ABIRATERONE ACETATE tablet, film coated
Abiraterone Acetate by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Abiraterone Acetate by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ABIRATERONE ACETATE TABLETS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ABIRATERONE ACETATE TABLETS.
ABIRATERONE ACETATE tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2011RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Abiraterone acetate tablets are a CYP17 inhibitor indicated in combination with prednisone for the treatment of patients with
- metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer:
- Abiraterone acetate tablets 1,000 mg orally once daily with prednisone 5 mg orally twice daily. (2.1)
Patients receiving abiraterone acetate tablets should also receive a gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) analog concurrently or should have had bilateral orchiectomy. Abiraterone acetate tablets must be taken on an empty stomach with water at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal. Do not crush or chew tablets. (2.3)
Dose Modification:
- For patients with baseline moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B), reduce the abiraterone acetate tablets starting dose to 250 mg once daily. (2.4)
- For patients who develop hepatotoxicity during treatment, hold abiraterone acetate tablets until recovery. Retreatment may be initiated at a reduced dose. Abiraterone acetate tablets should be discontinued if patients develop severe hepatotoxicity. (2.4)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- Film-Coated Tablet 250 mg (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Mineralocorticoid excess: Closely monitor patients with cardiovascular disease. Control hypertension and correct hypokalemia before treatment. Monitor blood pressure, serum potassium and symptoms of fluid retention at least monthly. (5.1)
- Adrenocortical insufficiency: Monitor for symptoms and signs of adrenocortical insufficiency. Increased dosage of corticosteroids may be indicated before, during and after stressful situations. (5.2)
- Hepatotoxicity: Can be severe and fatal. Monitor liver function and modify, interrupt, or discontinue abiraterone acetate dosing as recommended. (5.3)
- Increased fractures and mortality in combination with radium Ra 223 dichloride: Use of abiraterone acetate plus prednisone/prednisolone in combination with radium Ra 223 dichloride is not recommended. (5.4)
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Abiraterone acetate can cause fetal harm. Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception. (5.5, 8.1, 8.3)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (≥10%) are fatigue, arthralgia, hypertension, nausea, edema, hypokalemia, hot flush, diarrhea, vomiting, upper respiratory infection, cough, and headache. (6.1)
The most common laboratory abnormalities (>20%) are anemia, elevated alkaline phosphatase, hypertriglyceridemia, lymphopenia, hypercholesterolemia, hyperglycemia, and hypokalemia. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, Inc. at 1-888-838-2872 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- CYP3A4 Inducers: Avoid concomitant strong CYP3A4 inducers during abiraterone acetate treatment. If a strong CYP3A4 inducer must be coadministered, increase the abiraterone acetate dosing frequency. (2.5, 7.1)
- CYP2D6 Substrates: Avoid coadministration of abiraterone acetate with CYP2D6 substrates that have a narrow therapeutic index. If an alternative treatment cannot be used, exercise caution and consider a dose reduction of the concomitant CYP2D6 substrate. (7.2)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Do not use abiraterone acetate in patients with baseline severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C). (8.6)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 6/2019
- metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). (1)
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dose for Metastatic CRPC
2.3 Important Administration Instructions
2.4 Dose Modification Guidelines in Hepatic Impairment and Hepatotoxicity
2.5 Dose Modification Guidelines for Strong CYP3A4 Inducers
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypokalemia, Fluid Retention, and Cardiovascular Adverse Reactions due to Mineralocorticoid Excess
5.2 Adrenocortical Insufficiency
5.3 Hepatotoxicity
5.4 Increased Fractures and Mortality in Combination with Radium Ra 223 Dichloride
5.5 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Drugs that Inhibit or Induce CYP3A4 Enzymes
7.2 Effects of Abiraterone on Drug Metabolizing Enzymes
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Patients with Hepatic Impairment
8.7 Patients with Renal Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dose for Metastatic CRPC
The recommended dose of abiraterone acetate tablets is 1,000 mg (two 500 mg tablets or four 250 mg tablets) orally once daily with prednisone 5 mg orally twice daily.
2.3 Important Administration Instructions
Patients receiving abiraterone acetate tablets should also receive a gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) analog concurrently or should have had bilateral orchiectomy. Abiraterone acetate tablets must be taken on an empty stomach, at least one hour before or at least two hours after a meal [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. The tablets should be swallowed whole with water. Do not crush or chew tablets.
2.4 Dose Modification Guidelines in Hepatic Impairment and Hepatotoxicity
Hepatic Impairment
In patients with baseline moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B), reduce the recommended dose of abiraterone acetate tablets to 250 mg once daily. In patients with moderate hepatic impairment monitor ALT, AST, and bilirubin prior to the start of treatment, every week for the first month, every two weeks for the following two months of treatment and monthly thereafter. If elevations in ALT and/or AST greater than 5X upper limit of normal (ULN) or total bilirubin greater than 3X ULN occur in patients with baseline moderate hepatic impairment, discontinue abiraterone acetate tablets and do not re-treat patients with abiraterone acetate tablets [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Do not use abiraterone acetate tablets in patients with baseline severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C).
Hepatotoxicity
For patients who develop hepatotoxicity during treatment with abiraterone acetate tablets (ALT and/or AST greater than 5X ULN or total bilirubin greater than 3X ULN), interrupt treatment with abiraterone acetate tablets [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. Treatment may be restarted at a reduced dose of 750 mg once daily following return of liver function tests to the patient’s baseline or to AST and ALT less than or equal to 2.5X ULN and total bilirubin less than or equal to 1.5X ULN. For patients who resume treatment, monitor serum transaminases and bilirubin at a minimum of every two weeks for three months and monthly thereafter.
If hepatotoxicity recurs at the dose of 750 mg once daily, re-treatment may be restarted at a reduced dose of 500 mg once daily following return of liver function tests to the patient’s baseline or to AST and ALT less than or equal to 2.5X ULN and total bilirubin less than or equal to 1.5X ULN.
If hepatotoxicity recurs at the reduced dose of 500 mg once daily, discontinue treatment with abiraterone acetate tablets.
Permanently discontinue abiraterone acetate tablets for patients who develop a concurrent elevation of ALT greater than 3 x ULN and total bilirubin greater than 2 x ULN in the absence of biliary obstruction or other causes responsible for the concurrent elevation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
2.5 Dose Modification Guidelines for Strong CYP3A4 Inducers
Avoid concomitant strong CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., phenytoin, carbamazepine, rifampin, rifabutin, rifapentine, phenobarbital) during abiraterone acetate tablet treatment.
If a strong CYP3A4 inducer must be coadministered, increase the abiraterone acetate tablets dosing frequency to twice a day only during the coadministration period (e.g., from 1,000 mg once daily to 1,000 mg twice a day). Reduce the dose back to the previous dose and frequency, if the concomitant strong CYP3A4 inducer is discontinued [see Drug Interactions (7.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypokalemia, Fluid Retention, and Cardiovascular Adverse Reactions due to Mineralocorticoid Excess
Abiraterone acetate may cause hypertension, hypokalemia, and fluid retention as a consequence of increased mineralocorticoid levels resulting from CYP17 inhibition [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)]. Monitor patients for hypertension, hypokalemia, and fluid retention at least once a month. Control hypertension and correct hypokalemia before and during treatment with abiraterone acetate.
In the combined data from 4 placebo-controlled trials using prednisone 5 mg twice daily in combination with 1000 mg abiraterone acetate daily, grades 3 to 4 hypokalemia were detected in 4% of patients on the abiraterone acetate arm and 2% of patients on the placebo arm. Grades 3 to 4 hypertension were observed in 2% of patients each arm and grades 3 to 4 fluid retention in 1% of patients each arm.
