AMLODIPINE BESYLATE AND ATORVASTATIN CALCIUM tablet, film coated
amlodipine besylate and atorvastatin calcium by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
amlodipine besylate and atorvastatin calcium by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Physicians Total Care, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
DESCRIPTION
Amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets combine the calcium channel blocker amlodipine besylate with the lipid-lowering agent atorvastatin calcium.
The amlodipine besylate component of amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets is chemically described as 3-ethyl-5-methyl (±)-2-[(2-aminoethoxy)methyl]-4-(o-chlorophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-6-methyl-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate, monobenzenesulphonate. Its empirical formula is C20H25ClN2O5C6H6O3S.
The atorvastatin calcium component of amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets is chemically described as [R-(R*, R*)]-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-ß, δ-dihydroxy-5-(1-methylethyl)-3-phenyl-4-[(phenylamino)carbonyl]-1H-pyrrole-1-heptanoic acid, calcium salt (2:1) trihydrate. Its empirical formula is (C33H34 FN2O5)2Ca3H2O.
The structural formulae for amlodipine besylate and atorvastatin calcium are shown below.
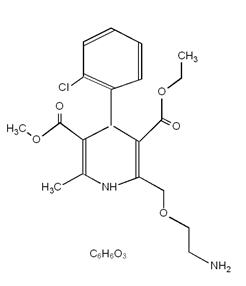
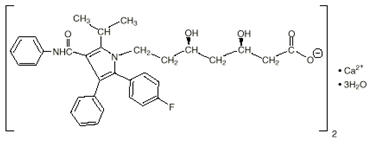
Amlodipine besylate Atorvastatin calcium Amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets contain amlodipine besylate, a white to off-white crystalline powder, and atorvastatin calcium, also a white to off-white crystalline powder. Amlodipine besylate has a molecular weight of 567.1 and atorvastatin calcium has a molecular weight of 1209.42. Amlodipine besylate is slightly soluble in water and sparingly soluble in ethanol. Atorvastatin calcium is insoluble in aqueous solutions of pH 4 and below. Atorvastatin calcium is very slightly soluble in distilled water, pH 7.4 phosphate buffer, and acetonitrile; slightly soluble in ethanol, and freely soluble in methanol.
Amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets are formulated for oral administration in the following strength combinations:
Table 1. Amlodipine Besylate/Atorvastatin Calcium Tablet Strengths 2.5 mg/ 10mg 2.5 mg/ 20mg 2.5 mg/ 40mg 5 mg/10 mg 5 mg/20 mg 5 mg/40 mg 5 mg/80 mg 10 mg/ 10 mg 10 mg/
20 mg10 mg/
40 mg10 mg/
80 mgamlodipine equivalent (mg) 2.5 2.5 2.5 5 5 5 5 10 10 10 10 atorvastatin equivalent (mg) 10 20 40 10 20 40 80 10 20 40 80 Each tablet also contains calcium carbonate, croscarmellose sodium, microcrystalline cellulose, pregelatinized starch, polysorbate 80, hydroxypropyl cellulose, purified water, colloidal silicon dioxide (anhydrous), magnesium stearate, Opadry® II White 85F28751 (polyvinyl alcohol, titanium dioxide, PEG 3000 and talc) or Opadry® II Blue 85F10919 (polyvinyl alcohol, titanium dioxide, PEG 3000, talc and FD&C blue #2). Combinations of atorvastatin with 2.5 mg and 5 mg amlodipine are film coated white, and combinations of atorvastatin with 10 mg amlodipine are film coated blue.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Amlodipine Besylate/Atorvastatin Calcium Tablets
Amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets are a combination of two drugs, a dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker amlodipine and an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor atorvastatin. The amlodipine component of amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets inhibits the transmembrane influx of calcium ions into vascular smooth muscle and cardiac muscle. The atorvastatin component of amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets is a selective, competitive inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase (statin), the rate-limiting enzyme that converts 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A to mevalonate, a precursor of sterols, including cholesterol.
Amlodipine
Experimental data suggest that amlodipine binds to both dihydropyridine and nondihydropyridine binding sites. The contractile processes of cardiac muscle and vascular smooth muscle are dependent upon the movement of extracellular calcium ions into these cells through specific ion channels. Amlodipine inhibits calcium ion influx across cell membranes selectively, with a greater effect on vascular smooth muscle cells than on cardiac muscle cells. Negative inotropic effects can be detected in vitro but such effects have not been seen in intact animals at therapeutic doses. Serum calcium concentration is not affected by amlodipine.
Amlodipine is a peripheral arterial vasodilator that acts directly on vascular smooth muscle to cause a reduction in peripheral vascular resistance and reduction in blood pressure.
The precise mechanisms by which amlodipine relieves angina have not been fully delineated, but are thought to include the following:
Exertional Angina: In patients with exertional angina, amlodipine reduces the total peripheral resistance (afterload) against which the heart works and reduces the rate pressure product, and thus myocardial oxygen demand, at any given level of exercise.
Vasospastic Angina: Amlodipine has been demonstrated to block constriction and restore blood flow in coronary arteries and arterioles in response to calcium, potassium epinephrine, serotonin, and thromboxane A2 analog in experimental animal models and in human coronary vessels in vitro. This inhibition of coronary spasm is responsible for the effectiveness of amlodipine in vasospastic (Prinzmetal's or variant) angina.
Atorvastatin
Cholesterol and triglycerides circulate in the bloodstream as part of lipoprotein complexes. With ultracentrifugation, these complexes separate into HDL (high-density lipoprotein), IDL (intermediate-density lipoprotein), LDL (low-density lipoprotein), and VLDL (very-low-density lipoprotein) fractions. Triglycerides (TG) and cholesterol in the liver are incorporated into VLDL and released into the plasma for delivery to peripheral tissues. LDL is formed from VLDL and is catabolized primarily through the high-affinity LDL receptor.
Clinical and pathologic studies show that elevated plasma levels of total cholesterol (total-C), LDL-cholesterol (LDL-C), and apolipoprotein B (apo B) promote human atherosclerosis and are risk factors for developing cardiovascular disease, while increased levels of HDL-C are associated with a decreased cardiovascular risk.
Epidemiologic investigations have established that cardiovascular morbidity and mortality vary directly with the level of total-C and LDL-C, and inversely with the level of HDL-C.
In animal models, atorvastatin lowers plasma cholesterol and lipoprotein levels by inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase and cholesterol synthesis in the liver and by increasing the number of hepatic LDL receptors on the cell-surface to enhance uptake and catabolism of LDL; atorvastatin also reduces LDL production and the number of LDL particles.
Atorvastatin reduces total-C, LDL-C, and apo B in patients with homozygous and heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (FH), nonfamilial forms of hypercholesterolemia, and mixed dyslipidemia. Atorvastatin also reduces VLDL-C and TG and produces variable increases in HDL-C and apolipoprotein A-1. Atorvastatin reduces total-C, LDL-C, VLDL-C, apo B, TG, and non-HDL-C, and increases HDL-C in patients with isolated hypertriglyceridemia. Atorvastatin reduces intermediate density lipoprotein cholesterol (IDL-C) in patients with dysbetalipoproteinemia.
Like LDL, cholesterol-enriched triglyceride-rich lipoproteins, including VLDL, intermediate density lipoprotein (IDL), and remnants, can also promote atherosclerosis. Elevated plasma triglycerides are frequently found in a triad with low HDL-C levels and small LDL particles, as well as in association with non-lipid metabolic risk factors for coronary heart disease. As such, total plasma TG has not consistently been shown to be an independent risk factor for CHD. Furthermore, the independent effect of raising HDL or lowering TG on the risk of coronary and cardiovascular morbidity and mortality has not been determined.
Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism
Absorption
Studies with amlodipine
After oral administration of therapeutic doses of amlodipine alone, absorption produces peak plasma concentrations between 6 and 12 hours. Absolute bioavailability has been estimated to be between 64% and 90%.
Studies with atorvastatin
After oral administration alone, atorvastatin is rapidly absorbed; maximum plasma concentrations occur within 1 to 2 hours. Extent of absorption increases in proportion to atorvastatin dose. The absolute bioavailability of atorvastatin (parent drug) is approximately 14% and the systemic availability of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitory activity is approximately 30%. The low systemic availability is attributed to presystemic clearance in gastrointestinal mucosa and/or hepatic first-pass metabolism. Plasma atorvastatin concentrations are lower (approximately 30% for Cmax and AUC) following evening drug administration compared with morning. However, LDL-C reduction is the same regardless of the time of day of drug administration (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Studies with amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets
Following oral administration of amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets, peak plasma concentrations of amlodipine and atorvastatin are seen at 6 to 12 hours and 1 to 2 hours post dosing, respectively. The rate and extent of absorption (bioavailability) of amlodipine and atorvastatin from amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets are not significantly different from the bioavailability of amlodipine and atorvastatin administered separately (see above).
The bioavailability of amlodipine from amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets was not affected by food. Food decreases the rate and extent of absorption of atorvastatin from amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets by approximately 32% and 11%, respectively, as it does with atorvastatin when given alone. LDL-C reduction is similar whether atorvastatin is given with or without food.
Distribution
Studies with amlodipine
Ex vivo studies have shown that approximately 93% of the circulating amlodipine drug is bound to plasma proteins in hypertensive patients. Steady-state plasma levels of amlodipine are reached after 7 to 8 days of consecutive daily dosing.
Studies with atorvastatin
Mean volume of distribution of atorvastatin is approximately 381 liters. Atorvastatin is ≥98% bound to plasma proteins. A blood/plasma ratio of approximately 0.25 indicates poor drug penetration into red blood cells. Based on observations in rats, atorvastatin calcium is likely to be secreted in human milk (see CONTRAINDICATIONS, Pregnancy and Lactation, and PRECAUTIONS, Nursing Mothers).
Metabolism
Studies with amlodipine
Amlodipine is extensively (about 90%) converted to inactive metabolites via hepatic metabolism.
Studies with atorvastatin
Atorvastatin is extensively metabolized to ortho- and parahydroxylated derivatives and various beta-oxidation products. In vitro inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase by ortho- and parahydroxylated metabolites is equivalent to that of atorvastatin. Approximately 70% of circulating inhibitory activity for HMG-CoA reductase is attributed to active metabolites. In vitro studies suggest the importance of atorvastatin metabolism by cytochrome P450 3A4, consistent with increased plasma concentrations of atorvastatin in humans following co-administration with erythromycin, a known inhibitor of this isozyme (see PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions). In animals, the ortho-hydroxy metabolite undergoes further glucuronidation.
Excretion
Studies with amlodipine
Elimination from the plasma is biphasic with a terminal elimination half-life of about 30–50 hours. Ten percent of the parent amlodipine compound and 60% of the metabolites of amlodipine are excreted in the urine.
Studies with atorvastatin
Atorvastatin and its metabolites are eliminated primarily in bile following hepatic and/or extra-hepatic metabolism; however, the drug does not appear to undergo enterohepatic recirculation. Mean plasma elimination half-life of atorvastatin in humans is approximately 14 hours, but the half-life of inhibitory activity for HMG-CoA reductase is 20 to 30 hours due to the contribution of active metabolites. Less than 2% of a dose of atorvastatin is recovered in urine following oral administration.
Specific Populations
Geriatric
Studies with amlodipine
Elderly patients have decreased clearance of amlodipine with a resulting increase in AUC of approximately 40–60%, and a lower initial dose of amlodipine may be required.
Studies with atorvastatin
Plasma concentrations of atorvastatin are higher (approximately 40% for Cmax and 30% for AUC) in healthy elderly subjects (age ≥65 years) than in young adults. Clinical data suggest a greater degree of LDL-lowering at any dose of atorvastatin in the elderly population compared to younger adults (see PRECAUTIONS, Geriatric Use).
Pediatric
Renal Impairment
Studies with amlodipine
The pharmacokinetics of amlodipine are not significantly influenced by renal impairment. Patients with renal failure may therefore receive the usual initial amlodipine dose.
Studies with atorvastatin
Renal disease has no influence on the plasma concentrations or LDL-C reduction of atorvastatin; thus, dose adjustment of atorvastatin in patients with renal dysfunction is not necessary (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION and WARNINGS, Skeletal Muscle).
Hemodialysis
While studies have not been conducted in patients with end-stage renal disease, hemodialysis is not expected to clear atorvastatin or amlodipine since both drugs are extensively bound to plasma proteins.
Hepatic Impairment
Atorvastatin is contraindicated in patients with active liver disease.
Studies with amlodipine
Elderly patients and patients with hepatic insufficiency have decreased clearance of amlodipine with a resulting increase in AUC of approximately 40–60%.
Studies with atorvastatin
In patients with chronic alcoholic liver disease, plasma concentrations of atorvastatin are markedly increased. Cmax and AUC are each 4-fold greater in patients with Childs-Pugh A disease. Cmax and AUC of atorvastatin are approximately 16-fold and 11-fold increased, respectively, in patients with Childs-Pugh B disease (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
Pharmacokinetic Studies of Atorvastatin and Co-Administered Drugs
TABLE 2. Effect of Co-administered Drugs on the Pharmacokinetics of Atorvastatin Co-administered drug and
dosing regimenAtorvastatin Dose (mg) Change in AUC* Change in Cmax* - * Data given as x-fold change represent a simple ratio between co-administration and atorvastatin alone (i.e., 1-fold = no change). Data given as % change represent % difference relative to atorvastatin alone (i.e., 0% = no change).
- † See WARNINGS, Skeletal Muscle and PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions for clinical significance.
- ‡ Greater increases in AUC (up to 2.5-fold) and/or Cmax (up to 71%) have been reported with excessive grapefruit consumption (≥ 750 mL – 1.2 liters per day).
- § Single sample taken 8–16 h post dose.
- ¶ Due to the dual interaction mechanism of rifampin, simultaneous co-administration of atorvastatin with rifampin is recommended, as delayed administration of atorvastatin after administration of rifampin has been associated with a significant reduction in atorvastatin plasma concentrations.
