Imiquimod by Padagis Israel Pharmaceuticals Ltd IMIQUIMOD cream
Imiquimod by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Imiquimod by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Padagis Israel Pharmaceuticals Ltd. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Imiquimod Cream safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Imiquimod Cream.
Imiquimod Cream, 5%
For topical use only
Initial U.S. Approval: 1997INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Imiquimod Cream is indicated for the topical treatment of:
Clinically typical, nonhyperkeratotic, nonhypertrophic actinic keratoses (AK) on the face or scalp in immunocompetent adults (1.1)
Biopsy-confirmed, primary superficial basal cell carcinoma (sBCC) in immunocompetent adults; maximum tumor diameter of 2.0 cm on trunk, neck, or extremities (excluding hands and feet), only when surgical methods are medically less appropriate and patient follow-up can be reasonably assured (1.2)
External genital and perianal warts/condyloma acuminata in patients 12 years old or older (1.3)
Limitations of Use: Efficacy was not demonstrated for molluscum contagiosum in children aged 2-12 (1.4, 8.4)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Imiquimod Cream is not for oral, ophthalmic, or intravaginal use (2)
Actinic keratosis: 2 times per week for a full 16 weeks (2.1)
Superficial basal cell carcinoma: 5 times per week for a full 6 weeks (2.2)
External genital warts (EGW): 3 times per week until total clearance or a maximum of 16 weeks (2.3)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Imiquimod Cream, 5%, is supplied in single-use packets (12 or 24 per box), each of which contains 250 mg of the cream, equivalent to 12.5 mg of imiquimod. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- None (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Intense local inflammatory reactions can occur (e.g., skin weeping, erosion). Dosing interruption may be required (2, 5.1, 6)
Severe local inflammatory reactions of the female external genitalia can lead to severe vulvar swelling. Severe vulvar swelling can lead to urinary retention; dosing should be interrupted or discontinued.
Flu-like systemic signs and symptoms including malaise, fever, nausea, myalgias and rigors may occur. Dosing interruption may be required (2, 5.2, 6)
Avoid exposure to sunlight and sunlamps. Wear sunscreen daily (5.3)
Safety and efficacy have not been established for repeat courses of treatment to the same area for AK (5.4)
Imiquimod Cream is not recommended for treatment of BCC subtypes other than the superficial variant, i.e., sBCC (5.5)
Treatment of urethral, intra-vaginal, cervical, rectal or intra-anal viral disease is not recommended (5.6)
Safety and efficacy in immunosuppressed patients have not been established (1.5)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions (incidence >28%) are application site reactions or local skin reactions: itching, burning, erythema, flaking/scaling/dryness, scabbing/crusting, edema, induration, excoriation, erosion, ulceration. Other reported reactions (1%) include fatigue, fever, and headache (6.1, 6.2, 6.3)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Perrigo at 1-866-634-9120 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or http://www.fda.gov/medwatchwww.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: November 2011
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 10/2018
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Actinic Keratosis
1.2 Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma
1.3 External Genital Warts
1.4 Limitations of Use
1.5 Unevaluated Populations
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Actinic Keratosis
2.2 Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma
2.3 External Genital Warts
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Local Inflammatory Reactions
5.2 Systemic Reactions
5.3 Ultraviolet Light Exposure
5.4 Unevaluated Uses: Actinic Keratosis
5.5 Unevaluated Uses: Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma
5.6 Unevaluated Uses: External Genital Warts
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience: Actinic Keratosis
6.2 Clinical Trials Experience: Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma
6.3 Clinical Trials Experience: External Genital Warts
6.4 Clinical Trials Experience: Dermal Safety Studies
6.5 Postmarketing Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Actinic Keratosis
14.2 Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma
14.3 External Genital Warts
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
17.1 General Information: All Indications
17.2 Local Skin Reactions: All Indications
17.3 Systemic Reactions: All Indications
17. 4 Patients Being Treated for Actinic Keratosis (AK)
17.5 Patients Being Treated for Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma (sBCC)
17.6 Patients Being Treated for External Genital Warts
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Actinic Keratosis
Imiquimod Cream is indicated for the topical treatment of clinically typical, nonhyperkeratotic, nonhypertrophic actinic keratoses on the face or scalp in immunocompetent adults.
1.2 Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma
Imiquimod Cream is indicated for the topical treatment of biopsy-confirmed, primary superficial basal cell carcinoma (sBCC) in immunocompetent adults, with a maximum tumor diameter of 2.0 cm, located on the trunk (excluding anogenital skin), neck, or extremities (excluding hands and feet), only when surgical methods are medically less appropriate and patient follow-up can be reasonably assured.
The histological diagnosis of superficial basal cell carcinoma should be established prior to treatment, since safety and efficacy of Imiquimod Cream have not been established for other types of basal cell carcinomas, including nodular and morpheaform (fibrosing or sclerosing) types.
1.3 External Genital Warts
Imiquimod Cream is indicated for the treatment of external genital and perianal warts/condyloma acuminata in patients 12 years old and older.
1.4 Limitations of Use
Imiquimod cream has been evaluated in children ages 2 to 12 years with molluscum contagiosum and these studies failed to demonstrate efficacy. [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
1.5 Unevaluated Populations
The safety and efficacy of Imiquimod Cream in immunosuppressed patients have not been established.
Imiquimod Cream should be used with caution in patients with pre-existing autoimmune conditions.
The efficacy and safety of Imiquimod Cream have not been established for patients with Basal Cell Nevus Syndrome or Xeroderma Pigmentosum.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The application frequency for Imiquimod Cream is different for each indication. Imiquimod Cream is not for oral, ophthalmic, or intravaginal use.
2.1 Actinic Keratosis
Imiquimod Cream should be applied 2 times per week for a full 16 weeks to a defined treatment area on the face or scalp (but not both concurrently). The treatment area is defined as one contiguous area of approximately 25 cm2 (e.g., 5 cm x 5 cm) on the face (e.g. forehead or one cheek) or on the scalp. Examples of 2 times per week application schedules are Monday and Thursday, or Tuesday and Friday. Imiquimod Cream should be applied to the entire treatment area and rubbed in until the cream is no longer visible. No more than one packet of Imiquimod Cream should be applied to the contiguous treatment area at each application. Imiquimod Cream shouldbe applied prior to normal sleeping hours and left on the skin for approximately 8 hours, after which time the cream should be removed by washing the area with mild soap and water. Theprescriber should demonstrate the proper application technique to maximize the benefit ofImiquimod Cream therapy.
It is recommended that patients wash their hands before and after applying Imiquimod Cream. Before applying the cream,the patient should wash the treatment area with mild soap and water and allow the area to dry thoroughly (at least 10 minutes).
Contact with the eyes, lips and nostrils should be avoided.
Local skin reactions in the treatment area are common. [see Adverse Reactions (6.1, 6.5)] A rest period of several days may be taken if required by the patient's discomfort or severity of the local skin reaction. However, the treatment period should not be extended beyond 16 weeks due tomissed doses or rest periods. Response to treatment cannot be adequately assessed until resolution of local skin reactions. Lesions that do not respond to treatment should be carefully re-evaluated and management reconsidered.
Imiquimod Cream is packaged in single-use packets, with 12 or 24 packets supplied per box. Patients should be prescribed no more than 36 packets for the 16-week treatment period. Unused packets should be discarded. Partially-used packets should be discarded and not reused.
