Carbamazepine Extended-Release Capsules100 mg, 200 mg and 300 mg Rx only
Carbamazepine by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Carbamazepine by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Bryant Ranch Prepack. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
CARBAMAZEPINE- carbamazepine capsule, extended release
Bryant Ranch Prepack
----------
Carbamazepine Extended-Release Capsules
100 mg, 200 mg and 300 mg
Rx only
WARNING
SERIOUS DERMATOLOGIC REACTIONS AND HLA-B*1502 ALLELE
SERIOUS AND SOMETIMES FATAL DERMATOLOGIC REACTIONS, INCLUDING TOXIC EPIDERMAL NECROLYSIS (TEN) AND STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME (SJS), HAVE BEEN REPORTED DURING TREATMENT WITH CARBAMAZEPINE. THESE REACTIONS ARE ESTIMATED TO OCCUR IN 1 TO 6 PER 10,000 NEW USERS IN COUNTRIES WITH MAINLY CAUCASIAN POPULATIONS, BUT THE RISK IN SOME ASIAN COUNTRIES IS ESTIMATED TO BE ABOUT 10 TIMES HIGHER. STUDIES IN PATIENTS OF CHINESE ANCESTRY HAVE FOUND A STRONG ASSOCIATION BETWEEN THE RISK OF DEVELOPING SJS/TEN AND THE PRESENCE OF HLA-B*1502, AN INHERITED ALLELIC VARIANT OF THE HLA-B GENE. HLA-B*1502 IS FOUND ALMOST EXCLUSIVELY IN PATIENTS WITH ANCESTRY ACROSS BROAD AREAS OF ASIA. PATIENTS WITH ANCESTRY IN GENETICALLY AT-RISK POPULATIONS SHOULD BE SCREENED FOR THE PRESENCE OF HLA-B*1502 PRIOR TO INITIATING TREATMENT WITH CARBAMAZEPINE EXTENDED-RELEASE CAPSULES. PATIENTS TESTING POSITIVE FOR THE ALLELE SHOULD NOT BE TREATED WITH CARBAMAZEPINE EXTENDED-RELEASE CAPSULES UNLESS THE BENEFIT CLEARLY OUTWEIGHS THE RISK (SEE WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS/LABORATORY TESTS).
APLASTIC ANEMIA AND AGRANULOCYTOSIS
APLASTIC ANEMIA AND AGRANULOCYTOSIS HAVE BEEN REPORTED IN ASSOCIATION WITH THE USE OF CARBAMAZEPINE. DATA FROM A POPULATION-BASED CASE-CONTROL STUDY DEMONSTRATE THAT THE RISK OF DEVELOPING THESE REACTIONS IS 5 to 8 TIMES GREATER THAN IN THE GENERAL POPULATION. HOWEVER, THE OVERALL RISK OF THESE REACTIONS IN THE UNTREATED GENERAL POPULATION IS LOW, APPROXIMATELY SIX PATIENTS PER ONE MILLION POPULATION PER YEAR FOR AGRANULOCYTOSIS AND TWO PATIENTS PER ONE MILLION POPULATION PER YEAR FOR APLASTIC ANEMIA.
ALTHOUGH REPORTS OF TRANSIENT OR PERSISTENT DECREASED PLATELET OR WHITE BLOOD CELL COUNTS ARE NOT UNCOMMON IN ASSOCIATION WITH THE USE OF CARBAMAZEPINE, DATA ARE NOT AVAILABLE TO ESTIMATE ACCURATELY THEIR INCIDENCE OR OUTCOME. HOWEVER, THE VAST MAJORITY OF THE CASES OF LEUKOPENIA HAVE NOT PROGRESSED TO THE MORE SERIOUS CONDITIONS OF APLASTIC ANEMIA OR AGRANULOCYTOSIS.
BECAUSE OF THE VERY LOW INCIDENCE OF AGRANULOCYTOSIS AND APLASTIC ANEMIA, THE VAST MAJORITY OF MINOR HEMATOLOGIC CHANGES OBSERVED IN MONITORING OF PATIENTS ON CARBAMAZEPINE ARE UNLIKELY TO SIGNAL THE OCCURRENCE OF EITHER ABNORMALITY. NONETHELESS, COMPLETE PRETREATMENT HEMATOLOGICAL TESTING SHOULD BE OBTAINED AS A BASELINE. IF A PATIENT IN THE COURSE OF TREATMENT EXHIBITS LOW OR DECREASED WHITE BLOOD CELL OR PLATELET COUNTS, THE PATIENT SHOULD BE MONITORED CLOSELY. DISCONTINUATION OF THE DRUG SHOULD BE CONSIDERED IF ANY EVIDENCE OF SIGNIFICANT BONE MARROW DEPRESSION DEVELOPS.
Before prescribing carbamazepine extended-release capsules, the physician should be thoroughly familiar with the details of this prescribing information, particularly regarding use with other drugs, especially those which accentuate toxicity potential.
DESCRIPTION
Carbamazepine extended-release capsules are an anticonvulsant and specific analgesic for trigeminal neuralgia, available for oral administration as 100 mg, 200 mg and 300 mg extended-release capsules of Carbamazepine, USP. Carbamazepine is a white to off-white powder, practically insoluble in water and soluble in alcohol and in acetone. Its molecular weight is 236.27 g/mol. Its chemical name is 5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine-5-carboxamide, and its structural formula is:
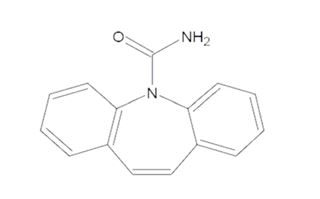
Carbamazepine extended-release capsules are a multi-component capsule formulation consisting of extended-release granules.
Inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, ethylcellulose, and stearic acid.
The 100 mg, 200 mg and 300 mg capsule shells contain FD&C Blue #2, gelatin, iron oxide yellow, titanium dioxide and are imprinted with black ink (S-1-8114 and S-1-8115) contain FD&C BLUE #2, FD&C RED #40, FD&C BLUE #1, D&C YELLOW #10 and shellac.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
In controlled clinical trials, carbamazepine has been shown to be effective in the treatment of psychomotor and grand mal seizures, as well as trigeminal neuralgia.
Mechanism of Action
Carbamazepine has demonstrated anticonvulsant properties in rats and mice with electrically and chemically induced seizures. It appears to act by reducing polysynaptic responses and blocking the post-tetanic potentiation. Carbamazepine greatly reduces or abolishes pain induced by stimulation of the infraorbital nerve in cats and rats. It depresses thalamic potential and bulbar and polysynaptic reflexes, including the linguomandibular reflex in cats. Carbamazepine is chemically unrelated to other anticonvulsants or other drugs used to control the pain of trigeminal neuralgia. The mechanism of action remains unknown.
The principal metabolite of carbamazepine, carbamazepine-10, 11-epoxide, has anticonvulsant activity as demonstrated in several in vivo animal models of seizures. Though clinical activity for the epoxide has been postulated, the significance of its activity with respect to the safety and efficacy of carbamazepine has not been established.
Pharmacokinetics
Carbamazepine (CBZ):
Taken every 12 hours, carbamazepine extended-release capsules provide steady state plasma levels comparable to immediate-release carbamazepine tablets given every 6 hours, when administered at the same total mg daily dose.
Following a single 200 mg oral extended-release dose of carbamazepine, peak plasma concentration was 1.9 ± 0.3 mcg/mL and the time to reach the peak was 19 ± 7 hours. Following chronic administration (800 mg every 12 hours), the peak levels were 11.0 ± 2.5 mcg/mL and the time to reach the peak was 5.9 ± 1.8 hours. The pharmacokinetics of extended-release carbamazepine is linear over the single dose range of 200 to 800 mg.
Carbamazepine is 76% bound to plasma proteins. Carbamazepine is primarily metabolized in the liver. Cytochrome P450 3A4 was identified as the major isoform responsible for the formation of carbamazepine-10, 11-epoxide. Since carbamazepine induces its own metabolism, the half-life is also variable. Following a single extended-release dose of carbamazepine, the average half-life range from 35 to 40 hours and 12 to 17 hours on repeated dosing. The apparent oral clearance following a single dose was 25 ± 5 mL/min and following multiple dosing was 80 ± 30 mL/min.