Closely monitor patients whose underlying medical conditions might be compromised by increases in blood pressure, hypokalemia or fluid retention, such as those with heart failure, recent myocardial infarction, cardiovascular disease, or ventricular arrhythmia. In postmarketing experience, QT prolongation and Torsades de Pointes have been observed in patients who develop hypokalemia while taking abiraterone acetate.
The safety of abiraterone acetate in patients with left ventricular ejection fraction < 50% or New York Heart Association (NYHA) Class III or IV heart failure (in COU-AA-301) or NYHA Class II to IV heart failure (in COU-AA-302) has not been established because these patients were excluded from these randomized clinical trials [see Clinical Studies (14)].
5.2 Adrenocortical Insufficiency
Adrenal insufficiency occurred in 0.3% of 2230 patients taking abiraterone acetate and in 0.1% of 1763 patients taking placebo in the combined data of randomized, placebo-controlled clinical studies. Adrenocortical insufficiency was reported in patients receiving abiraterone acetate in combination with prednisone, following interruption of daily steroids and/or with concurrent infection or stress.
Monitor patients for symptoms and signs of adrenocortical insufficiency, particularly if patients are withdrawn from prednisone, have prednisone dose reductions, or experience unusual stress.
Symptoms and signs of adrenocortical insufficiency may be masked by adverse reactions associated with mineralocorticoid excess seen in patients treated with abiraterone acetate. If clinically indicated, perform appropriate tests to confirm the diagnosis of adrenocortical insufficiency. Increased dosage of corticosteroids may be indicated before, during and after stressful situations [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
5.3 Hepatotoxicity
In postmarketing experience, there have been abiraterone acetate-associated severe hepatic toxicity, including fulminant hepatitis, acute liver failure and deaths [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
In the combined data of randomized clinical trials, grade 3 to 4 ALT or AST increases (at least 5X ULN) were reported in 6% of 2230 patients who received abiraterone acetate, typically during the first 3 months after starting treatment. Patients whose baseline ALT or AST were elevated were more likely to experience liver test elevation than those beginning with normal values. Treatment discontinuation due to ALT and AST increases or abnormal hepatic function occurred in 1.1% of 2230 patients taking abiraterone acetate. In these clinical trials, no deaths clearly related to abiraterone acetate were reported due to hepatotoxicity events.
Measure serum transaminases (ALT and AST) and bilirubin levels prior to starting treatment with abiraterone acetate, every two weeks for the first three months of treatment and monthly thereafter. In patients with baseline moderate hepatic impairment receiving a reduced abiraterone acetate dose of 250 mg, measure ALT, AST, and bilirubin prior to the start of treatment, every week for the first month, every two weeks for the following two months of treatment and monthly thereafter. Promptly measure serum total bilirubin, AST, and ALT if clinical symptoms or signs suggestive of hepatotoxicity develop. Elevations of AST, ALT, or bilirubin from the patient’s baseline should prompt more frequent monitoring. If at any time AST or ALT rise above five times the ULN, or the bilirubin rises above three times the ULN, interrupt abiraterone acetate treatment and closely monitor liver function.
Re-treatment with abiraterone acetate at a reduced dose level may take place only after return of liver function tests to the patient’s baseline or to AST and ALT less than or equal to 2.5X ULN and total bilirubin less than or equal to 1.5X ULN [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
Permanently discontinue abiraterone acetate for patients who develop a concurrent elevation of ALT greater than 3 x ULN and total bilirubin greater than 2 x ULN in the absence of biliary obstruction or other causes responsible for the concurrent elevation [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
The safety of abiraterone acetate re-treatment of patients who develop AST or ALT greater than or equal to 20X ULN and/or bilirubin greater than or equal to 10X ULN is unknown.
5.4 Increased Fractures and Mortality in Combination with Radium Ra 223 Dichloride
Abiraterone acetate plus prednisone/prednisolone is not recommended for use in combination with radium 223 dichloride outside of clinical trials.
The clinical efficacy and safety of concurrent initiation of abiraterone acetate plus prednisone/prednisolone and radium Ra 223 dichloride was assessed in a randomized, placebo-controlled multicenter study (ERA-223 trial) in 806 patients with asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic castration-resistant prostate cancer with bone metastases. The study was unblinded early based on an Independent Data Monitoring Committee recommendation.
At the primary analysis, increased incidences of fractures (28.6% vs 11.4%) and deaths (38.5% vs 35.5%) have been observed in patients who received abiraterone acetate plus prednisone/prednisolone in combination with radium Ra 223 dichloride compared to patients who received placebo in combination with abiraterone acetate plus prednisone/prednisolone.
5.5 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
The safety and efficacy of abiraterone acetate have not been established in females. Based on animal reproductive studies and mechanism of action, abiraterone acetate can cause fetal harm and loss of pregnancy when administered to a pregnant female. In animal reproduction studies, oral administration of abiraterone acetate to pregnant rats during organogenesis caused adverse developmental effects at maternal exposures approximately ≥ 0.03 times the human exposure (AUC) at the recommended dose. Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with abiraterone acetate and for 3 weeks after the last dose of abiraterone acetate [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)]. Abiraterone acetate should not be handled by females who are or may become pregnant [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following are discussed in more detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Hypokalemia, Fluid Retention, and Cardiovascular Adverse Reactions due to Mineralocorticoid Excess [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Adrenocortical Insufficiency [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- Increased Fractures and Mortality in Combination with Radium Ra 223 Dichloride [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
Two randomized placebo-controlled, multicenter clinical trials (COU-AA-301 and COU-AA-302) enrolled patients who had metastatic CRPC in which abiraterone acetate was administered orally at a dose of 1,000 mg daily in combination with prednisone 5 mg twice daily in the active treatment arms. Placebo plus prednisone 5 mg twice daily was given to patients on the control arm. Another randomized placebo-controlled, multicenter clinical trial enrolled patients who had another indication in which abiraterone acetate was administered in combination with prednisone. Placebos were administered to patients in the control arm. Additionally, two other randomized, placebo-controlled trials were conducted in patients with metastatic CRPC. The safety data pooled from 2230 patients in randomized controlled trials constitute the basis for the data presented in the Warnings and Precautions, Grade 1 to 4 adverse reactions, and Grade 1 to 4 laboratory abnormalities. In all trials, a gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) analog or prior orchiectomy was required in both arms.
In the pooled data, median treatment duration was 11 months (0.1, 43) for abiraterone acetate-treated patients and 7.2 months (0.1, 43) for placebo-treated patients. The most common adverse reactions (≥ 10%) that occurred more commonly (> 2%) in the abiraterone acetate arm were fatigue, arthralgia, hypertension, nausea, edema, hypokalemia, hot flush, diarrhea, vomiting, upper respiratory infection, cough, and headache. The most common laboratory abnormalities (> 20%) that occurred more commonly (≥ 2%) in the abiraterone acetate arm were anemia, elevated alkaline phosphatase, hypertriglyceridemia, lymphopenia, hypercholesterolemia, hyperglycemia, and hypokalemia. Grades 3 to 4 adverse events were reported for 53% of patients in the abiraterone acetate arm and 46% of patients in the placebo arm. Treatment discontinuation was reported in 14% of patients in the abiraterone acetate arm and 13% of patients in the placebo arm. The common adverse events (≥ 1%) resulting in discontinuation of abiraterone acetate and prednisone were hepatotoxicity and cardiac disorders.
Deaths associated with treatment-emergent adverse events were reported for 7.5% of patients in the abiraterone acetate arm and 6.6% of patients in the placebo arm. Of the patients in the abiraterone acetate arm, the most common cause of death was disease progression (3.3%). Other reported causes of death in > 5 patients included pneumonia, cardio-respiratory arrest, death (no additional information), and general physical health deterioration.
COU-AA-301: Metastatic CRPC Following Chemotherapy
COU-AA-301 enrolled 1195 patients with metastatic CRPC who had received prior docetaxel chemotherapy. Patients were not eligible if AST and/or ALT ≥ 2.5 X ULN in the absence of liver metastases. Patients with liver metastases were excluded if AST and/or ALT > 5X ULN.
