ZEGALOGUE- dasiglucagon injection, solution
Zegalogue by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Zegalogue by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Novo Nordisk. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ZEGALOGUE® safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ZEGALOGUE.
ZEGALOGUE (dasiglucagon) injection, for subcutaneous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2021INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ZEGALOGUE is an antihypoglycemic agent indicated for the treatment of severe hypoglycemia in pediatric and adult patients with diabetes aged 6 years and above. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- ZEGALOGUE autoinjector and prefilled syringe are for subcutaneous injection only. (2.1)
- The dose in adults and pediatric patients aged 6 years and older is 0.6 mg. (2.2)
- Administer ZEGALOGUE according to the printed instructions on the protective case label and the Instructions For Use. (2.1)
- Visually inspect ZEGALOGUE prior to administration. The solution should appear clear, colorless, and free from particles. If the solution is discolored or contains particulate matter, do not use. (2.1)
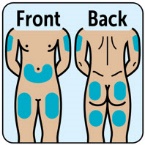
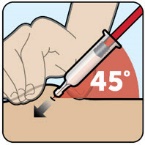
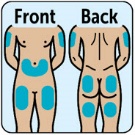
- Administer the injection into the lower abdomen, buttocks, thigh, or outer upper arm. (2.1)
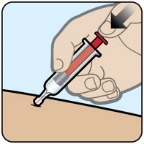
- Call for emergency assistance immediately after administering the dose. (2.1)
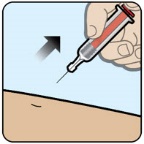
- If there has been no response after 15 minutes, an additional dose of ZEGALOGUE from a new device may be administered while waiting for emergency assistance. (2.1)
- When the patient has responded to treatment, give oral carbohydrates. (2.1)
- Do not attempt to reuse ZEGALOGUE. Each device contains a single dose of dasiglucagon and cannot be reused. (2.1)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Substantial Increase in Blood Pressure in Patients with Pheochromocytoma: Contraindicated in patients with pheochromocytoma because ZEGALOGUE may stimulate the release of catecholamines from the tumor. (4, 5.1)
- Hypoglycemia in Patients with Insulinoma: In patients with insulinoma, administration may produce an initial increase in blood glucose, but ZEGALOGUE may stimulate exaggerated insulin release from an insulinoma and cause subsequent hypoglycemia. If a patient develops symptoms of hypoglycemia after a dose of ZEGALOGUE, give glucose orally or intravenously. (4, 5.2)
- Hypersensitivity and Allergic Reactions: Allergic reactions have been reported with glucagon products and may include generalized rash, and in some cases anaphylactic shock with breathing difficulties and hypotension. (5.3)
- Lack of Efficacy in Patients with Decreased Hepatic Glycogen: ZEGALOGUE is effective in treating hypoglycemia only if sufficient hepatic glycogen is present. Patients in states of starvation, with adrenal insufficiency or chronic hypoglycemia may not have adequate levels of hepatic glycogen for ZEGALOGUE to be effective. Patients with these conditions should be treated with glucose. (5.4)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions (≥2%) associated with ZEGALOGUE are:
Adults: nausea, vomiting, headache, diarrhea, and injection site pain
Pediatrics: nausea, vomiting, headache, and injection site pain (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Novo Nordisk Inc., at 1-800-727-6500 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Beta-blockers: Patients taking beta-blockers may have a transient increase in pulse and blood pressure. (7)
- Indomethacin: In patients taking indomethacin, ZEGALOGUE may lose its ability to raise blood glucose or may produce hypoglycemia. (7)
- Warfarin: ZEGALOGUE may increase the anticoagulant effect of warfarin. (7)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 1/2023
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Administration Instructions
2.2 Recommended Dosage
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Substantial Increase in Blood Pressure in Patients with Pheochromocytoma
5.2 Hypoglycemia in Patients with Insulinoma
5.3 Hypersensitivity and Allergic Reactions
5.4 Lack of Efficacy in Patients with Decreased Hepatic Glycogen
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Immunogenicity
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Adult Patients
14.2 Pediatric Patients
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
16.2 Recommended Storage
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Administration Instructions
ZEGALOGUE autoinjector and prefilled syringe are for subcutaneous injection only.
Instruct patients and their caregivers on the signs and symptoms of severe hypoglycemia. Because severe hypoglycemia requires the help of others to recover, instruct the patient to inform those around them about ZEGALOGUE and its Instructions For Use. Administer ZEGALOGUE as soon as possible when severe hypoglycemia is recognized.
Instruct the patient or caregiver to read the Instructions For Use at the time they receive a prescription for ZEGALOGUE. Emphasize the following instructions to the patient or caregiver:
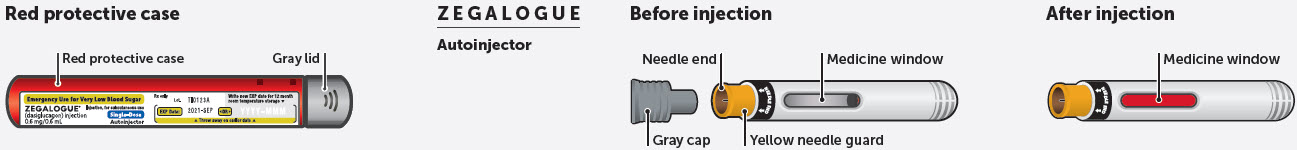
- Administer ZEGALOGUE according to the printed instructions on the protective case label and the Instructions For Use.