After oral administration of 14C-carbamazepine, 72% of the administered radioactivity was found in the urine and 28% in the feces. This urinary radioactivity was composed largely of hydroxylated and conjugated metabolites, with only 3% of unchanged carbamazepine.
Carbamazepine-10, 11-epoxide (CBZ-E):
Carbamazepine-10, 11-epoxide is considered to be an active metabolite of carbamazepine. Following a single 200 mg oral extended-release dose of carbamazepine, the peak plasma concentration of carbamazepine-10, 11-epoxide was 0.11 ± 0.012 mcg/mL and the time to reach the peak was 36 ± 6 hours. Following chronic administration of an extended-release dose of carbamazepine (800 mg every 12 hours), the peak levels of carbamazepine-10, 11-epoxide were 2.2 ± 0.9 mcg/mL and the time to reach the peak was 14 ± 8 hours. The plasma half-life of carbamazepine-10, 11-epoxide following administration of carbamazepine is 34 ± 9 hours. Following a single oral dose of extended-release carbamazepine (200 to 800 mg) the AUC and Cmax of carbamazepine-10, 11-epoxide were less than 10% of carbamazepine. Following multiple dosing of extended-release carbamazepine (800 to 1,600 mg daily for 14 days), the AUC and Cmax of carbamazepine-10, 11-epoxide were dose related, ranging from 15.7 mcg·hr/mL and 1.5 mcg/mL at 800 mg/day to 32.6 mcg·hr/mL and 3.2 mcg/mL at 1,600 mg/day, respectively, and were less than 30% of carbamazepine. Carbamazepine-10, 11-epoxide is 50% bound to plasma proteins.
Food Effect:
A high fat meal diet increased the rate of absorption of a single 400 mg dose (mean Tmax was reduced from 24 hours, in the fasting state, to 14 hours and Cmax increased from 3.2 to 4.3 mcg/mL) but not the extent (AUC) of absorption. The elimination half-life remains unchanged between fed and fasting state. The multiple dose study conducted in the fed state showed that the steady-state Cmax values were within the therapeutic concentration range. The pharmacokinetic profile of extended-release carbamazepine was similar when given by sprinkling the beads over applesauce compared to the intact capsule administered in the fasted state.
Special Populations
Hepatic Dysfunction:
The effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of carbamazepine is not known. However, given that carbamazepine is primarily metabolized in the liver, it is prudent to proceed with caution in patients with hepatic dysfunction.
Renal Dysfunction:
The effect of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of carbamazepine is not known.
Gender:
No difference in the mean AUC and Cmax of carbamazepine and carbamazepine-10, 11-epoxide was found between males and females.
Age:
Carbamazepine is more rapidly metabolized to carbamazepine-10, 11-epoxide in young children than adults. In children below the age of 15, there is an inverse relationship between CBZ-E/CBZ ratio and increasing age.
Race:
No information is available on the effect of race on the pharmacokinetics of carbamazepine.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Epilepsy
Carbamazepine extended-release capsules are indicated for use as an anticonvulsant drug. Evidence supporting efficacy of carbamazepine as an anticonvulsant was derived from active drug-controlled studies that enrolled patients with the following seizure types:
- Partial seizures with complex symptomatology (psychomotor, temporal lobe). Patients with these seizures appear to show greater improvements than those with other types.
- Generalized tonic-clonic seizures (grand mal).
- Mixed seizure patterns which include the above, or other partial or generalized seizures. Absence seizures (petit mal) do not appear to be controlled by carbamazepine (see PRECAUTIONS, General).
Trigeminal Neuralgia
Carbamazepine extended-release capsules are indicated in the treatment of the pain associated with true trigeminal neuralgia. Beneficial results have also been reported in glossopharyngeal neuralgia. This drug is not a simple analgesic and should not be used for the relief of trivial aches or pains.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Carbamazepine should not be used in patients with a history of previous bone marrow depression, hypersensitivity to the drug, or known sensitivity to any of the tricyclic compounds, such as amitriptyline, desipramine, imipramine, protriptyline and nortriptyline. Likewise, on theoretical grounds its use with monoamine oxidase inhibitors is not recommended. Before administration of carbamazepine, MAO inhibitors should be discontinued for a minimum of 14 days, or longer if the clinical situation permits.
Coadministration of carbamazepine and nefazodone may result in insufficient plasma concentrations of nefazodone and its active metabolite to achieve a therapeutic effect. Coadministration of carbamazepine with nefazodone is contraindicated.
Coadministration of carbamazepine is contraindicated with delavirdine due to the potential for loss of virologic response and possible resistance to delavirdine or to the class of non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors.
WARNINGS
Serious Dermatologic Reactions
Serious and sometimes fatal dermatologic reactions, including toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) and Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), have been reported with carbamazepine treatment. The risk of these events is estimated to be about 1 to 6 per 10,000 new users in countries with mainly Caucasian populations. However, the risk in some Asian countries is estimated to be about 10 times higher. Carbamazepine extended-release capsules should be discontinued at the first sign of a rash, unless the rash is clearly not drug-related. If signs or symptoms suggest SJS/TEN, use of this drug should not be resumed and alternative therapy should be considered.
SJS/TEN and HLA-B*1502 Allele
Retrospective case-control studies have found that in patients of Chinese ancestry there is a strong association between the risk of developing SJS/TEN with carbamazepine treatment and the presence of an inherited variant of the HLA-B gene, HLA-B*1502. The occurrence of higher rates of these reactions in countries with higher frequencies of this allele suggests that the risk may be increased in allele-positive individuals of any ethnicity.
Across Asian populations, notable variation exists in the prevalence of HLA-B*1502. Greater than 15% of the population is reported positive in Hong Kong, Thailand, Malaysia, and parts of the Philippines, compared to about 10% in Taiwan and 4% in North China. South Asians, including Indians, appear to have intermediate prevalence of HLA-B*1502, averaging 2 to 4%, but higher in some groups. HLA-B*1502 is present in <1% of the population in Japan and Korea.
HLA-B*1502 is largely absent in individuals not of Asian origin (e.g., Caucasians, African-Americans, Hispanics, and Native Americans).
Prior to initiating carbamazepine extended-release capsules therapy, testing for HLA-B*1502 should be performed in patients with ancestry in populations in which HLA-B*1502 may be present. In deciding which patients to screen, the rates provided above for the prevalence of HLA-B*1502 may offer a rough guide, keeping in mind the limitations of these figures due to wide variability in rates even within ethnic groups, the difficulty in ascertaining ethnic ancestry, and the likelihood of mixed ancestry. Carbamazepine extended-release capsules should not be used in patients positive for HLA-B*1502 unless the benefits clearly outweigh the risks. Tested patients who are found to be negative for the allele are thought to have a low risk of SJS/TEN (see WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS/Laboratory Tests).
Over 90% of carbamazepine treated patients who will experience SJS/TEN have this reaction within the first few months of treatment. This information may be taken into consideration in determining the need for screening of genetically at-risk patients currently on carbamazepine extended-release capsules.
The HLA-B*1502 allele has not been found to predict risk of less severe adverse cutaneous reactions from carbamazepine, such as maculopapular eruption [MPE] or to predict Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS).
Limited evidence suggests that HLA-B*1502 may be a risk factor for the development of SJS/TEN in patients of Chinese ancestry taking other anti-epileptic drugs associated with SJS/TEN, including phenytoin. Consideration should be given to avoiding use of other drugs associated with SJS/TEN in HLA-B*1502 positive patients, when alternative therapies are otherwise equally acceptable.
Patients should be made aware that carbamazepine extended-release capsules contain carbamazepine and should not be used in combination with any other medications containing carbamazepine.
Hypersensitivity Reactions and HLA-A*3101 Allele
Retrospective case-control studies in patients of European, Korean, and Japanese ancestry have found a moderate association between the risk of developing hypersensitivity reactions and the presence of HLA-A*3101, an inherited allelic variant of the HLA-A gene, in patients using carbamazepine. These hypersensitivity reactions include SJS/TEN, maculopapular eruptions, and Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (see DRESS/Multiorgan hypersensitivity below).
HLA-A*3101 is expected to be carried by more than 15% of patients of Japanese, Native American, Southern Indian (e.g., Tamil Nadu) and some Arabic ancestry; up to about 10% in patients of Han Chinese, Korean, European, Latin American and other Indian ancestry; and up to about 5% in African-Americans and patients of Thai, Taiwanese, and Chinese (Hong Kong) ancestry.
