DILTIAZEM HYDROCHLORIDE tablet, film coated
Diltiazem Hydrochloride by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Diltiazem Hydrochloride by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by NCS HealthCare of KY, Inc dba Vangard Labs. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
DESCRIPTION
Diltiazem hydrochloride is a calcium ion cellular influx inhibitor (slow channel blocker or calcium antagonist). Chemically, diltiazem hydrochloride is 1,5-Benzothiazepin-4(5H)one, 3-(acetyloxy)-5-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]-2,3-dihydro-2-(4-methoxyphenyl), monohydrochloride, (+)-cis-. The structural formula is:
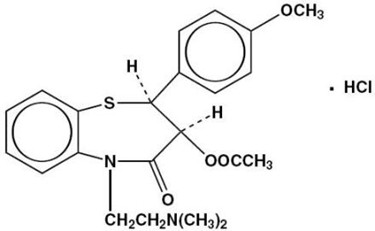
C22H26N2O4S HCl
M.W. 450.99Diltiazem hydrochloride, USP is a white to off-white crystalline powder with a bitter taste. It is soluble in water, methanol, and chloroform. Each tablet, for oral administration, contains 30 mg, 60 mg, 90 mg, or 120 mg diltiazem hydrochloride. In addition, each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: ethylcellulose, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, maltodextrin, polyethylene glycol, and sodium lauryl sulfate.
Diltiazem Hydrochloride Tablets, USP 30 mg, 60 mg, 90 mg and 120 mg meet USP Dissolution Test 2.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
The therapeutic benefits achieved with diltiazem are believed to be related to its ability to inhibit the influx of calcium ions during membrane depolarization of cardiac and vascular smooth muscle.
Mechanisms of Action
Although precise mechanisms of its antianginal actions are still being delineated, diltiazem is believed to act in the following ways:
1. Angina Due to Coronary Artery Spasm
Diltiazem has been shown to be a potent dilator of coronary arteries both epicardial and subendocardial. Spontaneous and ergonovine-induced coronary artery spasm are inhibited by diltiazem.
2. Exertional Angina
Diltiazem has been shown to produce increases in exercise tolerance, probably due to its ability to reduce myocardial oxygen demand. This is accomplished via reductions in heart rate and systemic blood pressure at submaximal and maximal exercise work loads.
In animal models, diltiazem interferes with the slow inward (depolarizing) current in excitable tissue. It causes excitation-contraction uncoupling in various myocardial tissues without changes in the configuration of the action potential. Diltiazem produces relaxation of coronary vascular smooth muscle and dilation of both large and small coronary arteries at drug levels which cause little or no negative inotropic effect. The resultant increases in coronary blood flow (epicardial and subendocardial) occur in ischemic and nonischemic models and are accompanied by dose dependent decreases in systemic blood pressure and decreases in peripheral resistance.
Hemodynamic and Electrophysiologic Effects
Like other calcium antagonists, diltiazem decreases sinoatrial and atrioventricular conduction in isolated tissues and has a negative inotropic effect in isolated preparations. In the intact animal, prolongation of the AH interval can be seen at higher doses.
In man, diltiazem prevents spontaneous and ergonovine-provoked coronary artery spasm. It causes a decrease in peripheral vascular resistance and a modest fall in blood pressure and, in exercise tolerance studies in patients with ischemic heart disease, reduces the heart rate-blood pressure product for any given workload. Studies to date, primarily in patients with good ventricular function, have not revealed evidence of a negative inotropic effect; cardiac output, ejection fraction, and left ventricular end diastolic pressure have not been affected. There are as yet few data on the interaction of diltiazem and beta-blockers. Resting heart rate is usually unchanged or slightly reduced by diltiazem.
Intravenous diltiazem hydrochloride in doses of 20 mg prolongs AH conduction time and AV node functional and effective refractory periods approximately 20%. In a study involving single oral doses of 300 mg of diltiazem hydrochloride in six normal volunteers, the average maximum PR prolongation was 14% with no instances of greater than first-degree AV block. Diltiazem-associated prolongation of the AH interval is not more pronounced in patients with first-degree heart block. In patients with sick sinus syndrome, diltiazem significantly prolongs sinus cycle length (up to 50% in some cases).
Chronic oral administration of diltiazem hydrochloride in doses of up to 240 mg/day has resulted in small increases in PR interval, but has not usually produced abnormal prolongation.
Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism
Diltiazem is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and is subject to an extensive first-pass effect, giving an absolute bioavailability (compared to intravenous dosing) of about 40%. Diltiazem undergoes extensive metabolism in which 2% to 4% of the unchanged drug appears in the urine. In vitro binding studies show diltiazem is 70% to 80% bound to plasma proteins. Competitive in vitro ligand binding studies have also shown diltiazem binding is not altered by therapeutic concentrations of digoxin, hydrochlorothiazide, phenylbutazone, propranolol, salicylic acid, or warfarin. The plasma elimination half-life following single or multiple drug administration is approximately 3.0 to 4.5 hours. Desacetyl diltiazem is also present in the plasma at levels of 10% to 20% of the parent drug and is 25% to 50% as potent as a coronary vasodilator as diltiazem. Minimum therapeutic plasma levels of diltiazem appear to be in the range of 50 to 200 ng/mL. There is a departure from linearity when dose strengths are increased. A study that compared patients with normal hepatic function to patients with cirrhosis found an increase in half-life and a 69% increase in AUC (area-under-the plasma concentration vs time curve) in the hepatically impaired patients. A single study in nine patients with severely impaired renal functions showed no difference in the pharmacokinetic profile of diltiazem as compared to patients with normal renal function.
