dmsa- Dimercaptosuccinic Acid injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Drug Details [pdf]
- N/A - Section Title Not Found In Database
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
DESCRIPTION
Each vial contains a sterile, pyrogen-free freeze-dried mixture of 1.0 mg dimercaptosuccinic acid, 0.42 mg stannous chloride dihydrate [0.38 mg (minimum) stannous chloride dihydrate (SnCl22H2O) and 0.46 mg (maximum) total tin expressed as stannous chloride dihydrate (SnCl22H2O)], 0.70 mg ascorbic acid, and 50.0 mg inositol. After freeze-drying, vials are sealed under a nitrogen atmosphere with a rubber closure. Sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid have been used for pH adjustment. When sterile, oxidant-free, pyrogen-free sodium pertechnetate Tc99m injection in isotonic saline is combined with the vial contents, following the instructions provided with the kit, a complex is formed. After 10 minutes incubation the reconstituted solution is ready for intravenous injection.
Chemical Name: meso-2,3-dimercaptosuccinic acid
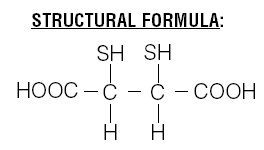
The succimer component of DMSA consists of more than 90% meso isomer and less than 10% d,l isomer.
-
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Technetium Tc99m decays by isomeric transition with a physical half-life of 6.02 hours1. The principal photon that is useful for detection and imaging studies is listed in Table 1.
Table 1. Principal Radiation Emission Data1 Radiation Mean % /
DisintegrationMean Energy
(keV)Gamma 2 89.07 140.5
- 1 Kocher, David C., "Radioactive Decay Data Tables," DOE/TIC-11026,108 (1981).
-
EXTERNAL RADIATION
The specific gamma ray constant for technetium Tc99m is 0.78 R/hr-mCi at 1 cm. The first half value layer is 0.017 cm of Pb. To facilitate control of the radiation exposure from millicurie amounts of this radionuclide, the use of a 0.25 cm thickness of Pb will attenuate the radiation emitted by a factor of about 1,000.
Table 2. Radiation Attenuation by Lead Shielding Shield Thickness
(Pb) cmCoefficient of Attenuation 0.02 0.5 0.08 0.1 0.16 0.01 0.25 0.001 0.33 0.0001 To correct for physical decay of this radionuclide, the fractions that remain at selected intervals after the time of calibration are shown in Table 3.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
After intravenous administration, technetium Tc99m succimer injection is distributed in the plasma, apparently bound to plasma proteins. There is negligible activity in the red blood cells. The activity is cleared from the plasma with a half-time of about 60 minutes and concentrates in the renal cortex. Approximately 16% of the activity is excreted in the urine within two hours. At six hours about 20% of the dose is concentrated in each kidney.
- INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
-
PRECAUTIONS
General
As in the use of any radioactive material, care should be taken to minimize radiation exposure to the patient consistent with proper patient management and to ensure minimum radiation exposure to occupational workers.
DMSA should be used between 10 minutes and 4 hours following reconstitution (see "Preparation" section). Any unused portion should be discarded after that time.
Some patients with advanced renal failure may exhibit poor renal intake of Tc99m DMSA. It has been reported that satisfactory images may be obtained in some of these patients by delaying imaging for up to 24 hours.
The contents of the kit vials are intended only for use in the preparation of DMSA Injection and are not to be directly administered to the patient.
The contents of the kit vials are not radioactive. However, after Tc99m is added, adequate shielding of the final preparation must be maintained.
Radiopharmaceuticals should be used only by physicians who are qualified by training and experience in the safe use and handling of radionuclides and whose experience and training have been approved by the appropriate government agency authorized to license the use of radionuclides.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No long term animal studies have been performed to evaluate carcinogenic potential, mutagenic potential, or whether technetium Tc99m succimer injection affects fertility in males or females.
Pregnancy Category C
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with technetium Tc99m succimer injection. It is also not known whether technetium Tc99m succimer injection can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Technetium Tc99m succimer injection should be administered to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Ideally, examinations using radiopharmaceuticals, especially those elective in nature, of a woman of child bearing capability should be performed during the first few (approximately 10) days following the onset of menses.
Nursing Mothers
Technetium Tc99m is excreted in human milk during lactation; therefore, formula feedings should be substituted for breast feedings.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of DMSA did not include sufficient numbers of subjects age 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function.
- ADVERSE REACTIONS
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The suggested dose range for slow I.V. administration to be employed in the average patient (70 kg) for renal parenchymal imaging is 74-222 MBq, 2-6 mCi technetium Tc99m succimer injection.
The product must be used between 10 minutes to 4 hours following preparation (see "Preparation" section). Acceptable renal images may be obtained beginning 1 to 2 hours post injection. Any unused portion should be discarded after that time.