The risks and benefits of carbamazepine therapy should be weighed before considering carbamazepine in patients known to be positive for HLA-A*3101.
General Information on HLA Genotyping and Hypersensitivity
Application of HLA genotyping as a screening tool has important limitations and must never substitute for appropriate clinical vigilance and patient management. Many HLA-B*1502-positive and HLA-A*3101-positive patients treated with carbamazepine will not develop SJS/TEN or other hypersensitivity reactions, and these reactions can still occur infrequently in HLA-B*1502-negative and HLA-A*3101-negative patients of any ethnicity. The role of other possible factors in the development of, and morbidity from, SJS/TEN and other hypersensitivity reactions, such as AED dose, compliance, concomitant medications, co-morbidities, and the level of dermatologic monitoring have not been studied.
Aplastic Anemia and Agranulocytosis
Aplastic anemia and agranulocytosis have been reported in association with the use of carbamazepine. (See BOXED WARNING.) Patients with a history of adverse hematologic reaction to any drug may be particularly at risk of bone marrow depression.
Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS)/Multiorgan Hypersensitivity
Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS), also known as multiorgan hypersensitivity, have occurred with carbamazepine. Some of these events have been fatal or life-threatening. DRESS typically, although not exclusively, presents with fever, rash, lymphadenopathy and/or facial swelling in association with other organ system involvement, such as hepatitis, nephritis, hematologic abnormalities, myocarditis, or myositis sometimes resembling an acute viral infection. Eosinophilia is often present. This disorder is variable in its expression, and other organ systems not noted here may be involved. It is important to note that early manifestations of hypersensitivity (e.g., fever, lymphadenopathy) may be present even though rash is not evident. If such signs or symptoms are present, the patient should be evaluated immediately. Carbamazepine should be discontinued if an alternative etiology for the signs or symptoms cannot be established.
Hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity reactions to carbamazepine have been reported in patients who previously experienced this reaction to anticonvulsants including phenytoin, primidone, and phenobarbital. A history of hypersensitivity reactions should be obtained for patients and their immediate family members. If such history is present, benefits and risks should be carefully considered, and, if carbamazepine is initiated, the signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity should be carefully monitored.
In patients who have exhibited hypersensitivity reactions to carbamazepine, approximately 25 to 30% may experience hypersensitivity reactions with oxcarbazepine (Trileptal®).
Anaphylaxis and Angioedema
Rare cases of anaphylaxis and angioedema involving the larynx, glottis, lips, and eyelids have been reported in patients after taking the first or subsequent doses of carbamazepine. Angioedema associated with laryngeal edema can be fatal. If a patient develops any of these reactions after treatment with carbamazepine extended-release capsules, the drug should be discontinued and an alternative treatment started. These patients should not be rechallenged with the drug.
Withdrawal Precipitated Seizure, Status Epilepticus
Antiepileptic drugs should not be abruptly discontinued because of the possibility of increased seizure frequency, including status epilepticus. When in the judgment of the clinician, the need for dosage reduction, discontinuation, or substitution of alternative anticonvulsant medication arises, this should be done gradually. However, in the event of an allergic or hypersensitivity reaction, more rapid substitution of alternative therapy may be necessary.
Suicidal Behavior and Ideation
Antiepileptic drugs (AEDs), including carbamazepine extended-release capsules, increase the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior in patients taking these drugs for any indication. Patients treated with any AED for any indication should be monitored for the emergence or worsening of depression, suicidal thoughts or behavior, and/or any unusual changes in mood or behavior.
Pooled analyses of 199 placebo-controlled clinical trials (mono- and adjunctive therapy) of 11 different AEDs showed that patients randomized to one of the AEDs had approximately twice the risk (adjusted Relative Risk 1.8, 95% CI:1.2, 2.7) of suicidal thinking or behavior compared to patients randomized to placebo. In these trials, which had a median treatment duration of 12 weeks, the estimated incidence rate of suicidal behavior or ideation among 27,863 AED-treated patients was 0.43%, compared to 0.24% among 16,029 placebo-treated patients, representing an increase of approximately one case of suicidal thinking or behavior for every 530 patients treated. There were four suicides in drug-treated patients in the trials and none in placebo-treated patients, but the number is too small to allow any conclusion about drug effect on suicide.
The increased risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior with AEDs was observed as early as one week after starting drug treatment with AEDs and persisted for the duration of treatment assessed. Because most trials included in the analysis did not extend beyond 24 weeks, the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior beyond 24 weeks could not be assessed.
The risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior was generally consistent among drugs in the data analyzed. The finding of increased risk with AEDs of varying mechanisms of action and across a range of indications suggests that the risk applies to all AEDs used for any indication. The risk did not vary substantially by age (5 to 100 years) in the clinical trials analyzed.
Table 1 shows absolute and relative risk by indication for all evaluated AEDs.
| Indication | Placebo Patients with Events Per 1000 Patients | Drug Patients with Events Per 1000 Patients | Relative Risk: Incidence of Events in Drug Patients/ Incidence in Placebo Patients | Risk Difference: Additional Drug Patients with Events Per 1000 Patients |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epilepsy | 1.0 | 3.4 | 3.5 | 2.4 |
| Psychiatric | 5.7 | 8.5 | 1.5 | 2.9 |
| Other | 1.0 | 1.8 | 1.9 | 0.9 |
| Total | 2.4 | 4.3 | 1.8 | 1.9 |
The relative risk for suicidal thoughts or behavior was higher in clinical trials for epilepsy than in clinical trials for psychiatric or other conditions, but the absolute risk differences were similar for the epilepsy and psychiatric indications.
Anyone considering prescribing carbamazepine extended-release capsules or any other AED must balance the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior with the risk of untreated illness. Epilepsy and many other illnesses for which AEDs are prescribed are themselves associated with morbidity and mortality and an increased risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior. Should suicidal thoughts and behavior emerge during treatment, the prescriber needs to consider whether the emergence of these symptoms in any given patient may be related to the illness being treated.
Hyponatremia, Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone Secretion, and Water Intoxication
Hyponatremia can occur as a result of treatment with carbamazepine extended-release capsules. In many cases, this hyponatremia appears to be the result of the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH). The risk of developing SIADH with carbamazepine treatment may be dose-related. Elderly patients and patients treated with diuretics are at greater risk of developing hyponatremia. Signs and symptoms of hyponatremia include headache, new or increased seizure frequency, difficulty concentrating, memory impairment, confusion, weakness, and unsteadiness, which can lead to falls. Consider discontinuing carbamazepine extended-release capsules in patients with symptomatic hyponatremia.
Usage in Pregnancy
Carbamazepine can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman.
Epidemiological data suggest that there may be an association between the use of carbamazepine during pregnancy and congenital malformations, including spina bifida. There have also been reports that associate carbamazepine with developmental disorders and congenital anomalies (e.g., craniofacial defects, cardiovascular malformations, and anomalies involving various body systems). Developmental delays have been reported. When treating or counseling women of childbearing potential, the prescribing physician will wish to weigh the benefits of therapy against the risks. If this drug is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus.
Retrospective case reviews suggest that, compared with monotherapy, there may be a higher prevalence of teratogenic effects associated with the use of anticonvulsants in combination therapy. Therefore, if therapy is to be continued, monotherapy may be preferable for pregnant women.
In humans, transplacental passage of carbamazepine is rapid (30 to 60 minutes), and the drug is accumulated in the fetal tissues, with higher levels found in liver and kidney than in brain and lung.
Carbamazepine has been shown to have adverse effects in reproduction studies in rats when given orally in dosages 10 to 25 times the maximum human daily dosage (MHDD) of 1,200 mg on a mg/kg basis or 1.5 to 4 times the MHDD on a mg/m2 basis. In rat teratology studies, 2 of 135 offspring showed kinked ribs at 250 mg/kg and 4 of 119 offspring at 650 mg/kg showed other anomalies (cleft palate, 1; talipes, 1; anophthalmos, 2). In reproduction studies in rats, nursing offspring demonstrated a lack of weight gain and an unkempt appearance at a maternal dosage level of 200 mg/kg.
Antiepileptic drugs should not be discontinued abruptly in patients in whom the drug is administered to prevent major seizures because of the strong possibility of precipitating status epilepticus with attendant hypoxia and threat to life. In individual cases where the severity and frequency of the seizure disorder are such that removal of medication does not pose a serious threat to the patient, discontinuation of the drug may be considered prior to and during pregnancy, although it cannot be said with any confidence that even minor seizures do not pose some hazard to the developing embryo or fetus.
