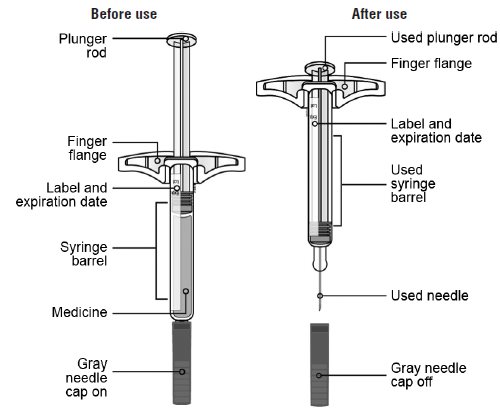
SILIQ- brodalumab injection
Siliq by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Siliq by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Bausch Health US LLC, Patheon Italia S.p.A.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use SILIQ safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for SILIQ.
SILIQ™ (brodalumab) injection, for subcutaneous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2017WARNING: SUICIDAL IDEATION AND BEHAVIOR
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- Suicidal ideation and behavior, including completed suicides, have occurred in patients treated with SILIQ. (5.1, 6.1)
- Prior to prescribing, weigh potential risks and benefits in patients with a history of depression and/or suicidal ideation or behavior. (5.1)
- Patients with new or worsening suicidal thoughts and behavior should be referred to a mental health professional, as appropriate. (5.1)
- Advise patients and caregivers to seek medical attention for manifestations of suicidal ideation or behavior, new onset or worsening depression, anxiety, or other mood changes. (5.1)
- SILIQ is available only through a restricted program called the SILIQ REMS Program. (5.2)
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
SILIQ is a human interleukin-17 receptor A (IL-17RA) antagonist indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in adult patients who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy and have failed to respond or have lost response to other systemic therapies. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Administer 210 mg of SILIQ by subcutaneous injection at Weeks 0, 1, and 2 followed by 210 mg every 2 weeks. (2.1)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- Injection: 210 mg/1.5 mL solution in a single-dose prefilled syringe. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Crohn’s disease (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Infections: Serious infections have occurred. Consider the risks and benefits prior to initiating SILIQ in patients with a chronic infection or a history of recurrent infection. Instruct patients to seek medical advice if signs or symptoms of clinically important chronic or acute infection occur. If a serious infection develops, discontinue SILIQ until the infection resolves. (5.3)
- Tuberculosis (TB): Evaluate patients for TB infection prior to initiating treatment with SILIQ. (5.4)
- Crohn’s Disease: Crohn’s disease occurred during clinical trials. Discontinue SILIQ if patient develops Crohn’s disease while taking SILIQ. (5.5)
- Immunizations: Avoid using live vaccines concurrently with SILIQ. (5.5)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥1%) were arthralgia, headache, fatigue, diarrhea, oropharyngeal pain, nausea, myalgia, injection site reactions, influenza, neutropenia, and tinea infections. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Valeant Pharmaceuticals North America LLC at 1-800-321-4576 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 5/2018
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING: SUICIDAL IDEATION AND BEHAVIOR
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosage
2.2 Tuberculosis Assessment Prior to Initiation of SILIQ
2.3 Important Administration Instructions
2.4 Preparation of SILIQ Prefilled Syringe
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Suicidal Ideation and Behavior
5.2 SILIQ REMS Program
5.3 Infections
5.4 Risk for Latent Tuberculosis Reactivation
5.5 Crohn’s Disease
5.6 Immunizations
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
6.2 Immunogenicity
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Live Vaccinations
7.2 CYP450 Substrates
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
16.2 Storage and Handling
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING: SUICIDAL IDEATION AND BEHAVIOR
Suicidal ideation and behavior, including completed suicides, have occurred in patients treated with SILIQ. Prior to prescribing SILIQ, weigh the potential risks and benefits in patients with a history of depression and/or suicidal ideation or behavior. Patients with new or worsening suicidal ideation and behavior should be referred to a mental health professional, as appropriate. Advise patients and caregivers to seek medical attention for manifestations of suicidal ideation or behavior, new onset or worsening depression, anxiety, or other mood changes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Because of the observed suicidal behavior in subjects treated with SILIQ, SILIQ is available only through a restricted program under a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) called the SILIQ REMS Program [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosage
The recommended SILIQ dose is 210 mg administered by subcutaneous injection at Weeks 0, 1, and 2 followed by 210 mg every 2 weeks.
If an adequate response has not been achieved after 12 to 16 weeks of treatment with SILIQ, consider discontinuing therapy. Continued treatment beyond 16 weeks in patients who have not achieved an adequate response is not likely to result in greater success.
2.2 Tuberculosis Assessment Prior to Initiation of SILIQ
Evaluate patients for tuberculosis (TB) infection prior to initiating treatment with SILIQ [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
2.3 Important Administration Instructions
Administer SILIQ subcutaneously. Each prefilled syringe is for single dose only.
Instruct patients to review the Medication Guide before use [see Medication Guide]. SILIQ is intended for use under the guidance and supervision of a healthcare professional. Patients may self-inject SILIQ when deemed appropriate by a healthcare professional and after proper training in subcutaneous injection technique using the prefilled syringe.
Advise patients who are self-administering to inject the full dose and to read the Instructions for Use before administration [see Instructions for Use].
Do not inject SILIQ into areas where the skin is tender, bruised, red, hard, thick, scaly, or affected by psoriasis.
2.4 Preparation of SILIQ Prefilled Syringe
- Allow SILIQ prefilled syringe to reach room temperature (approximately 30 minutes) before injecting. Do not warm in any other way. Do not remove the gray needle cap on the prefilled syringe while allowing it to reach room temperature.
- Visually inspect SILIQ for particles and discoloration prior to administration. SILIQ is a clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to slightly yellow solution. A few translucent to white, amorphous proteinaceous particles may be present. Do not use SILIQ if it is cloudy or discolored or if foreign matter is present.