2.2 Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma
Imiquimod Cream should be applied 5 times per week for a full 6 weeks to a biopsy-confirmed superficial basal cell carcinoma. An example of a 5 times per week application schedule is to apply Imiquimod Cream, once per day, Monday through Friday. Imiquimod Cream should be applied prior to normal sleeping hours and left on the skin for approximately 8 hours, after which time the cream should be removed by washing the area with mild soap and water. The prescriber should demonstrate the proper application technique to maximize the benefit of Imiquimod Cream therapy.
It is recommended that patients wash their hands before and after applying Imiquimod Cream. The patient should wash the treatment area with mild soap and water before applying the cream, and allow the area to dry thoroughly.
The target tumor should have a maximum diameter of 2 cm and be located on the trunk (excluding anogenital skin), neck, or extremities (excluding hands and feet). The treatment area should include a 1 cm margin of skin around the tumor. Sufficient cream should be applied to cover the treatment area, including 1 centimeter of skin surrounding the tumor. Imiquimod Cream should be rubbed into the treatment area until the cream is no longer visible.
TABLE 1. Amount of Imiquimod Cream to Use of SBcc
Target Tumor
Diameter
Size of Cream Droplet to be Used
(diameter)
Approximate Amount of Imiquimod to be Used
0.5 to < 1.0 cm
4 mm
10 mg
≥1.0 to <1.5 cm
5 mm
25 mg
≥1.5 to 2.0 cm
7 mm
40 mg
Contact with the eyes, lips and nostrils should be avoided.
Local skin reactions in the treatment area are common. [see Adverse Reactions (6.2, 6.5)] A rest period of several days may be taken if required by the patient's discomfort or severity of the local skin reaction.
Early clinical clearance cannot be adequately assessed until resolution of local skin reactions (e.g. 12 weeks post-treatment). Local skin reactions or other findings (e.g. infection) mayrequire that a patient be seen sooner than the post-treatment assessment for clinical clearance.If there is clinical evidence of persistent tumor at the post-treatment assessment for clinical clearance, a biopsy or other alternative intervention should be considered. Lesions that do not respond to therapy should be carefully re-evaluated and management reconsidered; the safety and efficacy of a repeat course of Imiquimod Cream treatment have not been established. If any suspicious lesion arises in the treatment area at any time after determination of clinical clearance, the patient should seek a medical evaluation. [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
Imiquimod Cream is packaged in single-use packets, with 12 or 24 packets supplied per box. Patients should be prescribed no more than 36 packets for the 6-week treatment period. Unused packets should be discarded. Partially-used packets should be discarded and not reused.
2.3 External Genital Warts
Imiquimod Cream should be applied 3 times per week to external genital/perianal warts. Imiquimod Cream treatment should continue until there is total clearance of the genital/perianal warts or for a maximum of 16 weeks. Examples of 3 times per week application schedules are: Monday, Wednesday, Friday or Tuesday, Thursday, Saturday. Imiquimod Cream should be applied prior to normal sleeping hours and left on the skin for 6 -10 hours, after which time the cream should be removed by washing the area with mild soap and water. The prescriber should demonstrate the proper application technique to maximize the benefit of Imiquimod Cream therapy.
It is recommended that patients wash their hands before and after applying Imiquimod Cream.
A thin layer of Imiquimod Cream should be applied to the wart area and rubbed in until the cream is no longer visible. The application site should not be occluded. Following the treatment period the cream should be removed by washing the treated area with mild soap and water.
Local skin reactions at the treatment site are common.[seeAdverse Reactions(6.3, 6.5)]. A rest period of several days may be taken if required by the patient's discomfort or severity of the local skin reaction. Treatment may resume once the reaction subsides. Non-occlusive dressings such as cotton gauze or cotton underwear may be used in the management of skin reactions.
Imiquimod Cream is packaged in single-use packets which contain sufficient cream to cover a wart area of up to 20 cm2; use of excessive amounts of cream should be avoided.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Local Inflammatory Reactions
Intense local inflammatory reactions including skin weeping or erosion can occur after a few applications of Imiquimod Cream and may require an interruption of dosing. [see
Dosage andAdministration(2) and Adverse Reactions (6)]. Imiquimod Cream has the potential to exacerbate inflammatory conditions of the skin, including chronic graft versus host disease.
Severe local inflammatory reactions of the female external genitalia can lead to severe vulvar swelling. Severe vulvar swelling can lead to urinary retention. Dosing should be interrupted or discontinued for severe vulvar swelling.
Administration of Imiquimod Cream is not recommended until the skin is completely healed from any previous drug or surgical treatment.
5.2 Systemic Reactions
Flu-like signs and symptoms may accompany, or even precede, local inflammatory reactions and may include malaise, fever, nausea, myalgias and rigors. An interruption of dosing should be considered. [see Adverse Reactions (6)]
5.3 Ultraviolet Light Exposure
Exposure to sunlight (including sunlamps) should be avoided or minimized during use of Imiquimod Cream because of concern for heightened sunburn susceptibility. Patients should be warned to use protective clothing (e.g., a hat) when using Imiquimod Cream. Patients with sunburn should be advised not to use Imiquimod Cream until fully recovered. Patients who may have considerable sun exposure, e.g. due to their occupation, and those patients with inherent sensitivity to sunlight should exercise caution when using Imiquimod Cream.
Imiquimod Cream shortened the time to skin tumor formation in an animal photo-cocarcinogenecity study [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)]. The enhancement of ultraviolet carcinogenicity is not necessarily dependent on phototoxic mechanisms. Therefore, patients should minimize or avoid natural or artificial sunlight exposure.
5.4 Unevaluated Uses: Actinic Keratosis
Safety and efficacy have not been established for Imiquimod Cream in the treatment of actinic keratosis with repeated use, i.e. more than one treatment course, in the same area.
The safety of Imiquimod Cream applied to areas of skin greater than 25 cm2 (e.g. 5 cm X 5 cm) or the treatment of actinic keratosis has not been established [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5.5 Unevaluated Uses: Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma
The safety and efficacy of Imiquimod Cream have not been established for other types of basal cell carcinomas (BCC), including nodular and morpheaform (fibrosing or sclerosing) types. Imiquimod Cream is not recommended for treatment of BCC subtypes other than thesuperficial variant (i.e., sBCC). Patients with sBCC treated with Imiquimod Cream should have regular follow-up of the treatment site. [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
The safety and efficacy of treating sBCC lesions on the face, head and anogenital area have not been established.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience: Actinic Keratosis
The data described below reflect exposure to imiquimod cream or vehicle in 436 subjects enrolled in two double-blind, vehicle-controlled studies. Subjects applied imiquimod cream or vehicle to a 25 cm2 contiguous treatment area on the face or scalp 2 times per week for 16 weeks.
