FIBRYGA (fibrinogen- human kit
Fibryga by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Fibryga by is a Other medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Octapharma USA Inc. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use FIBRYGA safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for FIBRYGA.
FIBRYGA®, Fibrinogen (Human)
Lyophilized Powder for Reconstitution, For Intravenous Use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2017INDICATIONS AND USAGE
FIBRYGA is a human fibrinogen concentrate indicated for the treatment of acute bleeding episodes in adults and adolescents with congenital fibrinogen deficiency, including afibrinogenemia and hypofibrinogenemia ( 1 ).
FIBRYGA is not indicated for dysfibrinogenemia.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For intravenous use only. Reconstitute prior to use. ( 2 )
Dose when fibrinogen level is known ( 2.1 ):
Dose (mg/kg body weight) =
[Target fibrinogen level (mg/dL) - measured fibrinogen level (mg/dL)]
1.8 (mg/dL per mg/kg body weight)
The recommended target fibrinogen plasma level is 100 mg/dL for minor bleeding and 150 mg/dL for major bleeding.
Dose when fibrinogen level is unknown: 70 mg/kg body weight ( 2.1 ).
The injection rate should not exceed 5 mL per minute ( 2.3 ).
Monitoring of patient’s fibrinogen level is recommended during treatment.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
FIBRYGA is available as a lyophilized powder in single-use bottles containing approximately 1 g fibrinogen concentrate per bottle ( 3 ).
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Anaphylactic or severe reactions to FIBRYGA or its components ( 4 ).
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Monitor patients for early signs of hypersensitivity or allergic reactions. If necessary, discontinue administration and institute appropriate treatment ( 5.1 ).
Thrombotic events have been reported in patients receiving human fibrinogen concentrate. Treatment with human fibrinogen concentrate has been associated with thrombosis at target plasma fibrinogen levels that were below 150 mg/dL. The thrombotic risks may be greater when the target fibrinogen plasma level is 150 mg/dL. Weigh the benefits of administration versus the risks of thrombosis ( 5.2 ).
FIBRYGA is made from pooled human plasma. Products made from human plasma may contain infectious agents, e.g., viruses and, theoretically, the Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) agent ( 5.3 ).
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most serious adverse reactions that may be observed with FIBRYGA are thromboembolic episodes and anaphylactic type reactions. The most common adverse reactions observed in more than one subject in clinical studies with FIBRYGA (> 5% of subjects) were vomiting, weakness and pyrexia (fever) ( 6 ).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Octapharma at 1-866-766-4860 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pediatric: There was no difference in the pharmacokinetics of FIBRYGA between adults and adolescents (12-17 years of age) ( 8.4 ).
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 9/2017
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosage
2.2 Preparation and Handling
2.3 Administration
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
5.2 Thrombosis
5.3 Transmissible Infectious Agents
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For intravenous use after reconstitution. Reconstitute prior to use.
2.1 Dosage
FIBRYGA dosing, duration of dosing, and frequency of administration should be individualized based on the extent of bleeding, laboratory values, and the clinical condition of the patient.
The recommended target fibrinogen plasma level is 100 mg/dL for minor bleeding and 150 mg/dL for major bleeding.
FIBRYGA dose when baseline fibrinogen level is known
Dose should be individually calculated for each patient based on the target plasma fibrinogen level for the type of bleeding, actual measured plasma fibrinogen level and body weight , using the following formula (see Pharmacokinetics [12.3] ):
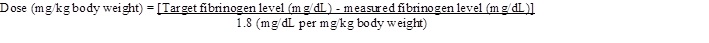
FIBRYGA dose when baseline fibrinogen level is not known
If the patient’s fibrinogen level is not known, the recommended dose is 70 mg per kg of body weight administered intravenously.
Monitor the patient’s fibrinogen level during treatment with FIBRYGA.
Additional infusions of FIBRYGA should be administered if the plasma fibrinogen level is below the accepted lower limit (80 mg/dL for minor bleeding, 130 mg/dL for major bleeding) of the target level until hemostasis is achieved.
2.2 Preparation and Handling
FIBRYGA package contains:
- 1 single-use bottle of FIBRYGA concentrate
- 1 transfer device (Octajet)
- 1 particle filter
Reconstitute FIBRYGA with 50 mL of sterile Water for Injection (not provided).
