Indomethacin by Hetero Drugs Ltd., / Hetero Drugs Limited INDOMETHACIN capsule
Indomethacin by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Indomethacin by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Hetero Drugs Ltd.,, Hetero Drugs Limited. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
BOXED WARNING
Cardiovascular Risk
NSAIDS may cause an increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, myocardial infarction, and stroke, which can be fatal. This risk may increase with duration of use. Patients with Cardiovascular disease or risk factors for cardiovascular disease may be at greater risk (see WARNINGS).
Indomethacin is contraindicated for the treatment of perioperative pain in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery(see WARNINGS).
Gastrointestinal Risk
NSAIDs cause an increased risk of serious gastrointestinal adverse events including bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach or intestines, which can be fatal. These events can occur at any time during use and without warning symptoms. Elderly patients are at greater risk for serious gastrointestinal events (see WARNINGS). -
DESCRIPTION
Indomethacin Capsules, USP for oral administration are provided in two dosage strengths which contain either 25 mg or 50 mg of indomethacin. Indomethacin is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory indole derivative designated chemically as 1-(4-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-1H-indole-3-acetic acid.
The structural formula is:
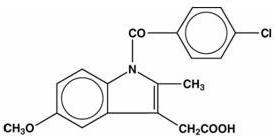
C19H16ClNO4 M.W. 357.79
Indomethacin, USP is practically insoluble in water and sparingly soluble in alcohol. It has a pKa of 4.5 and is stable in neutral or slightly acidic media and decomposes in strong alkali.
Each capsule for oral administration contains 25 mg or 50 mg of indomethacin and the following inactive ingredients: lactose monohydrate, sodium lauryl sulphate, sodium starch glycolate, colloidal silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate. The hard gelatin shell consists of gelatin, titanium dioxide USP, FD & C Blue 1, D & C Yellow 10. The capsules are printed with black ink containing black iron oxide E172 dye.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Indomethacin is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that exhibits antipyretic and analgesic properties. Its mode of action, like that of other anti-inflammatory drugs, is not known. However, its therapeutic action is not due to pituitary-adrenal stimulation.
Indomethacin is a potent inhibitor of prostaglandin synthesis in vitro. Concentrations are reached during therapy which have been demonstrated to have an effect in vivo as well. Prostaglandins sensitize afferent nerves and potentiate the action of bradykinin in inducing pain in animal models. Moreover, prostaglandins are known to be among the mediators of inflammation. Since indomethacin is an inhibitor of prostaglandin synthesis, its mode of action may be due to a decrease of prostaglandins in peripheral tissues.
Indomethacin has been shown to be an effective anti-inflammatory agent, appropriate for long-term use in rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and osteoarthritis.
Indomethacin affords relief of symptoms; it does not alter the progressive course of the underlying disease.
Indomethacin suppresses inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis as demonstrated by relief of pain, and reduction of fever, swelling and tenderness. Improvement in patients treated with indomethacin for rheumatoid arthritis has been demonstrated by a reduction in joint swelling, average number of joints involved, and morning stiffness; by increased mobility as demonstrated by a decrease in walking time; and by improved functional capability as demonstrated by an increase in grip strength. Indomethacin may enable the reduction of steroid dosage in patients receiving steroids for the more severe forms of rheumatoid arthritis. In such instances the steroid dosage should be reduced slowly and the patients followed very closely for any possible adverse effects.
Indomethacin has been reported to diminish basal and CO2 stimulated cerebral blood flow in healthy volunteers following acute oral and intravenous administration. In one study, after one week of treatment with orally administered indomethacin, this effect on basal cerebral blood flow had disappeared. The clinical significance of this effect has not been established.
Indomethacin capsules have been found effective in relieving the pain, reducing the fever, swelling, redness, and tenderness of acute gouty arthritis (see INDICATIONS AND USAGE).
Following single oral doses of indomethacin capsules 25 mg or 50 mg, indomethacin is readily absorbed, attaining peak plasma concentrations of about 1 and 2 mcg/mL, respectively, at about 2 hours. Orally administered indomethacin capsules are virtually 100% bioavailable, with 90% of the dose absorbed within 4 hours. A single 50 mg dose of indomethacin oral suspension was found to be bioequivalent to a 50 mg indomethacin capsule when each was administered with food.
Indomethacin is eliminated via renal excretion, metabolism, and biliary excretion. Indomethacin undergoes appreciable enterohepatic circulation. The mean half-life of indomethacin is estimated to be about 4.5 hours. With a typical therapeutic regimen of 25 mg or 50 mg t.i.d., the steady-state plasma concentrations of indomethacin are an average 1.4 times those following the first dose.
Indomethacin exists in the plasma as the parent drug and its desmethyl, desbenzoyl, and desmethyl-desbenzoyl metabolites, all in the unconjugated form. About 60 % of an oral dosage is recovered in urine as drug and metabolites (26 % as indomethacin and its glucuronide), and 33 % is recovered in feces (1.5 % as indomethacin).
About 99% of indomethacin is bound to protein in plasma over the expected range of therapeutic plasma concentrations. Indomethacin has been found to cross the blood-brain barrier and the placenta. -
INDICATIONS & USAGE
Carefully consider the potential benefits and risks of indomethacin capsules and other treatment options before deciding to use indomethacin. Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals (see WARNINGS).
Indomethacin Capsule, USP has been found effective in active stages of the following:
1. Moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis including acute flares of chronic disease.
2. Moderate to severe ankylosing spondylitis.
3. Moderate to severe osteoarthritis.
4. Acute painful shoulder (bursitis and/or tendinitis).
5. Acute gouty arthritis. -
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Indomethacin Capsule, USP is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to indomethacin or the excipients (see DESCRIPTION).
