Glipizide by Legacy Pharmaceutical Packaging, LLC GLIPIZIDE tablet
Glipizide by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Glipizide by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Legacy Pharmaceutical Packaging, LLC. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
DESCRIPTION
Glipizide is an oral blood-glucose-lowering drug of the sulfonylurea class.
The Chemical Abstracts name of glipizide is 1-cyclohexyl-3-[[p-[2-(5-methylpyrazine-carboxamido)ethyl]phenyl]sulfonyl]urea. The molecular formula is C21H27N5O4S; the molecular weight is 445.55; the structural formula is shown below:
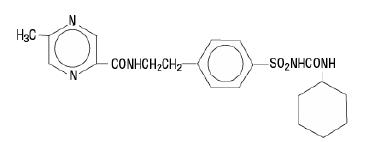
Glipizide is a whitish, odorless powder with a pKa of 5.9. It is insoluble in water and alcohols, but soluble in 0.1 N NaOH; it is freely soluble in dimethylformamide. Glipizide tablets, USP for oral use are available in 5 and 10 mg strengths.
Inert ingredients are: anhydrous lactose; colloidal silicon dioxide; magnesium stearate; sodium starch glycolate.
Meets USP Dissolution Test 2.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
The primary mode of action of glipizide in experimental animals appears to be the stimulation of insulin secretion from the beta cells of pancreatic islet tissue and is thus dependent on functioning beta cells in the pancreatic islets. In humans, glipizide appears to lower the blood glucose acutely by stimulating the release of insulin from the pancreas, an effect dependent upon functioning beta cells in the pancreatic islets. The mechanism by which glipizide lowers blood glucose during long-term administration has not been clearly established. In man, stimulation of insulin secretion by glipizide in response to a meal is undoubtedly of major importance. Fasting insulin levels are not elevated even on long-term glipizide administration, but the postprandial insulin response continues to be enhanced after at least 6 months of treatment. The insulinotropic response to a meal occurs within 30 minutes after an oral dose of glipizide in diabetic patients, but elevated insulin levels do not persist beyond the time of the meal challenge. Extrapancreatic effects may play a part in the mechanism of action of oral sulfonylurea hypoglycemic drugs.
Blood sugar control persists in some patients for up to 24 hours after a single dose of glipizide, even though plasma levels have declined to a small fraction of peak levels by that time (see Pharmacokinetics below).
Some patients fail to respond initially, or gradually lose their responsiveness to sulfonylurea drugs, including glipizide. Alternatively, glipizide may be effective in some patients who have not responded or have ceased to respond to other sulfonylureas.
Other Effects
It has been shown that glipizide therapy was effective in controlling blood sugar without deleterious changes in the plasma lipoprotein profiles of patients treated for NIDDM.
In a placebo-controlled, crossover study in normal volunteers, glipizide had no antidiuretic activity and, in fact, led to a slight increase in free water clearance.
Pharmacokinetics
Gastrointestinal absorption of glipizide in man is uniform, rapid, and essentially complete. Peak plasma concentrations occur 1 to 3 hours after a single oral dose. The half-life of elimination ranges from 2 to 4 hours in normal subjects, whether given intravenously or orally. The metabolic and excretory patterns are similar with the two routes of administration, indicating that first-pass metabolism is not significant. Glipizide does not accumulate in plasma on repeated oral administration. Total absorption and disposition of an oral dose was unaffected by food in normal volunteers, but absorption was delayed by about 40 minutes. Thus, glipizide was more effective when administered about 30 minutes before, rather than with, a test meal in diabetic patients. Protein binding was studied in serum from volunteers who received either oral or intravenous glipizide and found to be 98 to 99% one hour after either route of administration. The apparent volume of distribution of glipizide after intravenous administration was 11 liters, indicative of localization within the extracellular fluid compartment. In mice, no glipizide or metabolites were detectable autoradiographically in the brain or spinal cord of males or females, nor in the fetuses of pregnant females. In another study, however, very small amounts of radioactivity were detected in the fetuses of rats given labeled drug.
