BONDLIDO- lidocaine system
BONDLIDO by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
BONDLIDO by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by MEDRx USA, Inc., Sumika Chemical Analysis Services, Ltd., Delta Synthetic Co., Ltd.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use BONDLIDO® safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for BONDLIDO®.
BONDLIDO (lidocaine topical system )
Initial U.S. Approval: 1953INDICATIONS AND USAGE
BONDLIDO contains lidocaine, an amide local anesthetic, and is indicated in adults for relief of pain associated with post-herpetic neuralgia (PHN) (1).
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Due to differences in bioavailability, the efficacy of a lidocaine topical system does not necessarily correlate with dosage strength. Refer to the dosing instructions for the specific product being used (2).
- Apply BONDLIDO to intact skin to cover the most painful area. Apply the prescribed number of topical systems (maximum of two) only once for up to 12 hours in a 24-hour period (2).
- Apply firm pressure for 20 seconds to ensure adequate adherence.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Topical System: 10% lidocaine (3).
CONTRAINDICATIONS
BONDLIDO is contraindicated in patients with a known history of sensitivity to local anesthetics of the amide type, or to any other component of the product (4).
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Accidental Exposure: A used BONDLIDO topical system contains residual lidocaine after use. It is important for patients to store and dispose of BONDLIDO out of the reach of children, pets, and others (5.1).
- Excessive Dosing: Applying BONDLIDO to larger surface areas or for a longer duration than recommended could result in increased absorption and high blood concentrations of lidocaine, leading to serious adverse effects (5.2).
- Non-Intact Skin: May result in higher blood concentrations of lidocaine from increased absorption (5.2).
- External Heat Sources: External heat sources may increase drug exposure, leading to overexposure of lidocaine (5.2).
- Methemoglobinemia: Cases of methemoglobinemia have been reported in association with local anesthetic use (5.3).
- Application Site Reactions: Severe skin irritation may occur with BONDLIDO if applied for a longer period than instructed (5.4).
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: Patients with an allergy to PABA derivatives may have cross-sensitivity to BONDLIDO(5.5).
- Eye Exposure: If eye contact occurs, immediately wash out the eye with water or saline and protect the eye using, for example, eyeglasses/eye wear, until sensation returns (5.6).
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Common adverse reactions are application site reactions such as irritation, erythema, and pruritus (6).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact MEDRx USA, Inc. at TELEPHONE or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs: When BONDLIDO is used in patients receiving Class I antiarrhythmic drugs (such as tocainide or mexiletine), the toxic effects are additive and potentially synergistic. Consider risk/benefit during concomitant use (7.1).
- Local Anesthetics: When BONDLIDO is used concomitantly with other products containing local anesthetic agents, the effects are additive. The amount absorbed from all formulations must be considered for safe use (7.2).
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Lactation: Lidocaine is excreted into human milk. Caution should be exercised when BONDLIDO is administered to a nursing mother, especially when administered with other local anesthetics (8.2).
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 9/2025
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Dosage and Administration Information
2.2 Application Instructions
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Accidental Exposure
5.2 Excessive Dosing
5.3 Methemoglobinemia
5.4 Application Site Reactions
5.5 Hypersensitivity Reactions
5.6 Eye Exposure
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Antiarrhythmic Drugs
7.2 Local Anesthetics
7.3 Drugs That May Cause Methemoglobinemia When Used with BONDLIDO
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Dosage and Administration Information
Due to differences in bioavailability, the efficacy of a lidocaine topical system does not necessarily correlate with dosage strength (i.e., concentration). Comparing different products on a nominal percentage-for-percentage basis may be misleading and the appropriate strength for a given indication may vary by product. Refer to the dosing instructions for the specific product being used. [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
When BONDLIDO is used concomitantly with other products containing local anesthetic agents, the total amount of drug absorbed from all formulations must be considered.
2.2 Application Instructions
Clearly instruct and advise patients:
- to apply BONDLIDO to intact skin to cover the most painful area. Apply the prescribed number of topical systems (maximum of 2), only once for up to 12 hours within a 24-hour period. Safety has not been established for application of more than 2 BONDLIDO topical systems per day.
- to apply firm pressure for 20 seconds to ensure an adequate adherence.
- that clothing may be worn over the area of application.
- to remove BONDLIDO if irritation or a burning sensation occurs during application. Advise patients not to reapply until the irritation subsides.
- to wash hands immediately after handling BONDLIDO and to avoid contact with eyes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5), Patient Counseling Information (17)].
- to not store BONDLIDO outside of the sealed pouch.
- to apply immediately after removal from the protective pouch.
- to fold used BONDLIDO so that the adhesive side sticks to itself.
- to safely discard used BONDLIDO where children and pets cannot get to them.
- to never apply external heat sources, such as heating pads or electric blankets, directly to BONDLIDO because plasma lidocaine levels may be increased [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Patient Counseling Information (17)].
