MIRTAZAPINE tablet, film coated
Mirtazapine by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Mirtazapine by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Proficient Rx LP. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use MIRTAZAPINE TABLETS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for MIRTAZAPINE TABLETS.
MIRTAZAPINE tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1996
WARNING: SUICIDAL THOUGHTS AND BEHAVIORS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
Increased risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior in pediatric and young adult patients taking antidepressants. Closely monitor all antidepressant-treated patients for clinical worsening and emergence of suicidal thoughts and behaviors.
Mirtazapine tablets are not approved for use in pediatric patients. (5.1, 8.4)
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Mirtazapine tablets are indicated for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD) in adults. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- Tablets: 7.5 mg unscored, 15 mg scored, 30 mg scored and 45 mg unscored. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Agranulocytosis: If sore throat, fever, stomatitis or signs of infection occur, along with a low white blood cell count, treatment with mirtazapine should be discontinued and the patient should be closely monitored. (5.2)
- Serotonin Syndrome: Increased risk when co-administered with other serotonergic drugs (e.g., SSRI, SNRI, triptans), but also when taken alone. If it occurs, discontinue mirtazapine and initiate supportive treatment. (2.4, 4, 5.3, 7)
- Angle-Closure Glaucoma: Angle closure glaucoma has occurred in patients with untreated anatomically narrow angles treated with antidepressants. (5.4)
- QTc Prolongation: Use mirtazapine with caution in patients with risk factors for QTc prolongation. (5.5, 7)
- Increased Appetite/Weight Gain: mirtazapine has been associated with increased appetite and weight gain. (5.6)
- Somnolence: May impair judgment, thinking and/or motor skills. Use with caution when engaging in activities requiring alertness, such as driving or operating machinery. (5.7, 7)
- Activation of Mania/Hypomania: Screen patients for bipolar disorder prior to initiating treatment. (2.3, 5.8)
- Seizures: Use with caution in patients with a seizure disorder. (5.9)
- Elevated Cholesterol/Triglycerides: Has been reported with mirtazapine use. (5.10)
- Hyponatremia: May occur as a result of treatment with serotonergic antidepressants, including mirtazapine. (5.11)
- Transaminase Elevations: Clinically significant elevations have occurred. Use with caution in patients with impaired hepatic function. (5.12)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions (≥5% or greater and twice placebo) were somnolence, increased appetite, weight gain, and dizziness. (6.1) To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Rising Health, LLC at 1-833-395-6928 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Strong CYP3A inducers: Dosage increase may be needed for mirtazapine with concomitant use of strong CYP3A inducers. (2.5, 7)
- Strong CYP3A inhibitors: Dosage decrease may be needed when mirtazapine is coadministered with strong CYP3A inhibitors. (2.5, 7)
- Cimetidine: Dosage decrease may be needed when mirtazapine is coadministered with cimetidine. (2.5, 7)
- Warfarin: Monitor INR during concomitant use. (7)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Pregnancy: Use only if clearly needed. (8.1)
- Nursing Mothers: Caution should be exercised when administered to a nursing woman. (8.3)
- Geriatric Use: Use with caution in elderly patients. (5.11, 5.14, 8.5)
- Renal impairment: Dosage decrease may be needed in patients with moderate to severe renal impairment. (8.6)
- Hepatic impairment: Dosage decrease may be needed in patients with hepatic impairment. (8.6)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 8/2022
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING: SUICIDAL THOUGHTS AND BEHAVIORS
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage
2.3 Screen for Bipolar Disorder Prior to Starting Mirtazapine Tablets
2.4 Switching Patients to or from a Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor Antidepressant
2.5 Dosage Modifications Due to Drug Interactions
2.6 Discontinuation of Mirtazapine Tablets Treatment
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Suicidal Thoughts and Behaviors in Adolescents and Young Adults
5.2 Agranulocytosis
5.3 Serotonin Syndrome
5.4 Angle-Closure Glaucoma
5.5 QT Prolongation and Torsades de Pointes
5.6 Increased Appetite and Weight Gain
5.7 Somnolence
5.8 Activation of Mania or Hypomania
5.9 Seizures
5.10 Elevated Cholesterol and Triglycerides
5.11 Hyponatremia
5.12 Transaminase Elevations
5.13 Discontinuation Syndrome
5.14 Use in Patients with Concomitant Illness
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal or Hepatic Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING: SUICIDAL THOUGHTS AND BEHAVIORS
Antidepressants increased the risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors in pediatric and young adult patients in short-term studies. Closely monitor all antidepressant-treated patients for clinical worsening, and for emergence of suicidal thoughts and behaviors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Mirtazapine tablets are not approved for use in pediatric patients [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Mirtazapine tablets are indicated for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD) in adults [see Clinical Studies (14)].
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage
The recommended starting dose of mirtazapine tablets is 15 mg once daily, administered orally, preferably in the evening prior to sleep. If patients do not have an adequate response to the initial 15 mg dose, increase the dose up to a maximum of 45 mg per day. Dose changes should not be made in intervals of less than 1 to 2 weeks to allow sufficient time for evaluation of response to a given dose [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.3 Screen for Bipolar Disorder Prior to Starting Mirtazapine Tablets
Prior to initiating treatment with mirtazapine tablets or another antidepressant, screen patients for a personal or family history of bipolar disorder, mania, or hypomania [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
2.4 Switching Patients to or from a Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor Antidepressant
At least 14 days must elapse between discontinuation of a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) antidepressant and initiation of mirtazapine tablets. In addition, at least 14 days must elapse after stopping mirtazapine tablets before starting an MAOI antidepressant [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
2.5 Dosage Modifications Due to Drug Interactions
Strong CYP3A Inducers
An increase in dosage of mirtazapine tablets may be needed with concomitant strong CYP3A inducer (e.g., carbamazepine, phenytoin, rifampin) use. Conversely, a decrease in dosage of mirtazapine tablets may be needed if the CYP3A inducer is discontinued [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Strong CYP3A Inhibitors
A decrease in dosage of mirtazapine tablets may be needed with concomitant use of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, clarithromycin). Conversely, an increase in dosage of mirtazapine tablets may be needed if the CYP3A4 inhibitor is discontinued [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Cimetidine
A decrease in dosage of mirtazapine tablets may be needed with concomitant use of cimetidine. Conversely, an increase in dosage of mirtazapine tablets may be needed if cimetidine is discontinued [see Drug Interactions (7)].
2.6 Discontinuation of Mirtazapine Tablets Treatment
Adverse reactions may occur upon discontinuation or dose reduction of mirtazapine tablets [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)]. Gradually reduce the dosage of mirtazapine tablets rather than stopping abruptly whenever possible.
-
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Mirtazapine tablets USP are supplied as:
- 7.5 mg tablets: White, biconvex, capsule shaped film coated tablets with “11” debossed on one side and “A” debossed on the other side.
- 15 mg tablets: Yellow, biconvex, capsule shaped film coated tablets with a score line in between “0” and “8” on one side and “A” debossed on the other side.
- 30 mg tablets: Reddish brown, biconvex, capsule shaped film coated tablets with a score line in between “0” and “9” on one side and “A” debossed on the other side.
- 45 mg tablets: White, biconvex, capsule shaped film coated tablets with “10” debossed on one side and “A” debossed on the other side.
