CLINDAMYCIN PHOSPHATE AND BENZOYL PEROXIDE gel
Clindamycin Phosphate and Benzoyl Peroxide by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Clindamycin Phosphate and Benzoyl Peroxide by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Taro Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc., Taro Pharmaceuticals Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use CLINDAMYCIN PHOSPHATE and BENZOYL PEROXIDE Gel safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for CLINDAMYCIN PHOSPHATE and BENZOYL PEROXIDE Gel.
CLINDAMYCIN PHOSPHATE and
BENZOYL PEROXIDE gel, for topical use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2000INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel is a lincosamide antibiotic and benzoyl peroxide indicated for the topical treatment of acne vulgaris. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- Clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel contains clindamycin phosphate 1.2% and benzoyl peroxide 2.5% in a topical gel in 50 gram pumps. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel is contraindicated in:
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Colitis: Orally and parenterally administered clindamycin has been associated with severe colitis, which may result in death. Diarrhea, bloody diarrhea, and colitis (including pseudomembranous colitis) have been reported with the use of topical and systemic clindamycin. Clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel should be discontinued if significant diarrhea occurs. (5.1)
- Ultraviolet Light and Environmental Exposure: Minimize sun exposure following drug application. (5.2)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following selected adverse reactions occurred in less than 0.2% of patients: application site pain (0.1%); application site exfoliation (0.1%); and application site irritation (0.1%). (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Taro Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc., at 1-866-923-4914 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel should not be used in combination with erythromycin-containing products because of its clindamycin component. (7.1)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 6/2018
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
4.1 Hypersensitivity
4.2 Colitis/Enteritis
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Colitis
5.2 Ultraviolet Light and Environmental Exposure
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Erythromycin
7.2 Neuromuscular Blocking Agents
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanisms of Action
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
12.4 Microbiology
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
16.2 Dispensing Instructions for the Pharmacist
16.3 Storage and Handling
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Apply a pea-sized amount of clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel to the face once daily.
Use of clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel beyond 12 weeks has not been evaluated.
Concomitant topical acne therapy should be used with caution because a possible cumulative irritancy effect may occur, especially with the use of peeling, desquamating, or abrasive agents.
Clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel is not for oral, ophthalmic, or intravaginal use.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
4.1 Hypersensitivity
Clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel is contraindicated in those individuals who have shown hypersensitivity to clindamycin, benzoyl peroxide, any components of the formulation, or lincomycin. Anaphylaxis, as well as allergic reactions leading to hospitalization, has been reported in postmarketing use with clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel. [See Postmarketing Experience (6.2).]
4.2 Colitis/Enteritis
Clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel is contraindicated in patients with a history of regional enteritis, ulcerative colitis, or antibiotic-associated colitis. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Colitis
Systemic absorption of clindamycin has been demonstrated following topical use of clindamycin. Diarrhea, bloody diarrhea, and colitis (including pseudomembranous colitis) have been reported with the use of topical and systemic clindamycin. When significant diarrhea occurs, clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel should be discontinued.
Severe colitis has occurred following oral and parenteral administration of clindamycin with an onset of up to several weeks following cessation of therapy. Antiperistaltic agents such as opiates and diphenoxylate with atropine may prolong and/or worsen severe colitis. Severe colitis may result in death.
Studies indicate toxin(s) produced by Clostridia is one primary cause of antibiotic-associated colitis. The colitis is usually characterized by severe persistent diarrhea and severe abdominal cramps and may be associated with the passage of blood and mucus. Stool cultures for Clostridium difficile and stool assay for C. difficile toxin may be helpful diagnostically.
5.2 Ultraviolet Light and Environmental Exposure
Minimize sun exposure including use of tanning beds or sun lamps following drug application [See Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under prescribed conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trial may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Because clinical trials are also conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reactions observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot always be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The following selected adverse reactions occurred in less than 0.2% of patients treated with clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel: application site pain (0.1%); application site exfoliation (0.1%); and application site irritation (0.1%).
