NIKTIMVO- axatilimab-csfr injection
NIKTIMVO by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
NIKTIMVO by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Incyte Corporation. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use NIKTIMVO safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for NIKTIMVO.
NIKTIMVO™ (axatilimab-csfr) injection, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2024RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
Dosage and Administration (2.3) 1/2025 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
NIKTIMVO is a colony stimulating factor-1 receptor (CSF-1R)-blocking antibody indicated for the treatment of chronic graft-versus-host disease (cGVHD) after failure of at least two prior lines of systemic therapy in adult and pediatric patients weighing at least 40 kg. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Administer only as an intravenous infusion over 30 minutes. (2.3)
- The recommended dosage of NIKTIMVO is 0.3 mg/kg (maximum 35 mg) every 2 weeks in adult and pediatric patients weighing 40 kg and above. (2.1)
See Full Prescribing Information for dosage modifications for adverse reactions (2.2) and preparation and administration instructions. (2.3)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Infusion-Related Reactions: Interrupt or slow the rate of infusion or permanently discontinue NIKTIMVO based on severity of reaction. (2.2, 5.1)
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: May cause fetal harm. Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus and to use effective contraception. (5.2, 8.1, 8.3)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common (≥ 15%) adverse reactions, including laboratory abnormalities, are increased AST, infection (pathogen unspecified), increased ALT, decreased phosphate, decreased hemoglobin, viral infection, increased GGT, musculoskeletal pain, increased lipase, fatigue, increased amylase, increased calcium, increased CPK, increased ALP, nausea, headache, diarrhea, cough, bacterial infection, pyrexia, and dyspnea. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Incyte Corporation at 1-855-463-3463 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 1/2025
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage
2.2 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
2.3 Preparation and Administration
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Infusion-Related Reactions
5.2 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
12.6 Immunogenicity
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage
For patients weighing at least 40 kg, administer NIKTIMVO 0.3 mg/kg, up to a maximum dose of 35 mg, as an intravenous infusion over 30 minutes every 2 weeks until progression or unacceptable toxicity.
2.2 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
Monitor aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), creatine phosphokinase (CPK), amylase, and lipase prior to the start of NIKTIMVO therapy, every 2 weeks for the first month, and every 1 to 2 months thereafter until abnormalities are resolved.
For recommended NIKTIMVO dosage modifications due to adverse reactions, see Table 1.Table 1: Recommended NIKTIMVO Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions AST = aspartate aminotransferase; ALT = alanine aminotransferase; ULN = upper limit of normal; ALP = alkaline phosphatase; CPK = creatine phosphokinase.
- * Graded per National Cancer Institute (NCI) Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) v5.
Adverse Reaction Severity* Dosage Modification Infusion-related reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] Grade 1 or 2 - Temporarily interrupt the infusion until resolution or decrease infusion rate by 50%.
- Initiate symptomatic treatment (e.g., antihistamines and antipyretics).
- For subsequent infusions, premedicate and resume the infusion at 50% of the prior infusion rate.
Grade 3 or 4 Permanently discontinue NIKTIMVO. Elevation of AST or ALT (on the day of dosing) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] Grade 3 with total bilirubin ≤ Grade 1
Withhold NIKTIMVO until recovery to Grade 2, then resume NIKTIMVO at 0.2 mg/kg (maximum 23 mg) every 2 weeks.
Elevation of AST or ALT (regardless of the time of the reaction) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]
ALT or AST ≥ 3 times ULN with total bilirubin ≥ 2 times ULN and ALP < 2 times ULN
Withhold NIKTIMVO and investigate for drug-induced liver injury. If confirmed, permanently discontinue NIKTIMVO.
Grade 4 Permanently discontinue NIKTIMVO. Elevation of CPK, amylase, or lipase [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] ≥ Grade 3
- If diagnostic evaluation results show no evidence of end-organ damage, continue NIKTIMVO without dose reduction.
- If diagnostic evaluation results show evidence of end-organ damage, permanently discontinue NIKTIMVO.
Symptomatic ≥ Grade 3
Permanently discontinue NIKTIMVO.
Other Nonhematologic Adverse Reactions [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] Grade 3 Withhold NIKTIMVO until recovery to Grade 2:
- If delayed by ≤ 4 weeks from the planned infusion, resume NIKTIMVO at 0.2 mg/kg (maximum 23 mg) every 2 weeks.
- If delayed by > 4 weeks from the planned infusion, permanently discontinue NIKTIMVO.
Grade 4
Permanently discontinue NIKTIMVO.
2.3 Preparation and Administration
Preparation
- Use aseptic technique to prepare NIKTIMVO.
- Visually inspect the vial for particulate matter and discoloration prior to dilution. NIKTIMVO is a slightly opalescent, pale brownish yellow solution. Discard the vial if the solution is cloudy, discolored, or contains visible particles.
- Do not shake the vial.
- Determine the dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)] and total volume of NIKTIMVO solution needed. Each mL of NIKTIMVO contains 50 mg of axatilimab-csfr.
Dilution
- Withdraw the calculated volume of NIKTIMVO solution from the vial and add it into an intravenous infusion bag made of polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polyolefin, polyolefin with polyamide, or ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) containing 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection to achieve a final concentration between the range of 0.24 mg/mL and 0.75 mg/mL.
- Discard vial with any unused portion.
- Mix diluted solution by gentle inversion. Do not shake.
- Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. The diluted solution is a clear to slightly opalescent, colorless solution that may contain trace amounts of translucent to white particles. Discard if the solution is cloudy, discolored, or contains extraneous particulate matter other than trace amounts of translucent to white particles.
Storage of diluted NIKTIMVO solution
- Immediately use diluted NIKTIMVO solution. If not used immediately, the diluted solution can be stored:
- At room temperature [up to 25°C (77°F)] for no more than 4 hours from the time of preparation to the end of the infusion.
OR
- Refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) for no more than 24 hours. If refrigerated, allow the diluted solution to come to room temperature prior to administration. The diluted solution must be administered within 4 hours (including infusion time) once it is removed from the refrigerator.
- Do not freeze or shake the diluted solution.
Administration
- Administer diluted NIKTIMVO solution by intravenous infusion over 30 minutes through a dedicated infusion line that includes a sterile, low-protein binding 0.2-micron in-line or add-on polyethersulfone (PES) filter.
- Do not co‑administer other drugs through the same infusion line.
- After administration, flush the infusion line with 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Infusion-Related Reactions
NIKTIMVO can cause infusion-related reactions. Infusion-related reactions, including hypersensitivity reactions, occurred in 18% of patients who received NIKTIMVO in the clinical trial (AGAVE-201), with Grade 3 or 4 reactions in 1.3% [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Premedicate with an antihistamine and an antipyretic for patients who have previously experienced an infusion-related reaction to NIKTIMVO [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of infusion-related reactions, including fever, chills, rash, flushing, dyspnea, and hypertension. Interrupt or slow the rate of infusion or permanently discontinue NIKTIMVO based on severity of the reaction [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].5.2 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on its mechanism of action, NIKTIMVO may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to the fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with NIKTIMVO and for 30 days after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling.
- Infusion-Related Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Chronic Graft-Versus-Host Disease
The safety of NIKTIMVO was evaluated in 79 adult and pediatric patients with cGVHD treated with NIKTIMVO 0.3 mg/kg intravenously every 2 weeks in the AGAVE‑201 trial [see Clinical Studies (14)]. The median duration of treatment was 10.3 months (range: 0.5 to 28.6 months), and 73.4% were treated for more than 6 months.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 44% of patients who received NIKTIMVO. Serious adverse reactions in more than 2 patients included infection (pathogen unspecified), viral infection, and respiratory failure. Permanent discontinuation of NIKTIMVO due to an adverse reaction occurred in 10% of patients and dose reduction due to adverse reaction occurred in 8% of patients. Dose interruptions due to an adverse reaction occurred in 44% of patients. The adverse reactions leading to dose interruption in more than 2 patients were viral infection, infection (pathogen unspecified), bacterial infection, musculoskeletal pain, and pyrexia.
The most common (≥ 15%) adverse reactions, including laboratory abnormalities, were increased AST, infection (pathogen unspecified), increased ALT, decreased phosphate, decreased hemoglobin, viral infection, increased gamma glutamyl transferase (GGT), musculoskeletal pain, increased lipase, fatigue, increased amylase, increased calcium, increased CPK, increased ALP, nausea, headache, diarrhea, cough, bacterial infection, pyrexia, and dyspnea.
Table 2 summarizes the nonlaboratory adverse reactions in AGAVE-201.
Table 2: Adverse Reactions in ≥ 10% of Patients With cGVHD Who Received NIKTIMVO in AGAVE-201 Graded according to NCI CTCAE v5.0. - * Includes abscess jaw, atypical pneumonia, bacteremia, bronchitis, conjunctivitis, cystitis, device-related infection, enterocolitis infectious, gastroenteritis, gastrointestinal infection, groin abscess, hordeolum, liver abscess, nasopharyngitis, otitis media, otitis media acute, pneumonia, respiratory tract infection, rhinitis, sepsis, sinusitis, tooth infection, upper respiratory tract infection, urinary tract infection, and wound infection.
- † Includes adenoviral upper respiratory infection, BK virus infection, COVID-19, coronavirus infection, enterovirus infection, gastroenteritis astroviral, gastroenteritis viral, herpes simplex, herpes zoster, influenza, metapneumovirus bronchiolitis, metapneumovirus infection, norovirus infection, oral viral infection, parainfluenza viral bronchitis, parainfluenza virus infection, respiratory syncytial virus infection, rhinovirus infection, viral infection, and viral upper respiratory tract infection.
- ‡ Includes bacterial diarrhea, bacterial vaginosis, campylobacter gastroenteritis, campylobacter infection, cellulitis, clostridium difficile colitis, clostridium difficile infection, enterococcal infection, erysipelas, hemophilus infection, lower respiratory tract infection bacterial, pseudomonal skin infection, staphylococcal bacteremia, staphylococcal infection, stenotrophomonas infection, streptococcal infection, and urinary tract infection enterococcal.
- § Includes arthralgia, back pain, flank pain, musculoskeletal pain, myalgia, pain in extremity.
- ¶ Includes asthenia, fatigue, and malaise.
- # Includes localized edema and peripheral edema.
- Þ Includes nausea and vomiting.
- ß Includes colitis and diarrhea.
- à Includes headache and migraine.
- è Includes dizziness and dizziness postural.
- ð Includes cough and productive cough.
- ø Includes dyspnea and dyspnea exertional.
- ý Includes bronchospasm, flushing, hot flush, hypersensitivity, infusion-related hypersensitivity reaction, infusion-related reaction, and urticaria.