- Visually inspect ZEGALOGUE prior to administration. The solution should appear clear, colorless, and free from particles. If the solution is discolored or contains particulate matter, do not use.
- Administer the injection in the lower abdomen, buttocks, thigh, or outer upper arm.
- Call for emergency assistance immediately after administering the dose.
- If there has been no response after 15 minutes, an additional dose of ZEGALOGUE may be administered while waiting for emergency assistance.
- When the patient has responded to treatment, give oral carbohydrates to restore liver glycogen and prevent recurrence of hypoglycemia.
- Do not attempt to reuse ZEGALOGUE. Each ZEGALOGUE device contains a single dose of dasiglucagon and cannot be reused.
2.2 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dose of ZEGALOGUE in adults and pediatric patients aged 6 years and older is 0.6 mg administered by subcutaneous injection into the lower abdomen, buttocks, thigh, or outer upper arm.
If there has been no response after 15 minutes, an additional 0.6 mg dose of ZEGALOGUE from a new device may be administered.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
ZEGALOGUE is contraindicated in patients with:
- Pheochromocytoma because of the risk of substantial increase in blood pressure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Insulinoma because of the risk of hypoglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Substantial Increase in Blood Pressure in Patients with Pheochromocytoma
ZEGALOGUE is contraindicated in patients with pheochromocytoma because glucagon products may stimulate the release of catecholamines from the tumor [see Contraindications (4)]. If the patient develops a substantial increase in blood pressure and a previously undiagnosed pheochromocytoma is suspected, 5 to 10 mg of phentolamine mesylate, administered intravenously, has been shown to be effective in lowering blood pressure.
5.2 Hypoglycemia in Patients with Insulinoma
In patients with insulinoma, administration of glucagon products may produce an initial increase in blood glucose; however, ZEGALOGUE administration may directly or indirectly (through an initial rise in blood glucose) stimulate exaggerated insulin release from an insulinoma and cause hypoglycemia. ZEGALOGUE is contraindicated in patients with insulinoma [see Contraindications (4)]. If a patient develops symptoms of hypoglycemia after a dose of ZEGALOGUE, give glucose orally or intravenously.
5.3 Hypersensitivity and Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions have been reported with glucagon products; these include generalized rash, and in some cases anaphylactic shock with breathing difficulties and hypotension. Advise patients to seek immediate medical attention if they experience any symptoms of serious hypersensitivity reactions.
5.4 Lack of Efficacy in Patients with Decreased Hepatic Glycogen
ZEGALOGUE is effective in treating hypoglycemia only if sufficient hepatic glycogen is present. Patients in states of starvation, with adrenal insufficiency or chronic hypoglycemia may not have adequate levels of hepatic glycogen for ZEGALOGUE administration to be effective. Patients with these conditions should be treated with glucose.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following important adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hypersensitivity and Allergic Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of ZEGALOGUE cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In clinical trials, 316 adult patients with type 1 diabetes and 20 pediatric patients with type 1 diabetes were exposed to ZEGALOGUE.
The data in Table 1 reflect exposure of 116 adult patients to ZEGALOGUE in 2 placebo-controlled trials (mean age 40 years). Table 2 reflects exposure of 20 pediatric patients exposed to ZEGALOGUE in a placebo-controlled trial. Eight patients were 7 to 11 years old, and 12 were 12 to 17 years old [see Clinical Studies (14)].
Table 1. Adverse Reactions Occurring ≥2% and More Frequently than with Placebo in ZEGALOGUE-treated Adult Patients within 12 hours of Treatment in 2 Placebo-Controlled Trials Adverse reaction type Placebo
(N=53)Dasiglucagon
(N=116)% of Patients % of Patients Nausea
4%
57%
Vomiting
2%
25%
Headache
4%
11%
Diarrhea
0%
5%
Injection site pain
0%
2%
Table 2. Adverse Reactions Occurring ≥2% and More Frequently than with Placebo in ZEGALOGUE-treated Pediatric Patients within 12 hours of Treatment in a Placebo-Controlled Trial Adverse reaction type Placebo
(N=11)Dasiglucagon
Age 6-11 years
(N=8)Dasiglucagon
Age 12-17 years
(N=12)Dasiglucagon
All
(N=20)% of Patients % of Patients % of Patients % of Patients Nausea
0%
25%
92%
65%
Vomiting
0%
25%
67%
50%
Headache
0%
0%
17%
10%
Injection site pain
0%
0%
8%
5%
6.2 Immunogenicity
As with all therapeutic peptides, there is a potential for immunogenicity with ZEGALOGUE. The detection of antibody formation is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Additionally, the observed incidence of antibody (including neutralizing antibody) positivity in an assay may be influenced by several factors including assay methodology, sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medications, and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of the incidence of antibodies to ZEGALOGUE with the incidence of antibodies to other products may be misleading.
In clinical trials, 4/498 (<1%) of ZEGALOGUE-treated patients developed treatment-emergent anti-drug antibodies (ADAs). Two patients receiving a single dose of ZEGALOGUE had detectable ADAs to dasiglucagon for at least 14 months after dosing. One ADA-positive patient receiving multiple doses of ZEGALOGUE had ADAs with transient neutralizing activity and with cross-reactivity against native glucagon. Although no safety or efficacy concerns were noted for these ADA-positive subjects, it is unknown whether ADAs may affect pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety, and/or effectiveness of the drug [see Clinical Studies (14)].