Tests to detect defects using current accepted procedures should be considered a part of routine prenatal care in childbearing women receiving carbamazepine.
There have been a few cases of neonatal seizures and/or respiratory depression reported in association with maternal carbamazepine and other concomitant anticonvulsant drug use. A few cases of neonatal vomiting, diarrhea, and/or decreased feeding have also been reported in association with maternal carbamazepine use. These symptoms may represent a neonatal withdrawal syndrome.
To provide information regarding the effects of in utero exposure to carbamazepine extended-release capsules, physicians are advised to recommend that pregnant patients taking carbamazepine extended-release capsules enroll in the North American Antiepileptic Drug (NAAED) Pregnancy Registry. This can be done by calling the toll free number 1-888-233-2334, and must be done by patients themselves. Information on the registry can also be found at the website http://www.aedpregnancyregistry.org/.
General
Carbamazepine has shown mild anticholinergic activity; therefore, patients with increased intraocular pressure should be closely observed during therapy.
Because of the relationship of the drug to other tricyclic compounds, the possibility of activation of a latent psychosis and, in elderly patients, of confusion or agitation should be considered.
The use of carbamazepine should be avoided in patients with a history of hepatic porphyria (e.g., acute intermittent porphyria, variegate porphyria, porphyria cutanea tarda). Acute attacks have been reported in such patients receiving carbamazepine therapy. Carbamazepine administration has also been demonstrated to increase porphyrin precursors in rodents, a presumed mechanism for the induction of acute attacks of porphyria.
PRECAUTIONS
General
Before initiating therapy, a detailed history and physical examination should be made.
Carbamazepine should be used with caution in patients with a mixed seizure disorder that includes atypical absence seizures, since in these patients carbamazepine has been associated with increased frequency of generalized convulsions (see INDICATIONS AND USAGE).
Therapy should be prescribed only after critical benefit-to-risk appraisal in patients with a history of cardiac conduction disturbance, including second- and third-degree atrioventricular (AV) block; cardiac, hepatic, or renal damage; adverse hematologic or hypersensitivity reaction to other drugs including reactions to other anticonvulsants; or interrupted courses of therapy with carbamazepine.
AV block, including second- and third-degree block, has been reported following carbamazepine treatment. This occurred generally, but not solely, in patients with underlying EKG abnormalities or risk factors for conduction disturbances.
Hepatic effects, ranging from slight elevations in liver enzymes to rare cases of hepatic failure, have been reported (see ADVERSE REACTIONS and PRECAUTIONS, Laboratory Tests). In some cases, hepatic effects may progress despite discontinuation of the drug. In addition, rare instances of vanishing bile duct syndrome have been reported. This syndrome consists of a cholestatic process with a variable clinical course ranging from fulminant to indolent, involving the destruction and disappearance of the intrahepatic bile ducts. Some, but not all, cases are associated with features that overlap with other immunoallergenic syndromes such as multiorgan hypersensitivity/ DRESS and serious dermatologic reactions. As an example, there has been a report of vanishing bile duct syndrome associated with Stevens-Johnson syndrome and in another case an association with fever and eosinophilia.
Information for Patients
Patients should be informed of the availability of a Medication Guide and they should be instructed to read the Medication Guide before taking carbamazepine extended-release capsules.
Patients should be made aware of the early toxic signs and symptoms of potential hematologic, dermatologic, hypersensitivity, or hepatic reactions. These symptoms may include, but are not limited to, fever, sore throat, rash, ulcers in the mouth, easy bruising, lymphadenopathy and petechial or purpuric hemorrhage, and in the case of liver reactions, anorexia, nausea/vomiting, or jaundice. Patients should be advised that, because these signs and symptoms may signal a serious reaction, they must report any occurrence immediately to their physicians. In addition, the patient should be advised that these signs and symptoms should be reported even if mild or when occurring after extended use.
Patients should be advised that serious skin reactions have been reported in association with carbamazepine extended-release capsules. In the event a skin reaction should occur while taking carbamazepine extended-release capsules, patients should consult with their physician immediately (see WARNINGS).
Patients should be advised that anaphylactic reactions and angioedema may occur during treatment with carbamazepine extended-release capsules (see WARNINGS). Advise patients to immediately report signs and symptoms suggesting angioedema (swelling of the face, eyes, lips, or tongue, or difficulty in swallowing or breathing) and to stop taking the drug until they have consulted with their healthcare provider.
Patients, their caregivers, and families should be counseled that AEDs, including carbamazepine, may increase the risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior and should be advised of the need to be alert for the emergence or worsening of symptoms of depression, any unusual changes in mood or behavior, or the emergence of suicidal thoughts, behavior, or thoughts about self-harm. Behaviors of concern should be reported immediately to healthcare providers.
Carbamazepine extended-release capsules may interact with some drugs. Therefore, patients should be advised to report to their doctors the use of any other prescription or nonprescription medications or herbal products.
Caution should be exercised if alcohol is taken in combination with carbamazepine therapy, due to a possible additive sedative effect.
Since dizziness and drowsiness may occur, patients should be cautioned about the hazards of operating machinery or automobiles or engaging in other potentially dangerous tasks.
Patients should be encouraged to enroll in the NAAED Pregnancy Registry if they become pregnant. This registry is collecting information about the safety of antiepileptic drugs during pregnancy. To enroll, patients can call the toll-free number 1-888-233-2334 (see Warnings-Usage in Pregnancy).
If necessary, the carbamazepine extended-release capsules can be opened and the contents sprinkled over food, such as a teaspoon of applesauce or other similar food products. Carbamazepine extended-release capsules or their contents should not be crushed or chewed.
Carbamazepine extended-release capsules may interact with some drugs. Therefore, patients should be advised to report to their doctors the use of any other prescription or non-prescription medication or herbal products.
Patients, their caregivers, and families should be informed of the availability of a Medication Guide, and they should be instructed to read the Medication Guide prior to taking carbamazepine extended-release capsules. See FDA approved Medication Guide.
Laboratory Tests
For genetically at-risk patients (see WARNINGS), high-resolution ‘HLA-B*1502 typing’ is recommended. The test is positive if either one or two HLA-B*1502 alleles are detected and negative if no HLA-B*1502 alleles are detected.
Complete pretreatment blood counts, including platelets and possibly reticulocytes and serum iron, should be obtained as a baseline. If a patient in the course of treatment exhibits low or decreased white blood cell or platelet counts, the patient should be monitored closely. Discontinuation of the drug should be considered if any evidence of significant bone marrow depression develops.
Baseline and periodic evaluations of liver function, particularly in patients with a history of liver disease, must be performed during treatment with this drug since liver damage may occur (see PRECAUTIONS, General and ADVERSE REACTIONS, Liver). Carbamazepine extended-release capsules should be discontinued based on clinical judgement, if indicated by newly occurring or worsening clinical or laboratory evidence of liver dysfunction or hepatic damage, or in the case of active liver disease.
Baseline and periodic eye examinations, including slit-lamp, funduscopy, and tonometry, are recommended since many phenothiazines and related drugs have been shown to cause eye changes. Baseline and periodic complete urinalysis and BUN determinations are recommended for patients treated with this agent because of observed renal dysfunction.
Increases in total cholesterol, LDL and HDL have been observed in some patients taking anticonvulsants. Therefore, periodic evaluation of these parameters is also recommended.
Monitoring of blood levels (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY) has increased the efficacy and safety of anticonvulsants. This monitoring may be particularly useful in cases of dramatic increase in seizure frequency and for verification of compliance. In addition, measurement of drug serum levels may aid in determining the cause of toxicity when more than one medication is being used.
Thyroid function tests have been reported to show decreased values with carbamazepine administered alone.
Interference with some pregnancy tests has been reported.
Drug Interactions
Clinically meaningful drug interactions have occurred with concomitant medications and include, but are not limited to the following:
Agents Highly Bound to Plasma Protein:
Carbamazepine is not highly bound to plasma proteins; therefore, administration of carbamazepine extended-release capsules to a patient taking another drug that is highly protein bound should not cause increased free concentrations of the other drug.
