HYDROXYPROGESTERONE CAPROATE injection
Hydroxyprogesterone Caproate by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Hydroxyprogesterone Caproate by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Mylan Institutional LLC. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
DESCRIPTION
Hydroxyprogesterone Caproate Injection, USP is a sterile, long-acting preparation of the caproate ester of the naturally-occurring progestational hormone, hydroxyprogesterone, in an oil solution for intramuscular use.
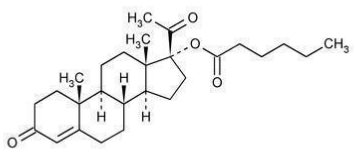
The chemical name for hydroxyprogesterone caproate is pregn-4-ene-3,20-dione, 17[(1-oxohexyl)oxy]. It has an empirical formula of C27H40O4 and a molecular weight of 428.60. Hydroxyprogesterone caproate exists as white to creamy white crystalline powder.
The structural formula is:
Each 5 mL multiple-dose vial contains hydroxyprogesterone caproate, 250 mg/mL, in castor oil (28.6% v/v) and benzyl benzoate (46% v/v) with the preservative benzyl alcohol (2% v/v).
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Hydroxyprogesterone is a potent, long-acting, progestational steroid ester which transforms proliferative endothelium into secretory endothelium, induces mammary gland duct development, and inhibits the production and/or release of gonadotropic hormone; it also shows slight estrogenic, androgenic, or corticoid effects as well, but should not be relied upon for these effects.
In advanced adenocarcinoma of the uterine corpus, Hydroxyprogesterone Caproate Injection in a dosage of 1,000 mg or more, one or more times each week, often induces regressive changes.
Absorption: Peak serum levels of hydroxyprogesterone caproate appeared after 3 to 7 days in non-pregnant female subjects following a single intramuscular injection of 1,000 mg hydroxyprogesterone caproate. The pharmacokinetics of the 250 mg dose of hydroxyprogesterone caproate has not been evaluated in a study.
Metabolism: The conjugated metabolites include sulfated and glucuronidated products. In vitro data indicate that the metabolism of hydroxyprogesterone caproate is predominantly mediated by CYP3A4 and CYP3A5.
Excretion: Both conjugated metabolites and free steroids are excreted in the urine and feces, with the conjugated metabolites being prominent.
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Hydroxyprogesterone Caproate Injection, USP is indicated in non-pregnant women: for the treatment of advanced adenocarcinoma of the uterine corpus (Stage III or IV); in the management of amenorrhea (primary and secondary) and abnormal uterine bleeding due to hormonal imbalance in the absence of organic pathology, such as submucous fibroids or uterine cancer; as a test for endogenous estrogen production and for the production of secretory endometrium and desquamation.
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Hydroxyprogesterone caproate is contraindicated in patients with known or suspected carcinoma of the breast, other hormone-sensitive cancer, or history of these conditions; undiagnosed abnormal vaginal bleeding; liver dysfunction or disease; missed abortion, and in those with a history of hypersensitivity to the drug. Hydroxyprogesterone caproate is also contraindicated as a diagnostic test for pregnancy and in patients with current or history of thrombotic or thromboembolic disorders.
-
WARNINGS
Thrombotic and Thromboembolic Events
Discontinue the medication pending examination if there is a sudden partial or complete loss of vision or if there is a sudden onset of proptosis, diplopia, or migraine. Medication should be stopped if examination reveals papilledema or retinal vascular lesions.
-
PRECAUTIONS
Detectable amounts of progestins have been identified in the milk of mothers receiving the drug. Many studies have found no adverse effects of progestins on breastfeeding performance, or on the health, growth, or development of the infant.
Because progestational drugs may cause some degree of fluid retention, conditions that might be influenced by this effect, such as asthma, migraine, epilepsy, or cardiac or renal dysfunction require careful observation.
The pretreatment physical examination should include examination of the breasts and pelvic organs and a Papanicolaou smear.
In relation to irregular bleeding which does not respond predictably to the hormone therapy, nonfunctional causes should be borne in mind and adequate diagnostic measures instituted.