†Cyclosporine 5.2 mg/kg/day, stable dose 10 mg QD for 28 days ↑ 8.7-fold ↑10.7-fold †Lopinavir 400 mg BID/ ritonavir 100 mg BID, 14 days 20 mg QD for 4 days ↑ 5.9-fold ↑ 4.7-fold †Ritonavir 400 mg BID/ saquinavir 400mg BID, 15 days 40 mg QD for 4 days ↑ 3.9-fold ↑ 4.3-fold †Clarithromycin 500 mg BID, 9 days 80 mg QD for 8 days ↑ 4.4-fold ↑ 5.4-fold †Itraconazole 200 mg QD, 4 days 40 mg SD ↑ 3.3-fold ↑ 20% †Grapefruit Juice, 240 mL QD ‡ 40 mg, SD ↑ 37% ↑ 16% Diltiazem 240 mg QD, 28 days 40 mg, SD ↑ 51% No change Erythromycin 500 mg QID, 7 days 10 mg, SD ↑ 33% ↑ 38% Amlodipine 10 mg, single dose 80 mg, SD ↑ 15% ↓ 12 % Cimetidine 300 mg QD, 4 weeks 10 mg QD for 2 weeks ↓ Less than 1% ↓ 11% Colestipol 10 mg BID, 28 weeks 40 mg QD for 28 weeks Not determined ↓ 26%§ Maalox TC® 30 mL QD, 17 days 10 mg QD for 15 days ↓ 33% ↓ 34% Efavirenz 600 mg QD, 14 days 10 mg for 3 days ↓ 41% ↓ 1% †Rifampin 600 mg QD, 7 days (co-administered)¶ 40 mg SD ↑ 30% ↑ 2.7-fold †Rifampin 600 mg QD, 5 days (doses separated)¶ 40 mg SD ↓ 80% ↓ 40% †Gemfibrozil 600mg BID, 7 days 40mg SD ↑ 35% ↓ Less than 1% †Fenofibrate 160mg QD, 7 days 40mg SD ↑ 3% ↑ 2% TABLE 3. Effect of Atorvastatin on the Pharmacokinetics of Co-administered Drugs Atorvastatin Co-administered drug and dosing regimen Drug/Dose (mg) Change in AUC Change in Cmax - * See PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions for clinical significance
80 mg QD for 15 days Antipyrine, 600 mg SD ↑ 3% ↓ 11% 80 mg QD for 14 days *Digoxin 0.25 mg QD, 20 days ↑ 15% ↑ 20 % 40 mg QD for 22 days Oral contraceptive QD, 2 months - norethindrone 1mg ↑ 28% ↑ 23% - ethinyl estradiol 35µg ↑ 19% ↑ 30% Pharmacodynamics
Hemodynamic Effects of Amlodipine
Following administration of therapeutic doses to patients with hypertension, amlodipine produces vasodilation resulting in a reduction of supine and standing blood pressures. These decreases in blood pressure are not accompanied by a significant change in heart rate or plasma catecholamine levels with chronic dosing. Although the acute intravenous administration of amlodipine decreases arterial blood pressure and increases heart rate in hemodynamic studies of patients with chronic stable angina, chronic administration of oral amlodipine in clinical trials did not lead to clinically significant changes in heart rate or blood pressures in normotensive patients with angina.
With chronic once daily oral administration of amlodipine, antihypertensive effectiveness is maintained for at least 24 hours. Plasma concentrations correlate with effect in both young and elderly patients. The magnitude of reduction in blood pressure with amlodipine is also correlated with the height of pretreatment elevation; thus, individuals with moderate hypertension (diastolic pressure 105–114 mmHg) had about a 50% greater response than patients with mild hypertension (diastolic pressure 90–104 mmHg). Normotensive subjects experienced no clinically significant change in blood pressures (+1/–2 mmHg).
In hypertensive patients with normal renal function, therapeutic doses of amlodipine resulted in a decrease in renal vascular resistance and an increase in glomerular filtration rate and effective renal plasma flow without change in filtration fraction or proteinuria.
As with other calcium channel blockers, hemodynamic measurements of cardiac function at rest and during exercise (or pacing) in patients with normal ventricular function treated with amlodipine have generally demonstrated a small increase in cardiac index without significant influence on dP/dt or on left ventricular end diastolic pressure or volume. In hemodynamic studies, amlodipine has not been associated with a negative inotropic effect when administered in the therapeutic dose range to intact animals and man, even when co-administered with beta-blockers to man. Similar findings, however, have been observed in normal or well-compensated patients with heart failure with agents possessing significant negative inotropic effects.
Electrophysiologic Effects of Amlodipine
Amlodipine does not change sinoatrial nodal function or atrioventricular conduction in intact animals or man. In patients with chronic stable angina, intravenous administration of 10 mg did not significantly alter A-H and H-V conduction and sinus node recovery time after pacing. Similar results were obtained in patients receiving amlodipine and concomitant beta blockers. In clinical studies in which amlodipine was administered in combination with beta-blockers to patients with either hypertension or angina, no adverse effects on electrocardiographic parameters were observed. In clinical trials with angina patients alone, amlodipine therapy did not alter electrocardiographic intervals or produce higher degrees of AV blocks.
LDL-C Reduction with Atorvastatin
Atorvastatin as well as some of its metabolites are pharmacologically active in humans. The liver is the primary site of action and the principal site of cholesterol synthesis and LDL clearance. Drug dosage, rather than systemic drug concentration, correlates better with LDL-C reduction. Individualization of drug dosage should be based on therapeutic response (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Clinical Studies
Clinical Studies with Amlodipine
Amlodipine Effects in Hypertension
Adult Patients
The antihypertensive efficacy of amlodipine has been demonstrated in a total of 15 double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized studies involving 800 patients on amlodipine and 538 on placebo. Once daily administration produced statistically significant placebo-corrected reductions in supine and standing blood pressures at 24 hours postdose, averaging about 12/6 mmHg in the standing position and 13/7 mmHg in the supine position in patients with mild to moderate hypertension. Maintenance of the blood pressure effect over the 24-hour dosing interval was observed, with little difference in peak and trough effect. Tolerance was not demonstrated in patients studied for up to 1 year. The 3 parallel, fixed doses, dose response studies showed that the reduction in supine and standing blood pressures was dose-related within the recommended dosing range. Effects on diastolic pressure were similar in young and older patients. The effect on systolic pressure was greater in older patients, perhaps because of greater baseline systolic pressure. Effects were similar in black patients and in white patients.
Pediatric Patients
Two-hundred sixty-eight hypertensive patients aged 6 to 17 years were randomized first to amlodipine 2.5 or 5 mg once daily for 4 weeks and then randomized again to the same dose or to placebo for another 4 weeks. Patients receiving 2.5 mg or 5 mg amlodipine at the end of 8 weeks had significantly lower systolic blood pressure than those secondarily randomized to placebo. The magnitude of the treatment effect is difficult to interpret, but it is probably less than 5 mmHg systolic on the 5 mg dose and 3.3 mmHg on the 2.5 mg dose. Adverse events were similar to those seen in adults.
Amlodipine Effects in Chronic Stable Angina
The effectiveness of 5–10 mg/day of amlodipine in exercise-induced angina has been evaluated in 8 placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trials of up to 6 weeks duration involving 1038 patients (684 amlodipine, 354 placebo) with chronic stable angina. In 5 of the 8 studies, significant increases in exercise time (bicycle or treadmill) were seen with the 10 mg dose. Increases in symptom-limited exercise time averaged 12.8% (63 sec) for amlodipine 10 mg, and averaged 7.9% (38 sec) for amlodipine 5 mg. Amlodipine 10 mg also increased time to 1 mm ST segment deviation in several studies and decreased angina attack rate. The sustained efficacy of amlodipine in angina patients has been demonstrated over long-term dosing. In patients with angina, there were no clinically significant reductions in blood pressures (4/1 mmHg) or changes in heart rate (+0.3 bpm).
Amlodipine Effects in Vasospastic Angina
In a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial of 4 weeks duration in 50 patients, amlodipine therapy decreased attacks by approximately 4/week compared with a placebo decrease of approximately 1/week (p<0.01). Two of 23 amlodipine and 7 of 27 placebo patients discontinued from the study due to lack of clinical improvement.
Amlodipine Effects in Documented Coronary Artery Disease
In PREVENT, 825 patients with angiographically documented coronary artery disease were randomized to amlodipine (5–10 mg once daily) or placebo and followed for 3 years. Although the study did not show significance on the primary objective of change in coronary luminal diameter as assessed by quantitative coronary angiography, the data suggested a favorable outcome with respect to fewer hospitalizations for angina and revascularization procedures in patients with CAD.
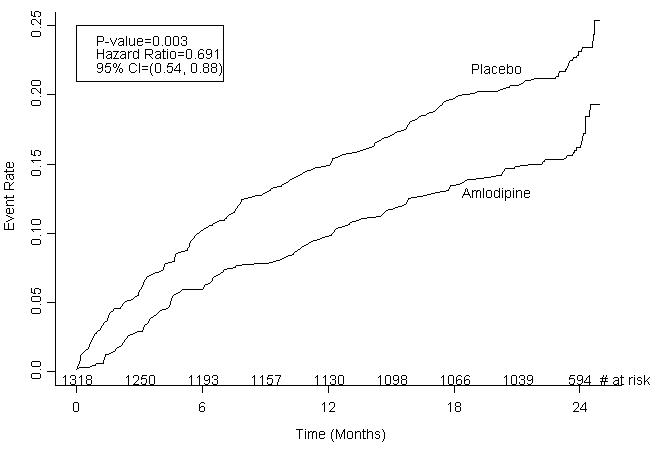
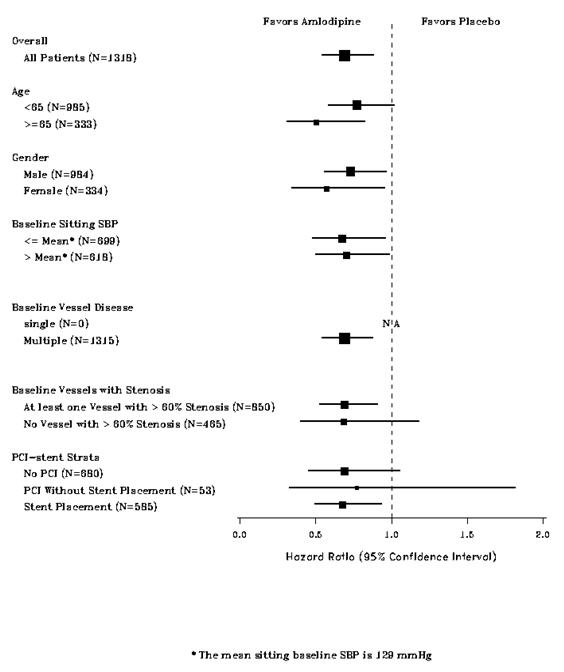
CAMELOT enrolled 1318 patients with CAD recently documented by angiography, without left main coronary disease and without heart failure or an ejection fraction <40%. Patients (76% males, 89% Caucasian, 93% enrolled at US sites, 89% with a history of angina, 52% without PCI, 4% with PCI and no stent, and 44% with a stent) were randomized to double-blind treatment with either amlodipine (5 – 10 mg once daily) or placebo in addition to standard care that included aspirin (89%), statins (83%), beta-blockers (74%), nitroglycerin (50%), anti-coagulants (40%), and diuretics (32%), but excluded other calcium channel blockers. The mean duration of follow-up was 19 months. The primary endpoint was the time to first occurrence of one of the following events: hospitalization for angina pectoris, coronary revascularization, myocardial infarction, cardiovascular death, resuscitated cardiac arrest, hospitalization for heart failure, stroke/TIA, or peripheral vascular disease. A total of 110 (16.6%) and 151 (23.1%) first events occurred in the amlodipine and placebo groups respectively for a hazard ratio of 0.691 (95% CI: 0.540–0.884, p = 0.003). The primary endpoint is summarized in Figure 1 below. The outcome of this study was largely derived from the prevention of hospitalizations for angina and the prevention of revascularization procedures (see Table 4). Effects in various subgroups are shown in Figure 2.
In an angiographic substudy (n=274) conducted within CAMELOT, there was no significant difference between amlodipine and placebo on the change of atheroma volume in the coronary artery as assessed by intravascular ultrasound.
Table 4 below summarizes the significant composite endpoint and clinical outcomes from the composites of the primary endpoint. The other components of the primary endpoint including cardiovascular death, resuscitated cardiac arrest, myocardial infarction, hospitalization for heart failure, stroke/TIA, or peripheral vascular disease did not demonstrate a significant difference between amlodipine and placebo.
Table 4. Incidence of Significant Clinical Outcomes for CAMELOT Clinical Outcomes
N (%)Amlodipine
(N=663)Placebo
(N=655)Risk Reduction
(p-value)- * Total patients with these events
Composite CV Endpoint 110
(16.6)151
(23.1)31%
(0.003)Hospitalization for Angina* 51
(7.7)84
(12.8)42%
(0.002)Coronary Revascularization* 78
(11.8)103
(15.7)27%
(0.033)Amlodipine Effects in Patients with Heart Failure
Amlodipine has been compared to placebo in four 8–12 week studies of patients with NYHA Class II/III heart failure, involving a total of 697 patients. In these studies, there was no evidence of worsened heart failure based on measures of exercise tolerance, NYHA classification, symptoms, or LVEF. In a long-term (follow-up at least 6 months, mean 13.8 months) placebo-controlled mortality/morbidity study of amlodipine 5–10 mg in 1153 patients with NYHA Classes III (n=931) or IV (n=222) heart failure on stable doses of diuretics, digoxin, and ACE inhibitors, amlodipine had no effect on the primary endpoint of the study which was the combined endpoint of all-cause mortality and cardiac morbidity (as defined by life-threatening arrhythmia, acute myocardial infarction, or hospitalization for worsened heart failure), or on NYHA classification, or symptoms of heart failure. Total combined all-cause mortality and cardiac morbidity events were 222/571 (39%) for patients on amlodipine and 246/583 (42%) for patients on placebo; the cardiac morbid events represented about 25% of the endpoints in the study.
Another study (PRAISE-2) randomized patients with NYHA Class III (80%) or IV (20%) heart failure without clinical symptoms or objective evidence of underlying ischemic disease, on stable doses of ACE inhibitors (99%), digitalis (99%) and diuretics (99%), to placebo (n=827) or amlodipine (n=827) and followed them for a mean of 33 months. There was no statistically significant difference between amlodipine and placebo in the primary endpoint of all cause mortality (95% confidence limits from 8% reduction to 29% increase on amlodipine). With amlodipine there were more reports of pulmonary edema.