Table 2: Selected Adverse Reactions Occurring in > 1% of Imiquimod-Treated Subjects and at a Greater Frequency than with Vehicle in the Combined Studies (Actinic Keratosis)
Preferred Term
Imiquimod Cream
(n= 215)
Vehicle
(n= 221)
Application Site Reaction
71 (33%)
32 (14%)
Upper Resp Tract Infection
33 (15%)
27 (12%)
Sinusitis
16 (7%)
14 (6%)
Headache
11 (5%)
7 (3%)
Carcinoma Squamous
8 (4%)
5 (2%)
Diarrhea
6 (3%)
2 (1%)
Eczema
4 (2%)
3 (1%)
Back Pain
3 (1%)
2 (1%)
Fatigue
3 (1%)
2 (1%)
Fibrillation Atrial
3 (1%)
2 (1%)
Infection Viral
3 (1%)
2 (1%)
Dizziness
3 (1%)
1 (<1%)
Vomiting
3 (1%)
1 (<1%)
Urinary Tract Infection
3 (1%)
1 (<1%)
Fever
3 (1%)
0 (0%)
Rigors
3 (1%)
0 (0%)
Alopecia
3 (1%)
0 (0%)
Table 3: Application Site Reactions Reported by > 1% of Imiquimod-Treated Subjects and at a Greater Frequency than with Vehicle in the Combined Studies (Actinic Keratosis)
Included Term
Imiquimod Cream
(n= 215)
Vehicle
(n= 221)
Itching
44 (20%)
17 (8%)
Burning
13 (6%)
4 (2%)
Bleeding
7 (3%)
1 (<1%)
Stinging
6 (3%)
2 (1%)
Pain
6 (3%)
2 (1%)
Induration
5 (2%)
3 (1%)
Tenderness
4 (2%)
3 (1%)
Irritation
4 (2%)
0 (0%)
Local skin reactions were collected independently of the adverse reaction "application site reaction" in an effort to provide a better picture of the specific types of local reactions that might be seen. The most frequently reported local skin reactions were erythema, flaking/scaling/dryness, and scabbing/crusting. The prevalence and severity of local skin reactions that occurred during controlled studies are shown in the following table.
Table 4: Local Skin Reactions in the Treatment Area as Assessed by the Investigator (Actinic Keratosis)
Imiquimod Cream
(n=215)
Vehicle
(n=220)
All Grades*
Severe
All Grades*
Severe
Erythema
209 (97%)
38 (18%)
206 (93%)
5 (2%)
Flaking/Scaling/Dryness
199 (93%)
16 (7%)
199 (91%)
7 (3%)
Scabbing/Crusting
169 (79%)
18 (8%)
92 (42%)
4 (2%)
Edema
106 (49%)
0 (0%)
22 (10%)
0 (0%)
Erosion/Ulceration
103 (48%)
5 (2%)
20 (9%)
0 (0%)
Weeping/Exudate
45 (22%)
0 (0%)
3 (1%)
0 (0%)
Vesicles
19 (9%)
0 (0%)
2 (1%)
0 (0%)
*Mild, Moderate, or Severe
The adverse reactions that most frequently resulted in clinical intervention (e.g., rest periods, withdrawal from study) were local skin and application site reactions. Overall, in the clinical studies, 2% (5/215) of subjects discontinued for local skin/application site reactions. Of the 215 subjects treated, 35 subjects (16%) on imiquimod cream and 3 of 220 subjects (1%) on vehicle cream had at least one rest period. Of these imiquimod cream subjects, 32 (91%) resumed therapy after a rest period.
In the AK studies, 22 of 678 (3.2%) of imiquimod-treated subjects developed treatment site infections that required a rest period off imiquimod cream and were treated with antibiotics (19 with oral and 3 with topical).
Of the 206 imiquimod subjects with both baseline and 8-week post-treatment scarring assessments, 6 (2.9%) had a greater degree of scarring scores at 8-weeks post-treatment than at baseline.
6.2 Clinical Trials Experience: Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma
The data described below reflect exposure to imiquimod cream or vehicle in 364 subjects enrolled in two double-blind, vehicle-controlled studies. Subjects applied imiquimod cream or vehicle 5 times per week for 6 weeks. The incidence of adverse reactions reported by > 1% of subjects during the studies is summarized below.
Table 5: Selected Adverse Reactions Reported by > 1% of Imiquimod-Treated Subjects and at a Greater Frequency than with Vehicle in the Combined Studies (Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma)
Preferred Term
Imiquimod Cream
(n= 185)
N%
Vehicle
(n= 179)
N%
Application Site Reaction
52 (28%)
5 (3%)
Headache
14 (8%)
4 (2%)
Back Pain
7 (4%)
1 (<1%)
Upper Resp Tract Infection
6 (3%)
2 (1%)
Rhinitis
5 (3%)
1 (<1%)
Lymphadenopathy
5 (3%)
1 (<1%)
Fatigue
4 (2%)
2 (1%)
Sinusitis
4 (2%)
1 (<1%)
Dyspepsia
3 (2%)
2 (1%)
Coughing
3 (2%)
1 (<1%)
Fever
3 (2%)
0 (0%)
Dizziness
2 (1%)
1 (<1%)
Anxiety
2 (1%)
1 (<1%)
Pharyngitis
2 (1%)
1 (<1%)
Chest Pain
2 (1%)
0 (0%)
Nausea
2 (1%)
0 (0%)
The most frequently reported adverse reactions were local skin and application site reactions including erythema, edema, induration, erosion, flaking/scaling, scabbing/crusting, itching and burning at the application site. The incidence of application site reactions reported by > 1% of the subjects during the 6 week treatment period is summarized in the table below.
Table 6: Application Site Reactions Reported by > 1% of Imiquimod-Treated Subjects and at a Greater Frequency than with Vehicle in the Combined Studies (Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma)
Included Term
Imiquimod Cream
n= 185
Vehicle
n= 179
Itching
30 (16%)
1 (1%)
Burning
11 (6%)
2 (1%)
Pain
6 (3%)
0 (0%)
Bleeding
4 (2%)
0 (0%)
Erythema
3 (2%)
0 (0%)
Papule(s)
3 (2%)
0 (0%)
Tenderness
2 (1%)
0 (0%)
Infection
2 (1%)
0 (0%)
Local skin reactions were collected independently of the adverse reaction "application site reaction" in an effort to provide a better picture of the specific types of local reactions that might be seen. The prevalence and severity of local skin reactions that occurred during controlled studies are shown in the following table.
Table 7: Local Skin Reactions in the Treatment Area as Assessed by the Investigator (Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma)
Imiquimod Cream
n=184
Vehicle
n=178
All Grades*
Severe
All Grades*
Severe
Erythema
184 (100%)
57 (31%)
173 (97%)
4 (2%)
Flaking/Scaling
167 (91%)
7 (4%)
135 (76%)
0 (0%)
Induration
154 (84%)
11 (6%)
94 (53%)
0 (0%)
Scabbing/Crusting
152 (83%)
35 (19%)
61 (34%)
0 (0%)
Edema
143 (78%)
13 (7%)
64 (36%)
0 (0%)
Erosion
122 (66%)
23 (13%)
25 (14%)
0 (0%)
Ulceration
73 (40%)
11 (6%)
6 (3%)
0 (0%)
Vesicles
57 (31%)
3 (2%)
4 (2%)
0 (0%)
*Mild, Moderate, or Severe
The adverse reactions that most frequently resulted in clinical intervention (e.g., rest periods, withdrawal from study) were local skin and application site reactions; 10% (19/185) of subjects received rest periods. The average number of doses not received per subject due to rest periods was 7 doses with a range of 2 to 22 doses; 79% of subjects (15/19) resumed therapy after a rest period. Overall, in the clinical studies, 2% (4/185) of subjects discontinued for local skin/application site reactions.
In the sBCC studies, 17 of 1266 (1.3%) imiquimod treated subjects developed treatment site infections that required a rest period and treatment with antibiotics.
6.3 Clinical Trials Experience: External Genital Warts
In controlled clinical trials for genital warts, the most frequently reported adverse reactions were local skin and application site reactions.
