DUVYZAT- givinostat suspension
DUVYZAT by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
DUVYZAT by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Italfarmaco SPA, CHEMI SpA, Italfarmaco S.A.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DUVYZAT safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DUVYZAT.
DUVYZAT (givinostat) oral suspension
Initial U.S. Approval: 2024INDICATIONS AND USAGE
DUVYZAT is a histone deacetylase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) in patients 6 years of age and older. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Obtain and evaluate baseline platelet counts and triglycerides prior to initiation of DUVYZAT. Do not initiate DUVYZAT in patients with a platelet count less than 150 x 10^9/L. (2.1, 5.1, 5.2)
- The dosage of DUVYZAT is based on patient’s body weight. (2.2)
- Administer orally twice daily with food. (2.2)
- Dosage modifications may be needed for decreased platelet counts, diarrhea, increased triglycerides, or QTc prolongation. (2.3, 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Oral suspension: 8.86 mg/mL givinostat. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Hematological Changes: DUVYZAT can cause dose-related thrombocytopenia and other signs of myelosuppression, including anemia and neutropenia. Monitor platelets; dosage adjustment or discontinuation may be needed. (2.3, 5.1)
- Increased Triglycerides: An increase in triglycerides can occur; dosage modification may be needed. Discontinuation may be needed. (2.3, 5.2)
- Gastrointestinal Disturbances: Adjust dosage if moderate or severe diarrhea occurs. Antiemetics or antidiarrheal medications may be considered during treatment with DUVYZAT. Discontinue DUVYZAT if the symptoms persist. (2.3, 5.3)
- QTc Prolongation: Avoid use of DUVYZAT in patients who are at an increased risk for ventricular arrhythmias. (2.1, 5.4, 7.2)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions (≥10% in DUVYZAT-treated patients) are diarrhea, abdominal pain, thrombocytopenia, nausea/vomiting, hypertriglyceridemia, and pyrexia. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact ITF Therapeutics, LLC. at 1-833-582-4312 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Closely monitor when DUVYZAT is used in combination with an oral CYP3A4 sensitive substrate or a sensitive substrate of the OCT2 transporter, for which a small change in substrate plasma concentration may lead to serious toxicities. (7.1)
- Avoid concomitant use with other drugs that prolong the QTc interval; monitor ECG if concomitant use cannot be avoided. (7.2)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 11/2024
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Evaluation and Testing Before Initiation of DUVYZAT
2.2 Recommended Dosage
2.3 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
2.4 Preparation and Administration Instructions
2.5 Missed Dose
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hematological Changes
5.2 Increased Triglycerides
5.3 Gastrointestinal Disturbances
5.4 QTc Prolongation
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effect of DUVYZAT on Other Drugs
7.2 Effect of Other Drugs on DUVYZAT
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
16.2 Storage and Handling
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Evaluation and Testing Before Initiation of DUVYZAT
Obtain and evaluate baseline platelet counts and triglycerides prior to initiation of DUVYZAT [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2)]. Do not initiate DUVYZAT in patients with a platelet count less than 150 x 109/L. Monitor platelet counts and triglycerides as recommended during treatment to determine if dosage modifications are needed [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
In addition, in patients with underlying cardiac disease or taking concomitant medications that cause QT prolongation, obtain ECGs when initiating treatment with DUVYZAT, during concomitant use, and as clinically indicated [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Warnings and Precautions (5.4), and Drug Interactions (7.2)].
2.2 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of DUVYZAT is based on body weight and administered orally twice daily with food (see Table 1) [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
Table 1: Recommended Dosage in Patients 6 Years of Age and Older for the Treatment of DMD Weight* Dosage Oral Suspension Volume - * Based on actual body weight
10 kg to less than 20 kg 22.2 mg twice daily 2.5 mL twice daily 20 kg to less than 40 kg 31 mg twice daily 3.5 mL twice daily 40 kg to less than 60 kg 44.3 mg twice daily 5 mL twice daily 60 kg or more 53.2 mg twice daily 6 mL twice daily 2.3 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
Decrease in Platelets, Diarrhea, Increase in Triglycerides
DUVYZAT may cause adverse reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.3)], which may necessitate a dosage modification (see Table 2) if the following occur:
- Platelet count <150 x 109/L verified in two assessments one week apart
or - Moderate or severe diarrhea
or - Fasting triglycerides >300 mg/dL verified by two assessments one week apart
Based on the severity of these adverse reactions, treatment interruption prior to dosage modification should be considered.
Table 2: Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions in Patients 6 Years of Age and Older for the Treatment of DMD First Dosage Modification* Second Dosage Modification† - * If the adverse reaction(s) persist after the first dosage modification, proceed to the second dosage modification.
- † If the adverse reaction(s) persist after the second dosage modification, DUVYZAT should be discontinued.