- Instruct patients to use the prefilled syringe and to inject the full amount (1.5 mL), which provides 210 mg of SILIQ, according to the directions provided in the Instructions for Use [see Instructions for Use].
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
SILIQ is contraindicated in patients with Crohn’s disease because SILIQ may cause worsening of disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Suicidal Ideation and Behavior
Suicidal ideation and behavior, including four completed suicides, occurred in subjects treated with SILIQ in the psoriasis clinical trials. There were no completed suicides in the 12-week placebo-controlled portion of the trials. SILIQ users with a history of suicidality or depression had an increased incidence of suicidal ideation and behavior as compared to users without such a history [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. A causal association between treatment with SILIQ and increased risk of suicidal ideation and behavior has not been established.
Prescribers should weigh the potential risks and benefits before using SILIQ in patients with a history of depression or suicidality. Patients with new or worsening symptoms of depression or suicidality should be referred to a mental health professional, as appropriate. Advise patients and caregivers to seek medical attention for manifestations of suicidal ideation and behavior, new onset or worsening depression, anxiety, or other mood changes. Prescribers should also re-evaluate the risks and benefits of continuing treatment with SILIQ if such events occur.
Because of the observed suicidal ideation and behavior in subjects treated with SILIQ, if an adequate response to SILIQ has not been achieved within 12 to 16 weeks, consider discontinuing therapy.
SILIQ is available only through a restricted program under a REMS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
5.2 SILIQ REMS Program
SILIQ is available only through a restricted program under a REMS called the SILIQ REMS Program because of the observed suicidal ideation and behavior in subjects treated with SILIQ [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Notable requirements of the SILIQ REMS Program include the following:
- Prescribers must be certified with the program.
- Patients must sign a Patient-Prescriber Agreement Form.
- Pharmacies must be certified with the program and must only dispense to patients who are authorized to receive SILIQ.
Further information, including a list of qualified pharmacies, is available at www.SILIQREMS.com or by calling the SILIQ REMS Program Call Center at 855-511-6135.
5.3 Infections
SILIQ may increase the risk of infections. In clinical trials, subjects treated with SILIQ had a higher rate of serious infections than subjects treated with placebo (0.5% versus 0.2%) and higher rates of fungal infections (2.4% versus 0.9%). One case of cryptococcal meningitis occurred in a subject treated with SILIQ during the 12-week randomized treatment period and led to discontinuation of therapy [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
During the course of clinical trials for plaque psoriasis, the exposure-adjusted rates for infections and serious infections were similar in the subjects treated with SILIQ and those treated with ustekinumab.
In patients with a chronic infection or a history of recurrent infection, consider the risks and benefits prior to prescribing SILIQ. Instruct patients to seek medical help if signs or symptoms of clinically important chronic or acute infection occur. If a patient develops a serious infection or is not responding to standard therapy for the infection, monitor the patient closely and discontinue SILIQ therapy until the infection resolves.
5.4 Risk for Latent Tuberculosis Reactivation
Evaluate patients for tuberculosis (TB) infection prior to initiating treatment with SILIQ. Do not administer SILIQ to patients with active TB infection. Initiate treatment for latent TB prior to administering SILIQ.
Consider anti-TB therapy prior to initiation of SILIQ in patients with a past history of latent or active TB in whom an adequate course of treatment cannot be confirmed. Closely monitor patients receiving SILIQ for signs and symptoms of active TB during and after treatment.
5.5 Crohn’s Disease
In psoriasis trials, which excluded subjects with active Crohn’s disease, Crohn’s disease occurred in one subject during treatment with SILIQ and led to discontinuation of therapy. In other trials, exacerbation of Crohn’s disease was observed with SILIQ use.
SILIQ is contraindicated in patients with Crohn’s disease.
Discontinue SILIQ if the patient develops Crohn’s disease while taking SILIQ.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of labeling:
- Suicidal Ideation and Behavior [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Crohn’s Disease [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The overall safety population included 4558 subjects (3066 SILIQ, 613 ustekinumab, 879 placebo) in controlled clinical trials and open-label extension studies. The majority of subjects were male (69%), white (91%), and aged 40-64 years old (58%). One third of subjects reported previous biologic use prior to enrollment. Across the clinical development program, 4464 subjects received at least one dose of SILIQ; 3755 subjects were exposed to SILIQ for at least 1 year.
Weeks 0 to 12:
Data from one multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled trial (Trial 1), two multicenter, randomized, placebo- and active-controlled trials (Trials 2 and 3), and one dose-finding trial (Trial 4) in plaque psoriasis were pooled to evaluate the safety of SILIQ (210 mg weekly at Weeks 0, 1, and 2, followed by treatments every 2 weeks [Q2W]) compared to placebo for up to 12 weeks after treatment initiation.
During the 12-week, randomized treatment period, about 1% of the subjects in the treatment groups (SILIQ, ustekinumab, and placebo) discontinued treatment because of adverse events. Adverse events leading to discontinuation of SILIQ included neutropenia, arthralgia, and urticaria. The proportion of subjects who developed serious adverse events was similar among the SILIQ, ustekinumab, and placebo groups.
Table 1 summarizes the adverse reactions that occurred at a rate of at least 1% and at a higher rate in the SILIQ 210 mg Q2W group than in the placebo group during the 12-week randomized treatment period of the pooled trials.
Table 1: Adverse Reactions Occurring in ≥ 1% of Subjects in the SILIQ Group and More Frequently than in the Placebo Group in Plaque Psoriasis Trials through Week 12 - * Subjects receiving 210 mg of SILIQ at Weeks 0, 1, and 2, followed by treatment every 2 weeks during the 12-week period
- † Trials 2 and 3 included the active comparator, ustekinumab.