Clinical Studies with Atorvastatin
Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease
In the Anglo-Scandinavian Cardiac Outcomes Trial (ASCOT), the effect of atorvastatin on fatal and non-fatal coronary heart disease was assessed in 10,305 hypertensive patients 40–80 years of age (mean of 63 years), without a previous myocardial infarction and with TC levels ≤251 mg/dl (6.5 mmol/l). Additionally all patients had at least 3 of the following cardiovascular risk factors: male gender (81.1%), age >55 years (84.5%), smoking (33.2%), diabetes (24.3%), history of CHD in a first-degree relative (26%), TC:HDL >6 (14.3%), peripheral vascular disease (5.1%), left ventricular hypertrophy (14.4%), prior cerebrovascular event (9.8%), specific ECG abnormality (14.3%), proteinuria/albuminuria (62.4%)]. In this double-blind, placebo-controlled study, patients were treated with anti-hypertensive therapy (Goal BP <140/90 mm Hg for non-diabetic patients; <130/80 mm Hg for diabetic patients) and allocated to either atorvastatin 10 mg daily (n=5168) or placebo (n=5137), using a covariate adaptive method which took into account the distribution of nine baseline characteristics of patients already enrolled and minimized the imbalance of those characteristics across the groups. Patients were followed for a median duration of 3.3 years.
The effect of 10 mg/day of atorvastatin on lipid levels was similar to that seen in previous clinical trials.
Atorvastatin significantly reduced the rate of coronary events [either fatal coronary heart disease (46 events in the placebo group vs. 40 events in the atorvastatin group) or nonfatal MI (108 events in the placebo group vs. 60 events in the atorvastatin group)] with a relative risk reduction of 36% [(based on incidences of 1.9% for atorvastatin vs. 3.0% for placebo), p=0.0005 (see Figure 3)]. The risk reduction was consistent regardless of age, smoking status, obesity, or presence of renal dysfunction. The effect of atorvastatin was seen regardless of baseline LDL levels. Due to the small number of events, results for women were inconclusive.
Figure 3: Effect of Atorvastatin 10 mg/day on Cumulative Incidence of Nonfatal Myocardial Infarction or Coronary Heart Disease Death (in ASCOT-LLA) 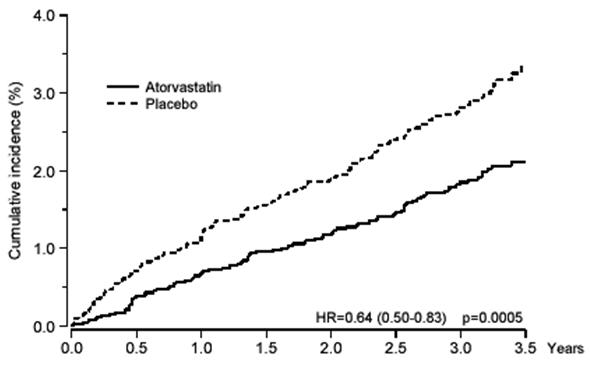
Atorvastatin also significantly decreased the relative risk for revascularization procedures by 42%. Although the reduction of fatal and non-fatal strokes did not reach a pre-defined significance level (p 0.01), a favorable trend was observed with a 26% relative risk reduction (incidences of 1.7% for atorvastatin and 2.3% for placebo). There was no significant difference between the treatment groups for death due to cardiovascular causes (p=0.51) or noncardiovascular causes (p=0.17).
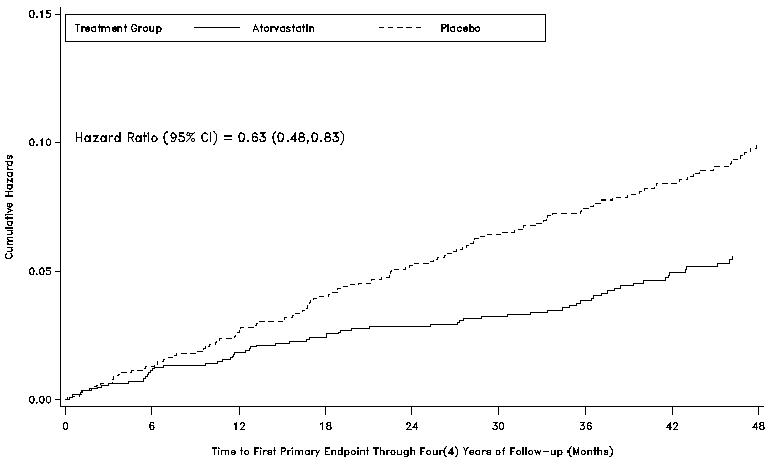
In the Collaborative Atorvastatin Diabetes Study (CARDS), the effect of atorvastatin on cardiovascular disease (CVD) endpoints was assessed in 2838 subjects (94% White, 68% male), ages 40–75 with type 2 diabetes based on WHO criteria, without prior history of cardiovascular disease and with LDL ≤ 160 mg/dL and TG ≤ 600 mg/dL. In addition to diabetes, subjects had 1 or more of the following risk factors: current smoking (23%), hypertension (80%), retinopathy (30%), or microalbuminuria (9%) or macroalbuminuria (3%). No subjects on hemodialysis were enrolled in the study. In this multicenter, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial, subjects were randomly allocated to either atorvastatin 10 mg daily (1429) or placebo (1411) in a 1:1 ratio and were followed for a median duration of 3.9 years. The primary endpoint was the occurrence of any of the major cardiovascular events: myocardial infarction, acute CHD death, unstable angina, coronary revascularization, or stroke. The primary analysis was the time to first occurrence of the primary endpoint.
Baseline characteristics of subjects were: mean age of 62 years, mean HbA1c 7.7%; median LDL-C 120 mg/dL; median TC 207 mg/dL; median TG 151 mg/dL; median HDL-C 52 mg/dL.
The effect of atorvastatin 10 mg/day on lipid levels was similar to that seen in previous clinical trials.
Atorvastatin significantly reduced the rate of major cardiovascular events (primary endpoint events) (83 events in the atorvastatin group vs 127 events in the placebo group) with a relative risk reduction of 37%, HR 0.63, 95% CI (0.48,0.83) (p=0.001) (see Figure 4). An effect of atorvastatin was seen regardless of age, sex, or baseline lipid levels.
Atorvastatin significantly reduced the risk of stroke by 48% (21 events in the atorvastatin group vs. 39 events in the placebo group), HR 0.52, 95% CI (0.31, 0.89) (p=0.016) and reduced the risk of MI by 42% (38 events in the atorvastatin group vs. 64 events in the placebo group), HR 0.58, 95.1% CI (0.39, 0.86) (p=0.007). There was no significant difference between the treatment groups for angina, revascularization procedures, and acute CHD death.
There were 61 deaths in the atorvastatin group vs. 82 deaths in the placebo group, (HR 0.73, p=0.059).
In the Treating to New Targets Study (TNT), the effect of atorvastatin calcium tablets 80 mg/day vs. atorvastatin calcium tablets 10 mg/day on the reduction in cardiovascular events was assessed in 10,001 subjects (94% white, 81% male, 38% ≥65 years) with clinically evident coronary heart disease who had achieved a target LDL-C level <130 mg/dL after completing an 8-week, open-label, run-in period with atorvastatin calcium tablets 10 mg/day. Subjects were randomly assigned to either 10 mg/day or 80 mg/day of atorvastatin calcium tablets and followed for a median duration of 4.9 years. The primary endpoint was the time-to-first occurrence of any of the following major cardiovascular events (MCVE): death due to CHD, non-fatal myocardial infarction, resuscitated cardiac arrest, and fatal and non-fatal stroke. The mean LDL-C, TC, TG, non-HDL, and HDL cholesterol levels at 12 weeks were 73, 145, 128, 98, and 47 mg/dL during treatment with 80 mg of atorvastatin calcium tablets and 99, 177, 152, 129, and 48 mg/dL during treatment with 10 mg of atorvastatin calcium tablets.
Treatment with atorvastatin calcium tablets 80 mg/day significantly reduced the rate of MCVE (434 events in the 80mg/day group vs. 548 events in the 10 mg/day group) with a relative risk reduction of 22%, HR 0.78, 95% CI (0.69,0.89), p=0.0002 (see Figure5 and Table 5). The overall risk reduction was consistent regardless of age (<65, ≥65) or gender.
Figure 5. Effect of Atorvastatin Calcium Tablets 80 mg/day vs. 10 mg/day on Time to Occurrence of Major Cardiovascular Events (TNT) 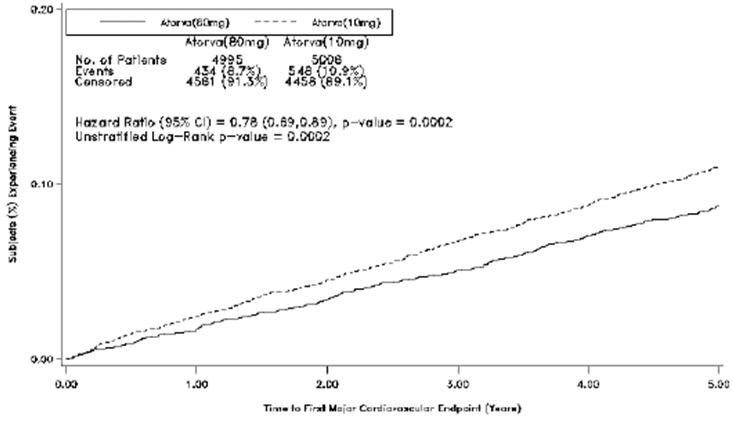
TABLE 5. Overview of Efficacy Results in TNT Endpoint Atorvastatin 10 mg
(N=5006)Atorvastatin 80 mg
(N=4995)HR* (95%CI) HR=hazard ratio; CHD=coronary heart disease; CI=confidence interval; MI=myocardial infarction; CHF=congestive heart failure; CV=cardiovascular; PVD=peripheral vascular disease; CABG=coronary artery bypass graft Confidence intervals for the Secondary Endpoints were not adjusted for multiple comparisons. - * Atorvastatin 80 mg: atorvastatin 10 mg
- † Secondary endpoints not included in primary endpoint
- ‡ Component of other secondary endpoints
PRIMARY ENDPOINT n (%) n (%) First major cardiovascular endpoint 548 (10.9) 434 (8.7) 0.78 (0.69, 0.89) Components of the Primary Endpoint CHD death 127 (2.5) 101 (2.0) 0.80 (0.61, 1.03) Non-fatal, non-procedure related MI 308 (6.2) 243 (4.9) 0.78 (0.66, 0.93) Resuscitated cardiac arrest 26 (0.5) 25 (0.5) 0.96 (0.56, 1.67) Stroke (fatal and non-fatal) 155 (3.1) 117 (2.3) 0.75 (0.59, 0.96) SECONDARY ENDPOINTS† First CHF with hospitalization 164 (3.3) 122 (2.4) 0.74 (0.59, 0.94) First PVD endpoint 282 (5.6) 275 (5.5) 0.97 (0.83, 1.15) First CABG or other coronary revascularization procedure‡ 904 (18.1) 667 (13.4) 0.72 (0.65, 0.80) First documented angina endpoint‡ 615 (12.3) 545 (10.9) 0.88 (0.79, 0.99) All cause mortality 282 (5.6) 284 (5.7) 1.01 (0.85, 1.19) Components of all cause mortality Cardiovascular death 155 (3.1) 126 (2.5) 0.81 (0.64, 1.03) Noncardiovascular death 127 (2.5) 158 (3.2) 1.25 (0.99, 1.57) Cancer death 75 (1.5) 85 (1.7) 1.13 (0.83, 1.55) Other non-CV death 43 (0.9) 58 (1.2) 1.35 (0.91, 2.00) Suicide, homicide and other
traumatic non-CV death9 (0.2) 15 (0.3) 1.67 (0.73, 3.82) Of the events that comprised the primary efficacy endpoint, treatment with atorvastatin calcium tablets 80 mg/day significantly reduced the rate of non-fatal, non-procedure related MI and fatal and non-fatal stroke, but not CHD death or resuscitated cardiac arrest (Table 5). Of the predefined secondary endpoints, treatment with atorvastatin calcium tablets 80 mg/day significantly reduced the rate of coronary revascularization, angina, and hospitalization for heart failure, but not peripheral vascular disease. The reduction in the rate of CHF with hospitalization was only observed in the 8% of patients with a prior history of CHF.
There was no significant difference between the treatment groups for all-cause mortality (Table 5). The proportions of subjects who experienced cardiovascular death, including the components of CHD death and fatal stroke, were numerically smaller in the atorvastatin calcium tablets 80 mg group than in the atorvastatin calcium tablets 10 mg treatment group. The proportions of subjects who experienced noncardiovascular death were numerically larger in the atorvastatin calcium tablets 80 mg group than in the atorvastatin calcium tablets 10 mg treatment group.
In the Incremental Decrease in Endpoints Through Aggressive Lipid Lowering Study (IDEAL), treatment with atorvastatin calcium tablets 80 mg/day was compared to treatment with simvastatin 20–40 mg/day in 8,888 subjects up to 80 years of age with a history of CHD to assess whether reduction in CV risk could be achieved. Patients were mainly male (81%), white (99%) with an average age of 61.7 years, and an average LDL-C of 121.5 mg/dL at randomization; 76% were on statin therapy. In this prospective, randomized, open-label, blinded endpoint (PROBE) trial with no run-in period, subjects were followed for a median duration of 4.8 years. The mean LDL-C, TC, TG, HDL, and non-HDL cholesterol levels at Week 12 were 78, 145, 115, 45, and 100 mg/dL during treatment with 80 mg of atorvastatin calcium tablets and 105, 179, 142, 47, and 132 mg/dL during treatment with 20–40 mg of simvastatin.
There was no significant difference between the treatment groups for the primary endpoint, the rate of first major coronary event (fatal CHD, nonfatal MI and resuscitated cardiac arrest): 411 (9.3%) in the atorvastatin calcium tablets 80 mg/day group vs. 463 (10.4%) in the simvastatin 20–40 mg/day group, HR 0.89, 95% CI ( 0.78, 1.01), p=0.07.
There were no significant differences between the treatment groups for all-cause mortality: 366 (8.2%) in the atorvastatin calcium tablets 80 mg/day group vs. 374 (8.4%) in the simvastatin 20–40 mg/day group. The proportions of subjects who experienced CV or non-CV death were similar for the atorvastatin calcium tablets 80 mg group and the simvastatin 20–40 mg group.