- ‡ Based on actual body weight
Weight‡ Dosage Oral Suspension Volume Dosage Oral Suspension Volume 10 kg to less than 20 kg 17.7 mg twice daily 2 mL twice daily 13.3 mg twice daily 1.5 mL twice daily 20 kg to less than 40 kg 22.2 mg twice daily 2.5 mL twice daily 17.7 mg twice daily 2 mL twice daily 40 kg to less than 60 kg 31 mg twice daily 3.5 mL twice daily 26.6 mg twice daily 3 mL twice daily 60 kg or more 39.9 mg twice daily 4.5 mL twice daily 35.4 mg twice daily 4 mL twice daily QTc Interval Prolongation
Withhold DUVYZAT if the QTc interval is > 500 ms or the change from baseline is > 60 ms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Drug Interactions (7.2)].
2.4 Preparation and Administration Instructions
See the Instructions for Use for further details.
- Before use, shake the DUVYZAT suspension for at least 30 seconds by inverting the bottle by 180°.
- Visually verify the homogeneity of the suspension.
- Using a graduated oral syringe, measure the appropriate volume of suspension corresponding to the prescribed dose of DUVYZAT.
- Administer orally with the provided graduated oral syringe.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hematological Changes
DUVYZAT can cause dose-related thrombocytopenia and other signs of myelosuppression, including decreased hemoglobin and neutropenia.
In Study 1 [see Clinical Studies (14)], thrombocytopenia occurred in 33% of patients treated with DUVYZAT compared to no patients on placebo. The maximum decrease in platelets occurred within the first 2 months of therapy and remained low throughout the course of therapy. In a few patients, thrombocytopenia was associated with bleeding events including epistaxis, hematoma or contusions. Low platelet counts resulted in DUVYZAT dose reduction in 28% of patients. Patients with baseline platelet counts below the lower limit of normal were excluded from the study.
Decreased hemoglobin and decreased neutrophils were also observed in patients treated with DUVYZAT compared to placebo.
Monitor blood counts every 2 weeks for the first 2 months of treatment, at month 3, and then every 3 months thereafter. Modify the dosage of DUVYZAT for confirmed thrombocytopenia [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. Treatment should be permanently discontinued if the abnormalities worsen despite dose modification. If a patient develops signs or symptoms of thrombocytopenia, obtain a platelet count as soon as possible, and hold dosing until platelet count is confirmed.
5.2 Increased Triglycerides
DUVYZAT can cause elevations in triglycerides. In Study 1 [see Clinical Studies (14)], hypertriglyceridemia occurred in 23% of patients treated with DUVYZAT (one of whom had familial hypertriglyceridemia) compared to 7% of patients on placebo. High triglycerides (i.e., levels greater than 300 mg/dL) resulted in discontinuation and led to dosage modification in 2% and 8%, respectively, of patients treated with DUVYZAT.
Monitor triglycerides at 1 month, 3 months, 6 months, and then every 6 months thereafter. Modify the dosage if fasting triglycerides are verified > 300 mg/dL [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. Treatment with DUVYZAT should be discontinued if triglycerides remain elevated despite adequate dietary intervention and dosage adjustment.
5.3 Gastrointestinal Disturbances
Gastrointestinal disturbances, including diarrhea, nausea/vomiting, and abdominal pain were common adverse reactions in DUVYZAT clinical trials in DMD. In Study 1, diarrhea was reported in 37% of patients treated with DUVYZAT (with 1 severe case reported) compared to 20% of patients on placebo. Diarrhea usually occurred within the first few weeks of initiation of treatment with DUVYZAT.
Vomiting and nausea, sometimes severe and usually occurring within the first 2 months of treatment, occurred in 32% of patients treated with DUVYZAT compared to 18% of patients on placebo. Abdominal pain occurred in 34% of patients treated with DUVYZAT compared to 25% of patients on placebo. One case of abdominal pain was serious.
Antiemetics or antidiarrheal medications may be considered during treatment with DUVYZAT. Fluid and electrolytes should be replaced as needed to prevent dehydration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]. Modify the dosage of DUVYZAT in patients with moderate or severe diarrhea, and treatment should be discontinued if significant symptoms persist [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.4 QTc Prolongation
DUVYZAT can cause prolongation of QTc interval [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. Avoid use of DUVYZAT in patients who are at an increased risk for ventricular arrhythmias (including torsades de pointes), such as those with congenital long QT syndrome, coronary artery disease, electrolyte disturbance [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)], concomitant use of other medicinal products known to cause QT prolongation [see Drug Interactions (7.2)]. Obtain ECGs prior to initiating treatment with DUVYZAT in patients with underlying cardiac disease or in patients who are taking concomitant medications that cause QT prolongation [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described below and elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hematological Changes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Increased Triglycerides [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Gastrointestinal Disturbances [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- QTc Prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In controlled and uncontrolled trials in patients with confirmed DMD, 222 male patients aged 6 years and older were treated with DUVYZAT, including 210 patients treated for ≥ 6 months, 187 patients for ≥ 12 months, and 105 patients for ≥ 24 months.
The safety profile of DUVYZAT is based on a double-blind, placebo-controlled, 18-month study in a total of 179 ambulant DMD patients aged 6 years or older on concomitant steroid treatment (Study 1) [see Clinical Studies (14)]. The dosage in Study 1 was weight-based [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. Patients were excluded from the study if they had the following abnormalities at the screening visit: platelet, white blood cell, or hemoglobin counts less than the lower limit of normal, triglycerides > 300 mg/dL (3.42 mmol/L) in fasting condition, or had a baseline-corrected QT interval, Fridericia’s correction (QTcF) of > 450 msec (mean of 3 consecutive readings 5 minutes apart) or a history of additional risk factors for torsades de pointes (e.g., heart failure, hypokalemia, or family history of long QT syndrome). Overall, 2% of the patients discontinued the study because of adverse reactions.