Do not use FIBRYGA beyond the expiration date. FIBRYGA contains no preservatives. Use aseptic technique when preparing and reconstituting FIBRYGA.
The procedures below are provided as general guidelines for preparation and reconstitution of FIBRYGA.
Reconstitute FIBRYGA as follows:
1. Warm both the powder and sterile Water for Injection (sWFI) in their closed bottles to room temperature. This temperature should be maintained during reconstitution. If a water bath is used for warming, prevent water from coming into contact with the rubber stoppers or the caps of the bottles. The temperature of the water bath should not exceed +37°C (98°F).
2. Remove the cap from the FIBRYGA bottle and the sWFI bottle to expose the central portion of the rubber stoppers. Clean the rubber stoppers with an alcohol swab and allow the rubber stoppers to dry.
3. Peel away the lid of the outer package of the Octajet transfer device. To maintain sterility, leave the Octajet device in the clear outer package.
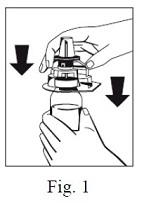
4. Take the Octajet in its outer package and invert it over the FIBRYGA bottle. Place the device while in the outer package onto the center of the FIBRYGA bottle until the clips of the product spike (colorless) are locked. While holding onto the FIBRYGA bottle, carefully remove the outer package from the Octajet, being careful not to touch the water spike (blue) and leave the Octajet attached firmly to the FIBRYGA bottle. (Fig. 1)
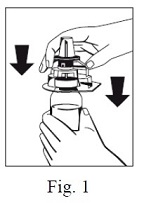
5. With the FIBRYGA bottle held firmly on a level surface, invert the sWFI bottle and place it at the center of the water spike. Push the blue plastic cannula of the Octajet firmly through the rubber stopper of the sWFI bottle. (Fig. 2)
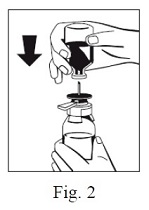
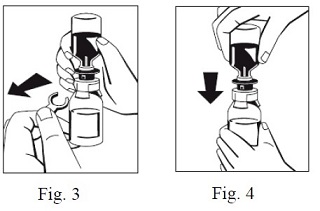
6. Remove the distance ring (Fig. 3) and press the sWFI bottle down (Fig. 4). sWFI will flow into the FIBRYGA bottle.
7. When transfer of the sWFI is complete, gently swirl the FIBRYGA bottle until the powder is fully dissolved. To avoid foam formation, do not shake the bottle. The powder should be dissolved completely within approximately 5 to 10 minutes.
8. Turn the blue sWFI bottle connector (in either direction) to bring the position markers together and remove the sWFI bottle together with the water spike (Fig. 5). Keep the concentrate bottle upright to avoid leaking.
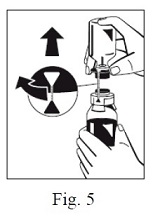
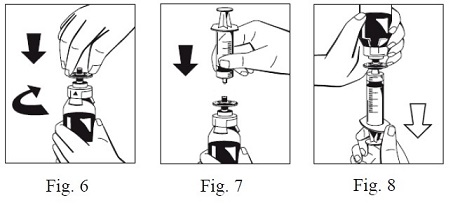
9. Firmly connect the provided particle filter on the remaining Luer Lock on the FIBRYGA bottle (Fig. 6) and withdraw the solution through the particle filter into a syringe. (Fig. 7,8)
10. Detach the filled syringe from the particle filter and discard the empty bottle and the filter.
- After reconstitution, the FIBRYGA solution should be almost colorless and slightly opalescent. Inspect the reconstituted FIBRYGA solution in the syringe for visible particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. Do not use if particulate matter or discoloration are observed.
The powder should be reconstituted only directly before injection. After reconstitution, do not refrigerate or freeze the FIBRYGA solution. Use the reconstituted FIBRYGA solution immediately or within 4 hours after reconstitution. Discard any remaining FIBRYGA solution.
2.3 Administration
For intravenous use only after reconstitution.
- Do not administer FIBRYGA in the same tubing or container as other medications.
