PARASITE-S- formaldehyde liquid
Parasite-S by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Parasite-S by is a Animal medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Western Chemical Inc., Bakelite Chemicals LLC. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
DESCRIPTION
Description
PARASITE-S is the aqueous solution of formaldehyde gas (this is equivalent to formalin 37% or
37grams of formaldehyde in 100mLof solution). U.S.P. grade PARASITE-S contains not less than
37% (by weight) of formaldehyde gas per weight of water and 6 to 14% methanol. In solution, formaldehyde
is present chiefly as HO(CH20)H. Its molecular weight is 30.93. PARASITE-S is readily
miscible with water, methanol, and ethanol and is slightly soluble in ether. It is a clear, colorless
liquid (Heyden Newport Chemical Corporation, 1961).Fish and Shrimp Toxicity Studies
The toxicity of PARASITE-S was measured by standard methods in laboratory bioassays with
rainbow trout, Atlantic salmon, lake trout, black bullhead, channel catfish, green sunfish, bluegill,
smallmouth bass, largemouth bass and striped bass. The 3,6,24 and 96-hour LC50 (lethal
concentration for 50% of the animals) values for trout range from 1,230 to 100 μL/L (455 to 37 ppm
formaldehyde); for catfish, from 495 to 65.8 μL/L (183 to 24 ppm formaldehyde); for bluegill,
from 1,230 to 100 μL/L (455 to 37 ppm formaldehyde); for catfish, from 495 to 65.8 μL/L (183 to 24 ppm formaldehyde);
for bluegill, from 2,290 to 100 μL/L (847 to 37 ppm formaldehyde); for largemouth bass,
the values for 6 to 96-hour LC50 range from 1,030 to 143 μL/L (381 to 53 ppm formaldehyde) (Bill et al. 1977)
and for striped bass the values for 6 to 96-hour LC50 range from 940 to 30 μL/L (347 to 11 ppm formaldehyde)
(Bills, Marking and Howe-1993). The 24, 48, 72 and 96 hour LC50 values for penaeid shrimp range
from 712 to 250 µL/L (ppm) (Johnson. 1974 and Williams, 1980).
-
Indications for Use
1. Parasiticide for Finfish: for the control of external protozoa (Chilodonella spp., Ichthyobodo spp., Epistylis spp., Ichthyophthirius spp., Ambiphrya spp. and Trichodina spp.), and the monogenetic trematode parasites (Cleidodiscus spp., Dactylogyrus spp., and Gyrodactylus spp.).
2. Parasiticide for Penaeld Shrimp: for the control of external protozoan parasites (Bodo spp., Epistylis spp., and Zoothamnium spp.).
3. Fungicide for Finflsh Eggs: for the control of fungi of the family Saprolegniaceae.
-
Directions for Use
1. Parasiticide for Finfish
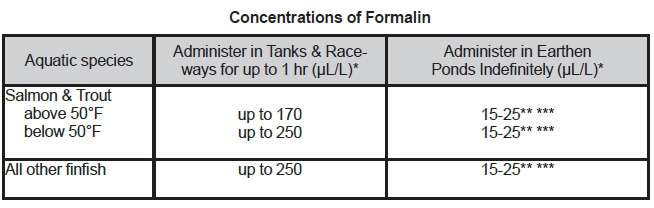
* Microliter per liter (μL/L) = parts per million (ppm).
** Use the lower concentration when ponds, tanks or raceways are heavily loaded with phytoplankton,
or fish, to avoid oxygen depletion due to the biological oxygen demand created by
decay of dead phytoplankton. Alternatively, a higher concentration might be used if dissolved
oxygen is strictly monitored.
*** Although the indicated concentrations are considered safe for cold and warm water finfish, a
small number of each lot or pond to be treated should always be used to check for any unusual
sensitivity to formalin before proceeding.
2. Parasiticide for Penaeld Shrimp

* Microliter per liter (μL/L) = parts per million (ppm).
** Treat for up to 4 hours daily. Treatment may be repeated daily until parasite control is achieved.
Use the lower concentration when ponds, tanks or raceways are heavily loaded with phytoplankton,
or shrimp, to avoid oxygen depletion due to the biological oxygen demand created by
decay of dead phytoplankton. Alternatively, a higher concentration might be used if dissolved
oxygen is strictly monitored.