Agents that Inhibit Cytochrome P450 Isoenzymes and/or Epoxide Hydrolase:
Carbamazepine is metabolized mainly by cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A4 to the active carbamazepine 10, 11-epoxide, which is further metabolized to the trans-diol by epoxide hydrolase. Therefore, the potential exists for interaction between carbamazepine and any agent that inhibits CYP3A4 and/or epoxide hydrolase. Agents that are CYP3A4 inhibitors that have been found, or are expected, to increase plasma levels of carbamazepine extended-release capsules include, for example, the following:
Acetazolamide, aprepitant, azole antifungals (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole, fluconazole, voriconazole), cimetidine, ciprofloxacin, clarithromycin, dalfopristin, danazol, dantrolene, delavirdine, diltiazem, erythromycin, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, grapefruit juice, ibuprofen, isoniazid, loratadine, macrolides, nefazodone, niacinamide, nicotinamide, olanzapine, omeprazole, oxybutynin, protease inhibitors, propoxyphene, quinine, quinupristin, ticlopidine, troleandomycin, valproate, verapamil, zileuton.
Human microsomal epoxide hydrolase has been identified as the enzyme responsible for the formation of the 10,11-transdiol derivative from carbamazepine-10,11 epoxide. Coadministration of inhibitors of human microsomal epoxide hydrolase may result in increased carbamazepine-10,11 epoxide plasma concentrations. Accordingly, the dosage of carbamazepine extended-release capsules should be adjusted and/or the plasma levels monitored when used concomitantly with loxapine, quetiapine, or valproic acid. Thus, if a patient has been titrated to a stable dosage of carbamazepine extended-release capsules, and then begins a course of treatment with one of these CYP3A4 or epoxide hydrolase inhibitors, it is reasonable to expect that a dose reduction for carbamazepine extended-release capsules may be necessary.
Agents that Induce Cytochrome P450 Isoenzymes:
Carbamazepine is metabolized by CYP3A4. Therefore, the potential exists for interaction between carbamazepine and any agent that induces CYP3A4. Agents that are CYP inducers that have been found, or are expected, to decrease plasma levels of carbamazepine extended-release capsules include, for example, the following:
Aminophylline, cisplatin, doxorubicin HCL, felbamate, fosphenytoin, methsuximide, phenobarbital, phenytoin(1), primidone, rifampin and theophylline.
(1)Phenytoin plasma levels have also been reported to increase and decrease in the presence of carbamazepine, see below.
Thus, if a patient has been titrated to a stable dosage on carbamazepine extended-release capsules, and then begins a course of treatment with one of these CYP3A4 inducers, it is reasonable to expect that a dose increase for carbamazepine extended-release capsules may be necessary.
Agents with Decreased Levels in the Presence of Carbamazepine due to Induction of Cytochrome P450 Enzymes:
Carbamazepine is a potent inducer of hepatic CYP3A4 and is also known to be an inducer of CYP1A2, 2B6, 2C9/19 and may therefore reduce plasma concentrations of co-medications mainly metabolized by CYP 1A2, 2B6, 2C9/19 and 3A4, through induction of their metabolism. When used concomitantly with carbamazepine extended-release capsules, monitoring of concentrations or dosage adjustment of these agents may be necessary:
- When carbamazepine is added to aripiprazole, the aripiprazole dose should be doubled. Additional dose increases should be based on clinical evaluation. If carbamazepine is later withdrawn, the aripiprazole dose should be reduced.
- When carbamazepine is used with tacrolimus, monitoring of tacrolimus blood concentrations and appropriate dosage adjustments are recommended.
- The use of concomitant strong CYP3A4 inducers such as carbamazepine should be avoided with temsirolimus. If patients must be coadministered carbamazepine with temsirolimus, an adjustment of temsirolimus dosage should be considered.
- The use of carbamazepine with lapatinib should generally be avoided. If carbamazepine is started in a patient already taking lapatinib, the dose of lapatinib should be gradually titrated up. If carbamazepine is discontinued, the lapatinib dose should be reduced.
- Concomitant use of carbamazepine with nefazodone results in plasma concentrations of nefazodone and its active metabolite insufficient to achieve a therapeutic effect. Coadministration of carbamazepine with nefazodone is contraindicated (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
- Monitor concentrations of valproate when carbamazepine extended-release capsules are introduced or withdrawn in patients using valproic acid.
In addition, carbamazepine causes, or would be expected to cause, decreased levels of, for example, the following drugs, for which monitoring of concentrations or dosage adjustment may be necessary:
Acetaminophen, albendazole, alprazolam, aprepitant, buprenorphine, apixaban(6), bupropion, buspirone, citalopram, clobazam, clonazepam, clozapine, corticosteroids (e.g. prednisolone, dexamethasone), cyclosporin, dabigatran(6), delavirdine, desipramine, diazepam, dicumarol, dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers (e.g., felodipine), doxycycline, edoxaban(6), eslicarbazepine, ethosuximide, everolimus, felbamate, haloperidol, imatinib, itraconazole, lamotrigine, levothyroxine, lorazepam, methadone, methsuximide, midazolam, mirtazapine, nefazodone, nortriptyline, olanzapine, oral and other hormonal contraceptives(2), oxcarbazepine, paliperidone, phenytoin(3), praziquantel, protease inhibitors, quetiapine, risperidone, rivaroxaban(6), sertraline, sirolimus, tadalafil, theophylline, tiagabine, topiramate, tramadol, triazolam, trazodone(4), tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., imipramine, amitriptyline, nortriptyline), valproate, warfarin(5), ziprasidone, and zonisamide.
(2) Concomitant use of carbamazepine with hormonal contraceptive products (e.g., oral and levonorgestrel subdermal implant contraceptives) may render the contraceptives less effective because the plasma concentrations of the hormones may be decreased. Breakthrough bleeding and unintended pregnancies have been reported with carbamazepine. Alternative or back-up methods of contraception should be considered.
(3)Phenytoin has also been reported to increase in the presence of carbamazepine. Careful monitoring of phenytoin plasma levels following co-medication with carbamazepine is advised.
(4) Following co-administration of carbamazepine 400 mg/day with trazodone 100 mg to 300 mg daily, carbamazepine reduced trough plasma concentrations of trazodone (as well as meta-chlorophenylpiperazine [mCPP]) by 76 and 60% respectively, compared to precarbamazepine values.
(5)Warfarin’s anticoagulant effect can be reduced in the presence of carbamazepine.
(6) Concomitant use of carbamazepine with rivaroxaban, apixaban, dabigatran, and edoxaban (direct acting oral anticoagulants) is expected to result in decreased plasma concentrations of these anticoagulants that may be insufficient to achieve the intended therapeutic effect. In general, coadministration of carbamazepine with rivaroxaban, apixaban, dabigatran, and edoxaban should be avoided.
Thus, if a patient has been titrated to a stable dosage on one of the agents in this category, and then begins a course of treatment with carbamazepine extended-release capsules, it is reasonable to expect that a dose increase for the concomitant agent may be necessary.
Agents with Increased Levels in the Presence of Carbamazepine
Carbamazepine extended-release capsules increase the plasma levels of the following agents.
Thus, if a patient has been titrated to a stable dosage on one of the agents in this category, and then begins a course of the treatment with carbamazepine extended-release capsules, it is reasonable to expect that a dose decrease for the concomitant agent may be necessary.
Clomipramine HCl, Phenytoin(7), and Primidone
Carbamazepine extended-release capsules can increase the concentrations of clomipramine, phenytoin, and primidone. If a patient has been titrated to a stable dosage on one of these agents in this category, and then begins treatment with carbamazepine extended-release capsules, it may be necessary to decrease the dose of these drugs.
(7)Phenytoin has also been reported to decrease in the presence of carbamazepine. Careful monitoring of phenytoin plasma levels following co-medication with carbamazepine is advised.
Cyclophosphamide
Cyclophosphamide is an inactive prodrug and is converted to its active metabolite in part by CYP3A. The rate of metabolism and the leukopenic activity of cyclophosphamide are reportedly increased by chronic co-administration of CYP3A4 inducers. There is a potential for increased cyclophosphamide toxicity when coadministered with carbamazepine.
Pharmacological/Pharmacodynamic Interactions with Carbamazepine:
Delavirdine
Coadministration of carbamazepine with delavirdine may lead to loss of virologic response and possible resistance to delavirdine or to the class of non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
Lithium
Concomitant administration of carbamazepine and lithium may increase the risk of neurotoxic side effects.
