Granisetron Hydrochloride Tablets USP, 1 mg
Granisetron Hydrochloride by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Granisetron Hydrochloride by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Taro Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc., Taro Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
GRANISETRON HYDROCHLORIDE- granisetron hydrochloride tablet, film coated
Taro Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc.
----------
Granisetron
Hydrochloride
Tablets USP, 1 mg
DESCRIPTION
Granisetron Hydrochloride Tablets USP contain granisetron hydrochloride USP, an antinauseant and antiemetic agent. Chemically it is endo-N-(9-methyl-9-azabicyclo [3.3.1] non-3-yl)-1-methyl-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide hydrochloride with a molecular weight of 348.9 (312.4 free base). Its empirical formula is C18H24N4OHCl, while its chemical structure is:
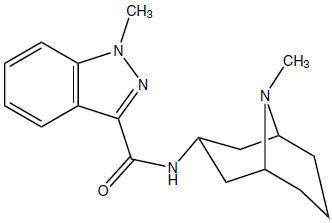
Granisetron hydrochloride USP is a white to off-white solid that is readily soluble in water and normal saline at 20°C.
Each round, white, film coated granisetron hydrochloride tablet USP contains 1.12 mg granisetron hydrochloride USP equivalent to granisetron, 1 mg. Inactive ingredients are: hypromellose 2910, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, opadry white YS-1-7003 (hypromellose, polyethylene glycol, polysorbate 80 and titanium dioxide) and sodium starch glycolate.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Granisetron is a selective 5-hydroxytryptamine3 (5-HT3) receptor antagonist with little or no affinity for other serotonin receptors, including 5-HT1; 5-HT1A; 5-HT1B/C; 5-HT2; for alpha1-, alpha2-, or beta-adrenoreceptors; for dopamine-D2; or for histamine-H1; benzodiazepine; picrotoxin or opioid receptors.
Serotonin receptors of the 5-HT3 type are located peripherally on vagal nerve terminals and centrally in the chemoreceptor trigger zone of the area postrema. During chemotherapy that induces vomiting, mucosal enterochromaffin cells release serotonin, which stimulates 5-HT3 receptors. This evokes vagal afferent discharge, inducing vomiting. Animal studies demonstrate that, in binding to 5-HT3 receptors, granisetron blocks serotonin stimulation and subsequent vomiting after emetogenic stimuli such as cisplatin. In the ferret animal model, a single granisetron injection prevented vomiting due to high-dose cisplatin or arrested vomiting within 5 to 30 seconds.
In most human studies, granisetron has had little effect on blood pressure, heart rate or ECG. No evidence of an effect on plasma prolactin or aldosterone concentrations has been found in other studies.
Following single and multiple oral doses, granisetron hydrochloride tablets USP slowed colonic transit in normal volunteers. However, granisetron hydrochloride USP had no effect on oro-cecal transit time in normal volunteers when given as a single intravenous (IV) infusion of 50 mcg/kg or 200 mcg/kg.
Pharmacokinetics
In healthy volunteers and adult cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy, administration of granisetron hydrochloride tablets USP produced mean pharmacokinetic data shown in Table 1.
| Peak Plasma Concentration (ng/mL) | Terminal Phase Plasma Half-Life (h) | Volume of Distribution (L/kg) | Total Clearance (L/h/kg) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N.D. Not determined. | ||||
|
|
||||
| Cancer Patients 1 mg bid, 7 days (n=27) | 5.99 [0.63 to 30.9] | N.D.* | N.D. | 0.52 [0.09 to 7.37] |
| Volunteers
single 1 mg dose (n=39) | 3.63 [0.27 to 9.14] | 6.23 [0.96 to 19.9] | 3.94 [1.89 to 39.4] | 0.41 [0.11 to 24.6] |
Absorption
When granisetron hydrochloride tablets USP were administered with food, AUC was decreased by 5% and Cmax increased by 30% in non-fasted healthy volunteers who received a single dose of 10 mg.
Distribution
Plasma protein binding is approximately 65% and granisetron distributes freely between plasma and red blood cells.
Metabolism
Granisetron metabolism involves N-demethylation and aromatic ring oxidation followed by conjugation. In vitro liver microsomal studies show that granisetron's major route of metabolism is inhibited by ketoconazole, suggestive of metabolism mediated by the cytochrome P-450 3A subfamily. Animal studies suggest that some of the metabolites may also have 5-HT3 receptor antagonist activity.