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Mirtazapine tablets are contraindicated in patients:
- Taking, or within 14 days of stopping, MAOIs (including the MAOIs linezolid and intravenous methylene blue) because of an increased risk of serotonin syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3), Drug Interactions (7)].
- With a known hypersensitivity to mirtazapine or to any of the excipients in mirtazapine tablets. Severe skin reactions, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome, bullous dermatitis, erythema multiforme and toxic epidermal necrolysis have been reported following the use of mirtazapine tablets [see Adverse Reactions 6.2].
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Suicidal Thoughts and Behaviors in Adolescents and Young Adults
In pooled analyses of placebo-controlled trials of antidepressant drugs (SSRIs and other antidepressant classes) that included approximately 77,000 adult patients and 4,500 pediatric patients, the incidence of suicidal thoughts and behaviors in antidepressant-treated patients age 24 years and younger was greater than in placebo-treated patients. There was considerable variation in risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors among drugs, but there was an increased risk identified in young patients for most drugs studied. There were differences in absolute risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors across the different indications, with the highest incidence in patients with MDD. The drug-placebo differences in the number of cases of suicidal thoughts and behaviors per 1000 patients treated are provided in Table 1.
Table 1: Risk Differences of the Number of Patients with Suicidal Thoughts and Behavior in the Pooled Placebo-Controlled Trials of Antidepressants in Pediatric and Adult Patients Age Range
Drug-Placebo Difference in Number of Patients with Suicidal Thoughts or Behaviors per 1000 Patients Treated
Increases Compared to Placebo
<18 years old
14 additional patients
18 to 24 years old
5 additional patients
Decreases Compared to Placebo
25 to 64 years old
1 fewer patient
≥65 years old
6 fewer patients
It is unknown whether the risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors in children, adolescents, and young adults extends to longer-term use, i.e., beyond four months. However, there is substantial evidence from placebo-controlled maintenance trials in adults with MDD that antidepressants delay the recurrence of depression and that depression itself is a risk factor for suicidal thoughts and behaviors.
Monitor all antidepressant-treated patients for any indication of clinical worsening and emergence of suicidal thoughts and behaviors, especially during the initial few months of drug therapy, and at times of dosage changes. Counsel family members or caregivers of patients to monitor for changes in behavior and to alert the healthcare provider. Consider changing the therapeutic regimen, including possibly discontinuing mirtazapine, in patients whose depression is persistently worse, or who are experiencing emergent suicidal thoughts or behaviors.
5.2 Agranulocytosis
In premarketing clinical trials, 2 (1 with Sjögren’s Syndrome) out of 2796 patients treated with mirtazapine developed agranulocytosis [absolute neutrophil count (ANC) <500/mm3 with associated signs and symptoms, e.g., fever, infection, etc.] and a third patient developed severe neutropenia (ANC <500/mm3 without any associated symptoms). For these 3 patients, onset of severe neutropenia was detected on days 61, 9, and 14 of treatment, respectively. All 3 patients recovered after mirtazapine was stopped. If a patient develops a sore throat, fever, stomatitis, or other signs of infection, along with a low white blood cell (WBC) count, treatment with mirtazapine should be discontinued and the patient should be closely monitored.
5.3 Serotonin Syndrome
Serotonergic antidepressants, including mirtazapine, can precipitate serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition. The risk is increased with concomitant use of other serotonergic drugs (including triptans, tricyclic antidepressants, fentanyl, lithium, tramadol, tryptophan, buspirone, amphetamines, and St. John’s Wort) and with drugs that impair metabolism of serotonin, i.e., MAOIs [see Contraindications (4), Drug Interactions (7)]. Serotonin syndrome can also occur when these drugs are used alone.
Serotonin syndrome signs and symptoms may include mental status changes (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, delirium, and coma), autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, labile blood pressure, dizziness, diaphoresis, flushing, hyperthermia), neuromuscular symptoms (e.g., tremor, rigidity, myoclonus, hyperreflexia, incoordination), seizures, and gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea).
The concomitant use of mirtazapine with MAOIs is contraindicated. In addition, do not initiate mirtazapine in a patient being treated with MAOIs such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue. No reports involved the administration of methylene blue by other routes (such as oral tablets or local tissue injection). If it is necessary to initiate treatment with an MAOI such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue in a patient taking mirtazapine, discontinue mirtazapine before initiating treatment with the MAOI [see Contraindications (4), Drug Interactions (7)].
Monitor all patients taking mirtazapine for the emergence of serotonin syndrome. Discontinue treatment with mirtazapine and any concomitant serotonergic agents immediately if the above symptoms occur, and initiate supportive symptomatic treatment. If concomitant use of mirtazapine with other serotonergic drugs is clinically warranted, inform patients of the increased risk for serotonin syndrome and monitor for symptoms.
5.4 Angle-Closure Glaucoma
The pupillary dilation that occurs following use of many antidepressant drugs, including mirtazapine, may trigger an angle-closure attack in a patient with anatomically narrow angles who does not have a patent iridectomy.
5.5 QT Prolongation and Torsades de Pointes
The effect of mirtazapine on QTc interval was assessed in a clinical randomized trial with placebo and positive (moxifloxacin) controls involving 54 healthy volunteers using exposure response analysis. This trial showed a positive relationship between mirtazapine concentrations and prolongation of the QTc interval. However, the degree of QT prolongation observed with both 45 mg and 75 mg (1.67 times the maximum recommended daily dose) doses of mirtazapine was not at a level generally considered to be clinically meaningful. During postmarketing use of mirtazapine, cases of QT prolongation, Torsades de Pointes, ventricular tachycardia, and sudden death, have been reported [see Adverse Reactions (6.1, 6.2)]. The majority of reports occurred in association with overdose or in patients with other risk factors for QT prolongation, including concomitant use of QTc-prolonging medicines [see Drug Interactions (7) and Overdosage (10)]. Exercise caution when mirtazapine is prescribed in patients with known cardiovascular disease or family history of QT prolongation, and in concomitant use with other drugs thought to prolong the QTc interval.
5.6 Increased Appetite and Weight Gain
In U.S. controlled clinical studies, appetite increase was reported in 17% of patients treated with mirtazapine, compared to 2% for placebo. In these same trials, weight gain of ≥7% of body weight was reported in 7.5% of patients treated with mirtazapine, compared to 0% for placebo. In a pool of premarketing U.S. clinical studies, including many patients for long-term, open-label treatment, 8% of patients receiving mirtazapine discontinued for weight gain.
In an 8-week-long pediatric clinical trial of doses between 15 to 45 mg/day, 49% of mirtazapine-treated pediatric patients had a weight gain of at least 7%, compared to 5.7% of placebo-treated patients. The safety and effectiveness of mirtazapine in pediatric patients with MDD have not been established [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
5.7 Somnolence
In U.S. controlled studies, somnolence was reported in 54% of patients treated with mirtazapine, compared to 18% for placebo. In these studies, somnolence resulted in discontinuation for 10.4% of mirtazapine-treated patients, compared to 2.2% for placebo. It is unclear whether tolerance develops to the somnolent effects of mirtazapine. Because of the potentially significant effects of mirtazapine on impairment of performance, caution patients about engaging in activities that require alertness, including operating hazardous machinery and motor vehicles, until they are reasonably certain that mirtazapine does not affect them adversely. The concomitant use of benzodiazepines and alcohol with mirtazapine should be avoided [see Drug Interactions (7)].