Some subjects also reported systemic reactions. Overall, 1.2% (4/327) of the subjects discontinued due to local skin/application site reactions. The incidence and severity of local skin reactions during controlled clinical trials are shown in the following table.
Table 8: Local Skin Reactions in the Treatment Area as Assessed by the Investigator (External Genital Warts)
Imiquimod Cream
Vehicle
Females
n=114
Males
n=156
Females
n=99
Males
n=157
All Grades*
Severe
All Grades*
Severe
All Grades*
Severe
All Grades*
Severe
Erythema
74(65%)
4 (4%)
90(58%)
6(4%)
21(21%)
0(0%)
34(22%)
0(0%)
Erosion
35(31%)
1 (1%)
47(30%)
2(1%)
8(8%)
0(0%)
10(6%)
0(0%)
Excoriation/
Flaking
21(18%)
0(0%)
40(26%)
1(1%)
8(8%)
0(0%)
12(8%)
0(0%)
Edema
20(18%)
1(1%)
19(12%)
0(0%)
5(5%)
0(0%)
1(1%)
0(0%)
Scabbing
4(4%)
0(0%)
20(13%)
0(0%)
0(0%)
0(0%)
4(3%)
0(0%)
Induration
6(5%)
0(0%)
11(7%)
0(0%)
2(2%)
0(0%)
3(2%)
0(0%)
Ulceration
9(8%)
3(3%)
7(4%)
0(0%)
1(1%)
0(0%)
1(1%)
0(0%)
Vesicles
3(3%)
0(0%)
3(2%)
0(0%)
0(0%)
0(0%)
0(0%)
0(0%)
*Mild, Moderate, or Severe
Remote site skin reactions were also reported. The severe remote site skin reactions reported for females were erythema (3%), ulceration (2%), and edema (1%); and for males, erosion (2%), and erythema, edema, induration, and excoriation/flaking (each 1%).
Selected adverse reactions judged to be probably or possibly related to imiquimod cream are listed below.
Table 9: Selected Treatment Related Reactions (External Genital Warts)
Females
Males
Imiquimod Cream
n=117
Vehicle
n=103
Imiquimod Cream
n=156
Vehicle
n=158
Application Site Disorders:
Application Site Reactions
Wart Site:
Itching
38(32%)
21(20%)
34(22%)
16(10%)
Burning
30(26%)
12(12%)
14(9%)
8(5%)
Pain
9(8%)
2(2%)
3(2%)
1(1%)
Soreness
3(3%)
0(0%)
0(0%)
1(1%)
Fungal Infection*
13(11%)
3(3%)
3(2%)
1(1%)
Systemic Reactions:
Headache
5(4%)
3(3%)
8(5%)
3(2%)
Influenza-like symptoms
4(3%)
2(2%)
2(1%)
0(0%)
Myalgia
1(1%)
0(0%)
2(1%)
1(1%)
*Incidences reported without regard to causality with imiquimod cream.
Adverse reactions judged to be possibly or probably related to imiquimod cream and reported by more than 1% of subjects included:
Application Site Disorders: burning, hypopigmentation, irritation, itching, pain, rash, sensitivity, soreness, stinging, tenderness
Remote Site Reactions: bleeding, burning, itching, pain, tenderness, tinea cruris
Body as a Whole: fatigue, fever, influenza-like symptoms
Central and Peripheral Nervous System Disorders: headache
Gastro-Intestinal System Disorders: diarrhea
Musculo-Skeletal System Disorders: myalgia
6.4 Clinical Trials Experience: Dermal Safety Studies
Provocative repeat insult patch test studies involving induction and challenge phases produced no evidence that imiquimod cream causes photoallergenicity or contact sensitization in healthy skin; however, cumulative irritancy testing revealed the potential for imiquimod cream to cause irritation, and application site reactions were reported in the clinical studies [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
6.5 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of imiquimod cream. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Application Site Disorders: tingling at the application site
Body as a Whole: angioedema
Cardiovascular: capillary leak syndrome, cardiac failure, cardiomyopathy, pulmonary edema, arrhythmias (tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, palpitations), chest pain, ischemia, myocardial infarction, syncope
Endocrine: thyroiditis
Gastro-Intestinal System Disorders: abdominal pain
Hematological: decreases in red cell, white cell and platelet counts (including idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura), lymphoma
Hepatic: abnormal liver function
Infections and Infestation: herpes simplex
Musculo-Skeletal System Disorders: arthralgia
Neuropsychiatric: agitation, cerebrovascular accident, convulsions (including febrile convulsions), depression, insomnia, multiple sclerosis aggravation, paresis, suicide
Respiratory: dyspnea
Urinary System Disorders: proteinuria, dysuria, urinary retention
Skin and Appendages: exfoliative dermatitis, erythema multiforme, hyperpigmentation, hypertrophic scar
Vascular: Henoch-Schonlein purpura syndrome
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C:
Note: The Maximum Recommended Human Dose (MRHD) was set at 2 packets per treatment of Imiquimod Cream (25 mg imiquimod) for the animal multiple of human exposure ratios presented in this label. If higher doses than 2 packets of imiquimod cream are used clinically, then the animal multiple of human exposure would be reduced for that dose. A non-proportional increase in systemic exposure with increased dose of imiquimod cream was noted in the clinical pharmacokinetic study conducted in actinic keratosis subjects [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. The AUC after topical application of 6 packets of imiquimod cream was 8 fold greater than the AUC after topical application of 2 packets of imiquimod cream in actinic keratosis subjects. Therefore, if a dose of 6 packets per treatment of imiquimod cream was topically administered to an individual, then the animal multiple of human exposure would be either 1/3 of the value provided in the label (based on body surface area comparisons) or 1/8 of the value provided in the label (based on AUC comparisons). The animal multiples of human exposure calculations were based on weekly dose comparisons for the carcinogenicity studies described in this label. The animal multiples of human exposure calculations were based on daily dose comparisons for the reproductive toxicology studies described in this label.
Systemic embryofetal development studies were conducted in rats and rabbits. Oral doses of 1, 5, and 20 mg/kg/day imiquimod were administered during the period of organogenesis (gestational days 6 – 15) to pregnant female rats. In the presence of maternal toxicity, fetal effects noted at 20 mg/kg/day (577X MRHD based on AUC comparisons) included increased resorptions, decreased fetal body weights, delays in skeletal ossification, bent limb bones, and two fetuses in one litter (2 of 1567 fetuses) demonstrated exencephaly, protruding tongues and low-set ears. No treatment related effects on embryofetal toxicity or teratogenicity were noted at 5 mg/kg/day (98X MRHD based on AUC comparisons).
Intravenous doses of 0.5, 1 and 2 mg/kg/day imiquimod were administered during the period of organogenesis (gestational days 6 – 18) to pregnant female rabbits. No treatment related effects on embryofetal toxicity or teratogenicity were noted at 2 mg/kg/day (1.5X MRHD based on BSA comparisons), the highest dose evaluated in this study, or 1 mg/kg/day (407X MRHD based on AUC comparisons).
A combined fertility and peri- and post-natal development study was conducted in rats. Oral doses of 1, 1.5, 3 and 6 mg/kg/day imiquimod were administered to male rats from 70 days prior to mating through the mating period and to female rats from 14 days prior to mating through parturition and lactation. No effects on growth, fertility, reproduction or post-natal development were noted at doses up to 6 mg/kg/day (87X MRHD based on AUC comparisons), the highest dose evaluated in this study. In the absence of maternal toxicity, bent limb bones were noted in the F1 fetuses at a dose of 6 mg/kg/day (87X MRHD based on AUC comparisons). This fetal effect was also noted in the oral rat embryofetal development study conducted with imiquimod. No treatment related effects on teratogenicity were noted at 3 mg/kg/day (41X MRHD based on AUC comparisons).