Elimination
Clearance is predominantly by hepatic metabolism. In normal volunteers, approximately 11% of the orally administered dose is eliminated unchanged in the urine in 48 hours. The remainder of the dose is excreted as metabolites, 48% in the urine and 38% in the feces.
Subpopulations
Gender
The effects of gender on the pharmacokinetics of granisetron hydrochloride tablets USP, have not been studied. However, after intravenous infusion of granisetron hydrochloride USP, no difference in mean AUC was found between males and females, although males had a higher Cmax generally.
In elderly and pediatric patients and in patients with renal failure or hepatic impairment, the pharmacokinetics of granisetron was determined following administration of intravenous granisetron hydrochloride USP.
Elderly
The ranges of the pharmacokinetic parameters in elderly volunteers (mean age 71 years), given a single 40 mcg/kg intravenous dose of granisetron hydrochloride injection USP, were generally similar to those in younger healthy volunteers; mean values were lower for clearance and longer for half-life in the elderly.
Renal Failure Patients
Total clearance of granisetron was not affected in patients with severe renal failure who received a single 40 mcg/kg intravenous dose of granisetron hydrochloride injection USP.
Hepatically Impaired Patients
A pharmacokinetic study with intravenous granisetron hydrochloride USP in patients with hepatic impairment due to neoplastic liver involvement showed that total clearance was approximately halved compared to patients without hepatic impairment. Given the wide variability in pharmacokinetic parameters noted in patients, dosage adjustment in patients with hepatic functional impairment is not necessary.
Pediatric Patients
A pharmacokinetic study in pediatric cancer patients (2 to 16 years of age), given a single 40 mcg/kg intravenous dose of granisetron hydrochloride injection USP, showed that volume of distribution and total clearance increased with age. No relationship with age was observed for peak plasma concentration or terminal phase plasma half-life. When volume of distribution and total clearance are adjusted for body weight, the pharmacokinetics of granisetron are similar in pediatric and adult cancer patients.
CLINICAL TRIALS
Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting
Granisetron hydrochloride tablets USP prevent nausea and vomiting associated with initial and repeat courses of emetogenic cancer therapy, as shown by 24-hour efficacy data from studies using both moderately- and highly-emetogenic chemotherapy.
Moderately Emetogenic Chemotherapy
The first trial compared granisetron hydrochloride USP tablets doses of 0.25 mg to 2 mg twice a day, in 930 cancer patients receiving, principally, cyclophosphamide, carboplatin, and cisplatin (20 mg/m2 to 50 mg/m2). Efficacy was based on complete response (ie, no vomiting, no moderate or severe nausea, no rescue medication), no vomiting, and no nausea. Table 2 summarizes the results of this study.
| Percentages of Patients Granisetron Hydrochloride Tablet USP Dose |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Efficacy Measures | 0.25 mg twice a day (n=229) % | 0.5 mg twice a day (n=235) % | 1 mg twice a day (n=233) % | 2 mg twice a day (n=233) % |
|
|
||||
| Complete Response† | 61 | 70‡ | 81‡§ | 72‡ |
| No Vomiting | 66 | 77‡ | 88‡ | 79‡ |
| No Nausea | 48 | 57 | 63‡ | 54 |
Results from a second double-blind, randomized trial evaluating granisetron hydrochloride tablets USP 2 mg once a day and granisetron hydrochloride tablets USP 1 mg twice a day were compared to prochlorperazine 10 mg twice a day derived from a historical control. At 24 hours, there was no statistically significant difference in efficacy between the two granisetron hydrochloride tablet USP regimens. Both regimens were statistically superior to the prochlorperazine control regimen (see Table 3).
| Percentages of Patients | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Efficacy Measures | Granisetron Hydrochloride Tablets USP, 1 mg twice a day (n=354) % | Granisetron Hydrochloride Tablets USP, 2 mg once a day (n=343) % | Prochlorperazine†
10 mg twice daily (n=111) % |
|
|
|||
| Complete Response‡ | 69§ | 64§ | 41 |
| No Vomiting | 82§ | 77§ | 48 |
| No Nausea | 51§ | 53§ | 35 |
| Total Control¶ | 51§ | 50§ | 33 |
Results from a granisetron hydrochloride tablets USP, 2 mg daily alone treatment arm in a third double-blind, randomized trial, were compared to prochlorperazine (PCPZ), 10 mg bid, derived from a historical control. The 24-hour results for granisetron hydrochloride tablets USP, 2 mg qd were statistically superior to PCPZ for all efficacy parameters: complete response (58%), no vomiting (79%), no nausea (51%), total control (49%). The PCPZ rates are shown in Table 3.