Diltiazem Hydrochloride Tablets
Diltiazem is absorbed from the tablet formulation to about 98% of a reference solution. Single oral doses of 30 mg to 120 mg of diltiazem hydrochloride tablets result in detectable plasma levels within 30 to 60 minutes and peak plasma levels 2 to 4 hours after drug administration. As the dose of diltiazem hydrochloride tablets is increased from a daily dose of 120 mg (30 mg qid) to 240 mg (60 mg qid) daily, there is an increase in area-under-the-curve of 2.3 times. When the dose is increased from 240 mg to 360 mg daily, there is an increase in area-under-the-curve of 1.8 times.
- INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Diltiazem hydrochloride tablets are contraindicated in (1) patients with sick sinus syndrome except in the presence of a functioning ventricular pacemaker, (2) patients with second- or third-degree AV block except in the presence of a functioning ventricular pacemaker, (3) patients with hypotension (less than 90 mm Hg systolic), (4) patients who have demonstrated hypersensitivity to the drug, and (5) patients with acute myocardial infarction and pulmonary congestion documented by X-ray on admission.
-
WARNINGS
1. Cardiac Conduction
Diltiazem prolongs AV node refractory periods without significantly prolonging sinus node recovery time, except in patients with sick sinus syndrome. This effect may rarely result in abnormally slow heart rates (particularly in patients with sick sinus syndrome) or second- or-third-degree AV block (six of 1,243 patients for 0.48%). Concomitant use of diltiazem with beta-blockers or digitalis may result in additive effects on cardiac conduction. A patient with Prinzmetal's angina developed periods of asystole (2 to 5 seconds) after a single dose of 60 mg of diltiazem. (See ADVERSE REACTIONS.)
2. Congestive Heart Failure
Although diltiazem has a negative inotropic effect in isolated animal tissue preparations, hemodynamic studies in humans with normal ventricular function have not shown a reduction in cardiac index nor consistent negative effects on contractility (dp/dt). Experience with the use of diltiazem alone or in combination with beta-blockers in patients with impaired ventricular function is very limited. Caution should be exercised when using the drug in such patients.
3. Hypotension
Decreases in blood pressure associated with diltiazem therapy may occasionally result in symptomatic hypotension.
4. Acute Hepatic Injury
In rare instances, significant elevations in enzymes such as alkaline phosphatase, LDH, SGOT, SGPT and other phenomena consistent with acute hepatic injury have been noted. These reactions have been reversible upon discontinuation of drug therapy. The relationship to diltiazem is uncertain in most cases, but probable in some. (See PRECAUTIONS.)
-
PRECAUTIONS
General
Diltiazem is extensively metabolized by the liver and excreted by the kidneys and in bile. As with any drug given over prolonged periods, laboratory parameters of renal and hepatic function should be monitored at regular intervals. The drug should be used with caution in patients with impaired renal or hepatic function. In subacute and chronic dog and rat studies designed to produce toxicity, high doses of diltiazem were associated with hepatic damage. In special subacute hepatic studies, oral doses of 125 mg/kg and higher in rats were associated with histological changes in the liver, which were reversible when the drug was discontinued. In dogs, doses of 20 mg/kg were also associated with hepatic changes; however, these changes were reversible with continued dosing. Dermatological events (see ADVERSE REACTIONS) may be transient and may disappear despite continued use of diltiazem. However, skin eruptions progressing to erythema multiforme and/or exfoliative dermatitis have also been infrequently reported. Should a dermatologic reaction persist, the drug should be discontinued.
Drug Interactions
Due to the potential for additive effects, caution and careful titration are warranted in patients receiving diltiazem concomitantly with any agents known to affect cardiac contractility and/or conduction. (See WARNINGS.)
Pharmacologic studies indicate that there may be additive effects in prolonging AV conduction when using beta-blockers or digitalis concomitantly with diltiazem. (See WARNINGS.)
As with all drugs, care should be exercised when treating patients with multiple medications. Diltiazem is both a substrate and an inhibitor of the cytochrome P-450 3A4 enzyme treatment. Other drugs that are specific substrates, inhibitors, or inducers of this enzyme system may have a significant impact on the efficacy and side effect profile of diltiazem. Patients taking other drugs that are substrates of CYP450 3A4, especially patients with renal and/or hepatic impairment, may require dosage adjustment when starting or stopping concomitantly administered diltiazem in order to maintain optimum therapeutic blood levels.
