CEFTAZIDIME AND DEXTROSE- ceftazidime injection, solution
Ceftazidime and Dextrose by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Ceftazidime and Dextrose by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by B. Braun Medical Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use CEFTAZIDIME for Injection USP and DEXTROSE Injection USP safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for CEFTAZIDIME for Injection USP and DEXTROSE Injection USP.
CEFTAZIDIME for injection USP and DEXTROSE injection USP, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1985To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Ceftazidime for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP and other antibacterial drugs, Ceftazidime for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP should be used only to treat infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria. (1)
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Ceftazidime for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP is a cephalosporin antibacterial indicated in the treatment of the following infections caused by susceptible isolates of the designated microorganisms: Lower respiratory tract infections (1.1); skin and skin-structure infections (1.2); bacterial septicemia (1.3); bone and joint infections (1.4); gynecologic infections (1.5); intra-abdominal infections (1.6); central nervous system infections (1.7).
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For intravenous use only over approximately 30 minutes. (2)
Recommended Dosage Schedule for Creatinine Clearance greater than 50 mL/min Adults Dose Frequency Bone and joint infections 2 grams IV every 12hr Uncomplicated pneumonia; mild skin and skin-structure infections 500 mg*–1 gram IV every 8hr Serious gynecologic and intra-abdominal infections 2 grams IV every 8hr Meningitis 2 grams IV every 8hr Very severe life-threatening infections, especially in immunocompromised patients 2 grams IV every 8hr * Use this formulation of ceftazidime only in patients who require the entire 1 or 2 gram dose and not any fraction thereof. (2.1)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- Injection: 1 g in 50 mL and 2 g in 50 mL in a DUPLEX® Container (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Hypersensitivity to ceftazidime or other cephalosporin class antibiotics, penicillins, or other beta-lactam antibiotics (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Hypersensitivity reactions: Include anaphylaxis and serious skin reactions. Cross-hypersensitivity may occur in up to 10% of patients with a history of penicillin allergy. If an allergic reaction occurs, discontinue the drug. (5.1)
- Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea: May range from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Evaluate if diarrhea occurs. (5.3)
- Neurologic Adverse Reactions in Patients with Renal Impairment: Include life-threatening or fatal occurrences of encephalopathy, myoclonus, or seizures. Dose adjustment is required for patients with CrCL less than or equal to 50 mL/min. (2.3, 5.4)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
- The most common adverse reactions occurring in less than 2% of patients include: hypersensitivity reactions, gastrointestinal symptoms, and central nervous system reactions. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact B. Braun Medical Inc. at 1-800-227-2862 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 7/2019
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Lower Respiratory Tract Infections
1.2 Skin and Skin-structure Infections
1.3 Bacterial Septicemia
1.4 Bone and Joint Infections
1.5 Gynecologic Infections
1.6 Intra-abdominal Infections
1.7 Central Nervous System Infections
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Adult and Pediatric Patients (Who Require the Full Adult Dose)
2.2 Pediatric Population
2.3 Patients with Renal Impairment
2.4 Preparation for Use of Ceftazidime for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP in DUPLEX® Container
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions to Ceftazidime, Cephalosporins, Penicillins, or Other Drugs
5.2 Hemolytic Anemia
5.3 Clostridium difficile-associated Diarrhea
5.4 Neurologic Adverse Reactions in Patients with Renal Impairment
5.5 Hypersensitivity to Dextrose-containing Products
5.6 Risk of Development of Drug-resistant Bacteria
5.7 Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
5.8 Inadvertent Intra-arterial Administration
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
6.3 Cephalosporin-class Adverse Reactions
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Aminoglycosides
7.2 Chloramphenicol
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Labor and Delivery
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Patients with Renal Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
12.4 Microbiology
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
15 REFERENCES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- MICROBIOLOGY
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Ceftazidime for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP and other antibacterial drugs, Ceftazidime for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP should be used only to treat infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
Ceftazidime for Injection and Dextrose Injection is indicated for the treatment of the following infections when caused by susceptible bacteria.
1.1 Lower Respiratory Tract Infections
Lower respiratory tract infections, including pneumonia, caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other Pseudomonas spp.; Haemophilus influenzae, including ampicillin-resistant isolates; Klebsiella spp.; Enterobacter spp.; Proteus mirabilis; Escherichia coli; Serratia spp.; Citrobacter spp.; Streptococcus pneumoniae; and Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-susceptible isolates).
1.2 Skin and Skin-structure Infections
Skin and skin-structure infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Klebsiella spp.; Escherichia coli; Proteus spp., including Proteus mirabilis and indole-positive Proteus; Enterobacter spp.; Serratia spp.; Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-susceptible isolates); and Streptococcus pyogenes (group A beta-hemolytic streptococci).