Indomethacin Capsule, USP should not be given to patients who have experienced asthma, urticaria, or allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs. Severe, rarely fatal, anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions to NSAIDs have been reported in such patients (see WARNINGS: Anaphylactic / Anaphylactoid Reactions , and PRECAUTIONS: General: Preexisting Asthma).
Indomethacin Capsule, USP is contraindicated for the treatment of perioperative pain in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery (see WARNINGS). -
WARNINGS
Cardiovascular Effects
Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events
Clinical trials of several COX-2 selective and nonselective NSAIDs of up to 3 years duration have shown an increased risk of serious cardiovascular (CV) thrombotic events, myocardial infarction, and stroke, which can be fatal. All NSAIDs, both COX-2 selective and nonselective, may have a similar risk. Patients with known CV disease or risk factors for CV disease may be at greater risk. To minimize the potential risk for an adverse CV event in patients treated with an NSAID, the lowest effective dose should be used for the shortest duration possible. Physicians and patients should remain alert for the development of such events, even in the absence of previous CV symptoms. Patients should be informed about the signs and/or symptoms of serious CV events and the steps to take if they occur.
There is no consistent evidence that concurrent use of aspirin mitigates the increased risk of serious CV thrombotic events associated with NSAID use. The concurrent use of aspirin and an NSAID does increase the risk of serious GI events (see WARNINGS: Gastrointestinal Effects).
Two large, controlled, clinical trials of a COX-2 selective NSAID for the treatment of pain in the first 10 to 14 days following CABG surgery found an increased incidence of myocardial infarction and stroke (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
Hypertension
NSAIDs, including indomethacin, can lead to onset of new hypertension or worsening of preexisting hypertension, either of which may contribute to the increased incidence of CV events. Patients taking thiazides or loop diuretics may have impaired response to these therapies when taking NSAIDs. NSAIDs, including indomethacin, should be used with caution in patients with hypertension. Blood pressure (BP) should be monitored closely during the initiation of NSAID treatment and throughout the course of therapy.
Congestive Heart Failure and Edema
Fluid retention and edema have been observed in some patients taking NSAIDs. Indomethacin should be used with caution in patients with fluid retention or heart failure.
In a study of patients with severe heart failure and hyponatremia, indomethacin was associated with significant deterioration of circulatory hemodynamics, presumably due to inhibition of prostaglandin dependent compensatory mechanisms.Gastrointestinal Effects
Risk of Ulceration, Bleeding, and Perforation
NSAIDs, including indomethacin, can cause serious gastrointestinal (GI) adverse events including inflammation, bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, or large intestine, which can be fatal. These serious adverse events can occur at any time, with or without warning symptoms, in patients treated with NSAIDs. Only one in five patients, who develop a serious upper GI adverse event on NSAID therapy is symptomatic. Upper GI ulcers, gross bleeding, or perforation caused by NSAIDs occur in approximately 1% of patients treated for 3 to 6 months, and in about 2 to 4% of patients treated for one year. These trends continue with longer duration of use, increasing the likelihood of developing a serious GI event at some time during the course of therapy. However, even short-term therapy is not without risk.
Rarely, in patients taking indomethacin, intestinal ulceration has been associated with stenosis and obstruction. Gastrointestinal bleeding without obvious ulcer formation and perforation of preexisting sigmoid lesions (diverticulum, carcinoma, etc.) have occurred. Increased abdominal pain in ulcerative colitis patients or the development of ulcerative colitis and regional ileitis have been reported to occur rarely.
NSAIDs should be prescribed with extreme caution in those with a prior history of ulcer disease or gastrointestinal bleeding. Patients with a prior history of peptic ulcer disease and/or gastrointestinal bleeding who use NSAIDs have a greater than 10-fold increased risk for developing a GI bleed compared to patients with neither of these risk factors. Other factors that increase the risk for GI bleeding in patients treated with NSAIDs include concomitant use of oral corticosteroids or anticoagulants, longer duration of NSAID therapy, smoking, use of alcohol, older age, and poor general health status. Most spontaneous reports of fatal GI events are in elderly or debilitated patients and therefore, special care should be taken in treating this population.
To minimize the potential risk for an adverse GI event in patients treated with an NSAID, the lowest effective dose should be used for the shortest possible duration. Patients and physicians should remain alert for signs and symptoms of GI ulceration and bleeding during NSAID therapy and promptly initiate additional evaluation and treatment if a serious GI adverse event is suspected. This should include discontinuation of the NSAID until a serious GI adverse event is ruled out. For high risk patients, alternate therapies that do not involve NSAIDs should be considered.Renal Effects
Long-term administration of NSAIDs has resulted in renal papillary necrosis and other renal injury. Renal toxicity has also been seen in patients in whom renal prostaglandins have a compensatory role in the maintenance of renal perfusion. In these patients, administration of a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug may cause a dose dependent reduction in prostaglandin formation and, secondarily, in renal blood flow, which may precipitate over renal decompensation. Patients at greatest risk of this reaction are those with impaired renal function, heart failure, liver dysfunction, those taking diuretics and ACE inhibitors, patients with volume depletion, and the elderly. Discontinuation of NSAID therapy is usually followed by recovery to the pretreatment state.
Increases in serum potassium concentration, including hyperkalemia, have been reported with use of indomethacin, even in some patients without renal impairment. In patients with normal renal function, these effects have been attributed to a hyporeninemic-hypoaldosteronism state (see PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions).