Adverse Reactions
Placebo
(N=879)
n (%)
SILIQ 210 mg
every 2 weeks*
(N=1496)
n (%)
Ustekinumab
(N=613)†
n (%)
Arthralgia
29 (3.3)
71 (4.7)
15 (2.4)
Headache
31 (3.5)
64 (4.3)
23 (3.8)
Fatigue
10 (1.1)
39 (2.6)
16 (2.6)
Diarrhea
10 (1.1)
33 (2.2)
5 (0.8)
Oropharyngeal pain
10 (1.1)
31 (2.1)
8 (1.3)
Nausea
10 (1.1)
28 (1.9)
6 (1.0)
Myalgia
3 (0.3)
26 (1.7)
4 (0.7)
Injection site reactions
(pain, erythema, bruising, hemorrhage, pruritus)
11 (1.3)
23 (1.5)
12 (2.0)
Influenza
4 (0.5)
19 (1.3)
7 (1.1)
Neutropenia
4 (0.5)
15 (1.0)
5 (0.8)
Tinea infections
(tinea pedis, versicolor, cruris)
2 (0.2)
15 (1.0)
3 (0.5)
Adverse reactions that occurred in less than 1% of subjects in the SILIQ group through Week 12 were conjunctivitis and candida infections (including oral [0.2%], genital [0.1%], and esophageal [0.1%] versus none in the placebo group).
Week 0 to End of Trial:
Through Week 52, exposure-adjusted rates of serious adverse events were similar between subjects treated with SILIQ and those treated with ustekinumab. Through the end of the trial, the exposure-adjusted rates of treatment-emergent serious adverse events were similar to those seen in the 52-week period in the subjects treated with SILIQ.
Specific Adverse Reactions:
Suicidal Ideation and Behavior
During the 12-week randomized treatment period in the pooled trials, one subject in the SILIQ group attempted suicide and none in the placebo or ustekinumab groups. From initiation through Week 52 of the trials, suicidal ideation or behavior occurred in 7 of 4019 subjects (0.2 per 100 subject-years) treated with SILIQ and in 2 of 613 subjects (0.4 per 100 subject-years) treated with ustekinumab.
During the course of the clinical trials for plaque psoriasis, suicidal ideation or behavior occurred in 34 of 4464 subjects treated with SILIQ (0.37 per 100 subject-years). Eight of the 10 subjects who attempted or completed suicide had a history of depression and/or suicidal ideation or behavior [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2)].
Infections
During the 12-week randomized treatment period, infections occurred in 25.4% of the SILIQ group compared to 23.4% of the placebo group. The majority of infections consisted of nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, pharyngitis, urinary tract infections, bronchitis, and influenza, and did not necessitate treatment discontinuation. The SILIQ group had a higher rate of fungal infections compared to the placebo group (1.8% vs 0.9%). The fungal infections were primarily non-serious skin and mucosal candida infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Neutropenia
During the 12-week randomized treatment period, neutropenia occurred in 0.7% of subjects in the SILIQ group. Most adverse reactions of neutropenia were transient. In subjects with normal absolute neutrophil count (ANC) at baseline, a reduction in ANC occurred in 6.8% of subjects in the SILIQ group, compared to 3.3% in the ustekinumab group, and 3.6% in the placebo group. Neutropenia ≥ Grade 3 (< 1000/mm3) occurred in 0.5% of subjects in the SILIQ group compared to 0.2% of subjects in the ustekinumab group and none in the placebo group. From Week 0 to end of trial, the exposure-adjusted rate of treatment-emergent neutropenia was 0.4 per 100 subject-years (0.1 per 100 subject-years were ≥ Grade 3). No serious infections were associated with cases of neutropenia.
6.2 Immunogenicity
As with all therapeutic proteins, there is potential for immunogenicity with SILIQ. Approximately 3% of subjects treated with SILIQ developed antibodies to brodalumab through the 52-week treatment period. Of the subjects who developed antibodies to brodalumab, none had antibodies that were classified as neutralizing. However, the assay to test for neutralizing antibodies had limitations detecting neutralizing antibodies in the presence of brodalumab; therefore, the incidence of neutralizing antibody development could be underestimated.
The detection of antibody formation is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Additionally, the observed incidence of antibody (including neutralizing antibody) positivity in an assay may be influenced by several factors, including assay methodology, sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medications, and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of the incidence of antibodies to SILIQ with the incidence of antibodies to other products may be misleading.
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Live Vaccinations
Avoid use of live vaccines in patients treated with SILIQ [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
7.2 CYP450 Substrates
The formation of CYP450 enzymes can be altered by increased levels of certain cytokines (e.g., IL-1, IL-6, IL-10, TNFα, IFN) during chronic inflammation. Treatment with SILIQ may modulate serum levels of some cytokines.
Therefore, upon initiation or discontinuation of SILIQ in patients who are receiving concomitant drugs which are CYP450 substrates, particularly those with a narrow therapeutic index, consider monitoring for effect (e.g., for warfarin) or drug concentration (e.g., for cyclosporine) and consider dosage modification of the CYP450 substrate [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no human data on SILIQ use in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk. Human IgG antibodies are known to cross the placental barrier; therefore, SILIQ may be transmitted from the mother to the developing fetus. In a combined embryofetal development and pre- and postnatal development study, no adverse developmental effects were observed in infants born to pregnant monkeys after subcutaneous administration of brodalumab during organogenesis through parturition at doses up to 26 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) [see Data].
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
A combined embryofetal development and pre- and postnatal development study was conducted in cynomolgus monkeys administered brodalumab. No brodalumab-related effects on embryofetal toxicity or malformations, or on morphological, functional, or immunological development were observed in infants from pregnant monkeys administered weekly subcutaneous doses of brodalumab up to 26 times the MRHD from the beginning of organogenesis to parturition (on a mg/kg basis of 90 mg/kg/week).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of brodalumab in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Brodalumab was detected in the milk of lactating cynomolgus monkeys. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for SILIQ and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from SILIQ or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of SILIQ have not been evaluated in pediatric patients.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 3066 plaque psoriasis subjects initially randomized to SILIQ in clinical trials, 192 (6%) were ≥ 65 years old and no subjects were ≥ 75 years old. Although no differences in safety or efficacy were observed between older and younger subjects, the number of subjects aged 65 years and older was not sufficient to determine whether they responded differently from younger subjects [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Brodalumab is a human monoclonal IgG2κ antibody directed against human interleukin-17 receptor A (IL-17RA). It is expressed in a Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cell line. Brodalumab is comprised of 1312 amino acids and has an estimated molecular mass of 144,000 Daltons.