Adverse reactions reported in >5% of DUVYZAT-treated patients at a frequency at least 5% greater than that of the placebo group are presented in Table 3 below.
Table 3. Adverse Reactions Reported in >5% of DUVYZAT-Treated Patients and at Least 5% Greater than Placebo in Study 1 Adverse Reaction DUVYZAT
N=118
%Placebo
N=61
%- * Thrombocytopenia includes platelet count decreased and thrombocytopenia
Diarrhea 37 20 Abdominal pain 34 25 Thrombocytopenia* 33 0 Nausea/Vomiting 32 18 Hypertriglyceridemia 23 7 Pyrexia 13 8 Myalgia 9 3 Rash 9 2 Arthralgia 8 2 Fatigue 8 0 Constipation 7 2 Decreased appetite 7 0 Less Common Adverse Reactions in Study 1
Adverse reactions of hypothyroidism and/or thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) increased occurred in 5% of patients treated with DUVYZAT compared to 2% of patients who received placebo.
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effect of DUVYZAT on Other Drugs
CYP3A4 Sensitive Substrates
Givinostat is a weak intestinal CYP3A4 inhibitor [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Closely monitor when DUVYZAT is used in combination with orally administered CYP3A4 sensitive substrates for which a small change in substrate plasma concentration may lead to serious toxicities.
OCT2 Sensitive Substrates
Givinostat is a weak inhibitor of the renal uptake transporter OCT2 [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Closely monitor when DUVYZAT is used in combination with drugs known as a sensitive substrate of the OCT2 transporter for which a small change in substrate plasma concentration may lead to serious toxicities.
7.2 Effect of Other Drugs on DUVYZAT
Drugs that Prolong the QTc Interval
Avoid concomitant use of DUVYZAT with other product(s) with a known potential to prolong the QTc interval. If concomitant use cannot be avoided, obtain ECGs when initiating, during concomitant use, and as clinically indicated [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]. Withhold DUVYZAT if the QTc interval is > 500 ms or the change from baseline is > 60 ms [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
DUVYZAT causes QTc interval prolongation [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. Concomitant use of DUVYZAT with other products that prolong the QTc interval may result in a greater increase in the QTc interval and adverse reactions associated with QTc interval prolongation, including Torsade de pointes, other serious arrythmias, and sudden death [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
DUVYZAT is indicated for the treatment of DMD, which is a disease of predominantly young male patients. Therefore, there are no adequate data available to assess the use of DUVYZAT in pregnant women. In animal studies, oral administration of givinostat during organogenesis resulted in decreased fetal body weight and increased structural variations; oral administration during pregnancy and lactation resulted in increased embryofetal and offspring mortality and neurobehavioral changes in the offspring. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
Oral administration of givinostat (0, 40, 80, or 160 mg/kg/day) to pregnant rats throughout organogenesis resulted in reduced fetal body weight at the highest dose tested and increases in the incidence of skeletal and visceral variations at the mid and high doses. The no-effect dose (40 mg/kg/day) for adverse effects on embryofetal development was associated with maternal plasma exposures (AUC) lower than that in humans at the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 53.2 mg twice daily.
Oral administration of givinostat (0, 40, 80, or 160 mg/kg/day) to pregnant rabbits throughout organogenesis resulted in maternal death at the highest dose tested, resulting in too few fetuses to evaluate. No adverse effects on embryofetal development were observed at the low and mid doses. Plasma exposures (AUC) at the higher no-effect dose (80 mg/kg) for adverse effects on embryofetal development were approximately 4 times that in humans at the MRHD.
Oral administration of givinostat (0, 40, 80, or 160 mg/kg/day) to rats throughout pregnancy and lactation resulted in increases in embryofetal mortality, stillbirths, and offspring mortality at the highest dose tested. When offspring were tested postweaning (postnatal day 49), adverse effects on behavior (decreased open field activity) were observed at all doses. A no-effect dose for adverse developmental effects was not identified; plasma exposures (AUC) at the lowest dose tested were lower than that in humans at the MRHD.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no human or animal data to assess the effect of DUVYZAT or its metabolites on milk production, the presence of givinostat in milk, or the effects on the breastfed infant. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for DUVYZAT and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from DUVYZAT or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
No human data are available on the effect of DUVYZAT on reproductive potential.
Animal studies indicate possible adverse effects on reproduction [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of DUVYZAT in children aged 6 years and older have been established [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients below the age of 6 years have not been established.
Juvenile Animal Data
In a study in juvenile male and female rats, givinostat was orally administered at doses of 0, 10, 20, or 40 mg/kg on postnatal days (PND) 7 to 27, doses of 0, 15, 30, or 60 mg/kg/day on PNDs 28 to 48, and doses of 0, 15, 45, or 90 mg/kg/day on PNDs 49 to 92. Adverse effects on behavior (increased locomotor activity and decreased auditory startle prepulse inhibition) were observed at the high dose at the end of the dosing period. Adverse effects on locomotor activity, but not prepulse inhibition, were observed at the end of the recovery period primarily at the mid and high doses. Persistent decreases in bone density were observed at all doses tested. A no-effect dose for adverse effects on postnatal development was not identified; the lowest dose tested was associated with plasma exposures (AUC) less than that in humans at the MRHD.
