MILRINONE LACTATE injection, solution
Milrinone Lactate by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Milrinone Lactate by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Mullan Pharmaceutical Inc., Shandong New Time Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
DESCRIPTION
Milrinone lactate injection is a member of a class of bipyridine inotropic/vasodilator agents with phosphodiesterase inhibitor activity, distinct from digitalis glycosides or catecholamines. Milrinone lactate is designated chemically as 1,6-dihydro-2-methyl-6-oxo-[3,4'-bipyridine]-5-carbonitrile lactate and has the following structure:
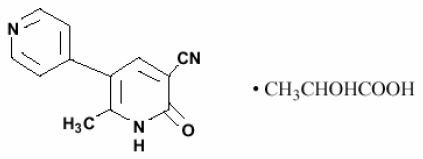
Milrinone is an off-white to tan crystalline compound with a molecular weight of 211.2 and an empirical formula of C 12H 9N 3O. It is slightly soluble in methanol, and very slightly soluble in chloroform and in water. As the lactate salt, it is stable and colorless to pale yellow in solution. Milrinone lactate is available as sterile aqueous solutions of the lactate salt of milrinone for injection or infusion intravenously.
Sterile, single-dose vials:Single-dose vials of 10 and 20 mL contain in each mL milrinone lactate equivalent to 1 mg milrinone and 47 mg Dextrose, Anhydrous, USP, in Water for Injection, USP. The pH is adjusted to between 3.2 and 4.0 with lactic acid or sodium hydroxide. The total concentration of lactic acid can vary between 0.95 mg/mL and 1.29 mg/mL. These vials require preparation of dilutions prior to administration to patients intravenously.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Milrinone lactate is a positive inotrope and vasodilator, with little chronotropic activity different in structure and mode of action from either the digitalis glycosides or catecholamines.
Milrinone lactate, at relevant inotropic and vasorelaxant concentrations, is a selective inhibitor of peak III cAMP phosphodiesterase isozyme in cardiac and vascular muscle. This inhibitory action is consistent with cAMP mediated increases in intracellular ionized calcium and contractile force in cardiac muscle, as well as with cAMP dependent contractile protein phosphorylation and relaxation in vascular muscle. Additional experimental evidence also indicates that milrinone lactate is not a beta-adrenergic agonist nor does it inhibit sodium-potassium adenosine triphosphatase activity as do the digitalis glycosides.
Clinical studies in patients with congestive heart failure have shown that milrinone lactate produces dose-related and plasma drug concentration-related increases in the maximum rate of increase of left ventricular pressure. Studies in normal subjects have shown that milrinone lactate produces increases in the slope of the left ventricular pressure-dimension relationship, indicating a direct inotropic effect of the drug. Milrinone lactate also produces dose-related and plasma concentration-related increases in forearm blood flow in patients with congestive heart failure, indicating a direct arterial vasodilator activity of the drug.
Both the inotropic and vasodilatory effects have been observed over the therapeutic range of plasma milrinone concentrations of 100 ng/mL to 300 ng/mL.
In addition to increasing myocardial contractility, milrinone lactate improves diastolic function as evidenced by improvements in left ventricular diastolic relaxation.
The acute administration of intravenous milrinone has also been evaluated in clinical trials in excess of 1600 patients, with chronic heart failure, heart failure associated with cardiac surgery, and heart failure associated with myocardial infarction. The total number of deaths, either on therapy or shortly thereafter (24 hours) was 15, less than 0.9%, few of which were thought to be drug-related.
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Milrinone Lactate Injection is indicated for the short-term intravenous treatment of patients with acute decompensated heart failure. Patients receiving milrinone lactate should be observed closely with appropriate electrocardiographic equipment. The facility for immediate treatment of potential cardiac events, which may include life threatening ventricular arrhythmias, must be available. The majority of experience with intravenous milrinone lactate has been in patients receiving digoxin and diuretics.
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
WARNINGS
Whether given orally or by continuous or intermittent intravenous infusion, milrinone lactate has not been shown to be safe or effective in the longer (greater than 48 hours) treatment of patients with heart failure. In a multicenter trial of 1088 patients with Class III and IV heart failure, long-term oral treatment with milrinone lactate was associated with no improvement in symptoms and an increased risk of hospitalization and death. In this study, patients with Class IV symptoms appeared to be at particular risk of life-threatening cardiovascular reactions. There is no evidence that milrinone lactate given by long-term continuous or intermittent infusion does not carry a similar risk.