1.3 Bacterial Septicemia
Bacterial septicemia caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella spp., Haemophilus influenzae, Escherichia coli, Serratia spp., Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-susceptible isolates).
1.4 Bone and Joint Infections
Bone and joint infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella spp., Enterobacter spp., and Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-susceptible isolates).
1.5 Gynecologic Infections
Gynecologic infections, including endometritis, pelvic cellulitis, and other infections of the female genital tract caused by Escherichia coli.
1.6 Intra-abdominal Infections
Intra-abdominal infections, including peritonitis caused by Escherichia coli, Klebsiella spp., and Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-susceptible isolates) and polymicrobial infections caused by aerobic and anaerobic organisms and Bacteroides spp. (many isolates of Bacteroides fragilis are resistant).
1.7 Central Nervous System Infections
Central nervous system infections, including meningitis, caused by Haemophilus influenzae and Neisseria meningitidis. Ceftazidime has also been used successfully in a limited number of cases of meningitis due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Streptococcus pneumoniae.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Adult and Pediatric Patients (Who Require the Full Adult Dose)
Ceftazidime for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP in the DUPLEX® Container should be used only in patients who require the entire 1 or 2 gram dose and not any fraction thereof. Ceftazidime for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP should be administered intravenously (IV) over approximately 30 minutes.
The guidelines for dosage of Ceftazidime for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP are listed in Table 1. The following dosage schedule is recommended.
Table 1: Recommended Dosage Schedule for Creatinine Clearance greater than 50 mL/min Adults Dose Frequency Bone and joint infections 2 grams IV every 12hr Uncomplicated pneumonia; mild skin and skin-structure infections 500 mg*–1 gram IV every 8hr Serious gynecologic and intra-abdominal infections 2 grams IV every 8hr Meningitis 2 grams IV every 8hr Very severe life-threatening infections, especially in immunocompromised patients 2 grams IV every 8hr * Use this formulation of ceftazidime only in patients who require the entire 1 or 2 gram dose and not any fraction thereof.
2.2 Pediatric Population
Ceftazidime for Injection and Dextrose Injection in the DUPLEX® Container is designed to deliver a 1 g or 2 g dose of ceftazidime. To prevent unintentional overdose, this product should not be used in pediatric patients who require less than the full adult dose of ceftazidime [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)]
2.3 Patients with Renal Impairment
Ceftazidime for Injection and Dextrose Injection in the DUPLEX® Container is designed to deliver a 1 g or 2 g dose of ceftazidime. To prevent unintentional overdose, this product should not be used in patients with creatinine clearance less than or equal to 15 mL/min who require less than a 1 g dose of ceftazidime.
In patients with impaired renal function (creatinine clearance less than or equal to 50 mL/min), it is recommended that the dosage of ceftazidime be reduced to compensate for its slower excretion. In patients with suspected renal insufficiency, an initial loading dose of 1 gram of Ceftazidime for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP may be given. An estimate of creatinine clearance should be made to determine the appropriate maintenance dosage. The recommended dosage is presented in Table 2.
Table 2: Recommended Maintenance Dosages of Ceftazidime for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP in Renal Insufficiency Creatinine Clearance (mL/min) Recommended Unit Dose of Ceftazidime for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP Frequency of Dosing 50–31 1 gram every 12hr 30–16 1 gram every 24hr NOTE: IF THE DOSE RECOMMENDED IN TABLE 1 ABOVE IS LOWER THAN THAT RECOMMENDED FOR PATIENTS WITH RENAL INSUFFICIENCY AS OUTLINED IN TABLE 2, THE LOWER DOSE SHOULD BE USED.
When only serum creatinine is available, the following formula (Cockcroft's equation)1 may be used to estimate creatinine clearance. The serum creatinine should represent a steady state of renal function:
Males: Creatinine Clearance (mL/min) = Weight (kg) × (140-age) 72 × serum creatinine (mg/dL) Females: 0.85 × above value In patients with severe infections who would normally receive 2 grams IV every 8hr of Ceftazidime for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP were it not for renal insufficiency, the unit dose given in the table above may be increased by 50% or the dosing frequency may be increased appropriately. Further dosing should be determined by therapeutic monitoring, severity of the infection, and susceptibility of the causative organism.
The creatinine clearance should be adjusted for body surface area or lean body mass, and the dosing frequency should be reduced in cases of renal insufficiency.
In patients undergoing hemodialysis, a loading dose of 1 gram is recommended, followed by 1 gram after each hemodialysis period.
2.4 Preparation for Use of Ceftazidime for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP in DUPLEX® Container
This reconstituted solution is for intravenous use only.
