ITRACONAZOLE- itraconazole capsules capsule
itraconazole by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
itraconazole by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Jubilant Cadista Pharmaceuticals Inc., Jubilant Generics Limited. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
BOXED WARNING
Congestive Heart Failure, Cardiac Effects and Drug Interactions:
Itraconazole capsules should not be administered for the treatment of onychomycosis in patients with evidence of ventricular dysfunction such as congestive heart failure (CHF) or a history of CHF. If signs or symptoms of congestive heart failure occur during administration of itraconazole capsules, discontinue administration. When itraconazole was administered intravenously to dogs and healthy human volunteers, negative inotropic effects were seen. (See CONTRAINDICATIONS, WARNINGS, PRECAUTIONS.
Drug Interactions, ADVERSE REACTIONS: Post-marketing Experience, and CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Special Populations for more information.)
Drug Interactions: Coadministration of the following drugs are contraindicated with itraconazole capsules: methadone, disopyramide, dofetilide, dronedarone, quinidine, isavuconazole, ergot alkaloids (such as dihydroergotamine, ergometrine (ergonovine), ergotamine, methylergometrine (methylergonovine)), irinotecan, lurasidone, oral midazolam, pimozide, triazolam, felodipine, nisoldipine, ivabradine, ranolazine, eplerenone, cisapride, naloxegol, lomitapide, lovastatin, simvastatin, avanafil, ticagrelor. In addition, coadministration with colchicine, fesoterodine and solifenacin is contraindicated in subjects with varying degrees of renal or hepatic impairment, and coadministration with eliglustat is contraindicated in subjects that are poor or intermediate metabolizers of CYP2D6 and in subjects taking strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitors. See PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions Section for specific examples. Coadministration with itraconazole can cause elevated plasma concentrations of these drugs and may increase or prolong both the pharmacologic effects and/or adverse reactions to these drugs. For example, increased plasma concentrations of some of these drugs can lead to QT prolongation and ventricular tachyarrhythmias including occurrences of torsades de pointes, a potentially fatal arrhythmia. See CONTRAINDICATIONS and WARNINGS Sections, and PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions Section for specific examples. -
DESCRIPTION
Itraconazole USP is an azole antifungal agent. Itraconazole is a 1:1:1:1 racemic mixture of four diastereomers (two enantiomeric pairs), each possessing three chiral centers. It may be represented by the following structural formula and nomenclature:
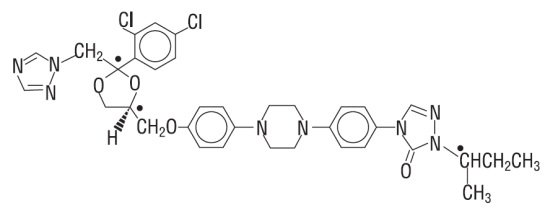
(±)-1-[(R*)-sec-butyl]-4-[p-[4-[p-[[(2R*,4S*)-2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl]methoxy]phenyl]-1-piperazinyl]phenyl]-Δ2-1,2,4-triazolin-5-one mixture with (±)-1-[(R*)-sec-butyl]-4-[p-[4-[p-[[(2S*,4R*)-2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl]methoxy]phenyl]-1-piperazinyl]phenyl]-Δ2-1,2,4-triazolin-5-one
or
(±)-1-[(RS)-sec-butyl]-4-[p-[4-[p-[[(2R,4S)-2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl]methoxy]phenyl]-1-piperazinyl]phenyl]-Δ2-1,2,4-triazolin-5-one
Itraconazole USP has a molecular formula of C35H38Cl2N8O4 and a molecular weight of 706. It is white or almost white powder. It is freely soluble in methylene chloride, sparingly soluble in tetrahydrofuran, very slightly soluble in alcohol and practically insoluble in water.
Each capsule, contain 100 mg of itraconazole USP. Inactive ingredients are hypromellose, polyethylene glycol (PEG) 20,000 and sugar spheres (composed of sucrose, corn starch, and purified water). The capsule shell contains: Gelatin, FD&C Blue No. 1, FD&C Blue No. 2 and titanium dioxide. -
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism:
General Pharmacokinetic Characteristics
Peak plasma concentrations of itraconazole are reached within 2 to 5 hours following oral administration. As a consequence of non-linear pharmacokinetics, itraconazole accumulates in plasma during multiple dosing. Steady-state concentrations are generally reached within about 15 days, with Cmax values of 0.5 mcg/mL, 1.1 mcg/mL and 2 mcg/mL after oral administration of 100 mg once daily, 200 mg once daily and 200 mg b.i.d., respectively. The terminal half-life of itraconazole generally ranges from 16 to 28 hours after single dose and increases to 34 to 42 hours with repeated dosing. Once treatment is stopped, itraconazole plasma concentrations decrease to an almost undetectable concentration within 7 to 14 days, depending on the dose and duration of treatment. Itraconazole mean total plasma clearance following intravenous administration is 278 mL/min. Itraconazole clearance decreases at higher doses due to saturable hepatic metabolism.
Absorption
Itraconazole is rapidly absorbed after oral administration. Peak plasma concentrations of itraconazole are reached within 2 to 5 hours following an oral capsule dose. The observed absolute oral bioavailability of itraconazole is about 55%.
The oral bioavailability of itraconazole is maximal when itraconazole capsules are taken immediately after a full meal. Absorption of itraconazole capsules is reduced in subjects with reduced gastric acidity, such as subjects taking medications known as gastric acid secretion suppressors (e.g., H2-receptor antagonists, proton pump inhibitors) or subjects with achlorhydria caused by certain diseases. (See PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions.) Absorption of itraconazole under fasted conditions in these subjects is increased when itraconazole capsules are administered with an acidic beverage (such as a non-diet cola). When itraconazole capsules were administered as a single 200 mg dose under fasted conditions with non-diet cola after ranitidine pretreatment, a H2-receptor antagonist, itraconazole absorption was comparable to that observed when itraconazole capsules were administered alone. (See PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions.)
Itraconazole exposure is lower with the Capsule formulation than with the Oral Solution when the same dose of drug is given. (See WARNINGS)Distribution
Most of the itraconazole in plasma is bound to protein (99.8%), with albumin being the main binding component (99.6% for the hydroxy-metabolite). It has also a marked affinity for lipids. Only 0.2% of the itraconazole in plasma is present as free drug. Itraconazole is distributed in a large apparent volume in the body (>700 L), suggesting extensive distribution into tissues. Concentrations in lung, kidney, liver, bone, stomach, spleen and muscle were found to be two to three times higher than corresponding concentrations in plasma, and the uptake into keratinous tissues, skin in particular, up to four times higher. Concentrations in the cerebrospinal fluid are much lower than in plasma.
Metabolism
Itraconazole is extensively metabolized by the liver into a large number of metabolites. In vitro studies have shown that CYP3A4 is the major enzyme involved in the metabolism of itraconazole. The main metabolite is hydroxy-itraconazole, which has in vitro antifungal activity comparable to itraconazole; trough plasma concentrations of this metabolite are about twice those of itraconazole.
Excretion
Itraconazole is excreted mainly as inactive metabolites in urine (35%) and in feces (54%) within one week of an oral solution dose. Renal excretion of itraconazole and the active metabolite hydroxy-itraconazole account for less than 1% of an intravenous dose. Based on an oral radiolabeled dose, fecal excretion of unchanged drug ranges from 3% to 18% of the dose.
