Liraglutide by Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc. / LUPIN LIMITED LIRAGLUTIDE injection
Liraglutide by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Liraglutide by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc., LUPIN LIMITED. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use LIRAGLUTIDE INJECTION safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for LIRAGLUTIDE INJECTION.
LIRAGLUTIDE injection, for subcutaneous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2010WARNING: RISK OF THYROID C-CELL TUMORS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
Liraglutide causes thyroid C-cell tumors at clinically relevant exposures in both genders of rats and mice. It is unknown whether liraglutide injection causes thyroid C-cell tumors, including medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC), in humans, as the human relevance of liraglutide-induced rodent thyroid C-cell tumors has not been determined (5.1, 13.1).
Liraglutide injection is contraindicated in patients with a personal or family history of MTC or in patients with Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2). Counsel patients regarding the potential risk of MTC and the symptoms of thyroid tumors (4, 5.1).
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
Indications and Usage. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. . . . . . . . . 05/2025
Warnings and Precautions
Severe Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions (5.6) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. . . .. . . . . 10/2025
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Liraglutide injection is a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist indicated:
- as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults and pediatric patients aged 10 years and older with type 2 diabetes mellitus (1).
Limitations of Use:
- Coadministration with other liraglutide-containing products is not recommended.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Adult Patients: Initiate at 0.6 mg injected subcutaneously once daily for one week then increase to 1.2 mg daily. If additional glycemic control is required, increase the dose to 1.8 mg daily after one week of treatment with the 1.2 mg daily dose. (2.1)
- Pediatric Patients: Initiate at 0.6 mg injected subcutaneously once daily for at least one week. If additional glycemic control is required increase the dose to 1.2 mg daily and if additional glycemic control is still required, increase the dose to 1.8 mg daily after at least one week of treatment with the 1.2 mg daily dose. (2.1)
- Inspect visually prior to each injection. Only use if solution is clear, colorless, and contains no particles. (2.3)
- Inject liraglutide injection subcutaneously once-daily at any time of day, independently of meals, in the abdomen, thigh or upper arm. (2.3)
- When using liraglutide injection with insulin, administer as separate injections. Never mix. (2.3)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Injection: 6 mg/mL solution in a prefilled, single-patient-use pen that delivers doses of 0.6 mg, 1.2 mg, or 1.8 mg. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- AcutePancreatitis: Has been observed in patients treated with GLP-1 receptor agonists, including liraglutide injection. Discontinue if pancreatitis is suspected. (5.2)
- Never Share a liraglutide injection PenBetween Patients, even if the needle is changed. (5.3)
- Hypoglycemia: Adult patients taking an insulin secretagogue or insulin may have an increased risk of hypoglycemia, including severe hypoglycemia. In pediatric patients 10 years of age and older, the risk of hypoglycemia was higher with liraglutide injection regardless of insulin and/or metformin use. Reduction in the dose of insulin secretagogues or insulin may be necessary. (5.4)
- Acute Kidney Injury Due to Volume Depletion: Monitor renal function in patients reporting adverse reactions that could lead to volume depletion. (5.5)
- Severe Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions: Use has been associated with gastrointestinal adverse reactions, sometimes severe. Liraglutide injection is not recommended in patients with severe gastroparesis. (5.6)
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: Postmarketing reports of serious hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., anaphylactic reactions and angioedema). Discontinue liraglutide injection and promptly seek medical advice. (5.7)
- Acute Gallbladder Disease: If cholelithiasis or cholecystitis are suspected, gallbladder studies are indicated. (5.8)
- Pulmonary Aspiration During General Anesthesia or Deep Sedation: Has been reported in patients receiving GLP-1 receptor agonists undergoing elective surgeries or procedures. Instruct patients to inform healthcare providers of any planned surgeries or procedures. (5.9)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
- Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥5%) in clinical trials are nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, decreased appetite, dyspepsia, constipation. (6.1)
- Immunogenicity-related events, including urticaria, were more common among liraglutide injection-treated patients (0.8%) than among comparator-treated patients (0.4%) in clinical trials. (12.6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-800-399-2561 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Effects of delayed gastric emptying on oral medications: Liraglutide injection delays gastric emptying and may impact absorption of concomitantly administered oral medications. (7)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy: Liraglutide injection should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. (8.1)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 11/2025
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING: RISK OF THYROID C-CELL TUMORS
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage
2.2 Recommendations Regarding Missed Dose
2.3 Important Administration Instructions
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Risk of Thyroid C-cell Tumors
5.2 Acute Pancreatitis
5.3 Never Share a Liraglutide Injection Pen Between Patients
5.4 Hypoglycemia
5.5 Acute Kidney Injury Due to Volume Depletion
5.6 Severe Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions
5.7 Hypersensitivity Reactions
5.8 Acute Gallbladder Disease
5.9 Pulmonary Aspiration During General Anesthesia or Deep Sedation
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effects of Delayed Gastric Emptying on Oral Medications
7.2 Concomitant Use with an Insulin Secretagogue (e.g., Sulfonylurea) or with Insulin
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
12.6 Immunogenicity
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Glycemic Control Trials in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
14.2 Glycemic Control Trial in Pediatric Patients Aged 10 Years and Older with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING: RISK OF THYROID C-CELL TUMORS
WARNING: RISK OF THYROID C-CELL TUMORS
Liraglutide causes dose-dependent and treatment-duration-dependent thyroid C-cell tumors at clinically relevant exposures in both genders of rats and mice. It is unknown whether liraglutide injection causes thyroid C-cell tumors, including medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC), in humans, as the human relevance of liraglutide-induced rodent thyroid C-cell tumors has not been determined [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
Liraglutide injection is contraindicated in patients with a personal or family history of MTC and in patients with Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2). Counsel patients regarding the potential risk for MTC with the use of liraglutide injection and inform them of symptoms of thyroid tumors (e.g., a mass in the neck, dysphagia, dyspnea, persistent hoarseness). Routine monitoring of serum calcitonin or using thyroid ultrasound is of uncertain value for early detection of MTC in patients treated with liraglutide injection [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Liraglutide injection is indicated:
- as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults and pediatric patients aged 10 years and older with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Limitations of Use:
Liraglutide injection contains liraglutide. Coadministration with other liraglutide-containing products is not recommended.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage
- The recommended starting dosage of liraglutide injection is 0.6 mg injected subcutaneously once daily for one week. The 0.6 mg once daily dosage is intended to reduce the risk of gastrointestinal adverse reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6), Adverse Reactions (6.1)]during initial titration and is not effective for glycemic control in adults.
- After one week at the 0.6 mg once daily dosage, increase the dosage to 1.2 mg injected subcutaneously once daily.
- If additional glycemic control is required, increase the dosage to the maximum recommended dosage of 1.8 mg injected subcutaneously once daily after at least one week of treatment with the 1.2 mg once daily dosage.
Pediatric Patients Aged 10 Years and Older
- The recommended starting dosage of liraglutide injection is 0.6 mg injected subcutaneously once daily.
- If additional glycemic control is required, increase the dosage in 0.6 mg increments after at least one week on the current dosage, to reduce the risk of gastrointestinal adverse reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6), Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
- The maximum recommended dosage is 1.8 mg injected subcutaneously once daily.
2.2 Recommendations Regarding Missed Dose
- Instruct patients who miss a dose of liraglutide injection to resume the once -daily dosage regimen as prescribed with the next scheduled dose. Do not administer an extra dose or increase the dose to make up for the missed dose.
- If more than 3 days have elapsed since the last liraglutide injection dose, reinitiate liraglutide injection at 0.6 mg once daily to reduce the risk of gastrointestinal adverse reactions associated with reinitiation of treatment. Upon reinitiation, liraglutide injection should be titrated at the discretion of the healthcare provider.
2.3 Important Administration Instructions
- Inspect visually prior to each injection. Only use if solution is clear, colorless, and contains no particles.
- Inject liraglutide injection subcutaneously once daily at any time of day, independently of meals.
- Inject liraglutide injection subcutaneously in the abdomen, thigh or upper arm. No dosage adjustment is needed if changing the injection site and/or timing.
- Rotate injection sites within the same region in order to reduce the risk of cutaneous amyloidosis [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
- When using liraglutide injection with insulin, administer as separate injections. Never mix. It is acceptable to inject liraglutide injection and insulin in the same body region but the injections should not be adjacent to each other.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Liraglutide injection is contraindicated in patients with a:
- personal or family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) or in patients with Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- serious hypersensitivity reaction to liraglutide or to any of the excipients in liraglutide injection. Serious hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylactic reactions and angioedema have been reported with liraglutide injection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Risk of Thyroid C-cell Tumors
Liraglutide causes dose-dependent and treatment-duration-dependent thyroid C-cell tumors (adenomas and/or carcinomas) at clinically relevant exposures in both genders of rats and mice [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)]. Malignant thyroid C-cell carcinomas were detected in rats and mice. It is unknown whether liraglutide injection will cause thyroid C-cell tumors, including medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC), in humans, as the human relevance of liraglutide-induced rodent thyroid C-cell tumors has not been determined.
Cases of MTC in patients treated with liraglutide injection have been reported in the postmarketing period; the data in these reports are insufficient to establish or exclude a causal relationship between MTC and liraglutide injection use in humans.
Liraglutide injection is contraindicated in patients with a personal or family history of MTC or in patients with MEN 2. Counsel patients regarding the potential risk for MTC with the use of liraglutide injection and inform them of symptoms of thyroid tumors (e.g., a mass in the neck, dysphagia, dyspnea, persistent hoarseness).
Routine monitoring of serum calcitonin or using thyroid ultrasound is of uncertain value for early detection of MTC in patients treated with liraglutide injection. Such monitoring may increase the risk of unnecessary procedures, due to low test specificity for serum calcitonin and a high background incidence of thyroid disease. Significantly elevated serum calcitonin may indicate MTC and patients with MTC usually have calcitonin values >50 ng/L. If serum calcitonin is measured and found to be elevated, the patient should be further evaluated. Patients with thyroid nodules noted on physical examination or neck imaging should also be further evaluated.
5.2 Acute Pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis, including fatal and non-fatal hemorrhagic or necrotizing pancreatitis, has been observed in patients treated with GLP-1 receptor agonists, including liraglutide [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
After initiation of liraglutide injection, observe patients carefully for signs and symptoms of acute pancreatitis which may include persistent or severe abdominal pain (sometimes radiating to the back) and which may or may not be accompanied by nausea or vomiting. If pancreatitis is suspected, discontinue liraglutide injection and initiate appropriate management.
5.3 Never Share a Liraglutide Injection Pen Between Patients
Liraglutide injection pens must never be shared between patients, even if the needle is changed. Pen-sharing poses a risk for transmission of blood-borne pathogens.
5.4 Hypoglycemia
Adult patients receiving liraglutide injection in combination with an insulin secretagogue (e.g., sulfonylurea) or insulin may have an increased risk of hypoglycemia, including severe hypoglycemia. In pediatric patients 10 years of age and older, the risk of hypoglycemia was higher with liraglutide injection regardless of insulin and/or metformin use. [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Drug Interactions (7.2)].
The risk of hypoglycemia may be lowered by a reduction in the dose of sulfonylurea (or other concomitantly administered insulin secretagogues) or insulin. Inform patients using these concomitant medications and pediatric patients of the risk of hypoglycemia and educate them on the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia.
5.5 Acute Kidney Injury Due to Volume Depletion
There have been postmarketing reports of acute kidney injury, in some cases requiring hemodialysis, in patients treated with liraglutide injection [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]. The majority of the reported events occurred in patients who experienced gastrointestinal reactions leading to dehydration such as nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Monitor renal function in patients reporting adverse reactions to liraglutide injection that could lead to volume depletion, especially during dosage initiation and escalation of liraglutide injection [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
5.6 Severe Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions
Use of GLP-1 receptor agonists, including liraglutide, has been associated with gastrointestinal adverse reactions, sometimes severe [see Adverse Reactions (6)]. In liraglutide injection clinical trials, severe gastrointestinal adverse reactions were reported more frequently among patients receiving liraglutide injection (1.2 mg 4.4 %, 1.8 mg 4.2 %) than placebo (1.1 %). Severe gastrointestinal adverse reactions have also been reported postmarketing with GLP-1 receptor agonists. Liraglutide injection is not recommended in patients with severe gastroparesis.
5.7 Hypersensitivity Reactions
There have been postmarketing reports of serious hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., anaphylactic reactions and angioedema) in patients treated with liraglutide injection [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]. If a hypersensitivity reaction occurs, discontinue liraglutide injection; treat promptly per standard of care, and monitor until signs and symptoms resolve.
Anaphylaxis and angioedema have been reported with other GLP-1 receptor agonists. Use caution in a patient with a history of anaphylaxis or angioedema with another GLP-receptor agonist because it is unknown whether such patients will be predisposed to these reactions with liraglutide injection. Liraglutide injection is contraindicated in patients who have had a serious hypersensitivity reaction to liraglutide or any of the excipients in liraglutide injection [see Contraindications (4)].
5.8 Acute Gallbladder Disease
Acute events of gallbladder disease such as cholelithiasis or cholecystitis have been reported in GLP-1 receptor agonist trials and postmarketing. If cholelithiasis is suspected, gallbladder studies and appropriate clinical follow-up are indicated.