Do not use plastic containers in series connections. Such use would result in air embolism due to residual air being drawn from the primary container before administration of the fluid from the secondary container is complete. If administration is controlled by a pumping device, care must be taken to discontinue pumping action before the container runs dry or air embolism may result.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. Use only if solution is clear and container and seals are intact.
DUPLEX® Container Storage
- To avoid inadvertent activation, the DUPLEX® Container should remain in the folded position until activation is intended.
Patient Labeling and Drug Powder/Diluent Inspection
- Apply patient-specific label on foil side of container. Use care to avoid activation. Do not cover any portion of foil strip with patient label.
- Unlatch side tab and unfold DUPLEX® Container (see Diagram 1).
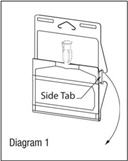
- Visually inspect diluent chamber for particulate matter.
- Use only if container and seals are intact.
- To inspect the drug powder for foreign matter or discoloration, peel foil strip from drug chamber (see Diagram 2).
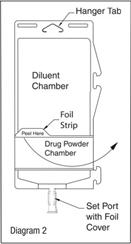
- Protect from light after removal of foil strip.
Note: If foil strip is removed, the container should be re-folded and the side tab latched until ready to activate. The product must then be used within 7 days, but not beyond the labeled expiration date.
Reconstitution (Activation)
- Do not use directly after storage by refrigeration, allow the product to equilibrate to room temperature before patient use.
- Unfold the DUPLEX® Container and point the set port in a downward direction. Starting at the hanger tab end, fold the DUPLEX® Container just below the diluent meniscus trapping all air above the fold. To activate, squeeze the folded diluent chamber until the seal between the diluent and powder opens, releasing diluent into the drug powder chamber (see Diagram 3).
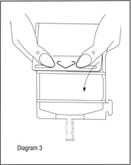
- Agitate the liquid-powder mixture until the drug powder is completely dissolved.
Note: Following reconstitution (activation), product must be used within 12 hours if stored at room temperature or within 3 days if stored under refrigeration.
Administration
- Visually inspect the reconstituted solution for particulate matter.
- Point the set port in a downwards direction. Starting at the hanger tab end, fold the DUPLEX® Container just below the solution meniscus trapping all air above the fold. Squeeze the folded DUPLEX® Container until the seal between reconstituted drug solution and set port opens, releasing liquid to set port (see Diagram 4).
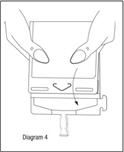
- Prior to attaching the IV set, check for minute leaks by squeezing container firmly. If leaks are found, discard container and solution as sterility may be compromised.
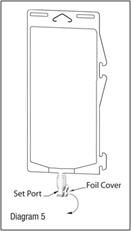
- Using aseptic technique, peel foil cover from the set port and attach sterile administration set (see Diagram 5).
- Refer to directions for use accompanying the administration set.
Important Administration Instructions
- Do not use in series connections.
- Do not introduce additives into the DUPLEX® Container.
- Administer Ceftazidime for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP intravenously over approximately 30 minutes.
- Intermittent intravenous infusion with a Y-type administration set can be accomplished with compatible solutions. However, during infusion of Ceftazidime for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP, it is advisable to discontinue the other solution.
- Vancomycin solution exhibits a physical incompatibility when mixed with a number of drugs, including ceftazidime. The likelihood of precipitation with ceftazidime is dependent on the concentrations of vancomycin and ceftazidime present. It is therefore recommended, when both drugs are to be administered by intermittent IV infusion, that they be given separately, flushing the IV lines (with 1 of the compatible IV fluids) between the administration of these 2 agents.
Note: Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter before administration whenever solution and container permit. Solutions of Ceftazidime for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP should not be added to solutions of aminoglycoside antibacterials because of potential inactivation. If concurrent therapy with Ceftazidime for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP and an aminoglycoside is indicated, each of these antibacterials should be administered separately to the same patient. - The IV route is preferable for patients with bacterial septicemia, bacterial meningitis, peritonitis, or other severe or life-threatening infections, or for patients who may be poor risks because of lowered resistance resulting from such debilitating conditions as malnutrition, trauma, surgery, diabetes, heart failure, or malignancy, particularly if shock is present or pending.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Hypersensitivity Reactions to Ceftazidime or the Cephalosporin Class of Antibiotics, Penicillins, or Other Beta-lactam Antibiotics
Ceftazidime for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP is contraindicated in patients who have a history of immediate hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., anaphylaxis, serious skin reactions) to ceftazidime or the cephalosporin class of antibiotics, penicillins, or other beta-lactam antibiotics. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions to Ceftazidime, Cephalosporins, Penicillins, or Other Drugs
Immediate hypersensitivity reactions to ceftazidime have been reported. Careful inquiry should be made to determine whether the patient has had previous hypersensitivity reactions with cephalosporins or penicillins. Exercise caution if this product is to be given to penicillin-sensitive patients because cross-hypersensitivity among beta-lactam antibacterials has been clearly documented and may occur in up to 10% of patients with a history of penicillin allergy. If an allergic reaction to Ceftazidime for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP occurs, discontinue the drug.