8.5 Geriatric Use
DMD is largely a disease of children and young adults; therefore, there is no experience with DUVYZAT in geriatric DMD patients.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
A dedicated clinical study was not conducted to evaluate the pharmacokinetics of DUVYZAT in subjects with hepatic impairment, and no recommendation for dosage adjustment can be made for patients with hepatic impairment. Because DUVYZAT is eliminated mainly through hepatic metabolism, hepatic impairment is expected to increase the exposure of givinostat [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
11 DESCRIPTION
DUVYZAT (givinostat) oral suspension contains givinostat hydrochloride monohydrate, a histone deacetylase inhibitor. Givinostat hydrochloride monohydrate is designated chemically as: [6-(diethylaminomethyl)naphthalen-2-yl]methyl[4(hydroxycarbamoyl) phenyl] carbamate hydrochloride monohydrate. The molecular formula is C24H27N3O4HClH2O and the molecular weight is 475.97 g/mol. Its structural formula is:
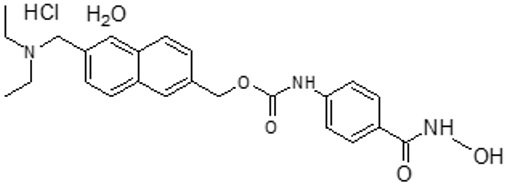
Givinostat hydrochloride monohydrate is a white to off-white, non-hygroscopic, crystalline powder that is very slightly to slightly soluble in aqueous media and slightly soluble in ethanol.
DUVYZAT contains givinostat 8.86 mg/mL (equivalent to givinostat hydrochloride monohydrate 10 mg/mL) and the following inactive ingredients: cream flavor, glycerin, non-crystallizing sorbitol solution, peach flavor, polysorbate 20, purified water, saccharin sodium, sodium benzoate, sodium hydroxide, tartaric acid, and tragacanth.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
DUVYZAT is a histone deacetylase inhibitor. The precise mechanism by which DUVYZAT exerts its effect in patients with DMD is unknown.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Muscle Fat Fraction as Assessed by MR Spectroscopy
The percentage of fat fraction present in the vastus lateralis muscles (VLM) of the thigh was measured in Study 1 [see Clinical Studies (14)] using magnetic resonance spectroscopy. At 18 months, for the patients with VLM fat fraction baseline in the range of >5% to ≤30%, a mean increase (absolute difference from baseline levels) of VLM fat fraction was 7.48% in the DUVYZAT-treated patients compared to a 10.89% increase in patients who received placebo.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
The largest mean increase in QTc interval of 13.6 ms (upper confidence interval of 17.1 ms) occurred 5 hours after administration of givinostat 265.8 mg to healthy subjects (approximately 5 times the 53.2 mg dose recommended for DMD patients weighing 60 kg or more) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Givinostat exhibits linear kinetics with the studied dose range. Systemic exposure to givinostat was dose-proportional across the therapeutic dose range. Steady-state concentrations are achieved within 5 to 7 days after twice daily dosing. An accumulation of less than 2-fold was observed for givinostat after twice daily administration.
Absorption
Absolute bioavailability was not determined. The time to maximum plasma concentrations is about 2 to 3 hours after oral administration.
Effect of Food
A high fat standard meal resulted in an increase in the exposure (about 40% increase in area under the plasma concentration-time curve [AUC] and about 23% increase in maximum plasma concentration [Cmax]) and a delay in time to maximum concentration (Tmax) from 2 to 3 hours [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Distribution
Givinostat is approximately 96% bound to human plasma proteins and is slightly partitioned into red blood cells (blood to plasma ratio = 1.3).
Elimination
In plasma, apparent elimination half-life of givinostat is about 6 hours.
Metabolism
In vitro studies with human enzymatic preparations together with animal metabolism showed that givinostat is extensively metabolized forming several metabolites. CYP450 and UGTs are not involved in the main metabolic reactions. Four major metabolites, which are not active with respect to the efficacy of givinostat, have been characterized in humans and preclinical species.
Excretion
The elimination of givinostat is likely dependent on metabolism followed by renal and biliary excretion of the resulting metabolites as suggested by the mass balance study in the rat. Urinary excretion of givinostat in humans is minimal (<3% of the dose).
Specific Populations
The population PK analyses show that the PK of givinostat can be affected by body weight, while age has no effects on the pharmacokinetics of givinostat.
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
The pharmacokinetics and safety of givinostat have not been studied in patients with hepatic impairment. Givinostat is highly metabolized and therefore the impact of hepatic impairment on the exposure of givinostat cannot be excluded [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Patients with Renal Impairment
The pharmacokinetics and safety of givinostat have not been studied in patients with renal impairment. However, renal impairment is not expected to impact the exposure of givinostat because renal excretion is not a significant route of givinostat elimination.