Table 1 shows adverse reactions on the abiraterone acetate arm in COU-AA-301 that occurred with a ≥ 2% absolute increase in frequency compared to placebo or were events of special interest. The median duration of treatment with abiraterone acetate with prednisone was 8 months.
Table 1: Adverse Reactions due to Abiraterone Acetate in COU-AA-301 Abiraterone Acetate with Prednisone
(N = 791)
Placebo with Prednisone
(N = 394)
System/Organ Class
Adverse reaction
All Grades1
%
Grade 3 to 4
%
All Grades
%
Grade 3 to 4
%
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
Joint swelling/discomfort2
30
4.2
23
4.1
Muscle discomfort3
26
3.0
23
2.3
General disorders
Edema4
27
1.9
18
0.8
Vascular disorders
Hot flush
19
0.3
17
0.3
Hypertension
8.5
1.3
6.9
0.3
Gastrointestinal disorders
Diarrhea
18
0.6
14
1.3
Dyspepsia
6.1
0
3.3
0
Infections and infestations
Urinary tract infection
12
2.1
7.1
0.5
Upper respiratory tract infection
5.4
0
2.5
0
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders
Cough
11
0
7.6
0
Renal and urinary disorders
Urinary frequency
7.2
0.3
5.1
0.3
Nocturia
6.2
0
4.1
0
Injury, poisoning and procedural complications
Fractures5
5.9
1.4
2.3
0
Cardiac disorders
Arrhythmia6
7.2
1.1
4.6
1.0
Chest pain or chest discomfort7
3.8
0.5
2.8
0
Cardiac failure8
2.3
1.9
1.0
0.3
1Adverse events graded according to CTCAE version 3.0.
2Includes terms Arthritis, Arthralgia, Joint swelling, and Joint stiffness.
3Includes terms Muscle spasms, Musculoskeletal pain, Myalgia, Musculoskeletal discomfort, and Musculoskeletal stiffness.
4Includes terms Edema, Edema peripheral, Pitting edema, and Generalized edema.
5Includes all fractures with the exception of pathological fracture.
6Includes terms Arrhythmia, Tachycardia, Atrial fibrillation, Supraventricular tachycardia, Atrial tachycardia, Ventricular tachycardia, Atrial
flutter, Bradycardia, Atrioventricular block complete, Conduction disorder, and Bradyarrhythmia.7Includes terms Angina pectoris, Chest pain, and Angina unstable. Myocardial infarction or ischemia occurred more commonly in the placebo arm
than in the abiraterone acetate arm (1.3% vs. 1.1% respectively).8Includes terms Cardiac failure, Cardiac failure congestive, Left ventricular dysfunction, Cardiogenic shock, Cardiomegaly, Cardiomyopathy, and
Ejection fraction decreased.
Table 2 shows laboratory abnormalities of interest from COU-AA-301.Table 2: Laboratory Abnormalities of Interest in COU-AA-301 Abiraterone Acetate with Prednisone
(N=791)Placebo with Prednisone
(N=394)Laboratory Abnormality
All Grades (%)
Grade 3 to 4 (%)
All Grades (%)
Grade 3 to 4 (%)
Hypertriglyceridemia
63
0.4
53
0
High AST
31
2.1
36
1.5
Hypokalemia
28
5.3
20
1.0
Hypophosphatemia
24
7.2
16
5.8
High ALT
11
1.4
10
0.8
High Total Bilirubin
6.6
0.1
4.6
0
COU-AA-302: Metastatic CRPC Prior to Chemotherapy
COU-AA-302 enrolled 1088 patients with metastatic CRPC who had not received prior cytotoxic chemotherapy. Patients were ineligible if AST and/or ALT ≥ 2.5X ULN and patients were excluded if they had liver metastases.
Table 3 shows adverse reactions on the abiraterone acetate arm in COU-AA-302 that occurred in ≥ 5% of patients with a ≥ 2% absolute increase in frequency compared to placebo. The median duration of treatment with abiraterone acetate with prednisone was 13.8 months.
Table 3: Adverse Reactions in ≥5% of Patients on the Abiraterone Acetate Arm in COU-AA-302 Abiraterone Acetate with Prednisone
(N=542)
Placebo with Prednisone
(N=540)
System/Organ Class
Adverse reaction
All Grades1
%
Grade 3 to 4
%
All Grades
%
Grade 3 to 4
%
General disorders
Fatigue
39
2.2
34
1.7
Edema2
25
0.4
21
1.1
Pyrexia
8.7
0.6
5.9
0.2
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
Joint swelling/discomfort3
30
2.0
25
2.0
Groin pain
6.6
0.4
4.1
0.7
Gastrointestinal disorders
Constipation
23
0.4
19
0.6
Diarrhea
22
0.9
18
0.9
Dyspepsia
11
0.0
5.0
0.2
Vascular disorders
Hot flush
22
0.2
18
0.0
Hypertension
22
3.9
13
3.0
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders
Cough
17
0.0
14
0.2
Dyspnea
12
2.4
9.6
0.9
Psychiatric disorders
Insomnia
14
0.2
11
0.0
Injury, poisoning and procedural complications
Contusion
13
0.0
9.1
0.0
Falls
5.9
0.0
3.3
0.0
Infections and infestations
Upper respiratory tract infection
13
0.0
8.0
0.0
Nasopharyngitis
11
0.0
8.1
0.0
Renal and urinary disorders
Hematuria
10
1.3
5.6
0.6
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Rash
8.1
0.0
3.7
0.0
1Adverse events graded according to CTCAE version 3.0.
2Includes terms Edema peripheral, Pitting edema, and Generalized edema.
3Includes terms Arthritis, Arthralgia, Joint swelling, and Joint stiffness.
Table 4 shows laboratory abnormalities that occurred in greater than 15% of patients, and more frequently (> 5%) in the abiraterone acetate arm compared to placebo in COU-AA-302.
Table 4: Laboratory Abnormalities in >15% of Patients in the Abiraterone Acetate Arm of COU-AA-302 Abiraterone Acetate with Prednisone
(N=542)Placebo with Prednisone
(N=540)Laboratory Abnormality
Grade 1 to 4
%
Grade 3 to 4
%
Grade 1 to 4
%
Grade 3 to 4
%
Hematology
Lymphopenia
38
8.7
32
7.4
Chemistry
Hyperglycemia1
57
6.5
51
5.2
High ALT
42
6.1
29
0.7
High AST
37
3.1
29
1.1
Hypernatremia
330.4
25
0.2
Hypokalemia
17
2.8
10
1.7
1Based on non-fasting blood draws.
Cardiovascular Adverse Reactions
In the combined data of randomized, placebo-controlled clinical studies, cardiac failure occurred more commonly in patients on the abiraterone acetate arm compared to patients on the placebo arm (2.6% versus 0.9%). Grade 3 to 4 cardiac failure occurred in 1.3% of patients taking abiraterone acetate and led to 5 treatment discontinuations and 4 deaths. Grade 3 to 4 cardiac failure occurred in 0.2% of patients taking placebo. There were no treatment discontinuations and two deaths due to cardiac failure in the placebo group.
In the same combined data, the majority of arrhythmias were grade 1 or 2. There was one death associated with arrhythmia and three patients with sudden death in the abiraterone acetate arms and five deaths in the placebo arms. There were 7 (0.3%) deaths due to cardiorespiratory arrest in the abiraterone acetate arms and 2 (0.1%) deaths in the placebo arms. Myocardial ischemia or myocardial infarction led to death in 3 patients in the placebo arms and 3 deaths in the abiraterone acetate arms.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following additional adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of abiraterone acetate with prednisone. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders: non-infectious pneumonitis.