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Imiquimod Cream should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether imiquimod is excreted in human milk following use of Imiquimod Cream. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when Imiquimod Cream is administered to nursing women.
8.4 Pediatric Use
AK and sBCC are not conditions generally seen within the pediatric population. The safety and efficacy of Imiquimod Cream for AK or sBCC in patients less than 18 years of age have not been established.
Safety and efficacy in patients with external genital/perianal warts below the age of 12 years have not been established.
Imiquimod cream was evaluated in two randomized, vehicle-controlled, double-blind trials involving 702 pediatric subjects with molluscum contagiosum (MC) (470 exposed to imiquimod; median age 5 years, range 2-12 years). Subjects applied imiquimod cream or vehicle 3 times weekly for up to 16 weeks. Complete clearance (no MC lesions) was assessed at Week 18. In Study 1, the complete clearance rate was 24% (52/217) in the imiquimod cream group compared with 26% (28/106) in the vehicle group. In Study 2, the clearance rates were 24% (60/253) in the imiquimod cream group compared with 28% (35/126) in the vehicle group. These studies failed to demonstrate efficacy.
Similar to the studies conducted in adults, the most frequently reported adverse reaction from 2 studies in children with molluscum contagiosum was application site reaction. Adverse events which occurred more frequently in Imiquimod-treated subjects compared with vehicle-treated subjects generally resembled those seen in studies in indications approved for adults and also included otitis media (5% imiquimod vs. 3% vehicle) and conjunctivitis (3% imiquimod vs. 2% vehicle).
Erythema was the most frequently reported local skin reaction. Severe local skin reactions reported by treated subjects in the pediatric studies included erythema (28%), edema (8%), scabbing/crusting (5%), flaking/scaling (5%), erosion (2%) and weeping/exudate (2%).
Systemic absorption of imiquimod across the affected skin of 22 subjects aged 2 to 12 years with extensive MC involving at least 10% of the total body surface area was observed after single and multiple doses at a dosing frequency of 3 applications per week for 4 weeks. The investigator determined the dose applied, either 1, 2 or 3 packets per dose, based on the size of the treatment area and the subject’s weight. The overall median peak serum drug concentrations at the end of week 4 was between 0.26 and 1.06 ng/mL except in a 2-year old female who was administered 2 packets of study drug per dose, had a Cmax of 9.66 ng/mL after multiple dosing. Children aged 2-5 years received doses of 12.5 mg (one packet) or 25 mg (two packets) of imiquimod and had median multiple-dose peak serum drug levels of approximately 0.2 or 0.5 ng/mL, respectively. Children aged 6-12 years received doses of 12.5 mg, 25 mg, or 37.5 mg (three packets) and had median multiple dose serum drug levels of approximately 0.1, 0.15, or 0.3 ng/mL, respectively. Among the 20 subjects with evaluable laboratory assessments, the median WBC count decreased by 1.4 x 109/L and the median absolute neutrophil count decreased by 1.42 x 109/L.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 215 subjects treated with imiquimod cream in the AK clinical studies, 127 subjects (59%) were 65 years and older, while 60 subjects (28%) were 75 years and older. Of the 185 subjects treated with imiquimod cream in the sBCC clinical studies , 65 subjects (35%) were 65 years and older, while 25 subjects (14%) were 75 years and older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects. No other clinical experience has identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger subjects, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
Topical overdosing of Imiquimod Cream could result in an increased incidence of severe local skin reactions and may increase the risk for systemic reactions.
The most clinically serious adverse event reported following multiple oral imiquimod doses of >200 mg (equivalent to imiquimod content of >16 packets) was hypotension, which resolved following oral or intravenous fluid administration.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Imiquimod Cream, 5% is an immune response modifier for topical administration. Each gram contains 50 mg of imiquimod in an off-white oil-in-water vanishing cream base consisting of benzyl alcohol, cetyl alcohol, glycerin, methylparaben, oleic acid, oleyl alcohol, polysorbate 60, propylparaben, purified water, stearyl alcohol, sorbitan monostearate, white petrolatum, and xanthan gum.
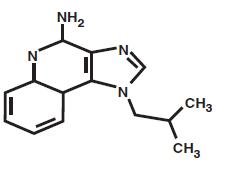
Chemically, imiquimod is 1-(2-methylpropyl)-1H-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-4-amine. Imiquimod has a molecular formula of C14H16N4 and a molecular weight of 240.3. Its structural formula is:
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of Imiquimod Cream in treating AK and sBCC lesions is unknown.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Actinic Keratosis
In a study of 18 subjects with AK comparing imiquimod cream to vehicle, increases from baseline in week 2 biomarker levels were reported for CD3, CD4, CD8, CD11c, and CD68 for imiquimod cream treated subjects; however, the clinical relevance of these findings is unknown.
Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma
An open label study in six subjects with sBCC suggests that treatment with imiquimod cream may increase the infiltration of lymphocytes, dendritic cells, and macrophages into the tumor lesion; however, the clinical significance of these findings is unknown.
External Genital Warts
Imiquimod has no direct antiviral activity in cell culture. A study in 22 subjects with genital/perianal warts comparing imiquimod cream and vehicle shows that imiquimod cream induces mRNA encoding cytokines including interferon-ɑ at the treatment site. In addition HPVL1 mRNA and HPV DNA are significantly decreased following treatment. However, the clinical relevance of these findings is unknown.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Systemic absorption of imiquimod across the affected skin of 58 subjects with AK was observed with a dosing frequency of 3 applications per week for 16 weeks. Mean peak serum drug concentrations at the end of week 16 were approximately 0.1, 0.2, and 3.5 ng/mL for the applications to face (12.5 mg imiquimod, 1 single-use packet), scalp (25 mg, 2 packets) and hands/arms (75 mg, 6 packets), respectively.
Table 10: Mean Serum Imiquimod Concentration in Adults Following
Administration of the Last Topical Dose During Week 16
(Actinic Keratosis)
Amount of Imiquimod Cream applied
Mean peak serum imiquimod
Concentration [Cmax]
12.5 mg (1 packet)
0.1 ng/mL
25 mg (2 packets)
0.2 ng/mL
75 mg (6 packets)
3.5 ng/mL
The application surface area was not controlled when more than one packet was used. Dose proportionality was not observed. However it appears that systemic exposure may be more dependent on surface area of application than amount of applied dose. The apparent half-life was approximately 10 times greater with topical dosing than the 2 hour apparent half-life seen following subcutaneous dosing, suggesting prolonged retention of drug in the skin. Mean urinary recoveries of imiquimod and metabolites combined were 0.08 and 0.15% of the applied dose in the group using 75 mg (6 packets) for males and females, respectively following 3 applications per week for 16 weeks.
