NOCITA- bupivacaine injection, suspension
NOCITA by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
NOCITA by is a Animal medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Elanco US Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
Description:
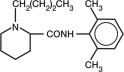
NOCITA (bupivacaine liposome injectable suspension) is a sterile, non-pyrogenic, white to off-white, preservative-free, aqueous suspension of multivesicular lipid-based particles containing bupivacaine. Each milliliter of NOCITA contains 13.3 mg of bupivacaine. Inactive ingredients and their nominal concentrations are: cholesterol, 4.7 mg/mL; 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3 phospho-rac-(1-glycerol) (DPPG), 0.9 mg/mL; tricaprylin, 2.0 mg/mL; and 1,2 dierucocylphosphatidylcholine (DEPC), 8.2 mg/mL. Bupivacaine is related chemically and pharmacologically to the amide-type local anesthetics. Chemically, bupivacaine is 1-butyl-N-(2, 6-dimethylphenyl)-2-piperidinecarboxamide with a molecular weight of 288.4. Bupivacaine structural formula is shown in the illustration to the right.
- Indication:
-
Dosage and Administration:
NOCITA is for single dose administration only. A dose of 5.3 mg/kg (0.4 mL/kg) is administered by infiltration injection into the tissue layers at the time of incisional closure. A single dose administered during surgical closure may provide up to 72 hours of pain control.
Dosing Instructions:
- Wear gloves when handling and administering NOCITA (see WARNINGS).
- NOCITA should not be allowed to come into contact with topical antiseptics. When a topical antiseptic such as povidone iodine or chlorhexidine is applied, the area should be allowed to dry before NOCITA is administered into the surgical site.
- Do not shake vial. Invert the vial multiple times to re-suspend the particles immediately prior to withdrawal of the product from the vial.
- Do not puncture the vial multiple times. Puncture the vial stopper once with a single 25 gauge or larger needle. Use aseptic technique to sequentially attach and fill sterile syringes for dosing. Each syringe should be prepared for single patient use only. Discard the vial after all doses are withdrawn.
- Following withdrawal from the vial into a syringe, NOCITA may be stored at controlled room temperature of 68° F to 77° F (20° C to 25° C) for up to 4 hours. Because the formulation does not contain preservative, the syringe(s) must be discarded after 4 hours.
-
If the dose volume of NOCITA (0.4 mL/kg) is not sufficient to cover the surgical site, add up to an equal volume of normal (0.9%) sterile saline or Lactated Ringer’s solution. If saline or Lactated Ringer’s is added to the NOCITA dose, administer the entire volume by tissue infiltration into the surgical site. Do not mix with water or other hypotonic solutions as it will result in disruption of the liposomal particles (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY).
Do not mix NOCITA with other local anesthetics or other drugs prior to administration (see PRECAUTIONS). - Use a 25 gauge or larger bore needle for administration.
- Administer by infiltration injection: Inject slowly into the tissues using an infiltration injection technique. To obtain adequate coverage, infiltrate all of the tissues in each surgical closure layer. Aspirate frequently to prevent intravascular administration (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
-
Contraindications:
Do not administer by intravenous or intra-arterial injection. If accidental intravascular administration occurs, monitor for cardiovascular (dysrhythmias, hypotension, hypertension) and neurologic (tremors, ataxia, seizures) adverse reactions.
Do not use for intra-articular injection. In humans, local anesthetics administered into a joint may cause chondrolysis.
- Warnings:
-
Precautions:
Do not administer concurrently with bupivacaine HCl, lidocaine or other amide local anesthetics. A safe interval from time of bupivacaine HCl, lidocaine or other amide local anesthetic administration to time of NOCITA administration has not been determined. The toxic effects of these drugs are additive and their administration should be used with caution including monitoring for neurologic and cardiovascular effects related to toxicity.
The safe use of NOCITA in dogs with cardiac disease has not been evaluated.
The safe use of NOCITA in dogs with hepatic or renal impairment has not been evaluated. NOCITA is metabolized by the liver and excreted by the kidneys.