5.9 Pulmonary Aspiration During General Anesthesia or Deep Sedation
Liraglutide injection delays gastric emptying [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. There have been rare postmarketing reports of pulmonary aspiration in patients receiving GLP-1 receptor agonists undergoing elective surgeries or procedures requiring general anesthesia or deep sedation who had residual gastric contents despite reported adherence to preoperative fasting recommendations.
Available data are insufficient to inform recommendations to mitigate the risk of pulmonary aspiration during general anesthesia or deep sedation in patients taking liraglutide injection, including whether modifying preoperative fasting recommendations or temporarily discontinuing liraglutide injection could reduce the incidence of retained gastric contents. Instruct patients to inform healthcare providers prior to any planned surgeries or procedures if they are taking liraglutide injection.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are described below or elsewhere in the prescribing information:
- Risk of Thyroid C-cell Tumors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Acute Pancreatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Hypoglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Acute Kidney Injury Due to Volume Depletion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Severe Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Acute Gallbladder Disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Pulmonary Aspiration During General Anesthesia or Deep Sedation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Common Adverse Reactions
The safety of liraglutide injection in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus was evaluated in 5 glycemic control, placebo-controlled trials in adults and one trial of 52 weeks duration in pediatric patients 10 years of age and older [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. The data in Table 1 reflect exposure of 1,673 adult patients to liraglutide injection and a mean duration of exposure to liraglutide injection of 37.3 weeks. The mean age of adult patients was 58 years, 4% were 75 years or older and 54% were male. The population was 79% White, 6% Black or African American, 13% Asian; 4% were of Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. At baseline the population had diabetes for an average of 9 years and a mean HbA1c of 8.4%. Baseline estimated renal function was normal or mildly impaired in 88% and moderately impaired in 12% of the pooled population.
Table 1 shows common adverse reactions in adults, excluding hypoglycemia, associated with the use of liraglutide injection for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. These adverse reactions occurred more commonly on liraglutide injection than on placebo and occurred in at least 5% of patients treated with liraglutide injection. Overall, the type, and severity of adverse reactions in pediatric patients 10 years of age and older and above were comparable to that observed in the adult population.
Table 1: Adverse reactions reported in ≥ 5% of Adult Patients Treated with Liraglutide Injection for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Cumulative proportions were calculated combining studies using Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel weights.
Placebo N=661
Liraglutide 1.2 mg
N= 645
Liraglutide 1.8 mg
N= 1024
Adverse Reaction
(%)
(%)
(%)
Nausea
5
18
20
Diarrhea
4
10
12
Headache
7
11
10
Nasopharyngitis
8
9
10
Vomiting
2
6
9
Decreased appetite
1
10
9
Dyspepsia
1
4
7
Upper Respiratory Tract Infection
6
7
6
Constipation
1
5
5
Back Pain
3
4
5
In an analysis of placebo- and active-controlled trials, the types and frequency of common adverse reactions, excluding hypoglycemia, were similar to those listed in Table 1.
Other Adverse Reactions
Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions:
In the pool of 5 glycemic control, placebo-controlled adult clinical trials, withdrawals due to gastrointestinal adverse reactions, occurred in 4.3% of liraglutide injection-treated patients and 0.5% of placebo-treated patients. Severe gastrointestinal adverse reactions were reported more frequently among patients receiving liraglutide injection (1.2 mg 4.4 %, 1.8 mg 4.2 %) than placebo (1.1 %). Withdrawal due to gastrointestinal adverse events mainly occurred during the first 2 to 3 months of the trials.
Injection site reactions:
Injection site reactions (e.g., injection site rash, erythema) were reported in approximately 2% of liraglutide injection-treated adult patients in the five double-blind, glycemic control trials of at least 26 weeks duration. Less than 0.2% of liraglutide injection-treated patients discontinued due to injection site reactions.
Hypoglycemia:
In 5 adult glycemic control, placebo-controlled clinical trials of at least 26 weeks duration, hypoglycemia requiring the assistance of another person for treatment occurred in 8 liraglutide injection-treated patients (7.5 events per 1,000 patient-years). Of these 8 liraglutide injection-treated patients, 7 patients were concomitantly using a sulfonylurea.
Table 2: Adult Incidence (%) and Rate (episodes/patient year) of Hypoglycemia in 26-Week Combination Therapy Placebo- controlled Trials "Patient not able to self-treat" is defined as an event requiring the assistance of another person for treatment.
Placebo Comparator
Liraglutide Injection Treatment
Add-on to Metformin
Placebo + Metformin
(N = 121)
Liraglutide Injection + Metformin
(N = 724)
Patient not able to self-treat
0
0.1 (0.001)
Patient able to self-treat
2.5 (0.06)
3.6 (0.05)
Add-on to Glimepiride
Placebo + Glimepiride
(N = 114)
Liraglutide Injection + Glimepiride
(N = 695)
Patient not able to self-treat
0
0.1 (0.003)
Patient able to self-treat
2.6 (0.17)
7.5 (0.38)
Not classified
0
0.9 (0.05)
Add-on to
Metformin + Rosiglitazone
Placebo + Metformin +
Rosiglitazone
(N = 175)
Liraglutide Injection + Metformin +
Rosiglitazone
(N = 355)
Patient not able to self-treat
0
0
Patient able to self-treat
4.6 (0.15)
7.9 (0.49)
Not classified
1.1 (0.03)
0.6 (0.01)
Add-on to
Metformin + Glimepiride
Placebo + Metformin +
Glimepiride
(N = 114)
Liraglutide Injection + Metformin +
Glimepiride
(N = 230)
Patient not able to self-treat
0
2.2 (0.06)
Patient able to self-treat
16.7 (0.95)
27.4 (1.16)
Not classified
0
0
In a 26-week placebo-controlled clinical trial in pediatric patients 10 years of age and older with a 26-week open-label extension, 21.2% of liraglutide injection-treated patients (mean age 14.6 years) with type 2 diabetes mellitus, had hypoglycemia with a blood glucose <54 mg/dL with or without symptoms (335 events per 1,000 patient years). No severe hypoglycemic episodes occurred in the liraglutide injection treatment group (severe hypoglycemia was defined as an episode requiring assistance of another person to actively administer carbohydrate, glucagon, or other resuscitative actions).
Papillary thyroid carcinoma:
In adult glycemic control trials of liraglutide injection, there were 7 reported cases of papillary thyroid carcinoma in patients treated with liraglutide injection and 1 case in a comparator-treated patient (1.5 vs. 0.5 cases per 1,000 patient- years). Most of these papillary thyroid carcinomas were <1 cm in greatest diameter and were diagnosed in surgical pathology specimens after thyroidectomy prompted by findings on protocol-specified screening with serum calcitonin or thyroid ultrasound.
Pancreatitis
In glycemic control trials of liraglutide injection, there have been 13 cases of pancreatitis among liraglutide injection -treated patients and 1 case in a comparator (glimepiride) treated patient (2.7 vs. 0.5 cases per 1,000 patient-years). Nine of the 13 cases with liraglutide injection were reported as acute pancreatitis and four were reported as chronic pancreatitis. In one case in a liraglutide injection-treated patient, pancreatitis, with necrosis, was observed and led to death; however clinical causality could not be established. Some patients had other risk factors for pancreatitis, such as a history of cholelithiasis or alcohol abuse.
Cholelithiasis and cholecystitis:
In adult glycemic control trials of liraglutide injection, the incidence of cholelithiasis was 0.3% in both liraglutide injection- treated and placebo-treated patients. The incidence of cholecystitis was 0.2% in both liraglutide injection-treated and placebo-treated patients.
Laboratory Tests
Bilirubin:
In the five adult glycemic control trials of at least 26 weeks duration, mildly elevated serum bilirubin concentrations (elevations to no more than twice the upper limit of the reference range) occurred in 4% of liraglutide injection-treated patients, 2.1% of placebo-treated patients and 3.5% of active-comparator-treated patients. This finding was not accompanied by abnormalities in other liver tests. The significance of this isolated finding is unknown.
Calcitonin:
Calcitonin, a biological marker of MTC, was measured throughout the clinical development program. At the end of the adult glycemic control trials, adjusted mean serum calcitonin concentrations were higher in liraglutide injection-treated patients compared to placebo-treated patients but not compared to patients receiving active comparator. Between group differences in adjusted mean serum calcitonin values were approximately 0.1 ng/L or less.
Among adult patients with pretreatment calcitonin <20 ng/L, calcitonin elevations to >20 ng/L occurred in 0.7% of liraglutide injection-treated patients, 0.3% of placebo-treated patients, and 0.5% of active-comparator-treated patients. The clinical significance of these findings is unknown.
Lipase and Amylase:
In one adult glycemic control trial in renal impairment patients, a mean increase of 33% for lipase and 15% for amylase from baseline was observed for liraglutide injection-treated patients while placebo-treated patients had a mean decrease in lipase of 3% and a mean increase in amylase of 1%.
The clinical significance of elevations in lipase or amylase with liraglutide injection is unknown in the absence of other signs and symptoms of pancreatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Vital signs
Liraglutide injection did not have adverse effects on blood pressure. Mean increases from baseline in heart rate of 2 to 3 beats per minute have been observed in adult patients treated with liraglutide injection compared to placebo.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following additional adverse reactions have been reported during post-approval use of liraglutide injection. Because these events are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is generally not possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Gastrointestinal: Acute pancreatitis; hemorrhagic and necrotizing pancreatitis sometimes resulting in death; ileus, intestinal obstruction, severe constipation including fecal impaction, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea leading to dehydration
- Hepatobiliary: Elevations of liver enzymes, hyperbilirubinemia, cholestasis, cholecystitis, cholelithiasis requiring cholecystectomy, hepatitis
- Hypersensitivity: Angioedema, anaphylactic reactions, pruritus
- Neoplasms: Medullary thyroid carcinoma
- Neurologic: Dysgeusia, dizziness, dysesthesia
- Pulmonary: Pulmonary aspiration has occurred in patients receiving GLP-1 receptor agonists undergoing elective surgeries or procedures requiring general anesthesia or deep sedation.
- Renal: Acute renal failure or worsening of chronic renal failure, sometimes requiring hemodialysis; and increased serum creatinine
- Skin and subcutaneous tissue: Cutaneous amyloidosis, alopecia
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effects of Delayed Gastric Emptying on Oral Medications
Liraglutide injection causes a delay of gastric emptying, and thereby has the potential to impact the absorption of concomitantly administered oral medications. In clinical pharmacology trials, liraglutide injection did not affect the absorption of the tested orally administered medications to any clinically relevant degree [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Nonetheless, caution should be exercised when oral medications are concomitantly administered with liraglutide injection.
7.2 Concomitant Use with an Insulin Secretagogue (e.g., Sulfonylurea) or with Insulin
Liraglutide injection stimulates insulin release in the presence of elevated blood glucose concentrations. Patients receiving liraglutide injection in combination with an insulin secretagogue (e.g., sulfonylurea) or insulin may have an increased risk of hypoglycemia, including severe hypoglycemia.When initiating liraglutide injection, consider reducing the dose of concomitantly administered insulin secretagogues (such as sulfonylureas) or insulin to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4), Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Based on animal reproduction studies, there may be risks to the fetus from exposure to liraglutide injection during pregnancy. Liraglutide injection should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Animal reproduction studies identified increased adverse developmental outcomes from exposure during pregnancy. Liraglutide exposure was associated with early embryonic deaths and an imbalance in some fetal abnormalities in pregnant rats administered liraglutide during organogenesis at doses that approximate clinical exposures at the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 1.8 mg/day. In pregnant rabbits administered liraglutide during organogenesis, decreased fetal weight and an increased incidence of major fetal abnormalities were seen at exposures below the human exposures at the MRHD (see Animal Data).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects for women with uncontrolled pre-gestational diabetes (Hemoglobin A1C >7) is 6 to 10%. The major birth defect rate has been reported to be as high as 20 to 25% in women with a Hemoglobin A1C >10. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-associated maternal and/or embryo/fetal risk:
Poorly controlled diabetes in pregnancy increases the maternal risk for diabetic ketoacidosis,
pre-eclampsia, spontaneous abortions, preterm delivery, and delivery complications. Poorly controlled diabetes increases the fetal risk for major birth defects, still birth, and macrosomia related morbidity.
Animal Data
Female rats given subcutaneous doses of 0.1, 0.25 and 1 mg/kg/day liraglutide beginning 2 weeks before mating through gestation day 17 had estimated systemic exposures 0.8-, 3-, and
11-times the human exposure at the MRHD based on plasma AUC comparison. The number of early embryonic deaths in the 1 mg/kg/day group increased slightly. Fetal abnormalities and variations in kidneys and blood vessels, irregular ossification of the skull, and a more complete state of ossification occurred at all doses. Mottled liver and minimally kinked ribs occurred at the highest dose. The incidence of fetal malformations in liraglutide-treated groups exceeding concurrent and historical controls were misshapen oropharynx and/or narrowed opening into larynx at 0.1 mg/kg/day and umbilical hernia at 0.1 and 0.25 mg/kg/day.
