HYDROCORTISONE BUTYRATE lotion
Hydrocortisone Butyrate by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Hydrocortisone Butyrate by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by The J. Molner Company LLC, The J. Molner Company OU, Ferndale Laboratories, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use HYDROCORTISONE BUTYRATE Lotion safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for HYDROCORTISONE BUTYRATE Lotion.
HYDROCORTISONE BUTYRATE Lotion, for topical use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1982INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion is a corticosteroid indicated for the topical treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in patients 3 months of age and older. ( 1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Apply a thin layer to the affected skin two times daily. ( 2)
- Rub in gently. ( 2)
- Discontinue Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion when control is achieved. ( 2)
- Reassess diagnosis if no improvement is seen within 2 weeks. Before prescribing for more than 2 weeks, any additional benefits of extending treatment to 4 weeks should be weighed against the risk of HPA axis suppression and local adverse reactions.( 2)
- Avoid use under occlusion or in the diaper area. ( 2)
- Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion is not for oral, ophthalmic, or intravaginal use. ( 2)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Lotion: 0.1% (1 mg/g) ( 3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None. ( 4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Endocrine System Adverse Reactions: (5)
o Reversible hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis suppression may occur, with the potential for glucocorticosteroid insufficiency. Consider periodic evaluations for HPA axis suppression if Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion is applied to large surface areas or used under occlusion. If HPA axis suppression is noted, reduce the application frequency, discontinue use, or switch to a lower potency corticosteroid. (5.1, 8.4) (5)
o Systemic effects of topical corticosteroids may also include manifestations of Cushing’s syndrome, hyperglycemia, and glucosuria. (5.1, 8.4) (5)
o Pediatric patients may be more susceptible to systemic toxicity due to their larger skin-surface-to-body-mass ratios. (5.1, 8.4) (5)
Ophthalmic Adverse Reactions: Topical corticosteroids, including Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion, may increase the risk of cataracts and glaucoma. If visual symptoms occur, consider referral to an ophthalmologist. (5.2) (5)
(5)
Skin Infections: Initiate appropriate therapy if concomitant skin infections develop. (5.3) (5)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (> 1%) are application site reactions. ( 6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact The J. Molner Company LLC at 1-800-552-8750 and/or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 11/2023
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 11/2023
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Endocrine System Adverse Reactions
5.2 Ophthalmic Adverse Reactions
5.3 Skin Infections
5.4 Allergic Contact Dermatitis
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Apply Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion for up to 2 weeks as a thin layer to the affected skin two times daily and rub in gently. Discontinue Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion when control is achieved.
- If no improvement is seen within 2 weeks, consider reassessment of the diagnosis. Before prescribing for more than 2 weeks, the additional benefits of extending treatment up to 4 weeks should be weighed against the risk of endocrine system adverse reactions and local adverse reactions [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Adverse Reactions (6.1, 6.2)].
- Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion is not for oral, ophthalmic, or intravaginal use.
- Do not use Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion [
see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]:
o With occlusive dressings unless directed by a healthcare provider. Avoid use in the diaper area, as diapers or plastic pants may constitute occlusive dressings.
o On the face, underarms, or groin areas unless directed by a healthcare provider.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Endocrine System Adverse Reactions
Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal (HPA) Axis Suppression
Use of topical corticosteroids, including Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion, can cause systemic adverse reactions including reversible hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis suppression with the potential for clinical glucocorticosteroid insufficiency. Factors that predispose a patient to HPA axis suppression include the use of high-potency steroids, large treatment surface areas, prolonged use, use of occlusive dressings, altered skin barrier, liver failure, and young age. Such patients should be considered for periodic evaluation of the HPA axis. This may be done by using cosyntropin (ACTH 1-24) stimulation testing (CST). If HPA axis suppression is noted, reduce the frequency of application or discontinue Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion, or substitute with a less potent corticosteroid. Signs and symptoms of glucocorticosteroid insufficiency may occur, requiring supplemental systemic corticosteroids [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
Studies conducted in pediatric subjects demonstrated reversible HPA axis suppression after use of Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion. Pediatric patients may be more susceptible than adults to systemic toxicity from equivalent doses of Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion due to their larger skin-surface-to-body-mass ratios [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
Cushing's Syndrome, Hyperglycemia, and Glucosuria
Systemic adverse reactions of topical corticosteroids, including Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion, may also include manifestations of Cushing’s syndrome, hyperglycemia, and glucosuria.
Additional Considerations for Endocrine Adverse Reactions
Use of more than one corticosteroid-containing product at the same time may increase total systemic corticosteroid exposure.