The ability of NOCITA to achieve effective anesthesia has not been studied. Therefore, NOCITA is not indicated for pre-incisional or pre-procedural loco-regional anesthetic techniques that require deep and complete sensory block in the area of administration.
The safe use of NOCITA for surgical procedures other than cranial cruciate ligament surgery has not been evaluated (see ANIMAL SAFETY and ADVERSE REACTIONS).
The safe use of NOCITA has not been evaluated in dogs younger than 5 months old.
The safe use of NOCITA has not been evaluated in dogs that are pregnant, lactating, or intended for breeding.
-
Adverse Reactions:
Safety was evaluated in 123 NOCITA treated dogs and 59 saline (placebo) treated dogs in a field study in dogs that underwent cranial cruciate ligament stabilization surgery. Dogs enrolled in the study were 1-13 years of age, and weighed 3.4 to 61.3 kg. NOCITA was administered by infiltrative injection at the surgical site at a dose of 5.3 mg/kg (0.4 mL/kg).
Table D-1. Adverse Reactions Reported During the Study in the Safety Population (any dog that received treatment)
Note: If an animal experienced the same event more than once, only the first occurrence was tabulated. Adverse Reaction
NOCITA
(n = 123)Saline
(n = 59)Discharge from the Incision
4 (3.3%)
0 (0.0%)
Incisional Inflammation
(erythema and/or edema)3 (2.4%)
0 (0.0%)
Vomiting
3 (2.4%)
0 (0.0%)
Abnormalities on Urinalysis
(isosthenuria ± proteinuria)2 (1.6%)
0 (0.0%)
Increased ALP
2 (1.6%)
0 (0.0%)
Surgical Limb Edema ± Erythema
1 (0.8%)
3 (5.1%)
Soft Stool/Diarrhea
1 (0.8%)
1 (1.7%)
Inappetence
1 (0.8%)
1 (1.7%)
Fever
1 (0.8%)
0 (0.0%)
-
Contact Information:
To report suspected adverse events, for technical assistance or to obtain a copy of the Safety Data Sheet (SDS), contact Elanco US Inc. at 1-888-545-5973.
For additional information about adverse drug experience reporting for animal drugs, contact FDA at 1-888-FDA-VETS or http://www.fda.gov/reportanimalae
-
Clinical Pharmacology:
Bupivacaine is an amide, non-opioid local anesthetic. It provides local analgesia by deactivating sodium channels on the nerve membrane, preventing the generation and propagation of nerve impulses. It is only present in small concentrations as uncharged molecules at tissue pH as it is a base with pKa of 8. This un-ionized form provides a lipophilicity that permits the drug to traverse across the nerve cell membrane and upon entering the cell, binds to the intracellular portion of voltage-gated sodium channels and blocks sodium influx into nerve cells, which prevents depolarization. Without depolarization, no initiation or conduction of a pain signal can occur.
Lipid Formulation
Liposomal encapsulation or incorporation in a lipid complex can substantially affect a drug’s functional properties relative to those of the unencapsulated or nonlipid-associated drug. In addition, different liposomal or lipid-complexed products with a common active ingredient may vary from one another in the chemical composition and physical form of the lipid component. Such differences may affect functional properties of these drug products. Do not substitute with other bupivacaine formulations.
After injection of NOCITA into the soft tissue, bupivacaine is released from the multivesicular liposomes over a period of time.
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetic characterization associated with bupivacaine after subcutaneous NOCITA (bupivacaine liposome injectable suspension) or bupivacaine HCl solution administered to Beagle dogs is provided in Table D-2.