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Table 3. Clinically Significant Drug Interactions with ZEGALOGUE Beta-Blockers
Clinical Impact:
Patients taking beta-blockers may have a transient increase in pulse and blood pressure when given ZEGALOGUE.
Indomethacin
Clinical Impact:
In patients taking indomethacin, ZEGALOGUE may lose its ability to raise blood glucose or may even produce hypoglycemia.
Warfarin
Clinical Impact:
- ZEGALOGUE may increase the anticoagulant effect of warfarin.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no available data on dasiglucagon use in pregnant women to evaluate for a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes.
Untreated hypoglycemia in pregnancy can cause complications and may be fatal.
In animal reproduction studies, daily subcutaneous administration of dasiglucagon to pregnant rabbits and rats during the period of organogenesis did not cause adverse developmental effects at exposures 7 and 709 times the human dose of 0.6 mg based on AUC, respectively (see Data).
Data
Animal Data
In an embryo-fetal development study, pregnant rats were treated daily with subcutaneous doses of 2, 10, and 24 mg/kg/day during the period of organogenesis (gestation day 6 to 17). Maternal toxicity, in terms of decreased body weight gain, lower fetal body weight, and delayed bone ossification, was observed at ≥10 mg/kg/day (≥475 times the human dose, based on AUC).
In an embryo-fetal development study, pregnant rabbits were treated daily with subcutaneous doses of 0.1, 0.3, and 1 mg/kg/day during the period of organogenesis (gestation day 6 to 19). Lower fetal body weight and delayed bone ossification were observed at 1 mg/kg/day (100 times the human dose, based on AUC), a dose that also induced maternal toxicity in terms of decreased body weight gain. At ≥0.3 mg/kg/day (≥20 times the human dose), dasiglucagon caused fetal skeletal and visceral malformations. No adverse fetal developmental effects were observed at 0.1 mg/kg/day, corresponding to exposure 7 times the human dose.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information on the presence of dasiglucagon in either human or animal milk, or the effects of the drug on the breastfed infant or milk production. Dasiglucagon is a peptide and would be expected to be broken down to its constituent amino acids in the infant's digestive tract and is therefore unlikely to cause harm to an exposed infant.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of ZEGALOGUE for the treatment of severe hypoglycemia in patients with diabetes have been established in pediatric patients aged 6 years and above. Use of ZEGALOGUE for this indication is supported by evidence from a study in 42 pediatric patients with type 1 diabetes [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
The safety and effectiveness of ZEGALOGUE have not been established in pediatric patients younger than 6 years of age.
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
If overdosage occurs, the patient may experience nausea, vomiting, inhibition of GI tract motility, and/or increases in blood pressure and heart rate. In case of suspected overdosing, serum potassium may decrease and should be monitored and corrected if needed. If the patient develops a marked increase in blood pressure, phentolamine mesylate has been shown to be effective in lowering blood pressure for the short time that control would be needed.
Appropriate supportive treatment should be initiated according to the patient's clinical signs and symptoms.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
ZEGALOGUE contains dasiglucagon hydrochloride, which is a glucagon analog and an antihypoglycemic agent. Dasiglucagon is comprised of 29 amino acids. The molecular formula of dasiglucagon (anhydrous, free-base) is C152H222N38O50, and its molecular mass is 3382 g/mol (anhydrous, free-base). Dasiglucagon hydrochloride has the following chemical structure:
ZEGALOGUE injection is a preservative free, sterile, aqueous, clear, and colorless solution for subcutaneous use in a single-dose prefilled syringe and an autoinjector. Each prefilled syringe and autoinjector contains 0.63 mg of dasiglucagon provided as dasiglucagon hydrochloride, which is a salt with 3 - 5 equivalents of hydrochloride, and contains the following inactive ingredients: 3.82 mg tromethamine, 6.44 mg sodium chloride, and water for injection. Hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide may have been added to adjust pH to 6.5.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Dasiglucagon is a glucagon receptor agonist, which increases blood glucose concentration by activating hepatic glucagon receptors, thereby stimulating glycogen breakdown and release of glucose from the liver. Hepatic stores of glycogen are necessary for dasiglucagon to produce an antihypoglycemic effect.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
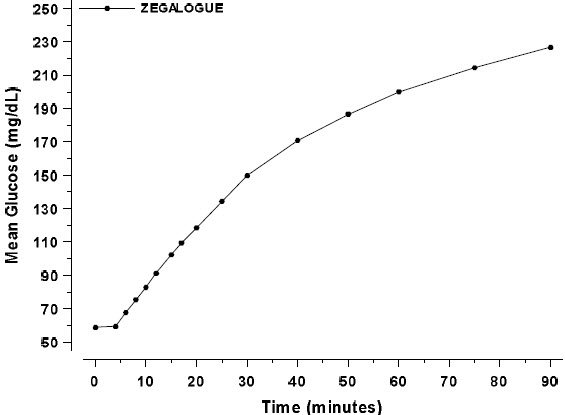
After administration of ZEGALOGUE in adult patients with type 1 diabetes, the mean glucose increase from baseline at 90 minutes was 168 mg/dL (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Mean plasma glucose over time in adults with type 1 diabetes administered 0.6 mg dasiglucagon
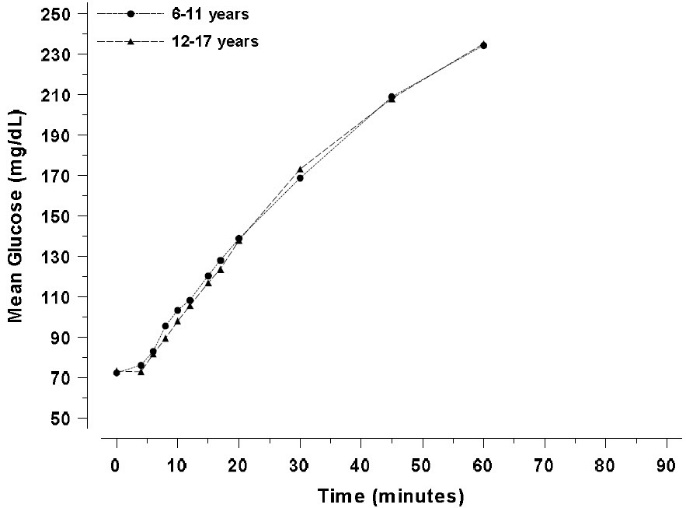
In pediatric patients (7 to 17 years) with type 1 diabetes, the mean glucose increase at 60 minutes after administration of ZEGALOGUE was 162 mg/dL (Figure 2).