Minimize systemic corticosteroid adverse reactions by mitigating the risk factors for increased systemic absorption and using Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion as recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
5.2 Ophthalmic Adverse Reactions
Use of topical corticosteroids, including Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion, may increase the risk of posterior subcapsular cataracts and glaucoma. Cataracts and glaucoma have been reported in post-marketing experience with the use of topical corticosteroid products [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
Avoid contact of Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion with eyes. Advise patients to report any visual symptoms and consider referral to an ophthalmologist for evaluation.
5.3 Skin Infections
Use of topical corticosteroids, including Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion, may delay healing or worsen concomitant skin infections. If skin infections are present or develop, an appropriate antimicrobial agent should be used. If a favorable response does not occur promptly, use of Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion should be discontinued until the infection has been adequately controlled [seeAdverse Reactions (6)].
5.4 Allergic Contact Dermatitis
Use of topical corticosteroids, including Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion, can cause allergic contact dermatitis [see Adverse Reactions (6)]. Allergic contact dermatitis with corticosteroids is usually diagnosed by observing a failure to heal rather than noticing a clinical exacerbation. Such an observation should be corroborated with appropriate patch testing. Discontinue Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion if the diagnosis is established .
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
HPA axis suppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Use in Specific Populations (8.4)]
Ophthalmic Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5. 2)]
Skin infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
Allergic contact dermatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of the drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety data described below reflect Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion applied topically twice daily for up to 4 weeks in vehicle-controlled clinical trials of 284 pediatric subjects 3 months to 18 years of age and 301 adult subjects with mild to moderate atopic dermatitis [see Clinical Studies (14)].
The incidence of selected adverse reactions reported by ≥1% of subjects during the studies is presented in Table 1 and Table 2.
TABLE 1. Frequency of adverse reactions in pediatric subjects with mild to moderate atopic dermatitis Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion
(n=139) n (%)
Vehicle
(n=145) n (%)
Application site reactions, including application site burning, pruritus, dermatitis, erythema, eczema, inflammation, or irritation
2 (1)
20 (14)
Infantile acne
1 (1)
0 (0)
Skin depigmentation
1 (1)
0 (0)
TABLE 2. Frequency of adverse reactions in adult subjects with mild to moderate atopic dermatitis Hydrocortisone ButyrateLotion
(n=151) n (%)
Vehicle
(n=150) n (%)
Application site reactions, including application site burning, dermatitis, eczema, erythema, or pruritus
5 (3)
7 (5)
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of topical corticosteroids, including Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion. Because these reactions are reported
voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Local Adverse Reactions: folliculitis, acneiform eruptions, perioral dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis, secondary infection, skin atrophy, striae, miliaria, and telangiectasia.
Ophthalmic Adverse Reactions: blurred vision, cataracts, glaucoma, and increased intraocular pressure.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no controlled or large-scale epidemiologic studies with Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion in pregnant women, and available data on hydrocortisone butyrate use in pregnant women have not identified a drug associated risk for major birth defects, miscarriages, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes.
In animal reproduction studies, when administered subcutaneously or topically to pregnant rats, rabbits, and mice, hydrocortisone butyrate induced adverse reproductive and developmental outcomes, including abortion, fetal death, malformation, delayed ossification, decrease in fetal weight, and delay in sexual maturation (see Data). The available data do not allow the calculation of relevant comparisons between the systemic exposure of hydrocortisone butyrate observed in animal studies and the systemic exposure that would be expected in humans after topical use of Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion.
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
Systemic embryofetal development studies were conducted in rats and rabbits. Subcutaneous doses of 0.6, 1.8, and 5.4 mg/kg/day hydrocortisone butyrate were administered to pregnant female rats during gestation days 6 – 17. In the presence of maternal toxicity, fetal effects noted at 5.4 mg/kg/day included increased ossification variations and unossified sternebra. No treatment-related embryofetal toxicity or malformation were noted at 5.4 and 1.8 mg/kg/day,
respectively.
Subcutaneous doses of 0.1, 0.2 and 0.3 mg/kg/day hydrocortisone butyrate were administered to pregnant female rabbits during gestation days 7 – 20. Increased abortion was noted at 0.3
mg/kg/day. In the absence of maternal toxicity, a dose-dependent decrease in fetal body weight was noted at doses ≥0.1 mg/kg/day. Embryofetal toxicities (reduction in litter size, decreased number of viable fetuses, and increased post-implantation loss) were noted at doses ≥0.2 mg/kg/day. Additional fetal effects included delayed ossification noted at doses ≥0.1 mg/kg/day and increased fetal malformations (primarily skeletal malformations) noted at doses ≥0.2 mg/kg/day. A dose at which no embryofetal toxicity or malformation was observed was not established in this study.