SILIQ (brodalumab) Injection is a sterile, preservative-free, clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to slightly yellow solution, delivered via subcutaneous injection. A few translucent to white amorphous particles may be present. SILIQ is supplied in a single-dose 2.25 mL syringe made from type 1 glass with stainless steel 27G x ½" needle. Each SILIQ single-dose prefilled syringe delivers 1.5 mL of solution containing 210 mg of brodalumab formulated in glutamate (6.5 mg), polysorbate 20 (0.15 mg), proline (36 mg), and Water for Injection, USP at pH 4.8.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Brodalumab is a human monoclonal IgG2 antibody that selectively binds to human IL-17RA and inhibits its interactions with cytokines IL-17A, IL-17F, IL-17C, IL-17A/F heterodimer, and IL-25. IL-17RA is a protein expressed on the cell surface and is a required component of receptor complexes utilized by multiple IL-17 family cytokines. Blocking IL-17RA inhibits IL-17 cytokine-induced responses including the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Elevated levels of IL-17A, IL-17C, and IL-17F are found in psoriatic plaques. Serum IL-17A levels, measured at Weeks 12, 24, and 48 of SILIQ 210 mg every 2 weeks of treatment, were higher than the baseline levels in subjects with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. The relationship between the pharmacodynamic activity and the mechanism(s) by which brodalumab exerts its clinical effects is unknown.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Following a single subcutaneous dose of 210 mg in subjects with plaque psoriasis, brodalumab reached peak mean (±SD) serum concentration (Cmax) of 13.4±7.3 mcg/mL by approximately 3 days post-dose. The mean (±SD) area-under-the-concentration-time curve (AUC) of brodalumab was 111±64 mcgday/mL.
Following multiple subcutaneous doses of 210 mg every 2 weeks, steady-state was achieved by Week 4. The mean (±SD) Cmax was 20.6±14.6 mcg/mL and the mean (±SD) AUC over the 2-week dosing interval was 227±167 mcgday/mL.
Following subcutaneous administration, brodalumab bioavailability was approximately 55%.
Distribution
Following a single subcutaneous administration of brodalumab 210 mg in subjects with plaque psoriasis, the mean (±SD) apparent volume of distribution (Vz/F) of brodalumab was 8.9±9.4 L.
Elimination
The metabolic pathway of brodalumab has not been characterized. As a human monoclonal IgG2 antibody, brodalumab is expected to be degraded into small peptides and amino acids via catabolic pathways in a manner similar to endogenous IgG.
Following a single subcutaneous administration of brodalumab 210 mg in subjects with plaque psoriasis, the mean (±SD) apparent total clearance (CL/F) was 3.0±3.5 L/day. The clearance of brodalumab increased with decreasing doses due to nonlinear elimination.
Dose Linearity
Brodalumab exhibited nonlinear pharmacokinetics with exposures that increased greater than dose-proportionally over a dose range from 140 mg (approximately 0.67 times the recommended dose) to 350 mg (approximately 1.67 times the recommended dose) following subcutaneous administrations in subjects with plaque psoriasis.
Weight
Brodalumab trough concentrations were lower in subjects with higher body weight.
Specific Populations
Hepatic or Renal Impairment
No trials were conducted to assess the effect of hepatic or renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of brodalumab.
Age: Geriatric Population
Population pharmacokinetic analysis indicated that age did not significantly influence the clearance of brodalumab in subjects with plaque psoriasis. Subjects who were 65 years or older had a similar brodalumab clearance as compared to subjects less than 65 years old.
Drug Interaction Studies
In subjects with plaque psoriasis, one week following a single subcutaneous administration of 210 mg brodalumab, the exposure of midazolam (CYP3A4 substrate) was increased by 24% [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Animal studies have not been conducted to evaluate the carcinogenic or mutagenic potential of SILIQ. The published literature is mixed on the potential effects on malignancy risk due to the inhibition of the IL-17RA, the pharmacological action of SILIQ. Some published literature suggests that IL-17A directly promotes cancer cell invasion, which suggests a potential beneficial effect of SILIQ. However, other reports indicate IL-17A promotes T-cell mediated tumor rejection, which suggests a potential adverse effect by SILIQ. However, inhibition of the IL-17RA with SILIQ has not been studied in these models. Therefore, the relevance of experimental findings in these models for malignancy risk in humans is unknown.
In cynomolgus monkeys, there were no effects on fertility parameters such as changes in reproductive organs or sperm analysis following subcutaneous administration of brodalumab at dose levels up to 90 mg/kg/week for 6 months (26 times the MRHD on a mg/kg basis). The monkeys were not mated in this study to evaluate effects on fertility.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Three multicenter, randomized, double-blind, controlled trials (Trials 1, 2, and 3) enrolled a total of 4373 subjects 18 years of age and older with at least a 6-month history of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, defined as having a minimum affected body surface area (BSA) of 10%, a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) score ≥ 12, a static Physician’s Global Assessment (sPGA) score ≥3 in the overall assessment (plaque thickness/induration, erythema, and scaling) of psoriasis on a severity scale of 0 to 5, and who were candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy. In all three trials, subjects were randomized to subcutaneous treatment with placebo or SILIQ 210 mg at Weeks 0, 1, and 2, followed by treatments every 2 weeks [Q2W] through Week 12. In the two active comparator trials (Trials 2 and 3), subjects randomized to ustekinumab received a 45 mg dose if their weight was less than or equal to 100 kg and a 90 mg dose if their weight was greater than 100 kg at Weeks 0, 4, and 16, followed by the same dose every 12 weeks.