- that BONDLIDO may not stick if it gets wet and to avoid contact with water, such as bathing, swimming, or showering, while a BONDLIDO topical system is applied. If the BONDLIDO topical system comes off completely and will not stick to the skin, advise patients that they may apply a replacement BONDLIDO topical system and take the replacement BONDLIDO topical system off at the usual removal time. Advise patients not to wear BONDLIDO for more than 12 hours within a 24-hour period.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Accidental Exposure
A used BONDLIDO topical system contains residual lidocaine after use. The potential exists for a small child or a pet to suffer serious adverse effects from chewing or ingesting new or used BONDLIDO. It is important for patients to store and dispose of BONDLIDO properly, and keep out of the reach of children, pets, and others [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
5.2 Excessive Dosing
Lidocaine toxicity could be expected at lidocaine blood concentrations above 5 µg/mL. The blood concentration of lidocaine is determined by the rate of systemic absorption and elimination. Longer duration of application, application of more than the recommended number of BONDLIDO, smaller patients, or impaired elimination may all contribute to increasing the blood concentration of lidocaine.
If lidocaine overdose is suspected, check drug blood concentration. Management of overdose includes close monitoring, supportive care, and symptomatic treatment [see Overdosage (10)].
Improper Application and Duration of Use: Application of more than the recommended number of BONDLIDO or applying BONDLIDO for longer than the recommended wearing time (12 hours of every 24 hours) could result in increased absorption and high blood concentrations of lidocaine, leading to adverse effects. Advise patients on proper application and duration [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
Hepatic Disease: Impaired elimination may contribute to increasing blood concentrations of lidocaine. Patients with severe hepatic disease are at greater risk of developing toxic blood concentrations of lidocaine because of their inability to metabolize lidocaine normally.
Non-Intact Skin: Application to broken or inflamed skin, although not tested, may result in higher blood concentrations of lidocaine from increased absorption. BONDLIDO is only recommended for use on intact skin. Advise patients not to apply BONDLIDO to non-intact skin [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
External Heat Sources: External heat sources may increase drug exposure, leading to overexposure to lidocaine. Advise patients not to apply external heat sources to BONDLIDO during administration [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
5.3 Methemoglobinemia
Cases of methemoglobinemia have been reported in association with local anesthetic use. Although all patients are at risk for methemoglobinemia, patients with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, congenital or idiopathic methemoglobinemia, cardiac or pulmonary compromise, infants under 6 months of age, and concurrent exposure to oxidizing agents or their metabolites are more susceptible to developing clinical manifestations of the condition. If local anesthetics must be used in these patients, close monitoring for symptoms and signs of methemoglobinemia is recommended.
Signs of methemoglobinemia may occur immediately or may be delayed some hours after exposure and are characterized by a cyanotic skin discoloration and/or abnormal coloration of the blood.
Methemoglobin levels may continue to rise; therefore, immediate treatment is required to avert more serious central nervous system and cardiovascular adverse effects, including seizures, coma, arrhythmias, and death. Discontinue BONDLIDO and any other oxidizing agents. Depending on the severity of the signs and symptoms, patients may respond to supportive care, i.e., oxygen therapy, hydration. A more severe clinical presentation may require treatment with methylene blue, exchange transfusion, or hyperbaric oxygen.
5.4 Application Site Reactions
During or immediately after treatment with BONDLIDO, the skin at the site of application may develop blisters, bruising, burning sensation, depigmentation, dermatitis, discoloration, edema, erythema, exfoliation, irritation, papules, petechia, pruritus, vesicles, or may be the locus of abnormal sensation. These reactions are generally mild and transient, resolving spontaneously within a few minutes to hours. If application site reactions occur while the topical system is being worn, advise the patient to remove BONDLIDO and not to reapply until skin reactions subside.
5.5 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Patients allergic to para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) derivatives (procaine, tetracaine, benzocaine, etc.) have not shown cross-sensitivity to lidocaine. However, be aware of the potential for cross-sensitivity in patients allergic to PABA derivatives, especially if the etiologic agent is uncertain. Manage hypersensitivity reactions by conventional means. The detection of sensitivity by skin testing is of doubtful value.
5.6 Eye Exposure
The contact of BONDLIDO with eyes, although not studied, should be avoided based on findings of severe eye irritation with the application of similar products in animals. If eye contact occurs, immediately wash out the eye with water or saline and protect the eye using, for example, eye glasses/eye wear, until sensation returns.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Accidental Exposure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Excessive Dosing/Overexposure to Lidocaine [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] Methemoglobinemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Application Site Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Eye Irritation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
The following adverse reactions associated with the use of lidocaine were identified in clinical trials or postmarketing reports for lidocaine. Because some of these reactions were reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Skin and subcutaneous tissues: blisters, bruising, burning sensation, depigmentation, dermatitis, discoloration, edema, erosions, erythema, exfoliation, flushing, irritation, papules, petechia, pruritus, vesicles, and abnormal sensation.