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders: myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis.
Hepatobiliary Disorders: fulminant hepatitis, including acute hepatic failure and death.
Cardiac Disorders: QT prolongation and Torsades de Pointes (observed in patients who developed hypokalemia or had underlying cardiovascular conditions).
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Drugs that Inhibit or Induce CYP3A4 Enzymes
Based on in vitro data, abiraterone acetate is a substrate of CYP3A4.
In a dedicated drug interaction trial, coadministration of rifampin, a strong CYP3A4 inducer, decreased exposure of abiraterone by 55%. Avoid concomitant strong CYP3A4 inducers during abiraterone acetate treatment. If a strong CYP3A4 inducer must be coadministered, increase the abiraterone acetate dosing frequency [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
In a dedicated drug interaction trial, coadministration of ketoconazole, a strong inhibitor of CYP3A4, had no clinically meaningful effect on the pharmacokinetics of abiraterone [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.2 Effects of Abiraterone on Drug Metabolizing Enzymes
Abiraterone acetate is an inhibitor of the hepatic drug-metabolizing enzymes CYP2D6 and CYP2C8. In a CYP2D6 drug-drug interaction trial, the Cmax and AUC of dextromethorphan (CYP2D6 substrate) were increased 2.8- and 2.9-fold, respectively, when dextromethorphan was given with abiraterone acetate 1,000 mg daily and prednisone 5 mg twice daily. Avoid coadministration of abiraterone acetate with substrates of CYP2D6 with a narrow therapeutic index (e.g., thioridazine). If alternative treatments cannot be used, consider a dose reduction of the concomitant CYP2D6 substrate drug [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
In a CYP2C8 drug-drug interaction trial in healthy subjects, the AUC of pioglitazone (CYP2C8 substrate) was increased by 46% when pioglitazone was given together with a single dose of 1,000 mg abiraterone acetate. Therefore, patients should be monitored closely for signs of toxicity related to a CYP2C8 substrate with a narrow therapeutic index if used concomitantly with abiraterone acetate [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
The safety and efficacy of abiraterone acetate have not been established in females. Based on findings from animal studies and the mechanism of action, abiraterone acetate can cause fetal harm and potential loss of pregnancy.
There are no human data on the use of abiraterone acetate tablets in pregnant women. In animal reproduction studies, oral administration of abiraterone acetate to pregnant rats during organogenesis caused adverse developmental effects at maternal exposures approximately ≥0.03 times the human exposure (AUC) at the recommended dose (see Data).
Data
Animal Data
In an embryo-fetal developmental toxicity study in rats, abiraterone acetate caused developmental toxicity when administered at oral doses of 10, 30 or 100 mg/kg/day throughout the period of organogenesis (gestational days 6 to 17). Findings included embryo-fetal lethality (increased post implantation loss and resorptions and decreased number of live fetuses), fetal developmental delay (skeletal effects) and urogenital effects (bilateral ureter dilation) at doses ≥10 mg/kg/day, decreased fetal ano-genital distance at ≥30 mg/kg/day, and decreased fetal body weight at 100 mg/kg/day. Doses ≥10 mg/kg/day caused maternal toxicity. The doses tested in rats resulted in systemic exposures (AUC) approximately 0.03, 0.1 and 0.3 times, respectively, the AUC in patients.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
The safety and efficacy of abiraterone acetate tablets have not been established in females. There is no information available on the presence of abiraterone acetate in human milk, or on the effects on the breastfed child or milk production.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Contraception
Males
Based on findings in animal reproduction studies and its mechanism of action, advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for 3 weeks after the final dose of abiraterone acetate tablets [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Infertility
Based on animal studies, abiraterone acetate may impair reproductive function and fertility in males of reproductive potential [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of abiraterone acetate tablets in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the total number of patients receiving abiraterone acetate tablets in randomized clinical trials, 70% of patients were 65 years and over and 27% were 75 years and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these elderly patients and younger patients. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
8.6 Patients with Hepatic Impairment
The pharmacokinetics of abiraterone were examined in subjects with baseline mild (N=8) or moderate (N=8) hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A and B, respectively) and in 8 healthy control subjects with normal hepatic function. The systemic exposure (AUC) of abiraterone after a single oral 1,000 mg dose of abiraterone acetate tablets increased by approximately 1.1-fold and 3.6-fold in subjects with mild and moderate baseline hepatic impairment, respectively compared to subjects with normal hepatic function.
In another trial, the pharmacokinetics of abiraterone were examined in subjects with baseline severe (N=8) hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C) and in 8 healthy control subjects with normal hepatic function. The systemic exposure (AUC) of abiraterone increased by approximately 7-fold and the fraction of free drug increased 2-fold in subjects with severe baseline hepatic impairment compared to subjects with normal hepatic function.
No dosage adjustment is necessary for patients with baseline mild hepatic impairment. In patients with baseline moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B), reduce the recommended dose of abiraterone acetate tablets to 250 mg once daily. Do not use abiraterone acetate tablets in patients with baseline severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C). If elevations in ALT or AST >5X ULN or total bilirubin >3X ULN occur in patients with baseline moderate hepatic impairment, discontinue abiraterone acetate treatment [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
For patients who develop hepatotoxicity during treatment, interruption of treatment and dosage adjustment may be required [see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Warnings and Precautions (5.3), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Patients with Renal Impairment
No dosage adjustment is necessary for patients with renal impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Abiraterone acetate, USP, the active ingredient of Abiraterone Acetate Tablets, USP is the acetyl ester of abiraterone. Abiraterone is an inhibitor of CYP17 (17α-hydroxylase/C17,20-lyase). Each Abiraterone Acetate Tablet USP contains 250 mg of abiraterone acetate, USP. Abiraterone acetate, USP is designated chemically as (3β)-17-(3-pyridinyl)androsta-5,16-dien-3-yl acetate and its structure is:
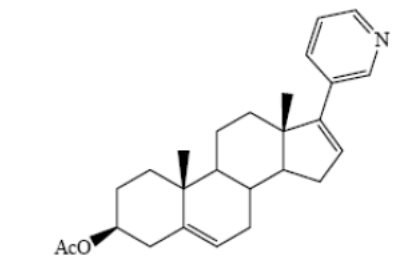
C26H33NO2 M.W. 391.55
Abiraterone acetate, USP is a white to off-white, non-hygroscopic, crystalline powder. Abiraterone acetate, USP is a lipophilic compound with an octanol-water partition coefficient of 5.12 (Log P) and is practically insoluble in water. The pKa of the aromatic nitrogen is 5.19.
Abiraterone Acetate Tablets, USP are available as 250 mg film-coated tablets with the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol (part hydrolyzed), povidone, sodium lauryl sulfate, talc, and titanium dioxide.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Abiraterone acetate is converted in vivo to abiraterone, an androgen biosynthesis inhibitor, that inhibits 17α-hydroxylase/C17,20-lyase (CYP17). This enzyme is expressed in testicular, adrenal, and prostatic tumor tissues and is required for androgen biosynthesis.
CYP17 catalyzes two sequential reactions: 1) the conversion of pregnenolone and progesterone to their 17α-hydroxy derivatives by 17α-hydroxylase activity and 2) the subsequent formation of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) and androstenedione, respectively, by C17, 20 lyase activity. DHEA and androstenedione are androgens and are precursors of testosterone. Inhibition of CYP17 by abiraterone can also result in increased mineralocorticoid production by the adrenals [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Androgen sensitive prostatic carcinoma responds to treatment that decreases androgen levels. Androgen deprivation therapies, such as treatment with GnRH agonists or orchiectomy, decrease androgen production in the testes but do not affect androgen production by the adrenals or in the tumor.
Abiraterone acetate decreased serum testosterone and other androgens in patients in the placebo-controlled clinical trial. It is not necessary to monitor the effect of abiraterone acetate on serum testosterone levels.