- Use aseptic technique when administering FIBRYGA.
- Administer FIBRYGA at room temperature by slow intravenous injection at a rate not exceeding 5 mL per minute.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions may occur. If early signs of hypersensitivity reactions (including hives, generalized urticaria, tightness of the chest, wheezing, hypotension, and anaphylaxis) or symptoms of allergic reactions occur, immediately discontinue administration (see Patient Counseling Information ). The treatment required depends on the nature and severity of the reaction.
5.2 Thrombosis
Thrombosis may occur spontaneously in patients with congenital fibrinogen deficiency with or without the use of fibrinogen replacement therapy. Thrombotic events have been reported in patients receiving human fibrinogen concentrate. Treatment with human fibrinogen concentrate has been associated with risk of thrombosis at target fibrinogen levels that were less than 150 mg/dL. The risk of thrombosis may be greater when the target fibrinogen plasma level is 150 mg/dL. Weigh the benefits of FIBRYGA administration versus the risks of thrombosis. Patients receiving FIBRYGA should be monitored for signs and symptoms of thrombosis. (see Patient Counseling Information )
5.3 Transmissible Infectious Agents
FIBRYGA is made from human plasma. Products made from human plasma may contain infectious agents (e.g., viruses and the CJD agent that can cause disease). Also, unknown infectious agents may be present in such products (see Patient Counseling Information ). The risk that such products will transmit an infectious agent has been reduced by screening plasma donors for prior exposure to certain viruses, by testing for the presence of certain current virus infections, and by a process demonstrated to inactivate and/or remove certain viruses during manufacturing. (see Description [ 11 ]). Despite these measures, such products may transmit disease. All infections thought by a physician possibly to have been transmitted by this product should be reported by the physician or other healthcare provider to Octapharma at 1-866-766-4860.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most serious adverse reactions that may potentially be observed for FIBRYGA are thromboembolic episodes and anaphylactic type reactions.
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to the rate in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Thirteen subjects received at least one dose of FIBRYGA for the treatment of bleeding episodes and/or perioperative management of bleeding. The most common adverse reactions observed in more than one subject in clinical studies with FIBRYGA (> 5% of subjects) were vomiting, weakness and pyrexia (fever).
One patient had a mild skin reaction (itchiness and redness) after FIBRYGA administration for a bleeding episode and was treated with diphenhydramine and hydrocortisone. Thereafter, the patient received another infusion of FIBRYGA for the treatment of the same bleeding episode and another FIBRYGA infusion for surgical prophylaxis during next week. For both of those FIBRYGA infusions the patient was treated with diphenhydramine and hydrocortisone prophylactically and did not experience any drug reactions.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no data with FIBRYGA use in pregnant women to determine whether there is a drug-associated risk. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with FIBRYGA. It is not known whether FIBRYGA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect fertility. FIBRYGA should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information regarding the presence of FIBRYGA in human milk, the effect on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for FIBRYGA and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from FIBRYGA or from the underlying maternal condition.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
FIBRYGA is a human plasma-derived, sterile, purified, virus-inactivated and nanofiltered (20 nm) fibrinogen concentrate.
FIBRYGA is supplied as a lyophilized powder for reconstitution for intravenous injection. FIBRYGA contains no preservatives. Each bottle contains approximately 1 g of fibrinogen. The diluent for reconstitution of the lyophilized powder is sterile Water for Injection.
The nominal composition of FIBRYGA is as follows:
Component Quantity/ mL Human Fibrinogen 20 mg Sodium Chloride 6 mg Sodium Citrate Dihydrate 1.5 mg Glycine 10 mg L-Arginine Hydrochloride 10 mg All units of human plasma used in the manufacture of FIBRYGA are provided by FDA-approved blood establishments, and are tested by FDA-licensed serological tests for Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg), antibodies to Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) and Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)-1/2. As an additional safety measure, the plasma is tested with Nucleic Acid Tests (NATs) for Hepatitis A Virus (HAV), Hepatitis B Virus (HBV), HCV and HIV-1 and found to be non-reactive (negative). The plasma is also screened for Human Parvovirus (B19V) by NAT. The limit for B19V DNA in the mini-pool is set not to exceed 10 3 IU/mL. Only plasma that passed virus screening is used for production.