5.2 Hemolytic Anemia
An immune mediated hemolytic anemia has been observed in patients receiving cephalosporin class antibacterials including ceftazidime. Severe cases of hemolytic anemia, including fatalities, have been reported during treatment with cephalosporin class antibiotics in both adults and children. If a patient develops anemia while on ceftazidime, the diagnosis of a cephalosporin associated anemia should be considered and ceftazidime stopped until the etiology is determined.
5.3 Clostridium difficile-associated Diarrhea
Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with use of nearly all antibacterial agents, including ceftazidime, and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of C. difficile.
C. difficile produces toxins A and B, which contribute to the development of CDAD. Hypertoxin-producing strains of C. difficile cause increased morbidity and mortality, as these infections can be refractory to antimicrobial therapy and may require colectomy. CDAD must be considered in all patients who present with diarrhea following antibiotic use. Careful medical history is necessary since CDAD has been reported to occur over two months after the administration of antibacterial agents.
If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibiotic use not directed against C. difficile may need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibiotic treatment of C. difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated.
5.4 Neurologic Adverse Reactions in Patients with Renal Impairment
Elevated levels of ceftazidime in patients with renal impairment can lead to seizures, encephalopathy, coma, asterixis, neuromuscular excitability, and myoclonus. Continued dosage should be determined by degree of renal impairment, severity of infection, and susceptibility of the causative organisms. [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]
5.5 Hypersensitivity to Dextrose-containing Products
Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, have been reported with administration of dextrose containing products. These reactions have been reported in patients receiving high concentrations of dextrose (i.e. 50% dextrose). The reactions have also been reported when corn-derived dextrose solutions were administered to patients with or without a history of hypersensitivity to corn products.
5.6 Risk of Development of Drug-resistant Bacteria
Prescribing Ceftazidime for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP in the absence of proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of the development of drug-resistant bacteria.
As with other antimicrobials, prolonged use of Ceftazidime for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP may result in overgrowth of nonsusceptible microorganisms. Repeated evaluation of the patient's condition is essential. Should superinfection occur during therapy, appropriate measures should be taken.
5.7 Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
Prothrombin Time
Many cephalosporins, including ceftazidime, have been associated with a fall in prothrombin activity. Those at risk include patients with renal or hepatic impairment, or poor nutritional state, as well as patients receiving a protracted course of antimicrobial therapy. Prothrombin time should be monitored in patients at risk, and exogenous vitamin K administered as indicated.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions to ceftazidime are described below and elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Hemolytic Anemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Neurologic Adverse Reactions in Patients with Renal Impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The following adverse reactions were reported in less than or equal to 2% of patients from clinical trials:
- Local reactions including phlebitis and inflammation at the site of injection.
- Hypersensitivity reactions including pruritus, rash, fever and immediate reactions, generally manifested by rash and/or pruritus. Toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and erythema multiforme have also been reported with cephalosporin antibiotics, including ceftazidime. Angioedema and anaphylaxis (bronchospasm and/or hypotension) have been reported.
- Gastrointestinal reactions including diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. The onset of pseudomembranous colitis symptoms may occur during or after treatment. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Central nervous system reactions included headache, dizziness, and paresthesia. Seizures have been reported with several cephalosporins, including ceftazidime. In addition, encephalopathy, coma, asterixis, neuromuscular excitability, and myoclonus have been reported in patients with renal impairment treated with unadjusted dosing regimens of ceftazidime. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Hematologic reactions including cases of hemolytic anemia have been reported. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Other adverse reactions include candidiasis (including oral thrush) and vaginitis.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been reported during postapproval use of ceftazidime. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to readily estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Anaphylaxis, allergic reactions, which, in rare instances, were severe (e.g., cardiopulmonary arrest), urticaria.
- Nephropathy, which may be severe (e.g., renal failure).
- Hyperbilirubinemia, jaundice.
- Pain at the injection site.
6.3 Cephalosporin-class Adverse Reactions
In addition to the adverse reactions listed above that have been observed in patients treated with ceftazidime, the following adverse reactions and altered laboratory tests have been reported for cephalosporin-class antibacterials:
- Adverse Reactions: hepatic dysfunction including cholestasis, aplastic anemia, hemorrhage, and pancytopenia.