The use of milrinone lactate both intravenously and orally has been associated with increased frequency of ventricular arrhythmias, including nonsustained ventricular tachycardia. Long-term oral use has been associated with an increased risk of sudden death. Hence, patients receiving milrinone lactate should be observed closely with the use of continuous electrocardiographic monitoring to allow the prompt detection and management of ventricular arrhythmias.
-
PRECAUTIONS
General
Milrinone lactate should not be used in patients with severe obstructive aortic or pulmonic valvular disease in lieu of surgical relief of the obstruction. Like other inotropic agents, it may aggravate outflow tract obstruction in hypertrophic subaortic stenosis.
Supraventricular and ventricular arrhythmias have been observed in the high-risk population treated. In some patients, injections of milrinone lactate and oral milrinone lactate have been shown to increase ventricular ectopy, including nonsustained ventricular tachycardia. The potential for arrhythmia, present in congestive heart failure itself, may be increased by many drugs or combinations of drugs. Patients receiving milrinone lactate should be closely monitored during infusion.
Milrinone lactate produces a slight shortening of AV node conduction time, indicating a potential for an increased ventricular response rate in patients with atrial flutter/fibrillation which is not controlled with digitalis therapy.
During therapy with milrinone lactate, blood pressure and heart rate should be monitored and the rate of infusion slowed or stopped in patients showing excessive decreases in blood pressure.
If prior vigorous diuretic therapy is suspected to have caused significant decreases in cardiac filling pressure, milrinone lactate should be cautiously administered with monitoring of blood pressure, heart rate, and clinical symptomatology.
There is no experience in controlled trials with infusions of milrinone for periods exceeding 48 hours. Cases of infusion site reaction have been reported with intravenous milrinone therapy (see ADVERSE REACTIONS). Consequently, careful monitoring of the infusion site should be maintainedto avoid possible extravasation.
Use in Acute Myocardial Infarction
No clinical studies have been conducted in patients in the acute phase of post myocardial infarction. Until further clinical experience with this class of drugs is gained, milrinone lactate is not recommended in these patients.
Laboratory Tests
Fluid and Electrolytes: Fluid and electrolyte changes and renal function should be carefully monitored during therapy with milrinone lactate. Improvement in cardiac output with resultant diuresis may necessitate a reduction in the dose of diuretic. Potassium loss due to excessive diuresis may predispose digitalized patients to arrhythmias. Therefore, hypokalemia should be corrected by potassium supplementation in advance of or during use of milrinone lactate.
Drug Interactions
No untoward clinical manifestations have been observed in limited experience with patients in whom milrinone lactate was used concurrently with the following drugs: digitalis glycosides; lidocaine, quinidine; hydralazine, prazosin; isosorbide dinitrate, nitroglycerin; chlorthalidone, furosemide, hydrochlorothiazide, spironolactone; captopril; heparin, warfarin, diazepam, insulin; and potassium supplements.
Chemical Interactions
There is an immediate chemical interaction which is evidenced by the formation of a precipitate when furosemide is injected into an intravenous line of an infusion of milrinone lactate. Therefore, furosemide should not be administered in intravenous lines containing milrinone lactate.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Twenty-four months of oral administration of milrinone lactate to mice at doses up to 40 mg/kg/day (about 50 times the human oral therapeutic dose in a 50 kg patient) was unassociated with evidence of carcinogenic potential. Neither was there evidence of carcinogenic potential when milrinone lactate was orally administered to rats at doses up to 5 mg/kg/day (about 6 times the human oral therapeutic dose) for twenty-four months or at 25 mg/kg/day (about 30 times the human oral therapeutic dose) for up to 18 months in males and 20 months in females. Whereas the Chinese Hamster Ovary Chromosome Aberration Assay was positive in the presence of a metabolic activation system, results from the Ames Test, the Mouse Lymphoma Assay, the Micronucleus Test, and the in vivo Rat Bone Marrow Metaphase Analysis indicated an absence of mutagenic potential. In reproductive performance studies in rats, milrinone lactate had no effect on male or female fertility at oral doses up to 32 mg/kg/day.