Table D-2. Mean (± SD) Plasma Pharmacokinetic Parameters for bupivacaine after single subcutaneous administration of NOCITA and bupivacaine HCl solution in male and female Beagle dogs in a laboratory study
a 5.3 mg/kg NOCITA bupivacaine base is equal to 6 mg/kg bupivacaine HCl. NOCITA doses in this table are in the bupivacaine HCl equivalent. b Median (Range) c Reported from steady state concentrations PK Parameter
NOCITAa
9 mg/kgNOCITAa
18 mg/kgNOCITAa
30 mg/kgbupivacaine HCl
9 mg/kgN, sex
6, (3M/3F)
6, (3M/3F)
6, (3M/3F)
6, (3M/3F)
Tmaxb
(hr)0.5
(0.5-0.5)0.5
(0.5-0.5)60.0
(0.5-72)0.5
(0.5-0.5)Cmax
(ng/mL)488
(335)560
(299)633
(280)1420
(355)AUC(0-72)
(ng*hr/mL)9100
(4460)12800
(2020)25600
(8160)9720
(1860)T1/2c
(hr)36.2
(12.4)25.7
(8.15)43.9
(12.5)10.1
(8.54)Following a single subcutaneous dose of 9 mg/kg and 18 mg/kg NOCITA, median time to reach Cmax was rapid (0.5 hr) but it was delayed significantly at a high dose of 30 mg/kg (60 hr). Following equivalent doses (9 mg/kg) of NOCITA and bupivacaine HCl solution, the mean bupivacaine AUC(0-72) and Tmax were comparable. However, due to the slow release mechanism of the NOCITA formulation, the mean Cmax and T½ were approximately 3-fold lower and 3.5-fold higher, respectively. Following an increase in dose of NOCITA, the bupivacaine pharmacokinetics was nonlinear with high variability in exposure parameters. Both Cmax and AUC(0-72) increase with dose but the increases were less than dose proportional. Further, the non-linear bupivacaine pharmacokinetics was made evident by an increase in the terminal phase half-life with the increase in dose.
-
Effectiveness:
Effectiveness was demonstrated in a multi-center, placebo-controlled, randomized and masked field study in client-owned dogs undergoing cranial cruciate ligament stabilization surgery. In this study, 182 dogs were enrolled in the study and randomized to treatment with NOCITA (n = 123) or saline (placebo, n = 59). The per protocol population for effectiveness was 112 NOCITA treated dogs and 52 saline dogs.
Dogs received an opioid analgesic just prior to general anesthesia and surgery. Surgical repair technique was at the discretion of the surgeon, and included extra-capsular repair, tibial plateau leveling osteotomy (TPLO), or tibial tuberosity advancement (TTA).
Table D-3 shows the number and percent of surgical procedures by treatment group.
Table D-3. Surgical Procedure by Treatment Group
Surgical Procedure
NOCITA
(n = 112)
n (%)Saline
(n = 52)
n (%)Total
(n = 164)
n (%)Extra-capsular repair
52 (46.4)
24 (46.2)
76 (46.3)
TPLO
50 (44.6)
22 (42.3)
72 (43.9)
TTA
10 (8.9)
6 (11.5)
16 (9.8)
Using an infiltration injection technique, a single dose of NOCITA or saline was infiltrated into the tissue layers during surgical closure. NOCITA or saline was administered either as is or with the addition of up to an equal volume of sterile saline. Pain was assessed by trained observers using the Glasgow Composite Measure Pain Scale-Short Form (CMPS-SF) for up to 72 hours following surgical closure. Pain assessments were conducted prior to surgery, and at 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8, 12, 24, 30, 36, 48, 56 and 72 hours post-surgery. Dogs with a CMPS-SF score ≥ 6 or were determined to be painful by the investigator received rescue analgesic medication and were classified as treatment failures. No further CMPS-SF pain assessments were recorded for dogs that received rescue analgesic medication. The primary variable for effectiveness was evaluated over the first 24-hour time interval. The percent of treatment success for NOCITA was significantly different from and greater than saline at the first 24-hour time interval (p = 0.0322). The 24-48 hour and 48-72 hour time intervals were evaluated as secondary variables and support effective use of NOCITA for up to 72 hours of analgesia.