Immune system: angioedema, bronchospasm, dermatitis, dyspnea, hypersensitivity, laryngospasm, pruritus, shock, and urticaria.
Central Nervous System: lightheadedness, nervousness, apprehension, euphoria, confusion, dizziness, drowsiness, tinnitus, blurred or double vision, sensations of heat, cold or numbness, twitching, tremors, convulsions, unconsciousness, somnolence, respiratory depression and arrest.
Cardiovascular: bradycardia, hypotension, and cardiovascular collapse leading to arrest.
Other: asthenia, disorientation, headache, hyperesthesia, hypoesthesia, metallic taste, nausea, pain exacerbated, paresthesia, taste alteration, and vomiting.
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Antiarrhythmic Drugs
When BONDLIDO is used in patients receiving Class I antiarrhythmic drugs (such as tocainide or mexiletine), the toxic effects are additive and potentially synergistic. Consider risk/benefit during concomitant use.
7.2 Local Anesthetics
When BONDLIDO is used concomitantly with other products containing local anesthetic agents, the effects are additive. The amount absorbed from all formulations must be considered for safe use.
7.3 Drugs That May Cause Methemoglobinemia When Used with BONDLIDO
Patients who are administered local anesthetics are at increased risk of developing methemoglobinemia when concurrently exposed to the following drugs, which could include other local anesthetics:
Examples of Drugs Associated with Methemoglobinemia:
Class Examples Nitrates/Nitrites nitric oxide, nitroglycerin, nitroprusside, nitrous oxide Local anesthetics articaine, benzocaine, bupivacaine, lidocaine, mepivacaine, prilocaine, procaine, ropivacaine, tetracaine Antineoplastic agents cyclophosphamide, flutamide, hydroxyurea, ifosfamide, rasburicase Antibiotics dapsone, nitrofurantoin, para-aminosalicylic acid, sulfonamides Antimalarials chloroquine, primaquine Anticonvulsants Phenobarbital, phenytoin, sodium valproate Other drugs acetaminophen, metoclopramide, quinine, sulfasalazine -
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
The limited human data with lidocaine in pregnant woman are not sufficient to inform drug-associated risk for major birth defects and miscarriage.
The use of lidocaine for labor neuraxial analgesia has not been associated with an increased incidence of adverse fetal effects either during delivery or during the neonatal period [see Data]. Should BONDLIDO be used concomitantly with other products containing lidocaine, consider total drug doses contributed by all formulations.
In a published animal reproduction study, pregnant rats administered lidocaine by continuous subcutaneous infusion at a dose approximately 12 times the maximum recommended daily dose (MRDD) of 400 mg in BONDLIDO during the period of organogenesis resulted in lower fetal body weights. In a published animal reproduction study, pregnant rats administered lidocaine, containing 1:100,000 epinephrine, injected into the masseter muscle of the jaw or into the gum of the lower jaw at approximately 0.14 times the MRDD on Gestation Day 11 resulted in developmental delays in neonates [see Data].
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies carry some risk of birth defects, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Human Data
In 22 parturient women given 1.5% lidocaine epidural anesthesia, there were no effects on neonatal behavior, using the early neonatal neurobehavioral scale (ENNS). Neuraxial analgesia also did not affect fetal heart rate, beat-to-beat variability, or uterine activity.
Animal Data
Reproductive studies with lidocaine have been performed in rats at doses up to 30 mg/kg (0.73 times the maximum recommended daily dose [MRDD] of 400 mg from BONDLIDO on a mg/m 2 basis) subcutaneously and have revealed no evidence of harm to the fetus due to lidocaine.
In a published study, lidocaine administered to pregnant rats by continuous subcutaneous infusion during the period of organogenesis at 100, 250, and 500 mg/kg/day, did not produce any structural abnormalities, but did result in lower fetal weights at 500 mg/kg/day dose (approximately 12 times the MRDD on a mg/m 2 basis) in the absence of maternal toxicity.
In a published study, lidocaine containing 1:100,000 epinephrine at a dose of 6 mg/kg (approximately 0.14 times the MRDD on a mg/m2 basis) injected into the masseter muscle of the jaw or into the gum of the lower jaw of pregnant Long-Evans hooded rats on Gestation Day 11 resulted in developmental delays in the neonates. Developmental delays were observed for negative geotaxis, static righting reflex, visual discrimination response, sensitivity and response to thermal and electrical shock stimuli, and water maze acquisition. The developmental delays of the neonatal animals were transient, with responses becoming comparable to untreated animals later in life. The clinical relevance of these animal data is uncertain.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Lidocaine is excreted into human milk. A milk:plasma ratio of 1.07 (for AUC) was observed when lidocaine was used as an epidural anesthetic for cesarean section in 27 women. Lactating women undergoing a dental procedure had a 0.4 milk:plasma ratio. In another dental procedure study, a single patient was administered 20 mg of lidocaine and the milk:plasma ratio was reported as 1.1 at five to six hours after injection. These data, and the low concentrations of lidocaine in the plasma after topical administration of BONDLIDO in recommended doses, suggest that a small amount of lidocaine would be ingested orally by a suckling infant. However, caution should be exercised when BONDLIDO is administered to a nursing mother, especially when administered with other local anesthetics.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of BONDLIDO did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be done with caution, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
Lidocaine overdose from cutaneous absorption is rare but could occur. If there is any suspicion of lidocaine overdose, drug blood concentration should be checked. The management of overdose includes close monitoring, supportive care, and symptomatic treatment. Dialysis is of negligible value in the treatment of acute overdose with lidocaine.