5.8 Activation of Mania or Hypomania
In patients with bipolar disorder, treating a depressive episode with mirtazapine or another antidepressant may precipitate a mixed/manic episode. In controlled clinical trials, patients with bipolar disorder were generally excluded; however, symptoms of mania or hypomania were reported in 0.2% of patients treated with mirtazapine. Prior to initiating treatment with mirtazapine, screen patients for any personal or family history of bipolar disorder, mania, or hypomania.
5.9 Seizures
Mirtazapine has not been systematically evaluated in patients with seizure disorders. In premarketing clinical trials, 1 seizure was reported among the 2796 U.S. and non-U.S. patients treated with mirtazapine. Mirtazapine should be prescribed with caution in patients with a seizure disorder.
5.10 Elevated Cholesterol and Triglycerides
In U.S. controlled studies, nonfasting cholesterol increases to ≥20% above the upper limits of normal were observed in 15% of patients treated with mirtazapine, compared to 7% for placebo. In these same studies, nonfasting triglyceride increases to ≥500 mg/dL were observed in 6% of patients treated with mirtazapine, compared to 3% for placebo.
5.11 Hyponatremia
Hyponatremia may occur as a result of treatment with serotonergic antidepressants, including mirtazapine. Cases with serum sodium lower than 110 mmol/L have been reported.
Signs and symptoms of hyponatremia include headache, difficulty concentrating, memory impairment, confusion, weakness, and unsteadiness, which may lead to falls. Signs and symptoms associated with more severe or acute cases have included hallucination, syncope, seizure, coma, respiratory arrest, and death. In many cases, this hyponatremia appears to be the result of the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH).
In patients with symptomatic hyponatremia, discontinue mirtazapine and institute appropriate medical intervention. Elderly patients, patients taking diuretics, and those who are volume-depleted may be at greater risk of developing hyponatremia [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
5.12 Transaminase Elevations
Clinically significant ALT (SGPT) elevations (≥3 times the upper limit of the normal range) were observed in 2.0% (8/424) of patients treated with mirtazapine in a pool of short-term, U.S. controlled trials, compared to 0.3% (1/328) of placebo patients. While some patients were discontinued for the ALT increases, in other cases, the enzyme levels returned to normal despite continued mirtazapine treatment. Mirtazapine should be used with caution in patients with impaired hepatic function [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5.13 Discontinuation Syndrome
There have been reports of adverse reactions upon the discontinuation of mirtazapine (particularly when abrupt), including but not limited to the following: dizziness, abnormal dreams, sensory disturbances (including paresthesia and electric shock sensations), agitation, anxiety, fatigue, confusion, headache, tremor, nausea, vomiting, and sweating, or other symptoms which may be of clinical significance.
A gradual reduction in the dosage, rather than an abrupt cessation, is recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)].
5.14 Use in Patients with Concomitant Illness
Mirtazapine has not been systematically evaluated or used to any appreciable extent in patients with a recent history of myocardial infarction or other significant heart disease. Mirtazapine was associated with significant orthostatic hypotension in early clinical pharmacology trials with normal volunteers. Orthostatic hypotension was infrequently observed in clinical trials with depressed patients [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Mirtazapine should be used with caution in patients with known cardiovascular or cerebrovascular disease that could be exacerbated by hypotension (history of myocardial infarction, angina, or ischemic stroke) and conditions that would predispose patients to hypotension (dehydration, hypovolemia, and treatment with antihypertensive medication).
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are described in more detail in other sections of the prescribing information:
- Hypersensitivity [see Contraindications (4)]
- Suicidal Thoughts and Behaviors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Agranulocytosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Serotonin Syndrome [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.3), Drug Interactions (7)]
- Angle-Closure Glaucoma [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- QT Prolongation and Torsades de Pointes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Increased Appetite and Weight Gain [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Somnolence [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Activation of Mania or Hypomania [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Seizures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Elevated Cholesterol and Triglycerides [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
- Hyponatremia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
- Transaminase Elevations [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]
- Discontinuation Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)]
- Use in Patients with Concomitant Illness [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14)]
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data described below are from clinical trials in which mirtazapine was administered to 2796 patients in phase 2 and 3 clinical studies. The trials consisted of double-blind controlled and open-label studies, inpatient and outpatient studies, fixed dose, and titration studies.
Adverse Reactions Leading to Discontinuation of Treatment
Approximately 16% of the 453 patients who received mirtazapine in U.S. 6-week placebo-controlled clinical trials discontinued treatment due to an adverse reaction, compared to 7% of the 361 placebo-treated patients in those studies. The most common reactions leading to discontinuation (≥1% and at a rate at least twice that of placebo) are included in Table 2.
Table 2: Adverse Reactions (≥1% and at least twice placebo) Leading to Discontinuation of Mirtazapine in 6-Week Clinical Trials in Patients with MDD Mirtazapine
(n=453)
Placebo
(n=361)
Somnolence
10.4%
2.2%
Nausea
1.5%
0%
Common Adverse Reactions
The most common adverse reactions (≥5% and twice placebo) associated with the use of mirtazapine are listed in Table 3.
Table 3: Adverse Reactions (≥5% and twice placebo) in 6-Week U.S. Clinical Trials of Mirtazapine in Patients with MDD Mirtazapine
(n=453)
Placebo
(n=361)
Somnolence
54%
18%
Increased Appetite
17%
2%
Weight Gain
12%
2%
Dizziness
7%
3%
Table 4 enumerates adverse reactions that occurred in ≥1% of mirtazapine -treated patients, and were more frequent than the placebo-treated patients, who participated in 6-week, U.S. placebo-controlled trials in which patients were dosed in a range of 5 to 60 mg/day. This table shows the percentage of patients in each group who had at least 1 episode of an adverse reaction at some time during their treatment.
Table 4: Adverse Reactions (≥1% and greater than placebo) in 6-Week U.S. Clinical Studies of Mirtazapine in Patients with MDD Mirtazapine
(n=453)
Placebo
(n=361)
Body as a Whole
Asthenia
8%
5%
Flu Syndrome
5%
3%
Back Pain
2%
1%
Digestive System
Dry Mouth
25%
15%
Increased Appetite
17%
2%
Constipation
13%
7%
Metabolic and Nutritional Disorders
Weight Gain
12%
2%
Peripheral Edema
2%
1%
Edema
1%
0%
Musculoskeletal System
Myalgia
2%
1%
Nervous System
Somnolence
54%
18%
Dizziness
7%
3%
Abnormal Dreams
4%
1%
Thinking Abnormal
3%
1%
Tremor
2%
1%
Confusion
2%
0%
Respiratory System
Dyspnea
1%
0%
Urogenital System
Urinary Frequency
2%
1%
ECG Changes
The electrocardiograms for 338 patients who received mirtazapine and 261 patients who received placebo in 6-week, placebo-controlled trials were analyzed. Mirtazapine was associated with a mean increase in heart rate of 3.4 bpm, compared to 0.8 bpm for placebo. The clinical significance of these changes is unknown.