During clinical trials, subjects were assessed for local cutaneous signs and symptoms of erythema, scaling, itching, burning and stinging. Most local skin reactions increased and peaked around week 4 and continually decreased over time reaching near baseline levels by week 12. The percentage of subjects that had symptoms present before treatment, the maximum value recorded during treatment, and the percent with symptoms present at week 12 are shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Local Skin Reactions - Percent of Subjects with Symptoms Present. Combined Results from the Two Phase 3 Trials (N = 773) Before Treatment
(Baseline)Maximum During Treatment End of Treatment
(Week 12)Mild Mod.* Severe Mild Mod.* Severe Mild Mod.* Severe - * Mod. = Moderate
Erythema 22 4 0 25 5 <1 15 2 0 Scaling 8 <1 0 18 3 0 8 1 0 Itching 10 2 0 15 2 0 6 <1 0 Burning 3 <1 0 8 2 0 2 <1 0 Stinging 2 <1 0 6 1 0 1 <1 0 6.2 Postmarketing Experience
Anaphylaxis, as well as allergic reactions leading to hospitalizations, has been reported in postmarketing use of products containing clindamycin/benzoyl peroxide. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Erythromycin
Clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel should not be used in combination with topical or oral erythromycin-containing products due to its clindamycin component. In vitro studies have shown antagonism between erythromycin and clindamycin. The clinical significance of this in vitro antagonism is not known.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C.
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women treated with clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel. Clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Animal reproductive/developmental toxicity studies have not been conducted with clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel or benzoyl peroxide. Developmental toxicity studies of clindamycin performed in rats and mice using oral doses of up to 600 mg/kg/day (240 and 120 times amount of clindamycin in the highest recommended adult human dose based on mg/m2, respectively) or subcutaneous doses of up to 200 mg/kg/day (80 and 40 times the amount of clindamycin in the highest recommended adult human dose based on mg/m2, respectively) revealed no evidence of teratogenicity.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether clindamycin is excreted in human milk after topical application of clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel. However, orally and parenterally administered clindamycin has been reported to appear in breast milk. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants, a decision should be made whether to use clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel while nursing, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Clindamycin Phosphate and Benzoyl Peroxide Gel, 1.2%/2.5% is a combination product with two active ingredients in a white to off-white, opaque, smooth, aqueous gel formulation intended for topical use. Clindamycin phosphate is a water-soluble ester of the semi-synthetic antibiotic produced by a 7(S)-chloro-substitution of the 7(R)-hydroxyl group of the parent antibiotic lincomycin.
The chemical name for clindamycin phosphate is Methyl 7-chloro-6,7,8-trideoxy-6-(1-methyl-trans-4-propyl-L-2-pyrrolidinecarboxamido)-1-thio-L-threo-α-D-galacto-octopyranoside 2-(dihydrogen phosphate). The structural formula for clindamycin phosphate is represented below:
Clindamycin phosphate:
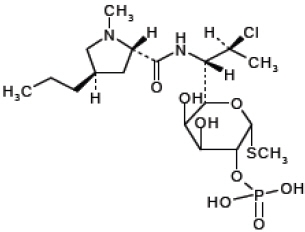
Molecular Formula: C18H34ClN2O8PS Molecular Weight: 504.97
Benzoyl peroxide is an antibacterial and keratolytic agent. The structural formula for benzoyl peroxide is represented below:
Benzoyl peroxide:
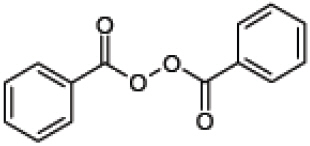
Molecular Formula: C14H10O4 Molecular Weight: 242.23
Clindamycin Phosphate and Benzoyl Peroxide Gel contains the following inactive ingredients: carbomer homopolymer type C, poloxamer 124, potassium hydroxide, propylene glycol, and purified water. Each gram of Clindamycin Phosphate and Benzoyl Peroxide Gel contains 1.2% of clindamycin phosphate which is equivalent to 1% clindamycin.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanisms of Action
Clindamycin: Clindamycin is a lincosamide antibacterial [See Microbiology (12.4)].
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The systemic absorption of clindamycin was investigated in an open-label, multiple-dose trial in 16 adult subjects with moderate to severe acne vulgaris treated with 1 gram of clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel applied to the face once daily for 30 days. Twelve subjects (75%) had at least one quantifiable clindamycin plasma concentration above the lower limit of quantification (LOQ = 0.5 ng/mL) on Day 1 or Day 30. On Day 1, the mean (± standard deviation) peak plasma concentration (Cmax) was 0.78 ± 0.22 ng/mL (n=9 with measurable concentrations), and the mean AUC0-t was 5.29 ± 0.81 h∙ng/mL (n=4). On Day 30, the mean Cmax was 1.22 ± 0.88 ng/mL (n=10), and the mean AUC0-t was 8.42 ± 6.01 h∙ng/mL (n=6). Clindamycin plasma concentrations were below LOQ in all subjects at 24 hours post-dose on the three tested days (Day 1, 15, and 30).