Figure 2. Mean plasma glucose over time in pediatric patients with type 1 diabetes administered 0.6 mg dasiglucagon
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
ZEGALOGUE absorption following subcutaneous injection of 0.6 mg resulted in a mean peak plasma concentration of 5110 pg/mL (1510 pmol/L) at around 35 minutes.
Distribution
The mean apparent volume of distribution was 47 L to 57 L following subcutaneous administration.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Long-term studies in animals to evaluate carcinogenicity of dasiglucagon have not been performed.
Mutagenesis
Dasiglucagon was not mutagenic or clastogenic in a standard battery of genotoxicity tests: bacterial mutagenicity (Ames), human lymphocyte chromosome aberration, and rat bone marrow micronucleus.
Impairment of Fertility
In a fertility and early embryofetal development study in rats, dasiglucagon administered by subcutaneous injection (0.5, 2, and 8 mg/kg/day) did not impair fertility in male and female rats at exposures 179 and 269 times the human dose of 0.6 mg (based on AUC), respectively.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Three randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trials were conducted in patients with type 1 diabetes. Two trials (Trial A and Trial B) were conducted in adult patients, and one trial (Trial C) was conducted in pediatric patients aged 6 to 17 years. In all 3 trials, patients were randomized to ZEGALOGUE 0.6 mg, placebo, or (in Trials A and C) glucagon for injection 1.0 mg. ZEGALOGUE and the comparators were administered as single subcutaneous injections following a controlled induction of hypoglycemia using intravenous administration of insulin. During this procedure, a plasma glucose concentration of <60 mg/dL was targeted in Trials A and B, whereas the target was <80 mg/dL in Trial C.
The primary efficacy endpoint for all 3 trials was time to plasma glucose recovery (treatment success), defined as an increase in blood glucose of ≥20 mg/dL from time of administration, without additional intervention within 45 minutes. In Trials A and B, plasma glucose values were collected and assessed at pre-dose, and at 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 15, 17, 20, 25, 30, 40, 45, 50, 60, 75, 90 minutes after treatment. Trial C assessed plasma glucose at the same timepoints as did Trials A and B, with the exception of the 25, 40, 50, 75 and 90-minute post-treatment timepoints. The primary hypothesis test was superiority of ZEGALOGUE versus placebo. There was no formal hypothesis test of ZEGALOGUE versus glucagon for injection.
14.1 Adult Patients
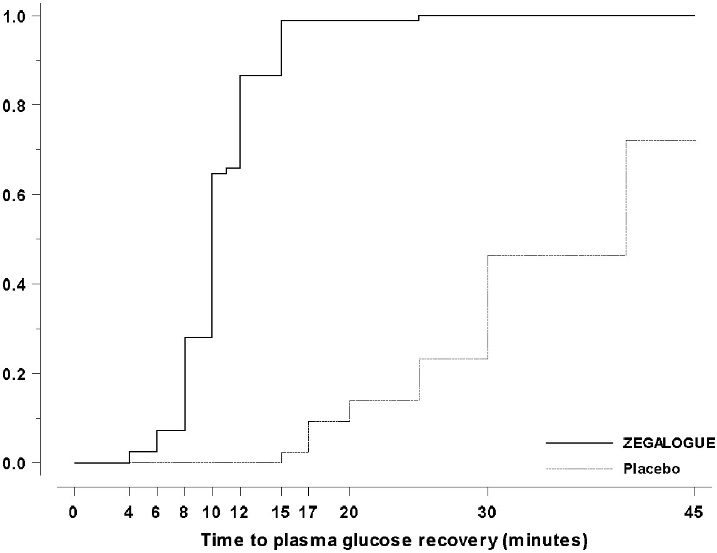
Trial A, NCT03378635: A total of 170 patients were randomized 2:1:1 to ZEGALOGUE, placebo, and glucagon for injection, stratified by injection sites (abdominal region, buttocks, thigh). The mean age of the patients was 39.1 years (96% were < 65 years), and the mean duration of diabetes was 20.0 years; 63% were male; 92% were White. The mean baseline plasma glucose was 58.8 mg/dL. The median time to plasma glucose recovery was statistically significantly shorter for ZEGALOGUE (10 minutes) versus placebo (40 minutes) (Table 4). Figure 3 shows the cumulative proportions of patients achieving plasma glucose recovery over time. The median time to plasma glucose recovery was numerically similar between ZEGALOGUE (10 minutes) and glucagon for injection (12 minutes).