Advanced Renal Disease
No information is available from controlled clinical studies regarding the use of indomethacin in patients with advanced renal disease. Therefore, treatment with indomethacin is not recommended in these patients with advanced renal disease. If indomethacin therapy must be initiated, close monitoring of the patient's renal function is advisable.Anaphylactic / Anaphylactoid Reactions
As with other NSAIDs, anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions may occur in patients without known prior exposure to indomethacin. Indomethacin should not be given to patients with the aspirin triad. This symptom complex typically occurs in asthmatic patients who experience rhinitis with or without nasal polyps, or who exhibit severe, potentially fatal bronchospasm after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs (see CONTRAINDICATIONS and PRECAUTIONS: General: Preexisting Asthma). Emergency help should be sought in cases where an anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reaction occurs.Skin Reactions
NSAIDs, including indomethacin, can cause serious skin adverse events such as exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), which can be fatal. These serious events may occur without warning. Patients should be informed about the signs and symptoms of serious skin manifestations and use of the drug should be discontinued at the first appearance of skin rash or any other sign of hypersensitivity.Pregnancy
In late pregnancy, as with other NSAIDs, indomethacin should be avoided because it may cause premature closure of the ductus arteriosus.Ocular Effects
Corneal deposits and retinal disturbances, including those of the macula, have been observed in some patients who had received prolonged therapy with indomethacin. The prescribing physician should be alert to the possible association between the changes noted and indomethacin. It is advisable to discontinue therapy if such changes are observed. Blurred vision may be a significant symptom and warrants a thorough ophthalmological examination. Since these changes may be asymptomatic, ophthalmologic examination at periodic intervals is desirable in patients where therapy is prolonged.Central Nervous System Effects
Indomethacin may aggravate depression or other psychiatric disturbances, epilepsy, and parkinsonism, and should be used with considerable caution in patients with these conditions. If severe CNS adverse reactions develop, indomethacin should be discontinued.
Indomethacin may cause drowsiness; therefore, patients should be cautioned about engaging in activities requiring mental alertness and motor coordination, such as driving a car. Indomethacin may also cause headache. Headache which persists despite dosage reduction requires cessation of therapy with indomethacin. -
PRECAUTIONS
General Precautions
Indomethacin cannot be expected to substitute for corticosteroids or to treat corticosteroid insufficiency. Abrupt discontinuation of corticosteroids may lead to disease exacerbation. Patients on prolonged corticosteroid therapy should have their therapy tapered slowly if a decision is made to discontinue corticosteroids.
The pharmacological activity of indomethacin in reducing fever and inflammation may diminish the utility of these diagnostic signs in detecting complications of presumed noninfectious, painful conditions.
Hepatic Effects
Borderline elevations of one or more liver tests may occur in up to 15% of patients taking NSAIDs, including indomethacin. These laboratory abnormalities may progress, may remain unchanged, or may be transient with continuing therapy. Notable elevations of ALT or AST (approximately three or more times the upper limit of normal) have been reported in approximately 1% of patients in clinical trials with NSAIDs. In addition, rare cases of severe hepatic reactions, including jaundice and fatal fulminant hepatitis, liver necrosis and hepatic failure, some of them with fatal outcomes have been reported.
A patient with symptoms and/or signs suggesting liver dysfunction, or in whom an abnormal liver test values has occurred, should be evaluated for evidence of the development of a more severe hepatic reaction while on therapy with indomethacin. If clinical signs and symptoms consistent with liver disease develop, or if systemic manifestations occur (e.g., eosinophilia, rash, etc.), indomethacin should be discontinued.
Hematological Effects
Anemia is sometimes seen in patients receiving NSAIDs, including indomethacin. This may be due to fluid retention, occult or gross GI blood loss, or an incompletely described effect upon erythropoiesis. Patients on long-term treatment with NSAIDs, including indomethacin, should have their hemoglobin or hematocrit checked if they exhibit any signs or symptoms of anemia.
NSAIDs inhibit platelet aggregation and have been shown to prolong bleeding time in some patients. Unlike aspirin, their effect on platelet function is quantitatively less, of shorter duration, and reversible. Patients receiving indomethacin who may be adversely affected by alterations in platelet function, such as those with coagulation disorders or patients receiving anticoagulants, should be carefully monitored.
Preexisting Asthma
Patients with asthma may have aspirin-sensitive asthma. The use of aspirin in patients with aspirin-sensitive asthma has been associated with severe bronchospasm which can be fatal. Since cross-reactivity, including bronchospasm, between aspirin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs has been reported in such aspirin-sensitive patients, indomethacin should not be administered to patients with this form of aspirin sensitivity and should be used with caution in patients with preexisting asthma.Information for Patients
Patients should be informed of the following information before initiating therapy with an NSAID and periodically during the course of ongoing therapy. Patients should also be encouraged to read the NSAID Medication Guide that accompanies each prescription dispensed.
1. Indomethacin, like other NSAIDs, may cause serious CV side effects, such as MI or stroke, which may result in hospitalization and even death. Although serious CV events can occur without warning symptoms, patients should be alert for the signs and symptoms of chest pain, shortness of breath, weakness, slurring of speech, and should ask for medical advice when observing any indicative sign or symptoms. Patients should be apprised of the importance of this follow-up (see WARNINGS: Cardiovascular Effects).
2. Indomethacin, like other NSAIDs, can cause GI discomfort and, rarely, serious GI side effects, such as ulcers and bleeding, which may result in hospitalization and even death. Although serious GI tract ulcerations and bleeding can occur without warning symptoms, patients should be alert for the signs and symptoms of ulcerations and bleeding, and should ask for medical advice when observing any indicative signs or symptoms including epigastric pain, dyspepsia, melena, and hematemesis. Patients should be apprised of the importance of this follow-up (see WARNINGS: Gastrointestinal Effects: Risk of Ulceration, Bleeding, and Perforation).
