QUARTERMASTER- penicillin g procaine and dihydrostreptomycin sulfate intramammary infusion suspension
Quartermaster by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Quartermaster by is a Animal medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by WG Critical Care, LLC, HQ Specialty Pharma Corporation. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
ATTENTION DOCTOR:
It is your responsibility to inform your client of the warnings stated above so as to avoid adulteration of meat or milk and possible prosecution under Federal law.
ATENCIÓN MÉDICO:
Es su responsabilidad informar al cliente las advertencias establecidas anteriormente con el fin de evitar la adulteración de la carne o la leche, y una posible acusación según la ley federal.
-
DESCRIPTION
Each 10 mL disposable syringe contains 1,000,000 units of Procaine Penicillin G, micronized, and 1 gram of Dihydrostreptomycin base, as Dihydrostreptomycin Sulfate, in an extended action base consisting of 1% w/v Hydrogenated Peanut Oil, 3% w/v Aluminum Monostearate, and Peanut Oil, q.s. Manufactured by a non-sterilizing process.
DESCRIPCIÓN:
Cada jeringa descartable de 10 ml contiene 1 000 000 de unidades de penicilina G procaína, micronizadas, y 1 gramo de dihidroestreptomicina base, como sulfato de dihidroestreptomicina, en una base de acción extensa que consiste en 1 % p/v de aceite de maní hidrogenado, 3 % p/v de monoestearato de aluminio y aceite de maní, c.s. Fabricado con un proceso sin esterilización.
-
ACTION
Infusion of antibiotics at the start of the drying off period has the following advantages: (1) it is active against existing infections; (2) it is prophylactic against new infections, during the time when cattle are likely to become infected [1]; (3) the antibiotic remains in the udder for a sufficiently long period to accomplish the intended objective and is not diluted with milk, as is the case in lactation therapy; (4) the danger of drug residues in the milk is reduced.
Antibiotic control is to be considered an adjunct to good herd hygiene management and milking management. Detailed field studies in England and the United States have demonstrated that a program consisting of treatment, at the time of drying off, with a highly effective antibiotic preparation in a slow-release base, and routine dipping of teats after each milking with an effective disinfectant, markedly reduces the incidence of all udder infections at calving [2,3,4].
It has recently been recommended that a disinfectant teat dip be used on unmilked cows, or at least be used for 10 days before parturition [5], to reduce the bacterial challenge to the depleted levels of antibiotic in the teat as freshening is approached [6].
When the herd infection level has been reduced, or when herds are not heavily infected initially, it may be desirable to be selective in treating dry quarters [7].
ACCIÓN:
La infusión de antibióticos al comienzo del período de secado tiene las siguientes ventajas: (1) es activa contra las infecciones existentes; (2) es profiláctica contra las nuevas infecciones durante el período en el que el ganado es propenso a contraer infecciones [1]; (3) el antibiótico permanence en la ubre por un período lo suficientemente largo como para lograr el objetivo y no se diluye con la leche, como pasa con la terapia en período de lactancia; (4) se reduce el peligro de que queden residuos del medicamento en la leche.
El control con antibióticos debe considerarse un auxiliar de la buena gestión de higiene del Ganado y la gestión del ordeñe. Estudios de campo detallados realizados en Inglaterra y Estados Unidos han demostrado que un programa constituido por un tratamiento al momento del secado, con una preparación de antibióticos de liberación lenta altamente efectiva, y el sellado frecuente de los pezones con un desinfectante eficaz después de cada ordeñe, reducen considerablemente la incidencia de todas las infecciones de ubre en la parición [2, 3, 4].
Recientemente, se ha recomendado usar un sellador desinfectante de pezones en vacas no ordeñadas, o al menos usarlo 10 días antes del parto [5] para reducir el riesgo bacteriano a los niveles más bajos de antibiótico en el pezón cuando se acerca el período de producción de leche [6].
Cuando se haya reducido el nivel de infección del ganado, o en caso de que el ganado no esté muy infectado, es conveniente ser selectivo en el tratamiento de cuartos secos [7].
- INDICATIONS
-
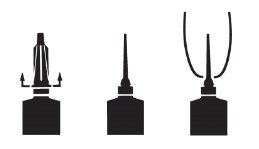
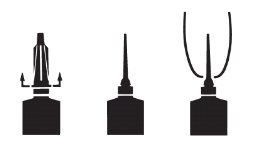
DIRECTIONS FOR USING THE FLEXIBLE TIP SYSTEM:
The flexible tip is designed to provide the choice of either insertion of the full cannula, as has traditionally been practiced, or insertion of no more than 1/8 inch of the cannula, as recommended by the National Mastitis Council.
a. Full Insertion: Remove the white end cap by pulling straight up as shown. Gently insert the full cannula into the teat canal; carefully infuse the product.
b. Partial
Insertion: Remove both the white end cap and the red cannula by pushing sideways as shown. Gently insert the exposed white tip into the teat canal; carefully infuse the product.