Drug Interaction Studies
In Vitro
Givinostat is not a substrate of cytochrome P450 (CYP450) enzymes and uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase (UGT). Therefore, coadministration of drugs that are inducers or inhibitors of major metabolizing enzymes will not significantly affect the systemic exposure of givinostat.
Givinostat and its metabolites ITF2374, ITF2375, ITF2440, and ITF2563 were investigated as inhibitors of the main CYP450 subfamilies, and the results indicated no inhibition is expected of CYP1A2, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, 2B6, 2C8, and 3A4. Givinostat showed induction of CYP1A2, 2B6, and CYP3A4.
In vitro studies indicate that givinostat is a substrate of the intestinal transporters: P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP). Givinostat showed the potential to inhibit the intestinal transporter P-gp (MDR1) and BCRP based on in vitro results. However, these interactions are not expected to be clinically meaningful.
In Vivo
A weak inhibition of the renal uptake transporter OCT2 by givinostat was seen in clinical trials by creatinine (OCT2 substate) measurements [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
A clinical drug interaction study was conducted in healthy volunteers to assess the effects of coadministration of givinostat with other drugs and results indicated that:
- givinostat has a weak inhibition of the intestinal CYP3A4 enzyme based on the exposure of a CYP3A4 substrate, midazolam, [see Drug Interactions (7.1)]
- givinostat does not likely inhibit P-gp transporters based on the exposure of dabigatran
- strong P-gp inhibitors have a weak effect on givinostat based on exposure of clarithromycin, which had an increase in Cmax by about 40% without a significant change of AUC.
The effect of BCRP inhibitors on givinostat PK was not studied in a clinical study. However, the effect of BCRP inhibitors on givinostat PK is expected to be smaller than P-gp inhibitors based on the comparison of the two transporters mediated efflux ratios determined in the in vitro cell models.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Studies to assess the carcinogenic potential of givinostat have not been conducted.
Mutagenesis
Givinostat was positive in a bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay, and negative in an in vitro mammalian cell (mouse lymphoma) mutation assay, an in vitro chromosomal aberration assay in mammalian (human lymphocytes) cells, and an in vivo gene mutation assay (with Pig-a endpoints) in Big Blue transgenic rats.
Impairment of Fertility
Oral administration of givinostat (0, 40, 80, or 160 mg/kg) prior to and throughout mating in male and female rats and continuing to gestation day 7 in females, resulted in no adverse effects on fertility. However, there was an increase in corpora lutea at the mid and high doses and increased pre- and postimplantation loss at all doses. A no-effect dose for adverse effects on early embryonic development was not identified; plasma exposures (AUC) at the lowest dose tested were lower than that in humans at the maximum recommended human dose of 53.2 mg twice daily.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The effectiveness of DUVYZAT for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) was evaluated in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled 18-month study (Study 1; NCT02851797). A total of 179 patients were randomized 2:1 to receive either DUVYZAT (n = 118) or placebo (n = 61). A weight-based dose regimen was applied [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. The study included male patients 6 years of age and older with a confirmed diagnosis of DMD who were ambulatory and on a stable dosage of corticosteroids. At baseline, patients had a mean age of 9.8 years, 90% were White, 3% were Asian, 3% were Black.
The primary endpoint was the change from baseline to Month 18 in 4-stair climb (4SC) time for DUVYZAT compared to placebo. The 4SC is a measure of muscle function that tests the time it takes to climb 4 stairs. A secondary efficacy endpoint was change from baseline to Month 18 in physical function as assessed by the North Star Ambulatory Assessment (NSAA).
The primary analysis population was based on a prespecified range of baseline muscle fat fraction as determined by MR spectroscopy. Patients treated with DUVYZAT showed statistically significant less decline in the 4-stair climb compared to placebo (see Table 4). Patients treated with givinostat experienced less worsening on the NSAA compared to placebo, which was nominally significant but not statistically significant based on the prespecified multiplicity adjustment.
Table 4. Change from Baseline to Month 18 on 4SC Compared to Placebo* Mean Baseline 4SC (seconds) Mean Change from Baseline Treatment Difference from Placebo
(95% CI)p-value - * Givinostat or placebo were administered in addition to a stable dose of corticosteroids throughout the study
DUVYZAT
(n = 81 )3.39 1.25 -1.78
(-3.46, -0.11)0.037 Placebo
(n = 39 )3.48 3.03 -
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
DUVYZAT (givinostat) oral suspension is a white to off-white or faintly pink, peach-cream flavored suspension. It is supplied in an amber polyethylene terephthalate bottle closed with a high-density polyethylene child-resistant, screw cap with low-density polyethylene syringe adapter, containing 140 mL of oral suspension (NDC: 11797-110-01). Each mL contains 8.86 mg of givinostat.
DUVYZAT is supplied in a carton, NDC: 11797-110-02, containing:
- one bottle containing 140 mL oral suspension
- one 5 mL graduated oral syringe
- Prescribing Information and Instructions for Use
The Medication Guide is available at www.duvyzat.com/medication-guide.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide and Instructions for Use).
Administration Instructions
Instruct patients or caregivers to [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)]:
- Shake DUVYZAT oral suspension well before measuring out each dose.