In the absence of massive topical overdose or oral ingestion, evaluation of symptoms of toxicity should include consideration of other etiologies for the clinical effects, or overdosage from other sources of lidocaine or other local anesthetics.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
BONDLIDO (lidocaine topical system) 10% is a drug-in-adhesive topical delivery system containing 200 mg lidocaine with a non-woven polyethylene terephthalate (PET) backing membrane and a PET film release liner.
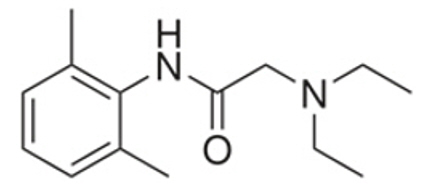
Lidocaine, an amide local anesthetic, is chemically designated as acetamide, 2-(diethylamino)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl) (C14H22N2O), has a molecular weight of 234.34 g/mol, an octanol:water partition ratio of 43 at pH 7.4, is very soluble in methanol and in ethanol, is soluble in acetic acid and in diethyl ether, is practically in-soluble in water, dissolves in dilute hydrochloric acid, and has the following structure:
Each BONDLIDO topical system is 10 cm × 14 cm × 0.066 cm and contains the following inactive ingredients: blue ink, hydrocarbon, lactic acid, mono- and di-glycerides, non-woven PET backing membrane, PET film, polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil, propylene carbonate, styrene/isoprene/styrene block copolymer, tartaric acid, and terpene resin.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Lidocaine is an amide-type local anesthetic and is suggested to stabilize neuronal membranes by inhibiting the ionic fluxes required for the initiation and conduction of impulses.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The penetration of lidocaine into intact skin after application of BONDLIDO is sufficient to produce an analgesic effect, but less than the amount necessary to produce a complete sensory block.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Bioavailability for topical systems such as BONDLIDO is dependent on multiple factors, including formulation, and does not necessarily correlate with dosage strength. In a single-dose, crossover study conducted in 32 healthy volunteers, BONDLIDO (lidocaine topical system 10%) demonstrated equivalent systemic exposure (AUC) and peak concentration (C max) of lidocaine to a lidocaine topical system 5%.
Absorption
The amount of lidocaine systemically absorbed from BONDLIDO topical system is directly related to both the duration of application and the surface area over which it is applied.
In a pharmacokinetic study, two BONDLIDO topical systems were applied on the back of the healthy volunteers for 12 hours. Blood samples were drawn for determination of lidocaine concentration during the topical system application and for 32 hours after removal of topical systems. The results are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1. Mean ± SD Pharmacokinetic Parameters of lidocaine from BONDLIDO in healthy volunteers (n = 32, 12-hour application time) Application Site Area (cm2) Cmax (ng/mL) AUC0-inf
(ng∙hr/mL)Tmax (hr)* - * median (min, max)
2 BONDLIDO topical system (2 × 200 mg = 400 mg total dose for 12 hours) Back 280 52.8 (38.9) 837 (37.7) 13.0
(8.0,18.0)Repeated application of three lidocaine topical systems 5% simultaneously for 12 hours (recommended maximum daily dose), once per day for three days, indicated that the lidocaine concentration does not increase with daily use. The mean plasma pharmacokinetic profile for the 15 healthy volunteers is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1. Mean lidocaine blood concentrations after three consecutive daily applications of three lidocaine topical systems 5% simultaneously for 12 hours per day in healthy volunteers (n = 15) 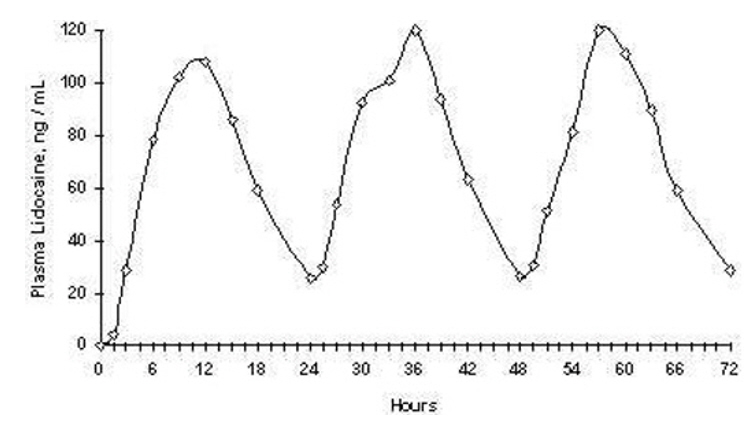
The pharmacokinetics of lidocaine delivered by BONDLIDO topical system was assessed in 20 healthy volunteers undergoing exercise (four 30 minute sessions of moderate exercise over the 12 hour period of BONDLIDO application) and following application of a transparent film occlusive dressing over BONDLIDO for the full 12 hour period of BONDLIDO application (occlusion) and results were compared to those obtained under resting conditions. Two hours of moderate exercise resulted in approximately 20% reduction in systemic exposure as measured by Cmax and AUC[0-inf] indicating a modest reduction in delivery from the topical system over the 12 hour period of topical system application. Exposure to total occlusion of the topical system for 12 hours produced no statistically significant changes in the absorption or pharmacokinetics of lidocaine from BONDLIDO topical system.