The FIBRYGA manufacturing process includes a solvent/detergent (S/D) step for virus inactivation, and a nanofiltration step (Planova 20N nanofilter or Pegasus SV4 nanofilter) for virus removal. The mean cumulative virus reduction factors of these steps are summarized in Table 1 below.
Table 1: Cumulative Virus Reduction Factors (Log 10 ) During FIBRYGA Manufacture
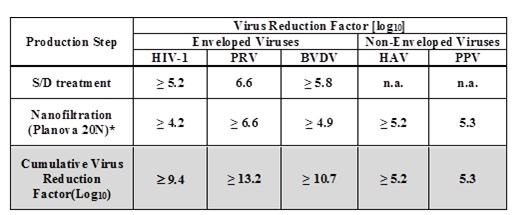
PRV: Pseudorabies Virus, model for large enveloped DNA viruses
BVDV: Bovine Virus Diarrhea Virus, model for HCV
PPV: Porcine Parvovirus, model for B19V
n.a.: not applicable
* When the nanofiltration step was performed using a Pegasus SV4 nanofilter, the virus reduction factors for HIV-1, PRV, BVDV, HAV, and PPV were ≥ 3.9, ≥ 6.3, ≥ 5.0, ≥ 5.2, and 4.5, respectively. The cumulative virus reduction factors (S/D treatment + Pegasus SV4 nanofiltration) were ≥ 9.0, ≥ 12.9, ≥ 10.8, ≥ 5.2, and 4.5, respectively.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Fibrinogen (Factor I) is a soluble plasma protein that, during the coagulation process, is converted to fibrin, one of the key components of the blood clot. Fibrinogen is a heterohexamer with a molecular weight of 340 kDa and composed of two sets of A alpha , B beta , and gamma polypeptide chains.
Following coagulation activation and thrombin generation, fibrinogen is cleaved by thrombin at specific sites on the A alpha and B beta chains to remove fibrinopeptide A (FPA) and fibrinopeptide B (FPB). The removal of FPA and FPB exposes binding sites on the fibrinogen molecule and leads to the formation of fibrin monomers that subsequently undergo polymerization. The resulting fibrin is stabilized by activated factor XIII. Factor XIIIa acts on fibrin to form cross links between fibrin polymers and renders the fibrin clot more resistant to fibrinolysis. The end product of the coagulation cascade is cross-linked fibrin which stabilizes the primary platelet plug and achieves secondary hemostasis.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Administration of FIBRYGA to patients with congenital fibrinogen deficiency supplements the missing coagulation factor or increases low plasma fibrinogen levels. Normal plasma fibrinogen level is in the range of 200 - 450 mg/dL.
An open-label, prospective, randomized, controlled, two-arm, cross-over study was conducted in 22 subjects with congenital fibrinogen deficiency (afibrinogenemia), ranging in age from 12 to 53 years (6 adolescents, 16 adults). Each subject received a single intravenous 70 mg/kg dose of FIBRYGA and the comparator product. Blood samples were drawn from the patients to measure the fibrinogen activity at baseline and up to 14 days after the infusion. Maximum Clot Firmness (MCF) was measured by thromboelastometry (ROTEM).
For each subject, MCF was determined before (baseline) and one hour after the single dose administration of FIBRYGA. In this cross-over study, the results were compared with another fibrinogen concentrate available on the US market. The results of the study demonstrated that the MCF values were significantly higher after administration of FIBRYGA than at baseline ( see Table 2 ). The mean change from pre-infusion to 1 hour post-infusion was 9.7 mm in the primary analysis (9.0 mm for subjects < 18 years old and 9.9 mm for subjects ≥ 18 to < 65 years old).