All three trials assessed the change from baseline to Week 12 compared to placebo in the two co-primary endpoints: 1) PASI 75, the proportion of subjects who achieved at least a 75% reduction in the PASI composite score that takes into consideration both the percentage of body surface area affected and the nature and severity of psoriatic changes (induration, erythema, and scaling) within the affected region, and 2) the proportion of subjects with an sPGA of 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear), and at least a 2-point improvement from baseline. In Trials 2 and 3, comparisons were also made to ustekinumab for the primary endpoint of the proportion of subjects who achieved a reduction in PASI score of 100% (PASI 100) from baseline at Week 12.
Other evaluated outcomes included the proportion of subjects who achieved an sPGA of 0 (clear) at Week 12, and the proportion of subjects who achieved a Psoriasis Symptom Inventory (PSI) score of 0 (not at all) or 1 (mild) on every item (itch, redness, scaling, burning, stinging, cracking, flaking, and pain) at Week 12. Baseline demographics and disease characteristics were generally consistent across all treatment groups in all three trials. Subjects were predominantly men (69%) and white (91%), with a mean age of 45 years. The mean baseline body weight was 90.5 kg and 28% of subjects had body weight greater than 100 kg. The baseline PASI score ranged from 9.4 to 72 (median: 17.4) and the baseline-affected BSA ranged from 10 to 97% (median: 21%). Baseline sPGA scores ranged from “3 (moderate)” (58%) to “5 (very severe)” (5%).
Approximately 21% of subjects had a history of psoriatic arthritis. Approximately 30% of subjects had previously received a biologic therapy and 12% of subjects had failed previous biologic therapy.
Clinical Response at Week 12
The results of Trials 1, 2, and 3 are presented in Table 2.
Table 2: Efficacy Results at Week 12 in Adults with Plaque Psoriasis in Trials 1, 2, and 3 (NRI*) - * NRI = non-responder imputation
- † Co-primary endpoints
Endpoint
Trial 1
Trial 2
Trial 3
SILIQ
210 mg Q2W
(N=222)
n (%)
Placebo
(N=220)
n (%)
SILIQ
210 mg Q2W
(N=612)
n (%)
Ustekinumab
(N=300)
n (%)
Placebo
(N=309)
n (%)
SILIQ
210 mg Q2W
(N=624)
n (%)
Ustekinumab
(N=313)
n (%)
Placebo
(N=315)
n (%)
PASI 75†
response
185 (83)
6 (3)
528 (86)
210 (70)
25 (8)
531 (85)
217 (69)
19 (6)
PASI 100
response
93 (42)
1 (<1)
272 (44) †
65 (22)
2 (1)
229 (37) †
58 (19)
1 (<1)
sPGA
success
clear (0)
or almost
clear (1)†
168 (76)
3 (1)
481 (79)
183 (61)
12 (4)
497 (80)
179 (57)
13 (4)
sPGA of
clear (0)
93 (42)
1 (<1)
274 (45)
65 (21)
2 (1)
229 (37)
58 (19)
1 (<1)
Examination of age, gender, race, use of prior systemic or phototherapy, and use of prior biologics did not identify differences in response to SILIQ among these subgroups.
At Week 12, compared to subjects in the placebo group, a greater proportion of subjects in SILIQ 210 mg Q2W group achieved a Psoriasis Symptom Inventory (PSI) score of 0 (not at all) or 1 (mild) on every item (itch, redness, scaling, burning, stinging, cracking, flaking, pain).
Maintenance of Effect
In Trial 1, subjects randomized to receive SILIQ and who were responders at Week 12 (i.e., sPGA of 0 or 1) were re-randomized to receive either placebo or SILIQ. Among responders at Week 12, 83% (69/83) of subjects re-randomized to continued treatment with SILIQ 210 mg Q2W maintained this response (sPGA of 0 or 1) at Week 52 compared to none (0/84) who were re-randomized to placebo and withdrawn from SILIQ. In addition, 87% (72/83) of subjects re-randomized to continued treatment with SILIQ 210 mg Q2W achieved PASI 75 response at Week 52 compared to none (0/84) who were re-randomized to placebo and withdrawn from SILIQ.
Trials 2 and 3 included a re-randomized phase during which subjects originally randomized to receive SILIQ during the first 12 weeks were re-randomized to one of four SILIQ regimens at the Week 12 visit and placebo subjects were crossed over to receive SILIQ 210 mg Q2W. Subjects receiving ustekinumab continued the same treatment until crossed over at Week 52 to SILIQ 210 mg Q2W. For sPGA 0 or 1 responders at Week 12, the percentage of subjects who maintained this response at Week 52 was 79% for subjects treated with SILIQ 210 mg Q2W. For PASI 100 responders at Week 12, 72% of the subjects who continued on SILIQ 210 mg Q2W maintained the response at Week 52.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
SILIQ (brodalumab) Injection is available in a single-dose prefilled syringe containing a sterile, preservative-free clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to slightly yellow solution that may contain a few translucent to white, amorphous particles.
- NDC: 0187-0004-02: Carton of two 210 mg/1.5 mL single-dose prefilled syringes
16.2 Storage and Handling
- Store refrigerated at 2° to 8°C (36° to 46°F) in the original carton to protect from light and physical damage during storage.
- When necessary, prefilled syringes can be stored at room temperature up to a maximum of 77°F (25°C) in the original carton for a maximum single period of 14 days with protection from light and sources of heat. Once the prefilled syringe has reached room temperature, do not place back into the refrigerator. Discard after 14 days at room temperature.
- Do not freeze.
- Do not shake.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide and Instructions for Use)before the patient starts using SILIQ, and each time the prescription is renewed, as there may be new information they need to know.
Suicidal Thoughts and Behavior
Instruct patients and their caregivers to monitor for the emergence of suicidal thoughts and behavior and promptly seek medical attention if the patient experiences suicidal thoughts, new or worsening depression, anxiety, or other mood changes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Instruct patients to carry the wallet card provided and to call the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline at 1-800-273-8255 if they experience suicidal thoughts.