Distribution
When lidocaine is administered intravenously to healthy volunteers, the volume of distribution is 0.7 to 2.7 L/kg (mean 1.5 ± 0.6 SD, n = 15). At concentrations produced by application of a lidocaine topical system 5%, lidocaine is approximately 70% bound to plasma proteins, primarily alpha-1-acid glycoprotein. At much higher plasma concentrations (1 to 4 µg/mL of free base), the plasma protein binding of lidocaine is concentration dependent. Lidocaine crosses the placental and blood brain barriers, presumably by passive diffusion.
Elimination
Metabolism:
It is not known if lidocaine is metabolized in the skin. Lidocaine is metabolized rapidly by the liver to a number of metabolites, including monoethylglycinexylidide (MEGX) and glycinexylidide (GX), both of which have pharmacologic activity similar to, but less potent than that of lidocaine. A minor metabolite, 2,6-xylidine, has unknown pharmacologic activity. The blood concentration of this metabolite is negligible following application of lidocaine topical system 5%. Following intravenous administration, MEGX and GX concentrations in serum range from 11 to 36% and from 5 to 11% of lidocaine concentrations, respectively.
Excretion:
Lidocaine and its metabolites are excreted by the kidneys. Less than 10% of lidocaine is excreted unchanged. The half-life of lidocaine elimination from the plasma following IV administration is 81 to 149 minutes (mean 107 ± 22 SD, n = 15). The systemic clearance is 0.33 to 0.90 L/minute (mean 0.64 ±0.18 SD, n = 15).
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Long-term studies in animals to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of BONDLIDO have not been conducted.
A metabolite, 2,6-xylidine, has been found to be carcinogenic in rats. The clinical significance is not known.
Mutagenesis
Lidocaine HCl was not mutagenic in the Salmonella/mammalian microsome test (Ames assay) and was not clastogenic in the chromosome aberration assay with human lymphocytes or in the mouse micronucleus test.
Impairment of Fertility
In a published study, female Sprague-Dawley rats were treated subcutaneously with lidocaine via osmotic pumps starting two weeks prior to mating, and reproductive effects were assessed. Rats dosed up to the high dose of 500 mg/kg/day (approximately 12 times the MRDD on a mg/m2 basis) showed no effects on copulatory rate, pregnancy rate, or the numbers of corpora lutea or implantations.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Single-dose treatment with a different lidocaine topical system was compared to treatment with vehicle system (without lidocaine), and to no treatment (observation only) in a double-blind, crossover clinical trial with 35 post-herpetic neuralgia patients. Pain intensity and pain relief scores were evaluated periodically for 12 hours. Lidocaine topical system performed statistically better than vehicle system in terms of pain intensity from 4 to 12 hours.
Multiple-dose, two-week treatment with a different lidocaine topical system was also compared to vehicle system (without lidocaine) in a double-blind, crossover clinical trial of withdrawal-type design conducted in 32 patients, who were considered as responders to the open-label use of lidocaine topical system prior to the study. The constant type of pain was evaluated but not the pain induced by sensory stimuli (dysesthesia).
Statistically significant differences favoring the lidocaine topical system were observed in terms of time to exit from the trial (14 versus 3.8 days at p-value <0.001), daily average pain relief, and patient's preference of treatment. About half of the patients also took oral medication commonly used in the treatment of post-herpetic neuralgia. The extent of use of concomitant medication was similar in the two treatment groups.
Based on a clinical study in adults wearing BONDLIDO covering the thoracic dermatomes T8-T10, 98 of 100 topical systems applied exhibited 75% or greater surface area adhesion at all timepoints evaluated (every 3 hours) throughout the 12-hour wear period.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
BONDLIDO (lidocaine topical system) 10% is a rectangular topical system with blue printing on one side and release liner on other. It is available as the following:
Carton of 28 topical systems, packaged into individual child-resistant pouches.
NDC: 83708-111-28
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Instructions for Use).