Atorvastatin Studies in Hyperlipidemia (Heterozygous Familial and Nonfamilial) and Mixed Dyslipidemia (Fredrickson Types IIa and IIb)
Atorvastatin reduces total-C, LDL-C, VLDL-C, apo B, and TG, and increases HDL-C in patients with hyperlipidemia and mixed dyslipidemia. Therapeutic response is seen within 2 weeks, and maximum response is usually achieved within 4 weeks and maintained during chronic therapy.
Atorvastatin is effective in a wide variety of patient populations with hyperlipidemia, with and without hypertriglyceridemia, in men and women, and in the elderly.
In two multicenter, placebo-controlled, dose-response studies in patients with hyperlipidemia, atorvastatin given as a single dose over 6 weeks, significantly reduced total-C, LDL-C, apo B, and TG (pooled results are provided in Table 6).
Table 6. Dose-Response in Patients With Primary Hyperlipidemia (Adjusted Mean Percent Change From Baseline)* Dose N TC LDL-C Apo B TG HDL-C Non-HDL-C/ HDL-C - * Results are pooled from 2 dose-response studies.
Placebo 21 4 4 3 10 -3 7 10 22 -29 -39 -32 -19 6 -34 20 20 -33 -43 -35 -26 9 -41 40 21 -37 -50 -42 -29 6 -45 80 23 -45 -60 -50 -37 5 -53 In patients with Fredrickson Types IIa and IIb hyperlipoproteinemia pooled from 24 controlled trials, the median (25th and 75th percentile) percent changes from baseline in HDL-C for atorvastatin 10, 20, 40, and 80 mg were 6.4 (-1.4, 14), 8.7 (0, 17), 7.8 (0, 16), and 5.1 (-2.7, 15), respectively. Additionally, analysis of the pooled data demonstrated consistent and significant decreases in total-C, LDL-C, TG, total-C/HDL-C, and LDL-C/HDL-C.
In three multicenter, double-blind studies in patients with hyperlipidemia, atorvastatin was compared to other statins. After randomization, patients were treated for 16 weeks with either atorvastatin 10 mg per day or a fixed dose of the comparative agent (Table 7).
Table 7. Mean Percent Change From Baseline at Endpoint (Double-Blind, Randomized, Active-Controlled Trials) Treatment
(Daily Dose)
N
Total-C
LDL-C
Apo B
TG
HDL-CNon-HDL-C/ HDL-C - * Significantly different from lovastatin, ANCOVA, p ≤0.05
- † A negative value for the 95% CI for the difference between treatments favors atorvastatin for all except HDL-C, for which a positive value favors atorvastatin. If the range does not include 0, this indicates a statistically significant difference.
- ‡ Significantly different from pravastatin, ANCOVA, p ≤0.05
- § Significantly different from simvastatin, ANCOVA, p ≤0.05
Study 1 Atorvastatin 10 mg 707 -27* -36* -28* -17* +7 -37* Lovastatin 20 mg 191 -19 -27 -20 - 6 +7 -28 95% CI for Diff† -9.2, -6.5 -10.7, -7.1 -10.0, -6.5 -15.2, -7.1 -1.7, 2.0 -11.1, -7.1 Study 2 Atorvastatin 10 mg 222 -25‡ -35‡ -27‡ -17‡ +6 -36‡ Pravastatin 20 mg 77 -17 -23 -17 - 9 +8 -28 95% CI for Diff† -10.8, -6.1 -14.5, -8.2 -13.4, -7.4 -14.1, -0.7 -4.9, 1.6 -11.5, -4.1 Study 3 Atorvastatin 10 mg 132 -29§ -37§ -34§ -23§ +7 -39§ Simvastatin 10 mg 45 -24 -30 -30 -15 +7 -33 95% CI for Diff† -8.7, -2.7 -10.1, -2.6 -8.0, -1.1 -15.1, -0.7 -4.3, 3.9 -9.6, -1.9 The impact on clinical outcomes of the differences in lipid-altering effects between treatments shown in Table 7 is not known. Table 7 does not contain data comparing the effects of atorvastatin 10 mg and higher doses of lovastatin, pravastatin, and simvastatin. The drugs compared in the studies summarized in the table are not necessarily interchangeable.
Atorvastatin Effects in Hypertriglyceridemia (Fredrickson Type IV)
The response to atorvastatin in 64 patients with isolated hypertriglyceridemia treated across several clinical trials is shown in the table below (Table 8). For the atorvastatin-treated patients, median (min, max) baseline TG level was 565 (267–1502).
Table 8. Combined Patients With Isolated Elevated TG: Median (min, max) Percent Changes From Baseline Placebo
(N=12)Atorvastatin 10 mg
(N=37)Atorvastatin 20 mg
(N=13)Atorvastatin 80 mg
(N=14)Triglycerides -12.4 (-36.6, 82.7) -41.0 (-76.2, 49.4) -38.7 (-62.7, 29.5) -51.8 (-82.8, 41.3) Total-C -2.3 (-15.5, 24.4) -28.2 (-44.9, -6.8) -34.9 (-49.6, -15.2) -44.4 (-63.5, -3.8) LDL-C 3.6 (-31.3, 31.6) -26.5 (-57.7, 9.8) -30.4 (-53.9, 0.3) -40.5 (-60.6, -13.8) HDL-C 3.8 (-18.6, 13.4) 13.8 (-9.7, 61.5) 11.0 (-3.2, 25.2) 7.5 (-10.8, 37.2) VLDL-C -1.0 (-31.9, 53.2) -48.8 (-85.8, 57.3) -44.6 (-62.2, -10.8) -62.0 (-88.2, 37.6) non-HDL-C -2.8 (-17.6, 30.0) -33.0 (-52.1, -13.3) -42.7 (-53.7, -17.4) -51.5 (-72.9, -4.3) Atorvastatin Effects in Dysbetalipoproteinemia (Fredrickson Type III)
The results of an open-label crossover study of atorvastatin in 16 patients (genotypes: 14 apo E2/E2 and 2 apo E3/E2) with dysbetalipoproteinemia (Fredrickson Type III) are shown in the table below (Table 9).
Table 9. Open-Label Crossover Study of 16 Patients With Dysbetalipoproteinemia (Fredrickson Type III) Median % Change (min, max) Median (min, max) at Baseline (mg/dL) Atorvastatin 10 mg Atorvastatin 80 mg Total-C 442 (225, 1320) -37 (-85, 17) -58 (-90, -31) Triglycerides 678 (273, 5990) -39 (-92, -8) -53 (-95, -30) IDL-C + VLDL-C 215 (111, 613) -32 (-76, 9) -63 (-90, -8) non-HDL-C 411 (218, 1272) -43 (-87, -19) -64 (-92, -36) Atorvastatin Effects in Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia
In a study without a concurrent control group, 29 patients ages 6 to 37 years with homozygous FH received maximum daily doses of 20 to 80 mg of atorvastatin. The mean LDL-C reduction in this study was 18%. Twenty-five patients with a reduction in LDL-C had a mean response of 20% (range of 7% to 53%, median of 24%); the remaining 4 patients had 7% to 24% increases in LDL-C. Five of the 29 patients had absent LDL-receptor function. Of these, 2 patients also had a portacaval shunt and had no significant reduction in LDL-C. The remaining 3 receptor-negative patients had a mean LDL-C reduction of 22%.
Atorvastatin Effects in Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemic Pediatric Patients
In a double-blind, placebo-controlled study followed by an open-label phase, 187 boys and postmenarchal girls 10–17 years of age (mean age 14.1 years) with heterozygous FH or severe hypercholesterolemia, were randomized to atorvastatin (n=140) or placebo (n=47) for 26 weeks and then all received atorvastatin for 26 weeks. Inclusion in the study required 1) a baseline LDL-C level ≥ 190 mg/dL or 2) a baseline LDL-C level ≥ 160 mg/dL and positive family history of FH or documented premature cardiovascular disease in a first- or second-degree relative. The mean baseline LDL-C value was 218.6 mg/dL (range: 138.5–385.0 mg/dL) in the atorvastatin group compared to 230.0 mg/dL (range: 160.0–324.5 mg/dL) in placebo group. The dosage of atorvastatin (once daily) was 10 mg for the first 4 weeks and up-titrated to 20 mg if the LDL-C level was > 130 mg/dL. The number of atorvastatin-treated patients who required up-titration to 20 mg after Week 4 during the double-blind phase was 80 (57.1%).
Atorvastatin significantly decreased plasma levels of total-C, LDL-C, triglycerides, and apolipoprotein B during the 26 week double-blind phase (see Table 10).
Table 10. Lipid-altering Effects of Atorvastatin in Adolescent Boys and Girls with Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia or Severe Hypercholesterolemia (Mean Percent Change From Baseline at Endpoint in Intention-to-Treat Population) DOSAGE N Total-C LDL-C HDL-C TG Apolipoprotein B Placebo 47 -1.5 -0.4 -1.9 1.0 0.7 Atorvastatin 140 -31.4 -39.6 2.8 -12.0 -34.0 The mean achieved LDL-C value was 130.7 mg/dL (range: 70.0–242.0 mg/dL) in the atorvastatin group compared to 228.5 mg/dL (range: 152.0–385.0 mg/dL) in the placebo group during the 26 week double-blind phase.
The safety and efficacy of atorvastatin doses above 20 mg have not been studied in controlled trials in children. The long-term efficacy of atorvastatin therapy in childhood to reduce morbidity and mortality in adulthood has not been established.
Clinical Study of Combined Amlodipine and Atorvastatin in Patients with Hypertension and Dyslipidemia
In a double-blind, placebo-controlled study, a total of 1660 patients with co-morbid hypertension and dyslipidemia received once daily treatment with eight dose combinations of amlodipine and atorvastatin (5/10, 10/10, 5/20, 10/20, 5/40, 10/40, 5/80, or 10/80 mg), amlodipine alone (5 mg or 10 mg), atorvastatin alone (10 mg, 20 mg, 40 mg, or 80 mg) or placebo. In addition to concomitant hypertension and dyslipidemia, 15% of the patients had diabetes mellitus, 22% were smokers and 14% had a positive family history of cardiovascular disease. At eight weeks, all eight combination-treatment groups of amlodipine and atorvastatin demonstrated statistically significant dose-related reductions in systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP) and LDL-C compared to placebo, with no overall modification of effect of either component on SBP, DBP and LDL-C (Table 11).
Table 11. Efficacy in Terms of Reduction in Blood Pressure and LDL-C
Efficacy of the Combined Treatments in Reducing Systolic BP Parameter / Analysis ATO 0 mg ATO 10 mg ATO 20 mg ATO 40 mg ATO 80 mg AML 0 mg Mean change (mmHg) -3.0 -4.5 -6.2 -6.2 -6.4 Difference versus placebo (mmHg) - -1.5 -3.2 -3.2 -3.4 AML 5 mg Mean change (mmHg) -12.8 -13.7 -15.3 -12.7 -12.2 Difference versus placebo (mmHg) -9.8 -10.7 -12.3 -9.7 -9.2 AML 10 mg Mean change (mmHg) -16.2 -15.9 -16.1 -16.3 -17.6 Difference versus placebo (mmHg) -13.2 -12.9 -13.1 -13.3 -14.6
Efficacy of the Combined Treatments in Reducing Diastolic BPParameter / Analysis ATO 0 mg ATO 10 mg ATO 20 mg ATO 40 mg ATO 80 mg AML 0 mg Mean change (mmHg) -3.3 -4.1 -3.9 -5.1 -4.1 Difference versus placebo (mmHg) - -0.8 -0.6 -1.8 -0.8 AML 5 mg Mean change (mmHg) -7.6 -8.2 -9.4 -7.3 -8.4 Difference versus placebo (mmHg) -4.3 -4.9 -6.1 -4.0 -5.1 AML 10 mg Mean change (mmHg) -10.4 -9.1 -10.6 -9.8 -11.1 Difference versus placebo (mmHg) -7.1 -5.8 -7.3 -6.5 -7.8
Efficacy of the Combined Treatments in Reducing LDL-C (% change)Parameter / Analysis ATO 0 mg ATO 10 mg ATO 20 mg ATO 40 mg ATO 80 mg AML 0 mg Mean % change -1.1 -33.4 -39.5 -43.1 -47.2 AML 5 mg Mean % change -0.1 -38.7 -42.3 -44.9 -48.4 AML 10 mg Mean % change -2.5 -36.6 -38.6 -43.2 -49.1 -
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets are indicated in patients for whom treatment with both amlodipine and atorvastatin is appropriate.
Amlodipine
- 1.
Hypertension: Amlodipine is indicated for the treatment of hypertension. It may be used alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents;
- 2. Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
Chronic Stable Angina: Amlodipine is indicated for the treatment of chronic stable angina. Amlodipine may be used alone or in combination with other antianginal or antihypertensive agents;
Vasospastic Angina (Prinzmetal's or Variant Angina): Amlodipine is indicated for the treatment of confirmed or suspected vasospastic angina. Amlodipine may be used as monotherapy or in combination with other antianginal drugs.
Angiographically Documented CAD: In patients with recently documented CAD by angiography and without heart failure or an ejection fraction <40%, amlodipine is indicated to reduce the risk of hospitalization due to angina and to reduce the risk of a coronary revascularization procedure. - 2. Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
AND
Atorvastatin
Therapy with lipid-altering agents should be only one component of multiple risk factor intervention in individuals at significantly increased risk for atherosclerotic vascular disease due to hypercholesterolemia. Drug therapy is recommended as an adjunct to diet when the response to a diet restricted in saturated fat and cholesterol and other nonpharmacologic measures alone has been inadequate. In patients with CHD or multiple risk factors for CHD, the atorvastatin component of amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets can be started simultaneously with diet restriction.
- 1.
Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease:
In adult patients without clinically evident coronary heart disease, but with multiple risk factors for coronary heart disease such as age, smoking, hypertension, low HDL-C, or a family history of early coronary heart disease, atorvastatin is indicated to:- Reduce the risk of myocardial infarction
- Reduce the risk of stroke
- Reduce the risk for revascularization procedures and angina
In patients with type 2 diabetes, and without clinically evident coronary heart disease, but with multiple risk factors for coronary heart disease such as retinopathy, albuminuria, smoking, or hypertension, atorvastatin calcium tablets are indicated to:- Reduce the risk of myocardial infarction
- Reduce the risk of stroke;
In patients with clinically evident coronary heart disease, atorvastatin calcium tablets are indicated to:- Reduce the risk of non-fatal myocardial infarction
- Reduce the risk of fatal and non-fatal stroke
- Reduce the risk for revascularization procedures
- Reduce the risk of hospitalization for CHF
- Reduce the risk of angina
- 2. Heterozygous Familial and Nonfamilial Hyperlipidemia: Atorvastatin is indicated as an adjunct to diet to reduce elevated total-C, LDL-C, apo B, and TG levels and to increase HDL-C in patients with primary hypercholesterolemia (heterozygous familial and nonfamilial) and mixed dyslipidemia (Fredrickson Types IIa and IIb);
- 3. Elevated Serum TG Levels: Atorvastatin is indicated as an adjunct to diet for the treatment of patients with elevated serum TG levels (Fredrickson Type IV);
- 4. Primary Dysbetalipoproteinemia: Atorvastatin is indicated for the treatment of patients with primary dysbetalipoproteinemia (Fredrickson Type III) who do not respond adequately to diet;
- 5. Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia: Atorvastatin is indicated to reduce total-C and LDL-C in patients with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia as an adjunct to other lipid-lowering treatments (e.g., LDL apheresis) or if such treatments are unavailable;
- 6. Pediatric Patients: Atorvastatin is indicated as an adjunct to diet to reduce total-C, LDL-C, and apo B levels in boys and postmenarchal girls, 10 to 17 years of age, with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia if after an adequate trial of diet therapy the following findings are present:
- a. LDL-C remains ≥ 190 mg/dL or
- b.
LDL-C remains ≥ 160 mg/dL and:
- there is a positive family history of premature cardiovascular disease or
- two or more other CVD risk factors are present in the pediatric patients.
The antidyslipidemic component of amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets has not been studied in conditions where the major lipoprotein abnormality is elevation of chylomicrons (Fredrickson Types I and V).
- 1.
Hypertension: Amlodipine is indicated for the treatment of hypertension. It may be used alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents;
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets contain atorvastatin and are therefore contraindicated in patients with active liver disease, which may include unexplained persistent elevations in hepatic transaminase levels.
Amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets are contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to any component of this medication.
Pregnancy and Lactation
Amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets contain atorvastatin and are therefore contraindicated in women who are pregnant or may become pregnant. The atorvastatin component of amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Serum cholesterol and triglycerides increase during normal pregnancy, and cholesterol or cholesterol derivatives are essential for fetal development. Atherosclerosis is a chronic process and discontinuation of lipid-lowering drugs during pregnancy should have little impact on the outcome of long-term therapy of primary hypercholesterolemia.
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of atorvastatin use during pregnancy; however in rare reports congenital anomalies were observed following intrauterine exposure to statins. In rat and rabbit animal reproduction studies, atorvastatin revealed no evidence of teratogenicity. AMLODIPINE BESYLATE/ATORVASTATIN CALCIUM TABLETS, WHICH INCLUDE ATORVASTATIN, SHOULD BE ADMINISTERED TO WOMEN OF CHILDBEARING AGE ONLY WHEN SUCH PATIENTS ARE HIGHLY UNLIKELY TO CONCEIVE AND HAVE BEEN INFORMED OF THE POTENTIAL HAZARDS. If the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, therapy should be discontinued immediately and the patient apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus (see PRECAUTIONS, Pregnancy).
It is not known whether atorvastatin or amlodipine are excreted into human milk; however a small amount of another statin does pass into breast milk. Because statins have the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants, women taking amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets should not breastfeed their infants (see PRECAUTIONS, Nursing Mothers).
-
WARNINGS
Skeletal Muscle
Rare cases of rhabdomyolysis with acute renal failure secondary to myoglobinuria have been reported with the atorvastatin component of amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets and with other statins. A history of renal impairment may be a risk factor for the development of rhabdomyolysis. Such patients merit closer monitoring for skeletal muscle effects.
The atorvastatin component of amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets, like other statins, occasionally causes myopathy, defined as muscle aches or muscle weakness in conjunction with increases in creatine phosphokinase (CPK) values >10 times ULN. The concomitant use of higher doses of atorvastatin with certain drugs such as cyclosporine and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., clarithromycin, itraconazole and HIV protease inhibitors) increases the risk of myopathy/rhabdomyolysis.
Myopathy should be considered in any patient with diffuse myalgias, muscle tenderness or weakness, or marked elevation of CPK. Patients should be advised to report promptly unexplained muscle pain, tenderness or weakness, particularly if accompanied by malaise or fever. Amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets therapy should be discontinued if markedly elevated CPK levels occur or myopathy is diagnosed or suspected.
The risk of myopathy during treatment with statins is increased with concurrent administration of cyclosporine, fibric acid derivatives, erythromycin, clarithromycin, combination of ritonavir plus saquinavir or lopinavir plus ritonavir, niacin, or azole antifungals. Physicians considering combined therapy with amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets and fibric acid derivatives, erythromycin, clarithromycin, a combination of ritonavir plus saquinavir or lopinavir plus ritonavir, immunosuppressive drugs, azole antifungals, or lipid-modifying doses of niacin should carefully weigh the potential benefits and risks and should carefully monitor patients for any signs or symptoms of muscle pain, tenderness, or weakness, particularly during the initial months of therapy and during any periods of upward dosage titration of either drug. Lower starting and maintenance doses of atorvastatin should be considered when taken concomitantly with the aforementioned drugs (see PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions). Periodic creatine phosphokinase (CPK) determinations may be considered in such situations, but there is no assurance that such monitoring will prevent the occurrence of severe myopathy.
Prescribing recommendations for atorvastatin, a component of amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets, and interacting agents are summarized in Table 12 (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION, PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions, and CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY).
TABLE 12 Atorvastatin Drug Interactions Associated with Increased Risk of Myopathy/Rhabdomyolysis Interacting Agents Prescribing Recommendations Cyclosporine
Do not exceed 10 mg atorvastatin daily Clarithromycin, Itraconazole, HIV protease inhibitors (ritonavir plus saquinavir or lopinavir plus ritonavir,) Caution when exceeding doses > 20mg atorvastatin daily. The lowest dose necessary should be used. In patients taking amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets, therapy should be temporarily withheld or discontinued in any patient with an acute, serious condition suggestive of a myopathy or having a risk factor predisposing to the development of renal failure secondary to rhabdomyolysis (e.g., severe acute infection, hypotension, major surgery, trauma, severe metabolic, endocrine and electrolyte disorders, and uncontrolled seizures).
Liver Dysfunction
Statins, like the atorvastatin component of amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets and like some other lipid-lowering therapies, have been associated with biochemical abnormalities of liver function. Persistent elevations (>3 times the upper limit of normal [ULN] occurring on 2 or more occasions) in serum transaminases occurred in 0.7% of patients who received atorvastatin in clinical trials. The incidence of these abnormalities was 0.2%, 0.2%, 0.6%, and 2.3% for 10, 20, 40, and 80 mg, respectively.
In clinical trials in patients taking the atorvastatin component of amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets, the following has been observed. One patient in clinical trials developed jaundice. Increases in liver function tests (LFT) in other patients were not associated with jaundice or other clinical signs or symptoms. Upon dose reduction, drug interruption, or discontinuation, transaminase levels returned to or near pretreatment levels without sequelae. Eighteen of 30 patients, with persistent LFT elevations continued treatment with a reduced dose of atorvastatin.
It is recommended that liver function tests be performed prior to and at 12 weeks following both the initiation of therapy and any elevation of dose, and periodically (e.g., semiannually) thereafter. Liver enzyme changes generally occur in the first 3 months of treatment with the atorvastatin component of amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets. Patients who develop increased transaminase levels should be monitored until the abnormalities resolve. Should an increase in ALT or AST of >3 times ULN persist, reduction of dose or withdrawal of amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets is recommended.
Active liver disease or unexplained persistent transaminase elevations are contraindications to the use of amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
-
PRECAUTIONS
Hypotension
Symptomatic hypotension is possible, particularly in patients with severe aortic stenosis. Because of the gradual onset of action, acute hypotension is unlikely.
Beta-Blocker Withdrawal
The amlodipine component of amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets is not a beta-blocker and therefore gives no protection against the dangers of abrupt beta-blocker withdrawal; any such withdrawal should be by gradual reduction of the dose of beta-blocker.
Endocrine Function
Statins, such as the atorvastatin component of amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets, interfere with cholesterol synthesis and theoretically might blunt adrenal and/or gonadal steroid production. Clinical studies have shown that atorvastatin does not reduce basal plasma cortisol concentration or impair adrenal reserve. The effects of statins on male fertility have not been studied in adequate numbers of patients. The effects, if any, on the pituitary-gonadal axis in premenopausal women are unknown. Use caution when administering a statin with drugs that may decrease the levels or activity of endogenous steroid hormones, such as ketoconazole, spironolactone, and cimetidine.
CNS Toxicity
Studies with atorvastatin
Brain hemorrhage was seen in a female dog treated with atorvastatin calcium for 3 months at a dose equivalent to 120 mg atorvastatin/kg/day. Brain hemorrhage and optic nerve vacuolation were seen in another female dog that was sacrificed in moribund condition after 11 weeks of escalating doses of atorvastatin calcium equivalent to up to 280 mg atorvastatin/kg/day. The 120 mg/kg dose of atorvastatin resulted in a systemic exposure approximately 16 times the human plasma area-under-the-curve (AUC, 0–24 hours) based on the maximum human dose of 80 mg/day. A single tonic convulsion was seen in each of 2 male dogs (one treated with atorvastatin calcium at a dose equivalent to 10 mg atorvastatin/kg/day and one at a dose equivalent to 120 mg atorvastatin/kg/day) in a 2-year study. No CNS lesions have been observed in mice after chronic treatment for up to 2 years at doses of atorvastatin calcium equivalent to up to 400 mg atorvastatin/kg/day or in rats at doses equivalent to up to 100 mg atorvastatin/kg/day. These doses were 6 to 11 times (mouse) and 8 to 16 times (rat) the human AUC (0–24) based on the maximum recommended human dose of 80 mg atorvastatin/day.
CNS vascular lesions, characterized by perivascular hemorrhages, edema, and mononuclear cell infiltration of perivascular spaces, have been observed in dogs treated with other statins. A chemically similar drug in this class produced optic nerve degeneration (Wallerian degeneration of retinogeniculate fibers) in clinically normal dogs in a dose-dependent fashion at a dose that produced plasma drug levels about 30 times higher than the mean drug level in humans taking the highest recommended dose.
Use in Patients with Recent Stroke or TIA
Studies with atorvastatin
In a post-hoc analysis of the Stroke Prevention by Aggressive Reduction in Cholesterol Levels (SPARCL) study where atorvastatin 80 mg vs. placebo was administered in 4,731 subjects without CHD who had a stroke or TIA within the preceding 6 months, a higher incidence of hemorrhagic stroke was seen in the atorvastatin 80 mg group compared to placebo (55, 2.3% atorvastatin vs. 33, 1.4% placebo; HR: 1.68, 95% CI: 1.09, 2.59; p=0.0168). The incidence of fatal hemorrhagic stroke was similar across treatment groups (17 vs. 18 for the atorvastatin and placebo groups, respectively). The incidence of nonfatal hemorrhagic stroke was significantly higher in the atorvastatin group (38, 1.6%) as compared to the placebo group (16, 0.7%). Some baseline characteristics, including hemorrhagic and lacunar stroke on study entry, were associated with a higher incidence of hemorrhagic stroke in the atorvastatin group (see ADVERSE REACTIONS, The Atorvastatin Component of Amlodipine Besylate/Atorvastatin Calcium Tablets).
Information for Patients
Because of the risk of myopathy with statins, the drug class to which the atorvastatin component of amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets belongs, advise patients to promptly report unexplained muscle pain, tenderness, or weakness, particularly if accompanied by malaise or fever.
Drug Interactions
Data from a drug-drug interaction study involving 10 mg of amlodipine and 80 mg of atorvastatin in healthy subjects indicate that the pharmacokinetics of amlodipine are not altered when the drugs are co-administered. The effect of amlodipine on the pharmacokinetics of atorvastatin showed no effect on the Cmax: 91% (90% confidence interval: 80 to 103%), but the AUC of atorvastatin increased by 18% (90% confidence interval: 109 to 127%) in the presence of amlodipine, which was not clinically meaningful.
No drug interaction studies have been conducted with amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets and other drugs, although studies have been conducted in the individual amlodipine and atorvastatin components, as described below:
Studies with Amlodipine
In vitro data in human plasma indicate that amlodipine has no effect on the protein binding of drugs tested (digoxin, phenytoin, warfarin, and indomethacin).
Cimetidine
Co-administration of amlodipine with cimetidine did not alter the pharmacokinetics of amlodipine.
Grapefruit Juice
Co-administration of 240 mL of grapefruit juice with a single oral dose of amlodipine 10 mg in 20 healthy volunteers had no significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of amlodipine.
Magnesium and Aluminum Hydroxide Antacid
Co-administration of magnesium and aluminum hydroxide antacid with a single dose of amlodipine had no significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of amlodipine.
Sildenafil
A single 100 mg dose of sildenafil in subjects with essential hypertension had no effect on the pharmacokinetic parameters of amlodipine. When amlodipine and sildenafil were used in combination, each agent independently exerted its own blood pressure lowering effect.
Digoxin
Co-administration of amlodipine with digoxin did not change serum digoxin levels or digoxin renal clearance in normal volunteers.
Ethanol (Alcohol)
Single and multiple 10 mg doses of amlodipine had no significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of ethanol.
Warfarin
Co-administration of amlodipine with warfarin did not change the warfarin prothrombin response time.
CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Co-administration of a 180 mg daily dose of diltiazem with 5 mg amlodipine in elderly hypertensive patients resulted in a 60% increase in amlodipine systemic exposure. Erythromycin co-administration in healthy volunteers did not significantly change amlodipine systemic exposure. However, strong inhibitors of CYP3A4 (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole, ritonavir) may increase the plasma concentrations of amlodipine to a greater extent. Monitor for symptoms of hypotension and edema when amlodipine is co-administered with CYP3A4 inhibitors.
