desonate- desonide gel
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Drug Details [pdf]
- N/A - Section Title Not Found In Database
-
DESCRIPTION
Desonate Gel contains desonide (pregna-1,4-diene-3, 20-dione,11, 21-dihydroxy-16, 17-[(1-methylethylidene) bis(oxy)]-, (11ß,16α)- a synthetic nonfluorinated corticosteroid for topical dermatologic use. Chemically, desonide is C24H32O6. It has the following structural formula:
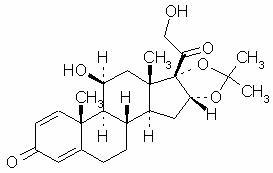
Desonide has the molecular weight of 416.52. It is a white to off-white odorless powder which is soluble in methanol and practically insoluble in water.
Each gram of Desonate Gel contains 0.5 mg of desonide in an aqueous gel base of purified water, glycerin, propylene glycol, edetate disodium dihydrate, methylparaben, propylparaben, sodium hydroxide, and Carbopol® 981.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Topical corticosteroids share anti-inflammatory, antipruritic and vasoconstrictive properties. The mechanism of the anti-inflammatory activity of the topical steroids, in general, is unclear. However, corticosteroids are thought to act by the induction of phospholipase A2 inhibitory proteins, collectively called lipocortins. It is postulated that these proteins control the biosynthesis of potent mediators of inflammation such as prostaglandins and leukotrienes by inhibiting the release of their common precursor arachidonic acid. Arachidonic acid is released from membrane phospholipids by phospholipase A2.
Pharmacokinetics
The extent of percutaneous absorption of topical corticosteroids is determined by many factors, including product formulation and the integrity of the epidermal barrier. Occlusion, inflammation and/or other disease processes in the skin may also increase percutaneous absorption. Topical corticosteroids can be absorbed from normal intact skin. Once absorbed through the skin, topical corticosteroids are handled through pharmacokinetic pathways similar to systemically administered corticosteroids. They are metabolized primarily in the liver and then are excreted by the kidneys. Some corticosteroids and their metabolites are also excreted in the bile.
In a controlled pharmacokinetic study, one of 37 (3%) pediatric subjects with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis covering at least 35% body surface area who applied Desonate Gel experienced suppression of the adrenal glands following 4 weeks of therapy (seePRECAUTIONS: General andPediatric Use). A follow-up evaluation of the subject’s adrenal axis was not performed; it is unknown whether the suppression was reversible.
-
CLINICAL STUDIES
In two randomized vehicle-controlled clinical studies, patients 3 months to 18 years of age with mild to moderate atopic dermatitis were treated twice daily for 4 weeks with either Desonate Gel or vehicle. Treatment success was defined as achieving clear or almost clear on the Investigator’s Global Severity Score (IGSS) with at least a 2 point change (decrease) from the subject’s baseline IGSS when compared to the Week 4 IGSS. The results of the 2 clinical trials are summarized in Table 1:
Table 1. Subjects Achieving Treatment Success Clinical Trial 1 Clinical Trial 2 Desonate Gel Vehicle Desonate Gel Vehicle N = 289 N = 92 N = 136 N = 65 128 (44%) 13 (14%) 38 (28%) 4 (6%) -
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Desonate Gel is indicated for the treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in patients 3 months of age and older. Patients should be instructed to use Desonate Gel for the minimum amount of time as necessary to achieve the desired results because of the potential for Desonate Gel to suppress the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis (seePRECAUTIONS). Treatment should not exceed 4 consecutive weeks.
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
PRECAUTIONS
General
The safety of Desonate Gel has not been established beyond 4 weeks of use.
Systemic absorption of topical corticosteroids can produce reversible hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis suppression with the potential for glucocorticosteroid insufficiency after withdrawal of treatment. Manifestations of Cushing's syndrome, hyperglycemia, and glucosuria can also be produced in some patients by systemic absorption of topical corticosteroids while on treatment.
Conditions which augment systemic absorption include the application of topical corticosteroids, over large body surface areas, prolonged use, or the addition of occlusive dressings. Therefore, patients applying a topical corticosteroid to a large body surface area or to areas under occlusion should be evaluated periodically for evidence of HPA axis suppression (seeLaboratory Tests).
If HPA axis suppression is noted, an attempt should be made to withdraw the drug, to reduce the frequency of application, or to substitute a less potent corticosteroid. Recovery of HPA axis function is generally prompt and complete upon discontinuation of topical corticosteroids. Infrequently, signs and symptoms of glucocorticosteroid insufficiency may occur, requiring supplemental systemic corticosteroids. For information on systemic supplementation, see prescribing information for those products.