Any influence of prolonged sex hormone medication on pituitary, ovarian, adrenal, hepatic, or uterine function awaits further study.
The pathologist should be advised of progesterone therapy when relevant specimens are submitted.
Patients who have a history of psychic depression should be carefully observed and the drug discontinued if the depression recurs to a serious degree.
Information For The Patient
Counsel patients that hydroxyprogesterone caproate injections may cause pain, soreness, swelling, itching or bruising. Inform the patient to contact her physician if she notices increased discomfort over time, oozing of blood or fluid, or inflammatory reactions at the injection site.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Mylan Pharmaceuticals Inc. at 1-877-446-3679 (1-877-4-INFO-RX) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
A. Serious arterial thrombotic and venous thromboembolic events, including cases of pulmonary emboli (some fatal), deep vein thrombosis, myocardial infarction, and strokes, have been reported in women using progestins.
B. Neuroocular lesions (e.g., retinal thrombosis and optic neuritis); nausea; vomiting; gastrointestinal symptoms (such as abdominal cramps or bloating); edema; breakthrough bleeding, spotting, or withdrawal bleeding; breast tenderness; changes in body weight (increase or decrease); headache; increase in cervical mucus; allergic rash; abscess; pain at the injection site; migraine headaches.
C. Chloasma or melasma, cholestatic jaundice, rise in blood pressure, mental depression, and amenorrhea during or after treatment.
D. Post-treatment anovulation, cystitis, hirsutism, loss of scalp hair, changes in libido, changes in appetite, dizziness, fatigue, backache, itching, or amenorrhea.
E. The following laboratory tests may be affected by progestins: hepatic function (increased sulfobromophthalein retention and other tests); coagulation tests (increase in prothrombin and Factors VII, VIII, IX, and X); thyroid function tests (increase in PBI and butanol extractable protein-bound iodine, decrease in T3 uptake values).
A few instances of coughing, dyspnea, constriction of the chest, and/or allergic-like reactions have occurred following hydroxyprogesterone caproate therapy; the likelihood of these occurring may be increased at higher dosage levels.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Suggested dosages are presented in the therapy guide. Because of the low viscosity of the vehicle, Hydroxyprogesterone Caproate Injection may be administered with a small gauge needle. Care should be taken to inject the preparation deeply into the upper outer quadrant of the gluteal muscle following the usual precautions for intramuscular injection. Since the 250 mg potency provides a high concentration in a small volume, particular care should be observed to administer the full dose.
Note: Use of a wet needle or syringe may cause the solution to become cloudy; however, this does not affect the potency of the material.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
Protect from light. Store vial in its box. Store upright. Discard any unused product within 28 days after first use.
THERAPY GUIDE
CYCLIC THERAPY SCHEDULE: (28-day cycle; repeated every 4 weeks)
Day 1 of each cycle: 20 mg Estradiol Valerate Injection, USP
2 weeks after Day 1: 250 mg Hydroxyprogesterone Caproate Injection, USP and 5 mg Estradiol Valerate Injection, USP
4 weeks after Day 1: This is Day 1 of next cycle
SUGGESTED CYCLIC REGIMEN Indications
Dosage
Started
Repeated
Stopped
Comments
Amenorrhea (primary and secondary): Abnormal uterine bleeding due to hormonal imbalance in the absence of organic pathology, such as submucous fibroids or uterine cancer.
375 mg
Any time
-
-
Genital malignancy should be excluded before hormone therapy is started. Hydroxyprogesterone caproate is used as a “Medical D and C” to eliminate any proliferated endometrium from previous estrogenic action by conversion to secretory endometrium and desquamation. To determine onset of normal cyclic functions, patient should be observed for 2 or 3 cycles after cessation of therapy.