As re-distribution of itraconazole from keratinous tissues appears to be negligible, elimination of itraconazole from these tissues is related to epidermal regeneration. Contrary to plasma, the concentration in skin persists for 2 to 4 weeks after discontinuation of a 4-week treatment and in nail keratin – where itraconazole can be detected as early as 1 week after start of treatment – for at least six months after the end of a 3-month treatment period.Special Populations:
Renal Impairment:
Limited data are available on the use of oral itraconazole in patients with renal impairment. A pharmacokinetic study using a single 200 mg oral dose of itraconazole was conducted in three groups of patients with renal impairment (uremia: n=7; hemodialysis: n=7; and continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis: n=5). In uremic subjects with a mean creatinine clearance of 13 mL/min. × 1.73 m2, the exposure, based on AUC, was slightly reduced compared with normal population parameters. This study did not demonstrate any significant effect of hemodialysis or continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis on the pharmacokinetics of itraconazole (Tmax, Cmax, and AUC0-8h). Plasma concentration-versus-time profiles showed wide intersubject variation in all three groups. After a single intravenous dose, the mean terminal half-lives of itraconazole in patients with mild (defined in this study as CrCl 50-79 mL/min), moderate (defined in this study as CrCl 20-49 mL/min), and severe renal impairment (defined in this study as CrCl <20 mL/min) were similar to that in healthy subjects (range of means 42-49 hours vs 48 hours in renally impaired patients and healthy subjects, respectively). Overall exposure to itraconazole, based on AUC, was decreased in patients with moderate and severe renal impairment by approximately 30% and 40%, respectively, as compared with subjects with normal renal function. Data are not available in renally impaired patients during long-term use of itraconazole. Dialysis has no effect on the half-life or clearance of itraconazole or hydroxy-itraconazole. (See PRECAUTIONS and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.)
Hepatic Impairment:
Itraconazole is predominantly metabolized in the liver. A pharmacokinetic study was conducted in 6 healthy and 12 cirrhotic subjects who were administered a single 100 mg dose of itraconazole as capsule. A statistically significant reduction in mean Cmax (47%) and a two fold increase in the elimination half-life (37 ± 17 hours vs. 16 ± 5 hours) of itraconazole were noted in cirrhotic subjects compared with healthy subjects. However, overall exposure to itraconazole, based on AUC, was similar in cirrhotic patients and in healthy subjects. Data are not available in cirrhotic patients during long-term use of itraconazole. (See CONTRAINDICATIONS, PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.)
Decreased Cardiac Contractility:
When itraconazole was administered intravenously to anesthetized dogs, a dose-related negative inotropic effect was documented. In a healthy volunteer study of itraconazole intravenous infusion, transient, asymptomatic decreases in left ventricular ejection fraction were observed using gated SPECT imaging; these resolved before the next infusion, 12 hours later. If signs or symptoms of congestive heart failure appear during administration of itraconazole capsules, itraconazole should be discontinued. (See BOXED WARNING, CONTRAINDICATIONS, WARNINGS, PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions and ADVERSE REACTIONS: Post-marketing Experience for more information.)
-
MICROBIOLOGY
Mechanism of Action:
In vitro studies have demonstrated that itraconazole inhibits the cytochrome P450-dependent synthesis of ergosterol, which is a vital component of fungal cell membranes.
Antimicrobial Activity:
Itraconazole exhibits in vitro activity against Blastomyces dermatitidis, Histoplasma capsulatum, Histoplasma duboisii, Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus fumigatus, and Trichophyton species (See INDICATIONS AND USAGE: Description of Clinical Studies).
Susceptibility Testing Methods:
For specific information regarding susceptibility test interpretive criteria and associated test methods and quality control standards recognized by FDA for this drug, please see: https://www.fda.gov/STIC.
Resistance:
Isolates from several fungal species with decreased susceptibility to itraconazole have been isolated in vitro and from patients receiving prolonged therapy.
Itraconazole is not active against Zygomycetes (e.g., Rhizopus spp., Rhizomucor spp., Mucor spp. and Absidia spp.), Fusarium spp., Scedosporium spp. and Scopulariopsis spp.
Cross-resistance:
Several in vitro studies have reported that some fungal clinical isolates with reduced susceptibility to one azole antifungal agent may also be less susceptible to other azole derivatives. The finding of cross-resistance is dependent on a number of factors, including the species evaluated, its clinical history, the particular azole compounds compared, and the type of susceptibility test that is performed.
Studies (both in vitro and in vivo) suggest that the activity of amphotericin B may be suppressed by prior azole antifungal therapy. As with other azoles, itraconazole inhibits the 14C-demethylation step in the synthesis of ergosterol, a cell wall component of fungi. Ergosterol is the active site for amphotericin B. In one study the antifungal activity of amphotericin B against Aspergillus fumigatus infections in mice was inhibited by ketoconazole therapy. The clinical significance of test results obtained in this study is unknown. -
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Itraconazole capsules are indicated for the treatment of the following fungal infections in immunocompromised and non-immunocompromised patients:
- Blastomycosis, pulmonary and extrapulmonary
- Histoplasmosis, including chronic cavitary pulmonary disease and disseminated, non-meningeal histoplasmosis, and
- Aspergillosis, pulmonary and extrapulmonary, in patients who are intolerant of or who are refractory to amphotericin B therapy.
Specimens for fungal cultures and other relevant laboratory studies (wet mount, histopathology, serology) should be obtained before therapy to isolate and identify causative organisms. Therapy may be instituted before the results of the cultures and other laboratory studies are known; however, once these results become available, antiinfective therapy should be adjusted accordingly.
Itraconazole capsules are also indicated for the treatment of the following fungal infections in non-immunocompromised patients:
- Onychomycosis of the toenail, with or without fingernail involvement, due to dermatophytes (tinea unguium), and
- Onychomycosis of the fingernail due to dermatophytes (tinea unguium).
Prior to initiating treatment, appropriate nail specimens for laboratory testing (KOH preparation, fungal culture, or nail biopsy) should be obtained to confirm the diagnosis of onychomycosis.
(See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Special Populations, CONTRAINDICATIONS, WARNINGS, and ADVERSE REACTIONS: Post-marketing Experience for more information.)
Description of Clinical Studies:
Blastomycosis:
Analyses were conducted on data from two open-label, non-concurrently controlled studies (N=73 combined) in patients with normal or abnormal immune status. The median dose was 200 mg/day. A response for most signs and symptoms was observed within the first 2 weeks, and all signs and symptoms cleared between 3 and 6 months. Results of these two studies demonstrated substantial evidence of the effectiveness of itraconazole for the treatment of blastomycosis compared with the natural history of untreated cases.
Histoplasmosis:
Analyses were conducted on data from two open-label, non-concurrently controlled studies (N=34 combined) in patients with normal or abnormal immune status (not including HIV-infected patients). The median dose was 200 mg/day. A response for most signs and symptoms was observed within the first 2 weeks, and all signs and symptoms cleared between 3 and 12 months. Results of these two studies demonstrated substantial evidence of the effectiveness of itraconazole for the treatment of histoplasmosis, compared with the natural history of untreated cases.
Histoplasmosis in HIV-infected patients:
Data from a small number of HIV-infected patients suggested that the response rate of histoplasmosis in HIV-infected patients is similar to that of non-HIV-infected patients. The clinical course of histoplasmosis in HIV-infected patients is more severe and usually requires maintenance therapy to prevent relapse.
Aspergillosis:
Analyses were conducted on data from an open-label, "single-patient-use" protocol designed to make itraconazole available in the U.S. for patients who either failed or were intolerant of amphotericin B therapy (N=190). The findings were corroborated by two smaller open-label studies (N=31 combined) in the same patient population. Most adult patients were treated with a daily dose of 200 mg to 400 mg, with a median duration of 3 months. Results of these studies demonstrated substantial evidence of effectiveness of itraconazole as a second-line therapy for the treatment of aspergillosis compared with the natural history of the disease in patients who either failed or were intolerant of amphotericin B therapy.