Accidental Exposure and Disposal
Advise patients to store BONDLIDO out of the reach of children, pets, and others. Advise patients to dispose of used BONDLIDO by folding used BONDLIDO so that the adhesive side sticks to itself and safely discarding used BONDLIDO where children, pets, and others cannot come in contact with them. [see Dosage and Administration (2), Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
Proper Application
Advise patients:
- to avoid getting BONDLIDO wet (e.g., bathing, swimming or showering) [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
- not to apply more than the prescribed number (up to 2 BONDLIDO) [see Dosage and Administration (2), Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- not to wear BONDLIDO longer than the recommended wearing time (12 hours of every 24 hours) [see Dosage and Administration (2), Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- not to apply BONDLIDO to non-intact skin [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Methemoglobinemia
Inform patients that use of local anesthetics may cause methemoglobinemia, a serious condition that must be treated promptly. Advise patients or caregivers to stop use and seek immediate medical attention if they or someone in their care experience the following signs or symptoms: pale, gray, or blue colored skin (cyanosis); headache; rapid heart rate; shortness of breath; lightheadedness; or fatigue [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Application Site Reactions
Inform patients that skin irritation and other skin reactions may occur at the site of BONDLIDO application. If skin reactions occur during wear, instruct patients to remove BONDLIDO and not to reapply until the skin reaction subsides [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Eye Exposure
Advise patients to wash hands immediately after handling BONDLIDO and to avoid contact with eyes. Instruct patients to, if eye contact should occur, immediately wash out the eye with water or saline and protect the eye until sensation returns [see Dosage and Administration (2), Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
PATIENT INFORMATION
BONDLIDO (BAHND-LYE-DOH)
(lidocaine topical system)This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Issued: 09/2025 What is BONDLIDO?
BONDLIDO is a prescription medicine used in adults for the relief of pain from damaged nerves (neuropathic pain) that follows healing of shingles.
It is not known if BONDLIDO is safe and effective in children.Do not use BONDLIDO if you: - have a history of allergic reactions to numbing medicines (local anesthetics). Ask your healthcare provider if you are not sure.
- are allergic to any of the ingredients in BONDLIDO. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in BONDLIDO.
Before using BONDLIDO, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you: - have liver problems
- have heart or lung problems
- are allergic to numbing medicines such as procaine, tetracaine, or benzocaine
- have been told that you have glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency
- were born with (congenital) methemoglobinemia or have had methemoglobinemia from an unknown cause
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if BONDLIDO will harm your unborn baby.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. BONDLIDO can pass into your breast milk. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby if you use BONDLIDO.
How should I use BONDLIDO?
Read the Instructions for Use at the end of this Patient Information leaflet for information about how to apply BONDLIDO.- Use BONDLIDO exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to use it.
- Do not apply more than your prescribed number of BONDLIDO. You may apply up to 2 BONDLIDO topical systems at one time.
- A BONDLIDO topical system may be worn only 1 time for up to 12 hours within a 24-hour period (12 hours on and 12 hours off).
- Apply BONDLIDO to intact skin only. Do not apply BONDLIDO to skin that is not intact, such as skin that is cut, scraped, burned or irritated.
- If the BONDLIDO you are wearing comes off completely and will not stick to your skin, throw it away as described below. You may apply a replacement (a new) BONDLIDO topical system. Take off the replacement BONDLIDO at your usual removal time. The total time you may wear the used and replacement BONDLIDO is 12 hours.
- To remove and properly throw away (dispose of) BONDLIDO, fold the used BONDLIDO so that the sticky sides stick together. Safely throw away the used BONDLIDO where children, pets, and others cannot get to them.
- You may wear clothing over the BONDLIDO application site.
- Do not apply external heat sources, such as heating pads or electric blankets, directly on BONDLIDO. This may cause increased levels of lidocaine in your blood.
- Avoid contact with water, such as bathing, swimming, or showering, while using BONDLIDO. BONDLIDO may not stick if it gets wet.
- Wash your hands right away after handling BONDLIDO (after you apply BONDLIDO, when you try to re-attach it, or when you remove it).
- If you start feeling irritation or burning when applying BONDLIDO, remove BONDLIDO. Do not reapply BONDLIDO until the irritation or burning goes away.
- If you apply more than 2 BONDLIDO topical systems or apply BONDLIDO for longer than 12 hours of a 24-hour period, call your healthcare provider.
What should I avoid while using BONDLIDO?
Avoid contact of your hands and fingers with your eyes while handling BONDLIDO. Contact of BONDLIDO with your eyes can cause severe eye irritation. Wash your hands right away after handling BONDLIDO. If the medicine in BONDLIDO comes in contact with your eye, wash out your eye with water or saline right away. Protect the eye (for example with eye glasses or eye wear) until the numbness goes away.What are the possible side effects of BONDLIDO?