Changes in serum prostate specific antigen (PSA) levels may be observed but have not been shown to correlate with clinical benefit in individual patients.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Cardiac Electrophysiology
In a multi-center, open-label, single-arm trial, 33 patients with metastatic CRPC received abiraterone acetate orally at a dose of 1,000 mg once daily at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal in combination with prednisone 5 mg orally twice daily. Assessments up to Cycle 2 Day 2 showed no large changes in the QTc interval (i.e., >20 ms) from baseline. However, small increases in the QTc interval (i.e., <10 ms) due to abiraterone acetate cannot be excluded due to study design limitations.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Following administration of abiraterone acetate, the pharmacokinetics of abiraterone and abiraterone acetate have been studied in healthy subjects and in patients with metastatic CRPC. In vivo, abiraterone acetate is converted to abiraterone. In clinical studies, abiraterone acetate plasma concentrations were below detectable levels (<0.2 ng/mL) in >99% of the analyzed samples.
Absorption
Following oral administration of abiraterone acetate to patients with metastatic CRPC, the median time to reach maximum plasma abiraterone concentrations is 2 hours. Abiraterone accumulation is observed at steady-state, with a 2-fold higher exposure (steady-state AUC) compared to a single 1,000 mg dose of abiraterone acetate.
At the dose of 1,000 mg daily in patients with metastatic CRPC, steady-state values (mean ± SD) of Cmax were 226 ± 178 ng/mL and of AUC were 993 ± 639 ng.hr/mL. No major deviation from dose proportionality was observed in the dose range of 250 mg to 1,000 mg. However, the exposure was not significantly increased when the dose was doubled from 1,000 to 2,000 mg (8% increase in the mean AUC).
Systemic exposure of abiraterone is increased when abiraterone acetate is administered with food. In healthy subjects abiraterone Cmax and AUC0-∞ were approximately 7- and 5-fold higher, respectively, when a single dose of abiraterone acetate was administered with a low-fat meal (7% fat, 300 calories) and approximately 17- and 10-fold higher, respectively, when a single dose of abiraterone acetate was administered with a high-fat (57% fat, 825 calories) meal compared to overnight fasting. Abiraterone AUC0-∞ was approximately 7-fold or 1.6-fold higher, respectively, when a single dose of abiraterone acetate was administered 2 hours after or 1 hour before a medium fat meal (25% fat, 491 calories) compared to overnight fasting.
Systemic exposures of abiraterone in patients with metastatic CRPC, after repeated dosing of abiraterone acetate were similar when abiraterone acetate was taken with low-fat meals for 7 days and increased approximately 2-fold when taken with high-fat meals for 7 days compared to when taken at least 2 hours after a meal and at least 1 hour before a meal for 7 days.
Given the normal variation in the content and composition of meals, taking abiraterone acetate tablets with meals has the potential to result in increased and highly variable exposures. Therefore, abiraterone acetate tablets must be taken on an empty stomach, at least one hour before or at least two hours after a meal. The tablets should be swallowed whole with water [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Distribution and Protein Binding
Abiraterone is highly bound (>99%) to the human plasma proteins, albumin and alpha-1 acid glycoprotein. The apparent steady-state volume of distribution (mean ± SD) is 19,669 ± 13,358 L. In vitro studies show that at clinically relevant concentrations, abiraterone acetate and abiraterone are not substrates of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and that abiraterone acetate is an inhibitor of P-gp.
Metabolism
Following oral administration of 14C-abiraterone acetate as capsules, abiraterone acetate is hydrolyzed to abiraterone (active metabolite). The conversion is likely through esterase activity (the esterases have not been identified) and is not CYP mediated. The two main circulating metabolites of abiraterone in human plasma are abiraterone sulphate (inactive) and N-oxide abiraterone sulphate (inactive), which account for about 43% of exposure each. CYP3A4 and SULT2A1 are the enzymes involved in the formation of N-oxide abiraterone sulphate and SULT2A1 is involved in the formation of abiraterone sulphate.
Excretion
In patients with metastatic CRPC, the mean terminal half-life of abiraterone in plasma (mean ± SD) is 12 ± 5 hours. Following oral administration of 14C-abiraterone acetate, approximately 88% of the radioactive dose is recovered in feces and approximately 5% in urine. The major compounds present in feces are unchanged abiraterone acetate and abiraterone (approximately 55% and 22% of the administered dose, respectively).
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
The pharmacokinetics of abiraterone was examined in subjects with baseline mild (N=8) or moderate (N=8) hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A and B, respectively) and in 8 healthy control subjects with normal hepatic function. Systemic exposure to abiraterone after a single oral 1,000 mg dose given under fasting conditions increased approximately 1.1-fold and 3.6-fold in subjects with mild and moderate baseline hepatic impairment, respectively. The mean half-life of abiraterone is prolonged to approximately 18 hours in subjects with mild hepatic impairment and to approximately 19 hours in subjects with moderate hepatic impairment.
In another trial, the pharmacokinetics of abiraterone were examined in subjects with baseline severe (N=8) hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C) and in 8 healthy control subjects with normal hepatic function. The systemic exposure (AUC) of abiraterone increased by approximately 7-fold in subjects with severe baseline hepatic impairment compared to subjects with normal hepatic function. In addition, the mean protein binding was found to be lower in the severe hepatic impairment group compared to the normal hepatic function group, which resulted in a two-fold increase in the fraction of free drug in patients with severe hepatic impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Patients with Renal Impairment
The pharmacokinetics of abiraterone were examined in patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) on a stable hemodialysis schedule (N=8) and in matched control subjects with normal renal function (N=8). In the ESRD cohort of the trial, a single 1,000 mg abiraterone acetate tablet dose was given under fasting conditions 1 hour after dialysis, and samples for pharmacokinetic analysis were collected up to 96 hours post dose. Systemic exposure to abiraterone after a single oral 1,000 mg dose did not increase in subjects with end-stage renal disease on dialysis, compared to subjects with normal renal function [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
Drug Interactions
In vitro studies with human hepatic microsomes showed that abiraterone has the potential to inhibit CYP1A2, CYP2D6, CYP2C8 and to a lesser extent CYP2C9, CYP2C19 and CYP3A4/5.
In an in vivo drug-drug interaction trial, the Cmax and AUC of dextromethorphan (CYP2D6 substrate) were increased 2.8- and 2.9-fold, respectively when dextromethorphan 30 mg was given with abiraterone acetate 1,000 mg daily (plus prednisone 5 mg twice daily). The AUC for dextrorphan, the active metabolite of dextromethorphan, increased approximately 1.3 fold [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
In a clinical study to determine the effects of abiraterone acetate 1,000 mg daily (plus prednisone 5 mg twice daily) on a single 100 mg dose of the CYP1A2 substrate theophylline, no increase in systemic exposure of theophylline was observed.
Abiraterone is a substrate of CYP3A4, in vitro. In a clinical pharmacokinetic interaction study of healthy subjects pretreated with a strong CYP3A4 inducer (rifampin, 600 mg daily for 6 days) followed by a single dose of abiraterone acetate 1,000 mg, the mean plasma AUC∞ of abiraterone was decreased by 55% [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
In a separate clinical pharmacokinetic interaction study of healthy subjects, coadministration of ketoconazole, a strong inhibitor of CYP3A4, had no clinically meaningful effect on the pharmacokinetics of abiraterone [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
In a CYP2C8 drug-drug interaction trial in healthy subjects, the AUC of pioglitazone was increased by 46% when pioglitazone was given together with a single dose of 1,000 mg abiraterone acetate [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
In vitro, abiraterone and its major metabolites were shown to inhibit the hepatic uptake transporter OATP1B1. There are no clinical data available to confirm transporter based interaction.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
A two-year carcinogenicity study was conducted in rats at oral abiraterone acetate doses of 5, 15, and 50 mg/kg/day for males and 15, 50, and 150 mg/kg/day for females. Abiraterone acetate increased the combined incidence of interstitial cell adenomas and carcinomas in the testes at all dose levels tested. This finding is considered to be related to the pharmacological activity of abiraterone. Rats are regarded as more sensitive than humans to developing interstitial cell tumors in the testes. Abiraterone acetate was not carcinogenic in female rats at exposure levels up to 0.8 times the human clinical exposure based on AUC. Abiraterone acetate was not carcinogenic in a 6-month study in the transgenic (Tg.rasH2) mouse.