Anesthetics
The depression of cardiac contractility, conductivity, and automaticity, as well as the vascular dilation associated with anesthetics, may be potentiated by calcium channel blockers. When used concomitantly, anesthetics and calcium blockers should be titrated carefully.
Benzodiazepines
Studies showed that diltiazem increased the AUC of midazolam and triazolam by 3- to 4-fold and the Cmax by 2-fold, compared to placebo. The elimination half-life of midazolam and triazolam also increased (1.5- to 2.5-fold) during coadministration with diltiazem. These pharmacokinetic effects seen during diltiazem coadministration can result in increased clinical effects (e.g., prolonged sedation) of both midazolam and triazolam.
Beta-Blockers
Controlled and uncontrolled domestic studies suggest that concomitant use of diltiazem and beta-blockers is usually well tolerated. Available data are not sufficient, however, to predict the effects of concomitant treatment, particularly in patients with left ventricular dysfunction or cardiac conduction abnormalities.
Administration of diltiazem concomitantly with propranolol in five normal volunteers resulted in increased propranolol levels in all subjects, and bioavailability of propranolol was increased approximately 50%. In vitro, propranolol appears to be displaced from its binding sites by diltiazem. If combination therapy is initiated or withdrawn in conjunction with propranolol, an adjustment in the propranolol dose may be warranted. (See WARNINGS.)
Buspirone
In nine healthy subjects, diltiazem significantly increased the mean buspirone AUC 5.5-fold and Cmax 4.1-fold compared to placebo. The T1/2 and Tmax of buspirone were not significantly affected by diltiazem. Enhanced effects and increased toxicity of buspirone may be possible during concomitant administration with diltiazem. Subsequent dose adjustments may be necessary during coadministration, and should be based on clinical assessment.
Carbamazepine
Concomitant administration of diltiazem with carbamazepine has been reported to result in elevated serum levels of carbamazepine (40% to 72% increase) resulting in toxicity in some cases. Patients receiving these drugs concurrently should be monitored for a potential drug interaction.
Cimetidine
A study in six healthy volunteers has shown a significant increase in peak diltiazem plasma levels (58%) and area-under-the-curve (53%) after a one-week course of cimetidine at 1,200 mg per day and a single dose of diltiazem 60 mg. Ranitidine produced smaller, non-significant increases. The effect may be mediated by cimetidine's known inhibition of hepatic cytochrome P-450, the enzyme system responsible for the first-pass metabolism of diltiazem. Patients currently receiving diltiazem therapy should be carefully monitored for a change in pharmacological effect when initiating and discontinuing therapy with cimetidine. An adjustment in the diltiazem dose may be warranted.
Clonidine
Sinus bradycardia resulting in hospitalization and pacemaker insertion has been reported in association with the use of clonidine concurrently with diltiazem. Monitor heart rate in patients receiving concomitant diltiazem and clonidine.
Cyclosporine
A pharmacokinetic interaction between diltiazem and cyclosporine has been observed during studies involving renal and cardiac transplant patients. In renal and cardiac transplant recipients, a reduction of cyclosporine trough dose ranging from 15% to 48% was necessary to maintain cyclosporine trough concentrations similar to those seen prior to the addition of diltiazem. If these agents are to be administered concurrently, cyclosporine concentrations should be monitored, especially when diltiazem therapy is initiated, adjusted or discontinued. The effect of cyclosporine on diltiazem plasma concentrations has not been evaluated.
Digitalis
Administration of diltiazem with digoxin in 24 healthy male subjects increased plasma digoxin concentrations approximately 20%. Another investigator found no increase in digoxin levels in 12 patients with coronary artery disease. Since there have been conflicting results regarding the effect of digoxin levels, it is recommended that digoxin levels be monitored when initiating, adjusting, and discontinuing diltiazem therapy to avoid possible over- or under-digitalization. (See WARNINGS.)
Quinidine
Diltiazem significantly increases the AUC (0→∞) of quinidine by 51%, T1/2 by 36%, and decreases its CLoral by 33%. Monitoring for quinidine adverse effects may be warranted and the dose adjusted accordingly.
Rifampin
Coadministration of rifampin with diltiazem lowered the diltiazem plasma concentrations to undetectable levels. Coadministration of diltiazem with rifampin or any known CYP3A4 inducer should be avoided when possible, and alternative therapy considered.
Statins
Diltiazem is an inhibitor of CYP3A4 and has been shown to increase significantly the AUC of some statins. The risk of myopathy and rhabdomyolysis with statins metabolized by CYP3A4 may be increased with concomitant use of diltiazem. When possible, use a non-CYP3A4-metabolized statin together with diltiazem; otherwise, dose adjustments for both diltiazem and the statin should be considered along with close monitoring for signs and symptoms of any statin related adverse events.
In a healthy volunteer cross-over study (N = 10), coadministration of a single 20 mg dose of simvastatin at the end of a 14-day regimen with 120 mg BID diltiazem SR resulted in a 5-fold increase in mean simvastatin AUC vs. simvastatin alone. Subjects with increased average steady-state exposures of diltiazem showed a greater fold increase in simvastatin exposure. Computer-based simulations showed that at a daily dose of 480 mg of diltiazem, an 8- to 9-fold mean increase in simvastatin AUC can be expected. If coadministration of simvastatin with diltiazem is required, limit the daily doses of simvastatin to 10 mg and diltiazem to 240 mg.