- £ Includes contusion, epistaxis, hematochezia, hematoma, and vaginal hemorrhage.
- ¥ Includes dermatitis bullous, dermatitis exfoliative generalized, rash, and rash maculo-papular.
Adverse Reaction
NIKTIMVO
0.3 mg/kg intravenously every 2 weeks
(N = 79)All Grades (%) Grades 3-4 (%) Infections and infestations
Infection (pathogen unspecified)* 57 14 Viral infection†
43 15 Bacterial infection‡
15 8 Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
Musculoskeletal pain§
35 3 General disorders and administration site conditions
Fatigue¶
32 4 Pyrexia
15 1 Edema#
13 1 Gastrointestinal disorders NauseaÞ
23 3 Diarrheaß 18 5 Nervous system disorders
Headacheà
20 1 Dizzinessè
11 0 Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders Coughð
18 0 Dyspneaø 15 3 Immune system disorders
Drug hypersensitivityý
13 3 Metabolism and nutrition disorders
Decreased appetite
11 4 Vascular disorders
Hemorrhage£ 11 1 Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Rash¥
10 0 Clinically relevant adverse reactions in < 10% of patients who received NIKTIMVO included:
- Eye disorders: periorbital edema
- Skin and subcutaneous skin disorders: pruritus
- Vascular disorders: hypertension
Table 3 summarizes the laboratory abnormalities in AGAVE-201.
Table 3: Selected Laboratory Abnormalities in Patients with cGVHD Who Received NIKTIMVO in AGAVE-201 NA = not applicable. - * The denominator used to calculate the rate varied from 78 to 79 based on the number of patients with at least 1 post-treatment value.
Laboratory Abnormality NIKTIMVO
0.3 mg/kg intravenously every 2 weeks
(N=79)All Grades*
(%)
Grade 3 or 4*
(%)Hematology Decreased hemoglobin
48 4 Chemistry Increased aspartate aminotransferase
61 5 Increased alanine aminotransferase
51 3 Decreased phosphate
51 NA Increased gamma glutamyl transferase
39 4 Increased lipase
34 3 Increased amylase
32 0 Increased calcium
31 1 Increased alkaline phosphatase
28 0 Increased creatine phosphokinase
25 0 Immunogenicity: Anti-Drug Antibody–Associated Adverse Reactions
In 276 patients with cGVHD who received NIKTIMVO in clinical trials, among the patients who developed anti-drug antibodies (ADAs), hypersensitivity reactions occurred in 26% (13/50) of patients with neutralizing antibodies (NAb) and in 4% (2/45) of those without NAb [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.6)].
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on its mechanism of action, NIKTIMVO may cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)]. There are no available data on the use of NIKTIMVO in pregnant women to evaluate for a drug-associated risk. No animal reproductive and developmental toxicity studies have been conducted with axatilimab-csfr.
Targeted mutation of CSF-1R or CSF-1 in rodent models results in prenatal and perinatal death, deficits in growth, and pleiotropic impact on multiple organ systems, including skeletal and reproductive. Regulation by CSF-1R on non-mononuclear phagocytic cells and macrophages plays a role in the innate immune protection of the fetus and in pregnancy maintenance and embryo-fetal development. Human immunoglobulin G (IgG) is known to cross the placenta; therefore, NIKTIMVO has the potential to be transmitted from the mother to the developing fetus. Advise women of the potential risk to the fetus.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of axatilimab-csfr in human milk or the effects on the breastfed child or milk production. Maternal IgG is known to be present in human milk. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in a breastfed child, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment and for 30 days after the last dose of NIKTIMVO.8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
NIKTIMVO may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Pregnancy Testing
Verify pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential prior to initiating NIKTIMVO [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Contraception
Females
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with NIKTIMVO and for 30 days after the last dose of NIKTIMVO.8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of NIKTIMVO for the treatment of cGVHD after failure of at least two prior lines of systemic therapy have been established in pediatric patients weighing at least 40 kg. Use of NIKTIMVO in pediatric patients weighing at least 40 kg is supported by evidence from clinical trials that included 3 children (ages 6 to less than 12 years old) and 5 adolescents (ages 12 to less than 17 years old) [see Clinical Studies (14)]. The safety and effectiveness of NIKTIMVO have not been established in pediatric patients weighing less than 40 kg.
Compared to adult and pediatric patients weighing 40 kg and above, patients weighing less than 40 kg had lower maximum concentration, trough concentration, and average concentration at the same weight-based dosage.
Based on findings of thickening of the growth plate and metaphysis and/or degeneration of the growth plate in the femur in animals, monitor bone growth and development in pediatric patients [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.2)].8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 79 patients with cGVHD treated with NIKTIMVO, 21 (26.6%) were 65 years and older, and 2 (2.5%) were 75 years and older [see Clinical Studies (14)]. No overall differences in the safety or effectiveness of NIKTIMVO have been observed between patients 65 years of age and older and younger patients.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Axatilimab-csfr is a CSF-1R–blocking antibody. Axatilimab-csfr is a humanized IgG4 (kappa light chain) monoclonal antibody produced in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Axatilimab-csfr has an approximate molecular weight of 150 kDa.
NIKTIMVO (axatilimab-csfr) injection is a sterile, preservative-free, slightly opalescent, pale brownish yellow solution for intravenous use. The solution is free from visible particles.