Studies with Atorvastatin
The risk of myopathy during treatment with statins is increased with concurrent administration of fibric acid derivatives, lipid-modifying doses of niacin, cyclosporine, or strong CYP 3A4 inhibitors (e.g., clarithromycin, HIV protease inhibitors, and itraconazole) (see WARNINGS, Skeletal Muscle, and CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY).
Strong Inhibitors of CYP 3A4
Atorvastatin is metabolized by cytochrome P450 3A4. Concomitant administration of atorvastatin with strong inhibitors of CYP 3A4 can lead to increases in plasma concentrations of atorvastatin. The extent of interaction and potentiation of effects depends on the variability of effect on CYP 3A4.
- Clarithromycin: Atorvastatin AUC was significantly increased with concomitant administration of atorvastatin 80 mg with clarithromycin (500 mg twice daily) compared to that of atorvastatin alone (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY). Therefore, in patients taking clarithromycin, use caution when administering atorvastatin doses >20 mg (see WARNINGS, Skeletal Muscle, and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
- Combination of Protease Inhibitors: Atorvastatin AUC was significantly increased with concomitant administration of atorvastatin 40 mg with ritonavir plus saquinavir (400 mg twice daily) or atorvastatin 20 mg with lopinavir plus ritonavir (400 mg + 100 mg twice daily) compared to that of atorvastatin alone (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY). Therefore, in patients taking HIV protease inhibitors, use caution when administering atorvastatin doses >20 mg (see WARNINGS, Skeletal Muscle, and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
- Itraconazole: Atorvastatin AUC was significantly increased with concomitant administration of atorvastatin 40 mg and itraconazole 200 mg (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY). Therefore, in patients taking itraconazole, use caution when administering atorvastatin doses >20 mg (see WARNINGS, Skeletal Muscle, and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Grapefruit juice
Contains one or more components that inhibit CYP 3A4 and can increase plasma concentrations of atorvastatin, especially with excessive grapefruit juice consumption (>1.2 liters per day).
Cyclosporine
Atorvastatin and atorvastatin-metabolites are substrates of the OATP1B1 transporter. Inhibitors of the OATP1B1 (e.g., cyclosporine) can increase the bioavailability of atorvastatin. Atorvastatin AUC was significantly increased with concomitant administration of atorvastatin 10 mg and cyclosporine 5.2 mg/kg/day compared to that of atorvastatin alone (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY). In cases where co-administration of atorvastatin with cyclosporine is necessary, the dose of atorvastatin should not exceed 10 mg (see WARNINGS, Skeletal Muscle).
Rifampin or other Inducers of Cytochrome P450 3A4
Concomitant administration of atorvastatin with inducers of cytochrome P450 3A4 (e.g., efavirenz, rifampin) can lead to variable reductions in plasma concentrations of atorvastatin. Due to the dual interaction mechanism of rifampin, simultaneous co-administration of atorvastatin with rifampin is recommended, as delayed administration of atorvastatin after administration of rifampin has been associated with a significant reduction in atorvastatin plasma concentrations.
Digoxin
When multiple doses of atorvastatin and digoxin were co-administered, steady-state plasma digoxin concentrations increased by approximately 20%. Patients taking digoxin should be monitored appropriately.
Oral Contraceptives
Co-administration of atorvastatin and an oral contraceptive increased AUC values for norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY). These increases should be considered when selecting an oral contraceptive for a woman taking amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Studies with amlodipine
Rats and mice treated with amlodipine maleate in the diet for up to two years, at concentrations calculated to provide daily dosage levels of 0.5, 1.25, and 2.5 mg amlodipine/kg/day, showed no evidence of a carcinogenic effect of the drug. For the mouse, the highest dose was, on a mg/m2 basis, similar to the maximum recommended human dose of 10 mg amlodipine/day1. For the rat, the highest dose level was, on a mg/m2 basis, about twice the maximum recommended human dose1.
Mutagenicity studies conducted with amlodipine maleate revealed no drug related effects at either the gene or chromosome levels.
There was no effect on the fertility of rats treated orally with amlodipine maleate (males for 64 days and females for 14 days prior to mating) at doses up to 10 mg amlodipine/kg/day (8 times1 the maximum recommended human dose of 10 mg/day on a mg/m2 basis).
- 1 Based on patent weight of 50 kg.
Studies with atorvastatin
In a 2-year carcinogenicity study with atorvastatin calcium in rats at dose levels equivalent to 10, 30, and 100 mg atorvastatin/kg/day, 2 rare tumors were found in muscle in high-dose females: in one, there was a rhabdomyosarcoma and, in another, there was a fibrosarcoma. This dose represents a plasma AUC (0–24) value of approximately 16 times the mean human plasma drug exposure after an 80 mg oral dose.
A 2-year carcinogenicity study in mice given atorvastatin calcium at dose levels equivalent to 100, 200, and 400 mg atorvastatin/kg/day resulted in a significant increase in liver adenomas in high-dose males and liver carcinomas in high-dose females. These findings occurred at plasma AUC (0–24) values of approximately 6 times the mean human plasma drug exposure after an 80 mg oral dose.
In vitro, atorvastatin was not mutagenic or clastogenic in the following tests with and without metabolic activation: the Ames test with Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli, the HGPRT forward mutation assay in Chinese hamster lung cells, and the chromosomal aberration assay in Chinese hamster lung cells. Atorvastatin was negative in the in vivo mouse micronucleus test.
There were no effects on fertility when rats were given atorvastatin calcium at doses equivalent to up to 175 mg atorvastatin/kg/day (15 times the human exposure). There was aplasia and aspermia in the epididymides of 2 of 10 rats treated with atorvastatin calcium at a dose equivalent to 100 mg atorvastatin/kg/day for 3 months (16 times the human AUC at the 80 mg dose); testis weights were significantly lower at 30 and 100 mg/kg/day and epididymal weight was lower at 100 mg/kg/day. Male rats given the equivalent of 100 mg atorvastatin/kg/day for 11 weeks prior to mating had decreased sperm motility, spermatid head concentration, and increased abnormal sperm. Atorvastatin caused no adverse effects on semen parameters, or reproductive organ histopathology in dogs given doses of atorvastatin calcium equivalent to 10, 40, or 120 mg atorvastatin/kg/day for two years.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category X
(see CONTRAINDICATIONS)
Amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets contain atorvastatin and are therefore contraindicated in women who are pregnant or may become pregnant. The atorvastatin component of amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets should be administered to women of childbearing potential only when such patients are highly unlikely to conceive and have been informed of the potential hazards. If the woman becomes pregnant while taking amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets, it should be discontinued immediately and the patient advised again as to the potential hazards to the fetus, and the lack of known clinical benefit with continued use during pregnancy.
Serum cholesterol and triglycerides increase during normal pregnancy, and cholesterol products are essential for fetal development. Atherosclerosis is a chronic process, and discontinuation of lipid-lowering drugs during pregnancy should have little impact on long-term outcomes of primary hypercholesterolemia therapy.
Studies with amlodipine
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. No evidence of teratogenicity or other embryo/fetal toxicity was found when pregnant rats and rabbits were treated orally with amlodipine maleate at doses up to 10 mg amlodipine/kg/day (respectively 8 times2 and 23 times2 the maximum recommended human dose of 10 mg/day on a mg/m2 basis) during their respective periods of major organogenesis. However, litter size was significantly decreased (by about 50%) and the number of intrauterine deaths was significantly increased (about 5-fold) in rats receiving amlodipine maleate at 10 mg amlodipine/kg/day for 14 days before mating and throughout mating and gestation. Amlodipine maleate has been shown to prolong both the gestation period and the duration of labor in rats at this dose.
- 2 Based on patient weight of 50 kg.
Studies with atorvastatin
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of atorvastatin use during pregnancy. There have been rare reports of congenital anomalies following intrauterine exposure to statins. In a review of about 100 prospectively followed pregnancies in women exposed to other statins, the incidences of congenital anomalies, spontaneous abortions, and fetal deaths/stillbirths did not exceed the rate expected in the general population. However, this study was only able to exclude a three-to-four-fold increased risk of congenital anomalies over background incidence. In 89% of these cases, drug treatment started before pregnancy and stopped during the first trimester when pregnancy was identified.
Atorvastatin crosses the rat placenta and reaches a level in fetal liver equivalent to that of maternal plasma. Atorvastatin was not teratogenic in rats at doses of atorvastatin calcium equivalent to up to 300 mg atorvastatin/kg/day or in rabbits at doses of atorvastatin calcium equivalent to up to 100 mg atorvastatin/kg/day. These doses resulted in multiples of about 30 times (rat) or 20 times (rabbit) the human exposure based on surface area (mg/m2).
In a study in rats given atorvastatin calcium at doses equivalent to 20, 100, or 225 mg atorvastatin/kg/day, from gestation day 7 through to lactation day 21 (weaning), there was decreased pup survival at birth, neonate, weaning, and maturity for pups of mothers dosed with 225 mg/kg/day. Body weight was decreased on days 4 and 21 for pups of mothers dosed at 100 mg/kg/day; pup body weight was decreased at birth and at days 4, 21, and 91 at 225 mg/kg/day. Pup development was delayed (rotorod performance at 100 mg/kg/day and acoustic startle at 225 mg/kg/day; pinnae detachment and eye opening at 225 mg/kg/day). These doses of atorvastatin correspond to 6 times (100 mg/kg) and 22 times (225 mg/kg) the human AUC at 80 mg/day.
Labor and Delivery
No studies have been conducted in pregnant women on the effect of amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets, amlodipine or atorvastatin on the mother or the fetus during labor or delivery, or on the duration of labor or delivery. Amlodipine has been shown to prolong the duration of labor in rats.
Nursing Mothers
Studies with amlodipine
It is not known whether the amlodipine component of amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets is excreted in human milk.
Studies with atorvastatin
It is not known whether the atorvastatin component of amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets is excreted in human milk, but a small amount of another drug in this class does pass into breast milk. Nursing rat pups taking atorvastatin had plasma and liver drug levels of 50% and 40%, respectively, of that in their mother's milk. Animal breast milk drug levels may not accurately reflect human breast milk levels. Because another drug in this class passes into human milk and because statins have a potential to cause serious adverse reactions in nursing infants, women taking amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets, which includes atorvastatin, should be advised not to nurse their infants (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
Pediatric Use
There have been no studies conducted to determine the safety or effectiveness of amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets in pediatric populations.
Studies with amlodipine
The effect of amlodipine on blood pressure in patients less than 6 years of age is not known.
Studies with atorvastatin
Safety and effectiveness in patients 10–17 years of age with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia have been evaluated in controlled clinical trials of 6 months duration in adolescent boys and postmenarchal girls. Patients treated with atorvastatin had an adverse experience profile generally similar to that of patients treated with placebo, the most common adverse experiences observed in both groups, regardless of causality assessment, were infections. Doses greater than 20 mg have not been studied in this patient population. In this limited controlled study, there was no significant effect on growth or sexual maturation in boys or on menstrual cycle length in girls. See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Clinical Studies section; ADVERSE REACTIONS, Pediatric Patients; and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION, Pediatric Patients (10–17 years of age) with Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia. Adolescent females should be counseled on appropriate contraceptive methods while on atorvastatin therapy (see CONTRAINDICATIONS and PRECAUTIONS, Pregnancy). Atorvastatin has not been studied in controlled clinical trials involving pre-pubertal patients or patients younger than 10 years of age.
Clinical efficacy with doses of atorvastatin up to 80 mg/day for 1 year have been evaluated in an uncontrolled study of patients with homozygous FH including 8 pediatric patients. See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Clinical Studies, Atorvastatin Effects in Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia.
Geriatric Use
There have been no studies conducted to determine the safety or effectiveness of amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets in geriatric populations.
In studies with amlodipine
Clinical studies of amlodipine did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection of the amlodipine component of amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy. Elderly patients have decreased clearance of amlodipine with a resulting increase of AUC of approximately 40–60%, and a lower initial dose may be required (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
In studies with atorvastatin
Of the 39,828 patients who received atorvastatin calcium tablets in clinical studies, 15,813 (40%) were ≥65 years old and 2,800 (7%) were ≥75 years old. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older adults cannot be ruled out. Advanced age (≥65 years) is a predisposing factor for myopathy.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Amlodipine Besylate/Atorvastatin Calcium Tablets
Amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets have been evaluated for safety in 1092 patients in double-blind placebo-controlled studies treated for co-morbid hypertension and dyslipidemia. In general, treatment with amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets was well tolerated. For the most part, adverse experiences have been mild or moderate in severity. In clinical trials with amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets, no adverse experiences peculiar to this combination have been observed. Adverse experiences are similar in terms of nature, severity, and frequency to those reported previously with amlodipine and atorvastatin.
The following information is based on the clinical experience with amlodipine and atorvastatin.
The Amlodipine Component of Amlodipine Besylate/Atorvastatin Calcium Tablets
Amlodipine has been evaluated for safety in more than 11,000 patients in U.S. and foreign clinical trials. In general, treatment with amlodipine was well tolerated at doses up to 10 mg daily. Most adverse reactions reported during therapy with amlodipine were of mild or moderate severity. In controlled clinical trials directly comparing amlodipine (N=1730) at doses up to 10 mg to placebo (N=1250), discontinuation of amlodipine due to adverse reactions was required in only about 1.5% of patients and was not significantly different from placebo (about 1%). The most common side effects are headache and edema. The incidence (%) of side effects that occurred in a dose related manner are as follows:
Adverse Event amlodipine 2.5 mg
N=2755.0 mg
N=29610.0 mg
N=268Placebo
N=520Edema 1.8 3.0 10.8 0.6 Dizziness 1.1 3.4 3.4 1.5 Flushing 0.7 1.4 2.6 0.0 Palpitations 0.7 1.4 4.5 0.6 Other adverse experiences that were not clearly dose-related but were reported with an incidence greater than 1.0% in placebo-controlled clinical trials include the following:
Placebo-Controlled Studies
Adverse Event amlodipine (%)
(N=1730)Placebo (%)
(N=1250)Headache 7.3 7.8 Fatigue 4.5 2.8 Nausea 2.9 1.9 Abdominal Pain 1.6 0.3 Somnolence 1.4 0.6 For several adverse experiences that appear to be drug and dose-related, there was a greater incidence in women than men associated with amlodipine treatment as shown in the following table:
Adverse Event amlodipine Placebo M=%
(N=1218)F=%
(N=512)M=%
(N=914)F=%
(N=336)Edema 5.6 14.6 1.4 5.1 Flushing 1.5 4.5 0.3 0.9 Palpitations 1.4 3.3 0.9 0.9 Somnolence 1.3 1.6 0.8 0.3 The following events occurred in ≤1% but >0.1% of patients treated with amlodipine in controlled clinical trials or under conditions of open trials or marketing experience where a causal relationship is uncertain; they are listed to alert the physician to a possible relationship:
Cardiovascular: arrhythmia (including ventricular tachycardia and atrial fibrillation), bradycardia, chest pain, hypotension, peripheral ischemia, syncope, tachycardia, postural dizziness, postural hypotension, vasculitis.