The effect of Desonate Gel on HPA axis function was investigated in pediatric subjects, 6 months to 6 years old, with atopic dermatitis covering at least 35% of their body, who were treated with Desonate Gel twice daily for 4 weeks. One of 37 subjects (3%) displayed adrenal suppression after 4 weeks of use, based on the cosyntropin stimulation test. As follow-up evaluation of the subject’s adrenal axis was not performed, it is unknown whether the suppression was reversible.
Pediatric patients may be more susceptible to systemic toxicity from equivalent doses due to their larger skin surface to body mass ratios (seePRECAUTIONS - Pediatric use).
If irritation develops, Desonate Gel should be discontinued and appropriate therapy instituted. Allergic contact dermatitis with corticosteroids is usually diagnosed by observing failure to heal rather than noting a clinical exacerbation as with most topical products not containing corticosteroids. Such an observation should be corroborated with appropriate diagnostic patch testing.
If concomitant skin infections are present or develop, an appropriate antifungal or antibacterial agent should be used. If a favorable response does not occur promptly, use of Desonate Gel should be discontinued until the infection has been adequately controlled.
Information for Patients
Patients using topical corticosteroids should receive the following information and instructions:
-
This medication is to be used as directed by the physician. It is for external use only. Avoid contact with the eyes.
-
This medication should not be used for any disorder other than that for which it was prescribed.
-
Unless directed by the physician, the treated skin area should not be bandaged or otherwise covered or wrapped so as to be occlusive.
-
Unless directed by a physician, this medication should not be used on the underarm or groin areas of pediatric patients.
-
Parents of pediatric patients should be advised not to use Desonate Gel in the treatment of diaper dermatitis. Desonate Gel should not be applied in the diaper area, as diapers or plastic pants may constitute occlusive dressing (seeDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
-
Patients should report to their physician any signs of local adverse reactions.
-
Other corticosteroid-containing products should not be used with Desonate Gel without first consulting with the physician.
-
As with other corticosteroids, therapy should be discontinued when control is achieved. If no improvement is seen within 4 weeks, contact the physician.
Laboratory Tests
The cosyntropin (ACTH1-24) stimulation test may be helpful in evaluating patients for HPA axis suppression.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, and Impairment of Fertility
Long-term animal studies have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic or photoco-carcinogenic potential of Desonate Gel or the effect on fertility of desonide.
Desonide revealed no evidence of mutagenic potential based on the results of an in vitro genotoxicity test (Ames assay) and an in vivo genotoxicity test (mouse micronucleus assay). Desonide was positive without S9 activation and was equivocal with S9 activation in an in vitro mammalian cell mutagenesis assay (L5178Y/TK+ mouse lymphoma assay). A dose response trend was not noted in this assay.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy Category C:
Corticosteroids have been shown to be teratogenic in laboratory animals when administered systemically at relatively low-dosage levels. Some corticosteroids have been shown to be teratogenic after dermal application in laboratory animals.
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Therefore, Desonate Gel should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
No reproductive studies in animals have been performed with Desonate Gel. Dermal embryofetal development studies were conducted in rats and rabbits with a desonide cream, 0.05% formulation. Topical doses of 0.2, 0.6, and 2.0 g cream/kg/day of a desonide cream, 0.05% formulation or 2.0 g/kg of the cream base were administered topically to pregnant rats (gestational days 6-15) and pregnant rabbits (gestational days 6 18). Maternal body weight loss was noted at all dose levels of the desonide cream, 0.05% formulation in rats and rabbits. Teratogenic effects characteristic of corticosteroids were noted in both species. The desonide cream, 0.05% formulation was teratogenic in rats at topical doses of 0.6 and 2.0 g cream/kg/day and in rabbits at a topical dose of 2.0 g cream/kg/day. No teratogenic effects were noted for the desonide cream, 0.05% formulation at a topical dose of 0.2 g cream/kg/day in rats and 0.6 g cream/kg/day in rabbits. These doses (0.2 g cream/kg/day and 0.6 g cream/kg/day) are similar to the maximum recommended human dose based on body surface area comparisons.
Nursing Mothers
Systemically administered corticosteroids appear in human milk and could suppress growth, interfere with endogenous corticosteroid production, or cause other untoward effects. It is not known whether topical administration of corticosteroids could result in sufficient systemic absorption to produce detectable quantities in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when Desonate Gel is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of Desonate Gel in pediatric patients less than 3 months of age have not been evaluated, and therefore its use in this age group is not recommended.