SILIQ REMS Program
Because of the observed suicidal thoughts and behavior in subjects treated with SILIQ, SILIQ is available only through a restricted program called the SILIQ REMS Program [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Inform the patient of the following:
- Patients must enroll in the program [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2)].
- Patients will be given a SILIQ Patient Wallet Card that they should carry with them at all times. This card describes symptoms which, if experienced, should prompt the patient to immediately seek medical evaluation. Advise the patient to show the SILIQ Patient Wallet Card to other treating healthcare providers.
SILIQ is available only from certified pharmacies participating in the program. Therefore, provide patients with the telephone number and website for information on how to obtain the product.
Infections
Inform patients that SILIQ may lower the ability of their immune system to fight infections. Instruct patients of the importance of communicating any history of infections to their healthcare providers and to contact their healthcare providers if they develop any signs or symptoms of infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Crohn’s Disease
Instruct patients to seek medical advice if they develop signs and symptoms of Crohn’s disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Instructions for Injection
Instruct the patient to perform the first self-injection under the guidance and supervision of a qualified healthcare professional for proper training in subcutaneous injection technique.
Instruct patients who are self-administering to inject the full dose of SILIQ [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) and Instructions for Use].
Instruct patients or caregivers in the technique of proper syringe and needle disposal [see Instructions for Use].
Manufactured for:
Valeant Pharmaceuticals North America LLC
Bridgewater, NJ 08807 USAManufactured by:
Valeant Pharmaceuticals Luxembourg S.à.r.l.
Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, L-1931, LuxembourgU.S. License Number: 2053
U.S. Patent Numbers: 7,767,206; 7,833,527; 7,786,284; 7,939,070; 8,435,518; 8,545,842; 8,790,648; 8,883,151; 9,073,999 and 9,096,673
SILIQ and Ortho Dermatologics are trademarks of Valeant Pharmaceuticals International, Inc. or its affiliates.
© 2019 Valeant Pharmaceuticals North America LLC
9643800
-
Medication Guide
SILIQ™ (SIL-EEK)
(brodalumab)
injection, for subcutaneous use
What is the most important information I should know about SILIQ?
SILIQ may cause serious side effects, including:-
Suicidal thoughts or behavior have happened in some people treated with SILIQ. Some people have ended their own lives. Your risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior may be increased if you have a history of suicidal thoughts or depression. It is not known if SILIQ causes suicidal thoughts or behavior. Get medical help right away if you or your caregiver notice any of the following symptoms:
- new or worsening depression or anxiety
- thoughts of suicide, dying, or hurting yourself
- changes in behavior or mood
- acting on dangerous impulses
- attempt to commit suicide
Your healthcare provider will give you a SILIQ Patient Wallet Card about symptoms you should get medical help for right away. Carry the card with you at all times during treatment with SILIQ and show it to all of your healthcare providers.
-
Serious infections. SILIQ may lower the ability of your immune system to fight infections and may increase your risk of infections. Your healthcare provider will check you for tuberculosis (TB) before starting treatment with SILIQ and may treat you for TB before you begin treatment with SILIQ if you have a history of TB or have active TB. Your healthcare provider should watch you closely for signs and symptoms of infection and TB during and after treatment with SILIQ.
Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have an infection or have symptoms of an infection, including:- fever, sweats, or chills
- muscle aches
- cough
- shortness of breath
- sore throat or difficulty swallowing
- warm, red, or painful skin or sores on your body
- diarrhea or stomach pain
- burning when you urinate or urinate more often than normal
See “What are the possible side effects of SILIQ?” for more information about side effects.
What is SILIQ?SILIQ is a prescription medicine used to treat adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis:
- who may benefit from taking injections or pills (systemic therapy) or phototherapy (ultraviolet light treatment), and
- who have not responded or lost response to other systemic therapy.
It is not known if SILIQ is safe and effective in children.
Do not use SILIQ if you have Crohn’s disease.
Before you use SILIQ, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:- have a history of mental problems, including suicidal thoughts, depression, anxiety, or mood problems.
- have an infection that does not go away or that keeps coming back.
- have TB or have been in close contact with someone with TB.
- have recently received or are scheduled to receive an immunization (vaccine). You should avoid receiving live vaccines during treatment with SILIQ.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if SILIQ can harm your unborn baby. If you are pregnant or plan on becoming pregnant, consult with your healthcare provider.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if SILIQ passes into your breast milk.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
How should I use SILIQ?- See the detailed “Instructions for Use” that comes with SILIQ for information on how to inject a dose of SILIQ and how to properly store and throw away (dispose of) used SILIQ prefilled syringes.
- Use SILIQ exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to use it.
- Your healthcare provider may stop SILIQ if your plaque psoriasis does not improve within 12 to 16 weeks of treatment.
What are the possible side effects of SILIQ?
SILIQ may cause serious side effects. See “What is the most important information I should know about SILIQ?”
- Crohn’s disease. Tell your healthcare provider if you develop diarrhea, painful diarrhea, bloody stools, stomach pain or cramping, sudden or uncontrollable bowel movements, loss of appetite, constipation, weight loss, fever, or tiredness.
The most common side effects of SILIQ include: joint pain, headache, tiredness, diarrhea, mouth or throat pain, nausea, muscle pain, injection site reactions, flu (influenza), low white blood count (neutropenia), and fungal infections of the skin.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
General information about safe and effective use of SILIQMedicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use SILIQ for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give SILIQ to other people even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about SILIQ that is written for health professionals.
Manufactured for: Valeant Pharmaceuticals North America LLC
Bridgewater, NJ 08807 USAManufactured by: Valeant Pharmaceuticals Luxembourg S.à.r.l.
Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, L-1931, LuxembourgU.S. License Number: 2053
For more information, go to www.SILIQ.com or call Valeant Pharmaceuticals at 1-800-321-4576.
U.S. Patent Numbers: 7,767,206; 7,833,527; 7,786,284; 7,939,070; 8,435,518; 8,545,842; 8,790,648; 8,883,151; 9,073,999 and 9,096,673
SILIQ and Ortho Dermatologics are trademarks of Valeant Pharmaceuticals International, Inc. or its affiliates.