Onychomycosis of the toenail:
Analyses were conducted on data from three double-blind, placebo-controlled studies (N=214 total; 110 given itraconazole capsules) in which patients with onychomycosis of the toenails received 200 mg of itraconazole capsules once daily for 12 consecutive weeks. Results of these studies demonstrated mycologic cure, defined as simultaneous occurrence of negative KOH plus negative culture, in 54% of patients. Thirty-five percent (35%) of patients were considered an overall success (mycologic cure plus clear or minimal nail involvement with significantly decreased signs) and 14% of patients demonstrated mycologic cure plus clinical cure (clearance of all signs, with or without residual nail deformity). The mean time to overall success was approximately 10 months. Twenty-one percent (21%) of the overall success group had a relapse (worsening of the global score or conversion of KOH or culture from negative to positive).
Onychomycosis of the fingernail:
Analyses were conducted on data from a double-blind, placebo-controlled study (N=73 total; 37 given itraconazole capsules) in which patients with onychomycosis of the fingernails received a 1-week course (pulse) of 200 mg of itraconazole capsules b.i.d., followed by a 3-week period without itraconazole, which was followed by a second 1-week pulse of 200 mg of itraconazole capsules b.i.d. Results demonstrated mycologic cure in 61% of patients. Fifty-six percent (56%) of patients were considered an overall success and 47% of patients demonstrated mycologic cure plus clinical cure. The mean time to overall success was approximately 5 months. None of the patients who achieved overall success relapsed.
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Congestive Heart Failure:
Itraconazole capsules should not be administered for the treatment of onychomycosis in patients with evidence of ventricular dysfunction such as congestive heart failure (CHF) or a history of CHF. (See BOXED WARNING, WARNINGS, PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions-Calcium Channel Blockers, ADVERSE REACTIONS: Post-marketing Experience, and CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Special Populations.)
Drug Interactions:
Coadministration of a number of CYP3A4 substrates are contraindicated with itraconazole. Plasma concentrations increase for the following drugs: methadone, disopyramide, dofetilide, dronedarone, quinidine, isavuconazole, ergot alkaloids (such as dihydroergotamine, ergometrine (ergonovine), ergotamine, methylergometrine (methylergonovine)), irinotecan, lurasidone, oral midazolam, pimozide, triazolam, felodipine, nisoldipine, ivabradine, ranolazine, eplerenone, cisapride, naloxegol, lomitapide, lovastatin, simvastatin, avanafil, ticagrelor. In addition, coadministration with colchicine, fesoterodine and solifenacin is contraindicated in subjects with varying degrees of renal or hepatic impairment, and coadministration with eliglustat is contraindicated in subjects that are poor or intermediate metabolizers of CYP2D6 and in subjects taking strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitors. (See PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions Section for specific examples.) This increase in drug concentrations caused by coadministration with itraconazole may increase or prolong both the pharmacologic effects and/or adverse reactions to these drugs. For example, increased plasma concentrations of some of these drugs can lead to QT prolongation and ventricular tachyarrhythmias including occurrences of torsade de pointes, a potentially fatal arrhythmia. Specific examples are listed in PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions.
Itraconazole should not be administered for the treatment of onychomycosis to pregnant patients or to women contemplating pregnancy.
Itraconazole is contraindicated for patients who have shown hypersensitivity to itraconazole. There is limited information regarding cross-hypersensitivity between itraconazole and other azole antifungal agents. Caution should be used when prescribing itraconazole to patients with hypersensitivity to other azoles. -
WARNINGS
Hepatic Effects:
Itraconazole has been associated with rare cases of serious hepatotoxicity, including liver failure and death. Some of these cases had neither pre-existing liver disease nor a serious underlying medical condition, and some of these cases developed within the first week of treatment. If clinical signs or symptoms develop that are consistent with liver disease, treatment should be discontinued and liver function testing performed. Continued itraconazole use or reinstitution of treatment with itraconazole is strongly discouraged unless there is a serious or life-threatening situation where the expected benefit exceeds the risk. (See PRECAUTIONS: Information for Patients and ADVERSE REACTIONS.)
Cardiac Dysrhythmias:
Life-threatening cardiac dysrhythmias and/or sudden death have occurred in patients using drugs such as cisapride, pimozide, methadone, or quinidine concomitantly with itraconazole and/or other CYP3A4 inhibitors. Concomitant administration of these drugs with itraconazole is contraindicated. (See BOXED WARNING, CONTRAINDICATIONS, and PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions.)
Cardiac Disease:
Itraconazole capsules should not be administered for the treatment of onychomycosis in patients with evidence of ventricular dysfunction such as congestive heart failure (CHF) or a history of CHF. Itraconazole capsules should not be used for other indications in patients with evidence of ventricular dysfunction unless the benefit clearly outweighs the risk.
For patients with risk factors for congestive heart failure, physicians should carefully review the risks and benefits of itraconazole therapy. These risk factors include cardiac disease such as ischemic and valvular disease; significant pulmonary disease such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; and renal failure and other edematous disorders. Such patients should be informed of the signs and symptoms of CHF, should be treated with caution, and should be monitored for signs and symptoms of CHF during treatment. If signs or symptoms of CHF appear during administration of itraconazole capsules, discontinue administration.
Itraconazole has been shown to have a negative inotropic effect. When itraconazole was administered intravenously to anesthetized dogs, a dose-related negative inotropic effect was documented. In a healthy volunteer study of itraconazole intravenous infusion, transient, asymptomatic decreases in left ventricular ejection fraction were observed using gated SPECT imaging; these resolved before the next infusion, 12 hours later.
Itraconazole has been associated with reports of congestive heart failure. In post-marketing experience, heart failure was more frequently reported in patients receiving a total daily dose of 400 mg although there were also cases reported among those receiving lower total daily doses.
Calcium channel blockers can have negative inotropic effects which may be additive to those of itraconazole. In addition, itraconazole can inhibit the metabolism of calcium channel blockers. Therefore, caution should be used when co-administering itraconazole and calcium channel blockers due to an increased risk of CHF. Concomitant administration of itraconazole and felodipine or nisoldipine is contraindicated.
Cases of CHF, peripheral edema, and pulmonary edema have been reported in the post-marketing period among patients being treated for onychomycosis and/or systemic fungal infections. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Special Populations, CONTRAINDICATIONS, PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions, and ADVERSE REACTIONS: Post-marketing Experience for more information.)Interaction potential:
Itraconazole has a potential for clinically important drug interactions. Coadministration of specific drugs with itraconazole may result in changes in efficacy of itraconazole and/or the coadministered drug, life-threatening effects and/or sudden death. Drugs that are contraindicated, not recommended or recommended for use with caution in combination with itraconazole are listed in PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions.
Interchangeability:
Itraconazole capsules and itraconazole oral solution should not be used interchangeably. This is because drug exposure is greater with the oral solution than with the capsules when the same dose of drug is given. In addition, the topical effects of mucosal exposure may be different between the two formulations. Only the oral solution has been demonstrated effective for oral and/or esophageal candidiasis. -
PRECAUTIONS
General:
Itraconazole capsules should be administered after a full meal. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism).
Under fasted conditions, itraconazole absorption was decreased in the presence of decreased gastric acidity. The absorption of itraconazole may be decreased with the concomitant administration of antacids or gastric acid secretion suppressors. Studies conducted under fasted conditions demonstrated that administration with 8 ounces of a non-diet cola beverage resulted in increased absorption of itraconazole in AIDS patients with relative or absolute achlorhydria. This increase relative to the effects of a full meal is unknown. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism).
Hepatotoxicity:
Rare cases of serious hepatotoxicity have been observed with itraconazole treatment, including some cases within the first week. It is recommended that liver function monitoring be considered in all patients receiving itraconazole. Treatment should be stopped immediately and liver function testing should be conducted in patients who develop signs and symptoms suggestive of liver dysfunction.
Neuropathy:
If neuropathy occurs that may be attributable to itraconazole capsules, the treatment should be discontinued.
Immunocompromised Patients:
In some immunocompromised patients (e.g., neutropenic, AIDS or organ transplant patients), the oral bioavailability of itraconazole capsules may be decreased. Therefore, the dose should be adjusted based on the clinical response in these patients.