Each single-dose vial contains 9 mg, 22 mg, or 50 mg of axatilimab-csfr at a concentration of 50 mg/mL. Each mL of solution contains citric acid monohydrate (3.6 mg), glycine (9.38 mg), polysorbate 80 (0.5 mg), sodium citrate (8.49 mg), sucrose (42.79 mg) and Water for Injection, USP. The pH is 5.0. -
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Axatilimab-csfr is a monoclonal antibody that binds to colony stimulating factor-1 receptors (CSF-1R) expressed on monocytes and macrophages. Blocking CSF-1R with axatilimab-csfr reduces the levels of these circulating proinflammatory and profibrotic monocytes and monocyte-derived macrophages, as demonstrated by a reduction of nonclassical monocyte counts in nonclinical studies with axatilimab-csfr, and inhibits the activity of pathogenic macrophages in tissues.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
CSF-1 and Interleukin (IL)-34
Axatilimab-csfr caused a dose-dependent increase from 0.15 mg/kg to 6 mg/kg (0.5 to 20 times the approved recommended dosage) in CSF-1 and interleukin (IL)-34 concentrations and a dose-dependent reduction in the levels of nonclassical monocytes in peripheral blood.12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Axatilimab-csfr pharmacokinetics are presented as geometric mean (coefficient of variation [%CV]) in adult patients with cGVHD following axatilimab-csfr 0.3 mg/kg (maximum 35 mg) every 2 weeks, unless otherwise specified. Axatilimab-csfr AUC increased in a greater than dose-proportional manner following single-dose administration of axatilimab-csfr over a dose range of 0.15 mg/kg to 3 mg/kg (0.5 to 10 times the approved recommended dosage) in healthy subjects.
There was no axatilimab-csfr systemic accumulation following the approved recommended dosage.
Distribution
Axatilimab-csfr volume of distribution is 6.06 L (16.3% CV).
Elimination
Axatilimab-csfr total clearance is 0.07 L/h (38.8% CV). The median (5th to 95th percentile) time to 97% reduction from Cmax after the end of infusion is 4.0 (2.3 to 7.2) days following axatilimab-csfr 0.3 mg/kg (maximum 35 mg).
The total clearance of axatilimab-csfr is composed of linear and non-linear components such that axatilimab-csfr clearance decreased from 2.32 mL/h/kg to 0.21 mL/h/kg and mean terminal half-life increased from 10.7 hours to 108 hours following single-dose administrations of axatilimab-csfr over a dose range of 0.15 mg/kg to 3 mg/kg (0.5 to 10 times the approved recommended dosage).
Metabolism
Axatilimab-csfr is expected to be metabolized into small peptides by catabolic pathways.
Specific Populations
No clinically meaningful differences in the exposure of axatilimab-csfr were observed in adult and pediatric patients based on age (12 to 81 years), sex, body weight (40 to 151 kg), race (White, Black, or Asian), mild to moderate renal impairment (estimated creatinine clearance 30-89 mL/min by the Cockcroft-Gault equation), or mild hepatic impairment (total bilirubin ≤ ULN and AST > ULN or total bilirubin 1 to ≤ 1.5 times ULN and any AST) following the approved recommended dosage of 0.3 mg/kg (maximum 35 mg) every 2 weeks.
The effect of severe renal impairment (estimated creatinine clearance 15-29 mL/min, Cockcroft-Gault equation) and moderate to severe hepatic impairment (total bilirubin > 1.5 times ULN and any AST) on axatilimab-csfr pharmacokinetics is unknown.
Pediatric Patients
Axatilimab-csfr exposures in pediatric patients weighing 40 kg and above are comparable to those in adults following the approved recommended dosage of 0.3 mg/kg (maximum 35 mg) every 2 weeks.
12.6 Immunogenicity
The observed incidence of ADAs is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Differences in assay methods preclude meaningful comparisons of the incidence of ADAs in the studies described below with the incidence of ADAs in other studies, including those of NIKTIMVO or of other axatilimab products.
ADAs were assessed in 276 patients with cGVHD who received NIKTIMVO. The incidence of axatilimab-csfr treatment-emergent ADAs was 33.7% (93/276) following a median exposure time of 7.8 months. NAb were detected in 47 of 93 cGVHD patients with treatment-emergent ADAs. There was no clinically meaningful effect of anti–axatilimab-csfr antibodies or NAb on the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, or effectiveness of NIKTIMVO. The presence of NAb correlated with the occurrence of hypersensitivity reactions [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. -
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No studies have been performed to assess the potential of axatilimab-csfr for carcinogenicity or genotoxicity.
Dedicated fertility studies have not been conducted with axatilimab-csfr. Administration of axatilimab-csfr to sexually mature cynomolgus monkeys in a 3-month toxicology study had no effect on menstrual cyclicity in females, sperm parameters (morphology, motility, or number) in males, and produced no histopathologic findings in female and male reproductive organs, indicating that axatilimab-csfr did not adversely affect reproductive function. Targeted deletion of CSF-1R or CSF-1 in rodent models resulted in impairment of fertility.13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
In a 6-month chronic toxicity study in sexually immature cynomolgus monkeys, axatilimab-csfr was administered once weekly at doses of 10, 30, or 100 mg/kg/week via intravenous injection. The primary findings included periorbital swelling, widespread accumulation of basophilic material, and effects on bone at doses ≥ 10 mg/kg/week. Alterations in bone included decreases in bone markers, thickening of the growth plate and metaphysis and/or degeneration of the growth plate in the femur. In a 3-month toxicity study in sexually mature monkeys, intravenous administration of axatilimab-csfr at doses of 10, 30, or 100 mg/kg/week resulted in decreases in bone biomarkers at doses ≥ 30 mg/kg/week.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of NIKTIMVO was evaluated in AGAVE-201 (NCT04710576), a randomized, open-label, multicenter study in adult and pediatric patients with recurrent or refractory cGVHD who had received at least 2 lines of systemic therapy and required additional treatment. Patients with platelet count ≥ 50 × 109/L, absolute neutrophil count ≥ 1 × 109/L, ALT and AST ≤ 2.5 × ULN (≤ 5 × ULN if liver cGVHD was present), total bilirubin ≤ 1.5 × ULN, and creatinine clearance ≥ 30 mL/minute were eligible. Patients with uncontrolled infections were not eligible.