The patient dose should be measured by a suitable radioactivity calibration system immediately prior to administration.
Do not use after the expiration date stated on the label. The components of the kit are supplied sterile and pyrogen-free. Aseptic procedures normally employed in making additions and withdrawals from sterile, pyrogen-free containers should be used during addition of sodium pertechnetate Tc99m injection solutions and during the withdrawal of doses for patient administration.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration.
-
RADIATION DOSIMETRY
The estimated absorbed radiation doses2,3 to an average adult (70 kg) are shown in Table 4.
Table 4. Absorbed Radiation Dose Tissue mGy /
222 MBqrads /
6 mCiBladder Wall 4.2 0.42 Kidneys (total) 37.8 3.78 Renal Cortices 51.0 5.10 Liver 1.9 0.19 Bone Marrow 1.3 0.13 Ovaries 0.8 0.08 Testes 0.4 0.04 Total Body 0.9 0.09
- 2 Method of Calculation: A schema for Absorbed-Dose Calculations for Biologically Distributed Radionuclides, Supplement No. 1, MIRD Pamphlet No. 1, J. Nucl. Med., p. 7, 1968.
- 3 Biological Data: Arnold, R.W; Subramanian, G.; McAfee, J.G.; Blair, R.J.; Thomas, F.D.; Comparison of Tc99m complexes for renal imaging, J. Nucl. Med., 16, pp. 357-367, 1975.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Kit Contents
- 5 Vials containing a freeze-dried mixture of 1.0 mg dimercaptosuccinic acid, 0.42 mg stannous chloride dihydrate [0.38 mg (minimum) stannous chloride dihydrate (SnCl22H2O) and 0.46 mg (maximum) total tin expressed as stannous chloride dihydrate (SnCl22H2O)], 0.70 mg ascorbic acid, and 50.0 mg inositol.
- 5 Labels
- 1 Package Insert
NDC: 017156-525-01
Preparation
The following directions must be carefully followed for optimum preparation of technetium Tc99m succimer injection:
Note: Use aseptic procedures throughout and take precautions to minimize radiation exposure by the use of suitable shielding. Waterproof gloves should be worn during the preparation procedure.
- Place one of the vials in a suitable shielding container and swab the closure with a bacteriostatic swab.
- Using a 10 mL sterile syringe, inject an appropriate amount (see notes 1 and 2) of the eluate from a Tc99m generator into the shielded vial. Before removing the syringe from the vial withdraw an equivalent volume of nitrogen from the space above the solution to normalize the pressure in the vial.
- Carefully invert the vial a few times until the powder is completely dissolved.
- Assay the total activity, complete the label provided and attach to the vial.
- Incubate the vial for at least 10 minutes at room temperature.
- Use the preparation between 10 minutes and 4 hours following reconstitution.
Note:
- Not more than 1.48 GBq, 40 mCi technetium-99m in a volume of 1-6 mL should be added to the vial.
- Before reconstitution, the eluate may be adjusted to the correct radioactive concentration by dilution with preservative-free, non-bacteriostatic saline for injection.
- The use of technetium-99m solution complying with the specifications prescribed by the USP Monograph on Sodium Pertechnetate (99mTc) injection will yield a preparation of an appropriate quality.
- It is recommended that with proper shielding and equipment, the final formulation be tested for radiochemical purity. If radiochemical purity is not adequate, discard the finished drug.
-
DISPOSAL
Any unused portion of the Tc99m-labeled kit must be stored and disposed of in accordance with the conditions of NRC radioactive materials license pursuant to 10 CFR Parts 20 and 35 or equivalent conditions pursuant to Agreement state regulation, or other regulatory agency authorized to license the use of radionuclides.
The unlabeled residual materials may be discarded in ordinary trash, provided that the vials and syringes read background with an appropriate low-range survey meter. It is suggested that all identification labels be destroyed before discarding.
This reagent kit is approved for use by persons licensed by the Illinois Emergency Management Agency pursuant to 32 Ill. Code Adm. Section, Section 330.260(a) and 335.4010 or under equivalent licenses of the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission, or an Agreement State.
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
DMSA
dimercaptosuccinic acid injection, powder, lyophilized, for solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 17156-525 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Dimercaptocuccinic Acid (UNII: 4S9JU7XF01) (Dimercaptocuccinic Acid - UNII:4S9JU7XF01) 1 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Stannous Chloride Dihydrate (UNII: 1BQV3749L5) 4.2 ug in 1 ascorbic acid (UNII: PQ6CK8PD0R) 0.70 mg in 1 inositol (UNII: 4L6452S749) 50.0 mg in 1 Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 17156-525-01 5 in 1 BOX 1 1 in 1 VIAL Labeler - GE Healthcare
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.