Systemic absorption of imiquimod was observed across the affected skin of 12 subjects with genital/perianal warts, with an average dose of 4.6 mg. Mean peak drug concentration of approximately 0.4 ng/mL was seen during the study. Mean urinary recoveries of imiquimod and metabolites combined over the whole course of treatment, expressed as percent of the estimated applied dose, were 0.11 and 2.41% in the males and females, respectively.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In an oral (gavage) rat carcinogenicity study, imiquimod was administered to Wistar rats on a 2X/week (up to 6 mg/kg/day) or daily (3 mg/kg/day) dosing schedule for 24 months. No treatment related tumors were noted in the oral rat carcinogenicity study up to the highest doses tested in this study of 6 mg/kg administered 2X/week in female rats (87X MRHD based on weekly AUC comparisons), 4 mg/kg administered 2X/week in male rats (75X MRHD based on weekly AUC comparisons) or 3 mg/kg administered 7X/week to male and female rats (153X MRHD based on weekly AUC comparisons).
In a dermal mouse carcinogenicity study, imiquimod cream (up to 5 mg/kg/application imiquimod or 0.3% imiquimod cream) was applied to the backs of mice 3X/week for 24 months. A statistically significant increase in the incidence of liver adenomas and carcinomas was noted in high dose male mice compared to control male mice (251X MRHD based on weekly AUC comparisons). An increased number of skin papillomas was observed in vehicle cream control group animals at the treated site only. The quantitative composition of the vehicle cream used in the dermal mouse carcinogenicity study is the same as the vehicle cream used for imiquimod cream, minus the active moiety (imiquimod).
In a 52-week dermal photo-cocarcinogenecity study, the median time to onset of skin tumor formation was decreased in hairless mice following chronic topical dosing (3X/week; 40 weeks of treatment followed by 12 weeks of observation) with concurrent exposure to UV radiation (5 days per week) with the imiquimod cream vehicle alone. No additional effect on tumor development beyond the vehicle effect was noted with the addition of the active ingredient, imiquimod, to the vehicle cream.
Imiquimod revealed no evidence of mutagenic or clastogenic potential based on the results of five in vitro genotoxicity tests (Ames assay, mouse lymphoma L5178Y assay, Chinese hamster ovary cell chromosome aberration assay, human lymphocyte chromosome aberration assay and SHE cell transformation assay) and three in vivo genotoxicity tests (rat and hamster bone marrow cytogenetics assay and a mouse dominant lethal test).
Daily oral administration of imiquimod to rats, throughout mating, gestation, parturition and lactation, demonstrated no effects on growth, fertility or reproduction, at doses up to 87X MRHD based on AUC comparisons.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Actinic Keratosis
In two double-blind, vehicle-controlled clinical studies, 436 subjects with AK were randomized to treatment with either imiquimod cream or vehicle cream 2 times per week for 16 weeks. The studies enrolled subjects with 4 to 8 clinically typical, visible, discrete, nonhyperkeratotic, nonhypertrophic AK lesions within a 25 cm2 contiguous treatment area on either the face or scalp. The 25 cm2 contiguous treatment area could be of any dimensions e.g., 5 cm x 5 cm, 3 cm by 8.3 cm, 2 cm by 12.5 cm. Study subjects ranged from 37 to 88 years of age (median 66 years) and 55% had Fitzpatrick skin type I or II. All imiquimod-treated subjects were Caucasians.
On a scheduled dosing day, the study cream was applied to the entire treatment area prior to normal sleeping hours and left on for approximately 8 hours. Twice weekly dosing was continued for a total of 16 weeks. The clinical response of each subject was evaluated 8 weeks after the last scheduled application of study cream. Efficacy was assessed by the complete clearance rate, defined as the proportion of subjects at the 8-week post-treatment visit with no (zero) clinically visible AK lesions in the treatment area. Complete clearance included clearance of all baseline lesions, as well as any new or sub-clinical AK lesions which appeared during therapy.
Complete and partial clearance rates are shown in the table below. The partial clearance rate was defined as the percentage of subjects in whom 75% or more baseline AK lesions were cleared.
Table 11: Clearance Rates (AK)
Complete Clearance Rates (100% AK Lesions Cleared)
Study
Imiquimod Cream
Vehicle
Study
46% (49/107)
3% (3/110)
AK1
Study
44% (48/108)
4% (4/111)
AK2
Partial and Complete Clearance Rates
(75% or More Baseline AK Lesions Cleared)
Study
Imiquimod Cream
Vehicle
Study
60% (64/107)
10% (11/110)
AK1
Study
58% (63/108)
14% (15/111)
AK2
Sub-clinical AK lesions may become apparent in the treatment area during treatment with imiquimod cream. During the course of treatment, 48% (103/215) of subjects experienced an increase in AK lesions relative to the number present at baseline within the treatment area. Subjects with an increase in AK lesions had a similar response to those with no increase in AK lesions.
14.2 Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma
In two double-blind, vehicle-controlled clinical studies, 364 subjects with primary sBCC were treated with imiquimod cream or vehicle cream 5 times per week for 6 weeks. Target tumors were biopsy-confirmed sBCC and had a minimum area of 0.5 cm2 and a maximum diameter of 2.0 cm (4.0 cm2). Target tumors were not to be located within 1.0 cm of the hairline, or on the anogenital area or on the hands or feet, or to have any atypical features. The population ranged from 31-89 years of age (median 60 years) and 65% had Fitzpatrick skin type I or II. On a scheduled dosing day, study cream was applied to the target tumor and approximately 1 cm (about 1/3 inch) beyond the target tumor prior to normal sleeping hours, and 5 times per week dosing was continued for a total of 6 weeks. The target tumor area was clinically assessed 12 weeks after the last scheduled application of study cream. The entire target tumor was then excised and examined histologically for the presence of tumor.
Efficacy was assessed by the complete response rate defined as the proportion of subjects with clinical (visual) and histological clearance of the sBCC lesion at 12 weeks post-treatment. Of imiquimod-treated subjects, 6% (11/178) who had both clinical and histological assessments post-treatment, and who appeared to be clinically clear had evidence of tumor on excision of the clinically-clear treatment area.
Data on composite clearance (defined as both clinical and histological clearance) are shown in the table below.
Table 12: Composite Clearance Rates at 12 Weeks Post-Treatment
for Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma
Study
Imiquimod
Cream
Vehicle
Cream
Study
sBCC1
70%
(66/94)
2%
(2/89)
Study
sBCC2
80%
(73/91)
1%
(1/90)
Total
75%
(139/185)
2%
(3/179)
A separate 5-year, open-label study was conducted to assess the recurrence of sBCC treated with imiquimod cream applied once daily 5 days per week for 6 weeks. Target tumor inclusion criteria were the same as for the studies described above. At 12-weeks post-treatment, subjects were clinically evaluated for evidence of persistent sBCC (no histological assessment). Subjects with no clinical evidence of sBCC entered the long-term follow-up period. At the 12 week post-treatment assessment, 90% (163/182) of the subjects enrolled had no clinical evidence of sBCC at their target site and 162 subjects entered the long-term follow-up period for up to 5 years. Two year (24 month) follow-up data are available from this study and are presented in the table below:
Table 13: Estimated Clinical Clearance Rates for Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma
Follow-up Period
Follow-up visit after 12-week post-treatment assessment
No. of Subjects who remained clinically clear
No. of Subjects with sBCC recurrence
No. of Subjects who discontinued at this visit with no sBCCa
Estimated Rate of Subjects who Clinically Cleared and remained Clearb
Month 3
153
4
5
87%
Month 6
149
4
0
85%
Month 12
143
2
4
84%
Month 24
139
4
0
79%
a Reasons for discontinuation included death, non-compliance, entry criteria violations, personal reasons, and treatment of nearby sBCC tumor.
b Estimated rate of subjects who clinically cleared and remained clear are estimated based on the time to event analysis employing the life table method beginning with the rate of clinical clearance at 12 weeks post-treatment.