Benzoyl peroxide has been shown to be absorbed by the skin where it is converted to benzoic acid.
12.4 Microbiology
Clindamycin binds to the 50S ribosomal subunits of susceptible bacteria and prevents elongation of peptide chains by interfering with peptidyl transfer, thereby suppressing bacterial protein synthesis.
Clindamycin and benzoyl peroxide individually have been shown to have in vitro activity against Propionibacterium acnes, an organism which has been associated with acne vulgaris; however, the clinical significance of this activity against P. acnes is not known.
P. acnes resistance to clindamycin has been documented. Resistance to clindamycin is often associated with resistance to erythromycin.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity, mutagenicity and impairment of fertility testing of clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel have not been performed.
Benzoyl peroxide has been shown to be a tumor promoter and progression agent in a number of animal studies. Benzoyl peroxide in acetone at doses of 5 and 10 mg administered topically twice per week for 20 weeks induced skin tumors in transgenic Tg.AC mice. The clinical significance of this is unknown.
Carcinogenicity studies have been conducted with a gel formulation containing 1% clindamycin and 5% benzoyl peroxide. In a 2-year dermal carcinogenicity study in mice, treatment with the gel formulation at doses of 900, 2700, and 15000 mg/kg/day (1.8, 5.4, and 30 times amount of clindamycin and 3.6, 10.8, and 60 times amount of benzoyl peroxide in the highest recommended adult human dose of 2.5 g clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel based on mg/m2, respectively) did not cause any increase in tumors. However, topical treatment with a different gel formulation containing 1% clindamycin and 5% benzoyl peroxide at doses of 100, 500, and 2000 mg/kg/day caused a dose-dependent increase in the incidence of keratoacanthoma at the treated skin site of male rats in a 2-year dermal carcinogenicity study in rats. In an oral (gavage) carcinogenicity study in rats, treatment with the gel formulation at doses of 300, 900 and 3000 mg/kg/day (1.2, 3.6, and 12 times amount of clindamycin and 2.4, 7.2, and 24 times amount of benzoyl peroxide in the highest recommended adult human dose of 2.5 g clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel based on mg/m2, respectively) for up to 97 weeks did not cause any increase in tumors. In a 52-week dermal photocarcinogenicity study in hairless mice, (40 weeks of treatment followed by 12 weeks of observation), the median time to onset of skin tumor formation decreased and the number of tumors per mouse increased relative to controls following chronic concurrent topical administration of the higher concentration benzoyl peroxide formulation (5000 and 10000 mg/kg/day, 5 days/week) and exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
Clindamycin phosphate was not genotoxic in the human lymphocyte chromosome aberration assay. Benzoyl peroxide has been found to cause DNA strand breaks in a variety of mammalian cell types, to be mutagenic in S. typhimurium tests by some but not all investigators, and to cause sister chromatid exchanges in Chinese hamster ovary cells.
Fertility studies have not been performed with clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel or benzoyl peroxide, but fertility and mating ability have been studied with clindamycin. Fertility studies in rats treated orally with up to 300 mg/kg/day of clindamycin (approximately 120 times the amount of clindamycin in the highest recommended adult human dose of 2.5 g clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel, based on mg/m2) revealed no effects on fertility or mating ability.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The safety and efficacy of once daily use of clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel were assessed in two 12-week multi-center, randomized, blinded trials in subjects 12 years and older with moderate to severe acne vulgaris. The two trials were identical in design and compared clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel to clindamycin in the vehicle gel, benzoyl peroxide in the vehicle gel, and the vehicle gel alone.
The co-primary efficacy variables were:
- (1)
Mean absolute change from baseline at week 12 in
- Inflammatory lesion counts
- Non-inflammatory lesion counts
- (2) Percent of subjects who had a two grade improvement from baseline on an Evaluator's Global Severity (EGS) score.