Pregnant rabbits given subcutaneous doses of 0.01, 0.025 and 0.05 mg/kg/day liraglutide from gestation day 6 through day 18 inclusive, had estimated systemic exposures less than the human exposure at the MRHD of 1.8 mg/day at all doses, based on plasma AUC. Liraglutide decreased fetal weight and dose-dependently increased the incidence of total major fetal abnormalities at all doses. The incidence of malformations exceeded concurrent and historical controls at
0.01 mg/kg/day (kidneys, scapula), ≥ 0.01 mg/kg/day (eyes, forelimb), 0.025 mg/kg/day (brain, tail and sacral vertebrae, major blood vessels and heart, umbilicus), ≥ 0.025 mg/kg/day (sternum) and at 0.05 mg/kg/day (parietal bones, major blood vessels). Irregular ossification and/or skeletal abnormalities occurred in the skull and jaw, vertebrae and ribs, sternum, pelvis, tail, and scapula; and dose-dependent minor skeletal variations were observed. Visceral abnormalities occurred in blood vessels, lung, liver, and esophagus. Bilobed or bifurcated gallbladder was seen in all treatment groups, but not in the control group.
In pregnant female rats given subcutaneous doses of 0.1, 0.25 and 1 mg/kg/day liraglutide from gestation day 6 through weaning or termination of nursing on lactation day 24, estimated systemic exposures were 0.8-, 3-, and 11-times human exposure at the MRHD of 1.8 mg/day, based on plasma AUC. A slight delay in parturition was observed in the majority of treated rats. Group mean body weight of neonatal rats from liraglutide-treated dams was lower than neonatal rats from control group dams. Bloody scabs and agitated behavior occurred in male rats descended from dams treated with 1 mg/kg/day liraglutide. Group mean body weight from birth to postpartum day 14 trended lower in F2 generation rats descended from liraglutide-treated rats compared to F2 generation rats descended from controls, but differences did not reach statistical significance for any group.
8.2 Lactation
There are no data on the presence of liraglutide injection in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Liraglutide was present in milk of lactating rats (see Data).
Developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for liraglutide injection and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from liraglutide injection or from the underlying maternal condition.
Data
In lactating rats, liraglutide was present unchanged in milk at concentrations approximately 50% of maternal plasma concentrations.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of liraglutide injection as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus have been established in pediatric patients 10 years of age and older. Use of liraglutide injection for this indication is supported by a 26-week placebo-controlled clinical trial and a 26-week open-label extension in 134 pediatric patients 10 to 17 years of age with type 2 diabetes mellitus, a pediatric pharmacokinetic study, and studies in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) and Clinical Studies (14.1,14.2)]. The risk of hypoglycemia was higher with liraglutide injection in pediatric patients regardless of insulin and/or metformin use [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
The safety and effectiveness of liraglutide injection have not been established in pediatric patients less than 10 years of age.
8.5 Geriatric Use
In the liraglutide injection treatment arms of the glycemic control trials, a total of 832 (19.3%) of the patients were 65 to 74 years of age and 145 (3.4%) were 75 years of age and over [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
No overall differences in safety or effectiveness for liraglutide injection have been observed between patients 65 years of age and older and younger patients.
8.6 Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment of liraglutide injection is recommended for patients with renal impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. The safety and efficacy of liraglutide injection was evaluated in a 26-week clinical study that included patients with moderate renal impairment (eGFR 30 to 60 mL/min/1.73 m2) [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
There is limited experience with liraglutide injection in patients with end stage renal disease.
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
There is limited experience in patients with mild, moderate or severe hepatic impairment. Therefore, liraglutide injection should be used with caution in this patient population. No dose adjustment of liraglutide injection is recommended for patients with hepatic impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
Overdoses have been reported in clinical trials and post-marketing use of liraglutide injection. Observed effects have included severe nausea, severe vomiting, and severe hypoglycemia. In the event of overdosage, consider contacting the Poison Help line (1-800-222-1222) or a medical toxicologist for additional overdosage management recommendations. Initiate appropriate supportive treatment according to the patient's clinical signs and symptoms.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Liraglutide injection contains liraglutide, an analog of human GLP-1 and acts as a GLP-1 receptor agonist. The liraglutide is produced by a solid phase synthesis and is 97% homologous to native human GLP-1 by substituting arginine for lysine at position 34 and attaching a C-16 fatty acid (palmitic acid) with a glutamic acid spacer on the remaining lysine residue at position 26. The molecular formula of liraglutide is C172H265N43O51 and the molecular weight is 3751.2 Daltons. The structural formula (Figure 1) is:
Figure 1: Structural Formula of Liraglutide
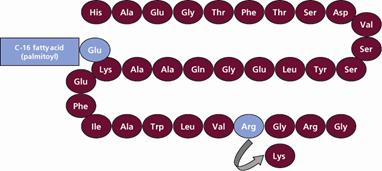
Liraglutide injection is a sterile, aqueous, clear, colorless solution for subcutaneous use. Each 1 mL of liraglutide injection solution contains 6 mg of liraglutide and the following inactive ingredients: disodium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate, 1.42 mg; phenol, 5.5 mg; propylene glycol, 14 mg; and water for injection. Liraglutide injection has a pH between 8.0 and 8.4, hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide may be added to adjust pH. Each prefilled pen contains a 3 mL solution of liraglutide injection equivalent to 18 mg liraglutide (free-base, anhydrous).
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Liraglutide is an acylated human GLP-1 receptor agonist with 97% amino acid sequence homology to endogenous human GLP-1(7 to 37). GLP-1(7 to 37) represents <20% of total circulating endogenous GLP-1. Like GLP-1(7 to 37), liraglutide activates the GLP-1 receptor, a membrane-bound cell-surface receptor coupled to adenylyl cyclase by the stimulatory G-protein, Gs, in pancreatic beta cells. Liraglutide increases intracellular cyclic AMP (cAMP) leading to insulin release in the presence of elevated glucose concentrations. This insulin secretion subsides as blood glucose concentrations decrease and approach euglycemia. Liraglutide also decreases glucagon secretion in a glucose-dependent manner. The mechanism of blood glucose lowering also involves a delay in gastric emptying.
GLP-1(7 to 37) has a half-life of 1.5 to 2 minutes due to degradation by the ubiquitous endogenous enzymes, dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) and neutral endopeptidases (NEP). Unlike native GLP-1, liraglutide is stable against metabolic degradation by both peptidases and has a plasma half-life of 13 hours after subcutaneous administration. The pharmacokinetic profile of liraglutide, which makes it suitable for once daily administration, is a result of
self-association that delays absorption, plasma protein binding and stability against metabolic degradation by DPP-4 and NEP.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Liraglutide injection's pharmacodynamic profile is consistent with its pharmacokinetic profile observed after single subcutaneous administration as liraglutide injection lowered fasting, premeal and postprandial glucose throughout the day [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Fasting and postprandial glucose was measured before and up to 5 hours after a standardized meal after treatment to steady state with 0.6, 1.2 and 1.8 mg liraglutide injection or placebo. Compared to placebo, the postprandial plasma glucose AUC0 to 300min was 35% lower after liraglutide injection 1.2 mg and 38% lower after liraglutide injection 1.8 mg.
Glucose-dependent insulin secretion
The effect of a single dose of 7.5 mcg/kg (~ 0.7 mg) liraglutide injection on insulin secretion rates (ISR) was investigated in 10 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus during graded glucose infusion. In these patients, on average, the ISR response was increased in a glucose-dependent manner (Figure 2).
Figure 2: Mean Insulin Secretion Rate (ISR) versus Glucose Concentration Following Single-Dose Liraglutide Injection 7.5 mcg/kg (~ 0.7 mg) or Placebo in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (N=10) During Graded Glucose Infusion
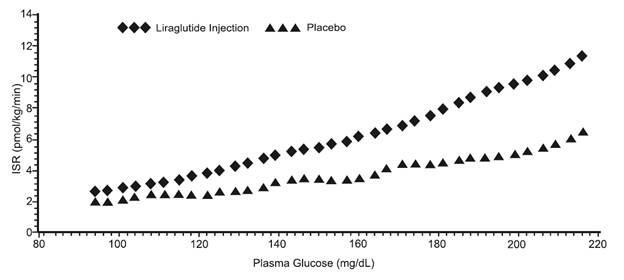
Liraglutide injection lowered blood glucose by stimulating insulin secretion and lowering glucagon secretion. A single dose of liraglutide injection 7.5 mcg/kg (~ 0.7 mg) did not impair glucagon response to low glucose concentrations.
Gastric emptying
Liraglutide injection causes a delay of gastric emptying, thereby reducing the rate at which postprandial glucose appears in the circulation.
Cardiac Electrophysiology (QTc)
The effect of liraglutide injection on cardiac repolarization was tested in a QTc study. Liraglutide injection at steady state concentrations with daily doses up to 1.8 mg did not produce QTc prolongation.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Following subcutaneous administration, maximum concentrations of liraglutide are achieved at 8 to 12 hours post dosing. The mean peak (Cmax) and total (AUC) exposures of liraglutide were 35 ng/mL and 960 ng·h/mL, respectively, for a subcutaneous single dose of 0.6 mg. After subcutaneous single dose administrations, Cmax and AUC of liraglutide increased proportionally over the therapeutic dose range of 0.6 mg to 1.8 mg. At 1.8 mg liraglutide injection, the average steady state concentration of liraglutide over 24 hours was approximately 128 ng/mL. AUC0 to ∞ was equivalent between upper arm and abdomen, and between upper arm and thigh. AUC0 to ∞ from thigh was 22% lower than that from abdomen. However, liraglutide exposures were considered comparable among these three subcutaneous injection sites. Absolute bioavailability of liraglutide following subcutaneous administration is approximately 55%.
Distribution
The mean apparent volume of distribution after subcutaneous administration of liraglutide injection 0.6 mg is approximately 13 L. The mean volume of distribution after intravenous administration of liraglutide injection is 0.07 L/kg. Liraglutide is extensively bound to plasma protein (>98%).
Elimination
The mean apparent clearance following subcutaneous administration of a single dose of liraglutide is approximately 1.2 L/h with an elimination half-life of approximately 13 hours.
Metabolism
During the initial 24 hours following administration of a single [3H]-liraglutide dose to healthy subjects, the major component in plasma was intact liraglutide. Liraglutide is endogenously metabolized in a similar manner to large proteins without a specific organ as a major route of elimination.
Excretion
Following a [3H]-liraglutide dose, intact liraglutide was not detected in urine or feces. Only a minor part of the administered radioactivity was excreted as liraglutide-related metabolites in urine or feces (6% and 5%, respectively). The majority of urine and feces radioactivity was excreted during the first 6 to 8 days.
Specific Populations
Geriatric Patients:
Age had no effect on the pharmacokinetics of liraglutide injection based on a pharmacokinetic study in healthy elderly subjects (65 to 83 years) and population pharmacokinetic analyses of patients 18 to 80 years of age [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
Pediatric Patients:
A population pharmacokinetic analysis was conducted for liraglutide injection using data from 72 pediatric patients (10 to 17 years of age) with type 2 diabetes mellitus. The pharmacokinetic profile of liraglutide injection in pediatric patients was consistent with that in adults.
Male and Female Patients:
Based on the results of population pharmacokinetic analyses, females have 25% lower weight-adjusted clearance of liraglutide injection compared to males.
Race or Ethnic Groups:
Race and ethnicity had no effect on the pharmacokinetics of liraglutide injection based on the results of population pharmacokinetic analyses that included White, Black or African American, Asian and Hispanic or Latino/Non-Hispanic or Latino subjects.
Body Weight:
Body weight significantly affects the pharmacokinetics of liraglutide injection based on results of population pharmacokinetic analyses. The exposure of liraglutide decreases with an increase in baseline body weight. However, the 1.2 mg and 1.8 mg daily doses of liraglutide injection provided adequate systemic exposures over the body weight range of 40 kg to 160 kg evaluated in the clinical trials. Liraglutide was not studied in patients with body weight >160 kg.
Patients with Renal Impairment:
The single-dose pharmacokinetics of liraglutide injection were evaluated in patients with varying degrees of renal impairment. Patients with mild (estimated creatinine clearance 50 to 80 mL/min) to severe (estimated creatinine clearance <30 mL/min) renal impairment and subjects with end-stage renal disease requiring dialysis were included in the trial. Compared to healthy subjects, liraglutide AUC in mild, moderate, and severe renal impairment and in end-stage renal disease was on average 35%, 19%, 29% and 30% lower, respectively [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Patients with Hepatic Impairment:
The single-dose pharmacokinetics of liraglutide injection were evaluated in patients with varying degrees of hepatic impairment. Patients with mild (Child Pugh score 5 to 6) to severe (Child Pugh score > 9) hepatic impairment were included in the trial. Compared to healthy subjects, liraglutide AUC in patients with mild, moderate and severe hepatic impairment was on average 11%, 14% and 42% lower, respectively [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
Drug Interaction Studies
In vitro assessment of drug-drug interactions:
Liraglutide injection has low potential for pharmacokinetic drug-drug interactions related to cytochrome P450 (CYP P450) and plasma protein binding.
In vivo assessment of drug-drug interactions:
The drug-drug interaction studies were performed at steady state with liraglutide injection 1.8 mg/day. Before administration of concomitant treatment, subjects underwent a 0.6 mg weekly dose increase to reach the maximum dose of 1.8 mg/day. Administration of the interacting drugs was timed so that Cmax of liraglutide injection (8 h to 12 h) would coincide with the absorption peak of the co-administered drugs.