Treatment consisted of NIKTIMVO 0.3 mg/kg administered intravenously every 2 weeks until disease progression, lack of efficacy by 9 months, or unacceptable toxicity. Continued treatment with GVHD prophylaxis and standard care systemic cGVHD therapies were permitted as long as the patient had been on a stable dose for at least 2 weeks prior to study. Initiation of new systemic cGVHD therapy while on study was not permitted.
Demographics and baseline characteristics of the 79 patients treated with NIKTIMVO 0.3 mg/kg every 2 weeks in AGAVE-201 are summarized in Table 4.Table 4: Demographics and Baseline Characteristics of Patients With cGVHD - * Prednisone equivalents/kilogram/day.
NIKTIMVO
0.3 mg/kg every 2 weeks
(N = 79)Median age, years (range)
50 (7, 76) Age ≥ 65 years, n (%)
21 (27) Male, n (%)
46 (58) Race, n (%)
White
67 (85) Asian
4 (5) Black
2 (3) Other
1 (1) Not reported
5 (6) Median (range) time (months) from cGVHD diagnosis
47 (4, 211) ≥ 4 Organs involved, n (%)
45 (57) Median (range) number of prior lines of therapy
4 (2, 12) Number of prior lines of therapy, n (%)
2
11 (14) 3
14 (18) 4
17 (22) ≥ 5
37 (47) Prior cGVHD treatment with ibrutinib, n (%)
27 (34) Prior cGVHD treatment with ruxolitinib, n (%)
57 (72) Prior cGVHD treatment with belumosudil, n (%)
16 (20) Refractory to last therapy, n (%)
37 (47) Severe cGVHD, n (%)
63 (80) Median (range) Global Severity Rating 7 (2, 10) Median (range) modified Lee Symptom Scale Score at baseline
24 (4, 55) Median (range) corticosteroid dose at baseline (PE/kg)*
0.21 (0.04, 2.12)
The efficacy of NIKTIMVO was based on overall response rate (ORR) through Cycle 7 Day 1, where overall response included complete response or partial response according to the 2014 NIH Consensus Development Project on Response Criteria. The ORR results from AGAVE-201 for the 0.3 mg/kg every 2 weeks dosage regimen are presented in Table 5. The median time to first response was 1.5 months (range, 0.9 to 5.1 months). The median duration of response, calculated from first response to progression, death, or new systemic therapies for cGVHD, was 1.9 months (95% CI: 1.6, 3.5). In patients who achieved response, no death or new systemic therapy initiation occurred in 60% (95% CI: 43, 74) of patients for at least 12 months since response.
Table 5: Efficacy Results From AGAVE-201 CI = confidence interval. Endpoint
NIKTIMVO
0.3 mg/kg every 2 weeks
(N = 79)Overall response rate, n (%)
95% CI
Complete response, n (%)
Partial response, n (%)59 (75%)
64, 84
0 (0%)
59 (75%)ORR results were supported by exploratory analyses of patient-reported symptom bother which showed at least a 7-point decrease in the modified Lee Symptom Scale score through Cycle 7 Day 1 in 56% (95% CI: 44, 67) of patients.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
NIKTIMVO (axatilimab-csfr) injection is a slightly opalescent, pale brownish yellow solution. It is supplied in a carton containing one single-dose vial either as:
- 9 mg/0.18 mL (NDC: 50881-034-12)
- 22 mg/0.44 mL (NDC: 50881-023-11)
- 50 mg/mL (NDC: 50881-012-10)
Store refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) in the original carton to protect from light. Do not freeze or shake.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Infusion-Related Reactions
Advise patients and caregivers that reactions related to the infusion may occur during NIKTIMVO treatment. Inform patients and caregivers of the signs and symptoms of infusion-related reactions and to seek medical care should signs and symptoms occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with NIKTIMVO and for 30 days after the last dose [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
Lactation
Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment and for 30 days after the last dose of NIKTIMVO [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Manufactured by:
Incyte Corporation
Wilmington, DE 19803
U.S. License No.2228Licensed from:
Syndax Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Waltham, MA 02451NIKTIMVO and the NIKTIMVO logo are trademarks of Incyte.
Patent Information: www.incyte.com/patents
© 2025 Incyte Corporation. All rights reserved. -
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
PATIENT INFORMATION
NIKTIMVO™ (nik tim voe)
(axatilimab-csfr)
injection, for intravenous useWhat is NIKTIMVO?
NIKTIMVO is a prescription medicine used to treat adults and children who weigh at least 88.2 pounds (40 kg) with chronic graft‑versus-host disease (cGVHD) after you have received at least 2 prior treatments (systemic therapy) and they did not work.