The EGS scoring scale used in all of the clinical trials for clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel is as follows:
Grade Description Clear Normal, clear skin with no evidence of acne vulgaris Almost Clear Rare non-inflammatory lesions present, with rare non-inflamed papules (papules must be resolving and may be hyperpigmented, though not pink-red) Mild Some non-inflammatory lesions are present, with few inflammatory lesions (papules/pustules only; no nodulocystic lesions) Moderate Non-inflammatory lesions predominate, with multiple inflammatory lesions evident: several to many comedones and papules/pustules, and there may or may not be one small nodulo-cystic lesion Severe Inflammatory lesions are more apparent, many comedones and papules/pustules, there may or may not be a few nodulocystic lesions Very Severe Highly inflammatory lesions predominate, variable number of comedones, many papules/pustules and many nodulocystic lesions The results of Trial 1 at week 12 are presented in Table 2:
Table 2: Trial 1 Results Trial 1 Clindamycin Phosphate and Benzoyl Peroxide Gel
N = 399Clindamycin Gel
N = 408Benzoyl Peroxide Gel
N = 406Vehicle Gel
N = 201EGSS Clear or Almost Clear 115 (29%) 84 (21%) 76 (19%) 29 (14%) 2 grade reduction from baseline 131 (33%) 100 (25%) 96 (24%) 38 (19%) Inflammatory Lesions: Mean absolute change 14.8 12.2 13 9 Mean percent (%) reduction 55% 47.1% 49.3% 34.5% Non-Inflammatory Lesions: Mean absolute change 22.1 17.9 20.6 13.2 Mean percent (%) reduction 45.3% 38% 40.2% 28.6% The results of Trial 2 at week 12 are presented in the Table 3:
Table 3: Trial 2 Results Trial 2 Clindamycin Phosphate and Benzoyl Peroxide Gel
N = 398Clindamycin Gel
N = 404Benzoyl Peroxide Gel
N = 403Vehicle Gel
N = 194EGSS Clear or Almost Clear 113 (28%) 94 (23%) 94 (23%) 21 (11%) 2 grade reduction from baseline 147 (37%) 114 (28%) 114 (28%) 27 (14%) Inflammatory Lesions: Mean absolute change 13.7 11.3 11.2 5.7 Mean percent (%) reduction 54.2% 45.3% 45.7% 23.3% Non-Inflammatory Lesions: Mean absolute change 19 14.9 15.2 8.3 Mean percent (%) reduction 41.2% 34.3% 34.5% 19.2% - (1)
Mean absolute change from baseline at week 12 in
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
Clindamycin Phosphate and Benzoyl Peroxide Gel, 1.2%/2.5% is supplied as a 50 g pump (NDC: 51672-1367-3).
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
- Patients who develop allergic reactions such as severe swelling or shortness of breath should discontinue use and contact their physician immediately.
- Clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel may cause irritation such as erythema, scaling, itching, or burning, especially when used in combination with other topical acne therapies.
- Excessive or prolonged exposure to sunlight should be limited. To minimize exposure to sunlight, a hat or other clothing should be worn. Sunscreen may also be used.
- Clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel may bleach hair or colored fabric.
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PATIENT INFORMATION Clindamycin Phosphate and Benzoyl Peroxide Gel, 1.2%/2.5%
IMPORTANT: For use on skin only (topical use). Do not get Clindamycin Phosphate and Benzoyl Peroxide Gel in your mouth, eyes, or vagina, or on your lips. Read the Patient Information that comes with clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel before you start using it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your medical condition or your treatment.
What is Clindamycin Phosphate and Benzoyl Peroxide Gel?
Clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel is a prescription medicine used on the skin (topical) to treat acne vulgaris in people 12 years and older. Clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel contains clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide.
It is not known if clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel is safe and effective for use longer than 12 weeks.
It is not known if clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel is safe and effective in children under 12 years of age.
Who should not use Clindamycin Phosphate and Benzoyl Peroxide Gel?
Do not use Clindamycin Phosphate and Benzoyl Peroxide Gel if you have:
- Crohn's disease
- ulcerative colitis
- had inflammation of the colon (colitis), or severe diarrhea with past antibiotic use
Talk with your doctor if you are not sure if you have one of these conditions.
What should I tell my doctor before using Clindamycin Phosphate and Benzoyl Peroxide Gel?
Before using Clindamycin Phosphate and Benzoyl Peroxide Gel, tell your doctor about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have any allergies.
- have any other medical conditions.
- are pregnant or planning to become pregnant. It is not known if clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel will harm your unborn baby.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breast-feed. It is not known if clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel passes into your breast milk. One of the medicines in clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel contains clindamycin. Clindamycin when taken by mouth or by injection has been reported to appear in breast milk. You and your doctor should decide whether you will use clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel while breast-feeding.