Trial B, NCT03688711: A total of 45 patients were randomized 3:1 to ZEGALOGUE and placebo stratified by injection sites (buttocks, deltoid). The mean age of the patients was 41.0 years (95% were < 65 years), and the mean duration of diabetes was 22.5 years; 57% were male; 93% were White. The mean baseline plasma glucose was 55.0 mg/dL. The median time to plasma glucose recovery was statistically significantly shorter for ZEGALOGUE (10 minutes) versus placebo (35 minutes) (Table 4).
Table 4. Plasma Glucose Recovery in Adult Patients Trial A Trial B ZEGALOGUE
N=82Placebo
N=43ZEGALOGUE
N=34Placebo
N=10N is the number of patients who were randomized and treated. - * log-log confidence interval
- † p < 0.001 versus placebo (log-rank test stratified by injection sites)
Median time to recovery [95% CI*]
10 min
[10; 10]†40 min
[30; 40]10 min
[8; 12]†35 min
[20; -)- Figure 3 Time to plasma glucose recovery in Trial A
14.2 Pediatric Patients
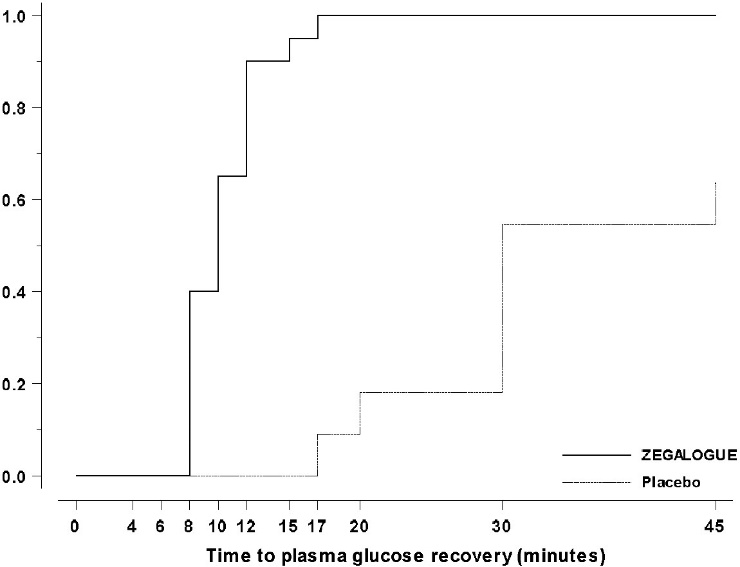
Trial C, NCT03667053: Pediatric patients aged 6 to 17 years and weighing ≥20 kg, were randomized 2:1:1 to ZEGALOGUE, placebo, and glucagon for injection, stratified by injection sites (abdominal region, thigh) and age groups (6-11 years and 12-17 years). A total of 42 patients were randomized. The mean age was 12.5 years (range 7 to 17 years), and the mean duration of diabetes was 5.9 years; 56% were male; 95% were White. The mean baseline plasma glucose was 72.0 mg/dL. The median time to plasma glucose recovery was statistically significantly shorter for ZEGALOGUE (10 minutes) versus placebo (30 minutes) (Table 5). Figure 4 shows the cumulative proportions of pediatric patients achieving plasma glucose recovery over time. The median time to plasma glucose recovery was numerically similar between ZEGALOGUE (10 minutes) and glucagon for injection (10 minutes).
Table 5. Plasma Glucose Recovery in Pediatric Patients Trial C ZEGALOGUE
N=20Placebo
N=11N is the number of patients who were randomized and treated. - * log-log confidence interval
- † p < 0.001 versus placebo (log-rank test stratified by injection site and age group)
Median time to recovery [95% CI*]
10 min [8; 12]†
30 min [20; -)
Figure 4. Time to plasma glucose recovery in Trial C
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
ZEGALOGUE injection is a clear, colorless solution supplied as follows:
Presentation Strength Package Size NDC Single-dose autoinjector
0.6 mg/0.6 mL
1
0169-1912-01
Single-dose autoinjector
0.6 mg/0.6 mL
2
0169-1912-02
Single-dose prefilled syringe
0.6 mg/0.6 mL
1
0169-1913-01
Single-dose prefilled syringe
0.6 mg/0.6 mL
2
0169-1913-02
16.2 Recommended Storage
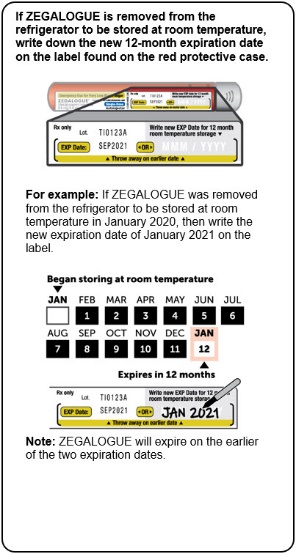
Store ZEGALOGUE in a refrigerator, 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Keep away from the cooling element. Do not freeze.
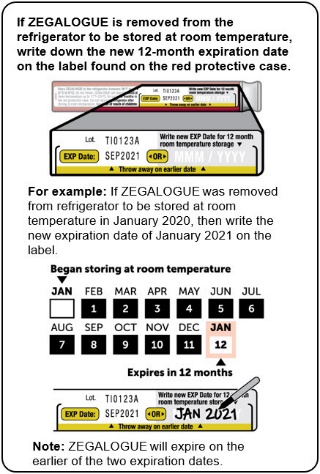
ZEGALOGUE can be kept at room temperature between 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) for up to 12 months. Record the date when the product was removed from the refrigerator in the space provided on the protective case. Do not return the product to the refrigerator after storing at room temperature. Store in the provided protective case and protect from light.
