Therapeutic effect in female children may be achieved with lower doses. Dose adjustment in adolescents (up to the adult maximum dose of 300 mg) may be indicated to achieve therapeutic benefit. The dose should be increased in 25 mg increments every 4 to 7 days, as tolerated, until maximum therapeutic benefit is achieved. It is advisable that a total daily dose of more then 50 mg should be given in two divided doses. If the two divided doses are not equal, the larger dose should be given at bedtime.
Dosage for Elderly or Hepatically Impaired Patients
Elderly patients and those with hepatic impairment have been observed to have a decreased clearance of fluvoxamine maleate. Consequently, it may be appropriate to modify the initial dose and the subsequent dose titration for these patient groups.
Maintenance/Continuation Extended Treatment
Although the efficacy of Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets beyond 10 weeks of dosing for OCD has not been documented in controlled trials, OCD is a chronic condition, and it is reasonable to consider continuation for a responding patient. Dosage adjustments should be made to maintain the patient on the lowest effective dosage, and patients should be periodically reassessed to determine the need for continued treatment.
Treatment of Pregnant Women During the Third Trimester
Neonates exposed to fluvoxamine maleate tablets and other SSRIs or SNRIs late in the third trimester have developed complications requiring prolonged hospitalization, respiratory support, and tube feeding (see PRECAUTIONS). When treating pregnant women with fluvoxamine maleate tablets during the third trimester, the physician should carefully consider the potential risks and benefits of treatment. The physician may consider tapering fluvoxamine maleate tablets in the third trimester.
Discontinuation of Treatment with Fluvoxamine Maleate Tablets
Symptoms associated with discontinuation of other SSRIs and SNRIs have been reported (see PRECAUTIONS). Patients should be monitored for these symptoms when discontinuing treatment. A gradual reduction in the dose rather than abrupt cessation is recommended whenever possible. If intolerable symptoms occur following a decrease in the dose or upon discontinuation of treatment, then resuming the previously prescribed dose may be considered. Subsequently, the physician may continue decreasing the dose but at a more gradual rate.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Tablets 25 mg: White to off-white, round, biconvex, film-coated tablets. The tablets are unscored and embossed with FLM 25" on one side.
Bottles of 30................................................................ NDC: 063672-1025-1
Bottles of 100.............................................................. NDC: 063672-1025-2
Bottles of 500.............................................................. NDC: 063672-1025-4Tablets 50 mg: White to off-white, round, biconvex, film-coated tablets. The tablets are scored on both sides and embossed with FLM 50" on one side.
Bottles of 30................................................................ NDC: 063672-1050-1
Bottles of 100.............................................................. NDC: 063672-1050-2
Bottles of 500.............................................................. NDC: 063672-1050-4Tablets 100 mg: White to off-white, round, biconvex, film-coated tablets. The tablets are scored on both sides and embossed with FLM 100" on one side.
Bottles of 30................................................................ NDC: 063672-1100-1
Bottles of 100.............................................................. NDC: 063672-1100-2
Bottles of 250.............................................................. NDC: 063672-1100-3 - SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
SUPPLEMENTAL PATIENT MATERIAL
Medication Guide
Antidepressant Medicines, Depression and other Serious Mental Illnesses, and Suicidal Thoughts or Actions
Read the Medication Guide that comes with you or your family member's antidepressant medicine. This Medication Guide is only about the risk of suicidal thoughts and actions with antidepressant medicines. Talk to your, or your family member's, healthcare provider about:
- all risks and benefits of treatment with antidepressant medicines
- all treatment choices for depression or other serious mental illness
What is the most important information I should know about antidepressant medicines, depression and other serious mental illnesses, and suicidal thoughts or actions?
- 1.
Antidepressant medicines may increase suicidal thoughts or actions in some children, teenagers, and young adults within the first few months of treatment.
- 2. Depression and other serious mental illnesses are the most important causes of suicidal thoughts and actions. Some people may have a particularly high risk of having suicidal thoughts or actions. These include people who have (or have a family history of) bipolar illness (also called manic-depressive illness) or suicidal thoughts or actions.
- 3. How can I watch for and try to prevent suicidal thoughts and actions in myself or a family member?
- Pay close attention to any changes, especially sudden changes, in mood, behaviors, thoughts, or feelings. This is very important when an antidepressant medicine is started or when the dose is changed.