INSTRUCCIONES DE USO DEL SISTEMA DE PUNTA FLEXIBLE:
La punta flexible está diseñada para brindar la opción de una inserción completa de la cánula, como se ha realizado tradicionalmente, o la inserción de no más de 1/8 pulgada de la cánula, como lo recomienda el Concejo Nacional de Mastitis.
a. Inserción completa: Tire hacia arriba para qui tar el tapón blanco, como se muest ra. Inserte suavemente toda la cánula en el canal del pezón; infunda el producto con cuidado.
b. Inserción parcial: Retire el tapón blanco y la cánula roja tirando de los laterales, como se muestra. Inserte suavemente la punta blanca expuesta en el canal del pezón; infunda el product con cuidado.
-
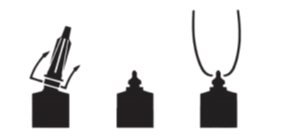
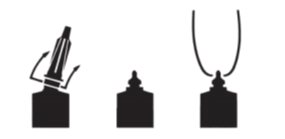
DIRECTIONS FOR USE:
At the last milking prior to drying off, completely milk out cow. Warm the syringe containing Quartermaster Suspension to body temperature; choose the desired insertion length (full or partial) and insert tip into teat canal; slowly infuse the entire contents. Instill the contents of one syringe into each quarter. Discard the syringe after use. Treated teats should then be dipped into an effective teat dip. The teat or quarter should not be manipulated again until the cow freshens. To achieve and maintain a lower frequency of infection, proper dipping of teats during lactation is recommended.
Shake vigorously for 10 seconds immediately before using.
INSTRUCCIONES DE USO:
En el último ordeñe, antes del secado, ordeñe la vaca por completo. Entibie la jeringa que contiene la SuspensiónQuartermaster a temperatura corporal; elija el largo de inserción deseado (completa o parcial) e inserte la punta en el canal del pezón; infunda lentamente todo el contenido. Instile el contenido de una jeringa en cada cuarto. Deseche la jeringa después de usarla. Los pezones tratados deben sumergirse en un sellador de pezones eficaz. No se deben volver a manipular el pezón ni el cuarto hasta que la vaca para. Para lograr reducer la frecuencia de infección, se recomienda el sellado adecuado de los pezones durante la lactancia.
Agitar con fuerza por 10 segundos justo antes de usar.
-
WARNINGS
For udder instillation upon drying off only. Not to be used within six (6) weeks of freshening. Not for use in lactating cows. Milk taken from animals within 96 hours (8 milkings) after calving must not be used for food. Animals infused with this product must not be slaughtered for food within 60 days from time of infusion nor within 96 hours after calving.
ADVERTENCIAS:
Únicamente para inst i lación al momento del secado. No utilizar dentro de las seis (6) semanas del período de producción de leche. No utilizar en vacas en período de lactancia. La leche ordeñada de los animales dentro de las 96 horas (8 ordeñes) después de la parición no se debe utilizar para alimentos. Los animales infundidos con este product no deben utilizarse como alimento dentro de los 60 días desde el momento de la infusión ni dentro de las 96 horas después de la parición.
- CAUTION:
- STORAGE CONDITIONS:
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Quartermaster Suspension is supplied as:
Packers of 12–10 mL (.33 Fl Oz) disposable syringes with 12 convenient single-use isopropyl alcohol pads NDC: 44567-901-03
Pails of 144–10 mL (.33 Fl Oz) disposable syringes with 144 convenient single-use isopropyl alcohol pads NDC: 44567-901-05
PRESENTACIÓN:
La suspensión Quartermaster se presenta de la siguiente forma:
Paquetes de 12–jeringas descartables de 10 ml (0,33 onzas líquidas) con 12 almohadillas con alcohol isopropílico de un solo uso . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . NDC: 44567-901-03
Cubos de 144–jeringas descartables de 10 ml (0,33 onzas líquidas) con 144 almohadillas con alcohol isopropílico de un solo uso . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . NDC: 44567-901-05
-
REFERENCES:
[1] Smith, A.; Westgarth, D.R.; Jones, M.R.; Neave, F.K.; Dodd, F.H.; & Brander, G.C., Methods of Reducing the Incidence of Udder Infection in Dry Cows, VETERINARY RECORD 81:504-510, 1967.
[2] Dodd, F.H. & Neave, F.K., Mastitis Control, N.I.R.D. BIENNIAL REVIEWS 1970, pp. 21-60.
[3] Roberts, S.J.; Meek, A.M.; Natzke, R.; & Guthrie, R., A Mastitis Control Program Combining Teat Dipping & Dry Cow Therapy, XIX WORLD VETERINARY CONGRESS (Mexico City, 8/15-21/71), PROCEEDINGS 3:935-939, 1971.