In a ten-subject randomized, open-label, 4-way cross-over study, coadministration of diltiazem (120 mg BID diltiazem SR for 2 weeks) with a single 20 mg dose of lovastatin resulted in 3- to 4-fold increase in mean lovastatin AUC and Cmax vs. lovastatin alone. In the same study, there was no significant change in 20 mg single dose pravastatin AUC and Cmax during diltiazem coadministration. Diltiazem plasma levels were not significantly affected by lovastatin or pravastatin.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
A 24-month study in rats and a 21-month study in mice showed no evidence of carcinogenicity. There was also no mutagenic response in in vitro bacterial tests. No intrinsic effect on fertility was observed in rats.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy Category C
Reproduction studies have been conducted in mice, rats, and rabbits. Administration of doses ranging from 5 to 10 times greater (on a mg/kg basis) than the daily recommended therapeutic dose has resulted in embryo and fetal lethality. These doses, in some studies, have been reported to cause skeletal abnormalities. In the perinatal/postnatal studies, there was some reduction in early individual pup weights and survival rates. There was an increased incidence of stillbirths at doses of 20 times the human dose or greater.
There are no well controlled studies in pregnant women; therefore, use diltiazem in pregnant women only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Nursing Mothers
Diltiazem is excreted in human milk. One report suggests that concentrations in breast milk may approximate serum levels. If use of diltiazem is deemed essential, an alternative method of infant feeding should be instituted.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of diltiazem did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Serious adverse reactions have been rare in studies carried out to date, but it should be recognized that patients with impaired ventricular function and cardiac conduction abnormalities usually have been excluded.
In domestic placebo-controlled angina trials, the incidence of adverse reactions reported during diltiazem therapy was not greater than that reported during placebo therapy.
The following represent occurrences observed in clinical studies of angina patients. In many cases, the relationship to diltiazem has not been established. The most common occurrences from these studies, as well their frequency of presentation, are edema (2.4%), headache (2.1%), nausea (1.9%), dizziness (1.5%), rash (1.3%), and asthenia (1.2%). In addition, the following events were reported infrequently (less than 1%):
Cardiovascular: Angina, arrhythmia, AV block (first-degree), AV block (second- or third-degree - see WARNINGS: Cardiac Conduction), bradycardia, bundle branch block, congestive heart failure, ECG abnormality, flushing, hypotension, palpitations, syncope, tachycardia, ventricular extrasystoles.
Nervous System: Abnormal dreams, amnesia, depression, gait abnormality, hallucinations, insomnia, nervousness, paresthesia, personality change, somnolence, tremor.
Gastrointestinal: Anorexia, constipation, diarrhea, dysgeusia, dyspepsia, mild elevations of alkaline phosphatase, SGOT, SGPT, and LDH (see WARNINGS: Acute Hepatic Injury), thirst, vomiting, weight increase.
Dermatological: Petechiae, photosensitivity, pruritus, urticaria.
Other: Amblyopia, CPK elevation, dry mouth, dyspnea, epistaxis, eye irritation, hyperglycemia, hyperuricemia, impotence, muscle cramps, nasal congestion, nocturia, osteoarticular pain, polyuria, sexual difficulties, tinnitus.
The following post-marketing events have been reported infrequently in patients receiving diltiazem: acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis, allergic reactions, alopecia, angioedema (including facial or periorbital edema), asystole, erythema multiforme (including Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis), extrapyramidal symptoms, gingival hyperplasia, hemolytic anemia, increased bleeding time, leukopenia, photosensitivity (including lichenoid keratosis and hyperpigmentation at sun-exposed skin areas), purpura, retinopathy, myopathy, and thrombocytopenia. There have been observed cases of a generalized rash, some characterized as leukocytoclastic vasculitis. In addition, events such as myocardial infarction have been observed, which are not readily distinguishable from the natural history of the disease in these patients. A definitive cause and effect relationship between these events and diltiazem therapy cannot yet be established. Exfoliative dermatitis (proven by rechallenge) has also been reported.
-
OVERDOSAGE
The oral LD50s in mice and rats range from 415 to 740 mg/kg and from 560 to 810 mg/kg, respectively. The intravenous LD50s in these species were 60 and 38 mg/kg, respectively. The oral LD50 in dogs is considered to be in excess of 50 mg/kg, while lethality was seen in monkeys at 360 mg/kg.
The toxic dose in man is not known. Due to extensive metabolism, blood levels after a standard dose of diltiazem can vary over 10-fold, limiting the usefulness of blood levels in overdose cases.
There have been reports of diltiazem overdose in amounts ranging from < 1 g to 18 g. Of cases with known outcome, most patients recovered and in cases with a fatal outcome, the majority involved multiple drug ingestion.