The metabolism of glipizide is extensive and occurs mainly in the liver. The primary metabolites are inactive hydroxylation products and polar conjugates and are excreted mainly in the urine. Less than 10% unchanged glipizide is found in the urine.
- INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
WARNINGS
SPECIAL WARNING ON INCREASED RISK OF CARDIOVASCULAR MORTALITY
The administration of oral hypoglycemic drugs has been reported to be associated with increased cardiovascular mortality as compared to treatment with diet alone or diet plus insulin. This warning is based on the study conducted by the University Group Diabetes Program (UGDP), a long-term prospective clinical trial designed to evaluate the effectiveness of glucose-lowering drugs in preventing or delaying vascular complications in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes. The study involved 823 patients who were randomly assigned to one of four treatment groups (Diabetes, 19, supp. 2: 747-830, 1970). UGDP reported that patients treated for 5 to 8 years with diet plus a fixed dose of tolbutamide (1.5 grams per day) had a rate of cardiovascular mortality approximately 21/2 times that of patients treated with diet alone. A significant increase in total mortality was not observed, but the use of tolbutamide was discontinued based on the increase in cardiovascular mortality, thus limiting the opportunity for the study to show an increase in overall mortality. Despite controversy regarding the interpretation of these results, the findings of the UGDP study provide an adequate basis for this warning. The patient should be informed of the potential risks and advantages of glipizide and of alternative modes of therapy.
Although only one drug in the sulfonylurea class (tolbutamide) was included in this study, it is prudent from a safety standpoint to consider that this warning may also apply to other oral hypoglycemic drugs in this class, in view of their close similarities in mode of action and chemical structure.
-
PRECAUTIONS
General
Macrovascular Outcomes
There have been no clinical studies establishing conclusive evidence of macrovascular risk reduction with glipizide or any other anti-diabetic drug.
Renal and Hepatic Disease
The metabolism and excretion of glipizide may be slowed in patients with impaired renal and/or hepatic function. If hypoglycemia should occur in such patients, it may be prolonged and appropriate management should be instituted.
Hypoglycemia
All sulfonylurea drugs are capable of producing severe hypoglycemia. Proper patient selection, dosage, and instructions are important to avoid hypoglycemic episodes. Renal or hepatic insufficiency may cause elevated blood levels of glipizide and the latter may also diminish gluconeogenic capacity, both of which increase the risk of serious hypoglycemic reactions. Elderly, debilitated or malnourished patients, and those with adrenal or pituitary insufficiency, are particularly susceptible to the hypoglycemic action of glucose-lowering drugs. Hypoglycemia may be difficult to recognize in the elderly, and in people who are taking beta-adrenergic blocking drugs. Hypoglycemia is more likely to occur when caloric intake is deficient, after severe or prolonged exercise, when alcohol is ingested, or when more than one glucose-lowering drug is used.
Loss of Control of Blood Glucose
When a patient stabilized on any diabetic regimen is exposed to stress such as fever, trauma, infection, or surgery, a loss of control may occur. At such times, it may be necessary to discontinue glipizide and administer insulin.
The effectiveness of any oral hypoglycemic drug, including glipizide, in lowering blood glucose to a desired level decreases in many patients over a period of time, which may be due to progression of the severity of the diabetes or to diminished responsiveness to the drug. This phenomenon is known as secondary failure, to distinguish it from primary failure in which the drug is ineffective in an individual patient when first given.
Hemolytic Anemia
Treatment of patients with glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency with sulfonylurea agents can lead to hemolytic anemia. Because glipizide belongs to the class of sulfonylurea agents, caution should be used in patients with G6PD deficiency and a non-sulfonylurea alternative should be considered. In post-marketing reports, hemolytic anemia has also been reported in patients who did not have known G6PD deficiency.
Laboratory Tests
Blood and urine glucose should be monitored periodically. Measurement of glycosylated hemoglobin may be useful.