Thyroid Effects with Other Anticonvulsant Medications
Alterations of thyroid function have been reported in combination therapy with other anticonvulsant medications.
Chloroquine and Mefloquine
Anti-malarial drugs, such as chloroquine and mefloquine, may antagonize the activity of carbamazepine.
Thus if a patient has been titrated to a stable dosage on one of the agents in this category, and then begins a course of treatment with carbamazepine extended-release capsules, it is reasonable to expect that a dose adjustment may be necessary.
CNS Depressants
The concomitant use of carbamazepine extended-release capsules and other CNS depressants can increase the risk of respiratory depression, profound sedation, hypotension, and syncope. CNS depressants include: alcohol, opioid analgesics, benzodiazepines, tricyclic antidepressants, sedative/hypnotics, anticonvulsants, antipsychotics, antihistamines, anticholinergics, alpha and beta blockers, general anesthetics, muscle relaxants, and illicit CNS depressants. Consider reducing the dose of CNS depressants or carbamazepine extended-release capsules when using these drugs concomitantly. Because of its primary CNS effect, caution should be used when carbamazepine extended-release capsules are taken with other centrally acting drugs and alcohol.
Neuromuscular Blocking Agents
Resistance to the neuromuscular blocking action of the nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocking agents pancuronium, vecuronium, rocuronium and cisatracurium has occurred in patients chronically administered carbamazepine. Whether or not carbamazepine has the same effect on other nondepolarizing agents is unknown. Patients should be monitored closely for more rapid recovery from neuromuscular blockade than expected, and infusion rate requirements may be higher.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility:
Administration of carbamazepine to Sprague-Dawley rats for two years in the diet at doses of 25, 75, and 250 mg/kg/day (low dose approximately 0.2 times the maximum human daily dose of 1,200 mg on a mg/m2 basis), resulted in a dose-related increase in the incidence of hepatocellular tumors in females and of benign interstitial cell adenomas in the testes of males.
Carbamazepine must, therefore, be considered to be carcinogenic in Sprague-Dawley rats. Bacterial and mammalian mutagenicity studies using carbamazepine produced negative results. The significance of these findings relative to the use of carbamazepine in humans is, at present, unknown.
Nursing Mothers
Carbamazepine and its epoxide metabolite are transferred to breast milk and during lactation. The concentrations of carbamazepine and its epoxide metabolite are approximately 50% of the maternal plasma concentration. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from carbamazepine, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use
Substantial evidence of carbamazepine effectiveness for use in the management of children with epilepsy (see INDICATIONS for specific seizure types) is derived from clinical investigations performed in adults and from studies in several in vitro systems which support the conclusion that (1) the pathogenic mechanisms underlying seizure propagation are essentially identical in adults and children, and (2) the mechanism of action of carbamazepine in treating seizures is essentially identical in adults and children.
Taken as a whole, this information supports a conclusion that the generally acceptable therapeutic range of total carbamazepine in plasma (i.e., 4 to 12 mcg/mL) is the same in children and adults.
The evidence assembled was primarily obtained from short-term use of carbamazepine. The safety of carbamazepine in children has been systematically studied up to 6 months. No longer term data from clinical trials is available.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
General:
If adverse reactions are of such severity that the drug must be discontinued, the physician must be aware that abrupt discontinuation of any anticonvulsant drug in a responsive patient with epilepsy may lead to seizures or even status epilepticus with its life-threatening hazards.
The most severe adverse reactions previously observed with carbamazepine were reported in the hemopoietic system and skin (see BOXED WARNING), and the cardiovascular system.
The most frequently observed adverse reactions, particularly during the initial phases of therapy, are dizziness, drowsiness, unsteadiness, nausea, and vomiting. To minimize the possibility of such reactions, therapy should be initiated at the lowest dosage recommended.
The following additional adverse reactions were previously reported with carbamazepine:
Hemopoietic System:
Aplastic anemia, agranulocytosis, pancytopenia, bone marrow depression, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, leukocytosis, eosinophilia, acute intermittent porphyria.
Skin:
Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) and Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) (see BOXED WARNING), Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis (AGEP), pruritic and erythematous rashes, urticaria, photosensitivity reactions, alterations in skin pigmentation, exfoliative dermatitis, erythema multiforme and nodosum, purpura, aggravation of disseminated lupus erythematosus, alopecia, diaphoresis, onychomadesis and hirsutism. In certain cases, discontinuation of therapy may be necessary.
Cardiovascular System:
Congestive heart failure, edema, aggravation of hypertension, hypotension, syncope and collapse, aggravation of coronary artery disease, arrhythmias and AV block, thrombophlebitis, thromboembolism, and adenopathy or lymphadenopathy. Some of these cardiovascular complications have resulted in fatalities. Myocardial infarction has been associated with other tricyclic compounds.
Immune system disorders: Hypogammaglobulinemia.
Liver:
Abnormalities in liver function tests, cholestatic and hepatocellular jaundice, hepatitis, and hepatic failure.
Pancreatic:
Pancreatitis.
Respiratory System:
Pulmonary hypersensitivity characterized by fever, dyspnea, pneumonitis, or pneumonia.
Genitourinary System:
Urinary frequency, acute urinary retention, oliguria with elevated blood pressure, azotemia, renal failure, and impotence. Albuminuria, glycosuria, elevated BUN, and microscopic deposits in the urine have also been reported. There have been rare reports of impaired male fertility and/or abnormal spermatogenesis.
Testicular atrophy occurred in rats receiving carbamazepine orally from 4 to 52 weeks at dosage levels of 50 to 400 mg/kg/day. Additionally, rats receiving carbamazepine in the diet for 2 years at dosage levels of 25, 75, and 250 mg/kg/day had a dose-related incidence of testicular atrophy and aspermatogenesis. In dogs, it produced a brownish discoloration, presumably a metabolite, in the urinary bladder at dosage levels of 50 mg/kg/day and higher. Relevance of these findings to humans is unknown.
Nervous System:
Dizziness, drowsiness, disturbances of coordination, confusion, headache, fatigue, blurred vision, visual hallucinations, transient diplopia, oculomotor disturbances, nystagmus, speech disturbances, abnormal involuntary movements, peripheral neuritis and paresthesias, depression with agitation, talkativeness, tinnitus, and hyperacusis.
There have been reports of associated paralysis and other symptoms of cerebral arterial insufficiency, but the exact relationship of these reactions to the drug has not been established.
Isolated cases of neuroleptic malignant syndrome have been reported with concomitant use of psychotropic drugs.
Digestive System:
Nausea, vomiting, gastric distress and abdominal pain, diarrhea, constipation, anorexia, and dryness of the mouth and pharynx, including glossitis and stomatitis.
Eyes:
Scattered punctate cortical lens opacities, as well as conjunctivitis, have been reported. Although a direct causal relationship has not been established, many phenothiazines and related drugs have been shown to cause eye changes.
Musculoskeletal System:
Bone loss, aching joints and muscles, and leg cramps.
Metabolism:
Fever and chills, decreased levels of plasma calcium leading to osteoporosis, and hyperammonemia have been reported.
Other:
Isolated cases of a lupus erythematosus-like syndrome have been reported. There have been occasional reports of elevated levels of cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and triglycerides in patients taking anticonvulsants.
A case of aseptic meningitis, accompanied by myoclonus and peripheral eosinophilia, has been reported in a patient taking carbamazepine in combination with other medications. The patient was successfully dechallenged, and the meningitis reappeared upon rechallenge with carbamazepine.
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
No evidence of abuse potential has been associated with carbamazepine, nor is there evidence of psychological or physical dependence in humans.
OVERDOSAGE
Acute Toxicity
Lowest known lethal dose: adults, >60 g (39-year-old man). Highest known doses survived: adults, 30 g (31-year-old woman); children, 10 g (6-year-old boy); small children, 5 g (3-year-old girl).
Oral LD50 in animals (mg/kg): mice, 1100 to 3750; rats, 3850 to 4025; rabbits, 1500 to 2680; guinea pigs, 920.
Signs and Symptoms
The first signs and symptoms appear after 1 to 3 hours. Neuromuscular disturbances are the most prominent. Cardiovascular disorders are generally milder, and severe cardiac complications occur only when very high doses (>60 g) have been ingested.
Respiration: Irregular breathing, respiratory depression.