Cisplatin-Based Chemotherapy
The first double-blind trial compared granisetron hydrochloride tablets USP, 1 mg bid, relative to placebo (historical control), in 119 cancer patients receiving high-dose cisplatin (mean dose 80 mg/m2). At 24 hours, granisetron hydrochloride tablets USP, 1 mg bid was significantly (P<0.001) superior to placebo (historical control) in all efficacy parameters: complete response (52%), no vomiting (56%) and no nausea (45%). The placebo rates were 7%, 14%, and 7%, respectively, for the three efficacy parameters.
Results from a granisetron hydrochloride tablets USP, 2 mg once a day alone treatment arm in a second double-blind, randomized trial, were compared to both granisetron hydrochloride tablets 1 mg twice a day and placebo historical controls. The 24-hour results for granisetron hydrochloride tablets USP, 2 mg once a day were: complete response (44%), no vomiting (58%), no nausea (46%), total control (40%). The efficacy of granisetron hydrochloride tablets USP, 2 mg once a day was comparable to granisetron hydrochloride tablets USP, 1 mg twice a day and statistically superior to placebo. The placebo rates were 7%, 14%, 7%, and 7%, respectively, for the four parameters.
No controlled study comparing granisetron injection with the oral formulation to prevent chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting has been performed.
Radiation-Induced Nausea and Vomiting
Total Body Irradiation
In a double-blind randomized study, 18 patients receiving granisetron hydrochloride tablets USP, 2 mg daily, experienced significantly greater antiemetic protection compared to patients in a historical negative control group who received conventional (non-5-HT3 antagonist) antiemetics. Total body irradiation consisted of 11 fractions of 120 cGy administered over 4 days, with three fractions on each of the first 3 days, and two fractions on the fourth day. Granisetron hydrochloride tablets USP were given one hour before the first radiation fraction of each day.
Twenty-two percent (22%) of patients treated with granisetron hydrochloride tablets USP did not experience vomiting or receive rescue antiemetics over the entire 4-day dosing period, compared to 0% of patients in the historical negative control group (P<0.01).
In addition, patients who received granisetron hydrochloride tablets USP also experienced significantly fewer emetic episodes during the first day of radiation and over the 4-day treatment period, compared to patients in the historical negative control group. The median time to the first emetic episode was 36 hours for patients who received granisetron hydrochloride tablets USP.
Fractionated Abdominal Radiation
The efficacy of granisetron hydrochloride tablets USP, 2 mg daily, was evaluated in a double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized trial of 260 patients. Granisetron hydrochloride tablets USP were given 1 hour before radiation, composed of up to 20 daily fractions of 180 to 300 cGy each. The exceptions were patients with seminoma or those receiving whole abdomen irradiation who initially received 150 cGy per fraction. Radiation was administered to the upper abdomen with a field size of at least 100 cm2.
The proportion of patients without emesis and those without nausea for granisetron hydrochloride tablets USP, compared to placebo, was statistically significant (P<0.0001) at 24 hours after radiation, irrespective of the radiation dose. Granisetron hydrochloride USP was superior to placebo in patients receiving up to 10 daily fractions of radiation, but was not superior to placebo in patients receiving 20 fractions.
Patients treated with granisetron hydrochloride tablets USP (n=134) had a significantly longer time to the first episode of vomiting (35 days vs. 9 days, P<0.001) relative to those patients who received placebo (n=126), and a significantly longer time to the first episode of nausea (11 days vs. 1 day, P<0.001). Granisetron hydrochloride USP provided significantly greater protection from nausea and vomiting than placebo.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Granisetron hydrochloride USP is indicated for the prevention of:
- Nausea and vomiting associated with initial and repeat courses of emetogenic cancer therapy, including high-dose cisplatin.