Cystic Fibrosis:
If a cystic fibrosis patient does not respond to itraconazole capsules, consideration should be given to switching to alternative therapy. For more information concerning the use of itraconazole in cystic fibrosis patients see the prescribing information for itraconazole oral solution.
Hearing Loss:
Transient or permanent hearing loss has been reported in patients receiving treatment with itraconazole. Several of these reports included concurrent administration of quinidine which is contraindicated (See BOXED WARNING: Drug Interactions, CONTRAINDICATIONS: Drug Interactions and PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions). The hearing loss usually resolves when treatment is stopped, but can persist in some patients.
Information for Patients:- The topical effects of mucosal exposure may be different between the itraconazole capsules and oral solution. Only the oral solution has been demonstrated effective for oral and/or esophageal candidiasis. Itraconazole capsules should not be used interchangeably with itraconazole oral solution.
- Instruct patients to take itraconazole capsules with a full meal. Itraconazole capsules must be swallowed whole.
- Instruct patients about the signs and symptoms of congestive heart failure, and if these signs or symptoms occur during itraconazole administration, they should discontinue itraconazole and contact their healthcare provider immediately.
- Instruct patients to stop itraconazole treatment immediately and contact their healthcare provider if any signs and symptoms suggestive of liver dysfunction develop. Such signs and symptoms may include unusual fatigue, anorexia, nausea and/or vomiting, jaundice, dark urine, or pale stools.
- Instruct patients to contact their physician before taking any concomitant medications with itraconazole to ensure there are no potential drug interactions.
- Instruct patients that hearing loss can occur with the use of itraconazole. The hearing loss usually resolves when treatment is stopped, but can persist in some patients. Advise patients to discontinue therapy and inform their physicians if any hearing loss symptoms occur.
- Instruct patients that dizziness or blurred/double vision can sometimes occur with itraconazole. Advise patients that if they experience these events, they should not drive or use machines.
Drug Interactions:
Effect of Itraconazole on Other Drugs
Itraconazole and its major metabolite, hydroxy-itraconazole, are potent CYP3A4 inhibitors. Itraconazole is an inhibitor of the drug transporters P-glycoprotein and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP). Consequently, itraconazole has the potential to interact with many concomitant drugs resulting in either increased or sometimes decreased concentrations of the concomitant drugs. Increased concentrations may increase the risk of adverse reactions associated with the concomitant drug which can be severe or life-threatening in some cases (e.g., QT prolongation, Torsade de Pointes, respiratory depression, hepatic adverse reactions, hypersensitivity reactions, myelosuppression, hypotension, seizures, angioedema, atrial fibrillation, bradycardia, priapism). Reduced concentrations of concomitant drugs may reduce their efficacy. Table 1 lists examples of drugs that may have their concentrations affected by itraconazole, but is not a comprehensive list. Refer to the approved product labeling to become familiar with the interaction pathways, risk potential, and specific actions to be taken with regards to each concomitant drug prior to initiating therapy with itraconazole.
Although many of the clinical drug interactions in Table 1 are based on information with a similar azole antifungal, ketoconazole, these interactions are expected to occur with itraconazole.Table 1 Drug Interactions with Itraconazole that Affect Concomitant Drug Concentrations Concomitant Drug Within Class Prevention or Management Drug Interactions with Itraconazole that Increase Concomitant Drug Concentrations and May Increase Risk of Adverse Reactions Associated with the Concomitant Drug Alpha Blockers Alfuzosin
Silodosin
TamsulosinNot recommended during and 2 weeks after itraconazole treatment. Analgesics Methadone Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after itraconazole treatment. Fentanyl Not recommended during and 2 weeks after itraconazole treatment. Alfentanil
Buprenorphine (IV and sublingual)
Oxycodonea
SufentanilMonitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. Antiarrhythmics Disopyramide
Dofetilide
Dronedarone
QuinidineaContraindicated during and 2 weeks after itraconazole treatment. Digoxina Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. Antibacterials Bedaquilineb Concomitant itraconazole not recommended for more than 2 weeks at any time during bedaquiline treatment. Rifabutin Not recommended 2 weeks before, during, and 2 weeks after itraconazole treatment. See also Table 2. Clarithromycin Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. See also Table 2. Trimetrexate Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. Anticoagulants and Antiplatelets Ticagrelor Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after itraconazole treatment. Apixaban
Rivaroxaban
VorapaxarNot recommended during and 2 weeks after itraconazole treatment. Cilostazol
Dabigatran
WarfarinMonitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. Anticonvulsants Carbamazepine Not recommended 2 weeks before, during, and 2 weeks after itraconazole treatment. See also Table 2. Antidiabetic Drugs Repaglinidea
SaxagliptinMonitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. Antihelminthics, Antifungals and Antiprotozoals Isavuconazonium Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after itraconazole treatment. Praziquantel Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. Artemether-lumefantrine
QuinineaMonitor for adverse reactions. Antimigraine Drugs Ergot alkaloids (e.g., dihydroergotamine, ergotamine) Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after itraconazole treatment. Eletriptan Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary Antineoplastics Irinotecan Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after itraconazole treatment. Axitinib
Bosutinib
Cabazitaxel
Cabozantinib
Ceritinib
Cobimetiniba
Crizotinib
Dabrafenib
DasatinibDocetaxel
Ibrutinib
Lapatinib
Nilotinib
Olapariba
Pazopanib
Sunitinib
Trabectedin
Trastuzumab-emtansine
Vinca alkaloidsNot recommended during and 2 weeks after itraconazole treatment. Bortezomib
Brentuximab
vedotin
Busulfana
Erlotinib
Gefitiniba
Idelalisib
Imatinib
IxabepiloneNintedanib
Panobinostat
Ponatinib
Ruxolitinib
Sonidegib
VandetanibaMonitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. For idelalisib, see also Table 2. Antipsychotics, Anxiolytics and Hypnotics Alprazolama
Aripiprazolea
Buspironea
Cariprazine
Diazepama
Haloperidola
Midazolam (IV)a
Quetiapine
Ramelteon
Risperidonea
SuvorexantMonitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. Zopiclonea Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. Lurasidone
Midazolam (oral)a
Pimozide
TriazolamaContraindicated during and 2 weeks after itraconazole treatment. Antivirals Simeprevir Not recommended during and 2 weeks after itraconazole treatment. Daclatasvir
Indinavira
MaravirocMonitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. For indinavir, see also Table 2. Cobicistat
Elvitegravir (ritonavir-boosted)
Ombitasvir/Paritaprevir/Ritonavir with or without Dasabuvir
Ritonavir
Saquinavir (unboosted)aMonitor for adverse reactions. See also Table 2. Elbasvir/grazoprevir
Glecaprevir/pibrentasvir
Tenofovir disoproxil fumarateNot recommended during and 2 weeks after itraconazole treatment. Monitor for adverse reactions. Monitor for adverse reactions. Beta Blockers Nadolola Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. Calcium Channel Blockers Felodipinea
NisoldipineContraindicated during and 2 weeks after itraconazole treatment. Diltiazem
Other dihydropyridines
VerapamilMonitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. For diltiazem, see also Table 2. Cardiovascular Drugs, Miscellaneous Ivabradine
RanolazineContraindicated during and 2 weeks after itraconazole treatment. Aliskirena
Riociguat
Sildenafil (for pulmonary hypertension)
Tadalafil (for pulmonary hypertension)Not recommended during and 2 weeks after itraconazole treatment. For sildenafil and tadalafil, see also Urologic Drugs below. Bosentan
GuanfacineMonitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. Contraceptives* Dienogest
UlipristalMonitor for adverse reactions. Diuretics Eplerenone Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after itraconazole treatment. Gastrointestinal Drugs Cisapride
NaloxegolContraindicated during and 2 weeks after itraconazole treatment. Aprepitant
LoperamideaMonitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. Netupitant Monitor for adverse reactions. Immunosuppressants Everolimus
Sirolimus
Temsirolimus (IV)Not recommended during and 2 weeks after itraconazole treatment. Budesonide (inhalation)a
Budesonide (non-inhalation) Ciclesonide (inhalation)
Cyclosporine (IV)a
Cyclosporine (non-IV)
Dexamethasonea
Fluticasone (inhalation)a Fluticasone (nasal) Methylprednisolonea
Tacrolimus (IV)a
Tacrolimus (oral)Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. Lipid-Lowering Drugs Lomitapide
Lovastatina
SimvastatinaContraindicated during and 2 weeks after itraconazole treatment. Atorvastatina Monitor for drug adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. Respiratory Drugs Salmeterol Not recommended during and 2 weeks after itraconazole treatment. SSRIs, Tricyclics and Related Antidepressants Venlafaxine Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. Urologic Drugs Avanafil Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after itraconazole treatment. Fesoterodine Patients with moderate to severe renal or hepatic impairment: Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after itraconazole treatment.