Cardiovascular System: Tachycardia, hypotension or hypertension, shock, conduction disorders.
Nervous System and Muscles: Impairment of consciousness ranging in severity to deep coma. Convulsions, especially in small children. Motor restlessness, muscular twitching, tremor, athetoid movements, opisthotonos, ataxia, drowsiness, dizziness, mydriasis, nystagmus, adiadochokinesia, ballism, psychomotor disturbances, dysmetria. Initial hyperreflexia, followed by hyporeflexia.
Gastrointestinal Tract: Nausea, vomiting.
Kidneys and Bladder: Anuria or oliguria, urinary retention.
Laboratory Findings: Isolated instances of overdosage have included leukocytosis, reduced leukocyte count, glycosuria, and acetonuria. ECG may show dysrhythmias.
Combined Poisoning: When alcohol, tricyclic antidepressants, barbiturates, or hydantoins are taken at the same time, the signs and symptoms of acute poisoning with carbamazepine may be aggravated or modified.
Treatment
For the most up to date information on management of carbamazepine overdose, please contact the poison center for your area by calling 1-800-222-1222. The prognosis in cases of carbamazepine poisoning is generally favorable. Of 5,645 cases of carbamazepine exposures reported to US poison centers in 2002, a total of 8 deaths (0.14% mortality rate) occurred. Over 39% of the cases reported to these poison centers were managed safely at home with conservative care. Successful management of large or intentional carbamazepine exposures requires implementation of supportive care, frequent monitoring of serum drug concentrations, as well as aggressive but appropriate gastric decontamination.
Elimination of the Drug:
The primary method for gastric decontamination of carbamazepine overdose is use of activated charcoal. For substantial recent ingestions, gastric lavage may also be considered. Administration of activated charcoal prior to hospital assessment has the potential to significantly reduce drug absorption. There is no specific antidote. In overdose, absorption of carbamazepine may be prolonged and delayed. More than one dose of activated charcoal may be beneficial in patients that have evidence of continued absorption (e.g., rising serum carbamazepine levels).
Measures to Accelerate Elimination:
The data on use of dialysis to enhance elimination in carbamazepine is scarce. Dialysis, particularly high flux or high efficiency hemodialysis, may be considered in patients with severe carbamazepine poisoning associated with renal failure or in cases of status epilepticus, or where there are rising serum drug levels and worsening clinical status despite appropriate supportive care and gastric decontamination. For severe cases of carbamazepine overdose unresponsive to other measures, charcoal hemoperfusion may be used to enhance drug clearance.
Respiratory Depression:
Keep the airways free; resort, if necessary, to endotracheal intubation, artificial respiration, and administration of oxygen.
Hypotension, Shock:
Keep the patient's legs raised and administer a plasma expander. If blood pressure fails to rise despite measures taken to increase plasma volume, use of vasoactive substances should be considered.
Convulsions:
Diazepam or barbiturates.
Warning:
Diazepam or barbiturates may aggravate respiratory depression (especially in children), hypotension, and coma. However, barbiturates should not be used if drugs that inhibit monoamine oxidase have also been taken by the patient either in overdosage or in recent therapy (within 1 week).
Surveillance:
Respiration, cardiac function (ECG monitoring), blood pressure, body temperature, pupillary reflexes, and kidney and bladder function should be monitored for several days.
Treatment of Blood Count Abnormalities:
If evidence of significant bone marrow depression develops, the following recommendations are suggested: (1) stop the drug, (2) perform daily CBC, platelet, and reticulocyte counts, (3) do a bone marrow aspiration and trephine biopsy immediately and repeat with sufficient frequency to monitor recovery.
Special periodic studies might be helpful as follows: (1) white cell and platelet antibodies, (2) 59Fe-ferrokinetic studies, (3) peripheral blood cell typing, (4) cytogenetic studies on marrow and peripheral blood, (5) bone marrow culture studies for colony-forming units, (6) hemoglobin electrophoresis for A2 and F hemoglobin, and (7) serum folic acid and B12 levels.
A fully developed aplastic anemia will require appropriate, intensive monitoring and therapy, for which specialized consultation should be sought.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Monitoring of blood levels has increased the efficacy and safety of anticonvulsants (see PRECAUTIONS, Laboratory Tests). Dosage should be adjusted to the needs of the individual patients. A low initial daily dosage with gradual increase is advised. As soon as adequate control is achieved, the dosage may be reduced very gradually to the minimum effective level. Carbamazepine extended-release capsules may be taken with or without food. Carbamazepine extended-release capsules may be swallowed whole or may be opened and all the beads sprinkled on a teaspoon of soft food such as applesauce. Make sure all of the food and medicine mixture is swallowed. Do not crush or chew carbamazepine extended-release capsules or the sprinkled beads.
Carbamazepine extended-release capsule is an extended-release formulation for twice a day administration. When converting patients from immediate release carbamazepine to carbamazepine extended-release capsules, the same total daily mg dose of carbamazepine should be administered. Following conversion to carbamazepine, patients should be closely monitored for seizure control. Depending on the therapeutic response after conversion, the total daily dose may need to be adjusted within the recommended dosing instructions.
Epilepsy (see INDICATIONS AND USAGE)
Adults and children over 12 years of age. Initial: 200 mg twice daily. Increase at weekly intervals by adding up to 200 mg/day until the optimal response is obtained. Dosage generally should not exceed 1,000 mg per day in children 12 to 15 years of age, and 1,200 mg daily in patients above 15 years of age. Doses up to 1,600 mg daily have been used in adults.
Maintenance: Adjust dosage to the minimum effective level, usually 800 to 1,200 mg daily.
Children under 12 years of age: Children taking total daily dosages of immediate-release carbamazepine of 400 mg or greater may be converted to the same total daily dosage of carbamazepine extended-release capsules, using a twice daily regimen. Ordinarily, optimal clinical response is achieved at daily doses below 35 mg/kg. If satisfactory clinical response has not been achieved, plasma levels should be measured to determine whether or not they are in the therapeutic range. No recommendation regarding the safety of carbamazepine extended-release capsules for use at doses above 35 mg/kg/24 hours can be made.
Combination Therapy: Carbamazepine extended-release capsules may be used alone or with other anticonvulsants. When added to existing anticonvulsant therapy, the drug should be added gradually while the other anticonvulsants are maintained or gradually decreased, except phenytoin, which may have to be increased (see PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions).
Trigeminal Neuralgia (see INDICATIONS AND USAGE)
Initial: On the first day, start with one 200 mg capsule. This daily dose may be increased by up to 200 mg/day every 12 hours only as needed to achieve freedom from pain. Do not exceed 1,200 mg daily.
Maintenance: Control of pain can be maintained in most patients with 400 to 800 mg daily. However, some patients may be maintained on as little as 200 mg daily, while others may require as much as 1200 mg daily. At least once every 3 months throughout the treatment period, attempts should be made to reduce the dose to the minimum effective level or even to discontinue the drug.
HOW SUPPLIED
Carbamazepine extended-release capsules 100 mg are hard gelatin capsules with white opaque body and blue-green opaque cap, imprinted “APO C100” in black ink with white to off-white granule fill. They are supplied as follows:
Bottles of 120s (NDC: 72162-2021-2)
Bottles of 60s (NDC: 72162-2021-6)
Store at 20˚C to 25°C (68˚F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15˚C to 30°C (59˚F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container [see USP].
Repackaged/Relabeled by:
Bryant Ranch Prepack, Inc.
Burbank, CA 91504
Medication Guide
Carbamazepine Extended-Release Capsules
(kar” ba maz’ e peen)
Medication Guide available at https://www.apotex.com/products/us/mg.asp
Read this Medication Guide before you start taking carbamazepine extended-release capsules and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or treatment.
What is the most important information I should know about carbamazepine extended-release capsules?
Do not stop taking carbamazepine extended-release capsules without first talking to your healthcare provider. Stopping carbamazepine extended-release capsules suddenly can cause serious problems.