It is not known if NIKTIMVO is safe and effective in adults and children weighing less than 88.2 pounds (40 kg).Before receiving NIKTIMVO, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have or have had liver problems.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. NIKTIMVO may harm your unborn baby.
Females who are able to become pregnant:- Your healthcare provider should do a pregnancy test before you start treatment with NIKTIMVO.
- You should use an effective method of birth control during your treatment and for 30 days after your last dose of NIKTIMVO. Talk to your healthcare provider about birth control methods that you can use during this time.
- Tell your healthcare provider right away if you become pregnant or think you may be pregnant during treatment with NIKTIMVO.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if NIKTIMVO passes into your breast milk. Do not breastfeed during treatment and for 30 days after your last dose of NIKTIMVO.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
How will I receive NIKTIMVO?
- Your healthcare provider will give you NIKTIMVO through an intravenous (IV) infusion over 30 minutes.
- NIKTIMVO is given every 2 weeks.
- Your healthcare provider will decide how many treatments you will need.
- Before you receive each NIKTIMVO infusion, your healthcare provider may give you medicines called diphenhydramine and acetaminophen to help prevent infusion-related reactions.
- Your healthcare provider will do blood tests to check you for side effects.
What are the possible side effects of NIKTIMVO?
NIKTIMVO may cause serious side effects, including:
- Infusion-related reactions. Infusion-related reactions are common with NIKTIMVO and can be serious. Your healthcare provider will monitor you for infusion-related reactions during your treatment. If you have a reaction, your healthcare provider may temporarily or completely stop your treatment with NIKTIMVO. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you get fever, chills, rash, flushing, shortness of breath, trouble breathing, nausea, vomiting, or symptoms of high blood pressure such as chest pain, headaches, or blurred vision during an infusion of NIKTIMVO.
The most common side effects of NIKTIMVO include:
- infections
- increased blood level of liver enzymes
- decreased blood level of phosphate
- low red blood cell count (anemia)
- muscle, bone, or joint pain
- increased blood level of pancreatic enzymes
- low energy
- increased blood level of calcium
- increased blood level of a muscle enzyme
- increased blood level of a bone enzyme
- nausea
- headache
- diarrhea
- cough
- fever
- shortness of breath
These are not all the possible side effects of NIKTIMVO.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1 800-FDA-1088.
You may also report side effects to Incyte Corporation at 1-855-463-3463.General information about the safe and effective use of NIKTIMVO.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. You can ask your healthcare provider for information about NIKTIMVO that is written for health professionals.What are the ingredients in NIKTIMVO?
Active ingredient: axatilimab-csfr
Inactive ingredients: citric acid monohydrate, glycine, polysorbate 80, sodium citrate, sucrose, and Water for Injection.Manufactured by: Incyte Corporation, Wilmington, DE 19803
U.S. License No.2228Licensed from: Syndax Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Waltham, MA 02451
NIKTIMVO and the NIKTIMVO logo are trademarks of Incyte.
© 2025 Incyte Corporation. All rights reserved.
For more information, call 1-855-463-3463 or go to www.incyte.com/patents.This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Issued: 1/2025
-
NIKTIMVO 50 MG/ML CARTON
NDC: 50881-012-10
Rx OnlyNIKTIMVO™
(axatilimab-csfr)
Injection
50 mg/mLFor intravenous infusion after dilution.
Contains one 1 mL single-dose vial.
Discard unused portion.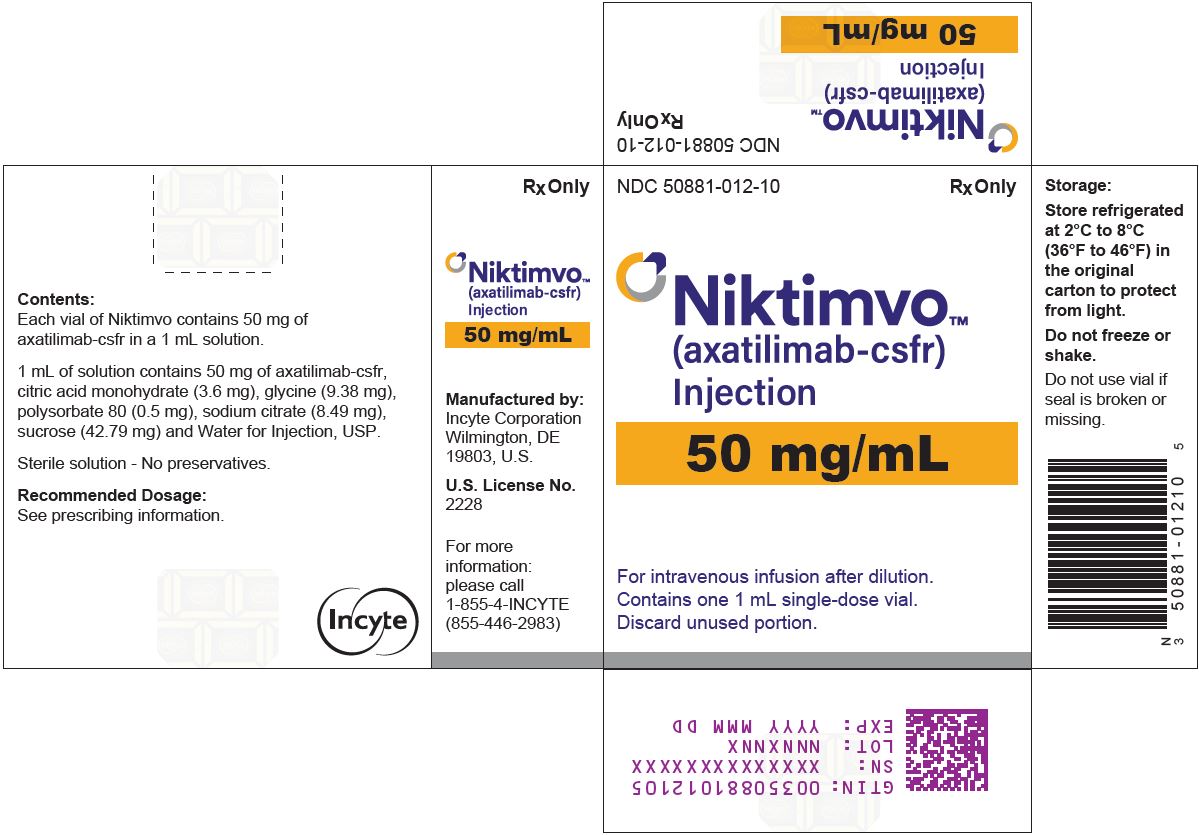
-
NIKTIMVO 9 MG/0.18ML CARTON
NDC: 50881-034-12
Rx OnlyNIKTIMVO™
(axatilimab-csfr)
Injection
9 mg/0.18mLFor intravenous infusion after dilution.