Events observed following diltiazem overdose included bradycardia, hypotension, heart block, and cardiac failure. Most reports of overdose described some supportive medical measure and/or drug treatment. Bradycardia frequently responded favorably to atropine, as did heart block, although cardiac pacing was also frequently utilized to treat heart block. Fluids and vasopressors were used to maintain blood pressure, and in cases of cardiac failure, inotropic agents were administered. In addition, some patients received treatment with ventilatory support, gastric lavage, activated charcoal, and/or intravenous calcium.
The effectiveness of intravenous calcium administration to reverse the pharmacological effects of diltiazem overdose has been inconsistent. In a few reported cases, overdose with calcium channel blockers associated with hypotension and bradycardia that was initially refractory to atropine became more responsive to atropine after the patients received intravenous calcium. In some cases intravenous calcium has been administered (1 g calcium chloride or 3 g calcium gluconate) over 5 minutes and repeated every 10 to 20 minutes as necessary. Calcium gluconate has also been administered as a continuous infusion at a rate of 2 g per hour for 10 hours. Infusions of calcium for 24 hours or more may be required. Patients should be monitored for signs of hypercalcemia.
In the event of overdose or exaggerated response, appropriate supportive measures should be employed in addition to gastrointestinal decontamination. Diltiazem does not appear to be removed by peritoneal or hemodialysis. Limited data suggest that plasmapheresis or charcoal hemoperfusion may hasten diltiazem elimination following overdose. Based on the known pharmacological effects of diltiazem and/or reported clinical experiences, the following measures may be considered:
Bradycardia: Administer atropine (0.60 mg to 1 mg). If there is no response to vagal blockade, administer isoproterenol cautiously.
High Degree AV Block: Treat as for bradycardia above. Fixed high-degree AV block should be treated with cardiac pacing.
Cardiac Failure: Administer inotropic agents (isoproterenol, dopamine, or dobutamine) and diuretics.
Hypotension: Vasopressors (e.g., dopamine or norepinephrine).