Information for Patients
Patients should be informed of the potential risks and advantages of glipizide and of alternative modes of therapy. They should also be informed about the importance of adhering to dietary instructions, of a regular exercise program, and of regular testing of urine and/or blood glucose.
The risks of hypoglycemia, its symptoms and treatment, and conditions that predispose to its development should be explained to patients and responsible family members. Primary and secondary failure should also be explained.
Physician Counseling Information for Patients
In initiating treatment for type 2 diabetes, diet should be emphasized as the primary form of treatment. Caloric restriction and weight loss are essential in the obese diabetic patient. Proper dietary management alone may be effective in controlling the blood glucose and symptoms of hyperglycemia. The importance of regular physical activity should also be stressed, and cardiovascular risk factors should be identified and corrective measures taken where possible. Use of glipizide or other antidiabetic medications must be viewed by both the physician and patient as a treatment in addition to diet and not as a substitution or as a convenient mechanism for avoiding dietary restraint. Furthermore, loss of blood glucose control on diet alone may be transient, thus requiring only short-term administration of glipizide or other antidiabetic medications. Maintenance or discontinuation of glipizide or other antidiabetic medications should be based on clinical judgment using regular clinical and laboratory evaluations.
Drug Interactions
The hypoglycemic action of sulfonylureas may be potentiated by certain drugs including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents, some azoles, and other drugs that are highly protein bound, salicylates, sulfonamides, chloramphenicol, probenecid, coumarins, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, quinolones and beta adrenergic blocking agents. When such drugs are administered to a patient receiving glipizide, the patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia. When such drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving glipizide, the patient should be observed closely for loss of control. In vitro binding studies with human serum proteins indicate that glipizide binds differently than tolbutamide and does not interact with salicylate or dicumarol. However, caution must be exercised in extrapolating these findings to the clinical situation and in the use of glipizide with these drugs.
Certain drugs tend to produce hyperglycemia and may lead to loss of control. These drugs include the thiazides and other diuretics, corticosteroids, phenothiazines, thyroid products, estrogens, oral contraceptives, phenytoin, nicotinic acid, sympathomimetics, calcium channel blocking drugs, and isoniazid. When such drugs are administered to a patient receiving glipizide, the patient should be closely observed for loss of control. When such drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving glipizide, the patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia.
A potential interaction between oral miconazole and oral hypoglycemic agents leading to severe hypoglycemia has been reported. Whether this interaction also occurs with the intravenous, topical, or vaginal preparations of miconazole is not known. The effect of concomitant administration of fluconazole and glipizide has been demonstrated in a placebo-controlled crossover study in normal volunteers. All subjects received glipizide alone and following treatment with 100 mg of fluconazole as a single daily oral dose for 7 days. The mean percentage increase in the glipizide AUC after fluconazole administration was 56.9% (range: 35 to 81).
In studies assessing the effect of colesevelam on the pharmacokinetics of glipizide ER in healthy volunteers, reductions in glipizide AUC0-∞ and Cmax of 12% and 13%, respectively were observed when colesevelam was coadministered with glipizide ER. When glipizide ER was administered 4 hours prior to colesevelam, there was no significant change in glipizide AUC0-∞ or Cmax, -4% and 0%, respectively. Therefore, glipizide should be administered at least 4 hours prior to colesevelam to ensure that colesevelam does not reduce the absorption of glipizide.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
A twenty month study in rats and an eighteen month study in mice at doses up to 75 times the maximum human dose revealed no evidence of drug-related carcinogenicity. Bacterial and in vivo mutagenicity tests were uniformly negative. Studies in rats of both sexes at doses up to 75 times the human dose showed no effects on fertility.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C
Glipizide was found to be mildly fetotoxic in rat reproductive studies at all dose levels (5 to 50 mg/kg). This fetotoxicity has been similarly noted with other sulfonylureas, such as tolbutamide and tolazamide. The effect is perinatal and believed to be directly related to the pharmacologic (hypoglycemic) action of glipizide. In studies in rats and rabbits, no teratogenic effects were found. There are no adequate and well controlled studies in pregnant women. Glipizide should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Because recent information suggests that abnormal blood glucose levels during pregnancy are associated with a higher incidence of congenital abnormalities, many experts recommend that insulin be used during pregnancy to maintain blood glucose levels as close to normal as possible.