- Nausea and vomiting associated with radiation, including total body irradiation and fractionated abdominal radiation.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Granisetron hydrochloride USP is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to the drug or any of its components.
WARNINGS
Serotonin Syndrome
The development of serotonin syndrome has been reported with 5-HT3 receptor antagonists. Most reports have been associated with concomitant use of serotonergic drugs (e.g., selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), monoamine oxidase inhibitors, mirtazapine, fentanyl, lithium, tramadol, and intravenous methylene blue). Some of the reported cases were fatal. Serotonin syndrome occurring with overdose of another 5-HT3 receptor antagonist alone has also been reported. The majority of reports of serotonin syndrome related to 5-HT3 receptor antagonist use occurred in a post-anesthesia care unit or an infusion center.
Symptoms associated with serotonin syndrome may include the following combination of signs and symptoms: mental status changes (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, delirium, and coma), autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, labile blood pressure, dizziness, diaphoresis, flushing, hyperthermia), neuromuscular symptoms (e.g., tremor, rigidity, myoclonus, hyperreflexia, incoordination), seizures, with or without gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea). Patients should be monitored for the emergence of serotonin syndrome, especially with concomitant use of granisetron and other serotonergic drugs. If symptoms of serotonin syndrome occur, discontinue granisetron and initiate supportive treatment. Patients should be informed of the increased risk of serotonin syndrome, especially if granisetron is used concomitantly with other serotonergic drugs [see Drug Interactions, Patient Counseling Information].
PRECAUTIONS
Granisetron hydrochloride USP is not a drug that stimulates gastric or intestinal peristalsis. It should not be used instead of nasogastric suction. The use of granisetron hydrochloride USP in patients following abdominal surgery or in patients with chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting may mask a progressive ileus and/or gastric distention.
An adequate QT assessment has not been conducted, but QT prolongation has been reported with granisetron hydrochloride USP. Therefore, granisetron hydrochloride USP should be used with caution in patients with pre-existing arrhythmias or cardiac conduction disorders, as this might lead to clinical consequences. Patients with cardiac disease, on cardio-toxic chemotherapy, with concomitant electrolyte abnormalities and/or on concomitant medications that prolong the QT interval are particularly at risk.
Drug Interactions
Granisetron does not induce or inhibit the cytochrome P-450 drug-metabolizing enzyme system in vitro. There have been no definitive drug-drug interaction studies to examine pharmacokinetic or pharmacodynamic interaction with other drugs; however, in humans, granisetron hydrochloride injection USP has been safely administered with drugs representing benzodiazepines, neuroleptics, and anti-ulcer medications commonly prescribed with antiemetic treatments. Granisetron hydrochloride injection USP also does not appear to interact with emetogenic cancer chemotherapies. Because granisetron is metabolized by hepatic cytochrome P-450 drug-metabolizing enzymes, inducers or inhibitors of these enzymes may change the clearance and, hence, the half-life of granisetron. No specific interaction studies have been conducted in anesthetized patients. In addition, the activity of the cytochrome P-450 subfamily 3A4 (involved in the metabolism of some of the main narcotic analgesic agents) is not modified by granisetron hydrochloride USP in vitro.
In in vitro human microsomal studies, ketoconazole inhibited ring oxidation of granisetron hydrochloride USP. However, the clinical significance of in vivo pharmacokinetic interactions with ketoconazole is not known. In a human pharmacokinetic study, hepatic enzyme induction with phenobarbital resulted in a 25% increase in total plasma clearance of intravenous granisetron. The clinical significance of this change is not known.
QT prolongation has been reported with granisetron hydrochloride USP. Use of granisetron hydrochloride USP in patients concurrently treated with drugs known to prolong the QT interval and/or are arrhythmogenic, this may result in to clinical consequences.
Serotonin syndrome (including altered mental status, autonomic instability, and neuromuscular symptoms) has been described following the concomitant use of 5-HT3 receptor antagonists and other serotonergic drugs, including selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin and noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) [see WARNINGS].