- Administer using the provided graduated oral syringe to measure the appropriate volume of suspension corresponding to the prescribed dose for the patient.
- Take DUVYZAT with food.
- Discard any unused DUVYZAT oral suspension remaining after 60 days of first opening the bottle.
Hematological Changes
Inform patients and/or caregivers that DUVYZAT can cause hematological changes including a decrease in platelet counts (thrombocytopenia), anemia, and a decrease in neutrophils (neutropenia) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Advise patients to notify their healthcare provider if they have any signs or symptoms of these adverse reactions (e.g., easy bruising, excessive bleeding from cuts, blood in the stool, fatigue). Instruct patients to adhere to the testing recommended to monitor for these adverse reactions. Inform patients that their dosage may need to be changed or their treatment may need to be stopped depending on the results of their test for platelet counts.
Increased Triglycerides
Inform patients and/or caregivers that DUVYZAT can cause an increase in triglycerides, [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Instruct patients to adhere to the testing recommended to monitor for this adverse reaction. Inform patients that their dosage may need to be changed or their treatment may need to be stopped depending on the results of their test for triglycerides.
Gastrointestinal Disturbances
Inform patients and/or caregivers that DUVYZAT can cause diarrhea and vomiting, which may require medication for treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. Advise patients to maintain hydration if diarrhea or vomiting occurs and contact their healthcare provider if the symptoms persist or become moderate to severe. Inform patients that their dosage may need to be changed or their treatment may need to be stopped depending on the severity of diarrhea.
QTc Prolongation
Inform patients and/or caregivers that DUVYZAT can cause prolongation of the QTc interval [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]. Instruct patients to notify their healthcare provider if they have or develop any symptoms of significant QTc prolongation (e.g., dizziness, lightheadedness, syncope) or new cardiac issues and before taking any over-the-counter (e.g., diphenhydramine), herbal (e.g., echinacea), or prescription medications (e.g., antibiotics).
Manufactured by:
Italfarmaco S.A.
Madrid, SpainDistributed by:
ITF Therapeutics, LLC
Concord, MA 01742DUVYZAT is a trademark owned by Italfarmaco S.p.A.
All rights reserved.
-
MEDICATION GUIDE
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Issued: 3/2024 MEDICATION GUIDE
DUVYZAT™ (doo' vi zat)
(givinostat)
oral suspensionWhat is the most important information I should know about DUVYZAT?
DUVYZAT can cause serious side effects including:- Low platelet counts in your blood (thrombocytopenia). Platelets are important for blood clotting, and a decrease in their numbers can lead to an increased risk of bleeding or bruising. Your healthcare provider will check your blood count before you start DUVYZAT and regularly during treatment for any signs of thrombocytopenia. Call your healthcare provider right away if you notice any unusual bleeding or small red or purple spots on the skin called petechiae. Your healthcare provider may change your dose of DUVYZAT if your blood platelet counts continue to be low or may stop your treatment with DUVYZAT.
- Increased levels of fat (triglycerides) in your blood. You may not have any symptoms, so your healthcare provider will do blood tests before you start DUVYZAT and regularly during treatment to check your triglyceride levels. Your healthcare provider may change your dose of DUVYZAT if your triglyceride levels continue to be high or may stop your treatment with DUVYZAT.
- Frequent watery loose stools (diarrhea) and vomiting. DUVYZAT can cause vomiting and moderate to severe diarrhea. If diarrhea occurs, you should keep track of the frequency and severity of your diarrhea symptoms, drink plenty of fluids, and contact your healthcare provider. Your healthcare provider may change your dose of DUVYZAT if the diarrhea cannot be managed or does not go away. Your healthcare provider may also stop your treatment with DUVYZAT.
What is DUVYZAT?
DUVYZAT is a prescription medicine that is used for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) in people 6 years of age and older.
It is not known if DUVYZAT is safe and effective in children under 6 years of age.Before taking DUVYZAT, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you: - have any heart problems or if you take any medicines that could increase your chance for irregular heart rhythms.
- have any bleeding problems.
Taking DUVYZAT with certain other medicines may affect each other. Taking DUVYZAT with other medicines can cause serious side effects. Do not start or stop other medicines without talking to your healthcare provider.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.How should I take DUVYZAT? - See the Instructions for Use that came with your DUVYZAT medicine for detailed instructions on how to take DUVYZAT the right way.
- Take DUVYZAT by mouth with food.
- Take DUVYZAT exactly as prescribed. Your healthcare provider will tell you how much DUVYZAT to take and when to take it.
- Your healthcare provider may change your dose of DUVYZAT if needed. Do not change your dose of DUVYZAT without talking to your healthcare provider.
- Shake the bottle for at least 30 seconds by continuously turning the bottle up and down. Stop when the DUVYZAT suspension looks the same throughout.
- Take the prescribed dose of DUVYZAT by mouth (orally) using the oral syringe that came with your DUVYZAT medicine. Do not throw away the oral syringe.
- DUVYZAT should not be mixed with water or other liquids.
- If you miss a dose of DUVYZAT, skip the missed dose and take your next dose of DUVYZAT as scheduled.
What are the possible side effects of DUVYZAT?