Table D-4. Number and Percent Effectiveness for NOCITA and Saline (Placebo) at each Time Interval*
*For dogs that were deemed treatment failures over any time interval, the failure was carried forward to all subsequent time intervals. Therefore, the time intervals for evaluating treatment success are equivalent to 0-24 hours, 0-48 hours, and 0-72 hours. Time Interval for
Pain EvaluationNOCITA
(n = 112)Saline
(n = 52)0-24 hours
77 (68.8%)
19 (36.5%)
24-48 hours
72 (64.3%)
18 (34.6%)
48-72 hours
69 (61.6%)
17 (32.7%)
-
Animal Safety:
In a 4-week laboratory study with a 4-week recovery period, 60 healthy dogs aged 5-6 months were administered NOCITA at 8, 16 and 26.6 mg/kg. These doses correspond to 1.5, 3 and 5 times the maximum labeled dose of 5.3 mg/kg bupivacaine base. The active control group was administered 9 mg/kg bupivacaine HCl (equivalent to 8 mg/kg bupivacaine base), and the placebo group was administered 1.2 mL/kg saline. All dogs were dosed by subcutaneous injection twice weekly for 4 weeks. Doses alternated between two injection sites to the right or left of dorsal midline near the scapula. There were 6 dogs/sex/group for the first 4 weeks, and then 3 dogs/sex/group were maintained and monitored during a 4-week recovery period.
All dogs survived the study, and there were no clinically relevant treatment-related effects on clinical observations, physical examination, body weight, electrocardiograms (ECG), hematology, serum chemistry, urinalysis, coagulation, and organ weights. Injection site reactions on histopathology included minimal to moderate edema, granulomatous inflammation and mineralization in the subcutaneous tissue in some dogs that received NOCITA. In dogs that were evaluated immediately after the 4-week treatment period, granulomatous inflammation was characterized by numerous vacuolated macrophages and fewer lymphocytes, plasma cells and/or multinucleated giant cells. The inflammation was often associated with mineralization and/or edema. In the dogs that were maintained for the 4-week recovery period, there were fewer dogs with granulomatous inflammation and mineralization at the injection sites. The inflammation was characterized by a greater number of giant cells. One 9 mg/kg NOCITA group male dog had minimal subcutaneous edema that was not associated with cellular inflammation. These inflammatory changes are associated with administration of the liposomal suspension, and did not occur in the saline and bupivacaine HCl groups.
- Storage Conditions:
-
How Supplied:
13.3 mg/mL bupivacaine liposome injectable suspension in 10 mL or 20 mL single use vial.
10 mL supplied in 4-vial carton. 20 mL supplied in a single vial carton and 4-vial carton.
Approved by FDA under NADA # 141-461
Manufactured for:
Elanco US Inc.
Indianapolis, IN 46221 USANocita, Elanco and the diagonal bar logo are trademarks of Elanco or its affiliates.
© 2025 Elanco or its affiliatesRev. date 05/2025
PA600561X
ElancoTM
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
Description:
NOCITA (bupivacaine liposome injectable suspension) is a sterile, non-pyrogenic white to off-white, preservative-free, aqueous suspension of multivesicular lipid-based particles containing bupivacaine. Each milliliter of NOCITA contains 13.3 mg/mL of bupivacaine. Inactive ingredients and their nominal concentrations are: cholesterol, 4.7 mg/mL; 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3 phospho-rac-(1-glycerol) (DPPG), 0.9 mg/mL; tricaprylin, 2.0 mg/mL; and 1,2 dierucocylphosphatidylcholine (DEPC), 8.2 mg/mL. Bupivacaine is related chemically and pharmacologically to the amide-type local anesthetics. Chemically, bupivacaine is 1-butyl-N-(2, 6-dimethylphenyl)-2-piperidinecarboxamide with a molecular weight of 288.4.
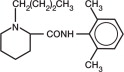
Bupivacaine structural formula is shown in the illustration to the right. - Indication:
-
Dosage and Administration:
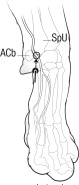
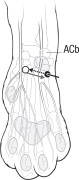
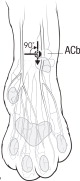
NOCITA is for administration only once prior to surgery. Administer 5.3 mg/kg per forelimb (0.4 mL/kg per forelimb, for a total dose of 10.6 mg/kg/cat) as a 4-point nerve block (described below) prior to onychectomy.