Additional systemic embryofetal development studies were conducted in rats and mice. Subcutaneous doses of 0.1 and 9 mg/kg/day hydrocortisone butyrate were administered to pregnant female rats during gestation days 9 – 15. In the presence of maternal toxicity, an increase in fetal death and fetal resorption and an increase in ossification of caudal vertebrae were noted at 9 mg/kg/day. No treatment-related embryofetal toxicity or malformation was noted at 0.1 mg/kg/day.
Subcutaneous doses of 0.2 and 1 mg/kg/day hydrocortisone butyrate were administered to pregnant female mice during gestation days 7 – 13. In the absence of maternal toxicity, an increased number of cervical ribs and one fetus with clubbed legs were noted at 1 mg/kg/day. No treatment-related embryofetal toxicity or malformation was noted at 1 and 0.2 mg/kg/day.
No topical embryofetal development studies were conducted with hydrocortisone butyrate lotion. However, topical embryofetal development studies were conducted in rats and rabbits with a hydrocortisone butyrate ointment formulation. Topical doses of 1% and 10% hydrocortisone butyrate ointment were administered to pregnant female rats during gestation days 6 – 15 or pregnant female rabbits during gestation days 6 – 18. A dose-dependent increase in fetal resorption was noted in rabbits and fetal resorptions were noted in rats at the 10% hydrocortisone butyrate ointment dose. No treatment-related embryofetal toxicity was noted at the 1% hydrocortisone butyrate ointment dose in rats. A dose at which no embryofetal toxicity was observed in rabbits after topical administration of hydrocortisone butyrate ointment was not established. No treatment-related malformation was noted at a dose of 10% hydrocortisone butyrate ointment in rats or rabbits.
A peri- and post-natal development study was conducted in rats. Subcutaneous doses of 0.6, 1.8 and 5.4 mg/kg/day hydrocortisone butyrate were administered to pregnant female rats from gestation day 6 to lactation day 20. In the presence of maternal toxicity, a dose-dependent decrease in fetal weight was noted at doses ≥1.8 mg/kg/day. No treatment-related fetal toxicity was noted at 0.6 mg/kg/day. A delay in sexual maturation was noted at 5.4 mg/kg/day. No treatment-related effects on sexual maturation were noted at 1.8 mg/kg/day. No treatment-related effects on behavioral development or subsequent reproductive performance were noted at 5.4 mg/kg/day.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of hydrocortisone butyrate in human or animal milk, effects on the breastfed infant, or effects on milk production.
Systemically administered corticosteroids appear in human milk and could suppress growth, interfere with endogenous corticosteroid production, or cause other untoward effects. It is not known whether topical administration of Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion could result in sufficient systemic absorption to produce detectable quantities in human milk.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion or from the underlying maternal condition.
Clinical Considerations
To minimize potential exposure to the breastfed infant via breast milk, use Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion on the smallest area of skin and for the shortest duration possible while breastfeeding. Advise breastfeeding women to wash off prior to breastfeeding any Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion that has been applied to the areas at risk for direct infant contact.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion for the topical treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis have been established in pediatric patients 3 months of age and older. Use of Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion for this indication is supported by evidence from an adequate and well-controlled trial in 284 pediatric patients 3 months to 18 years of age with mild to moderate atopic dermatitis.
The safety and effectiveness of Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion have not been established in pediatric patients younger than 3 months of age.
Endocrine Adverse Reactions
Eighty-four (84) pediatric subjects (3 months to less than 18 years of age) with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis affecting at least 25% of body surface area (BSA) treated with Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion three times daily for up to 4 weeks were assessed for HPA axis suppression. The disease severity (moderate to severe atopic dermatitis) and the dosing regimen (three times daily) in this HPA axis trial were different from the subject population (mild to moderate atopic dermatitis) and the dosing regimen (twice daily) for which Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion is indicated. Seven of the 82 evaluable subjects (8.5%) demonstrated laboratory evidence of HPA axis suppression, where the criterion for defining HPA axis suppression was a serum cortisol level of less than or equal to 18 mcg/dL after cosyntropin stimulation. Subjects with HPA axis suppression ranged from 1 to 12 years of age and, at the time of enrollment, had 35% to 90% BSA involvement. These subjects did not develop any other signs or symptoms of HPA axis suppression. At the first follow-up visit, approximately 1 month after the conclusion of treatment, cosyntropin stimulation results of all subjects had returned to normal, with the
exception of one subject. This last subject recovered adrenal function by the second post-treatment visit, 55 days post-treatment [seeClinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
Because of higher skin-surface-to-body-mass ratios, pediatric patients are at a greater risk than adults of HPA axis suppression when they are treated with topical corticosteroids [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. They are therefore also at a greater risk of glucocorticosteroid insufficiency after withdrawal of treatment and of Cushing’s syndrome while on treatment.