Other Adverse Reactions Observed During the Premarketing Evaluation of Mirtazapine
The following list does not include reactions: 1) already listed in previous tables or elsewhere in labeling, 2) for which a drug cause was remote, 3) which were so general or excessively specific so as to be uninformative, 4) which were not considered to have significant clinical implications, or 5) which occurred at a rate equal to or less than placebo.
Adverse reactions are categorized by body system according to the following definitions: frequent adverse reactions are those occurring in at least 1/100 patients; infrequent adverse reactions are those occurring in 1/100 to 1/1000 patients; rare adverse reactions are those occurring in fewer than 1/1000 patients.
Body as a Whole: frequent: malaise, abdominal pain, abdominal syndrome acute; infrequent: chills, fever, face edema, ulcer, photosensitivity reaction, neck rigidity, neck pain, abdomen enlarged; rare: cellulitis, chest pain substernal.
Cardiovascular System: frequent: hypertension, vasodilatation; infrequent: angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, bradycardia, ventricular extrasystoles, syncope, migraine, hypotension; rare: atrial arrhythmia, bigeminy, vascular headache, pulmonary embolus, cerebral ischemia, cardiomegaly, phlebitis, left heart failure.
Digestive System: frequent: vomiting, anorexia; infrequent: eructation, glossitis, cholecystitis, nausea and vomiting, gum hemorrhage, stomatitis, colitis, liver function tests abnormal; rare: tongue discoloration, ulcerative stomatitis, salivary gland enlargement, increased salivation, intestinal obstruction, pancreatitis, aphthous stomatitis, cirrhosis of liver, gastritis, gastroenteritis, oral moniliasis, tongue edema.
Endocrine System: rare: goiter, hypothyroidism.
Hemic and Lymphatic System: rare: lymphadenopathy, leukopenia, petechia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, lymphocytosis, pancytopenia.
Metabolic and Nutritional Disorders: frequent: thirst; infrequent: dehydration, weight loss; rare: gout, SGOT increased, healing abnormal, acid phosphatase increased, SGPT increased, diabetes mellitus, hyponatremia.
Musculoskeletal System: frequent: myasthenia, arthralgia; infrequent: arthritis, tenosynovitis; rare: pathologic fracture, osteoporosis fracture, bone pain, myositis, tendon rupture, arthrosis, bursitis.
Nervous System: frequent: hypesthesia, apathy, depression, hypokinesia, vertigo, twitching, agitation, anxiety, amnesia, hyperkinesia, paresthesia; infrequent: ataxia, delirium, delusions, depersonalization, dyskinesia, extrapyramidal syndrome, libido increased, coordination abnormal, dysarthria, hallucinations, manic reaction, neurosis, dystonia, hostility, reflexes increased, emotional lability, euphoria, paranoid reaction; rare: aphasia, nystagmus, akathisia (psychomotor restlessness), stupor, dementia, diplopia, drug dependence, paralysis, grand mal convulsion, hypotonia, myoclonus, psychotic depression, withdrawal syndrome, serotonin syndrome.
Respiratory System: frequent: cough increased, sinusitis; infrequent: epistaxis, bronchitis, asthma, pneumonia; rare: asphyxia, laryngitis, pneumothorax, hiccup.
Skin and Appendages: frequent: pruritus, rash; infrequent: acne, exfoliative dermatitis, dry skin, herpes simplex, alopecia; rare: urticaria, herpes zoster, skin hypertrophy, seborrhea, skin ulcer.
Special Senses: infrequent: eye pain, abnormality of accommodation, conjunctivitis, deafness, keratoconjunctivitis, lacrimation disorder, angle-closure glaucoma, hyperacusis, ear pain; rare: blepharitis, partial transitory deafness, otitis media, taste loss, parosmia.
Urogenital System: frequent: urinary tract infection; infrequent: kidney calculus, cystitis, dysuria, urinary incontinence, urinary retention, vaginitis, hematuria, breast pain, amenorrhea, dysmenorrhea, leukorrhea, impotence; rare: polyuria, urethritis, metrorrhagia, menorrhagia, abnormal ejaculation, breast engorgement, breast enlargement, urinary urgency.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of mirtazapine. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Cardiac disorders: ventricular arrhythmia (Torsades de Pointes)
Endocrine disorders: hyperprolactinemia (and related symptoms, e.g., galactorrhea and gynecomastia)
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: increased creatine kinase blood levels and rhabdomyolysis
Psychiatric disorders: somnambulism (ambulation and other complex behaviors out of bed)
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: severe skin reactions, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome, bullous dermatitis, erythema multiforme and toxic epidermal necrolysis
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Table 5 includes clinically important drug interactions with mirtazapine [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Table 5: Clinically Important Drug Interactions with Mirtazapine Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
Clinical Impact
The concomitant use of serotonergic drugs, including mirtazapine, and MAOIs increases the risk of serotonin syndrome.
Intervention
Mirtazapine is contraindicated in patients taking MAOIs, including MAOIs such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue [see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Examples
selegiline, tranylcypromine, isocarboxazid, phenelzine, linezolid, methylene blue
Other Serotonergic Drugs
Clinical Impact
The concomitant use of serotonergic drugs with mirtazapine increases the risk of serotonin syndrome.
Intervention
Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome, particularly during treatment initiation and dosage increases. If serotonin syndrome occurs, consider discontinuation of mirtazapine and/or concomitant serotonergic drugs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Examples
SSRIs, SNRIs, triptans, tricyclic antidepressants, fentanyl, lithium, amphetamines, St. John’s Wort, tramadol, tryptophan, buspirone
Strong CYP3A Inducers
Clinical Impact
The concomitant use of strong CYP3A inducers with mirtazapine decreases the plasma concentration of mirtazapine [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Intervention
Increase the dose of mirtazapine if needed with concomitant CYP3A inducer use. Conversely, a decrease in dosage of mirtazapine may be needed if the CYP3A inducer is discontinued [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
Examples
phenytoin, carbamazepine, rifampin
Strong CYP3A Inhibitors
Clinical Impact
The concomitant use of strong CYP3A inhibitors with mirtazapine may increase the plasma concentration of mirtazapine [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Intervention
Decrease the dose of mirtazapine if needed with concomitant strong CYP3A inhibitor use. Conversely, an increase in dosage of mirtazapine may be needed if the CYP3A inhibitor is discontinued [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
Examples
itraconazole, ritonavir, nefazodone
Cimetidine
Clinical Impact
The concomitant use of cimetidine, a CYP1A2, CYP2D6, and CYP3A inhibitor, with mirtazapine may increase the plasma concentration of mirtazapine [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Intervention
Decrease the dose of mirtazapine if needed with concomitant cimetidine use. Conversely, an increase in dosage of mirtazapine may be needed if cimetidine is discontinued [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
Benzodiazepines and Alcohol
Clinical Impact
The concomitant use of benzodiazepines or alcohol with mirtazapine increases the impairment of cognitive and motor skills produced by mirtazapine alone.
Intervention
Avoid concomitant use of benzodiazepines and alcohol with mirtazapine [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Examples
diazepam, alprazolam, alcohol
Drugs that Prolong QTc Interval
Clinical Impact
The concomitant use of other drugs which prolong the QTc interval with mirtazapine, increase the risk of QTc prolongation and/or ventricular arrhythmias (e.g., Torsades de Pointes).