Contains one 0.18 mL single-dose vial.
Discard unused portion.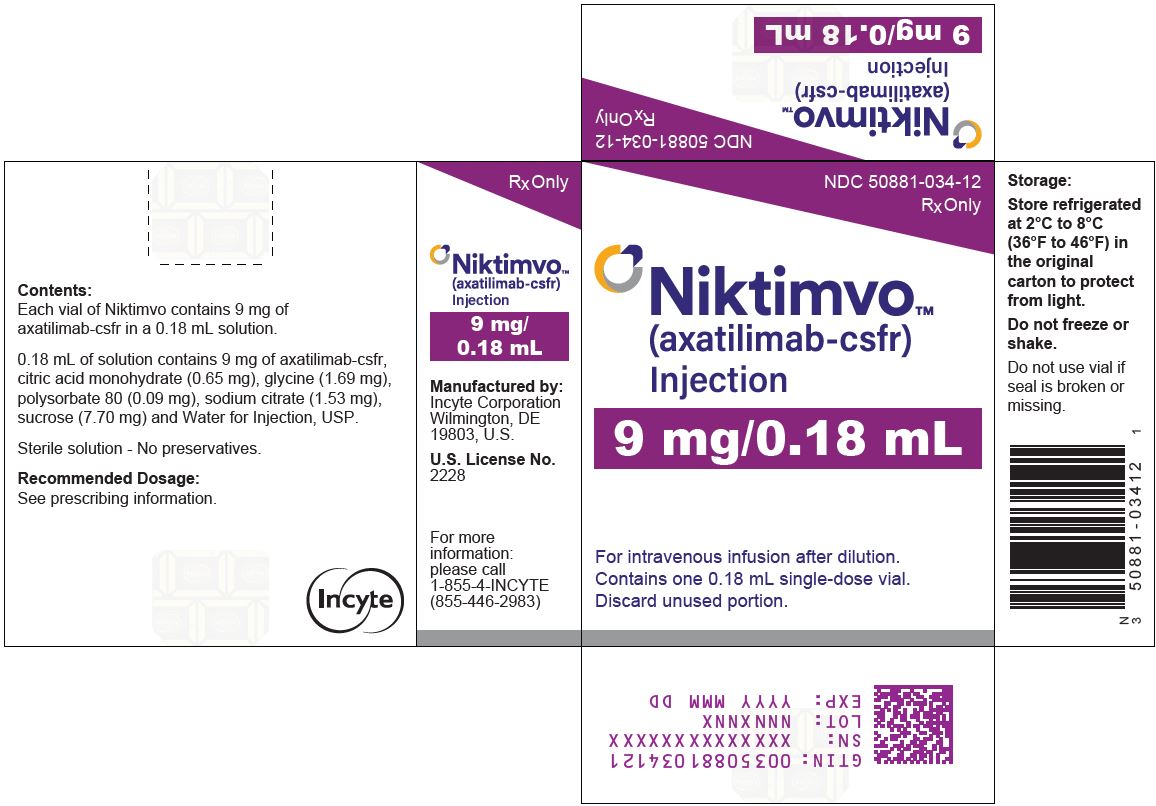
-
NIKTIMVO 22 MG/0.44ML CARTON
NDC: 50881-023-11
Rx OnlyNIKTIMVO™
(axatilimab-csfr)
Injection
22 mg/0.44mLFor intravenous infusion after dilution.
Contains one 0.44 mL single-dose vial.