Cyclic Therapy Schedule
After 4 days of desquamation or, if there is no bleeding, 21 days after Hydroxyprogesterone Caproate Injection alone
Every 4 weeks
After 4 cycles
Production of secretory endometrium and desquamation
Patients not on estrogen therapy: Cyclic Therapy Schedule
Any time
Every 4 weeks
When cyclic therapy is no longer required
If estrogen deficiency has been prolonged, menstruation may not occur until estrogen has been given for several months.
Patients currently on estrogen therapy: 375 mg Hydroxyprogesterone Caproate Injection
Any time
-
-
Cyclic Therapy Schedule
After 4 days of desquamation or, if there is no bleeding, 21 days after Hydroxyprogesterone Caproate Injection alone
Every 4 weeks
When cyclic therapy is no longer required
SUGGESTED NON-CYCLIC REGIMEN Indications
Dosage
Started
Repeated
Stopped
Comments
Adenocarcinoma of uterine corpus in advanced stage (Stage III or IV)
1,000 mg or more
At once
1 or more times each week (1 to 7 g per week)
When relapse occurs, or after 12 weeks with no objective response
Should not be used in early stage (Stage I or II) in place of established anticancer therapy. May be used in advanced stage concomitantly with other anticancer therapy (surgery, α radiation, or chemotherapy, or combination of these). Treatment results reported to date have been better in histologically well-differentiated forms of endometrial adenocarcinoma. (The drug has not been adequately studied in non-endometrioid adenocarcinoma of the uterine corpus).
Test for endogenous estrogen production ("Medical D and C")
250 mg
Any time
For confirmation, 4 weeks after 1st injection
After 2nd injection
Non-pregnant patient with responsive endometrium; bleeding 7 to 14 days after injection indicates endogenous estrogen.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Hydroxyprogesterone Caproate Injection, USP is available in vials providing hydroxyprogesterone caproate with a potency of 250 mg per mL. The product is formulated in castor oil and 46% benzyl benzoate and containing 2% (v/v) benzyl alcohol as a preservative. The product is available as a single, multiple-dose, 5 mL vial (NDC: 67457-886-05).
Storage
Hydroxyprogesterone Caproate Injection, USP should be stored at controlled room temperature 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F). Storage at low temperatures may result in the separation of some crystalline material which redissolves readily on heating in boiling water.
Protect from light. Store vial in its box. Store upright. Discard any unused product within 28 days after first use.
Manufactured for:
Mylan Institutional LLC
Rockford, IL 61103 U.S.A.by:
McGuff Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Santa Ana, CA 92704 U.S.A.MD381-0051a
Revised: 1/2017
MCG:HPCIJ:R1 -
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 1.25 g/5 mL
NDC: 67457-886-05
Hydroxyprogesterone
Caproate
Injection, USP
1.25 g/5 mL
(250 mg/mL)For Intramuscular
Use OnlyRx only 5 mL Multiple-Dose Vial
Sterile
Each mL provides: 250 mg
hydroxyprogesterone
caproate in castor oil
and 46% benzyl
benzoate (v/v) with 2%
benzyl alcohol (v/v) as a
preservative.Dosage and Administration:
See Insert for Dosage
Information.Store at 20° to 25°C
(68° to77°F). [See USP
ControlledRoom
Temperature.]Manufactured for:
Mylan Institutional LLC
Rockford, IL 61103 U.S.A.by:
McGuff Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Santa Ana, CA 92704 U.S.A.MD381-0049c
MCG:886:1C:R3
Mylan.com
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
HYDROXYPROGESTERONE CAPROATE
hydroxyprogesterone caproate injectionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 67457-886 Route of Administration INTRAMUSCULAR Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength HYDROXYPROGESTERONE CAPROATE (UNII: 276F2O42F5) (HYDROXYPROGESTERONE - UNII:21807M87J2) HYDROXYPROGESTERONE CAPROATE 250 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength CASTOR OIL (UNII: D5340Y2I9G) BENZYL BENZOATE (UNII: N863NB338G) BENZYL ALCOHOL (UNII: LKG8494WBH) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 67457-886-05 1 in 1 CARTON 09/22/2017 1 5 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA200271 09/22/2017 Labeler - Mylan Institutional LLC (790384502)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.