Discard ZEGALOGUE after the end of the 12-month period at room temperature storage, or after the expiration date stated on the product, whichever occurs first.
The inside of the gray cap on ZEGALOGUE autoinjector contains dry natural rubber (a derivative of latex).
The inside of the gray needle cover on ZEGALOGUE prefilled syringe contains dry natural rubber (a derivative of latex).
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient and family members or caregivers to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions For Use).
Recognition of Severe Hypoglycemia
Inform patient and family members or caregivers on how to recognize the signs and symptoms of severe hypoglycemia and the risks of prolonged hypoglycemia.
Administration
Review the Patient Information and Instructions For Use with the patient and family members or caregivers.
Serious Hypersensitivity
Inform patients that allergic reactions can occur with glucagon products like ZEGALOGUE. Advise patients to seek immediate medical attention if they experience any symptoms of serious hypersensitivity reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
Patient Information
ZEGALOGUE (ze' gah log)
(dasiglucagon) injection, for subcutaneous useWhat is ZEGALOGUE?
ZEGALOGUE is a prescription medicine used to treat very low blood sugar (severe hypoglycemia) in people with diabetes aged 6 years and older.
It is not known if ZEGALOGUE is safe and effective in children under 6 years of age.Do not use ZEGALOGUE if you:
- have a tumor called pheochromocytoma in the gland on top of your kidneys (adrenal gland).
- have a tumor called insulinoma in your pancreas.
Before using ZEGALOGUE, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have a tumor in your pancreas.
- are allergic to dasiglucagon or any other ingredients in ZEGALOGUE. See the end of this Patient Information for a complete list of ingredients in ZEGALOGUE.
- have not had food or water for a long time (prolonged fasting or starvation).
- have adrenal insufficiency.
- have low blood sugar that does not go away (chronic hypoglycemia).
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if ZEGALOGUE passes into your breast milk. You and your healthcare provider should decide if you can use ZEGALOGUE while breastfeeding.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
How should I use ZEGALOGUE?
- Read the detailed Instructions For Use that come with ZEGALOGUE.
- Use ZEGALOGUE exactly how your healthcare provider tells you to use it.
- Make sure your caregiver knows where you keep your ZEGALOGUE and how to use ZEGALOGUE the right way before you need it.
- Your caregiver must act quickly. Having very low blood sugar for a period of time may be harmful.
- Your healthcare provider will tell you how and when to use ZEGALOGUE.
- After giving ZEGALOGUE, your caregiver should call for emergency medical help right away.
- Once you are able to safely consume food or drink, your caregiver should give you a fast-acting source of sugar (such as fruit juice) and a long-acting source of sugar (such as crackers with cheese or peanut butter).
- If you do not respond to treatment after 15 minutes, your caregiver may give you another dose, if available.
- Tell your healthcare provider each time you use ZEGALOGUE. Your healthcare provider may need to change the dose of your other diabetes medicines.
What are the possible side effects of ZEGALOGUE?
ZEGALOGUE may cause serious side effects, including:- high blood pressure. ZEGALOGUE can cause high blood pressure in certain people with tumors in their adrenal glands.
- low blood sugar. ZEGALOGUE can cause certain people with tumors in their pancreas called insulinomas to have low blood sugar.
- serious allergic reaction. Call your healthcare provider or get medical help right away if you have a serious allergic reaction including: rash, difficulty breathing, or low blood pressure (hypotension).
The most common side effects of ZEGALOGUE include:
- 1. Adults
- 2. nausea
- 3. vomiting
- 4. headache
- 5. diarrhea
- 6. injection site pain
- 1. Children
- 2. nausea
- 3. vomiting
- 4. headache
- 5. injection site pain
These are not all of the possible side effects of ZEGALOGUE. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store ZEGALOGUE?
- Store ZEGALOGUE in a refrigerator between 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C).
- Do not freeze ZEGALOGUE.
- ZEGALOGUE can also be stored at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C) for up to 12 months. See example in the Instructions For Use for how to keep track of this 12-month period.
- Do not return ZEGALOGUE to the refrigerator after storing at room temperature.
- Throw away ZEGALOGUE if it has been stored at room temperature for more than 12 months.
- Replace ZEGALOGUE before the expiration date printed on the red protective case.
- Store ZEGALOGUE in the red protective case it comes in.
Keep ZEGALOGUE and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe use of ZEGALOGUE.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use ZEGALOGUE for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give ZEGALOGUE to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about ZEGALOGUE that is written for healthcare professionals.What are the ingredients in ZEGALOGUE?
Active ingredient: dasiglucagon, provided as dasiglucagon hydrochloride
Inactive ingredients: tromethamine, sodium chloride and water for injection. Hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide may be added to adjust pH
Distributed by: Novo Nordisk Inc., Plainsboro, NJ, USAManufactured by: Rechon Life Science AB, Malmö, Sweden
For more information go to www.zegalogue.com or call 1-800-727-6500.
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Revised: 01/2023
-
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
ZEGALOGUE® (ze' gah log)
(dasiglucagon) injection0.6 mg/0.6 mL
Emergency Use for Very Low Blood Sugar
Single-Dose
Prefilled Syringe
Injection, for subcutaneous useImportant: ZEGALOGUE is used to treat very low blood sugar (severe hypoglycemia) where you need help from others.