DUVYZAT can cause serious side effects, including:- see “What is the most important information I should know about DUVYZAT?”
- changes in the electrical activity of your heart called QT Prolongation. QT Prolongation can increase the risk of developing a type of irregular heart rhythm known as Torsades de Pointes. Call your healthcare provider right away if you feel faint, have an irregular heartbeat, feel dizzy, or lose consciousness.
- loose, watery stools (diarrhea)
- nausea
- vomiting
- stomach (abdominal) pain
- low platelet counts in the blood
- increased fat levels in the blood
- fever
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all of the possible side effects of DUVYZAT. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.General information about the safe and effective use of DUVYZAT.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use DUVYZAT for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give DUVYZAT to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about DUVYZAT that is written for healthcare professionals.What are the ingredients in DUVYZAT? Active ingredient: givinostat Inactive ingredients: cream flavor, glycerin, non-crystallizing sorbitol solution, peach flavor, polysorbate 20, purified water, saccharin sodium, sodium benzoate, sodium hydroxide, tartaric acid, and tragacanth.
Distributed by:
ITF Therapeutics, LLC
Concord, MA 01742
For more information, go to www.DUVYZAT.com or call 1-833-582-4312 -
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
DUVYZAT [doo' vi zat]
(givinostat)
oral suspensionThis Instructions for Use contains information on how to take DUVYZAT. Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist if you have any questions on how to take DUVYZAT.
Each DUVYZAT carton contains (see Figure A):
- 1 (one) bottle of 140 mL oral suspension
- 1 (one) 5 mL oral syringe
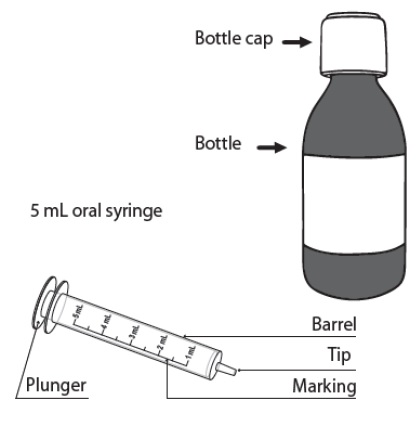
Figure A Important information you need to know before you take DUVYZAT:
- Keep these instructions for future use.
- Do not share DUVYZAT with anyone else.
- Do not mix DUVYZAT with water or other liquids.
- Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist to show you how to measure your prescribed dose.
- Do not throw away the oral syringe. Always use the oral syringe that comes with DUVYZAT to measure your prescribed dose.
- Use the medicine in the bottle within 60 days after you first open it. Throw away any unused DUVYZAT remaining in this bottle after 60 days. Write the date you open the bottle on the bottle label.
How to take DUVYZAT:
- Take DUVYZAT exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
- Take DUVYZAT by mouth (orally) 2 times each day.
- The dose of DUVYZAT is based on how much you weigh.
- Take DUVYZAT with food.
- Take DUVYZAT using the oral syringe that comes with DUVYZAT.
Remove the DUVYZAT bottle and the oral syringe from the carton (see Figure A above).
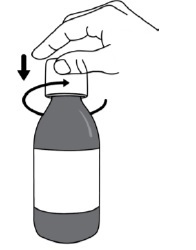
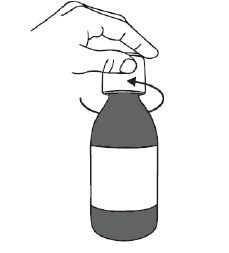
Step 1. Make sure the bottle is closed properly and shake the bottle for at least 30 seconds by continuously turning the bottle up and down (see Figure B). Stop when the DUVYZAT oral suspension is mixed well and looks the same throughout. Step 2. Open the bottle by pressing down on the bottle cap and turning it to the left (counter-clockwise) (see Figure C). Do not throw away the bottle cap. Step 3.
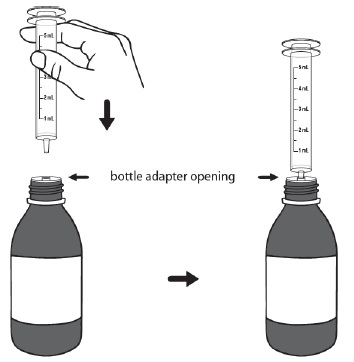
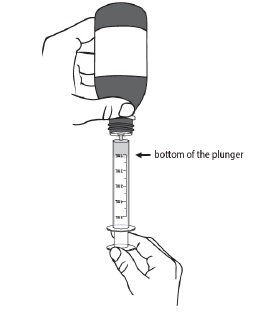
For first time use only: Take the provided oral syringe to be used and firmly insert the tip of the oral syringe into the bottle adapter opening (see Figure D).