14.3 External Genital Warts
In a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study, 209 otherwise healthy subjects 18 years of age and older with genital/perianal warts were treated with imiquimod cream or vehicle control 3 times per week for a maximum of 16 weeks. The median baseline wart area was 69 mm2 (range 8 to 5525 mm2). Subject accountability is shown in the figure below.
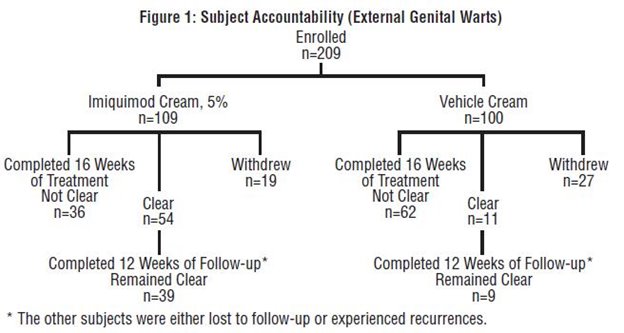
Data on complete clearance are listed in the table below. The median time to complete wart clearance was 10 weeks.Table 14: Complete Clearance Rates (External Genital Warts) – Study EGW1
Treatment
Subjects with
Complete
Clearance of Warts
Subjects
Without
Follow-up
Subjects with
Warts Remaining
At Week 16
Overall
Imiquimod Cream (n=109)
54(50%)
19(17%)
36(33%)
Vehicle (n=100)
11(11%)
27(27%)
62(62%)
Females
Imiquimod Cream (n=46)
33(72%)
5(11%)
8(17%)
Vehicle (n=40)
8(20%)
13(33%)
19(48%)
Males
Imiquimod Cream (n=63)
21(33%)
14(22%)
28(44%)
Vehicle (n=60)
3(5%)
14(23%)
43(72%)
- 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-Approved Patient Labeling
17.1 General Information: All Indications
Imiquimod Cream should be used as directed by a physician. [see Dosage and Administration (2)] Imiquimod Cream is for external use only. Contact with the eyes, lips and nostrils should be avoided. [see Indications and Usage (1)and Dosage and Administration (2)] The treatment area should not be bandaged or otherwise occluded. Partially-used packets should be discarded and not reused. The prescriber should demonstrate the proper application technique to maximize the benefit of Imiquimod Cream therapy.
It is recommended that patients wash their hands before and after applying Imiquimod Cream.
17.2 Local Skin Reactions: All Indications
Patients may experience local skin reactions during treatment with Imiquimod Cream (even with normal dosing). Potential local skin reactions include erythema, edema, vesicles, erosions/ulcerations, weeping/exudate, flaking/scaling/dryness, and scabbing/crusting. These reactions can range from mild to severe in intensity and may extend beyond the application site onto the surrounding skin. Patients may also experience application site reactions such as itching and/or burning. [see Adverse Reactions (6)]
Local skin reactions may be of such an intensity that patients may require rest periods from treatment. Treatment with Imiquimod Cream can be resumed after the skin reaction has subsided, as determined by the physician. Patients should contact their physician promptly if they experience any sign or symptom at the application site that restricts or prohibits their daily activity or makes continued application of the cream difficult
Because of local skin reactions, during treatment and until healed, the treatment area is likely to appear noticeably different from normal skin. Localized hypopigmentation and hyperpigmentation have been reported following use of Imiquimod Cream. These skin color changes may be permanent in some patients.
17.3 Systemic Reactions: All Indications
Patients may experience flu-like systemic signs and symptoms during treatment with Imiquimod Cream (even with normal dosing). Systemic signs and symptoms may include malaise, fever, nausea, myalgias and rigors. [see Adverse Reactions (6)] An interruption of dosing should be considered.
17. 4 Patients Being Treated for Actinic Keratosis (AK)
Dosing is 2 times per week for a full 16 weeks, unless otherwise directed by the physician. However, the treatment period should not be extended beyond 16 weeks due to missed doses or rest periods. [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]
It is recommended that the treatment area be washed with mild soap and water 8 hours following Imiquimod Cream application.
Most patients using Imiquimod Cream for the treatment of AK experience erythema, flaking/scaling/dryness and scabbing/crusting at the application site with normal dosing. [see Adverse Reactions(6.1)]
Use of sunscreen is encouraged, and patients should minimize or avoid exposure to natural or artificial sunlight (tanning beds or UVA/B treatment) while using Imiquimod Cream. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
Sub-clinical AK lesions may become apparent in the treatment area during treatment and may subsequently resolve. [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]
17.5 Patients Being Treated for Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma (sBCC)
Dosing is 5 times per week for a full 6 weeks, unless otherwise directed by the physician. However, the treatment period should not be extended beyond 6 weeks due to missed doses or rest periods. [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]
It is recommended that the treatment area be washed with mild soap and water 8 hours following Imiquimod Cream application. [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]
Most patients using Imiquimod Cream for the treatment of sBCC experience erythema, edema, induration, erosion, scabbing/crusting and flaking/scaling at the application site with normal dosing. [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]
Use of sunscreen is encouraged, and patients should minimize or avoid exposure to natural or artificial sunlight (tanning beds or UVA/B treatment) while using Imiquimod Cream. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
The clinical outcome of therapy can be determined after resolution of application site reactions and/or local skin reactions.
Patients with sBCC treated with Imiquimod Cream should have regular follow-up to re-evaluate the treatment site. [see Clinical Studies (14.2)]
17.6 Patients Being Treated for External Genital Warts
Dosing is 3 times per week to external genital/perianal warts. Imiquimod Cream treatment should continue until there is total clearance of the genital/perianal warts or for a maximum of 16 weeks.
It is recommended that the treatment area be washed with mild soap and water 6-10 hours following Imiquimod Cream application.
It is common for patients to experience local skin reactions such as erythema, erosion, excoriation/flaking, and edema at the site of application or surrounding areas. Most skin reactions are mild to moderate.
Sexual (genital, anal, oral) contact should be avoided while Imiquimod Cream is on the skin.
Application of Imiquimod Cream in the vagina is considered internal and should be avoided. Female patients should take special care if applying the cream at the opening of the vagina because local skin reactions on the delicate moist surfaces can result in pain or swelling, and may cause difficulty in passing urine or inability to urinate.
Uncircumcised males treating warts under the foreskin should retract the foreskin and clean the area daily.
New warts may develop during therapy, as Imiquimod Cream is not a cure.
The effect of Imiquimod Cream on the transmission of genital/perianal warts is unknown.
Imiquimod Cream may weaken condoms and vaginal diaphragms, therefore concurrent use is not recommended.
Should severe local skin reaction occur, the cream should be removed by washing the treatment area with mild soap and water.
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
Patient Information
IMIQUIMOD CREAM, 5%
Read the Patient Information that comes with Imiquimod Cream before you start using it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet does not take the place of talking with your healthcare provider about your medical condition or treatment. If you do not understand the information, or have any questions about Imiquimod Cream, talk with your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
What is Imiquimod Cream?
Imiquimod Cream is a prescription medicine for use on the skin only (topical) to treat:
actinic keratosis on the face or scalp in adults with a normal immune system. Actinic keratosis is caused by too much sun exposure.
superficial basal cell carcinoma in adults with a normal immune system when surgery is not recommended.