Nonteratogenic Effects
Prolonged severe hypoglycemia (4 to 10 days) has been reported in neonates born to mothers who were receiving a sulfonylurea drug at the time of delivery. This has been reported more frequently with the use of agents with prolonged half-lives. If glipizide is used during pregnancy, it should be discontinued at least one month before the expected delivery date.
Nursing Mothers
Although it is not known whether glipizide is excreted in human milk, some sulfonylurea drugs are known to be excreted in human milk. Because the potential for hypoglycemia in nursing infants may exist, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother. If the drug is discontinued and if diet alone is inadequate for controlling blood glucose, insulin therapy should be considered.
Geriatric Use
A determination has not been made whether controlled clinical studies of glipizide included sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to define a difference in response from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
In U.S. and foreign controlled studies, the frequency of serious adverse reactions reported was very low. Of 702 patients, 11.8% reported adverse reactions and in only 1.5% was glipizide discontinued.
Gastrointestinal
Gastrointestinal disturbances are the most common reactions. Gastrointestinal complaints were reported with the following approximate incidence: nausea and diarrhea, one in seventy; constipation and gastralgia, one in one hundred. They appear to be dose-related and may disappear on division or reduction of dosage. Cholestatic jaundice may occur rarely with sulfonylureas: glipizide should be discontinued if this occurs.
Dermatologic
Allergic skin reactions including erythema, morbilliform or maculopapular eruptions, urticaria, pruritus, and eczema have been reported in about one in seventy patients. These may be transient and may disappear despite continued use of glipizide; if skin reactions persist, the drug should be discontinued. Porphyria cutanea tarda and photosensitivity reactions have been reported with sulfonylureas.
Hematologic
Leukopenia, agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia, hemolytic anemia (see PRECAUTIONS), aplastic anemia, and pancytopenia have been reported with sulfonylureas.
Metabolic
Hepatic porphyria and disulfiram-like reactions have been reported with sulfonylureas. In the mouse, glipizide pretreatment did not cause an accumulation of acetaldehyde after ethanol administration. Clinical experience to date has shown that glipizide has an extremely low incidence of disulfiram-like alcohol reactions.
Endocrine Reactions
Cases of hyponatremia and the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH) secretion have been reported with this and other sulfonylureas.
Miscellaneous
Dizziness, drowsiness, and headache have each been reported in about one in fifty patients treated with glipizide. They are usually transient and seldom require discontinuance of therapy.
Laboratory Tests
The pattern of laboratory test abnormalities observed with glipizide was similar to that for other sulfonylureas. Occasional mild to moderate elevations of SGOT, LDH, alkaline phosphatase, BUN, and creatinine were noted. One case of jaundice was reported. The relationship of these abnormalities to glipizide is uncertain, and they have rarely been associated with clinical symptoms.
-
OVERDOSAGE
There is no well documented experience with glipizide overdosage. The acute oral toxicity was extremely low in all species tested (LD50 greater than 4 g/kg).