3. Indomethacin, like other NSAIDs, can cause serious skin side effects such as exfoliative dermatitis, SJS, and TEN, which may result in hospitalizations and even death. Although serious skin reactions may occur without warning, patients should be alert for the signs and symptoms of skin rash and blisters, fever, or other signs of hypersensitivity such as itching, and should ask for medical advice when observing any indicative signs or symptoms. Patients should be advised to stop the drug immediately if they develop any type of rash and contact their physicians as soon as possible.
4. Patients should promptly report signs or symptoms of unexplained weight gain or edema to their physicians.
5. Patients should be informed of the warning signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity (e.g., nausea, fatigue, lethargy, pruritus, jaundice, right upper quadrant tenderness and "flu-like" symptoms). If these occur, patients should be instructed to stop therapy and seek immediate medical therapy.
6. Patients should be informed of the signs of an anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reaction (e.g. difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat). If these occur, patients should be instructed to seek immediate emergency help (see WARNINGS).
7. In late pregnancy, as with other NSAIDs, indomethacin should be avoided because it may cause premature closure of the ductus arteriosus.Laboratory Tests
Because serious GI tract ulcerations and bleeding can occur without warning symptoms, physicians should monitor for signs or symptoms of GI bleeding. Patients on long-term treatment with NSAIDs should have their CBC and a chemistry profile checked periodically. If clinical signs and symptoms consistent with liver or renal disease develop, systemic manifestations occur (e.g., eosinophilia, rash, etc.) or if abnormal liver tests persist or worsen, indomethacin should be discontinued.Drug Interactions
ACE Inhibitors and Angiotensin II Antagonists
Reports suggest that NSAIDs may diminish the antihypertensive effect of ACE inhibitors and angiotensin II antagonists. Indomethacin can reduce the antihypertensive effects of captopril and losartan. These interactions should be given consideration in patients taking NSAIDs concomitantly with ACE inhibitors or angiotensin II antagonists. In some patients with compromised renal function, the coadministration of an NSAID and an ACE inhibitor or an angiotensin II antagonist may result in further deterioration of renal function, including possible acute renal failure, which is usually reversible.
Aspirin
When indomethacin is administered with aspirin, its protein binding is reduced, although the clearance of free indomethacin is not altered. The clinical significance of this interaction is not known.
The use of indomethacin in conjunction with aspirin or other salicylates is not recommended. Controlled clinical studies have shown that the combined use of indomethacin and aspirin does not produce any greater therapeutic effect than the use of indomethacin alone. In a clinical study of the combined use of indomethacin and aspirin, the incidence of gastrointestinal side effects was significantly increased with combined therapy.
In a study in normal volunteers, it was found that chronic concurrent administration of 3.6 g of aspirin per day decreases indomethacin blood levels approximately 20%.
Beta-Adrenoceptor Blocking Agents
Blunting of the antihypertensive effect of beta-adrenoceptor blocking agents by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs including indomethacin has been reported. Therefore, when using these blocking agents to treat hypertension, patients should be observed carefully in order to confirm that the desired therapeutic effect has been obtained.
Cyclosporin
Administration of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs concomitantly with cyclosporine has been associated with an increase in cyclosporine-induced toxicity, possibly due to decreased synthesis of renal prostacyclin. NSAIDs should be used with caution in patients taking cyclosporine, and renal function should be carefully monitored.
Diflunisal
In normal volunteers receiving indomethacin, the administration of diflunisal decreased the renal clearance and significantly increased the plasma levels of indomethacin. In some patients, combined use of indomethacin and diflunisal has been associated with fatal gastrointestinal hemorrhage. Therefore, diflunisal and indomethacin should not be used concomitantly.
Digoxin
Indomethacin given concomitantly with digoxin has been reported to increase the serum concentration and prolong the half-life of digoxin. Therefore, when indomethacin and digoxin are used concomitantly, serum digoxin levels should be closely monitored.
Diuretics
In some patients, the administration of indomethacin can reduce the diuretic, natriuretic, and antihypertensive effects of loop, potassium-sparing, and thiazide diuretics. This response has been attributed to inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis.
Indomethacin reduces basal plasma renin activity (PRA), as well as those elevations of PRA induced by furosemide administration, or salt or volume depletion. These facts should be considered when evaluating plasma renin activity in hypertensive patients.
It has been reported that the addition of triamterene to a maintenance schedule of indomethacin resulted in reversible acute renal failure in two of four healthy volunteers. Indomethacin and triamterene should not be administered together.
Indomethacin and potassium-sparing diuretics each may be associated with increased serum potassium levels. The potential effects of indomethacin and potassium-sparing diuretics on potassium kinetics and renal function should be considered when these agents are administered concurrently. Most of the above effects concerning diuretics have been attributed, at least in part, to mechanisms involving inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis by indomethacin.
During concomitant therapy with NSAIDs, the patient should be observed closely for signs of renal failure (see WARNINGS: Renal Effects), as well as to assure diuretic efficacy.
Lithium
Indomethacin capsules 50 mg t.i.d. produced a clinically relevant elevation of plasma lithium and reduction in renal lithium clearance in psychiatric patients and normal subjects with steady-state plasma lithium concentrations. This effect has been attributed to inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis. As a consequence, when NSAIDs and lithium are given concomitantly, the patient should be carefully observed for signs of lithium toxicity. (Read circulars for lithium preparations before use of such concomitant therapy.) In addition, the frequency of monitoring serum lithium concentration should be increased at the outset of such combination drug treatment.