Table 2: MCF [mm] (ITT population) n=22
Time point Mean ± SD Median (range) Pre-infusion 0 ± 0 0 (0-0) 1 hour post-infusion 9.7± 3.0 10.0 (4.0-16.0) Mean change (primary analysis) a 9.7 ± 3.0 10.0 (4.0-16.0) MCF = maximum clot firmness; mm = millimeter; ITT = intention-to-treat.
a p-value was <0.0001, 95% CI 8.37, 10.99
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
An open-label, prospective, randomized, controlled, two-arm, cross-over study was conducted in 22 subjects with congenital fibrinogen deficiency (afibrinogenemia), ranging in age from 12 to 53 years (6 adolescents, 16 adults). Each subject received a single intravenous 70 mg/kg dose of FIBRYGA and the comparator product. Blood samples were drawn from the subjects to determine the fibrinogen activity at baseline and up to 14 days after the infusion. The pharmacokinetic parameters of FIBRYGA (n=21) are summarized in Table 3 .
The incremental in vivo recovery (IVR) was determined from levels obtained up to 4 hours post-infusion. The median incremental IVR was a 1.8 mg/dL (range 1.1 – 2.6 mg/dL) increase per mg/kg. The median in vivo recovery indicates that a dose of 70 mg/kg will increase patients’ fibrinogen plasma concentration by approximately 125 mg/dL.
Table 3: Pharmacokinetic Parameters (n=21) for Fibrinogen Activity
Parameters Mean ± SD (range) Half-life [hr] 75.9± 23.8 (40.0-157.0) Cmax [mg/dL] 139.0 ± 36.9 (83.0-216.0) AUC [mg*hr/mL] 124.8 ± 34.6 (65.7-193.3) AUC norm for dose of 70 mg/kg [mg*hr/mL] 113.7± 31.5 (59.7-175.5) Clearance [mL/hr/kg] 0.7 ± 0.2 (0.4-1.2) Mean residence time [hr] 106.3 ± 30.9 (58.7-205.5) Volume of distribution at steady state [mL/kg] 70.2 ± 29.9 (36.9-149.1) C max = maximum plasma concentration; AUC = area under the curve; AUC norm = area under the curve normalized to the dose administered; SD = standard deviation
No difference in fibrinogen activity was observed between males and females. There was no difference in the pharmacokinetics of FIBRYGA between adults and adolescents (12-17 years of age).
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
An interim analysis of an ongoing prospective, open-label, uncontrolled, multicentre clinical study was conducted in 13 patients with congenital fibrinogen deficiency (afibrinogenemia and hypofibrinogenemia), ranging in age from 13 to 53 years (2 adolescents, 11 adults). The data below describes 22 minor bleeding events (BEs), with minor bleeding defined as mild joint bleeding or superficial muscle, soft tissue, and oral bleeding. 15 (68%) BEs were spontaneous and 7 (32%) BEs were traumatic.
The median number of infusions for BEs was 1. Two (9%) BEs required 2 infusions. None of the BEs required more than 2 infusions. The median dose of FIBRYGA per infusion for treatment of all BEs was 58 mg/kg.
The treatment of all of the minor BEs studied was assessed for efficacy using a 4-point haemostatic efficacy scale. The scale was based on criteria such as bleeding cessation, changes in hemoglobin, and use of any other hemostatic means. Of 22 evaluable bleeding events, 21 (95%) were assessed as having a successful efficacy outcome (rating of good or excellent efficacy) by both the investigator and by an independent adjudication committee. For one BE, the investigator’s assessment was missing. When considering only the first BE in each patient, all 10 BEs (100%) were assessed as having a successful efficacy outcome (rating of good or excellent efficacy) by both the investigator and the independent adjudication committee.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How supplied:
FIBRYGA is supplied in a single-use bottle.
The following nominal dosage form is available:
Carton NDC Number FIBRYGA 1g 68982-347-01 - The actual potency of fibrinogen in mg is stated on each FIBRYGA carton and bottle.
- FIBRYGA is supplied in a package with a single-dose bottle of powder together with an Octajet transfer device and a particle filter.
- Components used in the packaging of FIBRYGA are not made with natural rubber latex.
Storage and Handling:
- Store FIBRYGA for up to 30 months at +2°C to + 25°C (36°F to 77°F) from the date of manufacture.
- Do not use FIBRYGA beyond the expiration date printed on the carton and bottle.
- Do not freeze. Store in the original container to protect from light.
- After reconstitution, do not refrigerate or freeze the FIBRYGA solution. Use the reconstituted FIBRYGA solution immediately or within 4 hours after reconstitution.