Actual treatment and dosage should depend on the severity of the clinical situation and the judgment and experience of the treating physician.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Exertional Angina Pectoris Due to Atherosclerotic Coronary Artery Disease or Angina Pectoris at Rest Due to Coronary Artery Spasm
Dosage must be adjusted to each patient's needs. Starting with 30 mg 4 times daily, before meals and at bedtime, dosage should be increased gradually (given in divided doses 3 or 4 times daily) at one-to two-day intervals until optimum response is obtained. Although individual patients may respond to any dosage level, the average optimum dosage range appears to be 180 to 360 mg/day. There are no available data concerning dosage requirements in patients with impaired renal or hepatic function. If the drug must be used in such patients, titration should be carried out with particular caution.
Concomitant Use with Other Cardiovascular Agents
1. Sublingual NTG may be taken as required to abort acute anginal attacks during diltiazem therapy.
2. Prophylactic Nitrate Therapy: Diltiazem may be safely coadministered with short- and long-acting nitrates, but there have been no controlled studies to evaluate the antianginal effectiveness of this combination.
3. Beta-blockers (See WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS.)
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Diltiazem Hydrochloride Tablets, USP are available containing 30 mg, 60 mg, 90 mg or 120 mg of diltiazem hydrochloride, USP.
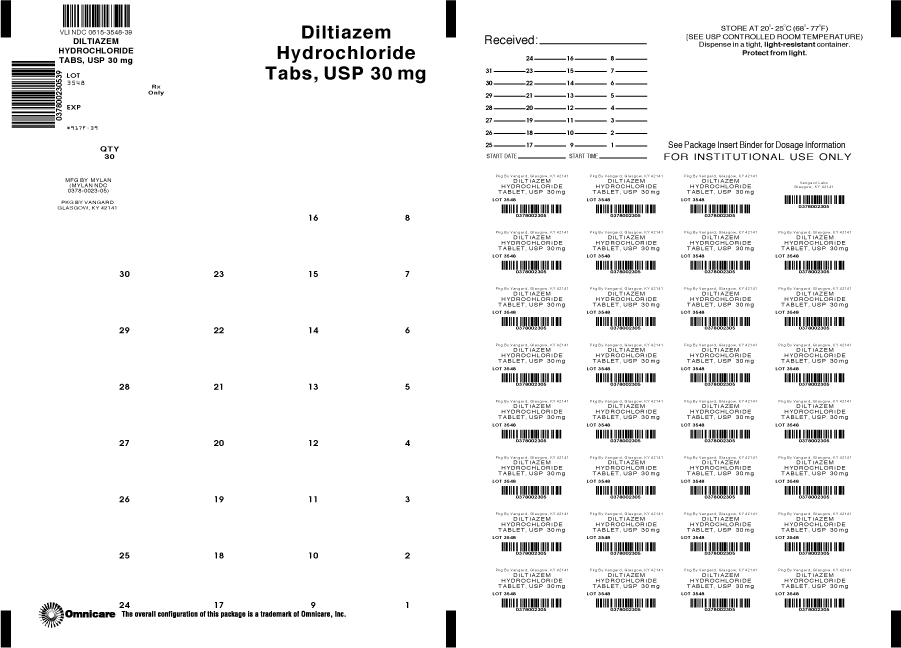
The 30 mg tablets are white film-coated, round, unscored, tablets debossed with M over 23 on one side of the tablet and blank on the other side. They are available as follows:
NDC: 0615-3548-39
blisterpacks of 30 tablets
NDC: 0615-3548-31
blisterpacks of 31 tabletsThe 60 mg tablets are white film-coated, round, tablets debossed with M over 45 on one side of the tablet and scored on the other side. They are available as follows:
NDC: 0615-3549-39
blisterpacks of 30 tabletsThe 90 mg tablets are white film-coated, capsule-shaped tablets debossed with M135 on one side of the tablet and scored on the other side. They are available as follows:
NDC: 0615-3550-39
blisterpacks of 30 tabletsThe 120 mg tablets are white film-coated, capsule-shaped tablets debossed with M525 on one side of the tablet and scored on the other side. They are available as follows:
NDC: 0615-3551-39