Tell your doctor about all the medicines and skin products you use. Especially tell your doctor if you will have surgery with general anesthesia. One of the medicines in clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel (clindamycin) can affect how certain medicines work when used in general anesthesia.
- Clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel should not be used with products that contain erythromycin.
- Other skin and topical acne products may increase the irritation of your skin when used with clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them and show it to your doctor and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I use Clindamycin Phosphate and Benzoyl Peroxide Gel?
- Use clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel exactly as prescribed.
- Your doctor will tell you how long to use clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel.
- Throw away (discard) any unused clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel.
Instructions for applying Clindamycin Phosphate and Benzoyl Peroxide Gel
- Apply clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel to your face one time each day as prescribed.
- Before you apply clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel, wash your face gently with a mild soap, rinse with warm water, and pat your skin dry.
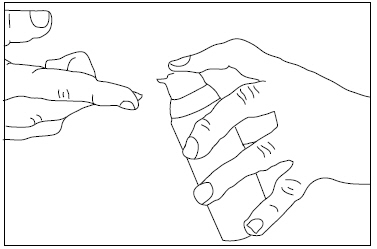
- To apply clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel to your face, use the pump to dispense one pea-sized amount of clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel onto your fingertip. See Figure 1. One pea-sized amount of clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel should be enough to cover your entire face.
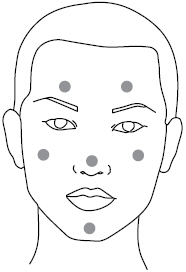
- Dot the one pea-sized amount of clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel onto six areas of your face (chin, left cheek, right cheek, nose, left forehead, right forehead). See Figure 2.
- After applying the clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel this way, spread the gel over your face and gently rub it in. It is important to spread the gel over your whole face.
- Wash your hands with soap and water after applying clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel.
- If your doctor tells you to put clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel on other areas of your skin with acne, be sure to ask how much you should use.
- Do not get clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel in your mouth, eyes, or nose, or on your lips. If this occurs, rinse the affected area with warm water and call your doctor right away if the area becomes very red, itchy, tender, or swollen.
- Do not get clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel on cuts or open wounds.
- Do not use more clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel than prescribed.
What should I avoid while using Clindamycin Phosphate and Benzoyl Peroxide Gel?
- Limit your time in sunlight. Avoid using tanning beds or sun lamps. If you have to be in sunlight, wear a wide-brimmed hat or other protective clothing, and a sunscreen with SPF 15 rating or higher. Your doctor can give you more information about why this is important.
- Do not wash your face more than 2 to 3 times a day. Washing your face too often or scrubbing it may make your acne worse.
- Avoid getting clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel in your hair or on colored fabric. Clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel may bleach hair or colored fabric.
What are possible side effects with Clindamycin Phosphate and Benzoyl Peroxide Gel?
Clindamycin Phosphate and Benzoyl Peroxide Gel can cause serious side effects including:
- Inflammation of the colon (colitis). Stop using clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel and call your doctor right away if you have severe watery diarrhea, or bloody diarrhea.
-
Allergic reactions. Stop using clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel, call your doctor and get help right away if you have any of the following symptoms:
- severe itching
- swelling of your face, eyes, lips, tongue or throat
- trouble breathing
Common side effects with Clindamycin Phosphate and Benzoyl Peroxide Gel include:
- Skin irritation. Stop using clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel and call your doctor if you have a skin rash or your skin becomes very red, itchy or swollen.
Talk to your doctor about any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects with clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for more information.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
You may also report side effects to Taro Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc. at 1-866-923-4914.
How should I store Clindamycin Phosphate and Benzoyl Peroxide Gel?
- Store clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F).
- The expiration date of clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel is 10 weeks from the date you fill your prescription.
- Safely throw away expired clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel.
- Do not freeze.
- Keep the container tightly closed.
Keep Clindamycin Phosphate and Benzoyl Peroxide Gel and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about Clindamycin Phosphate and Benzoyl Peroxide Gel
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for conditions that are not mentioned in Patient Information leaflets. Do not use clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel to other people, even if they have the same condition you have. It may harm them.
This leaflet summarizes the most important information about clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can also ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gel that is written for healthcare professionals.