ZEGALOGUE contains 1 dose of dasiglucagon in a prefilled syringe and cannot be reused.
Read and understand this Instructions For Use before an emergency happens.
Show your family and friends where you keep ZEGALOGUE and explain how to use it by sharing these instructions, so they know how to use ZEGALOGUE before an emergency happens.
The inside of the gray needle cover contains dry natural rubber, which may cause allergic reactions in people with latex allergy.
Read before Injecting ZEGALOGUE -
Do not use ZEGALOGUE if the:
- o expiration date has passed
- o gray needle cover is missing or
- o syringe appears damaged
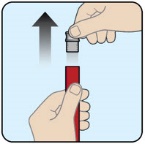
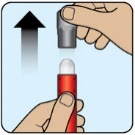
- When opening the red protective case make sure to hold it up straight (with the gray cap on top) to avoid dropping ZEGALOGUE.
- Do not remove the gray needle cover until you are ready to inject ZEGALOGUE.
- For questions or more information about ZEGALOGUE, call your healthcare provider.
After injection - After you have given the injection, roll the unconscious person on to their side to prevent choking.
- Call for emergency medical help or a healthcare provider right away after you have injected ZEGALOGUE. Even if the ZEGALOGUE injection helps the person to wake up, still call for emergency medical help right away. If the person does not respond after 15 minutes, another dose may be given, if available.
- Once the person is able to safely consume food or drink, give the person a fast-acting source of sugar (such as fruit juice) and a long-acting source of sugar (such as crackers with cheese or peanut butter).
- Replace the used ZEGALOGUE right away so you will have a new ZEGALOGUE in case you need it.
Hypoglycemia may happen again after receiving ZEGALOGUE treatment.
Early symptoms of hypoglycemia may include:
- sweating
- drowsiness
- dizziness
- sleep disturbances
- irregular heartbeat (palpitation)
- anxiety
- tremor
- blurred vision
- hunger
- slurred speech
- restlessness
- depressed mood
- tingling in the hands, feet, lips, or tongue
- irritability
- abnormal behavior
- lightheadedness
- unsteady movement
- inability to concentrate
- personality changes
- headache
If not treated early, hypoglycemia may worsen and the person may have severe hypoglycemia. Signs of severe hypoglycemia include confusion, seizures, unconsciousness, and death.
How to throw away (dispose of) ZEGALOGUE 
Dispose of your ZEGALOGUE and the gray needle cover in an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container.
Put your expired or used needles and syringes in an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use. Do not throw away (dispose of) loose needles and syringes in your household trash.
If you do not have an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
- made of a heavy-duty plastic
- can be closed with a tight-fitting, puncture-resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out
- upright and stable during use
- leak-resistant
- properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container
When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the correct way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used syringes. For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA's website at: http://www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal
Do not dispose of your used sharps disposal container in your household trash unless your community guidelines permit it.
Do not recycle your used sharps disposal container.
This Instructions For Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Distributed by:
Novo Nordisk Inc., Plainsboro, NJ, USA
Manufactured by:
Rechon Life Science AB, Malmö, Sweden
Revised 01/2023
-
Do not use ZEGALOGUE if the:
-
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
ZEGALOGUE® (ze' gah log)
(dasiglucagon) injection
0.6 mg/0.6 mL
Emergency Use for Very Low Blood Sugar
Single-Dose
Autoinjector
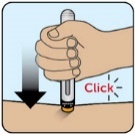
Injection, for subcutaneous use
Important: ZEGALOGUE is used to treat very low blood sugar (severe hypoglycemia) where you need help from others.
ZEGALOGUE contains 1 dose of dasiglucagon in a prefilled autoinjector and cannot be reused.
Read and understand this Instructions For Use before an emergency happens.
Show your family and friends where you keep ZEGALOGUE and explain how to use it by sharing these instructions, so they know how to use ZEGALOGUE before an emergency happens.
The inside of the gray cap contains dry natural rubber, which may cause allergic reactions in people with latex allergy.
Read before injecting ZEGALOGUE -
Do not use ZEGALOGUE if the:
- o expiration date has passed
- o gray cap is missing or
- o autoinjector appears damaged
- When opening the red protective case make sure to hold it up straight (with the gray lid on top) to avoid dropping ZEGALOGUE.
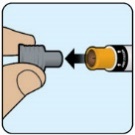
- Do not remove the gray cap until you are ready to inject ZEGALOGUE.
- For questions or more information about ZEGALOGUE, call your healthcare provider.
After injection - After you have given the injection, roll the unconscious person on to their side to prevent choking.
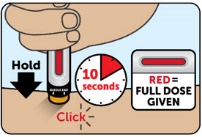
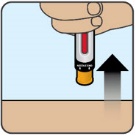
- Call for emergency medical help or a healthcare provider right away after you have injected ZEGALOGUE. Even if the ZEGALOGUE injection helps the person to wake up, still call for emergency medical help right away. If the person does not respond after 15 minutes, another dose may be given, if available.
- Once the person is able to safely consume food or drink, give the person a fast-acting source of sugar (such as fruit juice) and a long-acting source of sugar (such as crackers with cheese or peanut butter).
- Replace the used ZEGALOGUE right away so you will have a new ZEGALOGUE in case you need it.
Hypoglycemia may happen again after receiving ZEGALOGUE treatment.