Digoxin
A single dose of digoxin 1 mg was administered 7 hours after the dose of liraglutide injection at steady state. The concomitant administration with liraglutide injection resulted in a reduction of digoxin AUC by 16%; Cmax decreased by 31%. Digoxin median time to maximal concentration (Tmax) was delayed from 1 h to 1.5 h.
Lisinopril
A single dose of lisinopril 20 mg was administered 5 minutes after the dose of liraglutide injection at steady state. The coadministration with liraglutide injection resulted in a reduction of lisinopril AUC by 15%; Cmax decreased by 27%. Lisinopril median Tmax was delayed from 6 h to 8 h with liraglutide injection.
Atorvastatin
Liraglutide injection did not change the overall exposure (AUC) of atorvastatin following a single dose of atorvastatin 40 mg, administered 5 hours after the dose of liraglutide injection at steady state. Atorvastatin Cmax was decreased by 38% and median Tmax was delayed from 1 h to 3 h with liraglutide injection.
Acetaminophen
Liraglutide injection did not change the overall exposure (AUC) of acetaminophen following a single dose of acetaminophen 1000 mg, administered 8 hours after the dose of liraglutide injection at steady state. Acetaminophen Cmax was decreased by 31% and median Tmax was delayed up to 15 minutes.
Griseofulvin
Liraglutide injection did not change the overall exposure (AUC) of griseofulvin following coadministration of a single dose of griseofulvin 500 mg with liraglutide injection at steady state. Griseofulvin Cmax increased by 37% while median Tmax did not change.
Oral Contraceptives
A single dose of an oral contraceptive combination product containing 0.03 mg ethinylestradiol and 0.15 mg levonorgestrel was administered under fed conditions and 7 hours after the dose of liraglutide injection at steady state. Liraglutide injection lowered ethinylestradiol and levonorgestrel Cmax by 12% and 13%, respectively. There was no effect of liraglutide injection on the overall exposure (AUC) of ethinylestradiol. Liraglutide injection increased the levonorgestrel AUC0 to ∞ by 18%. Liraglutide injection delayed Tmax for both ethinylestradiol and levonorgestrel by 1.5 h.
Insulin Detemir
No pharmacokinetic interaction was observed between liraglutide injection and insulin detemir when separate subcutaneous injections of insulin detemir 0.5 Unit/kg (single-dose) and liraglutide injection 1.8 mg (steady state) were administered in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
12.6 Immunogenicity
The observed incidence of anti-drug antibodies is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Differences in assay methods preclude meaningful comparisons of the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in the studies described below with the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in other studies, including those with liraglutide injection or other liraglutide products.
A subset of liraglutide injection-treated patients (1,104 of 2,501, 44%) in five adult double-blind clinical trials of 26 weeks duration or longer were tested for the presence of anti-liraglutide antibodies at the end of treatment [see Clinical Studies (14.1)] and 102/1,104 (9%) of liraglutide injection-treated patients developed anti-liraglutide antibodies. Of these 102 liraglutide injection-treated patients, 56 (5%) patients developed antibodies that cross-reacted with native GLP-1. These cross-reacting antibodies were not tested for neutralizing effect against native GLP-1, and thus the potential for clinically significant neutralization of native GLP-1 was not assessed. Antibodies that had a neutralizing effect on liraglutide in an in vitro assay occurred in 12 (1%) of the liraglutide injection-treated patients. There was no identified clinically significant effect of anti-liraglutide antibodies on effectiveness of liraglutide injection.
In five double-blind adult glycemic control trials of liraglutide injection, events from a composite of adverse events potentially related to immunogenicity (e.g., urticaria, angioedema) occurred among 0.8% of liraglutide injection-treated patients and among 0.4% of comparator-treated patients. Urticaria accounted for approximately one-half of the events in this composite for liraglutide injection-treated patients. Patients who developed anti-liraglutide antibodies were not more likely to develop events from the immunogenicity events composite than were patients who did not develop anti-liraglutide antibodies.
In a clinical trial with pediatric patients aged 10 years and older [see Clinical Studies (14.2)], anti-liraglutide antibodies were detected in 1 (2%) liraglutide injection treated patient at week 26 and 5 (9%) liraglutide injection treated patients at week 53. None of the 5 patients had antibodies cross reactive to native GLP-1 or had neutralizing antibodies.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
A 104-week carcinogenicity study was conducted in male and female CD-1 mice at doses of 0.03, 0.2, 1, and 3 mg/kg/day liraglutide administered by bolus subcutaneous injection yielding systemic exposures 0.2-, 2-, 10- and 45-times the human exposure, respectively, at the MRHD of 1.8 mg/day based on plasma AUC comparison. A dose-related increase in benign thyroid C-cell adenomas was seen in the 1 and the 3 mg/kg/day groups with incidences of 13% and 19% in males and 6% and 20% in females, respectively. C-cell adenomas did not occur in control groups or 0.03 and 0.2 mg/kg/day groups. Treatment-related malignant C-cell carcinomas occurred in 3% of females in the 3.0 mg/kg/day group. Thyroid C-cell tumors are rare findings during carcinogenicity testing in mice. A treatment-related increase in fibrosarcomas was seen on the dorsal skin and subcutis, the body surface used for drug injection, in males in the 3 mg/kg/day group. These fibrosarcomas were attributed to the high local concentration of drug near the injection site. The liraglutide concentration in the clinical formulation (6 mg/mL) is
10-times higher than the concentration in the formulation used to administer 3 mg/kg/day liraglutide to mice in the carcinogenicity study (0.6 mg/mL).
A 104-week carcinogenicity study was conducted in male and female Sprague Dawley rats at doses of 0.075, 0.25 and 0.75 mg/kg/day liraglutide administered by bolus subcutaneous injection with exposures 0.5-, 2- and 8-times the human exposure, respectively, resulting from the MRHD based on plasma AUC comparison. A treatment-related increase in benign thyroid C-cell adenomas was seen in males in 0.25 and 0.75 mg/kg/day liraglutide groups with incidences of 12%, 16%, 42%, and 46% and in all female liraglutide-treated groups with incidences of 10%, 27%, 33%, and 56% in 0 (control), 0.075, 0.25, and 0.75 mg/kg/day groups, respectively. A treatment-related increase in malignant thyroid C-cell carcinomas was observed in all male liraglutide-treated groups with incidences of 2%, 8%, 6%, and 14% and in females at 0.25 and 0.75 mg/kg/day with incidences of 0%, 0%, 4%, and 6% in 0 (control), 0.075, 0.25, and 0.75 mg/kg/day groups, respectively. Thyroid C-cell carcinomas are rare findings during carcinogenicity testing in rats.
Studies in mice demonstrated that liraglutide-induced C-cell proliferation was dependent on the GLP-1 receptor and that liraglutide did not cause activation of the REarranged during Transfection (RET) proto-oncogene in thyroid C-cells.
Human relevance of thyroid C-cell tumors in mice and rats is unknown and has not been determined by clinical studies or nonclinical studies [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Liraglutide was negative with and without metabolic activation in the Ames test for mutagenicity and in a human peripheral blood lymphocyte chromosome aberration test for clastogenicity. Liraglutide was negative in repeat-dose in vivo micronucleus tests in rats.
In rat fertility studies using subcutaneous doses of 0.1, 0.25 and 1 mg/kg/day liraglutide, males were treated for 4 weeks prior to and throughout mating and females were treated 2 weeks prior to and throughout mating until gestation day 17. No direct adverse effects on male fertility was observed at doses up to 1 mg/kg/day, a high dose yielding an estimated systemic exposure 11- times the human exposure at the MRHD, based on plasma AUC. In female rats, an increase in early embryonic deaths occurred at 1 mg/kg/day. Reduced body weight gain and food consumption were observed in females at the 1 mg/kg/day dose.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Glycemic Control Trials in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
In glycemic control trials in adults, liraglutide injection has been studied as monotherapy and in combination with one or two oral anti-diabetic medications or basal insulin.
In each of the placebo controlled trials, treatment with liraglutide injection produced clinically and statistically significant improvements in hemoglobin A1c and fasting plasma glucose (FPG) compared to placebo.
All liraglutide injection-treated patients started at 0.6 mg/day. The dose was increased in weekly intervals by 0.6 mg to reach 1.2 mg or 1.8 mg for patients randomized to these higher doses. Liraglutide injection 0.6 mg is not effective for glycemic control and is intended only as a starting dose to reduce gastrointestinal intolerance [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
Monotherapy
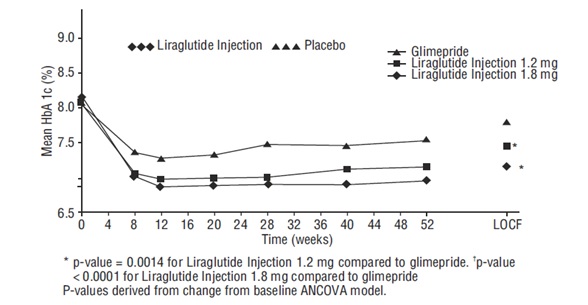
In this 52-week trial, 746 adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus were randomized to liraglutide injection 1.2 mg, liraglutide injection 1.8 mg, or glimepiride 8 mg. Patients who were randomized to glimepiride were initially treated with 2 mg daily for two weeks, increasing to 4 mg daily for another two weeks, and finally increasing to 8 mg daily. Treatment with liraglutide injection 1.8 mg and 1.2 mg resulted in a statistically significant reduction in HbA1c compared to glimepiride (Table 3). The percentage of patients who discontinued due to ineffective therapy was 3.6% in the liraglutide injection 1.8 mg treatment group, 6% in the liraglutide injection 1.2 mg treatment group, and 10.1% in the glimepiride-treatment group.
The mean age of participants was 53 years, and the mean duration of diabetes was 5 years. Participants were 49.7% male, 77.5% White, 12.6% Black or African American and 35% of Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. The mean BMI was 33.1 kg/m2.
Table 3: Results of a 52-week Monotherapy Trial in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus* - * Intent-to-treat population using last observation on study
- † Least squares mean adjusted for baseline value
- ‡ p-value <0.0001
- § p-value <0.05
Liraglutide Injection
1.8 mg
Liraglutide Injection
1.2 mg
Glimepiride
8 mg
Intent-to-Treat Population (N)
246
251
248
HbA1c (%) (Mean)
Baseline
Change from baseline (adjusted mean)†
Difference from glimepiride arm (adjusted mean)†
95% Confidence Interval
8.2
-1.1
-0.6‡
(-0.8, -0.4)
8.2
-0.8
-0.3§
(-0.5, -0.1)
8.2
-0.5
Percentage of patients achieving HbA1c <7%
51
43
28
Fasting Plasma Glucose (mg/dL) (Mean)
Baseline
Change from baseline (adjusted mean)†
Difference from glimepiride arm (adjusted mean)†
95% Confidence Interval
172
-26
-20‡
(-29, -12)
168
-15
-10§
(-19, -1)
172
-5
Body Weight (kg) (Mean)
Baseline
Change from baseline (adjusted mean)†
Difference from glimepiride arm (adjusted mean)†
95% Confidence Interval
92.6
-2.5
-3.6‡
(-4.3, -2.9)
92.1
-2.1
-3.2‡
(-3.9, -2.5)
93.3
+1.1
Figure 3: Mean HbA1c for Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus who Completed the 52-week Trial and for the Last Observation Carried Forward (LOCF, intent-to-treat) data at Week 52 (Monotherapy)
Add-on to Metformin:
In this 26-week trial, 1,091 adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus were randomized to liraglutide injection 0.6 mg, liraglutide injection 1.2 mg, liraglutide injection 1.8 mg, placebo, or glimepiride 4 mg (one-half of the maximal approved dose in the United States), all as add-on to metformin. Randomization occurred after a 6-week run-in period consisting of a 3-week initial forced metformin titration period followed by a maintenance period of another 3 weeks. During the titration period, doses of metformin were increased up to 2,000 mg/day. Treatment with liraglutide injection 1.2 mg and 1.8 mg as add-on to metformin resulted in a significant mean HbA1c reduction relative to placebo add-on to metformin and resulted in a similar mean HbA1c reduction relative to glimepiride 4 mg add-on to metformin (Table 4). The percentage of patients who discontinued due to ineffective therapy was 5.4% in the liraglutide injection 1.8 mg + metformin treatment group, 3.3% in the liraglutide injection 1.2 mg + metformin treatment group, 23.8% in the placebo + metformin treatment group, and 3.7% in the glimepiride + metformin treated group.
The mean age of participants was 57 years, and the mean duration of diabetes was 7 years. Participants were 58.2% male, 87.1% White and 2.4% Black or African American. The mean BMI was 31 kg/m2.
Table 4: Results of a 26-week Trial of liraglutide injection as Add-on to Metformin in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus* - * Intent-to-treat population using last observation on study
- † For glimepiride, one-half of the maximal approved United States dose.