For more information about Clindamycin Phosphate and Benzoyl Peroxide Gel, call Taro Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc. at 1-866-923-4914.
What are the ingredients in Clindamycin Phosphate and Benzoyl Peroxide Gel?
Active Ingredients: clindamycin phosphate 1.2% and benzoyl peroxide 2.5%
Inactive Ingredients: carbomer homopolymer type C, poloxamer 124, potassium hydroxide, propylene glycol, and purified water.
Manufactured by: Taro Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Brampton, Ontario, Canada L6T 1C1
Distributed by: Taro Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc.
Hawthorne, NY 10532This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Issued: June 2018
PK-7450-0
164 -
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 50 g Bottle Carton
NDC: 51672-1367-3
50 g
Clindamycin Phosphate
and Benzoyl Peroxide
Gel 1.2%/2.5%FOR TOPICAL USE ONLY.
One premixed 50 gram pump dispenserRx only
TARO
Keep this and all medications out of the reach of children.
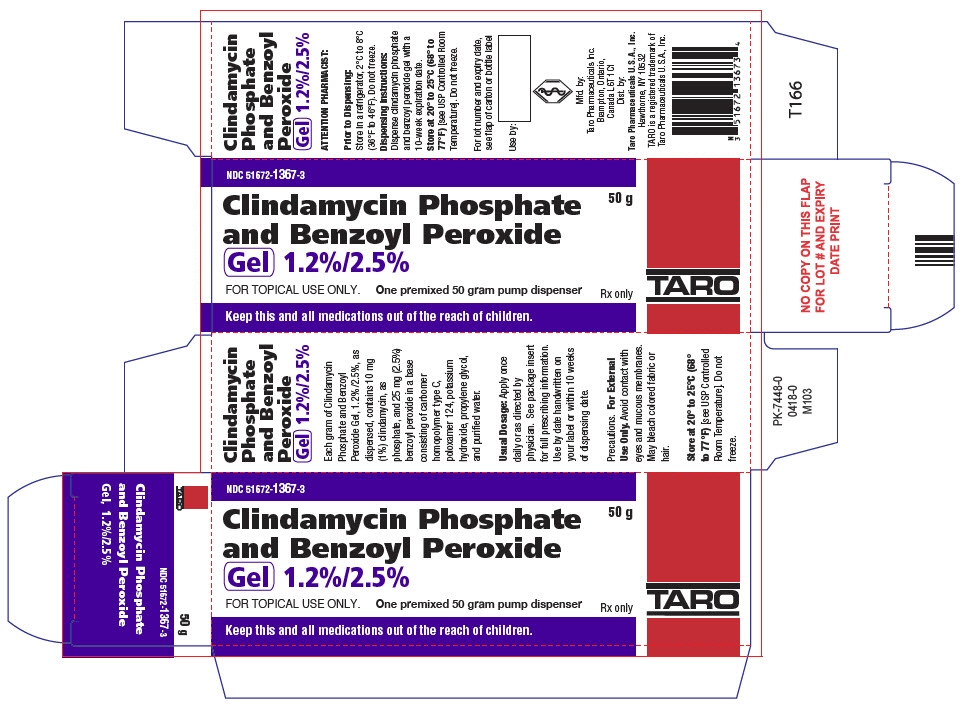
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
CLINDAMYCIN PHOSPHATE AND BENZOYL PEROXIDE
clindamycin phosphate and benzoyl peroxide gelProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 51672-1367 Route of Administration TOPICAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Clindamycin Phosphate (UNII: EH6D7113I8) (Clindamycin - UNII:3U02EL437C) Clindamycin 10 mg in 1 g Benzoyl Peroxide (UNII: W9WZN9A0GM) (Benzoyl Peroxide - UNII:W9WZN9A0GM) Benzoyl Peroxide 25 mg in 1 g Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength carbomer homopolymer type C (allyl pentaerythritol crosslinked) (UNII: 4Q93RCW27E) poloxamer 124 (UNII: 1S66E28KXA) potassium hydroxide (UNII: WZH3C48M4T) propylene glycol (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Product Characteristics Color WHITE (White to off-white) Score Shape Size Flavor Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 51672-1367-3 1 in 1 CARTON 08/19/2019 1 50 g in 1 BOTTLE, PUMP; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA206575 08/19/2019 Labeler - Taro Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc. (145186370) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Taro Pharmaceuticals Inc. 206263295 MANUFACTURE(51672-1367)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.