Early symptoms of hypoglycemia may include:
- sweating
- drowsiness
- dizziness
- sleep disturbances
- irregular heartbeat (palpitation)
- anxiety
- tremor
- blurred vision
- hunger
- slurred speech
- restlessness
- depressed mood
- tingling in the hands, feet, lips, or tongue
- irritability
- abnormal behavior
- lightheadedness
- unsteady movement
- inability to concentrate
- personality changes
- headache
If not treated early, hypoglycemia may worsen and the person may have severe hypoglycemia. Signs of severe hypoglycemia include confusion, seizures, unconsciousness, and death.
How to throw away (dispose of) ZEGALOGUE 
Dispose of your ZEGALOGUE and gray cap in an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container.
Put your expired or used ZEGALOGUE in an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use. Do not throw away (dispose of) autoinjectors, loose needles and syringes in your household trash.
If you do not have an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
- made of a heavy-duty plastic
- can be closed with a tight-fitting, puncture-resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out
- upright and stable during use
- leak-resistant
- properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container
When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the correct way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used autoinjectors. For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA's website at: http://www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal
Do not dispose of your used sharps disposal container in your household trash unless your community guidelines permit it.
Do not recycle your used sharps disposal container.
This Instructions For Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Distributed by:
Novo Nordisk Inc., Plainsboro, NJ, USA
Manufactured by:
Rechon Life Science AB, Malmö, Sweden
Revised 01/2023
-
Do not use ZEGALOGUE if the:
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 0.6 mg/0.6 mL Prefilled Syringe 1ct Carton
Emergency Use for Very Low Blood Sugar
ZEGALOGUE®
(dasiglucagon) injection
0.6 mg/0.6 mL*
Prefilled Syringe
Single-Dose
Injection, for subcutaneous use. Rx only
NDC: 0169-1913-01
List: 191301
Carton contents:
1 Single-Dose Prefilled Syringe
1 Prescribing Information
OPEN HERE
Novo Nordisk®
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 0.6 mg/0.6 mL Prefilled Syringe 2ct Carton
Emergency Use for Very Low Blood Sugar
ZEGALOGUE®
(dasiglucagon) injection
0.6 mg/0.6 mL*
Prefilled Syringe
2 Single-Dose Prefilled Syringes
- Injection, for subcutaneous use. Rx only Novo Nordisk ®
NDC: 0169-1913-02
List: 191302
Carton contents:
2 Single-Dose Prefilled Syringes
2 Prescribing Information
- OPEN HERE 2 PACK
-
Package/Label Display Panel - 0.6 mg/0.6 mL 1ct Autoinjector Carton
Emergency Use for Very Low Blood Sugar
ZEGALOGUE®
(dasiglucagon) injection
0.6 mg/0.6 mL*
Autoinjector
- Single-Dose Injection, for subcutaneous use. Rx only
NDC: 0169-1912-01
List: 191201
Carton contents:
1 Single-Dose Autoinjector
1 Prescribing Information
- OPEN HERE Novo Nordisk ®
-
Package/Label Display Panel - 0.6 mg/0.6 mL 2ct Autoinjector Carton
Emergency Use for Very Low Blood Sugar
ZEGALOGUE®
(dasiglucagon) injection
0.6 mg/0.6 mL*
Autoinjector
2 Single-Dose Autoinjectors
- Injection, for subcutaneous use. Rx only Novo Nordisk ®
NDC: 0169-1912-02
List: 191202
Carton contents:
2 Single-Dose Autoinjectors
2 Prescribing Information
- OPEN HERE 2 PACK
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
ZEGALOGUE
dasiglucagon injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0169-1913 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength DASIGLUCAGON (UNII: AD4J2O47FQ) (DASIGLUCAGON - UNII:AD4J2O47FQ) DASIGLUCAGON 0.6 mg in 0.6 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength TROMETHAMINE (UNII: 023C2WHX2V) 3.82 mg in 0.6 mL SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) 6.44 mg in 0.6 mL WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0169-1913-01 1 in 1 PACKAGE 06/26/2023 1 1 in 1 CONTAINER 1 0.6 mL in 1 SYRINGE, GLASS; Type 2: Prefilled Drug Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) 2 NDC: 0169-1913-02 2 in 1 CARTON 06/26/2023 2 NDC: 0169-1913-12 1 in 1 PACKAGE 2 1 in 1 CONTAINER 2 0.6 mL in 1 SYRINGE, GLASS; Type 2: Prefilled Drug Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA214231 06/26/2023 ZEGALOGUE
dasiglucagon injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0169-1912 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength DASIGLUCAGON (UNII: AD4J2O47FQ) (DASIGLUCAGON - UNII:AD4J2O47FQ) DASIGLUCAGON 0.6 mg in 0.6 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength TROMETHAMINE (UNII: 023C2WHX2V) 3.82 mg in 0.6 mL SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) 6.44 mg in 0.6 mL WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0169-1912-01 1 in 1 PACKAGE 06/26/2023 1 1 in 1 CONTAINER 1 0.6 mL in 1 SYRINGE, GLASS; Type 2: Prefilled Drug Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) 2 NDC: 0169-1912-02 2 in 1 CARTON 06/26/2023 2 NDC: 0169-1912-12 1 in 1 PACKAGE 2 1 in 1 CONTAINER 2 0.6 mL in 1 SYRINGE, GLASS; Type 2: Prefilled Drug Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA214231 06/26/2023 Labeler - Novo Nordisk (622920320)
Trademark Results [Zegalogue]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 ZEGALOGUE 79256691 5905935 Live/Registered |
ZEALAND PHARMA A/S 2019-01-14 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.