Intervention
Use caution when using mirtazapine concomitantly with drugs that prolong the QTc interval [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Warfarin
Clinical Impact
The concomitant use of warfarin with mirtazapine may result in an increase in INR [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Intervention
Monitor INR during concomitant use of warfarin with mirtazapine.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Reproduction studies in pregnant rats and rabbits at doses up to 100 mg/kg and 40 mg/kg, respectively [20 and 17 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) on an mg/m2 basis, respectively], have revealed no evidence of teratogenic effects. However, in rats, there was an increase in post-implantation losses in dams treated with mirtazapine. There was an increase in pup deaths during the first 3 days of lactation and a decrease in pup birth weights. The cause of these deaths is not known. The effects occurred at doses that were 20 times the MRHD, but not at 3 times the MRHD, on an mg/m2 basis. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, mirtazapine should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Mirtazapine may be excreted in breast milk. Exercise caution when administering mirtazapine to nursing women.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of mirtazapine have not been established in pediatric patients with MDD. Two placebo-controlled trials in 258 pediatric patients with MDD have been conducted with mirtazapine, and the data were insufficient to establish the safety and effectiveness of mirtazapine in pediatric patients with MDD.
Antidepressants increased the risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors in pediatric patients [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
In an 8-week-long clinical trial in pediatric patients receiving doses between 15 to 45 mg per day, 49% of mirtazapine-treated patients had a weight gain of at least 7%, compared to 5.7% of placebo-treated patients. The mean increase in weight was 4 kg (2 kg SD) for mirtazapine-treated patients versus 1 kg (2 kg SD) for placebo-treated patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Approximately 190 patients ≥65 years of age participated in clinical studies with mirtazapine. Mirtazapine is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney (75%), and the risk of decreased clearance of this drug is greater in patients with impaired renal function. Pharmacokinetic studies revealed a decreased clearance of mirtazapine in the elderly [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Sedating drugs, including mirtazapine, may cause confusion and over-sedation in the elderly. Elderly patients may be at greater risk of developing hyponatremia. Caution is indicated when administering mirtazapine to elderly patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11), (5.14) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be conservative, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
8.6 Renal or Hepatic Impairment
The clearance of mirtazapine is reduced in patients with moderate to severe renal or hepatic impairment. Consequently, plasma mirtazapine levels may be increased in these patient groups, compared to levels observed in patients without renal or hepatic impairment. Dosage decrease may be necessary when administering mirtazapine to patients with moderate to severe renal or hepatic impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12), Use in Specific Populations (8.5), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
Human Experience
In premarketing clinical studies, there were reports of mirtazapine overdose alone or in combination with other pharmacological agents. Signs and symptoms reported in association with overdose included disorientation, drowsiness, impaired memory, and tachycardia.
Based on postmarketing reports, serious outcomes (including fatalities) may occur at dosages higher than the recommended doses, especially with mixed overdoses. In these cases, QT prolongation and Torsades de Pointes have also been reported [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5), Adverse Reactions (6.2), and Drug Interactions (7)].
Overdose Management
No specific antidotes for mirtazapine are known.
Contact Poison Control (1-800-222-1222) for the latest recommendations.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
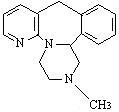
Mirtazapine tablets, USP contain mirtazapine USP. Mirtazapine has a tetracyclic chemical structure and belongs to the piperazino-azepine group of compounds. It is designated 1,2,3,4,10,14b-hexahydro-2-methylpyrazino [2,1-a] pyrido [2,3-c][2] benzazepine and has the molecular formula of C17H19N3. Its molecular weight is 265.35. The structural formula is the following and it is the racemic mixture:
Mirtazapine is a white to creamy white crystalline powder which is practically insoluble in water.
Mirtazapine tablets, USP are available for oral administration as scored film-coated tablets containing 15 or 30 mg of mirtazapine USP, and unscored film-coated tablets containing 7.5 or 45 mg of mirtazapine USP. Each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: corn starch, colloidal silicon dioxide, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, and titanium dioxide. In addition, the 15 mg contains iron oxide yellow and 30 mg contains iron oxide red, iron oxide black, and iron oxide yellow.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of mirtazapine for the treatment of major depressive disorder, is unclear. However, its efficacy could be mediated through its activity as an antagonist at central presynaptic α2-adrenergic inhibitory autoreceptors and heteroreceptors and enhancing central noradrenergic and serotonergic activity.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
In preclinical studies, mirtazapine acts as an antagonist at α2-adrenergic inhibitory autoreceptors and heteroreceptors and as an antagonist at serotonin 5-HT2 and 5-HT3 receptors. Mirtazapine has no significant affinity for the 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B receptors.
Mirtazapine also acts as an antagonist of histamine (H1) receptors, peripheral α1-adrenergic receptors, and muscarinic receptors. Actions at these receptors may explain some of the other clinical effects of mirtazapine (e.g., its prominent somnolent effects and orthostatic hypotension may be explained by its inhibition of histamine (H1) receptors and peripheral α1-adrenergic receptors, respectively).
Cardiac Electrophysiology
The effect of mirtazapine on QTc interval was assessed in healthy subjects. At a dose of 75 mg (1.67 times the maximum recommended dosage), mirtazapine does not prolong the QTc interval to a clinically meaningful extent.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Plasma levels of mirtazapine are linearly related to dose over a dose range of 15 to 80 mg (1.78 times the maximum recommended dose). Steady state plasma levels of mirtazapine are attained within 5 days, with about 50% accumulation (accumulation ratio=1.5). The (–) enantiomer has an elimination half-life that is approximately twice as long as the (+) enantiomer and therefore achieves plasma levels that are about 3 times as high as that of the (+) enantiomer.
Absorption
Mirtazapine has an absolute bioavailability of about 50% following oral administration. Peak plasma concentrations of mirtazapine are reached within about 2 hours post dose.
Food Effect
The presence of food in the stomach has a minimal effect on both the rate and extent of absorption.
Distribution
Mirtazapine is approximately 85% bound to plasma proteins over a concentration range of 0.01 to 10 mcg/mL.
Elimination
Mirtazapine has a half-life of about 20 to 40 hours following oral administration of mirtazapine.
Metabolism
Mirtazapine is extensively metabolized after oral administration. Major pathways of bio-transformation are demethylation and hydroxylation followed by glucuronide conjugation. In vitro data from human liver microsomes indicate that CYP2D6 and CYP1A2 are involved in the formation of the 8-hydroxy metabolite of mirtazapine, whereas CYP3A is considered to be responsible for the formation of the N-desmethyl and N-oxide metabolite. Several unconjugated metabolites possess pharmacological activity but are present in the plasma at very low levels.
Excretion
Mirtazapine and its metabolites are eliminated predominantly (75%) via urine with 15% in feces.
Specific Populations
Geriatric Patients
Following oral administration of mirtazapine tablets 20 mg/day for 7 days to subjects of varying ages (range 25 to 74 years old), oral clearance of mirtazapine was reduced in the elderly compared to the younger subjects. The clearance in elderly males was 40% lower compared to younger males, while the clearance was 10% lower in elderly females compared to younger females [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14), Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
Male and Female Patients
The mean elimination half-life of mirtazapine after oral administration ranges from approximately 20 to 40 hours across age and gender subgroups, with females of all ages exhibiting significantly longer elimination half-lives than males (mean half-life of 37 hours for females vs. 26 hours for males).