Discard unused portion.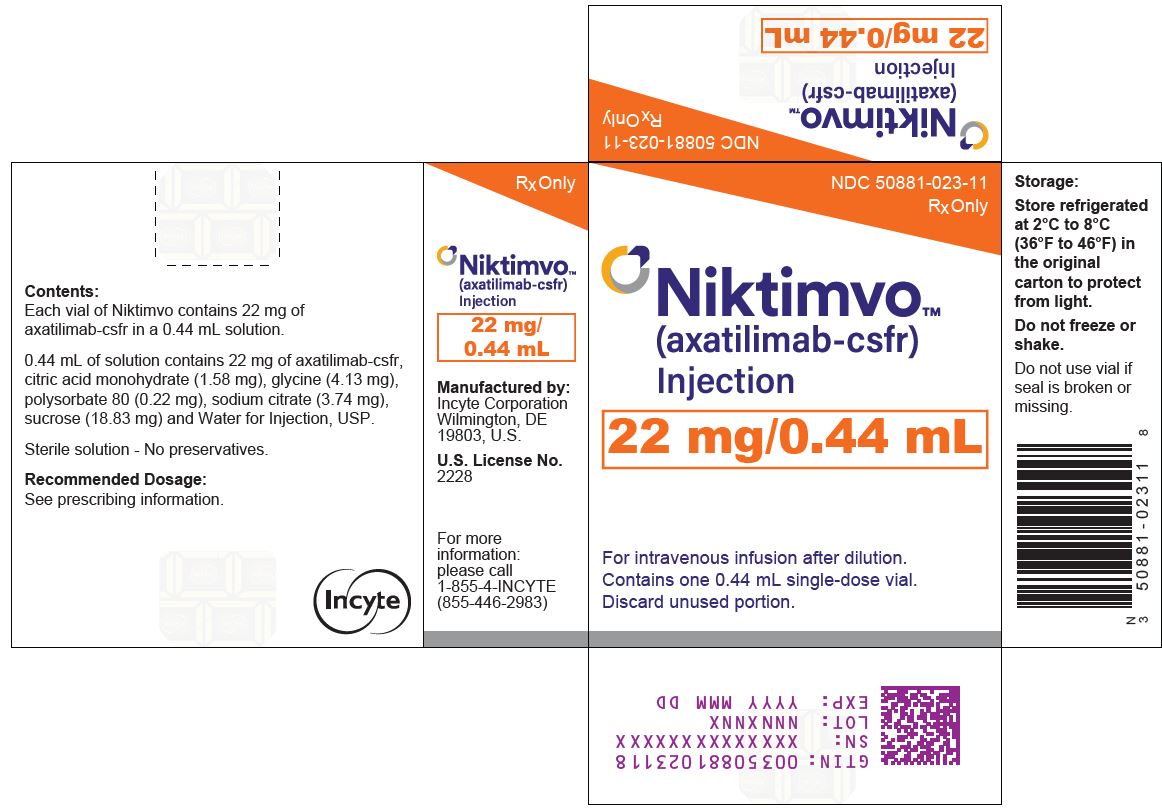
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
NIKTIMVO
axatilimab-csfr injectionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 50881-012 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength AXATILIMAB (UNII: R96Z451BMC) (AXATILIMAB - UNII:R96Z451BMC) AXATILIMAB 50 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength CITRIC ACID MONOHYDRATE (UNII: 2968PHW8QP) 3.60 mg in 1 mL GLYCINE (UNII: TE7660XO1C) 9.38 mg in 1 mL POLYSORBATE 80 (UNII: 6OZP39ZG8H) 0.50 mg in 1 mL SODIUM CITRATE (UNII: 1Q73Q2JULR) 8.49 mg in 1 mL SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) 42.79 mg in 1 mL WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 50881-012-10 1 in 1 CARTON 08/14/2024 1 1 mL in 1 VIAL, SINGLE-USE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA761411 08/14/2024 NIKTIMVO
axatilimab-csfr injectionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 50881-034 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength AXATILIMAB (UNII: R96Z451BMC) (AXATILIMAB - UNII:R96Z451BMC) AXATILIMAB 9 mg in 0.18 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength CITRIC ACID MONOHYDRATE (UNII: 2968PHW8QP) 0.65 mg in 0.18 mL GLYCINE (UNII: TE7660XO1C) 1.69 mg in 0.18 mL POLYSORBATE 80 (UNII: 6OZP39ZG8H) 0.09 mg in 0.18 mL SODIUM CITRATE (UNII: 1Q73Q2JULR) 1.53 mg in 0.18 mL SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) 7.70 mg in 0.18 mL WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 50881-034-12 1 in 1 CARTON 01/15/2025 1 0.18 mL in 1 VIAL, SINGLE-USE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA761411 01/15/2025 NIKTIMVO
axatilimab-csfr injectionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 50881-023 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength AXATILIMAB (UNII: R96Z451BMC) (AXATILIMAB - UNII:R96Z451BMC) AXATILIMAB 22 mg in 0.44 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength CITRIC ACID MONOHYDRATE (UNII: 2968PHW8QP) 1.58 mg in 0.44 mL GLYCINE (UNII: TE7660XO1C) 4.13 mg in 0.44 mL POLYSORBATE 80 (UNII: 6OZP39ZG8H) 0.22 mg in 0.44 mL SODIUM CITRATE (UNII: 1Q73Q2JULR) 3.74 mg in 0.44 mL SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) 18.83 mg in 0.44 mL WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 50881-023-11 1 in 1 CARTON 01/15/2025 1 0.44 mL in 1 VIAL, SINGLE-USE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA761411 01/15/2025 Labeler - Incyte Corporation (556967347)
Trademark Results [NIKTIMVO]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 NIKTIMVO 98655051 not registered Live/Pending |
Incyte Holdings Corporation 2024-07-18 |
 NIKTIMVO 97672310 not registered Live/Pending |
Incyte Holdings Corporation 2022-11-10 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.