- ‡ Least squares mean adjusted for baseline value
- § p-value <0.0001
- ¶ p-value <0.05
Liraglutide Injection
1.8 mg +
Metformin
Liraglutide Injection
1.2 mg +
Metformin
Placebo + Metformin
Glimepiride
4 mg† + Metformin
Intent-to-Treat Population (N)
242
240
121
242
HbA1c (%) (Mean)
Baseline
Change from baseline (adjusted mean)‡
Difference from placebo + metformin arm (adjusted mean)‡
95% Confidence Interval
Difference from glimepiride + metformin arm (adjusted mean)‡
95% Confidence Interval
8.4
-1
-1.1§
(-1.3, -0.9)
0
(-0.2, 0.2)
8.3
-1
-1.1§
(-1.3, -0.9)
0
(-0.2, 0.2)
8.4
+0.1
8.4
-1
Percentage of patients achieving HbA1c <7%
42
35
11
36
Fasting Plasma Glucose (mg/dL) (Mean)
Baseline
Change from baseline (adjusted mean)‡
Difference from placebo + metformin arm (adjusted mean)‡
95% Confidence Interval
Difference from glimepiride + metformin arm (adjusted mean)‡
95% Confidence Interval
181
-30
-38§
(-48, -27)
-7
(-16, 2)
179
-30
-37§
(-47, -26)
-6
(-15, 3)
182
+7
180
-24
Body Weight (kg) (Mean)
Baseline
Change from baseline (adjusted mean)‡
Difference from placebo + metformin arm (adjusted mean)‡
95% Confidence Interval
Difference from glimepiride + metformin arm (adjusted mean)‡
95% Confidence Interval
88
-2.8
-1.3¶
(-2.2, -0.4)
-3.8§
(-4.5, -3)
88.5
-2.6
-1.1¶
(-2, -0.2)
-3.5§
(-4.3, -2.8)
91
-1.5
89
+1
Liraglutide Injection Compared to Sitagliptin, Both as Add-on to Metformin:
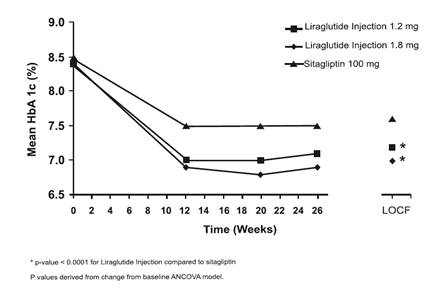
In this 26–week, open-label trial, 665 adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus on a background of metformin ≥1,500 mg per day were randomized to liraglutide injection 1.2 mg once daily, liraglutide injection 1.8 mg once daily or sitagliptin 100 mg once daily, all dosed according to approved labeling. Patients were to continue their current treatment on metformin at a stable, pre-trial dose level and dosing frequency.
The mean age of participants was 56 years, and the mean duration of diabetes was 6 years. Participants were 52.9% male, 86.6% White, 7.2% Black or African American and 16.2% of Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. The mean BMI was 32.8 kg/m2.
The primary endpoint was the change in HbA1c from baseline to Week 26. Treatment with liraglutide injection 1.2 mg and liraglutide injection 1.8 mg resulted in statistically significant reductions in HbA1c relative to sitagliptin 100 mg (Table 5). The percentage of patients who discontinued due to ineffective therapy was 3.1% in the liraglutide injection 1.2 mg group, 0.5% in the liraglutide injection 1.8 mg treatment group, and 4.1% in the sitagliptin 100 mg treatment group. From a mean baseline body weight of 94 kg, there was a mean reduction of 2.7 kg for liraglutide injection 1.2 mg, 3.3 kg for liraglutide injection 1.8 mg, and 0.8 kg for sitagliptin
100 mg.
Table 5: Results of a 26-week Open-Label Trial of Liraglutide Injection Compared to Sitagliptin (both in combination with metformin) in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus* - * Intent-to-treat population using last observation on study
- † Least squares mean adjusted for baseline value
- ‡ p-value <0.0001
Liraglutide Injection 1.8 mg +
Metformin
Liraglutide Injection 1.2 mg +
Metformin
Sitagliptin 100 mg + Metformin
Intent-to-Treat Population (N)
218
221
219
HbA1c (%) (Mean)
Baseline
Change from baseline (adjusted mean)
Difference from sitagliptin arm (adjusted mean)†
95% Confidence Interval
8.4
-1.5
-0.6‡
(-0.8, -0.4)
8.4
-1.2
-0.3‡
(-0.5, -0.2)
8.5
-0.9
Percentage of patients achieving HbA1c <7%
56
44
22
Fasting Plasma Glucose (mg/dL) (Mean)
Baseline
Change from baseline (adjusted mean)
Difference from sitagliptin arm (adjusted mean)†
95% Confidence Interval
179
-39
-24‡
(-31, -16)
182
-34
-19‡
(-26, -12)
180
-15
Figure 4: Mean HbA1c for Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus who Completed the 26-week Trial and for the Last Observation Carried Forward (LOCF, intent-to-treat) data at Week 26
Combination Therapy with Metformin and Insulin:
This 26-week open-label trial enrolled 988 adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus with inadequate glycemic control (HbA1c 7% to 10%) on metformin (≥1,500 mg/day) alone or inadequate glycemic control (HbA1c 7% to 8.5%) on metformin (≥1,500 mg/day) and a sulfonylurea. Patients who were on metformin and a sulfonylurea discontinued the sulfonylurea then all patients entered a 12-week run-in period during which they received add- on therapy with liraglutide injection titrated to 1.8 mg once-daily. At the end of the run-in period, 498 patients (50%) achieved HbA1c <7% with liraglutide injection 1.8 mg and metformin and continued treatment in a non-randomized, observational arm. Another 167 patients (17%) withdrew from the trial during the run-in period with approximately one-half of these patients doing so because of gastrointestinal adverse reactions [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. The remaining 323 patients with HbA1c ≥7% (33% of those who entered the run-in period) were randomized to 26 weeks of once-daily insulin detemir administered in the evening as add-on therapy (N=162) or to continued, unchanged treatment with liraglutide injection 1.8 mg and metformin (N=161). The starting dose of insulin detemir was 10 units/day and the mean dose at the end of the 26-week randomized period was 39 units/day. During the 26 week randomized treatment period, the percentage of patients who discontinued due to ineffective therapy was 11.2% in the group randomized to continued treatment with liraglutide injection 1.8 mg and metformin and 1.2% in the group randomized to add-on therapy with insulin detemir.
The mean age of participants was 57 years, and the mean duration of diabetes was 8 years. Participants were 55.7% male, 91.3% White, 5.6% Black or African American and 12.5% of Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. The mean BMI was 34 kg/m2.
Treatment with insulin detemir as add-on to liraglutide injection 1.8 mg + metformin resulted in statistically significant reductions in HbA1c and FPG compared to continued, unchanged treatment with liraglutide injection 1.8 mg + metformin alone (Table 6). From a mean baseline body weight of 96 kg after randomization, there was a mean reduction of 0.3 kg in the patients who received insulin detemir add-on therapy compared to a mean reduction of 1.1 kg in the patients who continued on unchanged treatment with liraglutide injection 1.8 mg + metformin alone.
Table 6: Results of a 26-week Open Label Trial of Insulin detemir as add on to Liraglutide Injection + Metformin Compared to Continued Treatment with Liraglutide Injection + Metformin alone in Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus not Achieving HbA1c < 7% after 12 weeks of Metformin and Liraglutide Injection* - * Intent-to-treat population using last observation on study
- † Least squares mean adjusted for baseline value
- ‡ p-value <0.0001
Insulin detemir + Liraglutide Injection +
Metformin
Liraglutide Injection +
Metformin
Intent-to-Treat Population (N)
162
157
HbA1c (%) (Mean)
Baseline (week 0)
Change from baseline (adjusted mean)
Difference from liraglutide injection + metformin arm (LS mean)†
95% Confidence Interval
7.6
-0.5
-0.5‡
(-0.7, -0.4)
7.6
0
Percentage of patients achieving HbA1c <7%
43
17
Fasting Plasma Glucose (mg/dL) (Mean)
Baseline (week 0)
Change from baseline (adjusted mean)
Difference from liraglutide injection + metformin arm (LS mean)†
95% Confidence Interval
166
-39
-31‡
(-39, -23)
159
-7
In this 26-week trial, 1,041 adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus were randomized to liraglutide injection 0.6 mg, liraglutide injection 1.2 mg, liraglutide injection 1.8 mg, placebo, or rosiglitazone 4 mg (one-half of the maximal approved dose in the United States), all as add-on to glimepiride. Randomization occurred after a 4-week run-in period consisting of an initial, 2-week, forced-glimepiride titration period followed by a maintenance period of another 2 weeks. During the titration period, doses of glimepiride were increased to 4 mg/day. The doses of glimepiride could be reduced (at the discretion of the investigator) from 4 mg/day to 3 mg/day or 2 mg/day (minimum) after randomization, in the event of unacceptable hypoglycemia or other adverse events.
The mean age of participants was 56 years, and the mean duration of diabetes was 8 years. Participants were 49.4% male, 64.4% White and 2.8% Black or African American. The mean BMI was 29.9 kg/m2.
Treatment with liraglutide injection 1.2 mg and 1.8 mg as add-on to glimepiride resulted in a statistically significant reduction in mean HbA1c compared to placebo add-on to glimepiride (Table 7). The percentage of patients who discontinued due to ineffective therapy was 3% in the liraglutide injection 1.8 mg + glimepiride treatment group, 3.5% in the liraglutide injection 1.2 mg + glimepiride treatment group, 17.5% in the placebo + glimepiride treatment group, and 6.9% in the rosiglitazone + glimepiride treatment group.
Table 7: Results of a 26-week Trial of liraglutide injection as add-on to Sulfonylurea in Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus* - * Intent-to-treat population using last observation on study
- † For rosiglitazone, one-half of the maximal approved United States dose.
- ‡ p-value <0.0001
- § Least squares mean adjusted for baseline value
Liraglutide injection
1.8 mg +
Glimepiride
Liraglutide injection
1.2 mg +
Glimepiride
Placebo + Glimepiride
Rosiglitazone 4 mg† + Glimepiride
Intent-to-Treat Population (N)
234
228
114
231
HbA1c (%) (Mean)
Baseline
8.5
-1.1
-1.4‡
8.5
-1.1
-1.3‡
8.4
+0.2
8.4
-0.4
Change from baseline (adjusted mean)§
Difference from placebo + glimepiride arm (adjusted mean)§
95% Confidence Interval
(-1.6, -1.1)
(-1.5, -1.1)
Percentage of patients achieving HbA1c <7%
42
35
7
22
Fasting Plasma Glucose (mg/dL) (Mean)
Baseline
Change from baseline (adjusted mean)§
Difference from placebo + glimepiride arm (adjusted mean)§
174
-29
-47‡
177
-28
-46‡
171
+18
179
-16
95% Confidence Interval
(-58, -35)
(-58, -35)
Body Weight (kg) (Mean)
Baseline
Change from baseline (adjusted mean)§
Difference from placebo + glimepiride arm (adjusted mean)§
83
-0.2
-0.1
80
+0.3
0.4
81.9
-0.1
80.6
+2.1
95% Confidence Interval
(-0.9, 0.6)
(-0.4, 1.2)
Add-on to Metformin and Sulfonylurea:
In this 26-week trial, 581 adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus were randomized to liraglutide injection 1.8 mg, placebo, or insulin glargine, all as add-on to metformin and glimepiride. Randomization took place after a
6-week run-in period consisting of a 3-week forced metformin and glimepiride titration period followed by a maintenance period of another 3 weeks. During the titration period, doses of metformin and glimepiride were to be increased up to 2,000 mg/day and 4 mg/day, respectively. After randomization, patients randomized to liraglutide injection 1.8 mg underwent a 2 week period of titration with liraglutide injection. During the trial, the liraglutide injection and metformin doses were fixed, although glimepiride and insulin glargine doses could be adjusted. Patients titrated glargine twice-weekly during the first 8 weeks of treatment based on self-measured fasting plasma glucose on the day of titration. After Week 8, the frequency of insulin glargine titration was left to the discretion of the investigator, but, at a minimum, the glargine dose was to be revised, if necessary, at Weeks 12 and 18. Only 20% of glargine-treated patients achieved the pre-specified target fasting plasma glucose of ≤100 mg/dL. Therefore, optimal titration of the insulin glargine dose was not achieved in most patients.
The mean age of participants was 58 years, and the mean duration of diabetes was 9 years. Participants were 56.5% male, 75.0% White and 3.6% Black or African American. The mean BMI was 30.5 kg/m2.
Treatment with liraglutide injection as add-on to glimepiride and metformin resulted in a statistically significant mean reduction in HbA1c compared to placebo add-on to glimepiride and metformin (Table 8). The percentage of patients who discontinued due to ineffective therapy was 0.9% in the liraglutide injection 1.8 mg + metformin + glimepiride treatment group, 0.4% in the insulin glargine + metformin + glimepiride treatment group, and 11.3% in the
placebo + metformin + glimepiride treatment group.
Table 8: Results of a 26-week Trial of Liraglutide Injection as Add-on to Metformin and Sulfonylurea in Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus* - * Intent-to-treat population using last observation on study
- † For insulin glargine, optimal titration regimen was not achieved for 80% of patients.