- Dispose of any unused product or waste material in accordance with local requirements.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- Inform patients of the early signs of hypersensitivity or allergic reactions to FIBRYGA, including hives, chest tightness, wheezing, hypotension, and anaphylaxis (see Warnings and Precautions [ 5.1 ]). Advise them to notify their physician immediately if they experience any of these symptoms.
- Inform patients that blood clots with or without consequent obstruction of blood flow may occur with FIBRYGA. Any symptoms of blood clots such as unexplained chest and/or leg pain or swelling of the legs or arms, coughing up blood, shortness of breath, increased rate of breathing or unexplained symptoms related to the nervous system such as stroke or weakness following administration of FIBRYGA should be reported to their physician immediately (see Warnings and Precautions [ 5.2 ]).
- Inform patients that FIBRYGA is made from human plasma (part of the blood) and may contain infectious agents, e.g., viruses and, theoretically, the Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease agent, that can cause disease. Explain the risk that FIBRYGA may transmit an infectious agent has been reduced by screening the plasma donors, by testing the donated plasma for certain virus infections, and by two processes demonstrated to inactivate and/or remove certain viruses during manufacturing (see Warnings and Precautions [ 5.3 ]). Symptoms of a possible virus infection include headache, fever, nausea, vomiting, weakness, malaise, diarrhea, or, in the case of hepatitis, jaundice.
Manufactured by:
Octapharma Pharmazeutika Produktionsges.m.b.H.
Oberlaaer Strasse 235
A-1100 Vienna, Austria
Octapharma AB
Lars Forssells gata 23
SE - 112 75, Sweden
U.S. License No. 1646
Distributed by:
Octapharma USA Inc.
121 River Street, Suite 1201
Hoboken, NJ 07030
Instructions for Use
FIBRYGA / fye bri ' gah /
Fibrinogen (Human)
Read these instructions carefully before using FIBRYGA for the first time. The general guidelines for mixing and infusing FIBRYGA are listed below. If you are unsure of any of these steps, please contact the manufacturer before using FIBRYGA.
FIBRYGA is supplied as a powder. Before it can be infused, it must be mixed with sterile Water for Injection.
FIBRYGA is provided with the Octajet transfer device for reconstitution of the FIBRYGA powder in sterile Water for Injection, and a particle filter to filter the reconstituted solution before injection.
Instructions for Mixing FIBRYGA
1. Warm both the powder and sterile Water for Injection (sWFI) in their closed bottles to room temperature. This temperature should be maintained during reconstitution. If a water bath is used for warming, prevent water from coming into contact with the rubber stoppers or the caps of the bottles. The temperature of the water bath should not exceed +37°C (98°F).
2. Remove the cap from the FIBRYGA bottle and the sWFI bottle to expose the central portion of the rubber stoppers. Clean the rubber stoppers with an alcohol swab and allow the rubber stoppers to dry.
3. Peel away the lid of the outer package of the Octajet transfer device. To maintain sterility, leave the Octajet device in the clear outer package.
4. Take the Octajet in its outer package and invert it over the FIBRYGA bottle. Place the device while in the outer package onto the center of the FIBRYGA bottle until the clips of the product spike (colorless) are locked. While holding onto the FIBRYGA bottle, carefully remove the outer package from the Octajet, being careful not to touch the water spike (blue) and leave the Octajet attached firmly to the FIBRYGA bottle. (Fig. 1)
5. With the FIBRYGA bottle held firmly on a level surface, invert the sWFI bottle and place it at the center of the water spike. Push the blue plastic cannula of the Octajet firmly through the rubber stopper of the sWFI bottle. (Fig. 2)
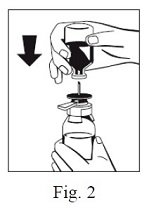
6. Remove the distance ring (Fig. 3) and press the sWFI bottle down (Fig. 4). sWFI will flow into the FIBRYGA bottle.
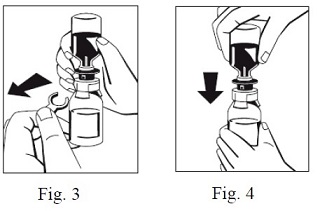
7. When transfer of the sWFI is complete, gently swirl the FIBRYGA bottle until the powder is fully dissolved. To avoid foam formation, do not shake the bottle. The powder should be dissolved completely within approximately 5 to 10 minutes.