Other patients: Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary.Solifenacin Patients with severe renal or moderate to severe hepatic impairment: Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after itraconazole treatment.
Other patients: Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary.Darifenacin
VardenafilNot recommended during and 2 weeks after itraconazole treatment. Dutasteride
Oxybutynina
Sildenafil (for erectile dysfunction)
Tadalafil (for erectile dysfunction and benign prostatic hyperplasia)
TolterodineMonitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. For sildenafil and tadalafil, see also Cardiovascular Drugs above. Miscellaneous Drugs and Other Substances Colchicine Patients with renal or hepatic impairment: Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after itraconazole treatment.
Other patients: Not recommended during and 2 weeks after itraconazole treatment.Eliglustat CYP2D6 EMsctaking a strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitor, CYP2D6 IMsc, or CYP2D6 PMsc: Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after itraconazole treatment.
CYP2D6 EMscnot taking a strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitor: Monitor for adverse reactions. Eliglustat dose reduction may be necessary.Lumacaftor/Ivacaftor Not recommended 2 weeks before, during, and 2 weeks after itraconazole treatment. Alitretinoin (oral)
Cabergoline
Cannabinoids
Cinacalcet
Galantamine
IvacaftorMonitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. Vasopressin Receptor Antagonists Conivaptan
TolvaptanNot recommended during and 2 weeks after itraconazole treatment. Drug Interactions with Itraconazole that Decrease Concomitant Drug Concentrations and May Reduce Efficacy of the Concomitant Drug Antineoplastics Regorafenib Not recommended during and 2 weeks after itraconazole treatment. Gastrointestinal Drugs Saccharomyces boulardii Not recommended during and 2 weeks after itraconazole treatment. Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Meloxicama Concomitant drug dose increase may be necessary. * CYP3A4 inhibitors (including itraconazole) may increase systemic contraceptive hormone concentrations.
a Based on clinical drug interaction information with itraconazole.
b Based on 400 mg bedaquiline once daily for 2 weeks.
c EMs: extensive metabolizers; IMs: intermediate metabolizers, PMs: poor metabolizers
Effect of Other Drugs on Itraconazole
Itraconazole is mainly metabolized through CYP3A4. Other substances that either share this metabolic pathway or modify CYP3A4 activity may influence the pharmacokinetics of itraconazole. Some concomitant drugs have the potential to interact with itraconazole resulting in either increased or sometimes decreased concentrations of itraconazole. Increased concentrations may increase the risk of adverse reactions associated with itraconazole. Decreased concentrations may reduce itraconazole efficacy.
Table 2 lists examples of drugs that may affect itraconazole concentrations, but is not a comprehensive list. Refer to the approved product labeling to become familiar with the interaction pathways, risk potential and specific actions to be taken with regards to each concomitant drug prior to initiating therapy with itraconazole.
Although many of the clinical drug interactions in Table 2 are based on information with a similar azole antifungal, ketoconazole, these interactions are expected to occur with itraconazole.Table 2. Drug Interactions with Other Drugs that Affect Itraconazole Concentrations Concomitant Drug Within Class Prevention or Management Drug Interactions with Other Drugs that Increase Itraconazole Concentrations and May Increase Risk of Adverse Reactions Associated with Itraconazole Antibacterials Ciprofloxacina
Erythromycina
ClarithromycinaMonitor for adverse reactions. Itraconazole dose reduction may be necessary. Antineoplastics Idelalisib Monitor for adverse reactions. Itraconazole dose reduction may be necessary. See also Table 1. Antivirals Cobicistat
Darunavir (ritonavir-boosted)
Elvitegravir (ritonavir-boosted)
Fosamprenavir (ritonavir-boosted)
Indinavira
Ombitasvir/ Paritaprevir/ Ritonavir with or without Dasabuvir
Ritonavir
SaquinavirMonitor for adverse reactions. Itraconazole dose reduction may be necessary. For, cobicistat, elvitegravir, indinavir, ombitasvir/ paritaprevir/ ritonavir with or without dasabuvir, ritonavir, and saquinavir, see also Table 1. Calcium Channel Blockers Diltiazem Monitor for adverse reactions. Itraconazole dose reduction may be necessary. See also Table 1. Drug Interactions with Other Drugs that Decrease Itraconazole Concentrations and May Reduce Efficacy of Itraconazole Antibacterials Isoniazid
RifampicinaNot recommended 2 weeks before and during itraconazole treatment. Rifabutina Not recommended 2 weeks before, during, and 2 weeks after itraconazole treatment. See also Table 1. Anticonvulsants Phenobarbital
PhenytoinaNot recommended 2 weeks before and during itraconazole treatment. Carbamazepine Not recommended 2 weeks before, during, and 2 weeks after itraconazole treatment. See also Table 1. Antivirals Efavirenza
NevirapineaNot recommended 2 weeks before and during itraconazole treatment. Gastrointestinal Drugs Drugs that reduce gastric acidity e.g. acid neutralizing medicines such as aluminum hydroxide, or acid secretion suppressors such as H2-receptor antagonists and proton pump inhibitors. Use with caution. Administer acid neutralizing medicines at least 2 hours before or 2 hours after the intake of itraconazole capsules Miscellaneous Drugs and Other Substances Lumacaftor/Ivacaftor Not recommended 2 weeks before, during, and 2 weeks after itraconazole treatment. aBased on clinical drug interaction information with itraconazole.
Pediatric Population
Interaction studies have only been performed in adults.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, and Impairment of Fertility:
Itraconazole showed no evidence of carcinogenicity potential in mice treated orally for 23 months at dosage levels up to 80 mg/kg/day (approximately 10 times the maximum recommended human dose [MRHD]). Male rats treated with 25 mg/kg/day (3.1 times the MRHD) had a slightly increased incidence of soft tissue sarcoma. These sarcomas may have been a consequence of hypercholesterolemia, which is a response of rats, but not dogs or humans, to chronic itraconazole administration. Female rats treated with 50 mg/kg/day (6.25 times the MRHD) had an increased incidence of squamous cell carcinoma of the lung (2/50) as compared to the untreated group. Although the occurrence of squamous cell carcinoma in the lung is extremely uncommon in untreated rats, the increase in this study was not statistically significant.
Itraconazole produced no mutagenic effects when assayed in DNA repair test (unscheduled DNA synthesis) in primary rat hepatocytes, in Ames tests with Salmonella typhimurium (6 strains) and Escherichia coli, in the mouse lymphoma gene mutation tests, in a sex-linked recessive lethal mutation (Drosophila melanogaster) test, in chromosome aberration tests in human lymphocytes, in a cell transformation test with C3H/10T½ C18 mouse embryo fibroblasts cells, in a dominant lethal mutation test in male and female mice, and in micronucleus tests in mice and rats.
Itraconazole did not affect the fertility of male or female rats treated orally with dosage levels of up to 40 mg/kg/day (5 times the MRHD), even though parental toxicity was present at this dosage level. More severe signs of parental toxicity, including death, were present in the next higher dosage level, 160 mg/kg/day (20 times the MRHD).