- ‡ Least squares mean adjusted for baseline value
- § p-value <0.0001
- ¶ p-value <0.05
Liraglutide Injection
1.8 mg + Metformin + Glimepiride
Placebo + Metformin + Glimepiride
Insulin glargine†
+
Metformin + Glimepiride
Intent-to-Treat Population (N)
230
114
232
HbA1c (%) (Mean)
Baseline
Change from baseline (adjusted mean)‡
Difference from placebo + metformin + glimepiride arm (adjusted mean)‡
95% Confidence Interval
8.3
-1.3
-1.1§
(-1.3, -0.9)
8.3
-0.2
8.1
-1.1
Percentage of patients achieving HbA1c <7%
53
15
46
Fasting Plasma Glucose (mg/dL) (Mean)
Baseline
Change from baseline (adjusted mean)‡
Difference from placebo + metformin + glimepiride arm (adjusted mean)‡
95% Confidence Interval
165
-28
-38§
(-46, -30)
170
+10
164
-32
Body Weight (kg) (Mean)
Baseline
Change from baseline (adjusted mean)‡
Difference from placebo + metformin + glimepiride arm (adjusted mean)‡
95% Confidence Interval
85.8
-1.8
-1.4¶
(-2.1, -0.7)
85.4
-0.4
85.2
1.6
Liraglutide Injection Compared to Exenatide, Both as Add-on to Metformin and/or Sulfonylurea Therapy:
In this 26–week, open-label trial, 464 adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus on a background of metformin monotherapy, sulfonylurea monotherapy or a combination of metformin and sulfonylurea were randomized to once daily liraglutide injection 1.8 mg or exenatide 10 mcg twice daily. Maximally tolerated doses of background therapy were to remain unchanged for the duration of the trial. Patients randomized to exenatide started on a dose of 5 mcg twice-daily for 4 weeks and then were escalated to 10 mcg twice-daily.
The mean age of participants was 57 years, and the mean duration of diabetes was 8 years. Participants were 51.9% male, 91.8% White, 5.4% Black or African American and 12.3% of Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. The mean BMI was 32.9 kg/m2.
Treatment with liraglutide injection 1.8 mg resulted in statistically significant reductions in HbA1c and FPG relative to exenatide (Table 9). The percentage of patients who discontinued for ineffective therapy was 0.4% in the liraglutide injection treatment group and 0% in the exenatide treatment group. Both treatment groups had a mean decrease from baseline in body weight of approximately 3 kg.
Table 9: Results of a 26-week Open-Label trial of liraglutide injection versus Exenatide (both in combination with metformin and/or sulfonylurea) in Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus* - * Intent-to-treat population using last observation carried forward
- † Least squares mean adjusted for baseline value
- ‡ p-value <0.0001
Liraglutide injection
1.8 mg once daily
+ metformin and/or sulfonylurea
Exenatide
10 mcg twice daily
+ metformin and/or sulfonylurea
Intent-to-Treat Population (N)
233
231
HbA1c (%) (Mean)
Baseline
Change from baseline (adjusted mean)†
Difference from exenatide arm (adjusted mean)†
95% Confidence Interval
8.2
-1.1
-0.3‡
(-0.5, -0.2)
8.1
-0.8
Percentage of patients achieving HbA1c<7%
54
43
Fasting Plasma Glucose (mg/dL) (Mean)
Baseline
Change from baseline (adjusted mean)†
Difference from exenatide arm (adjusted mean)†
95% Confidence Interval
176
-29
-18‡
(-25, -12)
171
-11
Add-on to Metformin and Thiazolidinedione:
In this 26-week trial, 533 adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus were randomized to liraglutide injection 1.2 mg, liraglutide injection 1.8 mg or placebo, all as add-on to rosiglitazone (8 mg) plus metformin (2,000 mg). Patients underwent a 9 week run-in period (3-week forced dose escalation followed by a 6-week dose maintenance phase) with rosiglitazone (starting at 4 mg and increasing to 8 mg/day within 2 weeks) and metformin (starting at 500 mg with increasing weekly increments of 500 mg to a final dose of 2,000 mg/day). Only patients who tolerated the final dose of rosiglitazone (8 mg/day) and metformin (2000 mg/day) and completed the 6-week dose maintenance phase were eligible for randomization into the trial.
The mean age of participants was 55 years, and the mean duration of diabetes was 9 years. Participants were 61.6% male, 84.2% White, 10.2% Black or African American and 16.4% of Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. The mean BMI was 33.9 kg/m2.
Treatment with liraglutide injection as add-on to metformin and rosiglitazone produced a statistically significant reduction in mean HbA1c compared to placebo add-on to metformin and rosiglitazone (Table 10). The percentage of patients who discontinued due to ineffective therapy was 1.7% in the liraglutide injection 1.8 mg + metformin + rosiglitazone treatment group, 1.7% in the liraglutide injection 1.2 mg + metformin + rosiglitazone treatment group, and 16.4% in the placebo + metformin + rosiglitazone treatment group.
Table 10: Results of a 26-week Trial of liraglutide injection as Add-on to Metformin and Thiazolidinedione in Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus* - * Intent-to-treat population using last observation on study
- † Least squares mean adjusted for baseline value
- ‡ p-value <0.0001
Liraglutide Injection
1.8 mg + Metformin + Rosiglitazone
Liraglutide Injection
1.2 mg + Metformin + Rosiglitazone
Placebo + Metformin + Rosiglitazone
Intent-to-Treat Population (N)
178
177
175
HbA1c (%) (Mean)
Baseline
Change from baseline (adjusted mean)†
Difference from placebo + metformin + rosiglitazone arm (adjusted mean)†
8.6
-1.5
-0.9‡
8.5
-1.5
-0.9‡
8.4
-0.5
95% Confidence Interval
(-1.1, -0.8)
(-1.1, -0.8)
Percentage of patients achieving HbA1c <7%
54
57
28
Fasting Plasma Glucose (mg/dL) (Mean)
Baseline
Change from baseline (adjusted mean)†
Difference from placebo + metformin + rosiglitazone arm (adjusted mean)†
185
-44
-36‡
181
-40
-32‡
179
-8
95% Confidence Interval
(-44, -27)
(-41, -23)
Body Weight (kg) (Mean)
Baseline
Change from baseline (adjusted mean)†
Difference from placebo + metformin + rosiglitazone arm (adjusted mean)†
94.9
-2
-2.6‡
95.3
-1
-1.6‡
98.5
+0.6
95% Confidence Interval
(-3.4, -1.8)
(-2.4, -1.0)
Liraglutide Injection Compared to Placebo Both With or Without metformin and/or Sulfonylurea and/or Pioglitazone and/or Basal or Premix insulin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Moderate Renal Impairment:
In this 26-week, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial in adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, 279 patients with moderate renal impairment, as per MDRD formula (eGFR 30−59 mL/min/1.73 m2), were randomized to liraglutide injection or placebo once daily. Liraglutide injection was added to the patient's stable pre-trial antidiabetic regimen (insulin therapy and/or metformin, pioglitazone, or sulfonylurea). The dose of liraglutide injection was escalated according to approved labeling to achieve a dose of 1.8 mg per day. The insulin dose was reduced by 20% at randomization for patients with baseline HbA1c ≤ 8% and fixed until liraglutide dose escalation was complete. Dose reduction of insulin and SU was allowed in case of hypoglycemia; up titration of insulin was allowed but not beyond the pre-trial dose.
The mean age of participants was 67 years, and the mean duration of diabetes was 15 years. Participants were 50.5% male, 92.3% White, 6.6% Black or African American, and 7.2% of Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. The mean BMI was 33.9 kg/m2. Approximately half of patients had an eGFR between 30 and < 45mL/min/1.73 m2.
Treatment with liraglutide injection resulted in a statistically significant reduction in HbA1c from baseline at Week 26 compared to placebo (see Table 11). 123 patients reached the 1.8 mg dose of liraglutide injection.
Table 11: Results of a 26-week Trial of Liraglutide Injection Compared to Placebo in Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Moderate Renal Impairment* - * Intent-to-treat population
- † Early treatment discontinuation, before week 26, occurred in 25% and 22% of liraglutide injection and placebo patients, respectively.
- ‡ p-value <0.0001
- § Based on the known number of subjects achieving HbA1c < 7%. When applying the multiple imputation method described in b) above, the estimated percents achieving HbA1c < 7% are 47.6% and 24.9% for liraglutide injection and placebo, respectively.
- ¶ Estimated using a mixed model for repeated measurement with treatment, country, stratification groups as factors and baseline as a covariate, all nested within visit.
- # p-value <0.05
Liraglutide Injection 1.8 mg + insulin and/or OAD
Placebo + insulin and/or OAD
Intent to Treat Population (N)
140
137
HbA1c (%)
Baseline (mean)
Change from baseline (estimated mean)b,c
Difference from placebob†
95% Confidence Interval
8.1
-0.9
-0.6‡
(-0.8, -0.3)
8
-0.4
Proportion achieving HbA1c < 7%§
39.3
19.7
FPG (mg/dL)
Baseline (mean)
Change from baseline (estimated mean)¶
Difference from placebo¶
95% Confidence Interval
171
-22
-12#
(-23, -0.8)
167
-10
14.2 Glycemic Control Trial in Pediatric Patients Aged 10 Years and Older with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Liraglutide injection was evaluated in a 26-week, double-blind, randomized, parallel group, placebo controlled multi-center trial (NCT01541215), in 134 pediatric patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus aged 10 years and older. Patients were randomized to liraglutide injection once-daily or placebo once-daily in combination with metformin with or without basal insulin treatment. All patients were on a metformin dose of 1000 to 2000 mg prior to randomization. The basal insulin dose was decreased by 20% at randomization and liraglutide injection was titrated weekly by 0.6 mg for 2 to 3 weeks based on tolerability and an average fasting plasma glucose goal
of ≤110 mg/dL.
The mean age was 14.6 years: 29.9% were ages 10 to 14 years, and 70.1% were greater than 14 years of age. 38.1% were male, 64.9% were White, 13.4% were Asian, 11.9% were Black or African American; 29.1% were of Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. The mean BMI was 33.9 kg/m2 and the mean BMI SDS was 2.9. 18.7% of patients were using basal insulin at baseline. The mean duration of diabetes was 1.9 years and the mean HbA1c was 7.8%.
At week 26, treatment with liraglutide injection was superior in reducing HbA1c from baseline versus placebo. The estimated treatment difference in HbA1c reduction from baseline between liraglutide injection and placebo was -1.06% with a 95% confidence interval of [-1.65%; -0.46%] (see Table 12).
Table 12: Results at week 26 in a trial comparing Liraglutide Injection in combination with metformin with or without basal insulin versus Placebo in combination with metformin with or without basal insulin in Pediatric Patients Aged 10 Years and Older with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus - * The change from baseline to end of treatment visit in HbA1c and FPG was analyzed using a pattern mixture model with multiple imputation. Missing observations (10.6% in the liraglutide injection, 14.5% in the placebo) were imputed from the placebo arm based on multiple (x10,000) imputations. The data for week 26 was then analyzed with an ANCOVA model containing treatment, sex and age group as fixed effects and baseline value as covariate.
- † p-value <0.001
- ‡ Categories are derived from continuous measurements of HbA1c using a pattern mixture model with multiple imputation for missing observations.
Liraglutide injection +metformin±basal insulin
Placebo+metformin±basal insulin
N
66
68
HbA1c (%)
Baseline
End of 26 weeks
Adjusted mean change from baseline after 26 weeks*
7.9
7.1
-0.64
7.7
8.2
0.42
Treatment difference [95% CI] Liraglutide Injection vs Placebo
-1.06 [-1.65; -0.46]†
Percentage of patients achieving HbA1c <7%‡
63.7
36.5
FPG (mg/dL)
Baseline
End of 26 weeks
Adjusted mean change from baseline after 26 weeks*
157
132
-19.4
147
166
14.4
Treatment difference [95% CI] Liraglutide Injection vs Placebo
-33.83 [-55.74 ; -11.92]
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Liraglutide Injection: 18 mg/3 mL (6 mg/mL) clear, colorless solution in a prefilled, single-patient-use pen that delivers doses of 0.6 mg, 1.2 mg, or 1.8 mg is available in the following package sizes:
2 x Liraglutide Injection Pen NDC: 70748-346-02
3 x Liraglutide Injection Pen NDC: 70748-346-03
Prior to first use, liraglutide injection should be stored in a refrigerator between 36ºF to 46ºF (2ºC to 8ºC). Do not store in the freezer or directly adjacent to the refrigerator cooling element. Do not freeze liraglutide injection and do not use liraglutide injection if it has been frozen.