Central and Peripheral Nervous System: hypoesthesia, neuropathy peripheral, paresthesia, tremor, vertigo.
Gastrointestinal: anorexia, constipation, dyspepsia,3 dysphagia, diarrhea, flatulence, pancreatitis, vomiting, gingival hyperplasia.
General: allergic reaction, asthenia,3 back pain, hot flushes, malaise, pain, rigors, weight gain, weight decrease.
Musculoskeletal System: arthralgia, arthrosis, muscle cramps,3 myalgia.
Psychiatric: sexual dysfunction (male3 and female), insomnia, nervousness, depression, abnormal dreams, anxiety, depersonalization.
Respiratory System: dyspnea,3 epistaxis.
Skin and Appendages: angioedema, erythema multiforme, pruritus,3 rash,3 rash erythematous, rash maculopapular.
Special Senses: abnormal vision, conjunctivitis, diplopia, eye pain, tinnitus.
Urinary System: micturition frequency, micturition disorder, nocturia.
Autonomic Nervous System: dry mouth, sweating increased.
Metabolic and Nutritional: hyperglycemia, thirst.
Hemopoietic: leukopenia, purpura, thrombocytopenia.
The following events occurred in ≤0.1% of patients treated with amlodipine in controlled clinical trials or under conditions of open trials or marketing experience: cardiac failure, pulse irregularity, extrasystoles, skin discoloration, urticaria, skin dryness, alopecia, dermatitis, muscle weakness, twitching, ataxia, hypertonia, migraine, cold and clammy skin, apathy, agitation, amnesia, gastritis, increased appetite, loose stools, coughing, rhinitis, dysuria, polyuria, parosmia, taste perversion, abnormal visual accommodation, and xerophthalmia.
Other reactions occurred sporadically and cannot be distinguished from medications or concurrent disease states such as myocardial infarction and angina.
Amlodipine therapy has not been associated with clinically significant changes in routine laboratory tests. No clinically relevant changes were noted in serum potassium, serum glucose, total triglycerides, total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, uric acid, blood urea nitrogen, or creatinine.
In the CAMELOT and PREVENT studies (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY Clinical Studies), the adverse event profile was similar to that reported previously (see above), with the most common adverse event being peripheral edema.
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of amlodipine. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
The following postmarketing event has been reported infrequently with amlodipine treatment where a causal relationship is uncertain: gynecomastia. In postmarketing experience, jaundice and hepatic enzyme elevations (mostly consistent with cholestasis or hepatitis), in some cases severe enough to require hospitalization, have been reported in association with use of amlodipine.
Amlodipine has been used safely in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, well-compensated congestive heart failure, coronary artery disease, peripheral vascular disease, diabetes mellitus, and abnormal lipid profiles.
- 3 These events occurred in less than 1% in placebo-controlled trials, but the incidence of these side effects was between 1% and 2% in all multiple-dose studies.
The Atorvastatin Component of Amlodipine Besylate/Atorvastatin Calcium Tablets
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the label:
Rhabdomyolysis and myopathy (see WARNINGS, Skeletal Muscle)
Liver enzyme abnormalities (see WARNINGS, Liver Dysfunction)
Clinical Adverse Experiences
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, the adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical studies of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
In the atorvastatin calcium tablets placebo-controlled clinical trial database of 16,066 patients (8755 atorvastatin calcium tablets vs. 7311 placebo; age range 10–93 years, 39% women, 91% Caucasians, 3% Blacks, 2% Asians, 4% other) with a median treatment duration of 53 weeks, 9.7% of patients on atorvastatin calcium tablets and 9.5% of the patients on placebo discontinued due to adverse reactions regardless of causality. The five most common adverse reactions in patients treated with atorvastatin calcium tablets that led to treatment discontinuation and occurred at a rate greater than placebo were: myalgia (0.7%), diarrhea (0.5%), nausea (0.4%), alanine aminotransferase increase (0.4%), and hepatic enzyme increase (0.4%).
The most commonly reported adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 2% and greater than placebo) regardless of causality, in patients treated with atorvastatin calcium tablets in placebo controlled trials (n=8755) were: nasopharyngitis (8.3%), arthralgia (6.9%), diarrhea (6.8%), pain in extremity (6.0%), and urinary tract infection (5.7%).
Table 13 summarizes the frequency of clinical adverse reactions, regardless of causality, reported in ≥ 2% and at a rate greater than placebo in patients treated with atorvastatin calcium tablets (n=8755), from seventeen placebo-controlled trials.
Table 13. Clinical adverse reactions occurring in ≥ 2% in patents treated with any dose of atorvastatin calcium tablets and at an incidence greater than placebo regardless of causality (% of patients). Adverse Reaction* Any dose
N=875510 mg
N=390820 mg
N=18840 mg
N=60480 mg
N=4055Placebo
N=7311- * Adverse Reaction ≥ 2% in any dose greater than placebo
Nasopharyngitis 8.3 12.9 5.3 7.0 4.2 8.2 Arthralgia 6.9 8.9 11.7 10.6 4.3 6.5 Diarrhea 6.8 7.3 6.4 14.1 5.2 6.3 Pain in extremity 6.0 8.5 3.7 9.3 3.1 5.9 Urinary tract infection 5.7 6.9 6.4 8.0 4.1 5.6 Dyspepsia 4.7 5.9 3.2 6.0 3.3 4.3 Nausea 4.0 3.7 3.7 7.1 3.8 3.5 Musculoskeletal pain 3.8 5.2 3.2 5.1 2.3 3.6 Muscle Spasms 3.6 4.6 4.8 5.1 2.4 3.0 Myalgia 3.5 3.6 5.9 8.4 2.7 3.1 Insomnia 3.0 2.8 1.1 5.3 2.8 2.9 Pharyngolaryngeal pain 2.3 3.9 1.6 2.8 0.7 2.1 Other adverse reactions reported in placebo-controlled studies include:
Body as a whole:malaise, pyrexia; Digestive system: abdominal discomfort, eructation, flatulence, hepatitis, cholestasis; Musculoskeletal system: musculoskeletal pain, muscle fatigue, neck pain, joint swelling; Metabolic and nutritional system: transaminases increase, liver function test abnormal, blood alkaline phosphatase increase, creatine phosphokinase increase, hyperglycemia; Nervous system: nightmare; Respiratory system: epistaxis; Skin and appendages: urticaria; Special senses: vision blurred, tinnitus; Urogenital system: white blood cells urine positive.
Anglo-Scandinavian Cardiac Outcomes Trial (ASCOT)
In ASCOT (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Clinical Studies, Clinical Studies with Atorvastatin) involving 10,305 participants (age range 40–80 years, 19% women; 94.6% Caucasians, 2.6% Africans, 1.5% South Asians, 1.3% mixed/other) treated with atorvastatin 10 mg daily (n=5,168) or placebo (n=5,137), the safety and tolerability profile of the group treated with atorvastatin was comparable to that of the group treated with placebo during a median of 3.3 years of follow-up.
Collaborative Atorvastatin Diabetes Study (CARDS)
In CARDS (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Clinical Studies, Clinical Studies with Atorvastatin) involving 2838 subjects (age range 39–77 years, 32% women; 94.3% Caucasians, 2.4% South Asians, 2.3% Afro-Caribbean, 1.0% other)with type 2 diabetes treated with atorvastatin calcium tablets 10 mg daily (n=1428) or placebo (n=1410), there was no difference in the overall frequency of adverse reactions or serious adverse reactions between the treatment groups during a median follow-up of 3.9 years. No cases of rhabdomyolysis were reported.
Treating to New Targets Study (TNT)
In TNT (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Clinical Studies) involving 10,001 subjects (age range 29–78 years, 19% women; 94.1% Caucasians, 2.9% Blacks, 1.0% Asians, 2.0% other) with clinically evident CHD treated with atorvastatin calcium tablets 10 mg daily (n=5006) or atorvastatin calcium tablets 80 mg daily (n=4995), there were more serious adverse reactions and discontinuations due to adverse reactions in the high-dose atorvastatin group (92, 1.8%; 497, 9.9%, respectively) as compared to the low-dose group (69, 1.4%; 404, 8.1%, respectively) during a median follow-up of 4.9 years. Persistent transaminase elevations (≥3 × ULN twice within 4–10 days) occurred in 62 (1.3%) individuals with atorvastatin 80 mg and in nine (0.2%) individuals with atorvastatin 10 mg. Elevations of CK (≥ 10 × ULN) were low overall, but were higher in the high-dose atorvastatin treatment group (13, 0.3%) compared to the low-dose atorvastatin group (6, 0.1%).
Incremental Decrease in Endpoints Through Aggressive Lipid Lowering Study (IDEAL)
In IDEAL (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Clinical Studies) involving 8,888 subjects (age range 26–80 years, 19% women; 99.3% Caucasians, 0.4% Asians, 0.3% Blacks, 0.04% other) treated with atorvastatin calcium tablets 80 mg/day (n=4439) or simvastatin 20–40 mg daily (n=4449), there was no difference in the overall frequency of adverse reactions or serious adverse reactions between the treatment groups during a median follow-up of 4.8 years.
Stroke Prevention by Aggressive Reduction in Cholesterol Levels (SPARCL)
In SPARCL involving 4731 subjects (age range 21–92 years, 40% women; 93.3% Caucasians, 3.0% Blacks, 0.6% Asians, 3.1% other) without clinically evident CHD but with a stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA) within the previous 6 months treated with atorvastatin calcium tablets 80 mg (n=2365) or placebo (n=2366) for a median follow-up of 4.9 years, there was a higher incidence of persistent hepatic transaminase elevations (≥ 3 × ULN twice within 4–10 days) in the atorvastatin group (0.9%) compared to placebo (0.1%). Elevations of CK (>10 × ULN) were rare, but were higher in the atorvastatin group (0.1%) compared to placebo (0.0%). Diabetes was reported as an adverse reaction in 144 subjects (6.1%) in the atorvastatin group and 89 subjects (3.8%) in the placebo group (see PRECAUTIONS).
In a post-hoc analysis, atorvastatin calcium tablets 80 mg reduced the incidence of ischemic stroke (218/2365, 9.2% vs. 274/2366, 11.6%) and increased the incidence of hemorrhagic stroke (55/2365, 2.3% vs. 33/2366, 1.4%) compared to placebo. The incidence of fatal hemorrhagic stroke was similar between groups (17 atorvastatin calcium tablets vs. 18 placebo). The incidence of non-fatal hemorrhagic strokes was significantly greater in the atorvastatin group (38 non-fatal hemorrhagic strokes) as compared to the placebo group (16 non-fatal hemorrhagic strokes). Subjects who entered the study with a hemorrhagic stroke appeared to be at increased risk for hemorrhagic stroke [7 (16%) atorvastatin calcium tablets vs. 2 (4%) placebo].
There were no significant differences between the treatment groups for all-cause mortality: 216 (9.1%) in the atorvastatin calcium tablets 80 mg/day group vs. 211 (8.9%) in the placebo group. The proportions of subjects who experienced cardiovascular death were numerically smaller in the atorvastatin calcium tablets 80 mg group (3.3%) than in the placebo group (4.1%). The proportions of subjects who experienced non-cardiovascular death were numerically larger in the atorvastatin calcium tablets 80 mg group (5.0%) than in the placebo group (4.0%).
Postintroduction Reports with Atorvastatin
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of the atorvastatin component of amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Adverse reactions associated with atorvastatin therapy reported since market introduction, that are not listed above, regardless of causality assessment, include the following: anaphylaxis, angioneurotic edema, bullous rashes (including erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and toxic epidermal necrolysis), rhabdomyolysis, fatigue, tendon rupture, hepatic failure, dizziness, memory impairment, depression, and peripheral neuropathy.
Pediatric Patients (ages 10–17 years)
In a 26-week controlled study in boys and postmenarchal girls (n=140, 31% female; 92% Caucasians, 1.6% Blacks, 1.6% Asians, 4.8% other), the safety and tolerability profile of atorvastatin 10 to 20 mg daily was generally similar to that of placebo (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Clinical Studies section and PRECAUTIONS, Pediatric Use).
-
OVERDOSAGE
There is no information on overdosage with amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets in humans.
Information on Amlodipine
Overdosage might be expected to cause excessive peripheral vasodilation with marked hypotension and possibly a reflex tachycardia. In humans, experience with intentional overdosage of amlodipine is limited.
Single oral doses of amlodipine maleate equivalent to 40 mg amlodipine/kg and 100 mg amlodipine/kg in mice and rats, respectively, caused deaths. Single oral amlodipine maleate doses equivalent to 4 or more mg amlodipine/kg in dogs (11 or more times the maximum recommended clinical dose on a mg/m2 basis) caused a marked peripheral vasodilation and hypotension.
If overdose should occur, initiate active cardiac and respiratory monitoring. Perform frequent blood pressure measurements. Should hypotension occur, provide cardiovascular support including elevation of the extremities and administration of fluids. If hypotension remains unresponsive to these conservative measures, consider administration of vasopressors (such as phenylephrine) with specific attention to circulating volume and urine output. As amlodipine is highly protein bound, hemodialysis is not likely to be of benefit.
Information on Atorvastatin
There is no specific treatment for atorvastatin overdosage. In the event of an overdose, the patient should be treated symptomatically, and supportive measures instituted as required. Due to extensive drug binding to plasma proteins, hemodialysis is not expected to significantly enhance atorvastatin clearance.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Dosage of amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets must be individualized on the basis of both effectiveness and tolerance for each individual component in the treatment of hypertension/angina and hyperlipidemia.