[4] Newbould, F.H.S.; Carey, P.G.; & Barnum, D.A., The Numbers of Intramammary Infections & Teat Duct Colonizations in a Herd of Twins During a Hygiene Experiment, CANADIANJOURNAL OF COMPARATIVE MEDICINE 34:203-208, 1970.
[5] Neave, F.K. & Jackson, E.R., The Prevention of Intramammary Infection, pp. 15-24 in TheControl of Bovine Mastitis (Proceedings, Joint Meeting, British Cattle Veterinary Association & The Agricultural Development Association, Reading University. 1/5-6/71), N.I.R.D., 1971.
[6] Feagan, J.T.; Hehir, A.F.; & White, B.R., The Effectiveness in Control of Mastitis of Iodine as a Post Milking Teat Dip, AUSTRALIAN JOURNALOF DAIRY TECHNOLOGY 25: 87-90, 1970.
[7] Supplement to Current Concepts of Bovine Mastitis. The National Mastitis Council Inc.,Washington, D.C. 22003, 1972, page 7.
BIBLIOGRAFÍA:
[1] Smith, A.; Westgarth, D.R.; Jones, M.R.; Neave, F.K.; Dodd, F.H.; & Brander, G.C., Methods of Reducing the Incidence of Udder Infection in Dry Cows, VETERINARY RECORD 81:504-510, 1967.
[2] Dodd, F.H. & Neave, F.K., Mastitis Control, N.I.R.D. BIENNIAL REVIEWS 1970, pp. 21-60.
[3] Roberts, S.J.; Meek, A.M.; Natzke, R.; & Guthrie, R., A Mastitis Control Program Combining Teat Dipping & Dry Cow Therapy, XIX WORLD VETERINARY CONGRESS (Mexico City, 8/15-21/71), PROCEEDINGS 3:935-939, 1971.
[4] Newbould, F.H.S.; Carey, P.G.; & Barnum, D.A., The Numbers of Intramammary Infections & Teat Duct Colonizations in a Herd of Twins During a Hygiene Experiment, CANADIANJOURNAL OF COMPARATIVE MEDICINE 34:203-208, 1970.
[5] Neave, F.K. & Jackson, E.R., The Prevention of Intramammary Infection, pp. 15-24 in TheControl of Bovine Mastitis (Proceedings, Joint Meeting, British Cattle Veterinary Association & The Agricultural Development Association, Reading University. 1/5-6/71), N.I.R.D., 1971.
[6] Feagan, J.T.; Hehir, A.F.; & White, B.R., The Effectiveness in Control of Mastitis of Iodine as a Post Milking Teat Dip, AUSTRALIAN JOURNALOF DAIRY TECHNOLOGY 25: 87-90, 1970.
[7] Supplement to Current Concepts of Bovine Mastitis. The National Mastitis Council Inc.,Washington, D.C. 22003, 1972, page 7.
WG Critical Care, LLC
Paramus, NJ 07652
Quartermaster is a trademark of West Agro, Inc.
Quartermaster es una marca de West Agro, Inc.
Rev. 11/2018
-
PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC: 44567-901-03
Quartermaster Suspension
Penicillin G Procaine and Dihydrostreptomycin Sulfate Intramammary Infusion
WG Critical Care
-
PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC: 44567-901-05
Quartermaster Suspension
Penicillin G Procaine and Dihydrostreptomycin Sulfate Intramammary Infusion
WG Critical Care
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
QUARTERMASTER
penicillin g procaine and dihydrostreptomycin sulfate intramammary infusion suspensionProduct Information Product Type PRESCRIPTION ANIMAL DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 44567-901 Route of Administration INTRAMAMMARY Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength PENICILLIN G PROCAINE (UNII: 17R794ESYN) (PENICILLIN G - UNII:Q42T66VG0C) PENICILLIN G 1000000 [iU] in 10 mL DIHYDROSTREPTOMYCIN SULFATE (UNII: T7D4876IUE) (DIHYDROSTREPTOMYCIN - UNII:P2I6R8W6UA) DIHYDROSTREPTOMYCIN 1 g in 10 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength PEANUT OIL, HYDROGENATED (UNII: FS8087FL3X) ALUMINUM MONOSTEARATE (UNII: P9BC99461E) PEANUT OIL (UNII: 5TL50QU0W4) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 44567-901-03 12 in 1 CARTON 1 10 mL in 1 SYRINGE 2 NDC: 44567-901-05 144 in 1 PAIL 2 10 mL in 1 SYRINGE Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NADA NADA055028 06/06/2014 Labeler - WG Critical Care, LLC (829274633) Registrant - HQ Specialty Pharma Corporation (962364332)
Trademark Results [Quartermaster]
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.