Administration prior to surgery may provide up to 72 hours of pain control.- Wear gloves when handling and administering NOCITA (see WARNINGS).
- NOCITA should not be allowed to come into contact with topical antiseptics. When a topical antiseptic such as povidone iodine or chlorhexidine is applied, the area should be allowed to dry before NOCITA is administered.
- Do not shake vial. Invert the vial multiple times to re-suspend the particles immediately prior to withdrawal of the product from the vial.
- Do not puncture the vial multiple times. Puncture the vial stopper once with a single 25 gauge or larger needle. Use aseptic technique to sequentially attach and fill sterile syringes. Each syringe should be prepared for single patient use only. Discard the vial after all doses are withdrawn.
- Following withdrawal from the vial into a syringe, NOCITA may be stored at controlled room temperature of 68° F to 77° F (20° C to 25° C) for up to 4 hours. Because the formulation does not contain preservative, the syringe(s) must be discarded after 4 hours.
-
Do not dilute NOCITA prior to use as a nerve block in cats.
Do not mix with water or other hypotonic solutions as it will result in disruption of the liposomal particles (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY).
Do not mix NOCITA with other local anesthetics or other drugs prior to administration (see PRECAUTIONS). - Use a 25 gauge or larger bore needle for administration.
Dose Administration:
- Aspirate prior to injecting to prevent intravascular administration (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
Table C-1. Dose Administration for One Forelimb.1
-
Contraindications:
Do not administer by intravenous or intra-arterial injection. If accidental intravascular administration occurs, monitor for cardiovascular (dysrhythmias, hypotension, hypertension) and neurologic (tremors, ataxia, seizures) adverse reactions.
Do not use for intra-articular injection. In humans, local anesthetics administered into a joint may cause chondrolysis.
- Warnings:
-
Precautions:
Do not administer concurrently with bupivacaine HCl, lidocaine or other amide local anesthetics. A safe interval from time of bupivacaine HCl, lidocaine or other amide local anesthetic administration to time of NOCITA administration has not been determined. The toxic effects of these drugs are additive and their administration should be used with caution including monitoring for neurologic and cardiovascular effects related to toxicity.
The safe use of NOCITA in cats with cardiac disease has not been evaluated.
The safe use of NOCITA in cats with hepatic or renal impairment has not been evaluated. NOCITA is metabolized by the liver and excreted by the kidneys.
The ability of NOCITA to achieve effective anesthesia has not been evaluated.
The safe use of NOCITA in cats for surgical procedures other than onychectomy has not been evaluated.
The safe use of NOCITA has not been evaluated in cats younger than 5 months old.
The safe use of NOCITA has not been evaluated in cats that are pregnant, lactating, or intended for breeding.
-
Adverse Reactions:
Safety was evaluated in 120 NOCITA treated cats and 121 saline (placebo) treated cats in a field study in cats undergoing onychectomy. Cats enrolled in the study were 5 months to 10 years of age, and weighed 2.0 to 9.3 kg. NOCITA was administered as a 4-point peripheral nerve block at a dose of 5.3 mg/kg per forelimb (0.4 mL/kg per forelimb).
Table C-2: Adverse Reactions Reported During the Study in the Safety Population (any cat that received treatment)
Note: If an animal experienced the same event more than once, only the first occurrence was tabulated. * Elevated body temperature was defined as temperature ≥ 103° F on Day 3 and normal before surgery. One of the NOCITA treated cats had an infection of one surgical site. No other cat with elevated body temperature showed evidence of infection or illness. Adverse Reaction
NOCITA (n = 120)
Saline (n = 121)
Elevated body temperature*
8 (6.7%)
5 (4.1%)
Surgical site infection
4 (3.3%)
1 (0.8%)
Chewing/licking of surgical site
3 (2.5%)
2 (1.7%)
Diarrhea
2 (1.7%)
1 (0.8%)
Injection site erythema
1 (0.8%)
0 (0.0%)
Swelling of paw; erythematous digits
1 (0.8%)
0 (0.0%)
Eight cats, 4 in each group, had normal platelet counts before treatment on Day 0 and platelet counts below the reference range (155,000-641,000/μL) on Day 3. The 4 cats treated with NOCITA had platelet counts of 42,000 to 100,000/μL, and the 4 cats in the saline group had platelet counts of 114,000 to 149,000/μL. Decreased platelet counts were not associated with clinical signs.