Animal Toxicity
Oral and intravenous administration of toxic dosages of milrinone lactate to rats and dogs resulted in myocardial degeneration/fibrosis and endocardial hemorrhage, principally affecting the left ventricular papillary muscles. Coronary vascular lesions characterized by periarterial edema and inflammation have been observed in dogs only. The myocardial/endocardial changes are similar to those produced by beta-adrenergic receptor agonists such as isoproterenol, while the vascular changes are similar to those produced by minoxidil and hydralazine. Doses within the recommended clinical dose range (up to 1.13 mg/kg/day) for congestive heart failure patients have not produced significant adverse effects in animals.
Pregnancy
Oral administration of milrinone lactate to pregnant rats and rabbits during organogenesis produced no evidence of teratogenicity at dose levels up to 40 mg/kg/day and 12 mg/kg/day, respectively. Milrinone lactate did not appear to be teratogenic when administered intravenously to pregnant rats at doses up to 3 mg/kg/day (about 2.5 times the maximum recommended clinical intravenous dose) or pregnant rabbits at doses up to 12 mg/kg/day, although an increased resorption rate was apparent at both 8 mg/kg/day and 12 mg/kg/day (intravenous) in the latter species. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Milrinone lactate should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Nursing Mothers
Caution should be exercised when milrinone lactate is administered to nursing women, since it is not known whether it is excreted in human milk.
Use in Elderly Patients
There are no special dosage recommendations for the elderly patient. Ninety percent of all patients administered milrinone lactate in clinical studies were within the age range of 45 to 70 years, with a mean age of 61 years. Patients in all age groups demonstrated clinically and statistically significant responses. No age-related effects on the incidence of adverse reactions have been observed. Controlled pharmacokinetic studies have not disclosed any age-related effects on the distribution and elimination of milrinone lactate.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Cardiovascular Effects
In patients receiving milrinone lactate in Phase II and III clinical trials, ventricular arrhythmias were reported in 12.1%: Ventricular ectopic activity, 8.5%; nonsustained ventricular tachycardia, 2.8%; sustained ventricular tachycardia, 1% and ventricular fibrillation, 0.2% (2 patients experienced more than one type of arrhythmia). Holter recordings demonstrated that in some patients injection of milrinone lactate increased ventricular ectopy, including nonsustained ventricular tachycardia. Life-threatening arrhythmias were infrequent and when present have been associated with certain underlying factors such as preexisting arrhythmias, metabolic abnormalities (e.g. hypokalemia), abnormal digoxin levels and catheter insertion. Milrinone lactate was not shown to be arrhythmogenic in an electrophysiology study. Supraventricular arrhythmias were reported in 3.8% of the patients receiving milrinone lactate. The incidence of both supraventricular and ventricular arrhythmias has not been related to the dose or plasma milrinone concentration.
Other cardiovascular adverse reactions include hypotension, 2.9% and angina/chest pain, 1.2%.
In the post marketing experience, there have been rare cases of “torsades de pointes” reported.
CNS Effects
Headaches, usually mild to moderate in severity, have been reported in 2.9% of patients receiving milrinone lactate.
Other Effects
Other adverse reactions reported, but not definitely related to the administration of milrinone lactate include hypokalemia, 0.6%; tremor, 0.4%; and thrombocytopenia, 0.4%.
Isolated spontaneous reports of bronchospasm and anaphylactic shock have been received; and in the post-marketing experience, liver function test abnormalities and skin reactions such as rash have been reported.
Post-Marketing Adverse Event Reports
In addition to adverse events reported from clinical trials, the following events have been reported from worldwide post-marketing experience with milrinone: Isolated spontaneous reports of bronchospasm and anaphylactic shock. Liver function test abnormalities and skin reactions such as rash. Administration site conditions: Infusion site reaction. To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Mullan Pharmaceutical Inc., at 1-800-673-9839 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
-
OVERDOSAGE
Doses of milrinone lactate may produce hypotension because of its vasodilator effect. If this occurs, administration of milrinone lactate should be reduced or temporarily discontinued until the patient’s condition stabilizes. No specific antidote is known, but general measures for circulatory support should be taken.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Milrinone Lactate Injection, USP should be administered with a loading dose followed by a continuous infusion (maintenance dose) according to the following guidelines:
LOADING DOSE
50 mcg/kg: Administer slowly over 10 minutes
The table below shows the loading dose in milliliters (mL) of milrinone lactate (1mg/mL) by patient body weight (kg). Loading Dose (mL) Using 1 mg/mL Concentration Patient Body Weight (kg) kg 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 mL 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 5.5 6 The loading dose may be given undiluted, but diluting to a rounded total volume of 10 or 20 mL (see Maintenance Dose for diluents) may simplify the visualization of the injection rate.