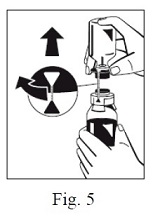
8. Turn the blue sWFI bottle connector (in either direction) to bring the position markers together and remove the sWFI bottle together with the water spike (Fig. 5). Keep the concentrate bottle upright to avoid leaking.
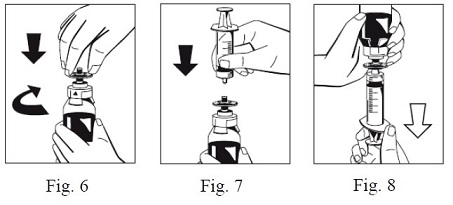
9. Firmly connect the provided particle filter on the remaining Luer Lock on the FIBRYGA bottle (Fig. 6) and withdraw the solution through the particle filter into a syringe. (Fig. 7,8)
10. Detach the filled syringe from the particle filter and discard the empty bottle and the filter.
Instructions for Injecting FIBRYGA
For intravenous use only after reconstitution.
- Inspect the reconstituted FIBRYGA solution in the syringe for visible particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. Do not use if particulate matter or discoloration are observed.
- Do not administer FIBRYGA in the same tubing or container as other medications.
- Clean the chosen injection site with an alcohol swab.
- Attach a standard infusion set to the syringe. Insert the needle of the infusion set into the chosen vein.
- Perform intravenous infusion. The rate of administration should be determined by the patient’s comfort level, at a recommended maximum rate of 5 mL per minute.
- After infusing FIBRYGA, remove and properly discard the infusion set. After the infusion, remove the peel-off label containing the batch number from the FIBRYGA bottle, and place it in the log book for record keeping. Discard the empty bottle.
Manufactured by:
Octapharma Pharmazeutika Produktionsges.m.b.H.
Oberlaaer Strasse 235
A-1100 Vienna, Austria
Octapharma AB
Lars Forssells gata 23
SE - 112 75, Sweden
U.S. License No. 1646
Distributed by:
Octapharma USA, Inc.
Waterfront Corporate Center
121 River Street, Suite 1201
Hoboken, NJ 07030
FIBRYGA is a registered trademark of Octapharma.
Issued September 2017.
-
PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Vial Label – Principal Display Panel
1g Range
NDC: 68982-348-01
Fibryga®
Fibrinogen (Human)
Lyophilized Powder for Reconstitution
Manufactured by:
Octapharma Pharmazeutika Produktionsges.m.b.H.
Oberlaaer Strasse 235
A-1100 Vienna, Austria
U.S. License No. 1646

Carton Label – Principal Display Panel
1g Range
NDC: 68982-347-01
Fibryga®
Fibrinogen (Human)
Lyophilized Powder for Reconstitution
Manufactured by:
Octapharma Pharmazeutika Produktionsges.m.b.H.
Oberlaaer Strasse 235
A-1100 Vienna, Austria
U.S. License No. 1646

-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
FIBRYGA
fibrinogen (human) kitProduct Information Product Type PLASMA DERIVATIVE Item Code (Source) NDC: 68982-347 Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 68982-347-01 1 in 1 CARTON Quantity of Parts Part # Package Quantity Total Product Quantity Part 1 1 BOTTLE, GLASS 50 mL Part 1 of 1 FIBRYGA
fibrinogen (human) powder, for solutionProduct Information Item Code (Source) NDC: 68982-348 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength FIBRINOGEN HUMAN (UNII: N94833051K) (FIBRINOGEN HUMAN - UNII:N94833051K) FIBRINOGEN HUMAN 20 mg in 1 mL Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 68982-348-01 50 mL in 1 BOTTLE, GLASS; Type 9: Other Type of Part 3 Combination Product (e.g., Drug/Device/Biological Product) Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA125612 10/16/2017 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA125612 10/16/2017 Labeler - Octapharma USA Inc (606121163)
Trademark Results [Fibryga]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 FIBRYGA 87466024 5364628 Live/Registered |
Octapharma AG 2017-05-26 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.