Pregnancy: Teratogenic effects:
Itraconazole was found to cause a dose-related increase in maternal toxicity, embryotoxicity, and teratogenicity in rats at dosage levels of approximately 40-160 mg/kg/day (5-20 times the MRHD), and in mice at dosage levels of approximately 80 mg/kg/day (10 times the MRHD). Itraconazole has been shown to cross the placenta in a rat model. In rats, the teratogenicity consisted of major skeletal defects; in mice, it consisted of encephaloceles and/or macroglossia.
There are no studies in pregnant women. Itraconazole should be used for the treatment of systemic fungal infections in pregnancy only if the benefit outweighs the potential risk.
Itraconazole should not be administered for the treatment of onychomycosis to pregnant patients or to women contemplating pregnancy. Itraconazole should not be administered to women of childbearing potential for the treatment of onychomycosis unless they are using effective measures to prevent pregnancy and they begin therapy on the second or third day following the onset of menses. Highly effective contraception should be continued throughout itraconazole therapy and for 2 months following the end of treatment.
During post-marketing experience, cases of congenital abnormalities have been reported. (See ADVERSE REACTIONS: Post-marketing Experience.)
Nursing Mothers:
Itraconazole is excreted in human milk; therefore, the expected benefits of itraconazole therapy for the mother should be weighed against the potential risk from exposure of itraconazole to the infant. The U.S. Public Health Service Centers for Disease Control and Prevention advises HIV-infected women not to breast-feed to avoid potential transmission of HIV to uninfected infants.
Pediatric Use:
The efficacy and safety of itraconazole have not been established in pediatric patients.
The long-term effects of itraconazole on bone growth in children are unknown. In three toxicology studies using rats, itraconazole induced bone defects at dosage levels as low as 20 mg/kg/day (2.5 times the MRHD). The induced defects included reduced bone plate activity, thinning of the zona compacta of the large bones, and increased bone fragility. At a dosage level of 80 mg/kg/day (10 times the MRHD) over 1 year or 160 mg/kg/day (20 times the MRHD) for 6 months, itraconazole induced small tooth pulp with hypocellular appearance in some rats.
Geriatric Use:
Clinical studies of itraconazole capsules did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 years and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. It is advised to use itraconazole capsules in these patients only if it is determined that the potential benefit outweighs the potential risks. In general, it is recommended that the dose selection for an elderly patient should be taken into consideration, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
Transient or permanent hearing loss has been reported in elderly patients receiving treatment with itraconazole. Several of these reports included concurrent administration of quinidine which is contraindicated (See BOXED WARNING: Drug Interactions, CONTRAINDICATIONS: Drug Interactions and PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions).
HIV-Infected Patients:
Because hypochlorhydria has been reported in HIV-infected individuals, the absorption of itraconazole in these patients may be decreased.
Renal Impairment:
Limited data are available on the use of oral itraconazole in patients with renal impairment. The exposure of itraconazole may be lower in some patients with renal impairment. Caution should be exercised when itraconazole is administered in this patient population and dose adjustment may be needed. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Special Populations and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.)
Hepatic Impairment:
Limited data are available on the use of oral itraconazole in patients with hepatic impairment. Caution should be exercised when this drug is administered in this patient population. It is recommended that patients with impaired hepatic function be carefully monitored when taking itraconazole. It is recommended that the prolonged elimination half-life of itraconazole observed in the single oral dose clinical trial with itraconazole capsules in cirrhotic patients be considered when deciding to initiate therapy with other medications metabolized by CYP3A4.
In patients with elevated or abnormal liver enzymes or active liver disease, or who have experienced liver toxicity with other drugs, treatment with itraconazole is strongly discouraged unless there is a serious or life-threatening situation where the expected benefit exceeds the risk. It is recommended that liver function monitoring be done in patients with pre-existing hepatic function abnormalities or those who have experienced liver toxicity with other medications. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Special Populations and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.) -
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
Itraconazole has been associated with rare cases of serious hepatotoxicity, including liver failure and death. Some of these cases had neither pre-existing liver disease nor a serious underlying medical condition. If clinical signs or symptoms develop that are consistent with liver disease, treatment should be discontinued and liver function testing performed. The risks and benefits of itraconazole use should be reassessed. (See WARNINGS: Hepatic Effects and PRECAUTIONS: Hepatotoxicity and Information for Patients.)Adverse Events in the Treatment of Systemic Fungal Infections
Adverse event data were derived from 602 patients treated for systemic fungal disease in U.S. clinical trials who were immunocompromised or receiving multiple concomitant medications. Treatment was discontinued in 10.5% of patients due to adverse events. The median duration before discontinuation of therapy was 81 days (range: 2 to 776 days). The table lists adverse events reported by at least 1% of patients.
Table 3: Clinical Trials of Systemic Fungal Infections: Adverse Events Occurring with an Incidence of Greater than or Equal to 1% Body System/Adverse Event Incidence (%) (N=602) Gastrointestinal Nausea 11 Vomiting 5 Diarrhea 3 Abdominal Pain 2 Anorexia 1 Body as a Whole Edema 4 Fatigue 3 Fever 3 Malaise 1 Skin and Appendages Rash* 9 Pruritus 3 Central/Peripheral Nervous System Headache 4 Dizziness 2 Psychiatric Libido Decreased 1 Somnolence 1 Cardiovascular Hypertension 3 Metabolic/Nutritional Hypokalemia 2 Urinary System Albuminuria 1 Liver and Biliary System Hepatic Function Abnormal 3 Reproductive System, Male Impotence 1 *Rash tends to occur more frequently in immunocompromised patients receiving immunosuppressive medications.
Adverse events infrequently reported in all studies included constipation, gastritis, depression, insomnia, tinnitus, menstrual disorder, adrenal insufficiency, gynecomastia, and male breast pain.
Adverse Events Reported in Toenail Onychomycosis Clinical Trials
Patients in these trials were on a continuous dosing regimen of 200 mg once daily for 12 consecutive weeks.
The following adverse events led to temporary or permanent discontinuation of therapy.
Table 4: Clinical Trials of Onychomycosis of the Toenail: Adverse Events Leading to Temporary or Permanent Discontinuation of Therapy Adverse Event Incidence (%)
Itraconazole (N=112)Elevated Liver Enzymes (greater than twice the upper limit of normal) 4 Gastrointestinal Disorders 4 Rash 3 Hypertension 2 Orthostatic Hypotension 1 Headache 1 Malaise 1 Myalgia 1 Vasculitis 1 Vertigo 1 The following adverse events occurred with an incidence of greater than or equal to 1% (N=112): headache: 10%; rhinitis: 9%; upper respiratory tract infection: 8%; sinusitis, injury: 7%; diarrhea, dyspepsia, flatulence, abdominal pain, dizziness, rash: 4%; cystitis, urinary tract infection, liver function abnormality, myalgia, nausea: 3%; appetite increased, constipation, gastritis, gastroenteritis, pharyngitis, asthenia, fever, pain, tremor, herpes zoster, abnormal dreaming: 2%.
Adverse Events Reported in Fingernail Onychomycosis Clinical Trials
Patients in these trials were on a pulse regimen consisting of two 1-week treatment periods of 200 mg twice daily, separated by a 3-week period without drug.
The following adverse events led to temporary or permanent discontinuation of therapy.
Table 5: Clinical Trials of Onychomycosis of the Fingernail: Adverse Events Leading to Temporary or Permanent Discontinuation of Therapy Adverse Event Incidence (%)
Itraconazole (N=37)Rash/Pruritus 3 Hypertriglyceridemia 3 The following adverse events occurred with an incidence of greater than or equal to 1% (N=37): headache: 8%; pruritus, nausea, rhinitis: 5%; rash, bursitis, anxiety, depression, constipation, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, ulcerative stomatitis, gingivitis, hypertriglyceridemia, sinusitis, fatigue, malaise, pain, injury: 3%.