After first use of the liraglutide injection pen, the pen can be stored for 30 days at controlled room temperature 59°F to 86°F (15°C to 30°C) or in a refrigerator 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C). Keep the pen cap on when not in use. Protect liraglutide injection from excessive heat and sunlight. Always remove and safely discard the needle after each injection and store the liraglutide injection pen without an injection needle attached. This will reduce the potential for contamination, infection, and leakage while also ensuring dosing accuracy. Always use a new needle for each injection to prevent contamination.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Risk of Thyroid C-cell Tumors
Inform patients that liraglutide causes benign and malignant thyroid C-cell tumors in mice and rats and that the human relevance of this finding is unknown. Counsel patients to report symptoms of thyroid tumors (e.g., a lump in the neck, hoarseness, dysphagia, or dyspnea) to their physician [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Acute Pancreatitis
Inform patients of the potential risk for acute pancreatitis and its symptoms: severe abdominal pain that may radiate to the back, and which may or may not be accompanied by nausea or vomiting. Instruct patients to discontinue liraglutide injection promptly and contact their physician if pancreatitis is suspected [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Never Share a Liraglutide Injection Pen Between Patients
Advise patients that they must never share a liraglutide injection pen with another person, even if the needle is changed, because doing so carries a risk for transmission of blood-borne pathogens [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Hypoglycemia
Inform patients that hypoglycemia has been reported when liraglutide injection is used with insulin secretagogues or insulin and may occur in pediatric patients regardless of concomitant antidiabetic treatment. Educate patients or caregivers on the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Acute Kidney Injury Due to Volume Depletion
Inform patients of the potential risk of acute kidney injury due to dehydration associated with gastrointestinal adverse reactions. Advise patients to take precautions to avoid fluid depletion. Inform patients of the signs and symptoms of acute kidney injury and instruct them to promptly report any of these signs or symptoms or persistent (or extended) nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea to their healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Severe Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions
Inform patients of the potential risk of severe gastrointestinal adverse reactions. Instruct patients to contact their healthcare provider if they have severe or persistent gastrointestinal symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Inform patients that serious hypersensitivity reactions have been reported during postmarketing use of liraglutide injection. Advise patients on the symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions and instruct them to stop taking liraglutide injection and seek medical advice promptly if such symptoms occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Acute Gallbladder Disease
Inform patients of the potential risk for cholelithiasis or cholecystitis. Instruct patients to contact their physician if cholelithiasis or cholecystitis is suspected for appropriate clinical follow-up [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Pulmonary Aspiration During General Anesthesia or Deep Sedation
Inform patients that liraglutide injection may cause their stomach to empty more slowly which may lead to complications with anesthesia or deep sedation during planned surgeries or procedures. Instruct patients to inform healthcare providers prior to any planned surgeries or procedures if they are taking liraglutide injection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
Missed Dose
Inform patients not to take an extra dose of liraglutide injection to make up for a missed dose. If a dose is missed, the once-daily regimen should be resumed as prescribed with the next scheduled dose. If more than 3 days have elapsed since the last dose, advise the patient to reinitiate liraglutide injection at 0.6 mg to mitigate any gastrointestinal symptoms associated with reinitiation of treatment. Liraglutide injection should be titrated at the discretion of the healthcare provider [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
The brands listed are trademarks of their respective owners and are not trademarks of Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc. The makers of these brands are not affiliated with and do not endorse Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc. or its products.
LUPIN and the
 are registered trademarks of Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
are registered trademarks of Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Manufactured for:
Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Naples, FL 34108
United States
Manufactured by:
Lupin Limited,
Nagpur 441 108
India
Revised: November 2025
-
MEDICATION GUIDE
Medication Guide
Liraglutide (LIR-a-GLOO-tide)
Injection, for subcutaneous use
Read this Medication Guide before you start using liraglutide injection and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment.
What is the most important information I should know about liraglutide injection? Liraglutide injection may cause serious side effects, including:
Possible thyroid tumors, including cancer. Tell your healthcare provider if you get a lump or swelling in your neck, hoarseness, trouble swallowing, or shortness of breath. These may be symptoms of thyroid cancer. In studies with rats and mice, liraglutide injection and medicines that work like liraglutide injection caused thyroid tumors, including thyroid cancer. It is not known if liraglutide injection will cause thyroid tumors or a type of thyroid cancer called medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) in people.
Do not use liraglutide injection if you or any of your family have ever had a type of thyroid cancer called medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC), or if you have an endocrine system condition called Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2).
What is liraglutide injection?
Liraglutide injection is an injectable prescription medicine used:
along with diet and exercise to improve blood sugar (glucose) in adults and children who are 10 years of age and older with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Liraglutide injection is not recommended for people who take liraglutide or other medicines called glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists.
It is not known if liraglutide injection is safe and effective to lower blood sugar (glucose) in children under 10 years of age.
Who should not use liraglutide injection?
Do not use liraglutide injection if:
you or any of your family have ever had a type of thyroid cancer called medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) or if you have an endocrine system condition called Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2).
you have had a serious allergic reaction to liraglutide or any of the ingredients in liraglutide injection. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of ingredients in liraglutide injection. See " What are the possible side effects of liraglutide injection? " for symptoms of a serious allergic reaction.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before using liraglutide injection?
Before using liraglutide injection, tell your healthcare provider if you have any other medical conditions, including if you:
have or have had problems with your pancreas.
have severe problems with your stomach, such as slowed emptying of your stomach (gastroparesis) or problems with digesting food.
are scheduled to have surgery or other procedures that use anesthesia or deep sleepiness (deep sedation).
are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if liraglutide injection will harm your unborn baby. Tell your healthcare provider if you become pregnant while using liraglutide injection.
are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if liraglutide passes into your breast milk. You should talk with your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby while using liraglutide injection.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Liraglutide injection may affect the way some medicines work and some medicines may affect the way liraglutide injection works.
Before using liraglutide injection, talk to your healthcare provider about low blood sugar and how to manage it. Tell your healthcare provider if you are taking other medicines to treat diabetes, including insulin or sulfonylureas.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I use liraglutide injection?
Read the Instructions for Use that comes with liraglutide injection.
Use liraglutide injection exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to.
Your healthcare provider should show you how to use liraglutide injection before you use it for the first time.
Inject your dose of liraglutide injection under the skin (subcutaneously) of your stomach (abdomen), thigh, or upper arm. Do not inject liraglutide injection into a muscle (intramuscularly) or vein (intravenously).
Use liraglutide injection 1 time each day, at any time of the day.
If you miss a dose of liraglutide injection, take the missed dose at the next scheduled dose. Do not take 2 doses of liraglutide injection at the same time
Liraglutide injection may be taken with or without food.
Do not mix insulin and liraglutide injection together in the same injection.
You may give an injection of liraglutide injection and insulin in the same body area (such as your stomach area), but not right next to each other.
Change (rotate) your injection site with each injection. Do not use the same site for each injection.
Do not share your liraglutide injection pen with other people, even if the needle has been changed. You may give other people a serious infection or get a serious infection from them.
If you take too much liraglutide injection, call your healthcare provider or the Poison Help line at 1-800-222-1222 or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
The liraglutide injection pen you are using should be thrown away 30 days after you start using it.
What are the possible side effects of liraglutide injection?
Liraglutide injection may cause serious side effects, including:
See "What is the most important information I should know about liraglutide injection?"
inflammation of your pancreas (pancreatitis). Stop using liraglutide injection and call your healthcare provider right away if you have severe pain in your stomach area (abdomen) that will not go away, with or without vomiting. You may feel the pain from your abdomen to your back.
low blood sugar (hypoglycemia). Your risk for getting low blood sugar may be higher if you use liraglutide injection with another medicine that can cause low blood sugar, such as a sulfonylurea or insulin. In children who are 10 years of age and older, the risk for low blood sugar may be higher with liraglutide injection regardless of use with another medicine that can also lower blood sugar.
Signs and symptoms of low blood sugar may include:
ο dizziness or light-headedness
ο sweating
ο confusion or drowsiness
ο headache
ο blurred vision
ο slurred speech
ο shakiness
ο fast heartbeat
ο anxiety, irritability, or mood changes
ο hunger
ο weakness
ο feeling jittery
dehydration leading to kidney problems. Diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting may cause a loss of fluids (dehydration) which may cause kidney problems. It is important for you to drink fluids to help reduce your chance of dehydration. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea that does not go away.
s evere stomach problems. Stomach problems, sometimes severe, have been reported in people who use liraglutide injection. Tell your healthcare provider if you have stomach problems that are severe or will not go away.
serious allergic reactions. Stop using liraglutide injection and get medical help right away, if you have any symptoms of a serious allergic reaction including:
ο swelling of your face, lips, tongue or throat
ο problems breathing or swallowing
ο severe rash or itching
ο fainting or feeling dizzy
ο very rapid heartbeat
gallbladder problems. Gallbladder problems have happened in some people who take liraglutide injection. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you get symptoms of gallbladder problems which may include:
ο pain in your upper stomach (abdomen)
ο fever
ο yellowing of skin or eyes (jaundice)
ο clay-colored stools
food or liquid getting into the lungs during surgery or other procedures that use anesthesia or deep sleepiness (deep sedation) . Liraglutide injection may increase the chance of food getting into your lungs during surgery or other procedures. Tell all your healthcare providers that you are taking liraglutide injection before you are scheduled to have surgery or other procedures.
The most common side effects of liraglutide injection may include nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, decreased appetite, indigestion and constipation.
Talk to your healthcare provider about any side effects that bothers you or does not go away. These are not all the possible side effects of liraglutide injection.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
General information about the safe and effective use of liraglutide injection.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use liraglutide injection for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give liraglutide injection to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider.
You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about liraglutide injection that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in liraglutide injection?
Active ingredient: liraglutide
Inactive ingredients: disodium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate, phenol, propylene glycol and water for injection, hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide may be added to adjust pH
For more information, go to www.lupinpharmaceuticals.com or call 1-800-399-2561.
LUPIN and the are registered trademarks of Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
are registered trademarks of Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Manufactured for:
Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Naples, FL 34108
United States
Manufactured by:
Lupin Limited,
Nagpur 441 108
India
Revised: November 2025
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
-
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Liraglutide (LIR-a-GLOO-tide) Injection
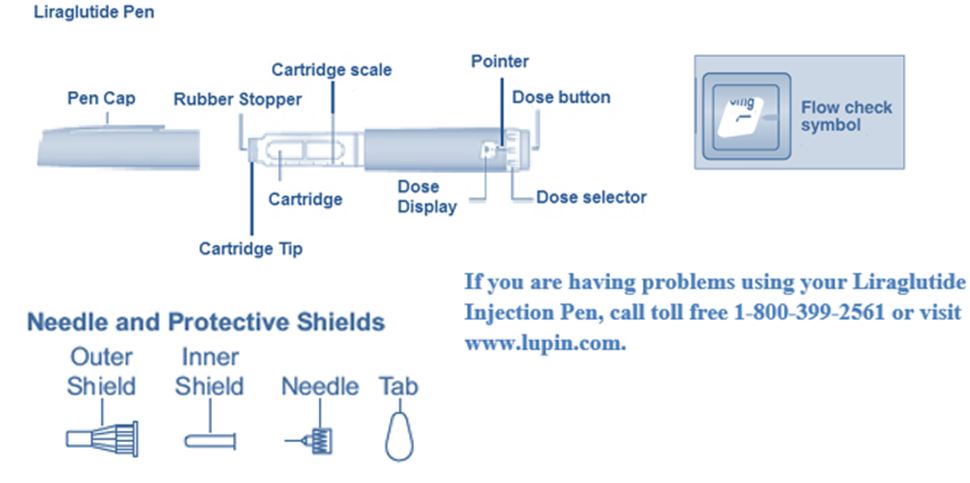
First read the Medication Guide that comes with your liraglutide injection single-patient use pen and then read this Instructions for Use for information about how to use your liraglutide injection pen the right way.
These instructions do not take the place of talking with your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment.
Do not share your Liraglutide Injection Pen with other people, even if the needle has been changed. You may give other people a serious infection, or get a serious infection from them.
Your liraglutide injection pen is a disposable single-patient-use prefilled pen injector that contains 3 mL of liraglutide injection and will deliver doses of 0.6 mg, 1.2 mg or 1.8 mg. The number of doses that you can take with a liraglutide injection pen depends on the dose of medicine that is prescribed for you. Your healthcare provider will tell you how much liraglutide injection to take.
Talk to your healthcare provider or pharmacist for more information about needles for your liraglutide injection pen.
Important Information
- Always use a new needle for each injection to prevent contamination.
- Always remove the needle after each injection, and store your pen without the needle attached. This reduces the risk of contamination, infection, leakage of liraglutide, blocked needles and inaccurate dosing.
- Keep your liraglutide injection pen and all medicines out of the reach of children.
- If you drop your liraglutide injection pen, repeat "First Time Use for Each New Pen" (steps A through D).
- Be careful not to bend or damage the needle.
- Do not use the cartridge scale to measure how much liraglutide injection to inject.
- Be careful when handling used needles to avoid needle stick injuries.
- You can use your liraglutide injection pen for up to 30 days after you use it the first time.
Supplies you will need to give your liraglutide injection:
- Liraglutide injection pen
- a new disposable needle
- alcohol swab
- cotton ball or gauze
- sharps disposal container for throwing away used liraglutide injection pens and needles.
See "Remove and Dispose of the Needle" at the end of these instructions.
First Time Use for Each New Pen
Step A. Check the Pen
Take your new liraglutide injection pen out of the refrigerator.
Wash hands with soap and water before use.
Check pen label before each use to make sure it is your liraglutide injection pen.
Pull off pen cap (See Figure A).
Check liraglutide injection in the cartridge. The liquid should be clear, colorless and free of particles. If not, do not use.
Wipe the rubber stopper with an alcohol swab.
Step B. Attach the Needle
Remove protective tab from outer needle cap.
Push outer needle cap containing the needle straight onto the pen, then screw needle on until secure (See Figure B).
Pull off outer needle cap (See Figure C). Do not throw away
Pull off inner needle cap and throw away (See Figure D). A small drop of liquid may appear. This is normal.
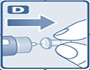
Step C. Dial to the Flow Check Symbol
This step is done only One Time for each new pen and is Only required the first time you use a new pen.
Turn dose selector until flow check
symbol ( ) lines up with pointer (See Figure E). The flow check symbol does not administer the dose as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
) lines up with pointer (See Figure E). The flow check symbol does not administer the dose as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
To select the dose prescribed by your healthcare provider, continue to Step G under "Routine Use".
