EPHEDRINE SULFATE injection, solution
Ephedrine Sulfate by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Ephedrine Sulfate by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Nexus Pharmaceuticals Inc. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
DESCRIPTION
Ephedrine Sulfate Injection, USP is a sterile solutionn of 50 mg ephedrine sulfate in Water for Injection.
Ephedrine ooccurs as fine, white, oodorless crystals or powder and darkens on exposure to light. It is freely soluble in water and sparingly soluble in alcohol.
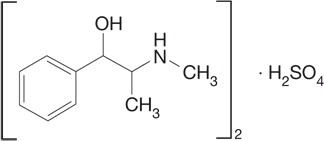
The chemical name of ephedrine sulfate is (C10H15NO)2H2SO4 benzenemethanol α-[l - (methylamino) ethyl] - sufate (2:1) (salt). Its molecular weight is 428 .54. The structural formula is:
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Ephedrine sulfate is a potent sympathomimetic that stimulates both α and β receptors and has clinical uses related to both actions. Its peripheral actions, which it owes in part to the release of norepinephrine, simulate responses that are obtained when adrenegenic nerves are stimulated. These include an increase in blood pressure, stimulation of heart muscle, constriction of arterioles, relaxation of the smooth muscle of the bronchi and gastrointestinal tract, and dilation of the pupils. In the bladder, relaxation of the detrusor muscle is not prominent, but the tone of the trigone and vesicle sphincter is increased.
Ephedrine sulfate also has a potent effect on the CNS. It stimulates the cerebral cortex and sub-cortical centers, which accounts for its use in narcolepsy.
The cardiovascular responses reported in man include moderate tachycardia, unchanged or augmened stroke volume, enhanced cardiac output, variable alterations in peripheral resistance and usually a rise in blood pressure. The action of ephedrine is more prominent on the heart than on the blood vessels. Ephedrine sulfate increases the flow of coronary, cerebral and muscle blood.
In patients with myasthenia gravis, administration of Ephedrine Sulfate Injection, USP produces a real but modest increase in motor power. The exact mechanism by which ephedrine sulfate affects skeletal muscle contractions is unknown.
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Ephedrine Sulfate Injectionn, USP is indicated in the treatment of allergic disorders, such as bronchial asthma The drug has long been used as a pressor agent, particularly during spinal anesthesia when hypotensionn frequently ooccurs. In Stokes-Adams syndromeme with complete heart block, ephedrine has a value similar to that of epinephrine. It is indicated as a central nervous system stimulant in narcolepsy and depressive states. It is also used in myasthenia gravis.
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
PRECAUTIONS
GENERAL - Special care should be used when administering Ephedrine Sulfate Injection, USP to patients with heart disease, angina pectoris, diabetes, hyperthyroidism, prostatic hypertrophy or hypertension and to patients receiving digitalis. Prolonged use may produce a syndrome resembling an anxiety state. Tolerance to ephedrine sulfate may develop, but temporary discontinuance to the drug restores its original effectiveness.
DRUG INTERACTIONS - Concurrent use of ephedrine sulfate with general anesthetics, especially cyclopropane or halogenated hydrocarbons or digitalis glycosides may cause cardiac arrhythmias, since these medications may sensitize the myocardium to the effects of ephedrine sulfate.
Therapeutic doses of ephedrine sulfate can inhibit the hypotensive effect of guanethidine, bethanidine, and debrisoquin by displacing the adrenergic blockers from their site of action in the sympathetic neurons. The effect in man is seen as a relative or a complete blockade of the antihypertensive drug by a sudden rise in blood pressure. Concomitant use of Ephedrine Sulfate Injection, USP and oxytocics may cause severe hypotension.
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors may potentiate the pressor effect of ephedrine sulfate, possibly resulting in a hypertensive crisis. Ephedrine Sulfate Injection, USP should not be administered during or within 14 days following the administration of MAO inhibitors.
PREGNANCY CATEGORY C - Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with Ephedrine Sulfate Injection, USP. Also, it is not known whether the drug can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Ephedrine Sulfate Injection, USP should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly indicated.
It is not known what effect Ephedrine Sulfate Injection, USP may have on the newborn or on the child's later growth and development when the drug is administered to the mother just before or during labor.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
With large doses of ephedrine sulfate most patients will experience nervousness, insomnia, vertigo, headache, tachycardia, palpitation and sweating. Some patients have nausea, vomiting and anorexia. Vesical sphincter spasm may occur and result in difficult and painful urination. Urinary retention may develop in males with prostatism.
Primordial pain and cardiac arrhythmias may occur following administration of Ephedrine Sulfate Injection, USP
-
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
Prolonged abuse of Ephedrine Sulfate Injection, USP can lead to symptoms of paranoid schizophrenia. When this occurs, patients exhibit such physical signs as tachycardia, poor nutrition and hygiene, fever, cold sweat and dilated pupils.
Some measure of tolerance may develop with prolonged or excessive use but addiction does not occur. Temporary cessation of medication and subsequent readministration restores its effectiveness.
-
OVERDOSAGE
SYMPTOMS - The principal manifestation of ephedrine sulfate poisoning is convulsions. In acute poisoning the following signs and symptoms may occur: nausea, vomiting, chills, cyanosis, irritability, nervousness, fever, suicidal behavior, tachycardia, dilated pupils, blurred vision, opisthotonos, spasms, convulsions, pulmonary edema, gasping respirations, coma and respiratory failure. Initially, the patient may have hypertension, followed later by hypotension accompanied by anuria.
TREATMENT - If respirations are shallow or cyanosis is present, artificial respiration should be administered. Vasopressors are contraindicated. In cardiovascular collapse blood pressure should be maintained.
ANTIDOTE - For hypertension, 5 mg phentolamine mesylate diluted in saline may be administered slowly intravenously, or 100 mg may be given orally. Convulsions may be controlled by diazepam or paraldehyde. Cool applications and dexamethasone 1 mg/kg, administered slowly intravenously, may control pyrexia.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
ADULTS - T he usual parenteral dose is 25 to 50 mg given subcutaneously or intramuscularly. Intravenously, 5 to 25 mg may be administered slowly, repeated in 5 to 10 minutes, if necessary.
CHILDREN - The usual subcutaneous or intramuscular dose is 0.5 mg/kg of body weight or 16 .7 mg/square meter of body surface every 4 to 6 hours.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
- HOW SUPPLIED
-
Principal Display Panel - Carton Label
NEXUS
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.10 x 2 mL Vials NDC: 14789-014-01
Ephedrine Sulfate
Injection, USP50 mg/mL
1 mL fill in a 2 mL Vial
Single Dose Vial
Preservative Free
For subcutaneous,
intramuscular or
intravenous use.Rx only
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
EPHEDRINE SULFATE
ephedrine sulfate injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 14789-014 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Ephedrine Sulfate (UNII: U6X61U5ZEG) (Ephedrine - UNII:GN83C131XS) Ephedrine Sulfate 50 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 14789-014-01 10 in 1 CARTON 1 1 mL in 1 VIAL, SINGLE-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date unapproved drug other 06/08/2015 Labeler - Nexus Pharmaceuticals Inc (620714787)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.