Amlodipine (Hypertension or angina)
Adults
The usual initial antihypertensive oral dose of amlodipine is 5 mg once daily with a maximum dose of 10 mg once daily. Small, fragile, or elderly patients, or patients with hepatic insufficiency may be started on 2.5 mg once daily and this dose may be used when adding amlodipine to other antihypertensive therapy.
Adjust dosage according to each patient's need. In general, titration should proceed over 7 to 14 days so that the physician can fully assess the patient's response to each dose level. Titration may proceed more rapidly, however, if clinically warranted, provided the patient is assessed frequently.
The recommended dose of amlodipine for chronic stable or vasospastic angina is 5–10 mg, with the lower dose suggested in the elderly and in patients with hepatic insufficiency. Most patients will require 10 mg for adequate effect (see ADVERSE REACTIONS).
The recommended dose range of amlodipine for patients with coronary artery disease is 5–10 mg once daily. In clinical studies the majority of patients required 10 mg (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Clinical studies).
Children
The effective antihypertensive oral dose of amlodipine in pediatric patients ages 6–17 years is 2.5 mg to 5 mg once daily. Doses in excess of 5 mg daily have not been studied in pediatric patients (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY).
Atorvastatin (Hyperlipidemia)
Hyperlipidemia (Heterozygous Familial and Nonfamilial) and Mixed Dyslipidemia (Fredrickson Types IIa and IIb)
The recommended starting dose of atorvastatin is 10 or 20 mg once daily. Patients who require a large reduction in LDL-C (more than 45%) may be started at 40 mg once daily. The dosage range of atorvastatin is 10 to 80 mg once daily. Atorvastatin can be administered as a single dose at any time of the day, with or without food. The starting dose and maintenance doses of atorvastatin should be individualized according to patient characteristics such as goal of therapy and response (see current NCEP Guidelines). After initiation and/or upon titration of atorvastatin, lipid levels should be analyzed within 2 to 4 weeks and dosage adjusted accordingly.
Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia in Pediatric Patients (10–17 years of age)
The recommended starting dose of atorvastatin is 10 mg/day; the maximum recommended dose is 20 mg/day (doses greater than 20 mg have not been studied in this patient population). Doses should be individualized according to the recommended goal of therapy (see current NCEP Pediatric Panel Guidelines4, CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, and INDICATIONS AND USAGE). Adjustments should be made at intervals of 4 weeks or more.
- 4 National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP): Highlights of the Report of the Expert Panel on Blood Cholesterol Levels in Children Adolescents. Pediatrics. 89(3):495–501. 1992.
Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia
The dosage of atorvastatin in patients with homozygous FH is 10 to 80 mg daily. Atorvastatin should be used as an adjunct to other lipid-lowering treatments (e.g., LDL apheresis) in these patients or if such treatments are unavailable. Note: a 2.5/80 mg amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablet is not available. Management of patients needing a 2.5/80 mg combination requires individual assessments of dyslipidemia and therapy with the individual components as a 2.5/80 mg amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablet is not available.
Concomitant Lipid Lowering Therapy
Atorvastatin may be used with bile acid resins. Monitor for signs of myopathy in patients receiving the combination of statins and fibrates (see WARNINGS, Skeletal Muscle, and PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions).
Dosage in Patients With Renal Impairment
Renal disease does not affect the plasma concentrations nor LDL-C reduction of atorvastatin; thus, dosage adjustment in patients with renal dysfunction is not necessary (see WARNINGS, Skeletal Muscle, and CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Specific Populations).
Dosage in Patients Taking Cyclosporine, Clarithromycin, Itraconazole, or a Combination of Ritonavir plus Saquinavir or Lopinavir plus Ritonavir
In patients taking cyclosporine, therapy should be limited to atorvastatin calcium tablets 10 mg once daily. In patients taking clarithromycin, itraconazole or in patients with HIV taking a combination of ritonavir plus saquinavir or lopinavir plus ritonavir, for doses of atorvastatin exceeding 20 mg, appropriate clinical assessment is recommended to ensure that the lowest dose necessary of atorvastatin is employed (see WARNINGS, Skeletal Muscle, and PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions).
Amlodipine Besylate/Atorvastatin Calcium Tablets
Amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets may be substituted for their individually titrated components. Patients may be given the equivalent dose of amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets or a dose of amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets with increased amounts of amlodipine, atorvastatin, or both for additional antianginal effects, blood pressure lowering, or lipid lowering effect.
Amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets may be used to provide additional therapy for patients already on one of their components. As initial therapy for one indication and continuation of treatment of the other, the recommended starting dose of amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets should be selected based on the continuation of the component being used and the recommended starting dose for the added monotherapy.
Amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets may be used to initiate treatment in patients with hyperlipidemia and either hypertension or angina. The recommended starting dose of amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets should be based on the appropriate combination of recommendations for the monotherapies. The maximum dose of the amlodipine component of amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets is 10 mg once daily. The maximum dose of the atorvastatin component of amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets is 80 mg once daily.
See above for detailed information related to the dosing and administration of amlodipine and atorvastatin.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets contain amlodipine besylate and atorvastatin calcium equivalent to amlodipine and atorvastatin in the dose strengths described below.
Amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets are differentiated by tablet color/size and have a unique number on one side and are blank on the other side. Amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets are supplied for oral administration in the following strengths and package configurations:
Table 14. Amlodipine Besylate/Atorvastatin Calcium Tablets Packaging Configurations Amlodipine Besylate/Atorvastatin Calcium Tablets Package Configuration Tablet Strength (amlodipine besylate/ atorvastatin calcium) mg NDC # Engraving Tablet Color Bottle of 30 10/80 54868-6335-0 AAT 108 Blue Bottle of 90
10/80
54868-6335-1
AAT 108
Blue
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PATIENT INFORMATION
AMLODIPINE BESYLATE/ATORVASTATIN CALCIUM TABLETS
Read the patient information that comes with amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets before you start taking them, and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not replace talking with your doctor about your condition or treatment. If you have any questions about amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
What are amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets?
Amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets are a prescription drug that combines amlodipine besylate and atorvastatin calcium in one pill.
Amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets are used in adults who need both amlodipine besylate and atorvastatin calcium.
Amlodipine besylate tablets are used to treat:
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Chest pain (angina)
- Blocked arteries of the heart (coronary artery disease)
Atorvastatin calcium tablets are used to lower the levels of "bad" cholesterol and triglycerides in your blood. They can also raise the levels of "good" cholesterol.
Atorvastatin calcium tablets are also used to lower the risk for heart attack, stroke, certain types of heart surgery, and chest pain in patients who have heart disease or risk factors for heart disease such as:
- age, smoking, high blood pressure, low HDL-C, heart disease in the family
Atorvastatin calcium tablets can lower the risk for heart attack or stroke in patients with diabetes and risk factors such as:
- diabetic eye or kidney problems, smoking, or high blood pressure.
Amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets have not been studied in children.
Who should not use amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets?
Do not use amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets if you:
- Are pregnant or think you may be pregnant, or are planning to become pregnant. Amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets may harm your unborn baby. If you get pregnant, stop taking amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets and call your doctor right away.
- Are breastfeeding. Amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets can pass into your breast milk and may harm your baby. Do not breastfeed if you take amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets.
- Have liver problems.
- Are allergic to anything in amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets. The active ingredients are atorvastatin calcium and amlodipine besylate. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients.
What should I tell my doctor before taking amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets?
Tell your doctor about all of your health conditions, including, if you have:
- heart disease
- muscle aches or weakness
- diabetes
- thyroid problems
- kidney problems
- or drink more than 2 glasses of alcohol daily
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins and herbal supplements. Amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets and some other medicines can interact, causing serious side effects. Especially tell your doctor if you take medicines for:
- your immune system
- infections
- cholesterol
- birth control
- heart failure
- HIV (AIDS)
You can use nitroglycerin and amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets together. If you take nitroglycerin for chest pain (angina), do not stop taking it while taking amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets.
Know all the medicines you take. Keep a list of them with you to show your doctor and pharmacist.
How should I take amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets?
- Take amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets once a day, exactly as your doctor tells you. Do not change your dose or stop amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets without talking to your doctor.
- Take amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets each day at any time of day, at about the same time each day. Amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets can be taken with or without food.
- Do not break the tablets before taking them. Talk to your doctor if you have a problem swallowing pills.
- Your doctor should start you on a low-fat diet before giving you amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets. Stay on this low-fat diet when you take amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets.
- Amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets come in many different strengths. Your doctor will test your cholesterol and blood pressure to find the right dose for you.
- If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. Do not take amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets if it has been more than 12 hours since your missed dose. Just take the next dose at your regular time. Do not take 2 doses of amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets at the same time.
- If too many amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets are taken by accident, call your doctor or poison control center, or go to the nearest emergency room.
What should I avoid while taking amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets?
- Avoid getting pregnant. If you get pregnant, stop taking amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets right away and call your doctor.
- Do not breastfeed. Amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets can pass into your breast milk and may harm your baby.
What are possible side effects of amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets?
Amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets can cause serious side effects. These side effects happen only to a small number of people. Your doctor can monitor you for them. These side effects usually go away if your dose is lowered or amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets are stopped. These serious side effects include:
-
- Muscle problems. Amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets can cause serious muscle problems that can lead to kidney problems, including kidney failure. You have a higher chance for muscle problems if you are taking certain other medicines with amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets.
- Liver problems. Amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets can cause liver problems. Your doctor may do blood tests to check your liver before you start taking amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets and while you take them.
- Call your doctor right away if:
-
- you have muscle problems like weakness, tenderness, or pain that happen without a good reason, especially if you also have a fever or feel more tired than usual
- allergic reactions including swelling of the face, lips, tongue, and/or throat that may cause difficulty in breathing or swallowing which may require treatment right away.
- you have nausea and vomiting, stomach pain
- you are passing brown or dark-colored urine
- you feel more tired than usual
- your skin and white of your eyes get yellow
- allergic skin reactions.
- Chest pain that does not go away or gets worse. Sometimes, when you start amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets or increase your dose, chest pain can get worse or a heart attack can happen. If this happens, call your doctor or go to the emergency room right away.
Common side effects of amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets include:
- headache
- tiredness
- stomach pain
- upset stomach
- dizziness
- extreme sleepiness
- nausea
- diarrhea
- swelling of your legs or ankles (edema)
- hot or warm feeling in your face (flushing)
- irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia)
- very fast heartbeat (heart palpitations)
- muscle and joint pain
- alterations in some laboratory blood tests
Additional side effects have been reported: tendon problems.
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist about side effects that bother you or do not go away.
There are other side effects of amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for a complete list.
How do I store amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets?
- Store amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets at room temperature, 68 to 77°F (20 to 25°C).
- Do not keep medicine that is out-of-date or that you no longer need.
- Keep amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets and all medicines out of the reach of children. Keep medicines in places where children cannot get it.
General information about amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for conditions that are not mentioned in patient information leaflets. Do not use amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets to other people, even if they have the same problem you have. It may harm them.
This leaflet summarizes the most important information about amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets. If you want more information, talk with your doctor. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets written for health professionals. You can also call Ranbaxy at 1-888-RANBAXY (1-888-726-2299).
What is high blood pressure (hypertension)?
You have high blood pressure when the force of blood against the walls of your arteries stays high. This can damage your heart and other parts of your body. Drugs that lower blood pressure lower your risk of having a stroke or heart attack.
What is angina (chest pain)?
Angina is a pain that keeps coming back when part of your heart does not get enough blood. It feels like something is pressing or squeezing your chest under the breastbone. Sometimes you can feel it in your shoulders, arms, neck, jaw, or back.
What is cholesterol?
Cholesterol is a fat-like substance made in your body. It is also found in foods. You need some cholesterol for good health, but too much is not good for you. Cholesterol can clog your blood vessels.
What is a heart attack?
A heart attack occurs when heart muscle does not get enough blood. Symptoms include chest pain, trouble breathing, nausea, and weakness. Heart muscle cells may be damaged or die. The heart cannot pump well or may stop beating.
What is a stroke?
A stroke occurs when nerve cells in the brain do not get enough blood. The cells may be damaged or die. The damaged cells may cause weakness or problems speaking or thinking.
What are the ingredients in amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium tablets?
Active ingredients: amlodipine besylate, atorvastatin calcium
Inactive ingredients: calcium carbonate, croscarmellose sodium, microcrystalline cellulose, pregelatinized starch, polysorbate 80, hydroxypropyl cellulose, purified water, colloidal silicon dioxide (anhydrous), magnesium stearate
Film coating: Opadry® II White 85F28751 (polyvinyl alcohol, titanium dioxide, PEG 3000, and talc) or Opadry® II Blue 85F10919 (polyvinyl alcohol, titanium dioxide, PEG 3000, talc, and FD&C blue #2)
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 mg/80 mg Tablet Label
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
AMLODIPINE BESYLATE AND ATORVASTATIN CALCIUM
amlodipine besylate and atorvastatin calcium tablet, film coatedProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 54868-6335(NDC: 63304-603) Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength amlodipine besylate (UNII: 864V2Q084H) (amlodipine - UNII:1J444QC288) amlodipine 10 mg atorvastatin calcium (UNII: 48A5M73Z4Q) (atorvastatin - UNII:A0JWA85V8F) atorvastatin 80 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength calcium carbonate (UNII: H0G9379FGK) croscarmellose sodium (UNII: M28OL1HH48) cellulose, microcrystalline (UNII: OP1R32D61U) polysorbate 80 (UNII: 6OZP39ZG8H) hydroxypropyl cellulose (UNII: RFW2ET671P) water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) silicon dioxide (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) magnesium stearate (UNII: 70097M6I30) polyvinyl alcohol (UNII: 532B59J990) titanium dioxide (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) polyethylene glycol 3000 (UNII: SA1B764746) talc (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) FD&C Blue No. 2 (UNII: L06K8R7DQK) Product Characteristics Color BLUE Score no score Shape OVAL Size 17mm Flavor Imprint Code AAT;108 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 54868-6335-0 30 in 1 BOTTLE 2 NDC: 54868-6335-1 90 in 1 BOTTLE Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA AUTHORIZED GENERIC NDA021540 03/08/2012 Labeler - Physicians Total Care, Inc. (194123980) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Physicians Total Care, Inc. 194123980 relabel
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.