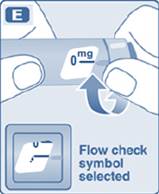
Step D. Prepare the Pen
Hold pen with needle pointing up.
Tap cartridge gently with your finger a few times to bring any air bubbles to the top of the cartridge (See Figure F).
Keep needle pointing up and press dose button until the black line indicating 0 mg lines up with pointer (See Figure G). Repeat steps C and D, up to 6 times, until a drop of liraglutide injection appears at the needle tip.
If you still see no drop of liraglutide injection, use a new pen and contact Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-800-399-2561.
Continue to Step G under "Routine Use"
→
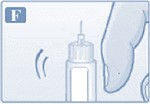
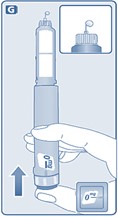
Routine Use
Step E. Check the Pen
Take your liraglutide injection pen from where it is stored.
Wash hands with soap and water before use.
Check pen label before each use to make sure it is your liraglutide injection pen.
Pull off pen cap (See Figure H).
Check liraglutide injection in the cartridge. The liquid should be clear, colorless and free of particles. If not, do not use.
Wipe the rubber stopper with an alcohol swab.
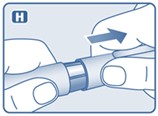
Step F. Attach the Needle
Remove protective tab from outer needle cap.
Push outer needle cap containing the needle straight onto the pen, then screw needle on until secure (See Figure I).
Pull off outer needle cap. Do not throw away (See Figure J).
Pull off inner needle cap and throw away (See Figure K). A small drop of liquid may appear. This is normal.
Step G. Dial the Dose
Liraglutide injection pen can give a dose of 0.6 mg (starting dose), 1.2 mg or 1.8 mg. Be sure that you know the dose of liraglutide injection that is prescribed for you.
Turn the dose selector until the black line indicating your needed dose lines up with the pointer (0.6 mg, 1.2 mg or 1.8 mg) (See Figure L).
You will hear a "click" every time you turn the dose selector. Do not set the dose by counting the number of clicks you hear.
If you select a wrong dose, change it by turning the dose selector backwards or forwards until the black line indicating the correct dose lines up with the pointer. Be careful not to press the dose button when turning the dose selector. This may cause liraglutide injection to come out.
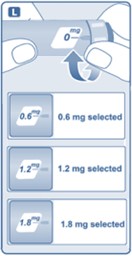
Step H. Injecting the Dose
Choose your injection site in either the stomach (abdomen), thigh, or upper arm (only if caregiver administered) and wipe the skin with an alcohol swab (See Figure M). Let the injection site dry before you inject your dose.
Insert needle into your skin using the injection technique shown to you by your healthcare provider. Do not inject liraglutide injection into a vein or muscle.
Press down on the center of the dose button to inject until the black line indicating 0 mg lines up with the pointer (See Figure N).
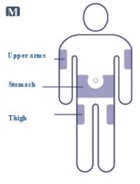
Be careful not to touch the dose display with your other fingers. This may block the injection.
Keep the dose button pressed down and make sure that you keep the needle under the skin for a full count of 6 seconds to make sure the full dose is injected. Keep your thumb on the injection button until you remove the needle from your skin (See Figure O).
Change (rotate) your injection sites within the area you choose for each dose. Do not use the same injection site for each injection.
Step I. Withdraw Needle
You may see a drop of liraglutide injection at the needle tip. This is normal and it does not affect the dose you just received. If blood appears after you take the needle out of your skin, apply light pressure with a cotton ball or gauze, but do not rub the area (See Figure P).
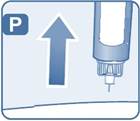
Step J. Remove and Dispose of the Needle
Carefully put the outer needle cap over the needle (See Figure Q). Unscrew the needle.
Safely remove the needle from your liraglutide injection pen after each use.
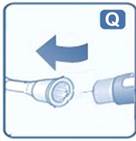
Put your used liraglutide injection pen and needles in a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use. Do not throw away (dispose of) loose needles and pens in your household trash.
If you do not have a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
ο made of a heavy-duty plastic
ο can be closed with a tight-fitting, puncture-resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out
ο upright and stable during use
ο leak-resistant
ο properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container
When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used needles and syringes. Do not reuse or share your needles with other people. For more information about the safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA's website at: http://www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal.
Do not dispose of your used sharps disposal container in your household trash unless your community guidelines permit this. Do not recycle your used sharps disposal container. Caring for your liraglutide injection pen
After removing the needle, put the pen cap on your liraglutide injection pen and store your liraglutide injection pen without the needle attached (See Figure R).
Do not try to refill your liraglutide injection pen – it is prefilled and is disposable.
Do not try to repair your pen or pull it apart.
Keep your liraglutide injection pen away from dust, dirt and liquids.
If cleaning is needed, wipe the outside of the pen with a clean, damp cloth.
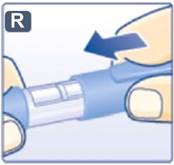
How should I store liraglutide injection?
Before use:
- Store your new, unused liraglutide injection pen in the refrigerator between 36ºF to 46ºF (2ºC to 8ºC).
- If liraglutide injection is stored outside of refrigeration (by mistake) prior to first use, it should be used or thrown away within 30 days.
- Do not freeze liraglutide injection or use liraglutide injection if it has been frozen. Do not store liraglutide injection near the refrigerator cooling element.
- Use a liraglutide injection pen for only 30 days. Throw away a used liraglutide injection pen 30 days after you start using it, even if some medicine is left in the pen.
- Store your liraglutide injection pen at room temperature between 59ºF to 86ºF (15ºC to 30ºC), or in a refrigerator between 36ºF to 46ºF (2°C to 8°C).
- When carrying the pen away from home, store the pen at room temperature between 59ºF to 86ºF (15ºC to 30ºC).
- If liraglutide injection has been exposed to temperatures above 86ºF (30ºC), it should be thrown away.
- Protect your liraglutide injection pen from heat and sunlight.
- Keep the pen cap on when your liraglutide injection pen is not in use.
- Always remove the needle after each injection and store your pen without the needle attached. This reduces the risk of contamination, infection, leakage and inaccurate dosing.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
LUPIN and the
 are registered trademarks of Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
are registered trademarks of Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Manufactured for:
Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Naples, FL 34108
United States
Manufactured by:
Lupin Limited,
Nagpur 441 108
India
Revised: November 2025 ID#:282313
-
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 70748-346-02
Liraglutide Injection
For Single Patient Use Only
18 mg/3 mL (6 mg/mL)
Each pen delivers doses of 0.6 mg, 1.2 mg or 1.8 mg
Subcutaneous use only
Discard pen 30 days after first use
REFRIGERATE - DO NOT FREEZE
Rx Only
Contains: 2 Liraglutide Injection Pens, Product Literature
PHARMACIST: Dispense the accompanying Medication Guide to each patient
Intended for use with disposable pen needles
2 Pens
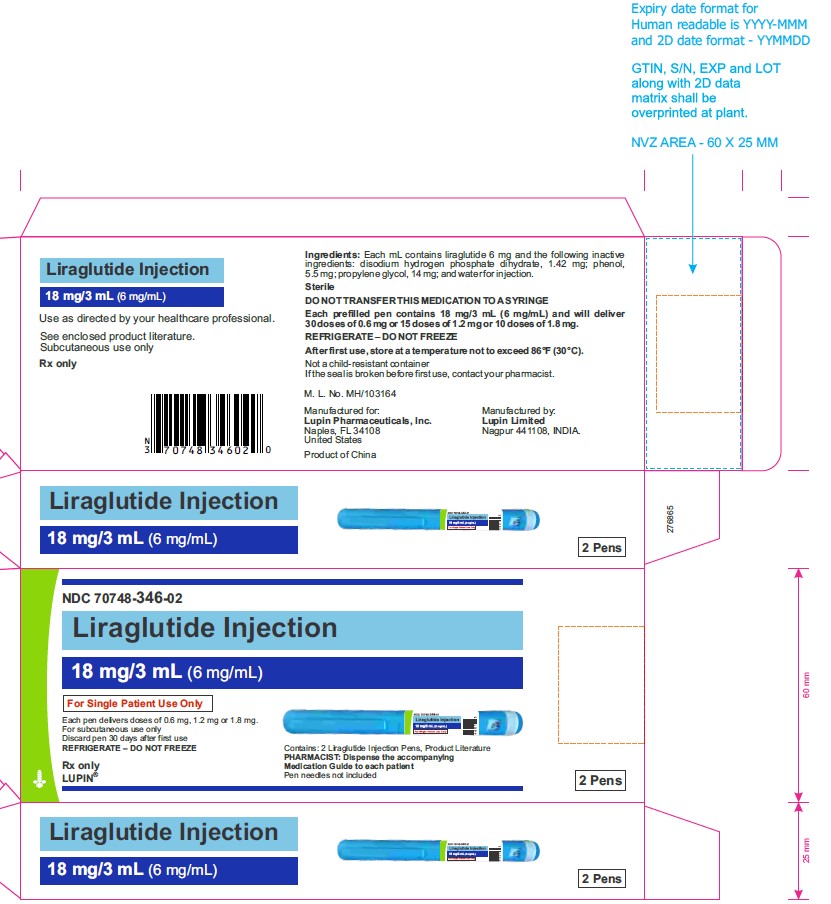
NDC 70748-346-03
Liraglutide Injection
For Single Patient Use Only
18 mg/3 mL (6 mg/mL)
Each pen delivers doses of 0.6 mg, 1.2 mg or 1.8 mg
Subcutaneous use only
Discard pen 30 days after first use
REFRIGERATE - DO NOT FREEZE
Rx Only
Contains: 3 Liraglutide Injection Pens, Product Literature
PHARMACIST: Dispense the accompanying Medication Guide to each patient
Intended for use with disposable pen needles
3 Pens
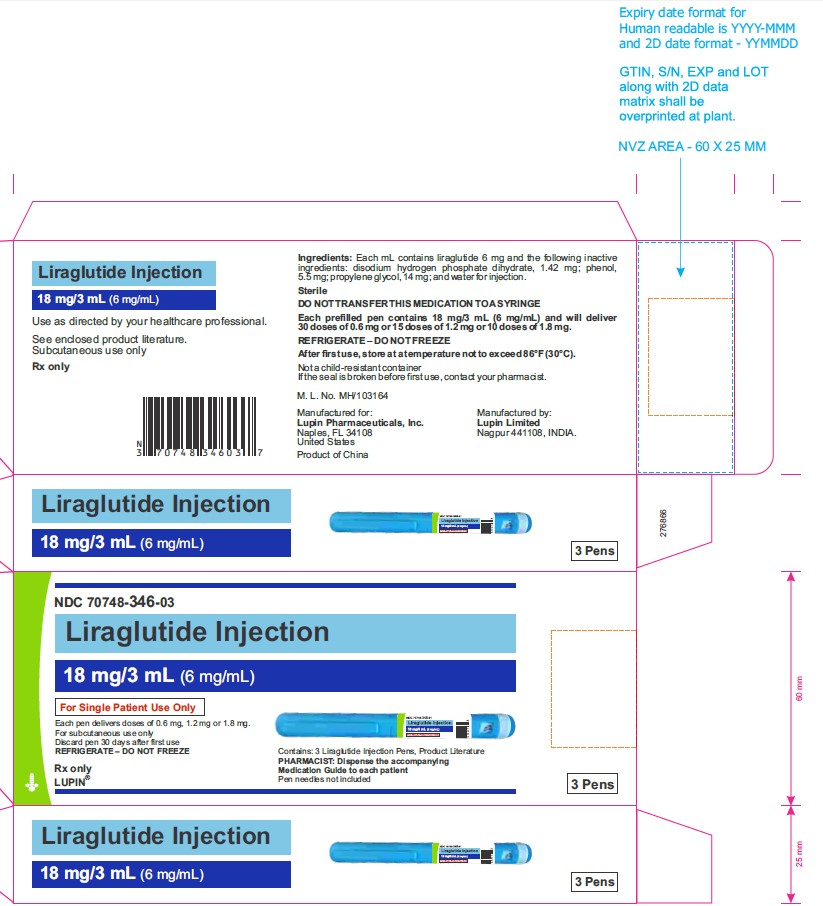
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
LIRAGLUTIDE
liraglutide injectionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 70748-346 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength LIRAGLUTIDE (UNII: 839I73S42A) (LIRAGLUTIDE - UNII:839I73S42A) LIRAGLUTIDE 6 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM PHOSPHATE DIBASIC DIHYDRATE (UNII: 94255I6E2T) 1.42 mg in 1 mL PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) 5.5 mg in 1 mL PROPYLENE GLYCOL (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) 14 mg in 1 mL WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Other Ingredients Ingredient Kind Ingredient Name Quantity May contain SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) May contain HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 70748-346-02 2 in 1 CARTON 10/02/2025 1 3 mL in 1 SYRINGE, PLASTIC; Type 2: Prefilled Drug Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) 2 NDC: 70748-346-03 3 in 1 CARTON 10/02/2025 2 3 mL in 1 SYRINGE, PLASTIC; Type 2: Prefilled Drug Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA215421 10/02/2025 Labeler - Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (089153071) Registrant - LUPIN LIMITED (675923163) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations LUPIN LIMITED 675485014 MANUFACTURE(70748-346) , PACK(70748-346)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.