Calcium Gluconate Injection USP
Calcium Gluconate by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Calcium Gluconate by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by A-S Medication Solutions. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
CALCIUM GLUCONATE - calcium gluconate injection, solution
A-S Medication Solutions
Disclaimer: This drug has not been found by FDA to be safe and effective, and this labeling has not been approved by FDA. For further information about unapproved drugs, click here.
----------
Calcium Gluconate Injection USP
DESCRIPTION:
Calcium Gluconate Injection, USP is a sterile, nonpyrogenic, supersaturated solution of calcium gluconate for intravenous use only.
Each mL contains: Calcium gluconate 94 mg; calcium saccharate (tetrahydrate) 4.5 mg; water for injection q.s. Hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide may have been added for pH adjustment (6.0 to 8.2).
Calcium saccharate provides 6% of the total calcium and stabilizes the supersaturated solution of calcium gluconate.
Each 10 mL of the injection provides 93 mg elemental calcium (Ca++) equivalent to 1 g of calcium gluconate.
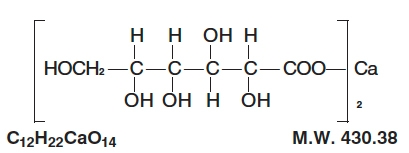
The structural formula is:
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY:
Calcium is the fifth most abundant element in the body and is essential for maintenance of the functional integrity of nervous, muscular and skeletal systems, cell membranes and capillary permeability. It is also an important activator in many enzymatic reactions and is essential to a number of physiologic processes including transmission of nerve impulses; contraction of cardiac, smooth and skeletal muscles; renal function; respiration; and blood coagulation. Calcium also plays regulatory roles in the release and storage of neurotransmitters and hormones; in the uptake and binding of amino acids; in cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12) absorption; and gastrin secretion.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE:
Calcium Gluconate Injection, USP is used to treat conditions arising from calcium deficiencies such as hypocalcemic tetany, hypocalcemia related to hypoparathyroidism and hypocalcemia due to rapid growth or pregnancy. It is also used in the treatment of black widow spider bites to relieve muscle cramping and as an adjunct in the treatment of rickets, osteomalacia, lead colic and magnesium sulfate overdosage. Calcium gluconate has also been employed to decrease capillary permeability in allergic conditions, nonthrombocytopenic purpura and exudative dermatoses such as dermatitis herpetiformis and for pruritus of eruptions caused by certain drugs. In hyperkalemia, calcium gluconate may aid in antagonizing the cardiac toxicity, provided the patient is not receiving digitalis therapy.
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
Calcium salts are contraindicated in patients with ventricular fibrillation or hypercalcemia. Intravenous administration of calcium is contraindicated when serum calcium levels are above normal.
WARNINGS:
For intravenous use only. Subcutaneous or intramuscular injection may cause severe necrosis and sloughing.
WARNING: This product contains aluminum that may be toxic. Aluminum may reach toxic levels with prolonged parenteral administration if kidney function is impaired. Premature neonates are particularly at risk because their kidneys are immature, and they require large amounts of calcium and phosphate solutions, which contain aluminum.
Research indicates that patients with impaired kidney function, including premature neonates, who receive parenteral levels of aluminum at greater than 4 to 5 mcg/kg/day accumulate aluminum at levels associated with central nervous system and bone toxicity. Tissue loading may occur at even lower rates of administration.
PRECAUTIONS:
General
To avoid undesirable reactions that may follow rapid intravenous administration of calcium gluconate, the drug should be given slowly, e.g., approximately 1.5 mL over a period of one minute. When injected intravenously, calcium gluconate should be injected through a small needle into a large vein in order to avoid too rapid an increase in serum calcium and extravasation of calcium solution into the surrounding tissue with resultant necrosis.
Rapid injection of calcium gluconate may cause vasodilation, decreased blood pressure, bradycardia, cardiac arrhythmias, syncope and cardiac arrest.
Because of the danger involved in simultaneous use of calcium salts and drugs of the digitalis group, a digitalized patient should not receive an intravenous injection of a calcium compound unless indications are clearly defined.
Drug Interactions
The inotropic and toxic effects of cardiac glycosides and calcium are synergistic, and arrhythmias may occur if these drugs are given together (particularly when calcium is given intravenously). Intravenous administration of calcium should be avoided in patients receiving cardiac glycosides; if necessary, calcium should be given slowly in small amounts.
Calcium complexes tetracycline antibiotics rendering them inactive. The two drugs should not be given at the same time orally nor should they be mixed for parenteral administration.
Calcium gluconate injection has been reported to be incompatible with intravenous solutions containing various drugs. Published data are too varied and/or limited to permit generalizations, and specialized reference should be consulted for specific information.
Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
Transient elevations of plasma 11-hydroxycorticosteroid levels (Glenn-Nelson technique) may occur when intravenous calcium is administered but levels return to control values after one hour. In addition, intravenous calcium gluconate can produce false-negative values for serum and urinary magnesium.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects: Pregnancy Category C—
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with calcium gluconate. It is also not known whether calcium gluconate can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Calcium gluconate should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
ADVERSE REACTIONS:
Patients may complain of tingling sensations, a sense of oppression or heat waves and a calcium or chalky taste following the intravenous administration of calcium gluconate.
Rapid intravenous injection of calcium salts may cause vasodilation, decreased blood pressure, bradycardia, cardiac arrhythmias, syncope and cardiac arrest. Use in digitalized patients may precipitate arrhythmias.
Local necrosis and abscess formation may occur with intramuscular injection.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION:
The dose is dependent on the requirements of the individual patient. Intravenous calcium gluconate injection must be administered slowly.
Usual Dosage
Adults—500 mg to 2 g (5 to 20 mL)
Pediatric patients—200 to 500 mg (2 to 5 mL)
Infants—Not more than 200 mg (not more than 2 mL)
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
| CALCIUM GLUCONATE
calcium gluconate injection, solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - A-S Medication Solutions (830016429) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| A-S Medication Solutions | 830016429 | RELABEL(50090-2362) | |