- Call the healthcare provider right away to report new or sudden changes in mood, behavior, thoughts, or feelings.
- Keep all follow-up visits with the healthcare provider as scheduled. Call the healthcare provider between visits as needed, especially if you have concerns about symptoms.
- 2. Depression and other serious mental illnesses are the most important causes of suicidal thoughts and actions. Some people may have a particularly high risk of having suicidal thoughts or actions. These include people who have (or have a family history of) bipolar illness (also called manic-depressive illness) or suicidal thoughts or actions.
Call a healthcare provider right away if you or your family member has any of the following symptoms, especially if they are new, worse, or worry you:
- thoughts about suicide or dying
- attempts to commit suicide
- new or worse depression
- new or worse anxiety
- feeling very agitated or restless
- panic attacks
- trouble sleeping (insomnia)
- new or worse irritability
- acting aggressive, being angry, or violent
- acting on dangerous impulses
- an extreme increase in activity and talking (mania)
- other unusual changes in behavior or mood
What else do I need to know about antidepressant medicines?
- Never stop an antidepressant medicine without first talking to a healthcare provider. Stopping an antidepressant medicine suddenly can cause other symptoms.
- Antidepressants are medicines used to treat depression and other illnesses. It is important to discuss all the risks of treating depression and also the risks of not treating it. Patients and their families or other caregivers should discuss all treatment choices with the healthcare provider, not just the use of antidepressants.
- Antidepressant medicines have other side effects. Talk to the healthcare provider about the side effects of the medicine prescribed for you or your family member.
- Antidepressant medicines can interact with other medicines. Know all of the medicines that you or your family member takes. Keep a list of all medicines to show the healthcare provider. Do not start new medicines without first checking with your healthcare provider.
- Not all antidepressant medicines prescribed for children are FDA approved for use in children. Talk to your child's healthcare provider for more information.
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for all antidepressants.
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
FLUVOXAMINE MALEATE
fluvoxamine maleate tablet, film coatedProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 63672-1025 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Fluvoxamine maleate (UNII: 5LGN83G74V) (Fluvoxamine - UNII:O4L1XPO44W) 25 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Hypromellose () mannitol (UNII: 3OWL53L36A) polyethylene glycol () pregelatinized starch (corn) () colloidal silicon dioxide () sodium stearyl fumarate () starch (corn) () titanium dioxide (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) talc (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) Product Characteristics Color WHITE Score no score Shape ROUND (round) Size 7mm Flavor Imprint Code FLM;25 Contains Coating true Symbol false Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 63672-1025-1 30 in 1 BOTTLE 2 NDC: 63672-1025-2 100 in 1 BOTTLE 3 NDC: 63672-1025-4 500 in 1 BOTTLE FLUVOXAMINE MALEATE
fluvoxamine maleate tablet, film coatedProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 63672-1050 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Fluvoxamine maleate (UNII: 5LGN83G74V) (Fluvoxamine - UNII:O4L1XPO44W) 50 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Hypromellose () mannitol (UNII: 3OWL53L36A) polyethylene glycol () pregelatinized starch (corn) () colloidal silicon dioxide () sodium stearyl fumarate () starch (corn) () titanium dioxide (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) talc (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) Product Characteristics Color WHITE Score 2 pieces Shape ROUND (round) Size 9mm Flavor Imprint Code FLM;50 Contains Coating true Symbol false Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 63672-1050-1 30 in 1 BOTTLE 2 NDC: 63672-1050-2 100 in 1 BOTTLE 3 NDC: 63672-1050-4 500 in 1 BOTTLE FLUVOXAMINE MALEATE
fluvoxamine maleate tablet, film coatedProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 63672-1100 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Fluvoxamine maleate (UNII: 5LGN83G74V) (Fluvoxamine - UNII:O4L1XPO44W) 100 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Hypromellose () mannitol (UNII: 3OWL53L36A) polyethylene glycol () pregelatinized starch (corn) () colloidal silicon dioxide () sodium stearyl fumarate () starch (corn) () titanium dioxide (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) talc (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) Product Characteristics Color WHITE Score 2 pieces Shape ROUND (round) Size 13mm Flavor Imprint Code FLM;100 Contains Coating true Symbol false Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 63672-1100-1 30 in 1 BOTTLE 2 NDC: 63672-1100-2 100 in 1 BOTTLE 3 NDC: 63672-1100-3 250 in 1 BOTTLE Labeler - Synthon Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.