MAINTENANCE DOSE Infusion Rate Total Daily Dose (24 Hours) Minimum 0.375 mcg/kg/min 0.59 mg/kg Administer as a continuous intravenous infusion Standard 0.5 mcg/kg/min 0.77 mg/kg Maximum 0.75 mcg/kg/min 1.13 mg/kg Milrinone lactate drawn from vials should be diluted prior to maintenance dose administration. The diluents that may be used are 0.45% Sodium Chloride Injection USP, 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection USP, or 5% Dextrose Injection USP. The table below shows the volume of diluent in milliliters (mL) that must be used to achieve 200 mcg/mL concentration for infusion, and the resultant total volumes.
Desired Infusion Concentration mcg/mL Milrinone Lactate Injection 1 mg/mL (mL) Diluent (mL) Total Volume (mL) 200 10 40 50 200 20 80 100 The infusion rate should be adjusted according to hemodynamic and clinical response. Patients should be closely monitored. In controlled clinical studies, most patients showed an improvement in hemodynamic status as evidenced by increases in cardiac output and reductions in pulmonary capillary wedge pressure.
Note: See Dosage Adjustment in Renally Impaired Patients. Dosage may be titrated to the maximum hemodynamic effect and should not exceed 1.13 mg/kg/day. Duration of therapy should depend upon patient responsiveness.
The maintenance dose in mL/hr by patient body weight (kg) may be determined by reference to the following table.
Milrinone Infusion Rate (mL/hr) Using 200 mcg/mL Concentration Maintenance Dose (mcg/kg/min) Patient Body Weight (kg) 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 0.375 3.4 4.5 5.6 6.8 7.9 9 10.1 11.3 12.4 13.5 0.4 3.6 4.8 6 7.2 8.4 9.6 10.8 12 13.2 14.4 0.5 4.5 6 7.5 9 10.5 12 13.5 15 16.5 18 0.6 5.4 7.2 9 10.8 12.6 14.4 16.2 18 19.8 21.6 0.7 6.3 8.4 10.5 12.6 14.7 16.8 18.9 21 23.1 25.2 0.75 6.8 9 11.3 13.5 15.8 18 20.3 22.5 24.8 27 When administering milrinone lactate by continuous infusion, it is advisable to use a calibrated electronic infusion device.
Intravenous drug products should be inspected visually and should not be used if particulate matter or discoloration is present.
Dosage Adjustment in Renally Impaired Patients
Data obtained from patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance = 0 to 30 mL/min) but without congestive heart failure have demonstrated that the presence of renal impairment significantly increases the terminal elimination half-life of milrinone lactate. Reductions in infusion rate may be necessary in patients with renal impairment. For patients with clinical evidence of renal impairment, the recommended infusion rate can be obtained from the following table:
Creatinine Clearance (mL/min/1.73m 2) Infusion Rate (mcg/kg/min) 5 0.2 10 0.23 20 0.28 30 0.33 40 0.38 50 0.43 -
HOW SUPPLIED
Milrinone Lactate Injection, USP is supplied as 10 mL single-dose vials in a box of 10, NDC: 83301-0016-2; as 20 mL single-dose vials box of 10, NDC: 83301-0017-2, containing a sterile, clear, colorless to pale yellow solution. Each mL contains milrinone lactate equivalent to 1 mg milrinone.
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Avoid freezing.
Discard unused portion after initial use.
Manufactured for:
Mullan Pharmaceutical Inc.
Pasadena, CA 91101
Manufactured by:
Shandong New Time Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.,
No. 1, North Outer Ring Road,
Feixian, Shandong 273400, China.