- Altered Laboratory Tests: Prolonged prothrombin time, false-positive test for urinary glucose. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Aminoglycosides
Renal function should be monitored carefully if high doses of aminoglycosides are to be administered with Ceftazidime for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP because of the increased potential of nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity of aminoglycoside antibacterials. Nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity were not noted when ceftazidime was given alone in clinical trials.
7.2 Chloramphenicol
Chloramphenicol has been shown to be antagonistic to beta-lactam antibacterials, including ceftazidime, based on in vitro studies and time kill curves with enteric gram-negative bacilli. Due to the possibility of antagonism in vivo, particularly when bactericidal activity is desired, this drug combination should be avoided.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category B
Reproduction studies have been performed in mice and rats at doses up to 40 times the human dose and have revealed no evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus due to ceftazidime. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
8.2 Labor and Delivery
Ceftazidime has not been studied for use during labor and delivery. Treatment should only be given if clearly indicated.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Ceftazidime is excreted in human milk in low concentrations. Caution should be exercised when Ceftazidime for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP is administered to a nursing woman.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Ceftazidime for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP in the DUPLEX® Container is designed to deliver a 1 g or 2 g dose of ceftazidime. To prevent unintentional overdose, this product should not be used in pediatric patients who require less than the full adult dose of ceftazidime. [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 2,221 subjects who received ceftazidime in 11 clinical studies, 824 (37%) were 65 and older while 391 (18%) were 75 and older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater susceptibility of some older individuals to drug effects cannot be ruled out. This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of adverse reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]
8.6 Patients with Renal Impairment
Ceftazidime is substantially eliminated by the kidneys, and the risk of adverse reactions to Ceftazidime may be greater in patients with renal impairment due to slower elimination by the kidneys. Consequently, dosage adjustment is required in patients with moderate (CrCl 30 to 50 mL/min) and severe (CrCl 16 to 29 mL/min) renal impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
Ceftazidime overdosage has occurred in patients with renal failure. Reactions have included seizure activity, encephalopathy, asterixis, neuromuscular excitability, and coma [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]. Patients who receive an acute overdosage should be carefully observed and given supportive treatment. In the presence of renal insufficiency, hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis may aid in the removal of ceftazidime from the body.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Ceftazidime is a semisynthetic, broad-spectrum, beta-lactam antibacterial for parenteral administration. The chemical name is 1-[[(6R,7R)-7-[2-(2-Amino-4-thiazolyl)glyoxylamido]-2-carboxy-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-en-3-yl]methyl]pyridinium hydroxide, inner salt, 72-(Z)-[O-(1-carboxy-1-methylethyl)oxime], pentahydrate. It has the following structure:
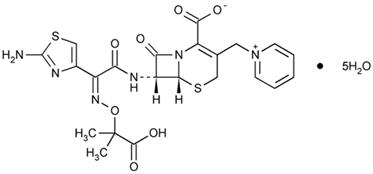
The molecular formula is C22H22N6O7S25H2O, representing a molecular weight of 636.6.
Ceftazidime for Injection USP is a sterile, dry-powdered mixture of ceftazidime pentahydrate and sodium carbonate. The sodium carbonate at a concentration of 118 mg/g of ceftazidime activity has been admixed to facilitate dissolution. The total sodium content of the mixture is approximately 54 mg (2.3 mEq)/g of ceftazidime activity.
Ceftazidime for Injection USP in sterile crystalline form is supplied in the DUPLEX® Container equivalent to 1 g or 2 g of anhydrous ceftazidime. The pH of freshly constituted solutions usually ranges from 5 to 7.5.
The diluent chamber contains 50 mL of 5% Dextrose Injection USP.
Solutions of Ceftazidime for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP range in color from light yellow to amber. The solution is intended for intravenous (IV) use only. The pH of solutions ranges from 5 to 7.5. Dextrose Injection USP is sterile, nonpyrogenic, and contains no bacteriostatic or antimicrobial agents.
Hydrous Dextrose USP has the following structural (molecular) formula:
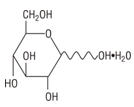
After removing the peelable foil strip, activating the seals, and thoroughly mixing, the reconstituted drug product is intended for single intravenous use. When reconstituted, the osmolality of the reconstituted solution of Ceftazidime for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP is approximately 340 mOsmol/kg for the 1 g dose and approximately 400 mOsmol/kg for the 2 g dose.
Not made with natural rubber latex, PVC, or DEHP.