Carbamazepine extended-release capsules can cause serious side effects, including:
1. Carbamazepine extended-release capsules may cause rare but serious rashes that may lead to death. These serious skin reactions are more likely to happen within the first four months of carbamazepine extended-release capsules treatment but may occur at later times. These reactions can happen in anyone, but are more likely in people of Asian descent. If you are of Asian descent you may need a genetic blood test before you take carbamazepine extended-release capsules to see if you are at a higher risk for serious skin reactions with this medicine. Symptoms may include:
- skin rash
- hives
- sores in your mouth
- blistering or peeling of the skin
2. Carbamazepine extended-release capsules can also cause other types of allergic reactions or serious problems that may affect organs and other parts of your body such as your liver or blood cells. You may or may not have a rash when you get these types of reactions. Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of these symptoms:
- swelling of your face, eyes, lips, or tongue
- trouble swallowing or breathing
- frequent fevers or fevers that do not go away
- frequent infections or an infection that does not go away
- unusual bruising or bleeding
- red or purple spots on your body
- severe fatigue or weakness
- unexpected muscle pain that does not go away
- swollen glands that do not go away
- yellowing of your skin or the whites of your eyes
- loss of appetite (anorexia) that does not go away
- nausea or vomiting that does not go away
These symptoms may be the first signs of a serious reaction. A healthcare provider should examine you to decide if you should continue taking carbamazepine extended-release capsules.
3. Like other antiepileptic drugs, carbamazepine extended-release capsules may cause suicidal thoughts or actions in a very small number of people, about 1 in 500.
Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of these symptoms, especially if they are new, worse, or worry you:
- thoughts about suicide or dying
- attempt to commit suicide
- new or worse depression
- new or worse anxiety
- feeling agitated or restless
- panic attacks
- trouble sleeping (insomnia)
- new or worse irritability
- acting aggressive, being angry, or violent
- acting on dangerous impulses
- an extreme increase in activity and talking (mania)
- other unusual changes in behavior or mood
How can I watch for early symptoms of suicidal thoughts and actions?
- Pay attention to any changes, especially sudden changes, in mood, behaviors, thoughts, or feelings.
- Keep all follow-up visits with your healthcare provider as scheduled.
- Call your healthcare provider between visits as needed, especially if you are worried about symptoms.
Do not stop carbamazepine extended-release capsules without first talking to a healthcare provider.
Stopping carbamazepine extended-release capsules suddenly can cause serious problems.
Suicidal thoughts or actions can be caused by things other than medicines. If you have suicidal thoughts or actions, your healthcare provider may check for other causes.
What is carbamazepine extended-release capsule?
Carbamazepine extended-release capsule is a medicine used to treat:
- certain types of seizures (partial, tonic-clonic, mixed)
- certain types of nerve pain (trigeminal and glossopharyngeal neuralgia).
Carbamazepine extended-release capsule is not a regular pain medicine and should not be used for aches or pains.
Who should not take carbamazepine extended-release capsules?
Do not take carbamazepine extended-release capsules if you:
- have a history of bone marrow depression
- are allergic to carbamazepine or any of the ingredients in carbamazepine extended-release capsules. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of ingredients in carbamazepine extended-release capsules.
- take nefazodone
- take delavirdine
- are allergic to antidepressant medications called tricyclic (TCAs).
- have taken a medicine called Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor (MAOI) in the last 14 days.
Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for a list of these medicines if you are not sure.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking carbamazepine extended-release capsules?
Before you take carbamazepine extended-release capsules, tell your healthcare provider if you:
- have or ever had heart problems
- have or ever had blood problems
- have or ever had liver or kidney problems
- have or ever had allergic reactions to medicines
- have or ever had increased pressure in your eye
- have or have had suicidal thoughts or actions, depression or mood problems
- have any other medical conditions
- drink grapefruit juice or eat grapefruit
- use birth control. Carbamazepine extended-release capsules may make your birth control less effective. Tell your healthcare provider if your menstrual bleeding changes while you take birth control and carbamazepine extended-release capsules.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. Carbamazepine extended-release capsules may harm your unborn baby. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you become pregnant while taking carbamazepine extended-release capsules. You and your healthcare provider should decide if you should take carbamazepine extended-release capsules while you are pregnant.
- If you become pregnant while taking carbamazepine extended-release capsules, talk to your healthcare provider about registering with the North American Antiepileptic Drug (NAAED) Pregnancy Registry. The purpose of this registry is to collect information about the safety of antiepileptic medicine during pregnancy. You can enroll in this registry by calling 1-888-233-2334.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. Carbamazepine passes into breast milk. You and your healthcare provider should discuss whether you should take carbamazepine extended-release capsules or breastfeed. You should not do both.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Taking carbamazepine extended-release capsules with certain other medicines can cause side effects or affect how well they work. Do not start or stop other medicines without talking to your healthcare provider.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them and show it to your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I take carbamazepine extended-release capsules?
- Take carbamazepine extended-release capsules exactly as prescribed. Your doctor will tell you how much carbamazepine extended-release capsules to take.
- Your healthcare provider may change your dose. Do not change your dose of carbamazepine extended-release capsules without talking to your healthcare provider.
- Do not stop taking carbamazepine extended-release capsules without first talking to your healthcare provider. Stopping carbamazepine extended-release capsules suddenly can cause serious problems. Stopping seizure medicine suddenly in a patient who has epilepsy can cause seizures that will not stop (status epilepticus).
- Take carbamazepine extended-release capsules with or without food.
- Do not crush, chew, or break carbamazepine extended-release capsules or the beads inside of the capsules. But, carbamazepine extended-release capsules can be opened and sprinkled over food such as a teaspoon of applesauce. Tell your healthcare provider if you can not swallow carbamazepine extended-release capsules whole.
- If you take too much carbamazepine extended-release capsules, call your healthcare provider or local Poison Control Center right away.
What should I avoid while taking carbamazepine extended-release capsules?
- Do not drink alcohol or take other drugs that may make you sleepy or dizzy while taking carbamazepine extended-release capsules until you talk to your healthcare provider. Carbamazepine extended-release capsules taken with alcohol or drugs may make your sleepiness or dizziness worse.
- Do not drive, or operate heavy machinery, or do other dangerous activities until you know how carbamazepine extended-release capsules affect you. Carbamazepine extended-release capsules can slow your thinking and motor skills.
What are the possible side effects of carbamazepine extended-release capsules?
See "What is the most important information I should know about carbamazepine extended-release capsules?"
Carbamazepine extended-release capsules may cause other serious side effects including:
- Irregular heartbeat - symptoms include:
- Fast, slow, or pounding heartbeat
- Shortness of breath
- Feeling lightheaded
- Fainting
- Liver problems - symptoms include:
- yellowing of your skin or the whites of your eyes
- dark urine
- pain on the right side of your stomach area (abdominal pain)
- easy bruising
- loss of appetite
- nausea or vomiting
Get medical help right away if you have any of the symptoms listed above or listed in "What is the most important information I should know about carbamazepine extended-release capsules".
The most common side effects of carbamazepine extended-release capsules include:
- dizziness
- drowsiness
- problems with walking and coordination (unsteadiness)
- nausea
- vomiting
These are not all the side effects of carbamazepine extended-release capsules. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store carbamazepine extended-release capsules?
Store at 20˚C to 25°C (68˚F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15˚C to 30°C (59˚F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container [see USP].
Keep carbamazepine extended-release capsules and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about carbamazepine extended-release capsules
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use carbamazepine extended-release capsules for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give carbamazepine extended-release capsules to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about carbamazepine extended-release capsules. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about carbamazepine extended-release capsules that is written for health professionals.
For more information call 1-800-667-4708.
What are the ingredients in carbamazepine extended-release capsules?
Active ingredient: carbamazepine
Inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, ethylcellulose, and stearic acid.
In addition:
- the 100 mg, 200 mg and 300 mg capsule shells contain FD&C Blue #2, gelatin, iron oxide yellow, titanium dioxide and are imprinted with black ink (S-1-8114 and S-1-8115) contain FD&C BLUE #2, FD&C RED #40, FD&C BLUE #1, D&C YELLOW #10 and shellac.
This Medication Guide has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration.
APOTEX INC.
CARBAMAZEPINE EXTENDED-RELEASE CAPSULES
100 mg, 200 mg and 300 mg
| Manufactured by: Apotex Inc. Toronto, Ontario Canada M9L 1T9 | Manufactured for: Apotex Corp. Weston, Florida USA 33326 |
Revised: May 2023
Rev. 11
| CARBAMAZEPINE
carbamazepine capsule, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Bryant Ranch Prepack (171714327) |
| Registrant - Bryant Ranch Prepack (171714327) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bryant Ranch Prepack | 171714327 | REPACK(72162-2021) , RELABEL(72162-2021) | |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.