In a pilot study with 62 cats undergoing onychectomy (31 cats treated with NOCITA and 31 with saline), one NOCITA treated cat had a motor deficit (unilateral knuckling) which resolved by the next morning following surgery. Another NOCITA treated cat had bruising at the injection sites.
-
Contact Information:
To report suspected adverse events, for technical assistance or to obtain a copy of the Safety Data Sheet (SDS), contact Elanco US Inc. at 1-888-545-5973.
For additional information about adverse drug experience reporting for animal drugs, contact FDA at 1-888-FDA-VETS or http://www.fda.gov/reportanimalae
-
Clinical Pharmacology:
Bupivacaine is an amide, non-opioid local anesthetic. It provides local analgesia by deactivating sodium channels on the nerve membrane, preventing the generation and propagation of nerve impulses. It is only present in small concentrations as uncharged molecules at tissue pH as it is a base with pKa of 8. This un-ionized form provides a lipophilicity that permits the drug to traverse across the nerve cell membrane and upon entering the cell, binds to the intracellular portion of voltage-gated sodium channels and blocks sodium influx into nerve cells, which prevents depolarization. Without depolarization, no initiation or conduction of a pain signal can occur.
Lipid Formulation
Liposomal encapsulation or incorporation in a lipid complex can substantially affect a drug's functional properties relative to those of the unencapsulated or nonlipid-associated drug. In addition, different liposomal or lipid-complexed products with a common active ingredient may vary from one another in the chemical composition and physical form of the lipid component. Such differences may affect functional properties of these drug products. Do not substitute with other bupivacaine formulations.
After injection of NOCITA, bupivacaine is released from the multivesicular liposomes over a period of time.
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetic characterization associated with bupivacaine after subcutaneous NOCITA (bupivacaine liposome injectable suspension) or bupivacaine HCl solution administered to cats evaluated for 168 hours is provided in Table C-3.
Table C-3. Plasma pharmacokinetic parameters for bupivacaine after single subcutaneous administration of NOCITA and bupivacaine HCl solution in male and female cats in a laboratory study.
a 5.3 mg/kg NOCITA bupivacaine base is equal to 6 mg/kg bupivacaine HCl. NOCITA doses in this table are in the bupivacaine HCl equivalent. b Median (range) c Mean (range) Tmax = time to maximum plasma concentration Tlast = time to last quantifiable plasma concentration Cmax = maximum plasma concentration AUClast = area under the curve from the time of dosing to the last quantifiable plasma concentration PK Parameter
NOCITAa 3 mg/kg
NOCITAa 9 mg/kg
NOCITAa 15 mg/kg
bupivacaine HCl 1 mg/kg
N
6
6
6
6
Tmaxb (hr)
12.5 (1-48)
10 (1-24)
1.5 (1-24)
1 (1-4)
Tlastb(hr)
108 (72-144)
120 (72-168)
144 (120-168)
18 (12-24)
Cmaxc (ng/mL)
311.4 (82.2-565)
620.2 (374-892)
709.7 (462-1090)
263.9 (60.5-506)
AUC(last)c (ng*hr/mL)
11347 (5176-15767)
32561 (19390-47532)
38475 (26460-48252)
1608 (314-2363)
Following a single subcutaneous dose of NOCITA, there was a less than dose proportional increase in Cmax and AUClast across the dose range tested (3-15 mg/kg). There was a high variability in all reported parameters. Half-life is not reported for NOCITA in cats because the prolonged absorption confounds the estimation of the terminal elimination phase. Therefore, Tlast is included as a more appropriate measure of the duration of quantifiable plasma concentrations.