Methotrexate
NSAIDs have been reported to competitively inhibit methotrexate accumulation in rabbit kidney slices. This may indicate that they could enhance the toxicity of methotrexate. Caution should be used when NSAIDs are administered concomitantly with methotrexate.
NSAIDs
The concomitant use of indomethacin with other NSAIDs is not recommended due to the increased possibility of gastrointestinal toxicity, with little or no increase in efficacy.
Oral anticoagulants
Clinical studies have shown that indomethacin does not influence the hypoprothrombinemia produced by anticoagulants. However, when any additional drug, including indomethacin, is added to the treatment of patients on anticoagulant therapy, the patients should be observed for alterations of the prothrombin time. In post-marketing experience, bleeding has been reported in patients on concomitant treatment with anticoagulants and indomethacin. Caution should be exercised when indomethacin and anticoagulants are administered concomitantly. The effects of warfarin and NSAIDs on GI bleeding are synergistic, such that users of both drugs together have a risk of serious GI bleeding higher than users of either drug alone.
Probenecid
When indomethacin is given to patients receiving probenecid, the plasma levels of indomethacin are likely to be increased. Therefore, a lower total daily dosage of indomethacin may produce a satisfactory therapeutic effect. When increases in the dose of indomethacin are made, they should be made carefully and in small increments.Drug & OR Laboratory Test Interactions
False-negative results in the dexamethasone suppression test (DST) in patients being treated with indomethacin have been reported. Thus, results of the DST should be interpreted with caution in these patients.Carcinogenesis & Mutagenesis & Impairment Of Fertility
In an 81-week chronic oral toxicity study in the rat at doses up to 1 mg/kg/day, indomethacin had no tumorigenic effect.
Indomethacin produced no neoplastic or hyperplastic changes related to treatment in carcinogenic studies in the rat (dosing period 73 to 110 weeks) and the mouse (dosing period 62 to 88 weeks) at doses up to 1.5 mg/kg/day.
Indomethacin did not have any mutagenic effect in in vitro bacterial tests (Ames test and E. coli with or without metabolic activation) and a series of in vivo tests including the host-mediated assay, sex-linked recessive lethals in Drosophila, and the micronucleus test in mice.
Indomethacin at dosage levels up to 0.5 mg/kg/day had no effect on fertility in mice in a two generation reproduction study or a two litter reproduction study in rats.Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects. Pregnancy Category C
Teratogenic studies were conducted in mice and rats at dosages of 0.5, 1, 2, and 4 mg/kg/day. Except for retarded fetal ossification at 4 mg/kg/day considered secondary to the decreased average fetal weights, no increase in fetal malformations was observed as compared with control groups. Other studies in mice reported in the literature using higher doses (5 to 15 mg/kg/day) have described maternal toxicity and death, increased fetal resorptions, and fetal malformations. Comparable studies in rodents using high doses of aspirin have shown similar maternal and fetal effects. However, animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response. There are no adequate and well controlled studies in pregnant women.
Indomethacin should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Nonteratogenic Effects
Because of the known effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on the fetal cardiovascular system (closure of ductus arteriosus), use during pregnancy (particularly late pregnancy) should be avoided.
The known effects of indomethacin and other drugs of this class on the human fetus during the third trimester of pregnancy include: constriction of the ductus arteriosus prenatally, tricuspid incompetence, and pulmonary hypertension; nonclosure of the ductus arteriosus postnatally which may be resistant to medical management; myocardial degenerative changes, platelet dysfunction with resultant bleeding, intracranial bleeding, renal dysfunction or failure, renal injury/dysgenesis which may result in prolonged or permanent renal failure, oligohydramnios, gastrointestinal bleeding or perforation, and increased risk of necrotizing enterocolitis.
In rats and mice, 4 mg/kg/day given during the last 3 days of gestation caused a decrease in maternal weight gain and some maternal and fetal deaths. An increased incidence of neuronal necrosis in the diencephalon in the live born fetuses was observed. At 2 mg/kg/day, no increase in neuronal necrosis was observed as compared to the control groups. Administration of 0.5 or 4 mg/kg/day during the first 3 days of life did not cause an increase in neuronal necrosis at either dose level.Labor & Delivery
In rat studies with NSAIDs, as with other drugs known to inhibit prostaglandin synthesis, an increased incidence of dystocia, delayed parturition, and decreased pup survival occurred. The effects of indomethacin on labor and delivery in pregnant women are unknown.Nursing Mothers
Indomethacin is excreted in the milk of lactating mothers. Indomethacin is not recommended for use in nursing mothers.Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients 14 years of age and younger have not been established.
Indomethacin should not be prescribed for pediatric patients 14 years of age and younger unless toxicity or lack of efficacy associated with other drugs warrants the risk.
In experience with more than 900 pediatric patients reported in the literature or to the manufacturer who were treated with indomethacin capsules, side effects in pediatric patients were comparable to those reported in adults. Experience in pediatric patients has been confined to the use of indomethacin capsules.