Adverse Events Reported from Other Clinical Trials
In addition, the following adverse drug reaction was reported in patients who participated in itraconazole capsules clinical trials: Hepatobiliary Disorders: hyperbilirubinemia.
The following is a list of additional adverse drug reactions associated with itraconazole that have been reported in clinical trials of itraconazole oral solution and itraconazole IV excluding the adverse reaction term “Injection site inflammation” which is specific to the injection route of administration:
Cardiac Disorders: cardiac failure, left ventricular failure, tachycardia;
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions: face edema, chest pain, chills;
Hepatobiliary Disorders: hepatic failure, jaundice;
Investigations: alanine aminotransferase increased, aspartate aminotransferase increased, blood alkaline phosphatase increased, blood lactate dehydrogenase increased, blood urea increased, gamma-glutamyltransferase increased, urine analysis abnormal;
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders: hyperglycemia, hyperkalemia, hypomagnesemia;
Psychiatric Disorders: confusional state;
Renal and Urinary Disorders: renal impairment;
Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders: dysphonia, cough;
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: rash erythematous, hyperhidrosis;
Vascular Disorders: hypotension
Post-marketing Experience
Adverse drug reactions that have been first identified during post-marketing experience with itraconazole (all formulations) are listed in the table below. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, reliably estimating their frequency or establishing a causal relationship to drug exposure is not always possible.
Table 6: Postmarketing Reports of Adverse Drug Reactions Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders: Leukopenia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia Immune System Disorders: Anaphylaxis; anaphylactic, anaphylactoid and allergic reactions; serum sickness; angioneurotic edema Nervous System Disorders: Peripheral neuropathy, paresthesia, hypoesthesia, tremor Eye Disorders: Visual disturbances, including vision blurred and diplopia Ear and Labyrinth Disorders: Transient or permanent hearing loss Cardiac Disorders: Congestive heart failure Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders: Pulmonary edema, dyspnea Gastrointestinal Disorders: Pancreatitis, dysgeusia Hepatobiliary Disorders: Serious hepatotoxicity (including some cases of fatal acute liver failure), hepatitis Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis, erythema multiforme, exfoliative dermatitis, leukocytoclastic vasculitis, alopecia, photosensitivity, urticaria Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders: Arthralgia Renal and Urinary Disorders: Urinary incontinence, pollakiuria Reproductive System and Breast Disorders: Erectile dysfunction General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions:
Investigations:Peripheral edema
Blood creatine phosphokinase increased
There is limited information on the use of itraconazole during pregnancy. Cases of congenital abnormalities including skeletal, genitourinary tract, cardiovascular and ophthalmic malformations as well as chromosomal and multiple malformations have been reported during post-marketing experience. A causal relationship with itraconazole has not been established. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Special Populations, CONTRAINDICATIONS, WARNINGS, and PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions for more information.)
-
OVERDOSAGE
Itraconazole is not removed by dialysis. In the event of accidental overdosage, supportive measures should be employed. Contact a certified poison control center for the most up to date information on the management of itraconazole capsules overdosage (1-800-222-1222 or www.poison.org).
In general, adverse events reported with overdose have been consistent with adverse drug reactions already listed in this package insert for itraconazole. (See ADVERSE REACTIONS.) -
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Itraconazole capsules should be taken with a full meal to ensure maximal absorption.
Itraconazole capsules must be swallowed whole. Itraconazole capsules is a different preparation than itraconazole oral solution and should not be used interchangeably.Treatment of Blastomycosis and Histoplasmosis:
The recommended dose is 200 mg once daily (2 capsules). If there is no obvious improvement, or there is evidence of progressive fungal disease, the dose should be increased in 100 mg increments to a maximum of 400 mg daily. Doses above 200 mg/day should be given in two divided doses.
Treatment in Life-Threatening Situations:
In life-threatening situations, a loading dose should be used.
Although clinical studies did not provide for a loading dose, it is recommended, based on pharmacokinetic data, that a loading dose of 200 mg (2 capsules) three times daily (600 mg/day) be given for the first 3 days of treatment.
Treatment should be continued for a minimum of three months and until clinical parameters and laboratory tests indicate that the active fungal infection has subsided. An inadequate period of treatment may lead to recurrence of active infection.
Itraconazole capsules and itraconazole oral solution should not be used interchangeably. Only the oral solution has been demonstrated effective for oral and/or esophageal candidiasis.Treatment of Onychomycosis:
Toenails with or without fingernail involvement: The recommended dose is 200 mg (2 capsules) once daily for 12 consecutive weeks.
Treatment of Onychomycosis:
Fingernails only: The recommended dosing regimen is 2 treatment pulses, each consisting of 200 mg (2 capsules) b.i.d. (400 mg/day) for 1 week. The pulses are separated by a 3-week period without itraconazole.
Use in Patients with Renal Impairment:
Limited data are available on the use of oral itraconazole in patients with renal impairment. Caution should be exercised when this drug is administered in this patient population. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Special Populations and PRECAUTIONS.)
Use in Patients with Hepatic Impairment:
Limited data are available on the use of oral itraconazole in patients with hepatic impairment. Caution should be exercised when this drug is administered in this patient population. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Special Populations, WARNINGS, and PRECAUTIONS.)
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Itraconazole Capsules are available containing 100 mg of itraconazole USP, with a blue colored opaque cap and pink colored transparent body, size '0' hard gelatin capsules, printed in white ink with 'C282' on cap and body containing cream colored beads.
Bottle pack of 30’s count: NDC: 59746-282-30
Carton of 7x4’s (7-Day Treatment Pack): NDC: 59746-282-22
Store at 20ºC to 25ºC (68ºF to 77ºF); excursions permitted to 15ºC to 30ºC (59ºF to 86ºF) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Protect from light and moisture.
Keep out of the reach of children. -
PATIENT INFORMATION
Itraconazole Capsules
100 mg
(it" ra kon' a zole)
Read this Patient Information that comes with itraconazole capsules before you start taking it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking with your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment.
What is the most important information I should know about itraconazole capsules?
Itraconazole capsules can cause serious side effects, including:
1. Heart failure. Do not take itraconazole capsules if you have had heart failure, including congestive heart failure.
Stop taking itraconazole capsules and call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of these symptoms of congestive heart failure:
● shortness of breath ● coughing up white or pink mucus (phlegm) ● swelling of your feet, ankles or legs ● fast heartbeat ● sudden weight gain ● waking up at night more than normal for you ● increased tiredness 2. Heart problems and other serious medical problems. Serious medical problems that affect the heart and other parts of your body can happen if you take itraconazole capsules with certain other medicines. Do not take itraconazole capsules if you also take the following medicines:
● methadone
● disopyramide
● dofetilide
● dronedarone
● quinidine
● isavuconazole
● ergot alkaloids (such as dihydroergotamine, ergometrine ergonovine)
● ergotamine● methylergometrine (methylergonovine)
● irinotecan
● lurasidone
● oral midazolam
● pimozide
● triazolam
● felodipine
● nisoldipine
● ivabradine● ranolazine
● eplerenone
● cisapride
● naloxegol
● lomitapide
● lovastatin
● simvastatin
● avanafil
● ticagrelorThis is not a complete list of medicines that can interact with itraconazole capsules. Itraconazole capsules may affect the way other medicines work, and other medicines may affect how itraconazole capsules works. You can ask your pharmacist for a list of medicines that interact with itraconazole capsules.
Before you start taking itraconazole capsules, tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Before you start any new medicine, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist if it is safe to take it with itraconazole capsules.
3. Liver problems. Itraconazole capsules can cause serious liver problems which may be severe and lead to death. Stop taking itraconazole capsules and call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of these symptoms of liver problems:● tiredness
● loss of appetite for several days or longer
● nausea or vomiting
● dark or “tea-colored” urine● your skin or the white part of your eyes turn yellow (jaundice)
● light-colored stools (bowel movement)For more information about side effects, see “What are the possible side effects of itraconazole capsules?”