Overdosage of sulfonylureas, including glipizide, can produce hypoglycemia. Mild hypoglycemic symptoms without loss of consciousness or neurologic findings should be treated aggressively with oral glucose and adjustments in drug dosage and/or meal patterns. Close monitoring should continue until the physician is assured that the patient is out of danger. Severe hypoglycemic reactions with coma, seizure, or other neurological impairment occur infrequently, but constitute medical emergencies requiring immediate hospitalization. If hypoglycemic coma is diagnosed or suspected, the patient should be given a rapid intravenous injection of concentrated (50%) glucose solution. This should be followed by a continuous infusion of a more dilute (10%) glucose solution at a rate that will maintain the blood glucose at a level above 100 mg/dL. Patients should be closely monitored for a minimum of 24 to 48 hours since hypoglycemia may recur after apparent clinical recovery. Clearance of glipizide from plasma would be prolonged in persons with liver disease. Because of the extensive protein binding of glipizide, dialysis is unlikely to be of benefit.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
There is no fixed dosage regimen for the management of diabetes mellitus with glipizide or any other hypoglycemic agent. In addition to the usual monitoring of urinary glucose, the patient's blood glucose must also be monitored periodically to determine the minimum effective dose for the patient; to detect primary failure, i.e., inadequate lowering of blood glucose at the maximum recommended dose of medication; and to detect secondary failure, i.e., loss of an adequate blood-glucose-lowering response after an initial period of effectiveness. Glycosylated hemoglobin levels may also be of value in monitoring the patient's response to therapy.
Short-term administration of glipizide may be sufficient during periods of transient loss of control in patients usually controlled well on diet.
In general, glipizide tablets should be given approximately 30 minutes before a meal to achieve the greatest reduction in postprandial hyperglycemia.
Initial Dose
The recommended starting dose is 5 mg, given before breakfast. Geriatric patients or those with liver disease may be started on 2.5 mg.
Titration
Dosage adjustments should ordinarily be in increments of 2.5 to 5 mg, as determined by blood glucose response. At least several days should elapse between titration steps. If response to a single dose is not satisfactory, dividing that dose may prove effective. The maximum recommended once daily dose is 15 mg. Doses above 15 mg should ordinarily be divided and given before meals of adequate caloric content. The maximum recommended total daily dose is 40 mg.
Maintenance
Some patients may be effectively controlled on a once-a-day regimen, while others show better response with divided dosing. Total daily doses above 15 mg should ordinarily be divided. Total daily doses above 30 mg have been safely given on a b.i.d. basis to long-term patients.
In elderly patients, debilitated or malnourished patients, and patients with impaired renal or hepatic function, the initial and maintenance dosing should be conservative to avoid hypoglycemic reactions (see PRECAUTIONS section).
Patients Receiving Insulin
As with other sulfonylurea-class hypoglycemics, many stable non-insulin-dependent diabetic patients receiving insulin may be safely placed on glipizide. When transferring patients from insulin to glipizide, the following general guidelines should be considered:
For patients whose daily insulin requirement is 20 units or less, insulin may be discontinued and glipizide therapy may begin at usual dosages. Several days should elapse between glipizide titration steps.
For patients whose daily insulin requirement is greater than 20 units, the insulin dose should be reduced by 50% and glipizide therapy may begin at usual dosages. Subsequent reductions in insulin dosage should depend on individual patient response. Several days should elapse between glipizide titration steps.
During the insulin withdrawal period, the patient should test urine samples for sugar and ketone bodies at least three times daily. Patients should be instructed to contact the prescriber immediately if these tests are abnormal. In some cases, especially when patient has been receiving greater than 40 units of insulin daily, it may be advisable to consider hospitalization during the transition period.
Patients Receiving Other Oral Hypoglycemic Agents
As with other sulfonylurea-class hypoglycemics, no transition period is necessary when transferring patients to glipizide. Patients should be observed carefully (1 to 2 weeks) for hypoglycemia when being transferred from longer half-life sulfonylureas (e.g., chlorpropamide) to glipizide due to potential overlapping of drug effect.
When colesevelam is coadministered with glipizide ER, maximum plasma concentration and total exposure to glipizide is reduced. Therefore, glipizide should be administered at least 4 hours prior to colesevelam.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Glipizide Tablets, USP are supplied as white to off-white, round, scored tablets, imprinted as follows: 5 mg- “APO” on the side and “GLP” over bisect “5” on the other side; 10 mg- “APO” on one side and “GLP” over bisect “10” on the other side.