Because of a higher ratio of skin surface area to body mass, pediatric patients are at a greater risk than adults of HPA axis suppression when they are treated with topical corticosteroids. They are therefore also at greater risk of glucocorticosteroid insufficiency after withdrawal of treatment and of Cushing's syndrome while on treatment. Adverse effects, including striae, have been reported with inappropriate use of topical corticosteroids in infants and children. HPA axis suppression, Cushing's syndrome, linear growth retardation, delayed weight gain and intracranial hypertension have been reported in children receiving topical corticosteroids. Manifestations of adrenal suppression in children include low plasma cortisol levels and absence of response to ACTH stimulation. Manifestations of intracranial hypertension include bulging fontanelles, headaches, and bilateral papilledema.
The effect of Desonate Gel on HPA axis function was investigated in pediatric subjects, 6 months to 6 years old, with atopic dermatitis covering at least 35% of their body, who were treated with Desonate Gel twice daily for 4 weeks. One of 37 subjects (3%) displayed adrenal suppression after 4 weeks of use based on the cosyntropin stimulation test. As follow-up evaluation of the subject’s adrenal axis was not performed; it is unknown whether the suppression was reversible.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of Desonate Gel did not include patients aged 65 and older to determine if they respond differently than younger patients. Treatment of this patient population should reflect the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
-
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
In controlled clinical studies of 425 Desonate Gel treated subjects and 157 Vehicle-treated subjects, adverse events occurred at the application site in 3% of subjects treated with Desonate Gel and the incidence rate was not higher compared with vehicle-treated subjects. The most common local adverse events in Desonate Gel- treated subjects were application site burning in 1% (4/425) and rash in 1% (3/425) followed by application site pruritus in <1% (2/425) .
Adverse events that resulted in premature discontinuation of study drug in Desonate Gel treated subjects were telangiectasia and worsening of atopic dermatitis in one subject each. Additional adverse events observed during clinical trials for patients treated with Desonate Gel included headache in 2% (8/425) compared with 1% (2/157) in those treated with vehicle.
The following additional local adverse reactions have been reported infrequently with topical corticosteroids. They may occur more frequently with the use of occlusive dressings, especially with higher potency corticosteroids. These reactions are listed in an approximate decreasing order of occurrence: folliculitis, acneiform eruptions, hypopigmentation, perioral dermatitis, secondary infection, skin atrophy, striae, and miliaria.
-
OVERDOSAGE
Topically applied Desonate Gel can be absorbed in sufficient amounts to produce systemic effects (SeePRECAUTIONS).
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Desonate Gel should be applied as a thin layer to the affected areas two times daily and rubbed in gently. Therapy should be discontinued when control is achieved. If no improvement is seen within 4 weeks, reassessment of diagnosis may be necessary. Treatment beyond 4 consecutive weeks is not recommended.
Desonate Gel should not be used with occlusive dressings.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Desonate Gel is supplied in:
3.5g Sample-Not for Sale (NDC: 67402-050-03)
60g (NDC: 67402-050-60) tubesSTORAGE CONDITIONS: Store at controlled room temperature: 25°C (77°F), excursions permitted between 15° - 30°C (59°– 86°F).
Avoid contact with eyes or other mucous membranes
Keep out of reach of childrenCAUTION: Federal law prohibits dispensing without a prescription.
________________________________________________________________________
Manufactured by:
CPL,
Buffalo, New York 14213
Distributed by:
SkinMedica
Carlsbad, CA 92010
866-867-0110; www.skinmedica.comThe Hydrogel Technology logo is a trademark of Dow Pharmaceutical Sciences, Inc.
Desonate is a trademark of SkinMedica.
03-6083 (flat)
03-6082 (folded)
10/2006 -
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
DESONATE
desonide gelProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 67402-050 Route of Administration TOPICAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength desonide (UNII: J280872D1O) (desonide - UNII:J280872D1O) 0.5 mg in 1 g Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Carbopol 981 () Edetate Disodium Dihydrate (UNII: 7FLD91C86K) Glycerin (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) Methylparaben () Propylparaben (UNII: Z8IX2SC1OH) Propylene Glycol (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) Water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Sodium Hydroxide (UNII: 55X04QC32I) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 67402-050-60 60 g in 1 TUBE 2 NDC: 67402-050-03 3.5 g in 5 TUBE Labeler - SkinMedica
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.