© 2019 Valeant Pharmaceuticals North America LLC
9643800
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Revised: 05/2018
Instructions for UseSILIQ is supplied as a single-dose prefilled syringe. Each prefilled syringe contains one 210 mg dose of SILIQ. Each SILIQ prefilled syringe can only be used one time.
Your healthcare provider has prescribed SILIQ and will tell you how often it should be injected. If your healthcare provider decides that you or a caregiver may be able to give your injections of SILIQ at home, you should receive training on the right way to prepare and inject SILIQ. Do not try to inject yourself until you have been shown the right way to give the injections by your healthcare provider.
Read all of the instructions before using the SILIQ prefilled syringe. Call your healthcare provider if you or your caregiver have any questions about the right way to inject SILIQ.
Instructions for Use
SILIQ™ (SIL-EEK)
(brodalumab)
injection, for subcutaneous use
Single-Dose Prefilled SyringeImportant: Needle is inside the gray needle cap.
ImportantStoring your SILIQ prefilled syringe
- Store SILIQ prefilled syringe in the refrigerator at 36° to 46°F (2° to 8°C).
- If needed, SILIQ prefilled syringe may be stored at room temperature up to 77°F (25°C) for up to 14 days. Do not place SILIQ prefilled syringe stored at room temperature back into the refrigerator.
- Throw away SILIQ prefilled syringe that has been stored at room temperature after 14 days.
- Protect SILIQ prefilled syringe from heat.
- Do not freeze.
- Keep SILIQ prefilled syringe in the original carton to protect from light and physical damage.
- Keep SILIQ prefilled syringe and all medicines out of reach of children.
Using your SILIQ prefilled syringe
- It is important that you do not try to give the injection unless you or your caregiver has received training from your healthcare provider.
- Do not use a SILIQ prefilled syringe after the expiration date on the label.
- Do not shake the SILIQ prefilled syringe.
- Do not remove the gray needle cap from the SILIQ prefilled syringe until you are ready to inject.
- Do not use a SILIQ prefilled syringe if it has been dropped on a hard surface. Part of the SILIQ prefilled syringe may be broken even if you cannot see the break. Use a new SILIQ prefilled syringe, and call 1-800-321-4576.
Step 1: PrepareA Remove one SILIQ prefilled syringe from the package.
Grab the syringe by the barrel to remove the prefilled syringe from the tray.
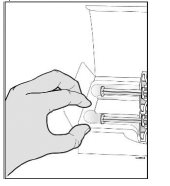
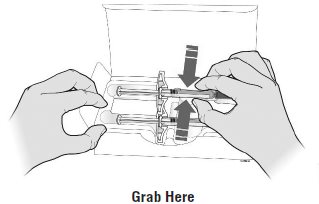
Place your finger or thumb
on the edge of the tray to
hold it while you remove
the prefilled syringe.
Put the original package with any unused prefilled syringes back in the refrigerator.For safety reasons:
- Do not grab the plunger rod.
- Do not grab the gray needle cap.
- Do not remove the gray needle cap until you are ready to inject.
Wait about 30 minutes to let the prefilled syringe warm to room temperature before you use it.
- Do not put the prefilled syringe back in the refrigerator after it has reached room temperature.
- Do not try to warm the prefilled syringe by using a heat source such as hot water or microwave.
- Do not leave the prefilled syringe in direct sunlight.
- Do not shake the prefilled syringe.
Important: Always hold the prefilled syringe by the syringe barrel.
B Inspect the SILIQ prefilled syringe.
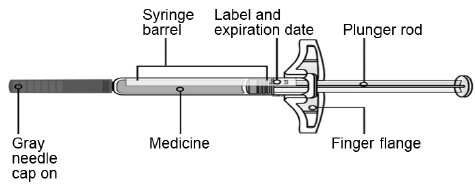
Make sure the medicine in the prefilled syringe is clear and colorless to slightly yellow.-
Do not use the syringe if:
- The medicine is cloudy or discolored or contains flakes or particles.
- Any part appears cracked or broken.
- The gray needle cap is missing or not securely attached.
- The expiration date printed on the label has passed.
In all cases, use a new prefilled syringe, and call 1-800-321-4576.
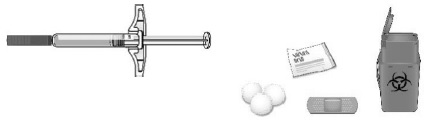
C Gather all materials needed for your injection.Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water.
On a clean, well-lit work surface, place the:
- Prefilled syringe
- Alcohol wipes
- Cotton ball or gauze pad
- Adhesive bandage
- Sharps disposal container
D Prepare and clean your injection site.
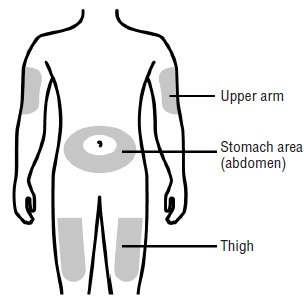
You can use:- Your thigh
- Stomach area (abdomen), except for a 2-inch area right around your navel (belly button)
- Outer area of upper arm (only if someone else is giving you the injection)
Clean your injection site with an alcohol wipe. Let your skin dry.
- Do not touch this area again before injecting.
- Choose a different site each time you give yourself an injection. If you want to use the same injection site, make sure it is not the same spot on the injection site that you used for a previous injection.
- Do not inject into areas where the skin is tender, bruised, red, or hard. Avoid injecting into areas with scars or stretch marks.
- Avoid injecting directly into raised, thick, red, or scaly skin patch or lesion.
Step 2: Get readyE Pull the gray needle cap straight off and away from your body when you are ready to inject.