-
Effectiveness:
Effectiveness was demonstrated in a multi-center, placebo-controlled, randomized and masked field study in client-owned cats undergoing bilateral forelimb onychectomy. In this study, 241 cats were enrolled in the study and randomized to treatment with NOCITA (n = 120) or saline (placebo, n = 121).
Cats received an opioid analgesic just prior to general anesthesia and surgery. The nerve block injection sites were shaved and a standard surgical preparation with chlorhexidine or povidone iodine was used. Prior to onychectomy, NOCITA or saline was administered as a 4-point nerve block (see DOSING INSTRUCTIONS).
Pain was assessed by trained observers using a modified version of the UNESP-Botucatu Multidimensional Composite Pain Scale for up to 72 hours following extubation. Pain assessments were conducted prior to surgery, and at 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8, 12, 24, 30, 36, 48, 56 and 72 hours post-surgery. Cats with a composite pain score ≥ 6 or that were determined to be painful by the assessor received rescue analgesic medication and were classified as treatment failures. After receiving rescue analgesia, cats did not have further pain assessments performed. The primary variable for effectiveness was evaluated over the first 24-hour time interval. The percent of treatment success for NOCITA was significantly greater than saline for the 0-24 hour time interval (p = 0.0252). The 0-48 hour and 0-72 hour time intervals were evaluated as secondary variables and support effective use of NOCITA for up to 72 hours of analgesia.
Table C-4. Number and Percent Effectiveness for NOCITA and Saline (Placebo) Groups at each Time Interval
Time Interval for Pain Evaluation
NOCITA
Saline
0-24 hours
88/117 (75.2%)
48/119 (40.3%)
0-48 hours
79/115 (68.7%)
41/118 (34.7%)
0-72 hours
78/114 (68.4%)
42/119 (35.3%)
The per protocol populations for effectiveness varied for each pain assessment time interval because of protocol deviations affecting only one of the three time intervals for some cats.
-
Animal Safety:
In a 22 day laboratory study, 40 healthy cats (4 cats/sex/group) aged 5-6 months were administered negative control (2.37 mL/kg saline), active control (5.3 mg/kg bupivacaine HCl), or NOCITA at 10.6, 21.2, or 31.8 mg/kg via injection using a suprainguinal approach for a femoral nerve block of the right hindlimb on Days 0, 9 and 18. These NOCITA doses correspond to 1, 2 and 3 times the maximum labeled total dose of 10.6 mg/kg/cat (representing 2, 4 and 6 times the maximum labeled dose of 5.3 mg/kg/forelimb).
Two cats died during the study. One male in the active control group died during recovery from anesthesia after the second dose and no definitive cause of death was determined. One female in the 31.8 mg/kg group was euthanized on Day 15. This cat developed a suppurative, open, necrotic wound over the region of the right stifle after the second dose administration.
For the cats who survived the study, there were no clinically relevant treatment-related effects on electrocardiograms, hematology, serum chemistry, urinalysis, coagulation, and organ weights. Right hindlimb impairment was expected because the entire dose was administered as a femoral nerve block. Right hindlimb impairment occurred in 23 of the 24 NOCITA cats which persisted for 1-5 days; 2 negative control cats which persisted for 1 day; and none of the active control cats. Left hindlimb impairment was observed the day after the first dose in one cat in the 21.2 mg/kg group. NOCITA treatment-related findings were observed on histopathology of soft tissue and the femoral nerve at the injection sites. Injection site soft tissue histopathology findings included subacute or chronic inflammation, mineralization, myofiber degeneration and myofiber necrosis. Injection site femoral nerve histopathology findings included subacute or chronic inflammation.
Sporadic clinical observations and histopathology findings throughout both negative and active control groups and NOCITA groups included: soft or watery or mucoid stool; inguinal swelling on the right hindlimb noted after only the first dose; abrasions or scabbing noted at the right abdominal and inguinal regions as well as on the right hindlimb and at the right stifle; histopathology findings at or near the injection site or right stifle included ulceration and suppurative crusts on the skin, histopathology findings at the injection site of subcutaneous foreign material and fibrosis, and myofiber regeneration.