If a decision is made to use indomethacin for pediatric patients 2 years of age or older, such patients should be monitored closely and periodic assessment of liver function is recommended. There have been cases of hepatotoxicity reported in pediatric patients with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, including fatalities. If indomethacin treatment is instituted, a suggested starting dose is 1 to 2 mg/kg/day given in divided doses. Maximum daily dosage should not exceed 3 mg/kg/day or 150 to 200 mg/day, whichever is less. Limited data are available to support the use of a maximum daily dosage of 4 mg/kg/day or 150 to 200 mg/day, whichever is less. As symptoms subside, the total daily dosage should be reduced to the lowest level required to control symptoms, or the drug should be discontinued.Geriatric Use
As with any NSAID, caution should be exercised in treating the elderly (65 years and older) since advancing age appears to increase the possibility of adverse reactions (see WARNINGS , Gastrointestinal Effects: Risk of Ulceration, Bleeding, and Perforationand DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION). Elderly patients seem to tolerate ulceration or bleeding less well than other individuals and many spontaneous reports of fatal GI events are in this population (see WARNINGS: Gastrointestinal Effects: Risk of Ulceration, Bleeding, and Perforation).
Indomethacin may cause confusion or, rarely, psychosis (see ADVERSE REACTIONS); physicians should remain alert to the possibility of such adverse effects in the elderly.
This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection and it may be useful to monitor renal function (see WARNINGS: Renal Effects). -
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The adverse reactions for indomethacin capsules listed in the following table have been arranged into two groups: (1) incidence greater than 1%; and (2) incidence less than 1%. The incidence for group (1) was obtained from 33 double-blind controlled clinical trials reported in the literature (1,092 patients). The incidence for group (2) was based on reports in clinical trials, in the literature, and on voluntary reports since marketing. The probability of a causal relationship exists between indomethacin and these adverse reactions, some of which have been reported only rarely.
Incidence greater than 1%
GASTROINTESTINAL
nausea1 with or without vomiting
dyspepsia1 (including indigestion, heartburn and epigastric pain)
diarrhea
abdominal distress or pain
constipation
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
headache (11.7%)
dizziness1
vertigo
somnolence
depression and fatigue (including malaise and listlessness)
SPECIAL SENSES
tinnitus
CARDIOVASCULAR
none
METABOLIC
none
INTEGUMENTARY
none
HEMATOLOGIC
none
HYPERSENSITIVITY
none
GENITOURINARY
none
MISCELLANEOUS
none
________________________________________
1 Reactions occurring in 3% to 9% of patients treated with indomethacin. (Those reactions occurring in less than 3% of the patients are unmarked.)
Incidence less than 1%
GASTROINTESTINAL
anorexia
bloating (includes distention)
flatulence
peptic ulcer
gastroenteritis
rectal bleeding
proctitis
single or multiple ulcerations, including perforation and hemorrhage of the esophagus, stomach, duodenum or small and large intestines
intestinal ulceration associated with stenosis and obstruction gastrointestinal bleeding without obvious ulcer formation and perforation of preexisting sigmoid lesions (diverticulum, carcinoma, etc.) development of ulcerative colitis and regional ileitis
ulcerative stomatitis
toxic hepatitis and jaundice (some fatal cases have been reported)
intestinal strictures (diaphragms)
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
anxiety (includes nervousness)
muscle weakness
involuntary muscle movements
insomnia
muzziness
psychic disturbances including psychotic episodes
mental confusion
drowsiness
light-headedness
syncope
paresthesia
aggravation of epilepsy and parkinsonism
depersonalization
coma
peripheral neuropathy
convulsions
dysarthria
SPECIAL SENSES
ocular-corneal deposits and retinal disturbances, including those of the macula, have been reported in some patients on prolonged therapy with indomethacin
blurred vision
diplopia
hearing disturbances, deafness
CARDIOVASCULAR
congestive heart failure
hypertension
hypotension
tachycardia
chest pain
arrhythmia; palpitations
METABOLIC
edema
weight gain
fluid retention
flushing or sweating
hyperglycemia
glycosuria
hyperkalemia
INTEGUMENTARY
pruritus
rash; urticaria
petechiae or ecchymosis
exfoliative dermatitis
erythema nodosum
loss of hair
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
erythema multiforme
toxic epidermal necrolysis
HEMATOLOGIC
leukopenia
bone marrow depression
anemia secondary to obvious or occult gastrointestinal bleeding
aplastic anemia
hemolytic anemia
agranulocytosis
thrombocytopenic purpura
disseminated intravascular coagulation
HYPERSENSITIVITY
acute anaphylaxis
acute respiratory distress
rapid fall in blood pressure resembling a shock-like state
angioedema
dyspnea
asthma
purpura
angiitis
pulmonary edema
fever
GENITOURINARY
hematuria
vaginal bleeding
proteinuria, nephrotic syndrome, interstitial nephritis
BUN elevation
renal insufficiency, including renal failure
MISCELLANEOUS
epistaxis
breast changes, including enlargement and tenderness, or gynecomastia
Causal Relationship Unknown
Other reactions have been reported but occurred under circumstances where a causal relationship could not be established. However, in these rarely reported events, the possibility cannot be excluded. Therefore, these observations are being listed to serve as alerting information to physicians:
Cardiovascular: thrombophlebitis
Hematologic: Although there have been several reports of leukemia, the supporting information is weak.
Genitourinary: urinary frequency
A rare occurrence of fulminant necrotizing fasciitis, particularly in association with Group A β-hemolytic streptococcus, has been described in persons treated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents, including indomethacin, sometimes with fatal outcome (see also PRECAUTIONS: General). -
OVERDOSAGE
The following symptoms may be observed following overdosage: nausea, vomiting, intense headache, dizziness, mental confusion, disorientation, or lethargy. There have been reports of paresthesias, numbness and convulsions.