Unit of use bottles of 30: 5 mg (NDC: 68645-574-54)
Unit of use bottles of 60: 10 mg (NDC: 68645-575-59)
-
RECOMMENDED STORAGE
Store at 20˚C to 25˚C (68˚F to 77˚F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container [see USP].
APOTEX INC.
GLIPIZIDE TABLETS, USP
5 mg and 10 mgManufactured by Manufactured for
Apotex Inc. Apotex Corp.
Toronto, Ontario Weston, Florida
Canada M9L 1T9 USA 33326Revised: May 2017
Rev. 8
-
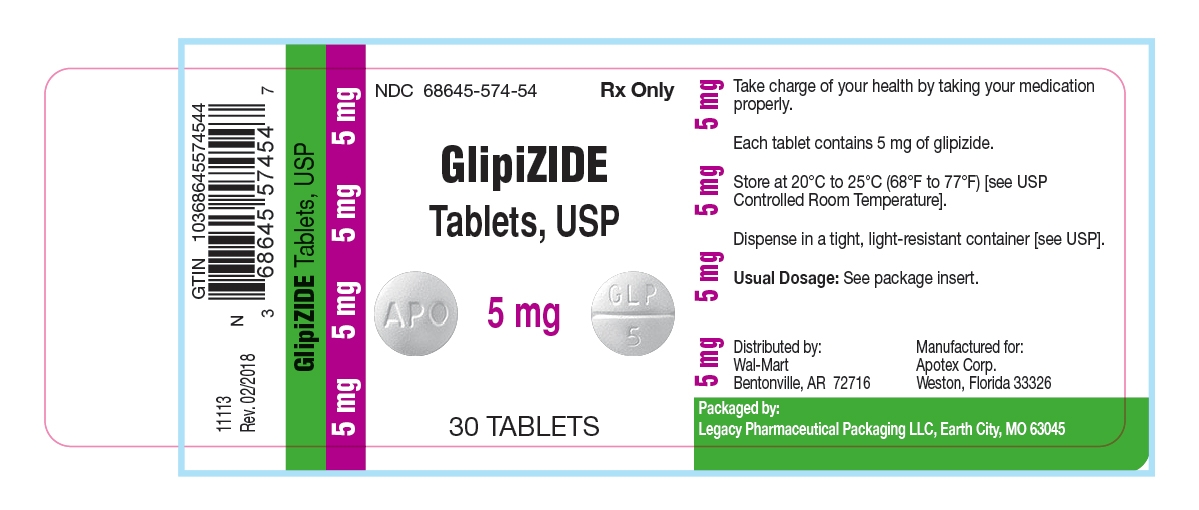
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL-5 mg
Representative sample of labeling (see HOW SUPPLIEDsection for complete listing)
NDC 68645-574-54
Glipizide Tablets, USP
5 mg
Rx
30 bottle count
-
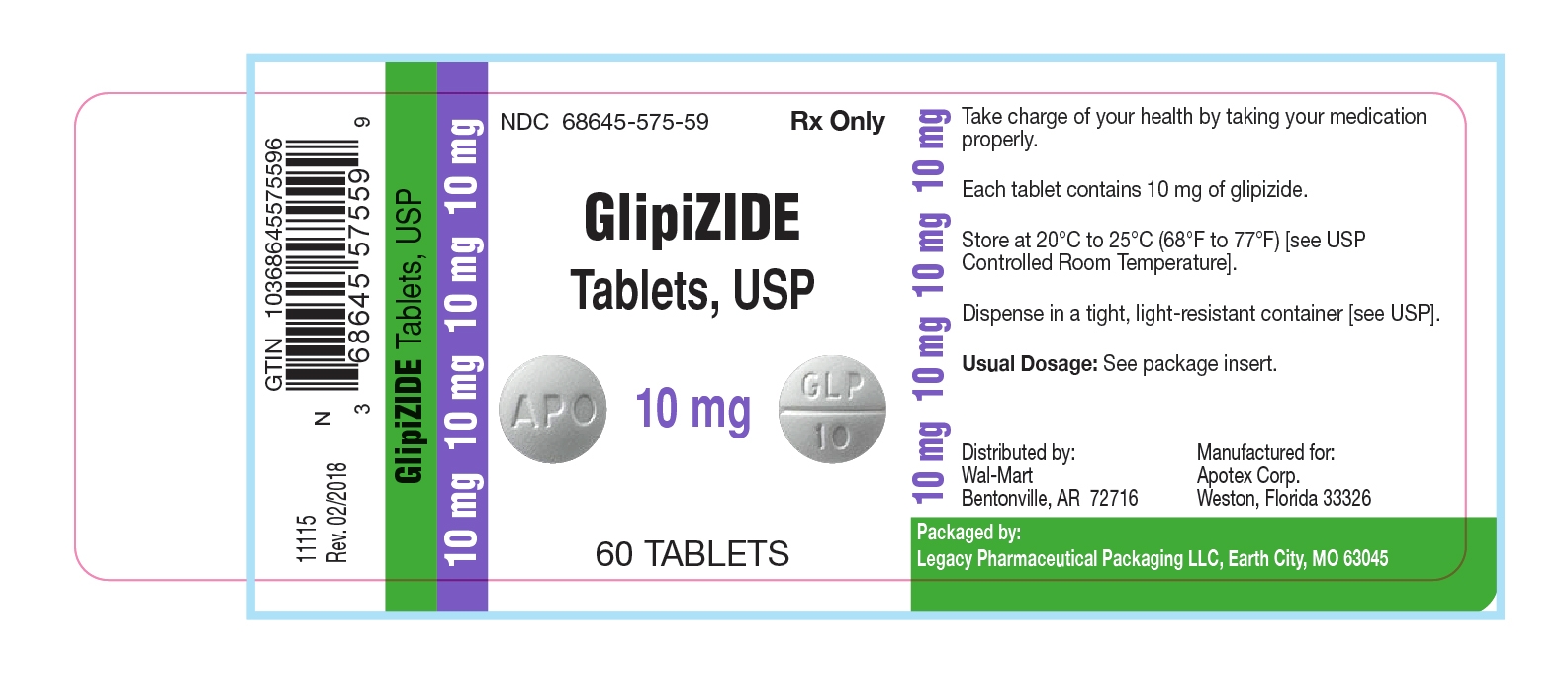
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL-10 mg
Representative sample of labeling (see HOW SUPPLIEDsection for complete listing)
NDC 68645-575-59
Glipizide Tablets, USP
10 mg
Rx
60 bottle count
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
GLIPIZIDE
glipizide tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 68645-574(NDC:60505-0141) Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength GLIPIZIDE (UNII: X7WDT95N5C) (GLIPIZIDE - UNII:X7WDT95N5C) GLIPIZIDE 5 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength ANHYDROUS LACTOSE (UNII: 3SY5LH9PMK) SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) SODIUM STARCH GLYCOLATE TYPE A POTATO (UNII: 5856J3G2A2) Product Characteristics Color WHITE Score 2 pieces Shape ROUND Size 6mm Flavor Imprint Code APO;GLP;5 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 68645-574-54 30 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 09/25/2002 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA075795 09/25/2002 GLIPIZIDE
glipizide tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 68645-575(NDC:60505-0142) Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength GLIPIZIDE (UNII: X7WDT95N5C) (GLIPIZIDE - UNII:X7WDT95N5C) GLIPIZIDE 10 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength ANHYDROUS LACTOSE (UNII: 3SY5LH9PMK) SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) SODIUM STARCH GLYCOLATE TYPE A POTATO (UNII: 5856J3G2A2) Product Characteristics Color WHITE Score 2 pieces Shape ROUND Size 8mm Flavor Imprint Code APO;GLP;10 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 68645-575-59 60 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 09/25/2002 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA075795 09/25/2002 Labeler - Legacy Pharmaceutical Packaging, LLC (143213275)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.