Abiraterone acetate and abiraterone was not mutagenic in an in vitro microbial mutagenesis (Ames) assay or clastogenic in an in vitro cytogenetic assay using primary human lymphocytes or an in vivo rat micronucleus assay.
In repeat-dose toxicity studies in male rats (13- and 26-weeks) and monkeys (39-weeks), atrophy, aspermia/hypospermia, and hyperplasia in the reproductive system were observed at ≥50 mg/kg/day in rats and ≥250 mg/kg/day in monkeys and were consistent with the antiandrogenic pharmacological activity of abiraterone. These effects were observed in rats at systemic exposures similar to humans and in monkeys at exposures approximately 0.6 times the AUC in humans.
In a fertility study in male rats, reduced organ weights of the reproductive system, sperm counts, sperm motility, altered sperm morphology and decreased fertility were observed in animals dosed for 4 weeks at ≥30 mg/kg/day orally. Mating of untreated females with males that received 30 mg/kg/day oral abiraterone acetate resulted in a reduced number of corpora lutea, implantations and live embryos and an increased incidence of pre-implantation loss. Effects on male rats were reversible after 16 weeks from the last abiraterone acetate administration.
In a fertility study in female rats, animals dosed orally for 2 weeks until day 7 of pregnancy at ≥30 mg/kg/day had an increased incidence of irregular or extended estrous cycles and pre-implantation loss (300 mg/kg/day). There were no differences in mating, fertility, and litter parameters in female rats that received abiraterone acetate. Effects on female rats were reversible after 4 weeks from the last abiraterone acetate administration.
The dose of 30 mg/kg/day in rats is approximately 0.3 times the recommended dose of 1,000 mg/day based on body surface area.
In 13- and 26-week studies in rats and 13- and 39-week studies in monkeys, a reduction in circulating testosterone levels occurred with abiraterone acetate at approximately one half the human clinical exposure based on AUC. As a result, decreases in organ weights and toxicities were observed in the male and female reproductive system, adrenal glands, liver, pituitary (rats only), and male mammary glands. The changes in the reproductive organs are consistent with the antiandrogenic pharmacological activity of abiraterone acetate.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
A dose-dependent increase in cataracts was observed in rats after daily oral abiraterone acetate administration for 26 weeks starting at ≥50 mg/kg/day (similar to the human clinical exposure based on AUC). In a 39-week monkey study with daily oral abiraterone acetate administration, no cataracts were observed at higher doses (2 times greater than the clinical exposure based on AUC).
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy and safety of abiraterone acetate with prednisone was established in three randomized placebo-controlled international clinical studies. All patients in these studies received a GnRH analog or had prior bilateral orchiectomy. Patients with prior ketoconazole treatment for prostate cancer and a history of adrenal gland or pituitary disorders were excluded from these trials. Concurrent use of spironolactone was not allowed during the study period.
COU-AA-301: Patients with metastatic CRPC who had received prior docetaxel chemotherapy
In COU-AA-301 (NCT00638690), a total of 1195 patients were randomized 2:1 to receive either abiraterone acetate orally at a dose of 1,000 mg once daily in combination with prednisone 5 mg orally twice daily (N=797) or placebo once daily plus prednisone 5 mg orally twice daily (N=398). Patients randomized to either arm were to continue treatment until disease progression (defined as a 25% increase in PSA over the patient’s baseline/nadir together with protocol-defined radiographic progression and symptomatic or clinical progression), initiation of new treatment, unacceptable toxicity or withdrawal.
The following patient demographics and baseline disease characteristics were balanced between the treatment arms. The median age was 69 years (range 39 to 95) and the racial distribution was 93% Caucasian, 3.6% Black, 1.7% Asian, and 1.6% Other. Eighty-nine percent of patients enrolled had an ECOG performance status score of 0 to 1 and 45% had a Brief Pain Inventory-Short Form score of ≥4 (patient’s reported worst pain over the previous 24 hours). Ninety percent of patients had metastases in bone and 30% had visceral involvement. Seventy percent of patients had radiographic evidence of disease progression and 30% had PSA-only progression. Seventy percent of patients had previously received one cytotoxic chemotherapy regimen and 30% received two regimens.
The protocol pre-specified interim analysis was conducted after 552 deaths and showed a statistically significant improvement in overall survival (OS) in patients treated with abiraterone acetate with prednisone compared to patients in the placebo with prednisone arm (Table 9 and Figure 1). An updated survival analysis was conducted when 775 deaths (97% of the planned number of deaths for final analysis) were observed. Results from this analysis were consistent with those from the interim analysis (Table 7).
Table 7: Overall Survival of Patients Treated with Either Abiraterone Acetate or Placebo in Combination with Prednisone in COU-AA-301 (Intent-to-Treat Analysis) Abiraterone Acetate with Prednisone
(N=797)
Placebo with Prednisone
(N=398)
Primary Survival Analysis
Deaths (%)
333 (42%)
219 (55%)
Median survival (months)
14.8 (14.1, 15.4)
10.9 (10.2, 12.0)
(95% CI)
p-value1
<0.0001
Hazard ratio (95% CI)2
0.646 (0.543, 0.768)
Updated Survival Analysis
Deaths (%)
501 (63%)
274 (69%)
Median survival (months)
15.8 (14.8, 17.0)
11.2 (10.4, 13.1)
(95% CI)
Hazard ratio (95% CI)2
0.740 (0.638, 0.859)
1p-value is derived from a log-rank test stratified by ECOG performance status score (0 to 1 vs. 2), pain score (absent vs. present), number of prior
chemotherapy regimens (1 vs. 2), and type of disease progression (PSA only vs. radiographic).2Hazard Ratio is derived from a stratified proportional hazards model. Hazard ratio <1 favors abiraterone acetate with prednisone.
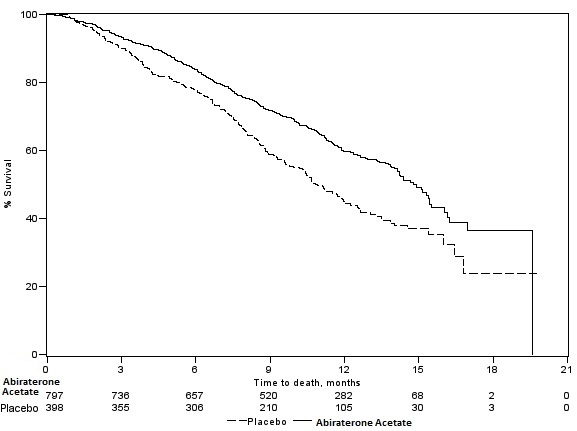
Figure 1: Kaplan-Meier Overall Survival Curves in COU-AA-301 (Intent-to-Treat Analysis)
COU-AA-302: Patients with metastatic CRPC who had not received prior cytotoxic chemotherapy
In COU-AA-302 (NCT00887198), 1088 patients were randomized 1:1 to receive either abiraterone acetate orally at a dose of 1,000 mg once daily (N=546) or Placebo orally once daily (N=542). Both arms were given concomitant prednisone 5 mg twice daily. Patients continued treatment until radiographic or clinical (cytotoxic chemotherapy, radiation or surgical treatment for cancer, pain requiring chronic opioids, or ECOG performance status decline to 3 or more) disease progression, unacceptable toxicity or withdrawal. Patients with moderate or severe pain, opiate use for cancer pain, or visceral organ metastases were excluded.