Treatment is symptomatic and supportive. The stomach should be emptied as quickly as possible if the ingestion is recent. If vomiting has not occurred spontaneously, the patient should be induced to vomit with syrup of ipecac. If the patient is unable to vomit, gastric lavage should be performed. Once the stomach has been emptied, 25 g or 50 g of activated charcoal may be given. Depending on the condition of the patient, close medical observation and nursing care may be required. The patient should be followed for several days because gastrointestinal ulceration and hemorrhage have been reported as adverse reactions of indomethacin. Use of antacids may be helpful.
The oral LD50 of indomethacin in mice and rats (based on 14 day mortality response) was 50 and 12 mg/kg, respectively. -
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
Carefully consider the potential benefits and risks of indomethacin and other treatment options before deciding to use indomethacin. Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals (see WARNINGS).
After observing the response to initial therapy with indomethacin, the dose and frequency should be adjusted to suit an individual patient's needs.
Indomethacin is available as 25 mg and 50 mg capsules.
Adverse reactions appear to correlate with the size of the dose of indomethacin in most patients but not all. Therefore, every effort should be made to determine the smallest effective dosage for the individual patient.
Pediatric Use
Indomethacin ordinarily should not be prescribed for pediatric patients 14 years of age and under (see WARNINGS).
Adult Use
Dosage Recommendations for Active Stages of the Following:
1. Moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis including acute flares of chronic disease; moderate to severe ankylosing spondylitis; and moderate to severe osteoarthritis.
Suggested Dosage: Indomethacin capsules 25 mg b.i.d. or t.i.d. If this is well tolerated, increase the daily dosage by 25 mg or by 50 mg, if required by continuing symptoms, at weekly intervals until a satisfactory response is obtained or until a total daily dose of 150 mg to 200 mg is reached. DOSES ABOVE THIS AMOUNT GENERALLY DO NOT INCREASE THE EFFECTIVENESS OF THE DRUG.
In patients who have persistent night pain and/or morning stiffness, the giving of a large portion, up to a maximum of 100 mg, of the total daily dose at bedtime may be helpful in affording relief. The total daily dose should not exceed 200 mg. In acute flares of chronic rheumatoid arthritis, it may be necessary to increase the dosage by 25 mg or, if required, by 50 mg daily.
If minor adverse effects develop as the dosage is increased, reduce the dosage rapidly to a tolerated dose and OBSERVE THE PATIENT CLOSELY.
If severe adverse reactions occur, STOP THE DRUG. After the acute phase of the disease is under control, an attempt to reduce the daily dose should be made repeatedly until the patient is receiving the smallest effective dose or the drug is discontinued.
Careful instructions to, and observations of, the individual patient are essential to the prevention of serious, irreversible, including fatal, adverse reactions.
As advancing years appear to increase the possibility of adverse reactions, indomethacin should be used with greater care in the elderly (see PRECAUTIONS: Geriatric Use).
2. Acute painful shoulder (bursitis and/or tendinitis).
Initial Dose: 75 mg to 150 mg daily in 3 or 4 divided doses. The drug should be discontinued after the signs and symptoms of inflammation have been controlled for several days. The usual course of therapy is 7 to 14 days
3. Acute gouty arthritis.
Suggested Dosage: Indomethacin capsules 50 mg t.i.d. until pain is tolerable. The dose should then be rapidly reduced to complete cessation of the drug. Definite relief of pain has been reported within 2 to 4 hours. Tenderness and heat usually subside in 24 to 36 hours, and swelling gradually disappears in 3 to 5 days. -
HOW SUPPLIED
Indomethacin Capsules, USP are available containing either 25 mg or 50 mg of Indomethacin, USP.
The 25 mg capsules are size ‘3’ hard gelatin capsules, with opaque light green cap imprinted with ‘H’ and opaque light green body imprinted with ‘103’, containing white to off-white powder.
Bottles of 30 capsules NDC: 65977-5042-0
Bottles of 100 capsules NDC: 65977-5042-1
Bottles of 500 capsules NDC: 65977-5042-2
Bottles of 1000 capsules NDC: 65977-5042-3
The 50 mg capsules are size ‘1’ hard gelatin capsules, with opaque light green cap imprinted with ‘H’ and opaque light green body imprinted with ‘104’, containing white to off-white powder.
Bottles of 30 capsules NDC: 65977-5043-0
Bottles of 100 capsules NDC: 65977-5043-1
Bottles of 500 capsules NDC: 65977-5043-2
Bottles of 1000 capsules NDC: 65977-5043-3
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Protect from light.
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP using a child-resistant closure.
PHARMACIST: Dispense a Medication Guide with each prescription.

-
SPL MEDGUIDE
INDOMETHACIN CAPSULES USP
Medication Guide for Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
(See the end of this Medication Guide for a list of prescription NSAID medicines.)
What is the most important information I should know about medicines called Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)?
NSAID medicines may increase the chance of a heart attack or stroke that can lead to death. This chance increases:
with longer use of NSAID medicines
in people who have heart disease
NSAID medicines should never be used right before or after a heart surgery called a "coronary artery bypass graft (CABG)."
NSAID medicines can cause ulcers and bleeding in the stomach and intestines at any time during treatment. Ulcers and bleeding:
can happen without warning symptoms
may cause death
The chance of a person getting an ulcer or bleeding increases with:
taking medicines called "corticosteroids" and "anticoagulants"
longer use
smoking
drinking alcohol
older age
having poor health
NSAID medicines should only be used:
exactly as prescribed
at the lowest dose possible for your treatment
for the shortest time needed
What are Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)?
NSAID medicines are used to treat pain and redness, swelling, and heat (inflammation) from medical conditions such as:
different types of arthritis
menstrual cramps and other types of short-term pain
Who should not take a Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug (NSAID)?