BONDLIDO may cause serious side effects, including:- Lidocaine overdose can happen if you apply more than the prescribed number of BONDLIDO, apply BONDLIDO for longer than 12 hours, have liver problems, use BONDLIDO on skin that is not intact, or if you apply external heat sources directly on BONDLIDO. This can result in increased levels of lidocaine in your blood. See "How should I use BONDLIDO?" for information on how to use BONDLIDO.
-
A serious blood problem called methemoglobinemia. Methemoglobinemia is a serious blood problem where too much methemoglobin is produced in the blood. Methemoglobinemia can happen with the use of local anesthetics and may not let enough oxygen reach the organs and tissues in your body. Anyone who uses or receives local anesthetics is at risk for methemoglobinemia, but certain people are more likely to have serious medical problems and need to be closely monitored by their healthcare provider during treatment with BONDLIDO, including:
- people with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency
- people with heart or lung problems
- babies under 6 months of age (BONDLIDO is not approved for use in children)
- people who were born with (congenital) or who have had methemoglobinemia from an unknown cause
- people exposed to certain chemicals at the same time that they use or receive local anesthetic
- pale, gray, or blue colored skin
- headache
- rapid heart beat
- shortness of breath
- lightheadedness
- tiredness
- Application site reactions. Skin irritation and other skin reactions at the BONDLIDO application site are common and are usually mild. These reactions can happen during or right after treatment with BONDLIDO. Application site reactions will usually go away within a few minutes to hours. Severe skin irritation may happen with BONDLIDO if you use it for a longer time than instructed. If you develop a skin reaction while wearing BONDLIDO, remove it. Do not reapply BONDLIDO until the site reaction goes away. Symptoms of application site reactions may include:
- blisters
- bruising
- burning or abnormal sensation
- change or loss of color of your skin
- swelling, redness, and pain of the skin
- peeling or flaking of skin
- irritation
- pimple-like raised skin
- itching
- Allergic reactions can happen if you have a history of allergic reactions to numbing medicines (anesthetics). Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have any symptoms of an allergic reaction such as swelling or shortness of breath.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.How should I store BONDLIDO? - Store BONDLIDO at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Do not store BONDLIDO outside the sealed pouch.
- Protect BONDLIDO from light.
- Each BONDLIDO topical system comes in a child-resistant pouch.
General information about the safe and effective use of BONDLIDO.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use BONDLIDO for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give BONDLIDO to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about BONDLIDO that is written for health professionals.What are the ingredients in BONDLIDO?
Active ingredient: lidocaine
Inactive ingredients: blue ink, hydrocarbon, lactic acid, mono- and di-glycerides, non-woven PET backing membrane, PET film, polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil, propylene carbonate, styrene/isoprene/styrene block copolymer, tartaric acid, and terpene resin.
Manufactured for: MEDRx USA, Inc., 2030 Main St., Suite 1300, Irvine, CA 92614, USA
For more information, go to www.bondlido.com or call 1-844-633-5436. -
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
BONDLIDO [BAHND-LYE-DOH]
(lidocaine topical system)This Instruction for Use contains information on how to apply, remove, and dispose of BONDLIDO. Read this Instructions for Use before you start using BONDLIDO and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical treatment or conditions.
Important Information You Need to Know Before Using BONDLIDO:
- BONDLIDO is for topical use only (apply on top of skin).
- Apply the prescribed number of BONDLIDO at one time.
- Do not apply more than your prescribed number of BONDLIDO. You may apply up to 2 BONDLIDO topical systems at one time.
- BONDLIDO may be worn only 1 time for up to 12 hours within a 24-hour period (12 hours on and 12 hours off).
- Apply BONDLIDO to intact skin only. Do not apply BONDLIDO to skin that is not intact, such as skin that is cut, scraped, burned or irritated.
- If the BONDLIDO you are wearing comes off completely and will not stick to your skin, see "How to apply a replacement (a new) BONDLIDO:"
- You may wear clothing over the BONDLIDO application site.
- Do not apply external heat sources, such as heating pads or electric blankets, directly on BONDLIDO. This may cause increased levels of lidocaine in your blood.
- Avoid contact with water, such as bathing, swimming, or showering while using BONDLIDO. BONDLIDO may not stick if it gets wet.
- Store BONDLIDO out of the reach of children, pets, and others.
Applying BONDLIDO:
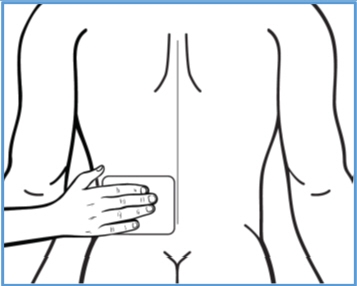
Step 1: Select the application site. - BONDLIDO should only be applied to clean, dry, and intact skin to cover the most painful area.
Step 2: Using scissors, carefully cut the pouch along the dotted line and open it to remove BONDLIDO. - Do not use BONDLIDO if it is damaged. Throw it away and get a new one.
- Do not open the BONDLIDO pouch until you are ready to use it.