Patient demographics were balanced between the treatment arms. The median age was 70 years. The racial distribution of patients treated with abiraterone acetate was 95% Caucasian, 2.8% Black, 0.7% Asian and 1.1% Other. The ECOG performance status was 0 for 76% of patients, and 1 for 24% of patients. Co-primary efficacy endpoints were overall survival and radiographic progression-free survival (rPFS). Baseline pain assessment was 0 to 1 (asymptomatic) in 66% of patients and 2 to 3 (mildly symptomatic) in 26% of patients as defined by the Brief Pain Inventory-Short Form (worst pain over the last 24 hours).
Radiographic progression-free survival was assessed with the use of sequential imaging studies and was defined by bone scan identification of 2 or more new bone lesions with confirmation (Prostate Cancer Working Group 2 criteria) and/or modified Response Evaluation Criteria In Solid Tumors (RECIST) criteria for progression of soft tissue lesions. Analysis of rPFS utilized centrally-reviewed radiographic assessment of progression.
The planned final analysis for OS, conducted after 741 deaths (median follow up of 49 months) demonstrated a statistically significant OS improvement in patients treated with abiraterone acetate with prednisone compared to those treated with placebo with prednisone (Table 8 and Figure 2). Sixty-five percent of patients on the abiraterone acetate arm and 78% of patients on the placebo arm used subsequent therapies that may prolong OS in metastatic CRPC. Abiraterone acetate was used as a subsequent therapy in 13% of patients on the abiraterone acetate arm and 44% of patients on the placebo arm.
Table 8: Overall Survival of Patients Treated with Either Abiraterone Acetate or Placebo in Combination with Prednisone in COU-AA-302 (Intent-to-Treat Analysis) Overall Survival
Abiraterone Acetate with Prednisone
(N=546)
Placebo with Prednisone
(N=542)
Deaths
354 (65%)
387 (71%)
Median survival (months)
(95% CI)
34.7
(32.7, 36.8)
30.3
(28.7, 33.3)
p-value1
0.0033
Hazard ratio2 (95% CI)
0.81 (0.70, 0.93)
1p-value is derived from a log-rank test stratified by ECOG performance status score (0 vs. 1).
2Hazard Ratio is derived from a stratified proportional hazards model. Hazard ratio <1 favors abiraterone acetate with prednisone.
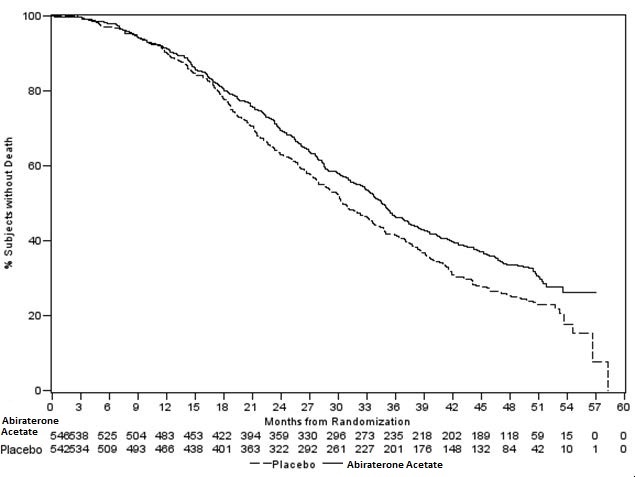
Figure 2: Kaplan Meier Overall Survival Curves in COU-AA-302
At the pre-specified rPFS analysis, 150 (28%) patients treated with abiraterone acetate with prednisone and 251 (46%) patients treated with placebo with prednisone had radiographic progression. A significant difference in rPFS between treatment groups was observed (Table 9 and Figure 3).Table 9: Radiographic Progression-free Survival of Patients Treated with Either Abiraterone Acetate or Placebo in Combination with Prednisone in COU-AA-302 (Intent-to-Treat Analysis) Radiographic Progression-free Survival
Abiraterone Acetate with Prednisone
(N=546)
Placebo with Prednisone
(N=542)
Progression or death
150 (28%)
251 (46%)
Median rPFS (months)
(95% CI)
NR
(11.66, NR)
8.28
(8.12, 8.54)
p-value1
<0.0001
Hazard ratio2 (95% CI)
0.425 (0.347, 0.522)
NR=Not reached
1p-value is derived from a log-rank test stratified by ECOG performance status score (0 vs. 1).
2Hazard Ratio is derived from a stratified proportional hazards model. Hazard ratio <1 favors abiraterone acetate with prednisone.
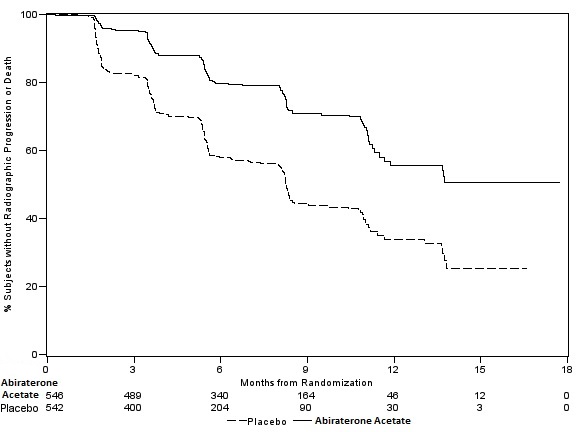
Figure 3: Kaplan Meier Curves of Radiographic Progression-free Survival in COU-AA-302 (Intent-to-Treat Analysis)
The primary efficacy analyses are supported by the following prospectively defined endpoints. The median time to initiation of cytotoxic chemotherapy was 25.2 months for patients in the abiraterone acetate arm and 16.8 months for patients in the placebo arm (HR = 0.580; 95% CI: [0.487, 0.691], p < 0.0001).
The median time to opiate use for prostate cancer pain was not reached for patients receiving abiraterone acetate and was 23.7 months for patients receiving placebo (HR = 0.686; 95% CI: [0.566, 0.833], p = 0.0001). The time to opiate use result was supported by a delay in patient reported pain progression favoring the abiraterone acetate arm.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Abiraterone Acetate Tablets USP, 250 mg are white, modified, oval-shaped, unscored, film-coated tablets, debossed with “TEVA” on one side and “1125” on the other side.
Abiraterone Acetate Tablets USP, 250 mg are available in bottles of 120 (NDC: 0093-1125-89).
Storage and Handling
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted in the range from 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Keep this and all medications out of the reach of children.
Based on its mechanism of action, abiraterone acetate tablets may harm a developing fetus. Women who are pregnant or women who may be pregnant should not handle abiraterone acetate tablets if broken, crushed, or damaged without protection, e.g., gloves [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information)
Hypokalemia, Fluid Retention, and Cardiovascular Adverse Reactions
- Inform patients that abiraterone acetate tablets are associated with hypertension, hypokalemia, and peripheral edema that may lead to QT prolongation and Torsades de Pointes in patients who develop hypokalemia while taking abiraterone acetate tablets. Advise patients that their blood pressure, serum potassium and signs and symptoms of fluid retention will be monitored clinically at least monthly. Advise patients to adhere to corticosteroids and to report symptoms of hypertension, hypokalemia, or edema to their healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Adrenocortical Insufficiency
- Inform patients that abiraterone acetate tablets with prednisone are associated with adrenal insufficiency. Advise patients to report symptoms of adrenocortical insufficiency to their healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Hepatotoxicity
- Inform patients that abiraterone acetate tablets are associated with severe hepatotoxicity. Inform patients that their liver function will be monitored using blood tests. Advise patients to immediately report symptoms of hepatotoxicity to their healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Use in Combination with Radium Ra 223 Dichloride
- Advise patients that radium Ra 223 dichloride showed an increase in mortality and an increased rate of fracture when used in combination with abiraterone acetate plus prednisone/prednisolone. Inform patients to speak with their healthcare provider about any other medications or treatment they are currently taking for prostate cancer [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Dosing and Administration
- Inform patients that abiraterone acetate tablets are taken once daily with prednisone (twice daily according to their healthcare provider’s instructions) and to not interrupt or stop either of these medications without consulting their healthcare provider.