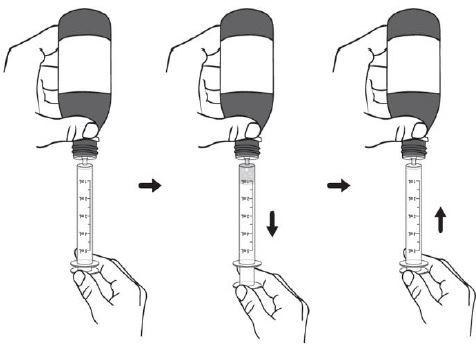
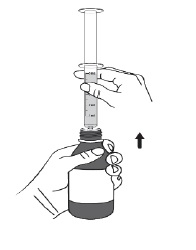
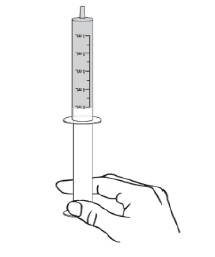
For all other uses: Take the provided oral syringe to be used, push the plunger all the way down (to remove the air) and firmly insert the tip of the oral syringe into the bottle adapter opening (see Figure D).Step 4. While holding the oral syringe in place, turn the bottle upside down. Slowly pull the plunger down to pull back a small amount of the suspension. Then push the plunger all the way up to remove any air bubbles (see Figure E). Step 5. Slowly pull the plunger down until the bottom of the plunger is even with the markings on the oral syringe for the prescribed dose of DUVYZAT (see Figure F). If your prescribed dose is more than 5 mL, you will need to use the same oral syringe more than one time. Step 6. While keeping the plunger in the same position, turn the bottle upright, and place it carefully on a flat surface. Remove the oral syringe by gently twisting or pulling it out from the bottle adapter opening. Do not hold the oral syringe by the plunger because the plunger may come out (see Figure G).
Take or give DUVYZAT right away after it is drawn up into the oral syringe. Do not store the filled oral syringe.Step 7. Check that the prescribed volume (mL) of DUVYZAT has been drawn up into the oral syringe (see Figure H). Figure H shows an example of a 5 mL dose. Your dose may be a different volume. Step 8. The child or adult should sit upright to take a dose of DUVYZAT. Place the tip of the oral syringe against the inside of the cheek. Slowly push the plunger all the way down until there is no more medicine left in the oral syringe.
If your prescribed dose is more than 5 mL, repeat Step 3 through Step 8 to give the remaining part of the dose.Step 9. After use, replace the bottle cap and turn the bottle cap to the right (clockwise) to close the bottle (see Figure I). Step 10. Wash the oral syringe in water and allow to dry. Keep the oral syringe for use with this bottle of DUVYZAT. Store the oral syringe in a clean, dry place.
How to store DUVYZAT:
- Store DUVYZAT at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Do not freeze DUVYZAT.
- Store DUVYZAT upright.
- After opening the bottle of DUVYZAT, use within 60 days. Throw away (dispose of) any DUVYZAT that is not used within 60 days after opening the bottle. Ask your pharmacist how to properly throw away (dispose of) medicines you no longer use.
- Do not use DUVYZAT after the expiration date (EXP) on the carton and the bottle. The expiration date is the last day of the expiration month.
- Keep the bottle tightly closed between each use.
- Keep DUVYZAT and all medicines out of the sight and reach of children.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Approved: 3/2024 - SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC: 11797-110-01
Rx only
DuvyzatTM
[givinostat]
Oral suspension
8.86 mg/mLFor Oral Administration Only
Shake bottle for 30 seconds
before use140 mL
Dispense a Medication Guide to each
patient. Print Medication Guides at
www.duvyzat.com/medication-guideITALFARMACO
Distributed by: ITF Therapeutics, LLC
Concord, MA 01742
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC: 11797-110-02
Rx only
DuvyzatTM
[givinostat]
Oral suspension
8.86 mg/mLFor Oral
Administration Only
Shake bottle for 30 seconds
before useSee enclosed Instructions for Use
Dispense a Medication Guide to each patient.
Print Medication Guides at
www.duvyzat.com/medication-guide140 mL

-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
DUVYZAT
givinostat suspensionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 11797-110 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength GIVINOSTAT (UNII: 5P60F84FBH) (GIVINOSTAT - UNII:5P60F84FBH) GIVINOSTAT 8.86 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength POLYSORBATE 20 (UNII: 7T1F30V5YH) GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) TRAGACANTH (UNII: 2944357O2O) SODIUM BENZOATE (UNII: OJ245FE5EU) PEACH (UNII: 3OKE88I3QG) COW MILK FAT (UNII: 463JZS0XJ3) SACCHARIN SODIUM (UNII: SB8ZUX40TY) NONCRYSTALLIZING SORBITOL SOLUTION (UNII: 9E0S3UM200) TARTARIC ACID (UNII: W4888I119H) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Product Characteristics Color WHITE (white to off-white or faintly pink) Score Shape Size Flavor PEACH (peach-cream) Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 11797-110-02 1 in 1 CARTON 03/21/2024 1 NDC: 11797-110-01 140 mL in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA217865 03/21/2024 Labeler - Italfarmaco SPA (428179329) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations CHEMI SpA 542987644 analysis(11797-110) , api manufacture(11797-110) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Italfarmaco S.A. 469466825 analysis(11797-110) , label(11797-110) , manufacture(11797-110) , pack(11797-110)
Trademark Results [DUVYZAT]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 DUVYZAT 98454709 not registered Live/Pending |
ITALFARMACO S.P.A. 2024-03-18 |
 DUVYZAT 97342645 not registered Live/Pending |
ITALFARMACO S.p.A. 2022-04-01 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.