The DUPLEX® dual chamber container is made from a specially formulated material. The product (diluent and drug) contact layer is a mixture of thermoplastic rubber and a polypropylene ethylene copolymer that contains no plasticizers. The safety of the container system is supported by USP biological evaluation procedures.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Similar to other beta-lactam antimicrobial agents, the time that the unbound plasma concentration of ceftazidime exceeds the MIC of the infecting organisms has been shown to best correlate with efficacy in animal models of infection. However, the pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic relationship for ceftazidime has not been evaluated in patients.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
After IV administration of 500 mg and 1 g doses of ceftazidime over 5 minutes to normal adult male volunteers, mean peak serum concentrations of 45 and 90 mcg/mL, respectively, were achieved. After IV infusion of 500 mg, 1 g, and 2 g doses of ceftazidime over 20 to 30 minutes to normal adult male volunteers, mean peak serum concentrations of 42, 69, and 170 mcg/mL, respectively, were achieved. The average serum concentrations following IV infusion of 500 mg, 1 g, and 2 g doses to these volunteers over an 8-hour interval are given in Table 3.
Table 3: Average Serum Concentrations of Ceftazidime Ceftazidime IV Dose Serum Concentrations (mcg/mL) 0.5 hr 1 hr 2 hr 4 hr 8 hr 500 mg 42 25 12 6 2 1 g 60 39 23 11 3 2 g 129 75 42 13 5 The absorption and elimination of ceftazidime were directly proportional to the size of the dose. The half-life following IV administration was approximately 1.9 hours. There was no evidence of accumulation of ceftazidime in the serum in individuals with normal renal function following multiple IV doses of 1 and 2 g every 8 hours for 10 days.
Distribution
Less than 10% of ceftazidime was protein bound. The degree of protein binding was independent of concentration. Therapeutic concentrations of ceftazidime are achieved in the following body tissues and fluids outlined in Table 4.
Table 4: Ceftazidime Concentrations in Body Tissues and Fluids Tissue or Fluid Dose/Route No. of Patients Time of Sample Postdose Average Tissue or Fluid Level (mcg/mL or mcg/g) Urine 2 g IV 6 0–2 hr 12,000.0 Bile 2 g IV 3 90 min 36.4 Synovial fluid 2 g IV 13 2 hr 25.6 Peritoneal fluid 2 g IV 8 2 hr 48.6 Sputum 1 g IV 8 1 hr 9.0 Cerebrospinal fluid 2 g every 8hr IV 5 120 min 9.8 (inflamed meninges) 2 g every 8hr IV 6 180 min 9.4 Aqueous humor 2 g IV 13 1–3 hr 11.0 Blister fluid 1 g IV 7 2–3 hr 19.7 Lymphatic fluid 1 g IV 7 2–3 hr 23.4 Bone 2 g IV 8 0.67 hr 31.1 Heart muscle 2 g IV 35 30–280 min 12.7 Skin 2 g IV 22 30–180 min 6.6 Skeletal muscle 2 g IV 35 30–280 min 9.4 Myometrium 2 g IV 31 1–2 hr 18.7
Excretion
After the IV administration of single 500 mg or 1 g doses, approximately 50% of the dose appeared in the urine in the first 2 hours. An additional 20% was excreted between 2 and 4 hours after dosing, and approximately another 12% of the dose appeared in the urine between 4 and 8 hours later. The elimination of ceftazidime by the kidneys resulted in high therapeutic concentrations in the urine (Table 4).
The mean renal clearance of ceftazidime was approximately 100 mL/min. The calculated plasma clearance of approximately 115 mL/min indicated nearly complete elimination of ceftazidime by the renal route. Administration of probenecid before dosing had no effect on the elimination kinetics of ceftazidime. This suggested that ceftazidime is eliminated by glomerular filtration and is not actively secreted by renal tubular mechanisms.
Specific Populations
Hepatic Impairment
The presence of hepatic dysfunction had no effect on the pharmacokinetics of ceftazidime in individuals administered 2 g intravenously every 8 hours for 5 days. Therefore, a dosage adjustment from the normal recommended dosage is not required for patients with hepatic dysfunction, provided renal function is not impaired.
12.4 Microbiology
Mechanism of Action
Ceftazidime is a bactericidal agent that acts by inhibition of bacterial cell wall synthesis. Ceftazidime has activity in the presence of some beta-lactamases, both penicillinases and cephalosporinases, of Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria.
Mechanism of Resistance
Resistance to ceftazidime is primarily through hydrolysis by beta-lactamase, alteration of penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs), and decreased permeability.
Interaction with Other Antimicrobials
In an in vitro study, antagonistic effects have been observed with the combination of chloramphenicol and ceftazidime.