Race
There have been no clinical studies to evaluate the effect of race on the pharmacokinetics of mirtazapine.
Patients with Renal Impairment
When compared to subjects with normal renal function, total body clearance of mirtazapine was reduced approximately 30% in renal impaired patients with GFR=11 to 39 mL/min/1.73 m2 and approximately 50% in renal impaired patients with GFR=<10 mL/min/1.73 m2) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14), Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Following a single 15 mg oral dose of mirtazapine, the oral clearance of mirtazapine in patients with hepatic impairment was decreased by approximately 30%, compared to subjects with normal hepatic function [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12, 5.14), Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Drug Interactions Studies
Warfarin
Mirtazapine (30 mg daily) at steady state caused a statistically significant increase (0.2) in the International Normalized Ratio (INR) in subjects treated with warfarin [see Drug Interactions (7)].
QTc-Prolonging Drugs
The risk of QT prolongation and/or ventricular arrhythmias (e.g., Torsades de Pointes) may be increased with concomitant use of medicines which prolong the QTc interval (e.g., some antipsychotics and antibiotics) and in mirtazapine overdose [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5), Adverse Reactions (6.1, 6.2), Drug Interactions (7), and Overdosage (10)].
Phenytoin
In healthy male subjects (n=18), phenytoin (200 mg daily, at steady state) increased mirtazapine (30 mg daily, at steady state) clearance about 2-fold, resulting in a decrease in average plasma mirtazapine concentrations of 45% [see Drug Interactions (7)]. Mirtazapine did not significantly affect the pharmacokinetics of phenytoin.
Carbamazepine
In healthy male subjects (n=24), carbamazepine (400 mg twice a day, at steady state) increased mirtazapine (15 mg twice a day, at steady state) clearance about 2-fold, resulting in a decrease in average plasma mirtazapine concentrations of 60% [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Cimetidine
In healthy male subjects (n=12), when cimetidine, a weak inhibitor of CYP1A2, CYP2D6, and CYP3A4, given at 800 mg b.i.d. at steady state was coadministered with mirtazapine (30 mg daily) at steady state, the Area Under the Curve (AUC) of mirtazapine increased more than 50% [see Drug Interactions (7)]. Mirtazapine did not cause relevant changes in the pharmacokinetics of cimetidine.
Ketoconazole
In healthy male Caucasian subjects (n=24), coadministration of the strong CYP3A4 inhibitor ketoconazole (200 mg b.i.d. for 6.5 days) increased the peak plasma levels and the AUC of a single 30 mg dose of mirtazapine by approximately 40% and 50%, respectively [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Amitriptyline
In healthy, CYP2D6 extensive metabolizer patients (n=32), amitriptyline (75 mg daily), at steady state, did not cause relevant changes to the pharmacokinetics of steady state mirtazapine (30 mg daily); mirtazapine also did not cause relevant changes to the pharmacokinetics of amitriptyline.
Paroxetine
In healthy CYP2D6 extensive metabolizer subjects (n=24), mirtazapine (30 mg/day), at steady state, did not cause relevant changes in the pharmacokinetics of steady state paroxetine (40 mg/day), a CYP2D6 inhibitor.
Lithium
No relevant clinical effects or significant changes in pharmacokinetics have been observed in healthy male subjects on concurrent treatment with lithium 600 mg/day for 10 days at steady state and a single 30 mg dose of mirtazapine. The effects of higher doses of lithium on the pharmacokinetics of mirtazapine are unknown.
Risperidone
Mirtazapine (30 mg daily) at steady state did not influence the pharmacokinetics of risperidone (up to 3 mg twice a day) in subjects (n=6) in need of treatment with an antipsychotic and antidepressant drug.
Alcohol
Concomitant administration of alcohol (equivalent to 60 g) had a minimal effect on plasma levels of mirtazapine (15 mg) in 6 healthy male subjects. However, the impairment of cognitive and motor skills produced by mirtazapine were shown to be additive with those produced by alcohol.
Diazepam
Concomitant administration of diazepam (15 mg) had a minimal effect on plasma levels of mirtazapine (15 mg) in 12 healthy subjects. However, the impairment of motor skills produced by mirtazapine has been shown to be additive with those caused by diazepam.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Carcinogenicity studies were conducted with mirtazapine given in the diet at doses of 2, 20, and 200 mg/kg/day to mice and 2, 20, and 60 mg/kg/day to rats. The highest doses used are approximately 20 and 12 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 45 mg/day, based on body surface area (mg/m2) in mice and rats, respectively. There was an increased incidence of hepatocellular adenoma and carcinoma in male mice at the high dose. In rats, there was an increase in hepatocellular adenoma in females at the mid and high doses and in hepatocellular tumors and thyroid follicular adenoma/cystadenoma and carcinoma in males at the high dose.
Mutagenesis
Mirtazapine was not mutagenic or clastogenic and did not induce general DNA damage as determined in several genotoxicity tests: Ames test, in vitro gene mutation assay in Chinese hamster V 79 cells, in vitro sister chromatid exchange assay in cultured rabbit lymphocytes, in vivo bone marrow micronucleus test in rats, and unscheduled DNA synthesis assay in HeLa cells.
Impairment of Fertility
In a fertility study in rats, mirtazapine was given at doses up to 100 mg/kg [20 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD), based on body surface area (mg/m2)]. Mating and conception were not affected by the drug, but estrous cycling was disrupted at doses that were 3 or more times the MRHD, and pre-implantation losses occurred at 20 times the MRHD.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of mirtazapine as a treatment for major depressive disorder was established in 4 placebo-controlled, 6-week trials in adult outpatients meeting DSM-III criteria for major depressive disorder. Patients were titrated with mirtazapine from a dose range of 5 mg to 35 mg/day. The mean mirtazapine dose for patients who completed these 4 studies ranged from 21 to 32 mg/day. Overall, these studies demonstrated mirtazapine to be superior to placebo on at least 3 of the following 4 measures: 21-Item Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HDRS) total score; HDRS Depressed Mood Item; CGI Severity score; and Montgomery and Asberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS). Superiority of mirtazapine over placebo was also found for certain factors of the HDRS, including anxiety/somatization factor and sleep disturbance factor.
Examination of age and gender subsets of the population did not reveal any differential responsiveness on the basis of these subgroupings.
In a longer-term study, patients meeting (DSM-IV) criteria for major depressive disorder who had responded during an initial 8 to 12 weeks of acute treatment on mirtazapine were randomized to continuation of mirtazapine or placebo for up to 40 weeks of observation for relapse. Response during the open phase was defined as having achieved a HAM-D 17 total score of ≤8 and a CGI-Improvement score of 1 or 2 at 2 consecutive visits beginning with week 6 of the 8 to 12 weeks in the open-label phase of the study. Relapse during the double-blind phase was determined by the individual investigators. Patients receiving continued mirtazapine treatment experienced significantly lower relapse rates over the subsequent 40 weeks compared to those receiving placebo. This pattern was demonstrated in both male and female patients.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Mirtazapine tablets, USP are supplied as:
15 mg Tablets – Yellow, biconvex, capsule shaped film coated tablets with a score line in between “0” and “8” on one side and “A” debossed on the other side.