*** Treatment may be repeated in 5 to 10 days, if needed
3. Fungicide for Finfish Eggs
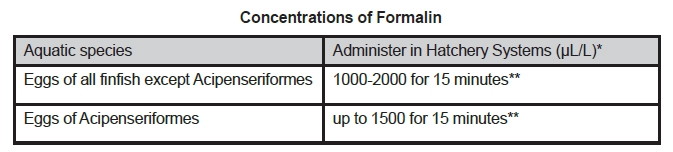
* Microliter per liter (μL/L) = parts per million (ppm).
** Apply in constant flow water supply of incubating facilities. A preliminary bioassay should be
conducted on a small subsample of fish eggs to determine sensitivity before treating an entire
group. This is necessary for all species because egg sensitivity can vary with species or strain
and the unique conditions at each facility. -
Methods of Application
APPLICATION TO TANKS AND RACEWAYS -Turn off water supply, provide aeration, apply
appropriate amount of PARASITE-S, and thoroughly dilute and mix to assure equal distribution of
PARASITE-S. Treat for up to 1 hour for fish and up to 4 hours for penaeid shrimp, then drain the
solution and refill the tank with fresh, well-aerated water. While tank is under treatment, adequate
oxygen must be present to maintain the fish or shrimp. If needed. aeration should be provided to
prevent oxygen depletion. Treatments may be repeated daily until parasite control is achieved.
APPLICATION TO PONDS - Apply greatly diluted PARASITE-S to the pond evenly using a pump,
sprayer, boat bailer, or other suitable device to assure even distribution. Allow PARASITE-S to dissipate
naturally. Single treatments usually control most parasites, but may be repeated in 5 to 10 days if
needed. Treatments for Ichthyophthirius should be made at 2-day intervals until control is achieved.
APPLICATION TO EGG INCUBATORS - Apply PARASITE-S into a constant water supply flowing
around the eggs. A drip or pressure system should be used and timed. Apply PARASITE-S under
the surface of the water flow. - WARNINGS
-
USER SAFETY WARNINGS
DANGER POISON
User Safety Warnings
Exposure to high concentrations of formaldehyde vapor causes severe respiratory irritation
which can be life-threatening. Lower vapor levels can cause irritation to the eyes, respiratory
tract, and skin. Swallowing formaldehyde can be life-threatening. Formaldehyde is an irritant
when splashed on skin or Into the eyes. It can cause severe eye damage, even blindness.
Keep out of reach of children.
Use only with adequate ventilation.
Keep container tightly closed when not in use.
May aggravate a pre-existing asthmatic condition and allergic rhinitis.
Moderate fire and explosion hazard exists when exposed to heat or flame.
Contains methanol - cannot be made non-poisonous. Prolonged exposure to methanol has
been associated with reproduction disorders.
Potential Cancer Hazard: Formaldehyde vapor may be carcinogenic if inhaled. Use applicable
safety protection. (Note: This drug, used as labeled, does not cause formaldehyde
tissue residues in fish).
Employers: Refer to Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) regulation 29
CFR 1910.1048 for human safety guidance that may be applicable to your specific operation.
OSHA’s “action level” concentration for airborne formaldehyde is 0.5 part per million
(ppm), calculated as an 8 hour time-weighted average (TWA). Use respiratory, skin, and eye
protection when needed (refer to OSHA’s regulation 29 CFR 1910.1048). OSHA’s airborne
exposure limits (without use of a respirator) for formaldehyde shall not exceed 1) 0.75 part
per million (ppm) as an 8-hour, time-weighted average (TWA) or 2) 2 parts per million (ppm)
as a 15-minute, short term exposure limit (STEL). NOTE: The odor of formaldehyde in the air
can generally be detected at about 0.5 to 0.8 ppm (range about 0.05 to 1 ppm). -
User Exposure Emergency Aid
INHALATION (Breathing): Get medical aid immediately. Remove victim from exposure
wearing protective clothing and respiratory protection appropriate to the type and degree of
contamination. Move victim to fresh air immediately. If breathing is difficult, give oxygen. DO
NOT use mouth-to-mouth respiration. If breathing has ceased, induce artificial respiration
with the aid of a pocket mask equipped with a one-way valve or other proper respiratory
medical device.INGESTION (Swallowing): DO NOT induce vomiting. If the person is conscious, dilute,
inactivate, or absorb the formaldehyde by giving milk, activated charcoal, or water. Get
medical help immediately. If vomiting occurs, keep head lower than hips.EYE CONTACT: Immediately flush eye(s) with large amounts of water for at least 15 minutes,
lifting the lower and upper eyelids occasionally, until no evidence of chemical remains.
