Ergocalciferol by Dispensing Solutions, Inc. / PSS World Medical, Inc. ERGOCALCIFEROL capsule
Ergocalciferol by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Ergocalciferol by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Dispensing Solutions, Inc., PSS World Medical, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
DESCRIPTION
Ergocalciferol Capsules, USP is a synthetic calcium regulator for oral administration.
Ergocalciferol is a white, colorless crystal, insoluble in water, soluble in organic solvents, and slightly soluble in vegetable oils. It is affected by air and by light. Ergosterol or provitamin D2 is found in plants and yeast and has no antirachitic activity.
There are more than 10 substances belonging to a group of steroid compounds, classified as having vitamin D or antirachitic activity.
One USP Unit of vitamin D2 is equivalent to one International Unit (IU), and 1 mcg of vitamin D2 is equal to 40 IU.
Each softgel capsule, for oral administration, contains Ergocalciferol, USP 1.25 mg (equivalent to 50,000 USP units of Vitamin D), in an edible vegetable oil.
Ergocalciferol, also called vitamin D2 ,is 9, 10-secoergosta-5, 7,10(19),22-tetraen-3-ol,(3β,5Z,7E,22E)-; (C28H44O) with a molecular weight of 396.65, and has the following structural formula:
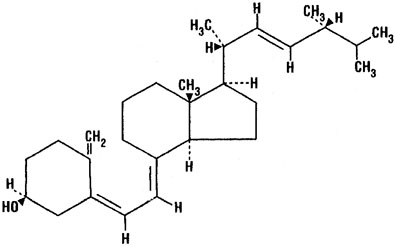
Chemical Structure
Inactive Ingredients: D and C Yellow #10, FD and C Blue #1, Gelatin, Glycerin, Purified Water, Refined Soybean Oil.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
The in vivo synthesis of the major biologically active metabolites of vitamin D occurs in two steps. The first hydroxylation of ergocalciferol takes place in the liver (to 25-hydroxyvitamin D) and the second in the kidneys (to 1,25-dihydroxy- vitamin D). Vitamin D metabolites promote the active absorption of calcium and phosphorus by the small intestine, thus elevating serum calcium and phosphate levels sufficiently to permit bone mineralization. Vitamin D metabolites also mobilize calcium and phosphate from bone and probably increase the reabsorption of calcium and perhaps also of phosphate by the renal tubules.
There is a time lag of 10 to 24 hours between the administration of vitamin D and the initiation of its action in the body due to the necessity of synthesis of the active metabolites in the liver and kidneys. Parathyroid hormone is responsible for the regulation of this metabolism in the kidneys.
- INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Hypervitaminosis D is characterized by effects on the following organ system:
Renal: Impairment of renal function with polyuria, nocturia, polydipsia, hypercalciuria, reversible azotemia, hypertension, nephrocalcinosis, generalized vascular calcification, or irreversible renal insufficiency which may result in death.
CNS: Mental retardation.
Soft Tissues: Widespread calcification of the soft tissues, including the heart, blood vessels, renal tubules, and lungs.
Skeletal: Bone demineralization (osteoporosis) in adults occurs concomitantly.
Decline in the average rate of linear growth and increased mineralization of bones in infants and children (dwarfism), vague aches, stiffness, and weakness.Gastrointestinal: Nausea, anorexia, constipation.
Metabolic: Mild acidosis, anemia, weight loss.
-
OVERDOSAGE
The effects of administered vitamin D can persist for two or more months after cessation of treatment.
Hypervitaminosis D is characterized by:
- Hypercalcemia with anorexia, nausea, weakness, weight loss, vague aches and stiffness, constipation, mental retardation, anemia, and mild acidosis.
- Impairment of renal function with polyuria, nocturia, polydipsia, hypercalciuria, reversible azotemia, hypertension, nephrocalcinosis, generalized vascular calcification, or irreversible renal insufficiency which may result in death.
- Widespread calcification of the soft tissues, including the heart, blood vessels, renal tubules, and lungs. Bone demineralization (osteoporosis) in adults occurs concomitantly.
- Decline in the average rate of linear growth and increased mineralization of bones in infants and children (dwarfism).
The treatment of hypervitaminosis D with hypercalcemia consists of immediate withdrawal of the vitamin, a low calcium diet, generous intake of fluids, along with symptomatic and supportive treatment. Hypercalcemic crisis with dehydration, stupor, coma, and azotemia requires more vigorous treatment. The first step should be hydration of the patient. Intravenous saline may quickly and significantly increase urinary calcium excretion. A loop diuretic (furosemide or ethacrynic acid) may be given with the saline infusion to further increase renal calcium excretion. Other reported therapeutic measures include dialysis or the administration of citrates, sulfates, phosphates, corticosteroids, EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid), and mithramycin via appropriate regimens. With appropriate therapy, recovery is the usual outcome when no permanent damage has occurred. Deaths via renal or cardiovascular failure have been reported.
The LD50 in animals is unknown. The toxic oral dose of ergocalciferol in the dog is 4 mg/kg.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
THE RANGE BETWEEN THERAPEUTIC AND TOXIC DOSES IS NARROW.
Vitamin D Resistant Rickets: 12,000 to 500,000 USP units daily.
Hypoparathyroidism: 50,000 to 200,000 USP units daily concomitantly with calcium lactate 4 g, six times per day.
DOSAGE MUST BE INDIVIDUALIZED UNDER CLOSE MEDICAL SUPERVISION.
Calcium intake should be adequate. Blood calcium and phosphorus determinations must be made every 2 weeks or more frequently if necessary. X-rays of the bones should be taken every month until condition is corrected and stabilized.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Each green, oval softgel capsule is imprinted with A3 and contains 1.25 mg (50,000 USP units vitamin D) of ergocalciferol, USP.
Bottles of 100 Softgel Capsules (NDC: 51991-604-01).
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
ERGOCALCIFEROL
ergocalciferol capsuleProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 66336-907(NDC: 51991-604) Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Ergocalciferol (UNII: VS041H42XC) (Ergocalciferol - UNII:VS041H42XC) Ergocalciferol 1.25 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength D&C Yellow No. 10 (UNII: 35SW5USQ3G) FD&C Blue No. 1 (UNII: H3R47K3TBD) Gelatin (UNII: 2G86QN327L) Glycerin (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) Water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Soybean Oil (UNII: 241ATL177A) Product Characteristics Color green Score no score Shape OVAL Size 13mm Flavor Imprint Code A3 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 66336-907-06 6 in 1 BOTTLE 2 NDC: 66336-907-44 4 in 1 BOTTLE Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA040833 08/17/2009 Labeler - Dispensing Solutions, Inc. (066070785) Registrant - PSS World Medical, Inc. (101822682) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Dispensing Solutions, Inc. 066070785 relabel, repack
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.
