oxybutynin chloride- Oxybutynin Chloride syrup
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Drug Details [pdf]
- N/A - Section Title Not Found In Database
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
DESCRIPTION
Each teaspoonful (5 mL) of Oxybutynin Chloride Syrup USP for oral administration contains:
Oxybutynin Chloride ………………………………. 5 mg
Also contains: citric acid, glycerin, methylparaben, propylene glycol, propylparaben, purified water, sodium citrate, sorbitol solution, sucrose, FD&C Green #3 and natural and artificial peppermint flavor.
Chemically, oxybutynin chloride is 4-(Diethylamino)-2-butynyl (±)-α-phenylcyclohexaneglycolate hydrochloride. The molecular formula of oxybutynin chloride is C22H31NO3 HCl. The structural formula appears below:
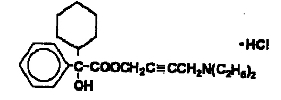
Oxybutynin chloride is a white crystalline solid with a molecular weight of 393.96. It is readily soluble in water and acids, but relatively insoluble in alkalis.
Therapeutic Category: Antispasmodic, anticholinergic.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Oxybutynin chloride exerts direct antispasmodic effect on smooth muscle and inhibits the muscarinic action of acetylcholine on smooth muscle. Oxybutynin chloride exhibits only one fifth of the anticholinergic activity of atropine on the rabbit detrusor muscle, but four to ten times the antispasmodic activity. No blocking effects occur at skeletal neuromuscular junctions or autonomic ganglia (antinicotinic effects).
Oxybutynin chloride relaxes bladder smooth muscle. In patients with conditions characterized by involuntary bladder contractions, cystometric studies have demonstrated that oxybutynin chloride increases bladder (vesical) capacity, diminishes the frequency of uninhibited contractions of the detrusor muscle, and delays the initial desire to void. Oxybutynin chloride thus decreases urgency and the frequency of both incontinent episodes and voluntary urination.
Oxybutynin chloride was well tolerated in patients administered the drug in controlled studies of 30 days’ duration and in uncontrolled studies in which some of the patients received the drug for 2 years. Pharmacokinetic information is not currently available.
- INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Oxybutynin chloride is contraindicated in patients with untreated angle closure glaucoma and in patients with untreated narrow anterior chamber angles since anticholinergic drugs may aggravate these conditions.
It is also contraindicated in partial or complete obstruction of the gastrointestinal tract, paralytic ileus, intestinal atony of the elderly or debilitated patient, megacolon, toxic megacolon complicating ulcerative colitis, severe colitis, and myasthenia gravis. It is contraindicated in patients with obstructive uropathy and in patients with unstable cardiovascular status in acute hemorrhage.
Oxybutynin chloride is contraindicated in patients who have demonstrated hypersensitivity to the product.
-
WARNINGS
Oxybutynin chloride, when administered in the presence of high environmental temperature, can cause heat prostration (fever and heat stroke due to decreased sweating).
Diarrhea may be an early symptom of incomplete intestinal obstruction, especially in patients with ileostomy or colostomy. In this instance, treatment with oxybutynin chloride would be inappropriate and possibly harmful.
Oxybutynin chloride may produce drowsiness or blurred vision. The patient should be cautioned regarding activities requiring mental alertness such as operating a motor vehicle or other machinery or performing hazardous work while taking this drug.
Alcohol or other sedative drugs may enhance the drowsiness caused by oxybutynin chloride.
-
PRECAUTIONS
Oxybutynin chloride should be used with caution in the elderly and in all patients with autonomic neuropathy, hepatic or renal disease. Oxybutynin chloride may aggravate the symptoms of hyperthyroidism, coronary heart disease, congestive heart failure, cardiac arrhythmias, hiatal hernia, tachycardia, hypertension and prostatic hypertrophy. Administration of oxybutynin chloride to patients with ulcerative colitis may suppress intestinal motility to the point of producing a paralytic ileus and precipitate or aggravate toxic megacolon, a serious complication of the disease.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
A 24-month study in rats at dosages up to approximately 400 times the recommended human dosage showed no evidence of carcinogenicity.