Bottles of 30 NDC: 71205-481-30
Bottles of 60 NDC: 71205-481-60
- Bottles of 90 NDC: 71205-481-90
StorageStore at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect from light and moisture.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Error! Hyperlink reference not valid.).
Suicidal Thoughts and Behaviors
Advise patients and caregivers to look for the emergence of suicidality, especially early during treatment and when the dosage is adjusted up or down, and instruct them to report such symptoms to the healthcare provider [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Agranulocytosis
Advise patients to contact their physician if they experience fever, chills, sore throat, mucous membrane ulceration, flu-like complaints, or other symptoms that might suggest infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Serotonin Syndrome
Caution patients about the risk of serotonin syndrome, particularly with the concomitant use of mirtazapine with other serotonergic drugs including triptans, tricyclic antidepressants, fentanyl, lithium, tramadol, tryptophan, buspirone, amphetamines, St. John’s Wort, and with drugs that impair metabolism of serotonin (in particular, MAOIs, both those intended to treat psychiatric disorders and also others, such as linezolid). Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider or report to the emergency room if they experience signs or symptoms of serotonin syndrome [see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.3), Drug Interactions (7)].
QTc Prolongation and Torsades de Pointes
Inform patients to consult their physician immediately if they feel faint, lose consciousness, or have heart palpitations [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5), Drug Interactions (7), Overdosage (10)]. Advise patients to inform physicians that they are taking mirtazapine before any new drug is taken.
Somnolence
Advise patients that mirtazapine may impair judgment, thinking, and particularly, motor skills, because of its prominent sedative effect. Caution patients about performing activities requiring mental alertness, such as operating hazardous machinery or operating a motor vehicle, until they are reasonably certain that mirtazapine therapy does not adversely affect their ability to engage in such activities. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Alcohol
Advise patients to avoid alcohol while taking mirtazapine [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7), Drug Interactions (7)].
Activation of Mania/Hypomania
Advise patients and their caregivers to observe for signs of activation of mania/hypomania and instruct them to report such symptoms to the healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Discontinuation Syndrome
Advise patients not to abruptly discontinue mirtazapine and to discuss any tapering regimen with their healthcare provider. Adverse reactions can occur when mirtazapine is discontinued [see Dosage and Administration (2.6), Warnings and Precautions (5.13)].
Allergic Reactions
Advise patients to notify their healthcare provider if they develop an allergic reaction such as rash, hives, swelling, or difficulty breathing [see Contraindications (4), Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
Pregnancy
Advise patients to notify their physician if they become pregnant or intend to become pregnant during mirtazapine therapy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Nursing
Advise patients to notify their physician if they are breastfeeding an infant [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Angle-Closure Glaucoma
Patients should be advised that taking mirtazapine can cause mild pupillary dilation, which in susceptible individuals, can lead to an episode of angle-closure glaucoma. Pre-existing glaucoma is almost always open-angle glaucoma because angle-closure glaucoma, when diagnosed, can be treated definitively with iridectomy. Open-angle glaucoma is not a risk factor for angle-closure glaucoma. Patients may wish to be examined to determine whether they are susceptible to angle-closure, and have a prophylactic procedure (e.g., iridectomy), if they are susceptible [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4).]
For more information about mirtazapine tablets, call Rising Health, LLC at 1-833-395-6928.
Dispense with medication guide available at : http://www.risingpharma.com/med-guides.html
Distributed by:
Rising Health, LLC
Saddle Brook, NJ 07663
Made in India
Code: TS/DRUGS/19/1993Repackaged and Relabeled by:
Proficient Rx LP
Thousand Oaks, CA 91320
Revised: 04/2020 -
MEDICATION GUIDE
MEDICATION GUIDE
Mirtazapine Tablets, USP for oral use
(mir taz’ a peen)
What is the most important information I should know about mirtazapine tablets?
Mirtazapine tablets may cause serious side effects, including:
- Increased risk of suicidal thoughts or actions in some children and young adults. Mirtazapine tablets, and other antidepressant medicines may increase suicidal thoughts or actions in some people 24 years of age and younger, especially within the first few months of treatment or when the dose is changed. Mirtazapine tablets are not for use in children.
- Depression or other serious mental illnesses are the most important causes of suicidal thoughts or actions.
How can I watch for and try to prevent suicidal thoughts and actions?
- Pay close attention to any changes, especially sudden changes in mood, behavior, thoughts, or feelings, or if you develop suicidal thoughts or actions. This is very important when an antidepressant medicine is started or when the dose is changed.
- Call your healthcare provider right away to report new or sudden changes in mood, behavior, thoughts, or feelings.
- Keep all follow-up visits with your healthcare provider as scheduled. Call your healthcare provider between visits as needed, especially if you have concerns about symptoms.
Call your healthcare provider or get emergency medical help right away if you or your family member have any of the following symptoms, especially if they are new, worse, or worry you:
- attempts to commit suicide
- acting on dangerous impulses
- acting aggressive, being angry or violent
- thoughts about suicide or dying
- new or worse depression
- new or worse anxiety
- panic attacks
- feeling very agitated or restless
- new or worse irritability
- trouble sleeping
- an extreme increase in activity or talking (mania)
- other unusual changes in behavior or mood
What are mirtazapine tablets?
Mirtazapine tablets are prescription medicines used to treat a certain type of depression called Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) in adults.
It is not known if mirtazapine tablets are safe and effective for use to treat MDD in children.
Who should not take mirtazapine tablets?
Do not take mirtazapine tablets if you:
- take a Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor (MAOI)
- have stopped taking an MAOI in the last 14 days
- are being treated with the antibiotic linezolid or intravenous methylene blue
- if you are allergic to mirtazapine or any of the ingredients in mirtazapine tablets. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of ingredients in mirtazapine tablets.
Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist if you are not sure if you take an MAOI, including the antibiotic linezolid or intravenous methylene blue.
Do not start taking an MAOI for at least 14 days after you stop treatment with mirtazapine tablets.
Before taking mirtazapine tablets, tell your healthcare provider about all your medical conditions, including if you:
- have a history of suicide or depression
- have a history or family history of bipolar disorder, mania or hypomania
- have a low white blood cell count
- have glaucoma (high pressure in the eye)
- have or had heart problems or stroke
- have an abnormal heart beat called QT prolongation or a family history of QT prolongation
- have seizures
- have high cholesterol or triglyceride levels
- have low sodium levels in your blood
- have or had kidney or liver problems
- have low blood pressure
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if mirtazapine tablets will harm your unborn baby. Talk to your healthcare provider if you become pregnant or think you may be pregnant during treatment with mirtazapine tablets.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. Mirtazapine may pass into your breast milk. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby during treatment with mirtazapine tablets.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Mirtazapine tablets and other medicines may affect each other causing possible serious side effects. Mirtazapine tablets may affect the way other medicines work and other medicines may affect the way mirtazapine and mirtazapine tablets work.
Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take:
- MAOIs
- medicines to treat migraine headaches known as triptans
- tricyclic antidepressants
- fentanyl
- lithium
- tramadol
- tryptophan
- buspirone
- amphetamines
- benzodiazepines
- St. John’s Wort
- medicines used to treat mood, anxiety, psychotic or thought disorders, including selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs)
- medicines that may affect your heart rhythm (such as certain antibiotics and some antipsychotics)
Ask your healthcare provider if you are not sure if you are taking any of these medicines. Your healthcare provider can tell you if it is safe to take mirtazapine tablets with your other medicines.
Do not start or stop any other medicines during treatment with mirtazapine tablets without talking to your healthcare provider first. Stopping mirtazapine tablets suddenly may cause you to have serious side effects. See, “What are the possible side effects of mirtazapine tablets?”
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show to your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I take mirtazapine tablets?
- Take mirtazapine tablets exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to. Do not change your dose or stop taking mirtazapine tablets without first talking to your healthcare provider.
- Your healthcare provider may need to change the dose of mirtazapine tablets until it is the right dose for you.
- Take mirtazapine tablets 1 time each day, preferably in the evening at bedtime.
- If you take too much mirtazapine call your healthcare provider or poison control center at 1-800-222-1222 right away or go to the nearest hospital emergency room.
What should I avoid while taking mirtazapine tablets?
- Do not drive, operate heavy machinery, or do other dangerous activities until you know how mirtazapine tablets affects you. Mirtazapine tablets can cause sleepiness or may affect your ability to make decisions, think clearly, or react quickly.
- Avoid drinking alcohol during treatment with mirtazapine tablets.
- Avoid taking medicines used to treat anxiety, insomnia, and seizures, called benzodiazepines, during treatment with mirtazapine tablets. Ask your healthcare provider if you are not sure if you take one of these medicines.
What are the possible side effects of mirtazapine tablets?
Mirtazapine tablets may cause serious side effects, including:
- See, “What is the most important information I should know about mirtazapine tablets?”
-
Low white blood cell count. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you develop any signs or symptoms of a low white blood cell count, including:
- fever
- chills
- sore throat
- mouth or nose sores
- flu-like symptoms
- infections
-
Serotonin syndrome. A potentially life-threatening problem called serotonin syndrome can happen when you take mirtazapine tablets with certain other medicines. See, “Who should not take mirtazapine tablets?” Stop taking mirtazapine tablets and call your healthcare provider or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away if you have any of the following signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome:
- agitation
- seeing or hearing things that are not real (hallucinations)
- confusion
- coma
- fast heart beat
- blood pressure changes
- dizziness
- sweating
- flushing
- high body temperature (hyperthermia)
- tremors, stiff muscles, or muscle twitching
- loss of coordination
- seizures
- nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
- Eye problems (angle-closure glaucoma). Mirtazapine tablets may cause a certain type of eye problem called angle-closure glaucoma. Call your healthcare provider if you have eye pain, changes in your vision, or swelling or redness in or around the eye. Only some people are at risk for these problems. You may want to undergo an eye examination to see if you are at risk and receive preventative treatment if you are.
- Heart rhythm problems.
- Increased appetite and weight gain.
- Sleepiness. See, “What should I avoid while taking mirtazapine tablets?”
-
Mania or hypomania (manic episodes) in people who have a history of bipolar disorder. Symptoms may include:
- greatly increased energy
- severe trouble sleeping
- racing thoughts
- reckless behavior
- unusually grand ideas
- excessive happiness or irritability
- talking more or faster than usual
- Seizures (convulsions).
- Increased fat levels (cholesterol and triglycerides) in your blood.
-
Low sodium levels in your blood (hyponatremia). Low sodium levels in your blood may be serious and may cause death. Elderly people may be at greater risk for this. Signs and Symptoms of low sodium levels in your blood may include:
- headache
- difficulty concentrating
- memory changes
- confusion
- weakness and unsteadiness on your feet which can lead to falls
In severe or more sudden cases, signs and symptoms include:
- hallucinations (seeing or hearing things that are not real)
- fainting
- seizures
- coma
- respiratory arrest
- death
- Changes in liver function tests.
-
Discontinuation syndrome. Suddenly stopping mirtazapine tablets may cause you to have serious side effects. Your healthcare provider may want to decrease your dose slowly. Symptoms may include:
- dizziness
- nausea and vomiting
- headache
- irritability and agitation
- problems sleeping
- abnormal dreams
- anxiety
- tiredness
- changes in your mood
- sweating
- confusion
- hypomania
- seizures
- electric shock sensation (paresthesia)
- ringing in your ears (tinnitus)
- shaking (tremor)
The most common side effects of mirtazapine tablets include:
- sleepiness
- increased appetite
- weight gain
- dizziness
These are not all the possible side effects of mirtazapine tablets.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store mirtazapine tablets?
- Store mirtazapine tablets at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F).
- Keep mirtazapine tablets away from light and moisture.
Keep mirtazapine tablets, and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of mirtazapine tablets.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use mirtazapine tablets for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give mirtazapine tablets to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. They may harm them. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about mirtazapine tablets that is written for healthcare professionals.
What are the ingredients in mirtazapine tablets?
Active ingredient: mirtazapine
Inactive ingredients: corn starch, colloidal silicon dioxide, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, and titanium dioxide. In addition, the 15 mg contains iron oxide yellow and 30 mg contains iron oxide red, iron oxide black, and iron oxide yellow.
For more information about mirtazapine tablets, call Rising Health, LLC at 1-833-395-6928.
The brands listed are trademarks of their respective owners and are not trademarks of Aurobindo Pharma Limited. The makers of these brands are not affiliated with and do not endorse Aurobindo Pharma Limited or its products.
Dispense with medication guide available at: http://www.risingpharma.com/med-guides.html
Distributed by:
Rising Health, LLC
Saddle Brook, NJ 07663
Made in India
Code: TS/DRUGS/19/1993Repackaged and Relabeled by:
Proficient Rx LP
Thousand Oaks, CA 91320
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration
Revised: 04/2020
-
PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 15 mg (30 Tablet Bottle)
NDC: 71205-481-30
Mirtazapine
Tablets, USP
15 mg
PHARMACIST: PLEASE DISPENSE WITH
MEDICATION GUIDE PROVIDED SEPARATELY
30 Tablets Rx only -
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
MIRTAZAPINE
mirtazapine tablet, film coatedProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 71205-481(NDC:57237-008) Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength MIRTAZAPINE (UNII: A051Q2099Q) (MIRTAZAPINE - UNII:A051Q2099Q) MIRTAZAPINE 15 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength STARCH, CORN (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) LOW-SUBSTITUTED HYDROXYPROPYL CELLULOSE, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 2165RE0K14) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) HYPROMELLOSE 2910 (6 MPA.S) (UNII: 0WZ8WG20P6) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) HYDROXYPROPYL CELLULOSE (1600000 WAMW) (UNII: RFW2ET671P) FERRIC OXIDE YELLOW (UNII: EX438O2MRT) Product Characteristics Color YELLOW Score 2 pieces Shape CAPSULE (Biconvex) Size 9mm Flavor Imprint Code 0;8;A Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 71205-481-30 30 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 10/01/2020 2 NDC: 71205-481-60 60 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 10/01/2020 3 NDC: 71205-481-90 90 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 10/01/2020 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA076921 10/22/2004 Labeler - Proficient Rx LP (079196022) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Proficient Rx LP 079196022 REPACK(71205-481) , RELABEL(71205-481)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.