Cushing’s syndrome, linear growth retardation, delayed weight gain, and intracranial hypertension have been reported in pediatric patients receiving topical corticosteroids. Manifestations of adrenal suppression in pediatric patients include low plasma cortisol levels to an absence of response to ACTH stimulation. Manifestations of intracranial hypertension include
bulging fontanelles, headaches, and bilateral papilledema.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion, 0.1% contains hydrocortisone butyrate, a non-fluorinated hydrocortisone ester, for topical use.
Hydrocortisone butyrate is a corticosteroid.
The chemical name of hydrocortisone butyrate is Pregn-4-ene-3,20-dione, 11,21-dihydroxy-17-[(1-oxobutyl)oxy(11β)-]. It has the following structural formula:
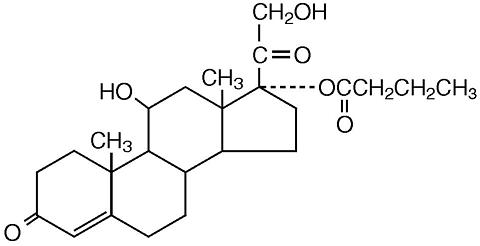
Hydrocortisone butyrate is a white to off-white powder with a molecular weight of 432.56, and a molecular formula of C 25H 36O 6. It is practically insoluble in water, slightly soluble in ether, soluble in methanol, alcohol, and acetone, and freely soluble in chloroform.
Each gram of Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion contains 1 mg of hydrocortisone butyrate in a white to off-white lotion base consisting of anhydrous citric acid, ceteth-20, cetostearyl alcohol, butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT), butylparaben, light mineral oil, propylparaben, purified water, sodium citrate, and white petrolatum.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Corticosteroids play a role in cellular signaling, immune function, inflammation, and protein regulation; however, the precise mechanism of action in atopic dermatitis is unknown.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacodynamics of Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion is unknown.
Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal (HPA) Axis Suppression
Eighty-four (84) pediatric subjects (3 months to less than 18 years of age) with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis affecting at least 25% of body surface area (BSA) treated with Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion three times daily for up to 4 weeks were assessed for HPA axis suppression. The disease severity (moderate to severe atopic dermatitis) and the dosing regimen (three times daily) in this HPA axis trial were different from the subject population (mild to moderate atopic dermatitis) and the dosing regimen (twice daily) for which Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion is indicated. Seven of the 82 evaluable subjects (8.5%) demonstrated laboratory evidence of HPA axis suppression, where the criterion for defining HPA axis suppression was a serum cortisol level of less than or equal to 18 mcg/dL after cosyntropin stimulation. Subjects with HPA axis suppression ranged from 1 to 12 years of age and, at the time of enrollment, had 35% to 90% BSA involvement. These subjects did not develop any other signs or symptoms of HPA axis suppression. At the first follow-up visit, approximately 1 month after the conclusion of treatment, cosyntropin stimulation results of all subjects had returned to normal, with the exception of one subject. This last subject recovered adrenal function by the second post-treatment visit, 55 days post-treatment [seeWarnings and Precautions (5.1), Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
No studies were conducted to determine the pharmacokinetics of Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion.
The extent of percutaneous absorption of topical corticosteroids is determined by many factors, including the vehicle, the integrity of the epidermal barrier, and the use of occlusive dressings.
Topical corticosteroids can be absorbed through normal intact skin. Inflammation and/or other disease processes in the skin, occlusive dressings, or widespread application may increase percutaneous absorption.
Once absorbed through the skin, topical corticosteroids are handled through pharmacokinetic pathways similar to systemically administered corticosteroids.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In a 2-year dermal rat carcinogenicity study with Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion, hydrocortisone butyrate was administered to Sprague-Dawley rats at topical doses of 0.05, 0.15, and 0.3 mg/kg/day in males and 0.1, 0.25, and 0.5 mg/kg/day in females (0.1% lotion). No drug-related tumors were noted in this study up to the highest doses evaluated in this study of
0.3 mg/kg/day in males and 0.5 mg/kg/day in females.
Hydrocortisone butyrate revealed no evidence of mutagenic or clastogenic potential based on the results of two in vitro genotoxicity tests (Ames test and L5178Y/TK+/- mouse lymphoma assay) and one in vivo genotoxicity test (mouse micronucleus assay).