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In a 24-month carcinogenicity study, rats were treated orally with granisetron 1, 5 or 50 mg/kg/day (6, 30 or 300 mg/m2/day). The 50 mg/kg/day dose was reduced to 25 mg/kg/day (150 mg/m2/day) during week 59 due to toxicity. For a 50 kg person of average height (1.46 m2 body surface area), these doses represent 4, 20, and 101 times the recommended clinical dose (1.48 mg/m2, oral) on a body surface area basis. There was a statistically significant increase in the incidence of hepatocellular carcinomas and adenomas in males treated with 5 mg/kg/day (30 mg/m2/day, 20 times the recommended human dose based on body surface area) and above, and in females treated with 25 mg/kg/day (150 mg/m2/day, 101 times the recommended human dose based on body surface area). No increase in liver tumors was observed at a dose of 1 mg/kg/day (6 mg/m2/day, 4 times the recommended human dose based on body surface area) in males and 5 mg/kg/day (30 mg/m2/day, 20 times the recommended human dose based on body surface area) in females. In a 12-month oral toxicity study, treatment with granisetron 100 mg/kg/day (600 mg/m2/day, 405 times the recommended human dose based on body surface area) produced hepatocellular adenomas in male and female rats while no such tumors were found in the control rats. A 24-month mouse carcinogenicity study of granisetron did not show a statistically significant increase in tumor incidence, but the study was not conclusive.
Because of the tumor findings in rat studies, granisetron hydrochloride USP should be prescribed only at the dose and for the indication recommended (see INDICATIONS AND USAGE and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Granisetron was not mutagenic in in vitro Ames test and mouse lymphoma cell forward mutation assay, and in vivo mouse micronucleus test and in vitro and ex vivo rat hepatocyte UDS assays. It, however, produced a significant increase in UDS in HeLa cells in vitro and a significant increased incidence of cells with polyploidy in an in vitro human lymphocyte chromosomal aberration test.
Granisetron at oral doses up to 100 mg/kg/day (600 mg/m2/day, 405 times the recommended human dose based on body surface area) was found to have no effect on fertility and reproductive performance of male and female rats.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy Category B
Reproduction studies have been performed in pregnant rats at oral doses up to 125 mg/kg/day (750 mg/m2/day, 507 times the recommended human dose based on body surface area) and pregnant rabbits at oral doses up to 32 mg/kg/day (378 mg/m2/day, 255 times the recommended human dose based on body surface area) and have revealed no evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus due to granisetron. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
QT prolongation has been reported with granisetron hydrochloride USP (see PRECAUTIONS and Drug Interactions).
Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting
Over 3700 patients have received granisetron tablets in clinical trials with emetogenic cancer therapies consisting primarily of cyclophosphamide or cisplatin regimens.
In patients receiving granisetron hydrochloride tablets USP, 1 mg bid for 1, 7 or 14 days, or 2 mg daily for 1 day, adverse experiences reported in more than 5% of the patients with comparator and placebo incidences are listed in Table 4.
| Percent of Patients With Event | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Granisetron Hydrochloride Tablets USP,* 1 mg twice a day (n=978) | Granisetron Hydrochloride Tablets USP,* 2 mg once a day (n=1450) | Comparator†
(n=599) | Placebo (n=185) |
|
|
|
||||
| Headache | 21% | 20% | 13% | 12% |
| Constipation | 18% | 14% | 16% | 8% |
| Asthenia | 14% | 18% | 10% | 4% |
| Diarrhea | 8% | 9% | 10% | 4% |
| Abdominal pain | 6% | 4% | 6% | 3% |
| Dyspepsia | 4% | 6% | 5% | 4% |
Other adverse events reported in clinical trials were:
Gastrointestinal: In single-day dosing studies in which adverse events were collected for 7 days, nausea (20%) and vomiting (12%) were recorded as adverse events after the 24-hour efficacy assessment period.
Hepatic: In comparative trials, elevation of AST and ALT (>2 times the upper limit of normal) following the administration of granisetron hydrochloride tablets USP occurred in 5% and 6% of patients, respectively. These frequencies were not significantly different from those seen with comparators (AST: 2%; ALT: 9%).
Cardiovascular: Hypertension (1%); hypotension, angina pectoris, atrial fibrillation, and syncope have been observed rarely.
Central Nervous System: Dizziness (5%), insomnia (5%), anxiety (2%), somnolence (1%). One case compatible with, but not diagnostic of, extrapyramidal symptoms has been reported in a patient treated with granisetron hydrochloride tablets USP.