What are itraconazole capsules?- Itraconazole capsules are prescription medicine used to treat the following fungal infections of the toenails, fingernails and other parts of the body: blastomycosis, histoplasmosis, aspergillosis, and onychomycosis.
- It is not known if itraconazole capsules are safe and effective in children.
Do not take itraconazole capsules if you:
- have or have had heart failure, including congestive heart failure.
- take certain medicines. See “What is the most important information I should know about itraconazole capsules?”
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. Itraconazole capsules can harm your unborn baby. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you become pregnant while taking itraconazole capsules. Females who are able to become pregnant must use effective forms of birth control during treatment and for 2 months after stopping treatment with itraconazole capsules.
- are allergic to itraconazole or any of the ingredients in itraconazole capsules. See the end of this Patient Information leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in itraconazole capsules.
Before taking itraconazole capsules, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have heart problems.
- have liver problems.
- have kidney problems.
- have a weakened immune system (immunocompromised).
- have lung problems including cystic fibrosis.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. Itraconazole can pass into your breast milk. You and your healthcare provider should decide if you will take itraconazole capsules or breastfeed.
Taking itraconazole capsules with certain medicines may affect each other. Taking itraconazole capsules with other medicines can cause serious side effects.
How should I take itraconazole capsules?
- Take itraconazole capsules exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Your healthcare provider will tell you how much itraconazole capsules to take and when to take it.
- You will receive itraconazole capsules in a blister pack, bottle or 7-Day Treatment Pack. Your healthcare provider will decide the type of itraconazole capsules that is right for you.
- Take itraconazole capsules with a full meal.
- Swallow itraconazole capsules whole.
- You should not take itraconazole oral solution instead of itraconazole capsules, because they will not work the same way.
- If you take too much itraconazole capsules, call your healthcare provider or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
What should I avoid while taking itraconazole capsules?
Itraconazole capsules can cause dizziness and vision problems. Do not drive or operate machinery until you know how itraconazole capsules affects you.
What are the possible side effects of itraconazole capsules?
Itraconazole capsules may cause serious side effects, including:- See “What is the most important information I should know about itraconazole capsules?”
- Nerve problems (neuropathy). Call your healthcare provider right away if you have tingling or numbness in your hands or feet. Your healthcare provider may stop your treatment with itraconazole capsules if you have nerve problems.
- Hearing loss. Hearing loss can happen for a short time or permanently in some people who take itraconazole capsules. Stop taking itraconazole capsules and call your healthcare provider right away if you have any changes in your hearing.
The most common side effects of itraconazole capsules include: headache, rash, and digestive system problems (such as nausea and vomiting). Additional possible side effects include upset stomach, vomiting, constipation, fever, inflammation of the pancreas, menstrual disorder, erectile dysfunction, dizziness, muscle pain, painful joints, unpleasant taste, or hair loss.
These are not all the possible side effects of itraconazole capsules.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store itraconazole capsules?- Store itraconazole capsules at 20ºC to 25ºC (68ºF to 77ºF); excursions permitted to 15ºC to 30ºC (59ºF to 86ºF) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
- Keep itraconazole capsules dry and away from light.
Keep itraconazole capsules and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of itraconazole capsules.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use itraconazole capsules for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give itraconazole capsules to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about itraconazole capsules that is written for health professionals.
For more information about itraconazole capsules contact Jubilant Cadista Pharmaceuticals Inc. at 1-800-313-4623.
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration
What are the ingredients in itraconazole capsules?
Active ingredients: itraconazole USP
Inactive ingredients: hypromellose, polyethylene glycol (PEG) 20,000 and sugar spheres (composed of sucrose, corn starch, and purified water). The capsule shell contains: Gelatin, FD&C Blue No. 1, FD&C Blue No. 2 and titanium dioxide.
Rx Only
Manufacured by:
Jubilant Generics Limited
Roorkee - 247661, India
Marketed by:
Jubilant Cadista Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Salisbury, MD 21801, USA
Revised: 03/2019 -
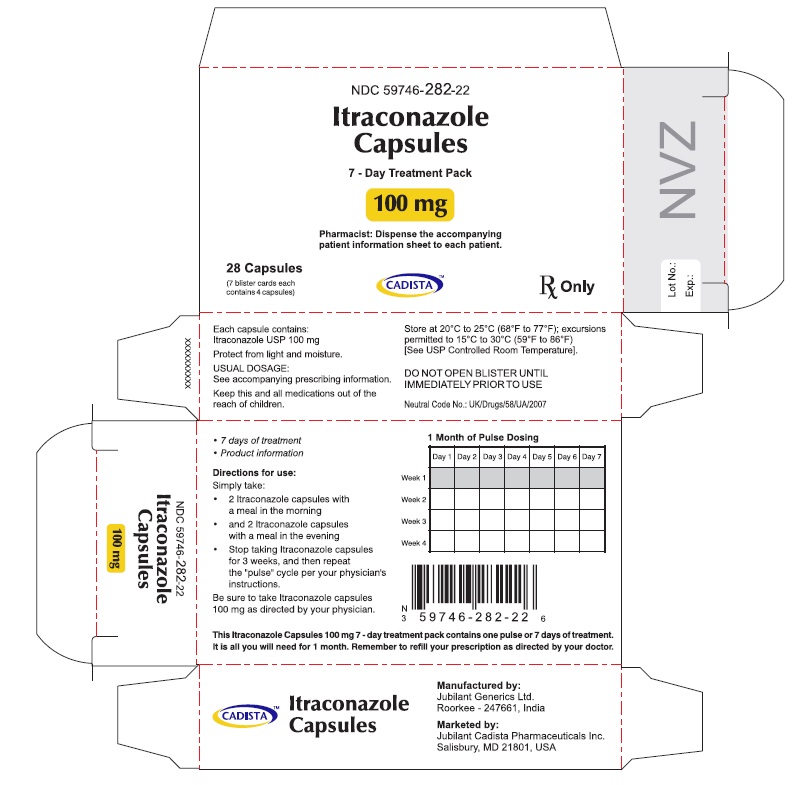
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
30's BOTTLE LABEL:
NDC: 59746-282-30
Itraconazole Capsules
100 mg
Pharmacist: Dispense the accompanying patient information to each patient.
30 Capsules Rx Only
CADISTATM
28's BLISTER CARTON:
NDC: 59746-282-22
Itraconazole Capsules
7 - Day Treatment Pack
100 mg
Pharmacist: Dispense the accompanying patient information sheet to each patient.
28 Capsules (7 blister cards each contains 4 capsules) Rx Only
CADISTATM
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
ITRACONAZOLE
itraconazole capsules capsuleProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 59746-282 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Itraconazole (UNII: 304NUG5GF4) (Itraconazole - UNII:304NUG5GF4) Itraconazole 100 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Hypromelloses (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) Polyethylene Glycol 20000 (UNII: 5WKN5KL2O8) Sucrose (UNII: C151H8M554) Gelatin (UNII: 2G86QN327L) Fd&c Blue No. 1 (UNII: H3R47K3TBD) Fd&c Blue No. 2 (UNII: L06K8R7DQK) Titanium Dioxide (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) Starch, Corn (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) Product Characteristics Color PINK (capsule body) , BLUE (capsule cap) Score no score Shape CAPSULE Size 21mm Flavor Imprint Code C282 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 59746-282-30 30 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 02/23/2017 2 NDC: 59746-282-22 7 in 1 CARTON 02/23/2017 2 4 in 1 BLISTER PACK; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA203445 02/23/2017 Labeler - Jubilant Cadista Pharmaceuticals Inc. (022490515) Registrant - Jubilant Generics Limited (650801538) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Jubilant Generics Limited 650369221 manufacture(59746-282)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.