- Inform patients receiving GnRH therapy that they need to maintain this treatment during the course of treatment with abiraterone acetate tablets.
- Instruct patients to take abiraterone acetate tablets on an empty stomach, at least one hour before or at least two hours after a meal. Abiraterone acetate tablets taken with food causes increased exposure and may result in adverse reactions. Instruct patients to swallow tablets whole with water and not to crush or chew the tablets [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
- Inform patients that if they miss a dose of abiraterone acetate tablets or prednisone, they should take their normal dose the following day. If more than one daily dose is skipped, inform patients to contact their healthcare provider [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
- Inform patients that abiraterone acetate tablets may harm a developing fetus and can cause loss of pregnancy.
- Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for 3 weeks after the final dose of abiraterone acetate tablets [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
- Advise females who are pregnant or women who may be pregnant not to handle abiraterone acetate tablets if broken, crushed, or damaged without protection, e.g., gloves [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) and How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16)].
Infertility
- Advise male patients that abiraterone acetate tablets may impair fertility [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Manufactured In Israel By:
Teva Pharmaceutical Ind. Ltd.
Jerusalem, 9777402, Israel
Manufactured For:
Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, Inc.
North Wales, PA 19454Rev. D 6/2019
-
PATIENT INFORMATION
Abiraterone Acetate (aʺ bir aʹ ter one asʹ e tate) Tablets
What are abiraterone acetate tablets?
Abiraterone acetate tablets are a prescription medicine that is used along with prednisone. Abiraterone acetate tablets are used to treat men with prostate cancer that has spread to other parts of the body.
It is not known if abiraterone acetate tablets are safe and effective in females or children.
Before taking abiraterone acetate tablets, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have heart problems
- have liver problems
- have a history of adrenal problems
- have a history of pituitary problems
- are receiving any other treatment for prostate cancer
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. Abiraterone acetate tablets can cause harm to your unborn baby and loss of pregnancy (miscarriage). Females who are or may become pregnant should not handle abiraterone acetate tablets if broken, crushed, or damaged without protection, such as gloves.
- have a partner who is pregnant or may become pregnant.
- Males who have female partners who are able to become pregnant should use effective birth control (contraception) during treatment with abiraterone acetate tablets and for 3 weeks after the last dose of abiraterone acetate tablets.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if abiraterone acetate passes into your breast milk.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take or treatments you receive, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Abiraterone acetate tablets can interact with many other medicines.
You should not start or stop any medicine before you talk with the healthcare provider that prescribed abiraterone acetate tablets.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them with you to show to your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I take abiraterone acetate tablets?
- Take abiraterone acetate tablets and prednisone exactly as your healthcare provider tells you.
- Take your prescribed dose of abiraterone acetate tablets 1 time a day.
- Your healthcare provider may change your dose if needed.
- Do not change or stop taking your prescribed dose of abiraterone acetate tablets or prednisone without talking with your healthcare provider first.
- Take abiraterone acetate tablets on an empty stomach, at least one hour before or at least two hours after a meal. Do not take abiraterone acetate tablets with food. Taking abiraterone acetate tablets with food may cause more of the medicine to be absorbed by the body than is needed and this may cause side effects.
- Swallow abiraterone acetate tablets whole. Do not crush or chew tablets.
- Take abiraterone acetate tablets with water.
- If you miss a dose of abiraterone acetate tablets or prednisone, take your prescribed dose the following day. If you miss more than 1 dose, tell your healthcare provider right away.
- Your healthcare provider will do blood tests to check for side effects.
What are the possible side effects of abiraterone acetate tablets?
Abiraterone acetate tablets may cause serious side effects including:
- High blood pressure (hypertension), low blood potassium levels (hypokalemia), fluid retention (edema), and irregular heartbeats can happen during treatment with abiraterone acetate tablets.This can be life threatening. To decrease the chance of this happening, you must take prednisone with abiraterone acetate tablets exactly as your healthcare provider tells you. Your healthcare provider will check your blood pressure, do blood tests to check your potassium levels, and check for any signs and symptoms of fluid retention every month during treatment with abiraterone acetate tablets.
Tell your healthcare provider if you get any of the following symptoms:
- dizziness
- confusion
- fast or irregular heartbeats
- muscle weakness
- feel faint or lightheaded
- pain in your legs
- headache
- swelling in your legs or feet
-
Adrenal problems may happen if you stop taking prednisone, get an infection, or are under stress.
-
Liver problems. You may develop changes in liver function blood test. Your healthcare provider will do blood tests to check your liver before treatment with abiraterone acetate tablets and during treatment with abiraterone acetate tablets. Liver failure may occur, which can lead to death. Tell your healthcare provider if you notice any of the following changes:
- yellowing of the skin or eyes
- darkening of the urine
- severe nausea or vomiting
- Increased risk of bone fracture and death when abiraterone acetate tablets and prednisone or prednisolone, is used in combination with a type of radiation called radium Ra 223 dichloride. Tell your healthcare provider about any other treatments you are taking for prostate cancer.
The most common side effects of abiraterone acetate tablets include:- feeling very tired
- vomiting
- joint pain
- infected nose, sinuses, or throat (cold)
- high blood pressure
- cough
- nausea
- headache
- swelling in your legs or feet
- low red blood cells (anemia)
- low blood potassium levels
- high blood cholesterol and triglycerides
- hot flushes
- high blood sugar levels
- diarrhea
- certain other abnormal blood tests
Abiraterone acetate tablets may cause fertility problems in males, which may affect the ability to father children. Talk to your healthcare provider if you have concerns about fertility.
These are not all the possible side effects of abiraterone acetate tablets. Call your healthcare provider for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.How should I store abiraterone acetate tablets?
- Store abiraterone acetate tablets at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
Keep abiraterone acetate tablets and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about abiraterone acetate tablets.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use abiraterone acetate tablets for a condition for which they were not prescribed. Do not give abiraterone acetate tablets to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. They may harm them.
You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about abiraterone acetate tablets that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients of abiraterone acetate tablets?
Active ingredient: abiraterone acetate
Inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol (part hydrolyzed), povidone, sodium lauryl sulfate, talc, and titanium dioxide.
Manufactured In Israel By:
Teva Pharmaceutical Ind. Ltd.
Jerusalem, 9777402, Israel
Manufactured For:
Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, Inc.
North Wales, PA 19454
For more information, call 1-888-838-2872.
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Rev. D 6/2019
- PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
ABIRATERONE ACETATE
abiraterone acetate tablet, film coatedProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0093-1125 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength ABIRATERONE ACETATE (UNII: EM5OCB9YJ6) (ABIRATERONE - UNII:G819A456D0) ABIRATERONE ACETATE 250 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) CROSCARMELLOSE SODIUM (UNII: M28OL1HH48) LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL 3350 (UNII: G2M7P15E5P) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL 4000 (UNII: 4R4HFI6D95) POVIDONE K30 (UNII: U725QWY32X) SODIUM LAURYL SULFATE (UNII: 368GB5141J) TALC (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) MICROCRYSTALLINE CELLULOSE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) POLYVINYL ALCOHOL, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 532B59J990) Product Characteristics Color WHITE Score no score Shape OVAL Size 16mm Flavor Imprint Code TEVA;1125 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0093-1125-89 120 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 11/21/2018 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA208432 11/21/2018 Labeler - Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, Inc. (001627975)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.