blisterpacks of 30 tablets - SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
- Principal Display Panel
-
Principal Display Panel
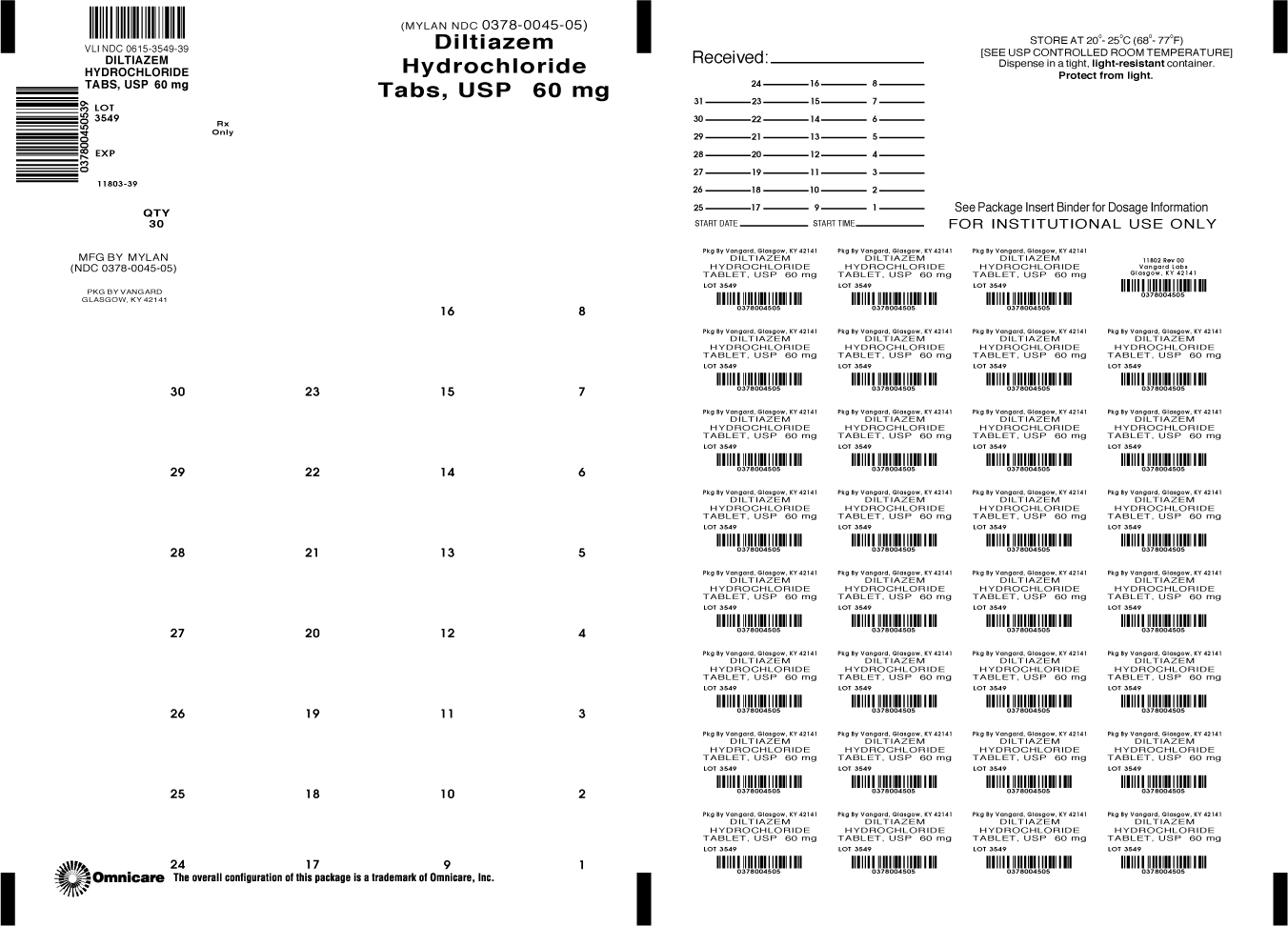
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 60 mg
NDC: 0615-3549-39
Diltiazem
Hydrochloride
Tablets, USP60 mg
Rx only 30 TABLETS
-
Principal Display Panel
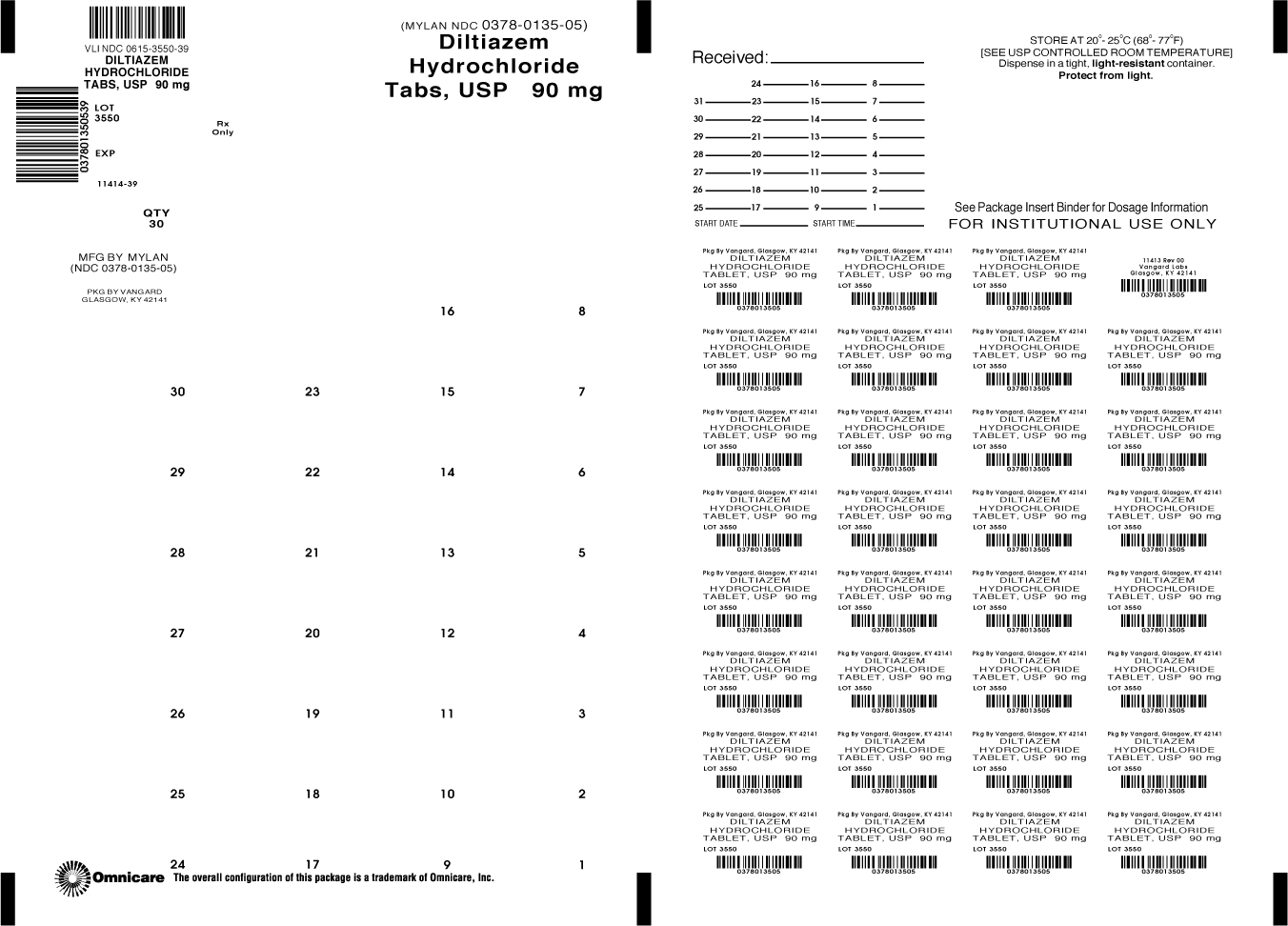
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 90 mg
NDC: 0615-3550-39
Diltiazem
Hydrochloride
Tablets, USP90 mg
Rx only 30 TABLETS
-
Principal Display Panel
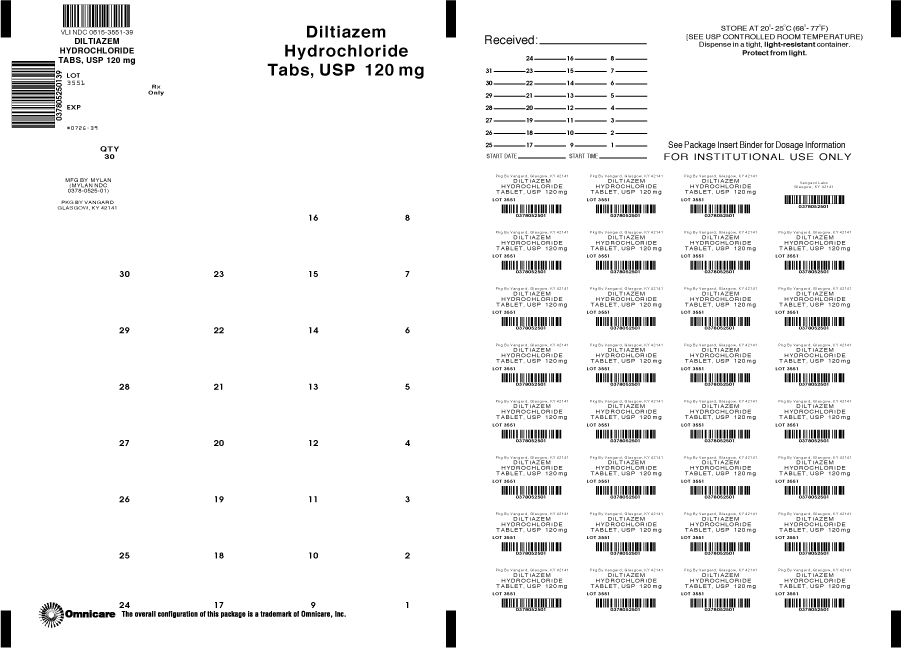
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 120 mg
NDC: 0615-3551-39
Diltiazem
Hydrochloride
Tablets, USP120 mg
Rx only 30 TABLETS
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
DILTIAZEM HYDROCHLORIDE
diltiazem hydrochloride tablet, film coatedProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0615-3548(NDC:0378-0023) Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength DILTIAZEM HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: OLH94387TE) (DILTIAZEM - UNII:EE92BBP03H) DILTIAZEM HYDROCHLORIDE 30 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength ETHYLCELLULOSES (UNII: 7Z8S9VYZ4B) HYPROMELLOSES (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) MALTODEXTRIN (UNII: 7CVR7L4A2D) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOLS (UNII: 3WJQ0SDW1A) SODIUM LAURYL SULFATE (UNII: 368GB5141J) Product Characteristics Color WHITE Score no score Shape ROUND Size 8mm Flavor Imprint Code M;23 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0615-3548-31 31 in 1 BLISTER PACK; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 0615-3548-39 30 in 1 BLISTER PACK; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA072838 12/04/2012 DILTIAZEM HYDROCHLORIDE
diltiazem hydrochloride tablet, film coatedProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0615-3549(NDC:0378-0045) Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength DILTIAZEM HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: OLH94387TE) (DILTIAZEM - UNII:EE92BBP03H) DILTIAZEM HYDROCHLORIDE 60 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength ETHYLCELLULOSES (UNII: 7Z8S9VYZ4B) HYPROMELLOSES (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) MALTODEXTRIN (UNII: 7CVR7L4A2D) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOLS (UNII: 3WJQ0SDW1A) SODIUM LAURYL SULFATE (UNII: 368GB5141J) Product Characteristics Color WHITE Score 2 pieces Shape ROUND Size 10mm Flavor Imprint Code M;45 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0615-3549-39 30 in 1 BLISTER PACK; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA072838 12/04/2012 DILTIAZEM HYDROCHLORIDE