Seek medical attention immediately. DO NOT allow victim to rub eyes or keep eyes closed
for burns to eyes may have a delayed effect.SKIN CONTACT: Remove contaminated clothing (including shoes) immediately. Wash affected
area of body with soap and large amounts of water until no evidence of chemical
remains (at least 15 minutes). If there are chemical burns, or appreciable eye or respiratory
irritation, get medical help immediately. -
Precautions
Store PARASITE-S indoors away from direct sunlight, heat, sparks, and open flames, and
ventilate storage area. Do not subject PARASITE-S to temperatures below 40°F (4.4°C).
PARASITE-S subjected to temperatures below 40°F causes the formation of paraformaldehyde,
a substance which is toxic to fish. Paraformaldehyde can be recognized as a white
precipitate at the bottom or on the walls of the container.Tolerance to PARASITE-S may vary with strain and species of fish, eggs and shrimp. While
the indicated concentrationaare considered safe for the indicated use, a smallnumber of
each lot to be treated should be used to check for any unusual sensitivity to PARASITE-S
before proceeding.Under some conditions, fish or penaeid shrimp may be stressed by normal treatment concentrations.
Heavily parasitized or diseased fish or penaeid shrimp often have a greatly
reduced tolerance to PARASITE-S. Such animals do not tolerate the normal tank treatment
regimen the first time they are treated. Therefore, time and dosage may need to be reduced.
If they show evidence of distress (by piping at the surface), the solution should be removed
and replaced with fresh, well aerated water. Careful observations should always be made
throughout the treatment period whenever tank or raceway treatments are made. Treatment
should never exceed 1 hour for fish or 4 hours for penaeid shrimp (even if they show no sign
of distress), nor should it exceed 15 minutes for fish eggs.Do not apply PARASITE-S to fish ponds, tanks or raceways with water warmer than 27°C
(80°F) when a heavy bloom of phytoplankton is present, or when the concentration of dissolved
oxygen is less than 5 mg/L (5 ppm). Do not apply to penaeid shrimp ponds when the
concentration of the dissolved oxygen is less than 3 to 4 mg/L (ppm). PARASITE-S may kill
phytoplankton and can cause depletion of dissolved oxygen. If an oxygen depletion occurs,
add fresh, well-aerated water to dilute the solution and to provide oxygen.Because formalin may harm a biofilter, biofilters should be bypassed during treatment, and
the system should be flushed and replaced with untreated water before reconnecting the
biofilter.Do not use PARASITE-S in a tank, pond or raceway in which methylene blue, or other dyes
which are absorbed, have been recently used -
Environmental Precautions
Do not discharge the contents of fish treatment tanks into natural streams or ponds without
thorough dilution (greater than or equal to 10X). Do not discharge the contents of egg treatment
tanks without a 100X dilution. This will avoid damage to PARASITE-S sensitive phytoplankton,
zooplankton, and fish populations and avoid depletion of dissolved oxygen.Formaldehyde is identified by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) as a toxic pollutant
and hazardous substance and is required by regulation (40 CFR, Part 122) to be identified
as a discharge for NPDES permits for aquatic animal production facilities, aquaculture
projects and other facilities. Formaldehyde is subject to SARA Title Ill, Section 313 reporting.Use, storage, and disposal of this product must be handled in accordance with applicable
local, state and Federal laws. - Storage
- Parasite-S Label
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
PARASITE-S
formaldehyde liquidProduct Information Product Type OTC ANIMAL DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 50378-010 Route of Administration TOPICAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Formaldehyde (UNII: 1HG84L3525) (Formaldehyde - UNII:1HG84L3525) Formaldehyde 370 g in 1 L Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Methyl alcohol (UNII: Y4S76JWI15) 120 g in 1 L Water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) 510 g in 1 L Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 50378-010-01 208 L in 1 DRUM 2 NDC: 50378-010-05 3.8 L in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC 3 NDC: 50378-010-10 19 L in 1 PAIL 4 NDC: 50378-010-99 1000 L in 1 CONTAINER Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NADA NADA140989 07/31/1992 Labeler - Western Chemical Inc. (085803500) Registrant - Western Chemical Inc. (085803500) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Western Chemical Inc. 085803500 label, analysis
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.