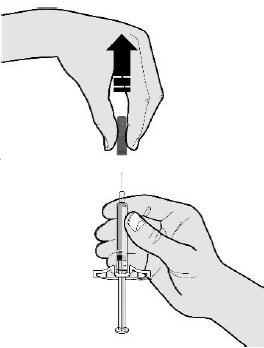
It is normal to see a drop of liquid at the end of the needle.
- Do not twist or bend the gray needle cap.
- Do not put the gray needle cap back onto the prefilled syringe.
- Do not remove the gray needle cap from the prefilled syringe until you are ready to inject.
Important: Throw the needle cap into the sharps disposal container provided.
F Pinch your injection site to create a firm surface.
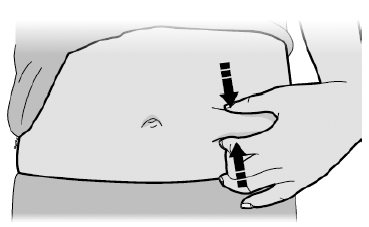
Pinch skin firmly between your thumb and fingers, creating an area about 2 inches wide.
Important: Keep skin pinched while injecting.
Step 3: InjectG Hold the pinch. Insert the needle into your skin at 45 to 90 degrees.
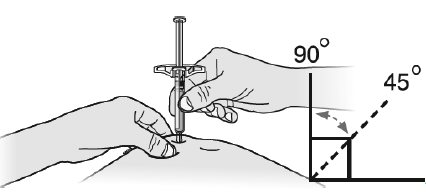
Do not place your finger on the plunger rod while inserting the needle.
H Using slow and constant pressure, push the plunger rod all the way down until it reaches the bottom.
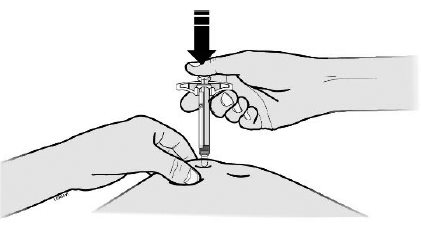
I When done, release your thumb, and gently lift the syringe and pull the needle out of your skin.
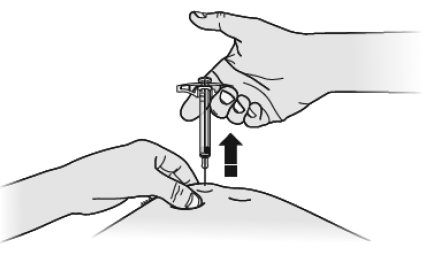
J Inspect the syringe. If there is still medicine in the syringe barrel, this means you have not received a full dose. Call your healthcare provider right away.
Step 4: FinishK Discard (throw away) the used syringe.
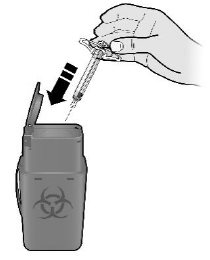
- Put the used SILIQ syringe in an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use. Do not throw away (dispose of) the syringe in your household trash.
-
If you do not have an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
- made of a heavy-duty plastic,
- can be closed with a tight-fitting, puncture-resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out,
- upright and stable during use,
- leak-resistant, and
- properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container.
- When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used needles and syringes. For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA’s website at: http://www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal.
- Do not reuse the syringe.
- Do not recycle the syringe or sharps disposal container or throw them into household trash.
Important: Always keep the sharps disposal container out of the reach of children.
L Examine the injection site.
If there is blood, press a cotton ball or gauze pad on your injection site. Do not rub the injection site. Apply an adhesive bandage if needed.
Manufactured for:
Valeant Pharmaceuticals North America LLC
Bridgewater, NJ 08807 USAManufactured by:
Valeant Pharmaceuticals Luxembourg S.à.r.l.
Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, L-1931, Luxembourg
U.S. License Number 2053For more information, go to www.SILIQ.com or call Valeant Pharmaceuticals at 1-800-321-4576.
U.S. Patent Numbers: 7,767,206; 7,833,527; 7,786,284; 7,939,070; 8,435,518; 8,545,842; 8,790,648; 8,883,151; 9,073,999 and 9,096,673
SILIQ and Ortho Dermatologics are trademarks of Valeant Pharmaceuticals International, Inc. or its affiliates.
© 2019 Valeant Pharmaceuticals North America LLC
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
9643800
Revised: 05/2018
-
Suicidal thoughts or behavior have happened in some people treated with SILIQ. Some people have ended their own lives. Your risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior may be increased if you have a history of suicidal thoughts or depression. It is not known if SILIQ causes suicidal thoughts or behavior. Get medical help right away if you or your caregiver notice any of the following symptoms:
-
PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Contains 2 Single-Dose Prefilled Syringes
NDC 0187-0004-02
SILIQ™
(brodalumab)
Injection
210 mg/1.5 mLFor Subcutaneous Use Only
210 mg/1.5 mLSee package insert for dosing
information and Instructions for Use.
Carton contents:
2 Prefilled Syringes
1 Package Insert
1 Instructions for Use
1 Medication Guide
ATTENTION: Dispense with enclosed medication guide.
Sterile Solution – No Preservative
KEEP OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN.Rx only
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
SILIQ
brodalumab injectionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0187-0004 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength BRODALUMAB (UNII: 6ZA31Y954Z) (BRODALUMAB - UNII:6ZA31Y954Z) BRODALUMAB 210 mg Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0187-0004-02 2 in 1 CARTON 02/15/2017 1 NDC: 0187-0004-00 1 in 1 SYRINGE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA761032 02/15/2017 Labeler - Bausch Health US LLC (831922468) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Patheon Italia S.p.A. 338336589 MANUFACTURE(0187-0004)
Trademark Results [Siliq]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 SILIQ 88152405 5888704 Live/Registered |
Valeant Pharmaceuticals Ireland Limited 2018-10-12 |
 SILIQ 88152405 5888704 Live/Registered |
BAUSCH HEALTH IRELAND LIMITED 2018-10-12 |
 SILIQ 86396790 5813726 Live/Registered |
VALEANT PHARMACEUTICALS IRELAND LIMITED 2014-09-16 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.