No evidence of impairment of fertility or effect on mating performance was observed in a fertility and general reproductive performance study conducted in male and female rats at subcutaneous doses up to 1.8 mg/kg/day. Mild effects on maternal animals, such as reduced food consumption and a subsequent reduction in body weight gain, were seen at doses ≥0.6 mg/kg/day.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
In a multicenter, randomized, vehicle-controlled trial of 284 pediatric subjects 3 months to 18 years of age with mild to moderate atopic dermatitis, Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion or vehicle was applied twice daily for up to 4 weeks. Treatment success was assessed at day 29 (after 28 days of treatment) and was defined as the proportion of subjects who achieved both “clear” or “almost clear” and at least a 2-grade improvement from baseline on a 5-point Physician’s Global Assessment (PGA) scale. The trial results are shown in Table 3.
TABLE 3. Efficacy results at Day 29 in Pediatric Subjects 3 Months to 18 Years of Age with Mild to Moderate Atopic Dermatitis Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion
(n=139)
Vehicle
(n=145)
Number (%) successes
68 (49%)
35 (24%)
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion, 0.1% is white to off-white in color and supplied in:
- 2 fl. oz. bottle: NDC: 83148-012-02
- 4 fl. oz. bottle: NDC: 83148-012-04
Storage and Handling
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect from freezing.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Patients using Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion should receive the following information and instructions:
Administration Instructions
Instruct patients to apply a thin layer to the affected skin two times daily and rub in gently [ see Dosage and Administration (2)].
Advise patients to discontinue Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion when control is achieved [ see Dosage and Administration (2)].
Advise patients to avoid use for longer than 2 weeks. Instruct patients to contact their healthcare provider if no improvement is seen within 2 weeks [ see Dosage and Administration (2)].
Advise patients to NOT[see Dosage and Administration (2) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]:
- Bandage, otherwise cover, or wrap the affected skin area unless directed by their healthcare provider.
- Use Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion in the diaper area, as diapers or plastic pants may constitute occlusive dressings.
- Use Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion on the face, underarms, or groin areas unless directed by their healthcare provider.
Endocrine System Adverse Reactions
Instruct patients not to use other corticosteroid-containing products while using Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion without first consulting their healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Ophthalmic Adverse Reactions
Advise patients to avoid contact with the eyes. Instruct patients to report any visual symptoms to their healthcare providers [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Lactation
Advise breastfeeding women to use Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion on the smallest area of skin and for the shortest duration possible while breastfeeding. Advise to wash off prior to breastfeeding any Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion that has been applied to the areas at risk for direct infant contact. [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Distributed by:
The J. Molner Company LLC,
Jersey City, NJ 07302
Revised: 11/2023
PI012
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Hydrocortisone Butyrate Lotion, 0.1% - 2 fl oz 59 mL carton
NDC: 83148-012-02
Hydrocortisone Butyrate
Lotion, 0.1%For topical use only.
Not for eye use.Rx only
2 fl oz
(59 mL)J. MOLNER
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
HYDROCORTISONE BUTYRATE
hydrocortisone butyrate lotionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 83148-012 Route of Administration TOPICAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength HYDROCORTISONE BUTYRATE (UNII: 05RMF7YPWN) (HYDROCORTISONE - UNII:WI4X0X7BPJ) HYDROCORTISONE BUTYRATE 1 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength ANHYDROUS CITRIC ACID (UNII: XF417D3PSL) CETETH-20 (UNII: I835H2IHHX) CETOSTEARYL ALCOHOL (UNII: 2DMT128M1S) BUTYLATED HYDROXYTOLUENE (UNII: 1P9D0Z171K) BUTYLPARABEN (UNII: 3QPI1U3FV8) LIGHT MINERAL OIL (UNII: N6K5787QVP) PROPYLPARABEN (UNII: Z8IX2SC1OH) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) SODIUM CITRATE, UNSPECIFIED FORM (UNII: 1Q73Q2JULR) WHITE PETROLATUM (UNII: B6E5W8RQJ4) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 83148-012-02 1 in 1 CARTON 11/06/2023 1 59 mL in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 83148-012-04 1 in 1 CARTON 11/06/2023 2 118 mL in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA209556 11/06/2023 Labeler - The J. Molner Company LLC (119066049) Registrant - The J. Molner Company OU (402460324) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Ferndale Laboratories, Inc. 005320536 label(83148-012) , manufacture(83148-012) , pack(83148-012) , analysis(83148-012)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.