- Storage Conditions:
-
How Supplied:
13.3 mg/mL bupivacaine liposome injectable suspension in 10 mL or 20 mL single use vial.
10 mL supplied in 4-vial carton. 20 mL supplied in a single vial carton and 4-vial carton.
Approved by FDA under NADA # 141-461
Manufactured for: Elanco US Inc., Indianapolis, IN 46221 USA
Nocita, Elanco and the diagonal bar logo are trademarks of Elanco or its affiliates.
Rev. date 05/2025
- REFERENCES
- Principal Display Panel - 10 mL Carton Label
-
Principal Display Panel - 10 mL Vial Label
nocita™
(bupivacaine liposome injectable suspension)Local anesthetic
13.3 mg/mL
For use in dogs and cats
Approved by FDA under NADA # 141-461
Warnings: Not for use
in humans. Keep out of
reach of children.See package insert
for complete product
information.Single use vial
10 mL
injectable
suspension -
Principal Display Panel - 20 mL Carton Label
1 VIAL
nocita™
(bupivacaine liposome injectable suspension)Local anesthetic
13.3 mg/mL
For use in dogs and cats
20 mL
injectable
suspensionCaution: Federal law restricts
this drug to use by or on the order
of a licensed veterinarian.Approved by FDA under NADA # 141-461
ElancoTM
4 VIALS
nocita™
(bupivacaine liposome injectable suspension)Local anesthetic
13.3 mg/mL
For use in dogs and cats
20 mL
injectable
suspensionCaution: Federal law restricts this drug to use by or on the order of a licensed veterinarian.
Approved by FDA under NADA # 141-461
ElancoTM
-
Principal Display Panel - 20 mL Vial Label
nocita™
(bupivacaine liposome injectable suspension)Local anesthetic
13.3 mg/mL
For use in dogs and cats
Caution: Federal law restricts this
drug to use by or on the order of
a licensed veterinarian.20 mL injectable suspension
Approved by FDA under NADA # 141-461
Warnings: Not for use
in humans. Keep out
of reach of children.
NOCITA is an amide local
anesthetic. In case of
accidental injection or
accidental topical exposure,
contact a physician and
seek medical attention
immediately. Wear
gloves when handling
vials to prevent accidental
topical exposure.Please refer to the
package insert for
complete information.Single use vial
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
NOCITA
bupivacaine injection, suspensionProduct Information Product Type PRESCRIPTION ANIMAL DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 58198-5531 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength BUPIVACAINE (UNII: Y8335394RO) (BUPIVACAINE - UNII:Y8335394RO) BUPIVACAINE 13.3 mg in 1 mL Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 58198-5531-3 4 in 1 CARTON 1 10 mL in 1 VIAL 2 NDC: 58198-5531-2 1 in 1 CARTON 2 NDC: 58198-5531-1 20 mL in 1 VIAL 3 NDC: 58198-5531-4 4 in 1 CARTON 3 NDC: 58198-5531-1 20 mL in 1 VIAL Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NADA NADA141461 10/31/2016 Labeler - Elanco US Inc. (966985624)
Trademark Results [NOCITA]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 NOCITA 86979204 4994934 Live/Registered |
ARATANA THERAPEUTICS, INC. 2014-12-02 |
 NOCITA 86976369 4757713 Live/Registered |
ARATANA THERAPEUTICS, INC. 2013-12-19 |
 NOCITA 86469459 not registered Dead/Abandoned |
ARATANA THERAPEUTICS, INC. 2014-12-02 |
 NOCITA 86148955 4983665 Live/Registered |
ARATANA THERAPEUTICS, INC. 2013-12-19 |
 NOCITA 73080010 1094628 Dead/Expired |
PRIMO IMPORTING & DISTRIBUTING CO. LIMITED 1976-03-12 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.