diltiazem hydrochloride tablet, film coatedProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0615-3550(NDC:0378-0135) Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength DILTIAZEM HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: OLH94387TE) (DILTIAZEM - UNII:EE92BBP03H) DILTIAZEM HYDROCHLORIDE 90 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength ETHYLCELLULOSES (UNII: 7Z8S9VYZ4B) HYPROMELLOSES (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) MALTODEXTRIN (UNII: 7CVR7L4A2D) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOLS (UNII: 3WJQ0SDW1A) SODIUM LAURYL SULFATE (UNII: 368GB5141J) Product Characteristics Color WHITE Score 2 pieces Shape CAPSULE Size 18mm Flavor Imprint Code M135 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0615-3550-39 30 in 1 BLISTER PACK; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA072838 12/04/2012 DILTIAZEM HYDROCHLORIDE
diltiazem hydrochloride tablet, film coatedProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0615-3551(NDC:0378-0525) Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength DILTIAZEM HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: OLH94387TE) (DILTIAZEM - UNII:EE92BBP03H) DILTIAZEM HYDROCHLORIDE 120 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength ETHYLCELLULOSES (UNII: 7Z8S9VYZ4B) HYPROMELLOSES (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) MALTODEXTRIN (UNII: 7CVR7L4A2D) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOLS (UNII: 3WJQ0SDW1A) SODIUM LAURYL SULFATE (UNII: 368GB5141J) Product Characteristics Color WHITE Score 2 pieces Shape CAPSULE Size 19mm Flavor Imprint Code M525 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0615-3551-39 30 in 1 BLISTER PACK; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA072838 12/04/2012 Labeler - NCS HealthCare of KY, Inc dba Vangard Labs (050052943) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations NCS HealthCare of KY, Inc dba Vangard Labs 050052943 REPACK(0615-3548, 0615-3549, 0615-3550, 0615-3551)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.