- Apply BONDLIDO right away after removing it from the pouch.
Step 3a: Remove the center part of the transparent release liner (clear plastic backing). 
Apply the adhesive (sticky) side of the center part of BONDLIDO onto your skin. - Apply BONDLIDO to intact skin only.
- Do not touch the sticky side with your fingers.
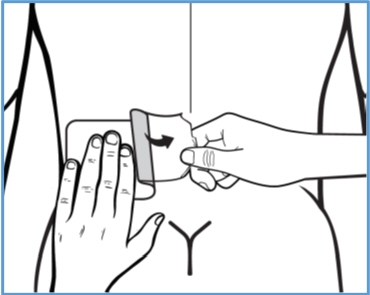
Step 3b: While removing the right part of the clear plastic backing with one hand, use your other hand to apply BONDLIDO onto your skin and smooth it down with your fingers. - Do not touch the sticky side with your fingers.
Step 3c: Hold the left part of the clear plastic backing, then slowly peel it away and smooth BONDLIDO down onto your skin with your fingers.
Press BONDLIDO firmly with the palm of your hand for 20 seconds to make sure it sticks well to your skin.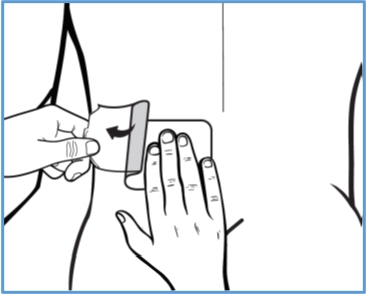
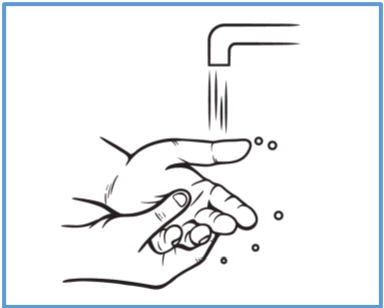
Step 4: Wash your hands right away after applying BONDLIDO. - Avoid contact of your hands or fingers with your eyes until your hands are washed.
Removing and disposing of BONDLIDO:
Step 5: Remove BONDLIDO from your skin after you have worn it for up to 12 hours. - Fold the used BONDLIDO so that the sticky sides stick together.

Step 6: Throw away (dispose of) the used BONDLIDO where children, pets, and others cannot get to them. - Wash your hands right away after removing BONDLIDO.
How to apply a replacement (a new) BONDLIDO:
- If the BONDLIDO you are wearing comes off completely and will not stick to your skin, throw away the used BONDLIDO as instructed above in Steps 5 and 6.
- You may apply a replacement BONDLIDO the same way you would apply a new BONDLIDO as described above in Steps 1 through 4.
- Take off the replacement BONDLIDO at your usual removal time.
- The total time you may wear the used and replacement BONDLIDO is 12 hours. You should not wear BONDLIDO for more than 12 hours within a 24-hour period.
Storing BONDLIDO:
- Store BONDLIDO at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Do not store BONDLIDO outside the sealed pouch.
- Protect BONDLIDO from light.
- Each BONDLIDO topical system comes in a child-resistant pouch.
Store BONDLIDO and all medicines out of the reach of children, pets, and others.
Manufactured for: MEDRx USA, Inc., 2030 Main St., Suite 1300, Irvine, CA 92614, USA
For more information, go to www.bondlido.com or call 1-844-633-5436.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Approved: 09/2025 -
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 28 Patch Pouch Carton
NDC: 83708-1111-28
Rx OnlyBONDLIDO®
lidocaine topical system 10%For topical use only
28 topical systems
1 Pouch containing 1 Topical System EachMEDRx®

-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
BONDLIDO
lidocaine systemProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 83708-111 Route of Administration TOPICAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength lidocaine (UNII: 98PI200987) (lidocaine - UNII:98PI200987) lidocaine 200 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Lactic Acid, Unspecified Form (UNII: 33X04XA5AT) Glyceryl Mono- and Dipalmitostearate Type B (UNII: SLW8D5K6WL) Polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil (UNII: 7YC686GQ8F) Propylene carbonate (UNII: 8D08K3S51E) Styrene/isoprene/styrene block copolymer (UNII: K7S96QM8DV) Tartaric acid (UNII: W4888I119H) Terpene resin (UNII: GR35AH6YDN) Product Characteristics Color Score Shape RECTANGLE Size Flavor Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 83708-111-01 1 in 1 PATCH 10/08/2025 1 NDC: 83708-111-28 28 in 1 CARTON; Type 2: Prefilled Drug Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA215029 10/08/2025 Labeler - MEDRx USA, Inc. (088505981) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Sumika Chemical Analysis Services, Ltd. 696888804 ANALYSIS(83708-111) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Delta Synthetic Co., Ltd. 656128618 API MANUFACTURE(83708-111) , ANALYSIS(83708-111)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.