Ceftazidime has been shown to be active against most isolates of the following bacteria both in vitro and in clinical infections as described in the INDICATIONS AND USAGE section (1):
Gram-negative bacteria
- Citrobacter species
- Enterobacter species
- Escherichia coli
- Haemophilus influenzae
- Klebsiella species
- Neisseria meningitidis
- Proteus mirabilis
- Proteus vulgaris
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Serratia species
Gram-positive bacteria
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Streptococcus pyogenes
- Streptococcus agalactiae
Anaerobic bacteria
- Bacteroides species (Note: many isolates of Bacteroides species are resistant)
The following in vitro data are available, but their clinical significance is unknown. At least 90 percent of the following microorganisms exhibit an in vitro minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) less than or equal to the susceptible breakpoint for ceftazidime. However, the efficacy of ceftazidime in treating clinical infections due to these microorganisms has not been established in adequate and well-controlled clinical trials.
Gram-negative bacteria
- Acinetobacter species
- Citrobacter diversus
- Citrobacter freundii
- Providencia species (including Providencia rettgeri)
- Salmonella species
- Shigella species
- Haemophilus parainfluenzae
- Morganella morganii
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Yersinia enterocolitica
Gram-positive bacteria
-
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Anaerobic bacteria
- Clostridium species (Not including Clostridium difficile)
- Peptostreptococcus species
Susceptibility Testing
For specific information regarding susceptibility test interpretive criteria, and associated test methods and quality control standards recognized by FDA for this drug, please see: http://www.fda.gov/STIC.
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- 15 REFERENCES
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Ceftazidime for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP in the DUPLEX® Container is a flexible dual chamber container supplied in two concentrations. The diluent chamber contains approximately 50 mL of 5% Dextrose Injection. After reconstitution, the concentrations are equivalent to 11g and 21g ceftazidime.
Ceftazidime for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP is supplied sterile and nonpyrogenic in the DUPLEX® Container packaged 24 units per case.
- 1 Anhydrous basis.
Store the unactivated unit at 20-25°C (68-77°F). Excursions permitted to 15-30°C (59-86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.]. Protect from light. Freezing solutions of Ceftazidime for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP is not recommended.
As with other cephalosporins, Ceftazidime for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP powder, as well as solutions, tend to darken depending on storage conditions; within the stated recommendations, however, product potency is not adversely affected.
Use only if prepared solution is clear and free from particulate matter.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- Patients should be advised that allergic reactions, including serious allergic reactions could occur and that serious reactions require immediate treatment and discontinuation of ceftazidime. Patients should report to their health care provider any previous allergic reactions to ceftazidime, cephalosporins, penicillins, or other similar antibacterials.
- Advise patients of neurological adverse reactions that could occur with Ceftazidime for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP use. Instruct patients to inform a healthcare provider at once of any neurological signs and symptoms, including encephalopathy (disturbance of consciousness including confusion, hallucinations, stupor, and coma), myoclonus, and seizures, for immediate treatment, dosage adjustment, or discontinuation of Ceftazidime for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP.
- Patients should be advised that diarrhea is a common problem caused by antibacterials which usually ends when the antibacterial is discontinued. Sometimes after starting treatment with antibacterials, patients can develop watery and bloody stools (with or without stomach cramps and fever) even as late as 2 or more months after having taken the last dose of the antibacterial. If this occurs, patients should contact their physician as soon as possible.
- Patients should be counseled that antibacterial drugs, including Ceftazidime for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP, should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They do not treat viral infections (e.g., the common cold). When Ceftazidime for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP is prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may: (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment, and (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by Ceftazidime for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP or other antibacterial drugs in the future.
-
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
Rx only
DUPLEX is a registered trademark of B. Braun Medical Inc.
ATCC is a registered trademark of the American Type Culture Collection
Clinitest is a registered trademark of Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics Inc.
Clinistix is a registered trademark of Bayer HealthCare LLC.B. Braun Medical Inc.
Bethlehem, PA 18018-3524 USA
1-800-227-2862
Prepared in USA. API from USA and Brazil.Y36-002-993 LD-101-6
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 1 g Container Label
Ceftazidime for Injection USP
and Dextrose Injection USP1 g*
REF 3143-11
NDC: 0264-3143-11DUPLEX® CONTAINER
50 mL
Use only after mixing contents of both chambers.
For IV Use Only Hyperosmotic Single Dose Sterile/Nonpyrogenic
* Contains sterile ceftazidime pentahydrate USP equivalent to 1 g of ceftazidime
and sodium carbonate to facilitate dissolution.Reconstitution: Hold container with set port in a downward direction and fold the
diluent chamber just below the solution meniscus. To activate seal, squeeze folded diluent
chamber until seal between diluent and drug chamber opens, releasing diluent into drug
chamber. Agitate the reconstituted solution until the drug powder is completely dissolved.