Oxybutynin chloride showed no increase of mutagenic activity when tested in Schizosaccharomyces pompholiciformis, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Salmonella typhimurium test systems. Reproduction studies in the hamster, rabbit, rat and mouse have shown no definite evidence of impaired fertility.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects, Pregnancy Category B.
Reproduction studies in the hamster, rabbit, rat and mouse have shown no definite evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the animal fetus. The safety of oxybutynin chloride administered to women who are or who may become pregnant has not been established. Therefore, oxybutynin chloride should not be given to a pregnant woman unless, in the judgement of the physician, the probable clinical benefits outweigh the possible hazards.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when oxybutynin chloride is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
The safety and efficacy of oxybutynin chloride administration have been demonstrated for pediatric patients 5 years of age and older (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION). However, as there is insufficient clinical data for pediatric populations under age 5, oxybutynin chloride is not recommended for this age group.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Following administration of oxybutynin chloride, the symptoms that can be associated with the use of other anticholinergic drugs may occur:
Cardiovascular: Palpitations, tachycardia, vasodilation.
Dermatologic: Decreased sweating, rash.
Gastrointestinal/Genitourinary: Constipation, decreased gastrointestinal motility, dry mouth, nausea, urinary hesitance and retention.
Nervous System: Asthenia, dizziness, drowsiness, hallucinations, insomnia, restlessness.
Ophthalmic: Amblyopia, cycloplegia, decreased lacrimation, mydriasis.
Other: Impotence, suppression of lactation.
-
OVERDOSAGE
The symptoms of overdosage with oxybutynin chloride may be any of those seen with other anticholinergic agents. Symptoms may include signs of central nervous system excitation (e.g., restlessness, tremor, irritability, convulsions, delirium, hallucinations), flushing, fever, nausea, vomiting, tachycardia, hypotension or hypertension, respiratory failure, paralysis and coma.
In the event of an overdose or exaggerated response, treatment should be symptomatic and supportive. Maintain respiration and induce emesis or perform gastric lavage (emesis is contraindicated in precomatose, convulsive, or psychotic state). Activated charcoal may be administered as well as a cathartic. Physotigmine may be considered to reverse symptoms of anticholinergic intoxication. Hyperpyrexia may be treated symptomatically with ice bags or other cold applications and alcohol sponqes.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Adults: The usual dose is one teaspoonful (5 mL) two to three times a day. The maximum recommended dose is one teaspoonful (5 mL) four times a day.
Pediatric patients over 5 years of age: The usual dose is one teaspoonful (5 mL) two times a day. The maximum recommended dose is one teaspoonful (5 mL) three times a day.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Oxybutynin Chloride Syrup USP (5 mg per 5 mL) is a blue-green colored, peppermint flavored liquid supplied in bottles of 16 fluid ounces (473 mL), NDC: 46672-634-16.
Pharmacist:Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container with a child-resistant closure.
Store at controlled room temperature, 15° - 30°C (59° - 86°F).
Rx only.
Manufactured by:
MIKART, INC.
Atlanta, GA 30318
Code 740Z00
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
OXYBUTYNIN CHLORIDE
oxybutynin chloride syrupProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 46672-634 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength oxybutynin chloride (UNII: S547MDN7WX) (oxybutynin - UNII:K9P6MC7092) 5 mg in 5 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength citric acid (UNII: 2968PHW8QP) FD&C green#3 () glycerin (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) methylparaben () natural and peppermint flavor () propylene glycol (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) propylparaben (UNII: Z8IX2SC1OH) water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) sodium citrate (UNII: 1Q73Q2JULR) sorbitol solution () sucrose (UNII: C151H8M554) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 46672-634-16 473 mL in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC Labeler - MIKART, INC.
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.