Rev. 10/2023 -
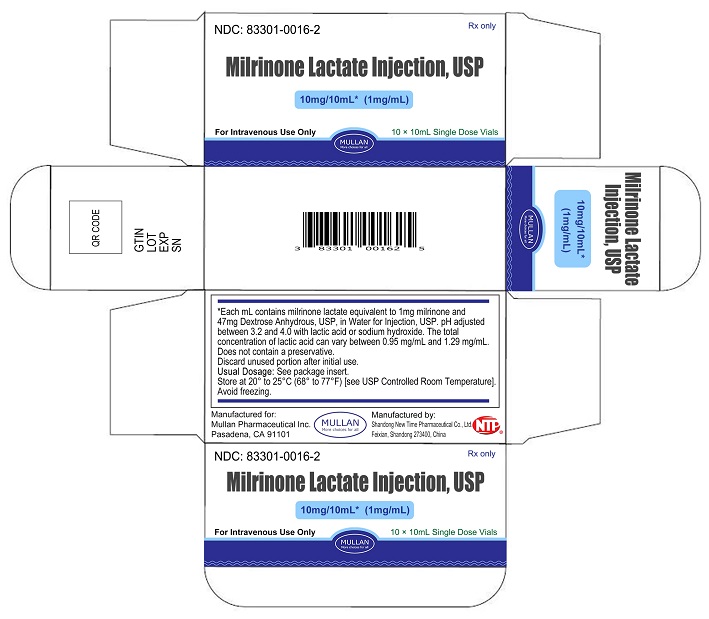
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL -10 mL Vial Container and Carton
10 mL Vial Container
Milrinone Lactate Injection
10 mg/ 10 mL (1 mg/mL)
NDC: 83301-0016-1
Rx only
For Intravenous Use Only

10 mL Vial Carton
Milrinone Lactate Injection
10 mg/ 10 mL (1 mg/mL)
NDC: 83301-0016-2
Rx only
For Intravenous Use Only
-
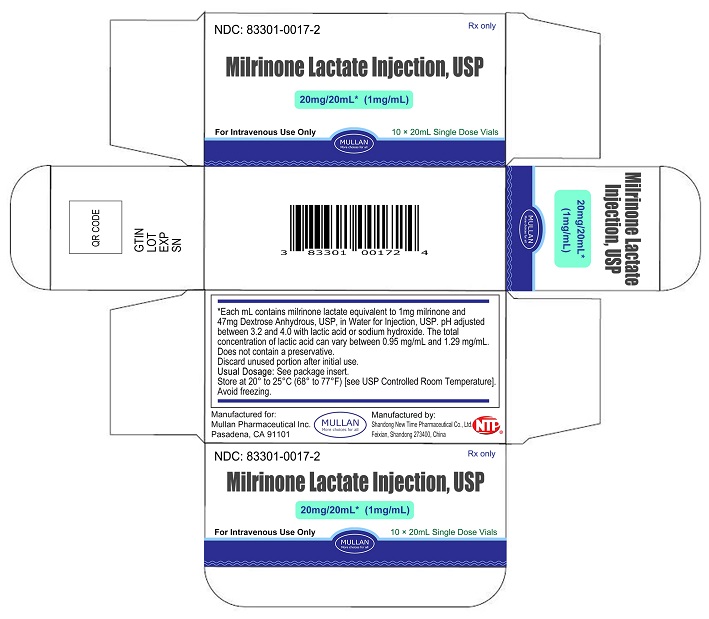
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL -20 mL Vial Container and Carton
20 mL Vial Container
Milrinone Lactate Injection
20 mg/ 20 mL (1 mg/mL)
NDC: 83301-0017-1
Rx only
For Intravenous Use Only

20 mL Vial Carton
Milrinone Lactate Injection
20 mg/ 20 mL (1 mg/mL)
NDC: 83301-0017-2
Rx only
For Intravenous Use Only
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
MILRINONE LACTATE
milrinone lactate injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 83301-0016 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength MILRINONE LACTATE (UNII: 9K8XR81MO8) (MILRINONE - UNII:JU9YAX04C7) MILRINONE 1 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength ANHYDROUS DEXTROSE (UNII: 5SL0G7R0OK) 47 mg in 1 mL LACTIC ACID (UNII: 33X04XA5AT) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 83301-0016-2 10 in 1 CARTON 09/18/2023 1 NDC: 83301-0016-1 1 mL in 1 VIAL; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA216373 09/18/2023 MILRINONE LACTATE
milrinone lactate injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 83301-0017 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength MILRINONE LACTATE (UNII: 9K8XR81MO8) (MILRINONE - UNII:JU9YAX04C7) MILRINONE 1 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength ANHYDROUS DEXTROSE (UNII: 5SL0G7R0OK) 47 mg in 1 mL LACTIC ACID (UNII: 33X04XA5AT) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 83301-0017-2 10 in 1 CARTON 09/18/2023 1 NDC: 83301-0017-1 1 mL in 1 VIAL; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA216373 09/18/2023 Labeler - Mullan Pharmaceutical Inc. (123283167) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Shandong New Time Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. 545298254 manufacture(83301-0016, 83301-0017)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.