Fold the container a second time and squeeze until seal between drug chamber and set
port opens.Drug chamber contains 118 mg of sodium carbonate. The sodium content is approximately
54 mg (2.3 mEq). After reconstitution each 50 mL single dose unit contains: Ceftazidime
for Injection (equivalent to 1 g ceftazidime) with approximately 2.83 g (5% w/v) Hydrous
Dextrose USP in Water for Injection USP. Approximate osmolality: 340 mOsmol/kgPrior to Reconstitution: Store between 15° and 30°C (59° and 86°F). Use only if
container and seals are intact. Do not peel foil strip until ready for use. After foil strip
removal, product must be used within 7 days, but not beyond the labeled expiration date.
Protect from light after removal of foil strip. Color changes do not affect potency.After Reconstitution: Use only if prepared solution is clear and free from particulate
matter. Use within 12 hours if stored at room temperature or within 3 days if stored under
refrigeration. Do not use in a series connection. Do not introduce additives into this
container. Prior to administration check for minute leaks by squeezing container firmly. If
leaks are found, discard container and solution as sterility may be impaired. Do not freeze.Not made with natural rubber latex, PVC or DEHP.
Rx only
Y37-002-551
LD-102-4B. Braun Medical Inc.
Bethlehem, PA 18018-3524Prepared in USA. API from USA and Brazil.
EXP
LOT
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 2 g Container Label
Ceftazidime for Injection USP
and Dextrose Injection USP2 g*
REF 3145-11
NDC: 0264-3145-11DUPLEX® CONTAINER
50 mL
Use only after mixing contents of both chambers.
For IV Use Only Hyperosmotic Single Dose Sterile/Nonpyrogenic
* Contains sterile ceftazidime pentahydrate USP equivalent to 2 g of ceftazidime
and sodium carbonate to facilitate dissolution.Reconstitution: Hold container with set port in a downward direction and fold the
diluent chamber just below the solution meniscus. To activate seal, squeeze folded diluent
chamber until seal between diluent and drug chamber opens, releasing diluent into drug
chamber. Agitate the reconstituted solution until the drug powder is completely dissolved.
Fold the container a second time and squeeze until seal between drug chamber and set
port opens.Drug chamber contains 236 mg of sodium carbonate. The sodium content is approximately
108 mg (4.7 mEq). After reconstitution each 50 mL single dose unit contains: Ceftazidime
for Injection (equivalent to 2 g ceftazidime) with approximately 2.83 g (5% w/v) Hydrous
Dextrose USP in Water for Injection USP. Approximate osmolality: 400 mOsmol/kgPrior to Reconstitution: Store between 15° and 30°C (59° and 86°F). Use only if
container and seals are intact. Do not peel foil strip until ready for use. After foil strip
removal, product must be used within 7 days, but not beyond the labeled expiration date.
Protect from light after removal of foil strip. Color changes do not affect potency.After Reconstitution: Use only if prepared solution is clear and free from particulate
matter. Use within 12 hours if stored at room temperature or within 3 days if stored under
refrigeration. Do not use in a series connection. Do not introduce additives into this
container. Prior to administration check for minute leaks by squeezing container firmly. If
leaks are found, discard container and solution as sterility may be impaired. Do not freeze.Not made with natural rubber latex, PVC or DEHP.
Rx only
Y37-002-552
LD-103-4B. Braun Medical Inc.
Bethlehem, PA 18018-3524Prepared in USA. API from USA and Brazil.
EXP
LOT

- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
CEFTAZIDIME AND DEXTROSE
ceftazidime injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0264-3143 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength CEFTAZIDIME (UNII: 9M416Z9QNR) (CEFTAZIDIME ANHYDROUS - UNII:DZR1ENT301) CEFTAZIDIME ANHYDROUS 1 g in 50 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength DEXTROSE (UNII: IY9XDZ35W2) 2.83 g in 50 mL WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0264-3143-11 24 in 1 CASE 06/13/2011 1 50 mL in 1 CONTAINER; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA050823 06/13/2011 CEFTAZIDIME AND DEXTROSE
ceftazidime injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0264-3145 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength CEFTAZIDIME (UNII: 9M416Z9QNR) (CEFTAZIDIME ANHYDROUS - UNII:DZR1ENT301) CEFTAZIDIME ANHYDROUS 2 g in 50 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength DEXTROSE (UNII: IY9XDZ35W2) 2.83 g in 50 mL WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0264-3145-11 24 in 1 CASE 06/13/2011 1 50 mL in 1 CONTAINER; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA050823 06/13/2011 Labeler - B. Braun Medical Inc. (002397347)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.