Hypersensitivity: Rare cases of hypersensitivity reactions, sometimes severe (e.g., anaphylaxis, shortness of breath, hypotension, urticaria) have been reported.
Other: Fever (5%). Events often associated with chemotherapy also have been reported: leukopenia (9%), decreased appetite (6%), anemia (4%), alopecia (3%), thrombocytopenia (2%).
Over 5000 patients have received injectable granisetron hydrochloride USP in clinical trials.
Table 5 gives the comparative frequencies of the five commonly reported adverse events (≥3%) in patients receiving granisetron hydrochloride injection USP, 40 mcg/kg, in single-day chemotherapy trials. These patients received chemotherapy, primarily cisplatin, and intravenous fluids during the 24-hour period following granisetron hydrochloride injection USP administration.
| Percent of Patients with Event | ||
|---|---|---|
| Granisetron Hydrochloride Injection USP* 40 mcg/kg (n=1268) | Comparator†(n=422) | |
|
|
||
| Headache | 14% | 6% |
| Asthenia | 5% | 6% |
| Somnolence | 4% | 15% |
| Diarrhea | 4% | 6% |
| Constipation | 3% | 3% |
In the absence of a placebo group, there is uncertainty as to how many of these events should be attributed to granisetron hydrochloride USP, except for headache, which was clearly more frequent than in comparison groups.
Radiation-Induced Nausea and Vomiting
In controlled clinical trials, the adverse events reported by patients receiving granisetron hydrochloride tablets USP and concurrent radiation were similar to those reported by patients receiving granisetron hydrochloride tablets USP prior to chemotherapy. The most frequently reported adverse events were diarrhea, asthenia, and constipation. Headache, however, was less prevalent in this patient population.
Postmarketing Experience
QT prolongation has been reported with granisetron hydrochloride USP (see PRECAUTIONS and Drug Interactions).
OVERDOSAGE
There is no specific treatment for granisetron hydrochloride USP overdosage. In case of overdosage, symptomatic treatment should be given. Overdosage of up to 38.5 mg of granisetron hydrochloride injection USP has been reported without symptoms or only the occurrence of a slight headache.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Emetogenic Chemotherapy
The recommended adult dosage of oral granisetron hydrochloride USP is 2 mg once daily or 1 mg twice daily. In the 2 mg once-daily regimen, two 1 mg tablets are given up to 1 hour before chemotherapy. In the 1 mg twice-daily regimen, the first 1 mg tablet is given up to 1 hour before chemotherapy, and the second tablet 12 hours after the first. Either regimen is administered only on the day(s) chemotherapy is given. Continued treatment, while not on chemotherapy, has not been found to be useful.
Use in the Elderly, Renal Failure Patients or Hepatically Impaired Patients
No dosage adjustment is recommended (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Pharmacokinetics).
HOW SUPPLIED
Granisetron Hydrochloride Tablets USP, 1 mg are available as:
1 mg, round, white, film coated tablets, embossed with "T" on one side and "G1" on the other side.
Bottle of 20 tablets – NDC: 51672-4138-6
Bottle of 100 tablets – NDC: 51672-4138-1
Unit Dose of 100 (10 ×10) – NDC: 51672-4138-0
Storage
Store between 20° and 25°C (68° and 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Keep container closed tightly. Protect from light.
PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise patients of the possibility of serotonin syndrome with concomitant use of granisetron and another serotonergic agent such as medications to treat depression and migraines. Advise patients to seek immediate medical attention if the following symptoms occur: changes in mental status, autonomic instability, neuromuscular symptoms with or without gastrointestinal symptoms.
Mfd. by: Taro Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Haifa Bay, Israel 2624761
Dist. by: Taro Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc., Hawthorne, N.Y. 10532
Issued: August 2014
70838-0814-1
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 1 mg Tablet Bottle Label
NDC: 51672-4138-6
20 Tablets
Granisetron
Hydrochloride
Tablets USP, 1 mg *
Keep this and all medications
out of the reach of children.
Rx only

| GRANISETRON HYDROCHLORIDE
granisetron hydrochloride tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Taro Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc. (145186370) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Taro Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. | 600072078 | ANALYSIS(51672-4138) , API MANUFACTURE(51672-4138) , MANUFACTURE(51672-4138) | |