Warts on or around the genitals or anus in people 12 years and older.
Imiquimod Cream will not cure your genital or perianal warts. New warts may develop during treatment with Imiquimod Cream. It is not known if Imiquimod Cream can stop you from spreading genital or perianal warts to other people.
It is not known if Imiquimod Cream is safe and effective in:
people who do not have a normal immune system.
the treatment of basal cell nevus syndrome.
the treatment of xeroderma pigmentosum.
the treatment of actinic keratosis with more than one treatment course in the same affected area.
the treatment of certain basal cell carcinoma.
It is not known if Imiquimod Cream is safe and effective in children younger than 18 years of age for the treatment of actinic keratosis or superficial basal cell carcinoma. Children usually do not get actinic keratosis or basal cell carcinoma.
It is not known if Imiquimod Cream is safe and effective in children younger than 12 years of age for the treatment of genital and perianal warts.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before using Imiquimod Cream?
Before using Imiquimod Cream, tell your healthcare provider if you:
have problems with your immune system.
are being treated or have been treated for actinic keratosis with other medicines or surgery. You should not use Imiquimod Cream until you have healed from other treatments.
have any other skin problems
have any other medical conditions
are pregnant or planning to become pregnant. It is not known if Imiquimod Cream can harm your unborn baby. Talk to your healthcare provider if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant.
are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if Imiquimod Cream passes into your breast milk and if it can harm your baby. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby if you use Imiquimod Cream.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins and herbal supplements.
Especially tell your healthcare provider if you have had other treatments for genital warts or warts around your anus, or actinic keratosis, or superficial basal cell carcinoma. Imiquimod Cream should not be used until your skin has healed from other treatments. Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I use Imiquimod Cream?
Do not get Imiquimod Cream in or near your mouth, eyes, nose or vagina.
Use Imiquimod Cream exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to use it. Your healthcare provider will tell you where to apply Imiquimod Cream and how often and for how long to apply it for your condition.
Imiquimod Cream is used for different skin conditions. Use Imiquimod Cream only on the area of your body to be treated. Do not apply Imiquimod Cream to other areas.
Do not use Imiquimod Cream longer than prescribed. Using too much Imiquimod Cream, or using it too often, or for too long can increase your chances for having a severe skin reaction or other side effect.
You should follow-up with your healthcare provider regularly for check-ups while using Imiquimod Cream.
Talk to your healthcare provider if you think Imiquimod Cream is not working for you.
Applying Imiquimod Cream
Imiquimod Cream should be applied just before your bedtime.
Wash the area where the cream will be applied with mild soap and water. Uncircumcised males treating warts under their penis foreskin must pull their foreskin back and clean the area before treatment, and clean the area daily during treatment.
Allow the area to dry for at least 10 minutes.
Wash your hands.
Open a new packet of Imiquimod Cream.
Apply a thin layer of Imiquimod Cream only to the affected area. Do not use more Imiquimod Cream than is needed to cover the affected area.
Rub the cream into your skin until you can not see the Imiquimod Cream. After applying Imiquimod Cream, wash your hands well.
Leave the cream on the treated area for the amount of time your healthcare provider tells you. The length of time that Imiquimod Cream is left on the skin is different for each skin condition that Imiquimod Cream is used to treat. Do not take a bath or get the treated area wet during this time.
After the right amount of time has passed, wash the treated area with mild soap and water.
If you get Imiquimod Cream in your mouth or in your eyes, rinse well with water right away.
What should I avoid while using Imiquimod Cream?
Do not cover the treated area with bandages or other closed dressings.
Do not use sunlamps or tanning beds, and avoid sunlight as much as possible during treatment with Imiquimod Cream. Use sunscreen and wear protective clothing if you go outside during daylight.
Do not have sexual contact including genital, anal, or oral sex when Imiquimod Cream is on your genitals or the skin around your anus. Imiquimod Cream may weaken condoms and vaginal diaphragms. This means they may not work as well to prevent pregnancy.
What are the possible side effects of Imiquimod Cream?
Imiquimod Cream may cause serious side effects including:
Local skin reactions, including:
skin drainage (weeping)
ulcers
severe swelling near the vagina. This may lead to pain or trouble passing urine or cause you not to be able to urinate. Female patients should take special care when applying Imiquimod Cream at the opening of the vagina.
Flu-like symptoms: tiredness, fever, nausea, muscle pain and chills.
Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the symptoms listed above.
The most common side effects of Imiquimod Cream include:
itching
burning
redness
flaking and scaling
dryness
scabbing and crusting
swelling
skin that becomes hard or thickened
sores, blisters, or ulcers
changes in skin color that do not always go away
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the side effects of Imiquimod Cream. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to Perrigo at 1-866-634-9120 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
How do I store Imiquimod Cream?
Store Imiquimod Cream between 39ºF to 77°F (4ºC to 25ºC).
Do not freeze.
Safely throw away unused Imiquimod Cream or partially used Imiquimod Cream packets that you do not need.
Keep Imiquimod Cream and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of Imiquimod Cream
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in this Patient Information leaflet. Do not use Imiquimod Cream for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Imiquimod Cream to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
This Patient Information leaflet summarizes the most important information about Imiquimod Cream. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about Imiquimod Cream that is written for the healthcare professionals.
What are the ingredients in Imiquimod Cream?
Active Ingredient: imiquimod
Inactive ingredients: benzyl alcohol, cetyl alcohol, glycerin, methylparaben, oleic acid, oleyl alcohol, polysorbate 60, propylparaben, purified water, stearyl alcohol, sorbitan monostearate, white petrolatum, and xanthan gum.
Made in Israel
Manufactured by Perrigo
Yeruham 80500, Israel
Distributed By
Allegan, MI 49010www.perrigo.com
Rev 09-13
2H100 RC IC3
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Rx Only
Imiquimod Cream, 5%
For Dermatologic Use Only. Not for Ophthalmic Use.
24 single-use packets
NET WT per Packet 0.25g
NET WT per Carton 6g
The following image is a placeholder representing the product identifier that is either affixed or imprinted on the drug package label during the packaging operation.
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
IMIQUIMOD
imiquimod creamProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 45802-368 Route of Administration TOPICAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength IMIQUIMOD (UNII: P1QW714R7M) (IMIQUIMOD - UNII:P1QW714R7M) IMIQUIMOD 12.5 mg in 0.25 g Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength BENZYL ALCOHOL (UNII: LKG8494WBH) CETYL ALCOHOL (UNII: 936JST6JCN) GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) METHYLPARABEN (UNII: A2I8C7HI9T) OLEIC ACID (UNII: 2UMI9U37CP) OLEYL ALCOHOL (UNII: 172F2WN8DV) POLYSORBATE 60 (UNII: CAL22UVI4M) PROPYLPARABEN (UNII: Z8IX2SC1OH) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) STEARYL ALCOHOL (UNII: 2KR89I4H1Y) SORBITAN MONOSTEARATE (UNII: NVZ4I0H58X) PETROLATUM (UNII: 4T6H12BN9U) XANTHAN GUM (UNII: TTV12P4NEE) Product Characteristics Color WHITE (OFF) Score Shape Size Flavor Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 45802-368-53 12 in 1 CARTON 07/12/2012 1 0.25 g in 1 PACKET; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 45802-368-62 24 in 1 CARTON 11/09/2010 2 0.25 g in 1 PACKET; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA078837 11/09/2010 Labeler - Perrigo New York Inc (078846912)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.