Do not take an NSAID medicine:
if you had an asthma attack, hives, or other allergic reaction with aspirin or any other NSAID medicine
for pain right before or after heart bypass surgery
Tell your healthcare provider:
about all of your medical conditions.
about all of the medicines you take. NSAIDs and some other medicines can interact with each other and cause serious side effects. Keep a
list of your medicines to show to your healthcare provider and pharmacist.
if you are pregnant. NSAID medicines should not be used by pregnant women late in their pregnancy.
if you are breastfeeding. Talk to your doctor.
What are the possible side effects of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)?
serious side effects include: Other side effects include:
heart attack
stroke
high blood pressure
heart failure from body swelling (fluid Retension)
kidney problems including kidney failure
bleeding and ulcers in the stomach and intestine
low red blood cells (anemia)
life-threatening skin reactions
life-threatening allergic reactions
liver problems including liver failure
asthma attacks in people who have asthma
stomach pain
constipation
diarrhea
gas
heartburn
nausea
vomiting
dizziness
Get emergency help right away if you have any of the following symptoms:
shortness of breath or trouble breathing
chest pain
weakness in one part or side of your body
slurred speech
swelling of the face or throat
Stop your NSAID medicine and call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following symptoms:
nausea
more tired or weaker than usual
itching
your skin or eyes look yellow
stomach pain
flu-like symptoms
vomit blood
there is blood in your bowel movement or it is black and sticky like tar
unusual weight gain
skin rash or blisters with fever
swelling of the arms and legs, hands and feet
These are not all the side effects with NSAID medicines. Talk to your healthcare provider or pharmacist for more information about NSAID medicines. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
Other information about Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
Aspirin is an NSAID medicine but it does not increase the chance of a heart attack.
Aspirin can cause bleeding in the brain, stomach, and intestines. Aspirin can also
cause ulcers in the stomach and intestines.
Some of these NSAID medicines are sold in lower doses without a prescription (over-
the-counter). Talk to your healthcare provider before using over-the-counter NSAIDs
for more than 10 days.
NSAID medicines that need a prescription
Generic Name Trade name
Celecoxib
Diclofenac
Diflunisal
Etodolac
Fenoprofen
Flurbiprofen
Ibuprofen
Indomethacin
Ketoprofen
Ketorolac
MefenamicAcid
Meloxicam
Nabumetone
Naproxen
Oxaprozin
Piroxicam
Sulindac
Tolmetin
Celebrex
Cataflam, Voltaren, Arthrotec (combined with misoprostol)
Dolobid
Lodine, Lodine XL
Nalfon, Nalfon 200
Ansaid
Motrin, Tab-Profen, Vicoprofen*(combined with hydrocodone), Combunox (combined with oxycodone)
Indocin, Indocin SR, Indo-Lemmon, Indomethagan
Oruvail
Toradol
Ponstel
Mobic
Relafen
Naprosyn, Anaprox, Anaprox DS, EC-Naprosyn, Naprelan, Naprapac (copackaged with lansoprazole)
Daypro
Feldene
Clinoril
Tolectin, Tolectin DS, Tolectin 600
*Vicoprofen contains the same dose of ibuprofen as over-the-counter (OTC) NSAIDs, and is usually used for less than 10 days to treat pain. The OTC NSAIDS label warns that long term continuous use may increase the risk of heart attack or stroke.
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
INDOMETHACIN
indomethacin capsuleProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 65977-5042 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength INDOMETHACIN (UNII: XXE1CET956) (INDOMETHACIN - UNII:XXE1CET956) INDOMETHACIN 25 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) SODIUM LAURYL SULFATE (UNII: 368GB5141J) SODIUM STARCH GLYCOLATE TYPE A POTATO (UNII: 5856J3G2A2) COLLOIDAL SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) GELATIN (UNII: 2G86QN327L) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) FD&C BLUE NO. 1 (UNII: H3R47K3TBD) D&C YELLOW NO. 10 (UNII: 35SW5USQ3G) FERROSOFERRIC OXIDE (UNII: XM0M87F357) Product Characteristics Color GREEN Score no score Shape CAPSULE Size 16mm Flavor Imprint Code H;103 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 65977-5042-0 30 in 1 BOTTLE 2 NDC: 65977-5042-1 100 in 1 BOTTLE 3 NDC: 65977-5042-2 500 in 1 BOTTLE 4 NDC: 65977-5042-3 1000 in 1 BOTTLE Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA091240 04/12/2011 INDOMETHACIN
indomethacin capsuleProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 65977-5043 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength INDOMETHACIN (UNII: XXE1CET956) (INDOMETHACIN - UNII:XXE1CET956) INDOMETHACIN 50 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) SODIUM LAURYL SULFATE (UNII: 368GB5141J) SODIUM STARCH GLYCOLATE TYPE A POTATO (UNII: 5856J3G2A2) COLLOIDAL SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) GELATIN (UNII: 2G86QN327L) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) FD&C BLUE NO. 1 (UNII: H3R47K3TBD) D&C YELLOW NO. 10 (UNII: 35SW5USQ3G) FERROSOFERRIC OXIDE (UNII: XM0M87F357) Product Characteristics Color GREEN Score no score Shape CAPSULE Size 19mm Flavor Imprint Code H;104 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 65977-5043-0 30 in 1 BOTTLE 2 NDC: 65977-5043-1 100 in 1 BOTTLE 3 NDC: 65977-5043-2 500 in 1 BOTTLE 4 NDC: 65977-5043-3 1000 in 1 BOTTLE Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA091240 04/12/2011 Labeler - Hetero Drugs Ltd., (650229163) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Hetero Drugs Limited 676162024 ANALYSIS, MANUFACTURE
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.

