Phenytoin by Atlantic Biologicals Corps PHENYTOIN suspension
Phenytoin by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Phenytoin by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Atlantic Biologicals Corps. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
DESCRIPTION
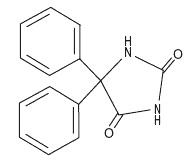
Phenytoin is related to the barbiturates in chemical structure, but has a five-membered ring. The chemical name is 5,5-Diphenylhydantoin, having the following structural formula:
Each 5 mL (teaspoonful) of suspension contains 125 mg of phenytoin, USP with an alcohol content of 0.35 percent. Also contains carboxymethylcellulose sodium, citric acid anhydrous, dehydrated alcohol, FD&C Yellow No. 6, glycerin, liquid sugar, magnesium aluminum silicate, orange flavor, polysorbate 40, purified water, sodium benzoate, sodium citrate dihydrate and vanillin. It may contain 10% citric acid solution or 10% sodium citrate solution to adjust pH. The pH range is between 3.6 and 5.2.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Phenytoin is an antiepileptic drug which can be useful in the treatment of epilepsy. The primary site of action appears to be where spread of seizure activity is inhibited. Possibly by promoting sodium efflux from neurons, phenytoin tends to the threshold against hyperexcitability caused by excessive stimulation or environmental changes capable of reducing membrane sodium gradient. This includes the reduction of posttetanic potentiation at synapses. Loss of posttetanic potentiation prevents cortical seizure foci from detonating adjacent cortical areas. Phenytoin reduces the maximal activity of brain stem centers responsible for the tonic phase of tonic-clonic (grand mal) seizures. the motor cortexstabilize
The plasma half-life in man after oral administration of phenytoin averages 22 hours, with a range of 7 to 42 hours. Steady-state therapeutic levels are achieved at least 7 to 10 days (5–7 half-lives) after initiation of therapy with recommended doses of 300 mg/day.
When serum level determinations are necessary, they should be obtained at least 5–7 half-lives after treatment initiation, dosage change, or addition or subtraction of another drug to the regimen so that equilibrium or steady-state will have been achieved. Trough levels provide information about clinically effective serum level range and confirm patient compliance and are obtained just prior to the patient's next scheduled dose. Peak levels indicate an individual's threshold for emergence of dose-related side effects and are obtained at the time of expected peak concentration. For Phenytoin Oral Suspension peak levels occur 1½–3 hours after administration.
Optimum control without clinical signs of toxicity occurs more often with serum levels between 10 and 20 mcg/mL, although some mild cases of tonic-clonic (grand mal) epilepsy may be controlled with lower serum levels of phenytoin.
In most patients maintained at a steady dosage, stable phenytoin serum levels are achieved. There may be wide interpatient variability in phenytoin serum levels with equivalent dosages. Patients with unusually low levels may be noncompliant or hypermetabolizers of phenytoin. Unusually high levels result from liver disease, congenital enzyme deficiency, or drug interactions which result in metabolic interference. The patient with large variations in phenytoin plasma levels, despite standard doses, presents a difficult clinical problem. Serum level determinations in such patients may be particularly helpful. As phenytoin is highly protein bound, free phenytoin levels may be altered in patients whose protein binding characteristics differ from normal.
Most of the drug is excreted in the bile as inactive metabolites which are then reabsorbed from the intestinal tract and excreted in the urine. Urinary excretion of phenytoin and its metabolites occurs partly with glomerular filtration but more importantly, by tubular secretion. Because phenytoin is hydroxylated in the liver by an enzyme system which is saturable at high plasma levels small incremental doses may increase the half-life and produce very substantial increases in serum levels, when these are in the upper range. The steady-state level may be disproportionately increased, with resultant intoxication, from an increase in dosage of 10% or more.
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Phenytoin Oral Suspension is indicated for the control of tonic-clonic (grand mal) and psychomotor (temporal lobe) seizures.
Phenytoin serum level determinations may be necessary for optimal dosage adjustments (see and sections). DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONCLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
WARNINGS
Effects of Abrupt Withdrawal
Abrupt withdrawal of phenytoin in epileptic patients may precipitate status epilepticus. When in the judgment of the clinician the need for dosage reduction, discontinuation, or substitution of alternative anticonvulsant medication arises, this should be done gradually. In the event of an allergic or hypersensitivity reaction, more rapid substitution of alternative therapy may be necessary. In this case, alternative therapy should be an anticonvulsant not belonging to the hydantoin chemical class.
Suicidal Behavior and Ideation
Antiepileptic drugs (AEDs), including phenytoin, increase the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior in patients taking these drugs for any indication. Patients treated with any AED for any indication should be monitored for the emergence or worsening of depression, suicidal thoughts or behavior, and/or any unusual changes in mood or behavior.
Pooled analyses of 199 placebo-controlled clinical trials (mono- and adjunctive therapy) of 11 different AEDs showed that patients randomized to one of the AEDs had approximately twice the risk (adjusted Relative Risk 1.8, 95% CI:1.2, 2.7) of suicidal thinking or behavior compared to patients randomized to placebo. In these trials, which had a median treatment duration of 12 weeks, the estimated incidence rate of suicidal behavior or ideation among 27,863 AED-treated patients was 0.43%, compared to 0.24% among 16,029 placebo-treated patients, representing an increase of approximately one case of suicidal thinking or behavior for every 530 patients treated. There were four suicides in drug-treated patients in the trials and none in placebo-treated patients, but the number is too small to allow any conclusion about drug effect on suicide.
The increased risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior with AEDs was observed as early as one week after starting drug treatment with AEDs and persisted for the duration of treatment assessed. Because most trials included in the analysis did not extend beyond 24 weeks, the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior beyond 24 weeks could not be assessed.
The risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior was generally consistent among drugs in the data analyzed. The finding of increased risk with AEDs of varying mechanisms of action and across a range of indications suggests that the risk applies to all AEDs used for any indication. The risk did not vary substantially by age (5-100 years) in the clinical trials analyzed.
Table 1 shows absolute and relative risk by indication for all evaluated AEDs.
Table 1: Risk by indication for antiepileptic drugs in the pooled analysis Indication Placebo Patients with Events Per 1000 Patients Drug Patients with Events Per 1000 Patients Relative Risk: Incidence of Events in Drug Patients/Incidence in Placebo Patients Risk Difference: Additional Drug Patients with Events Per 1000 Patients Epilepsy 1.0 3.4 3.5 2.4 Psychiatric 5.7 8.5 1.5 2.9 Other 1.0 1.8 1.9 0.9 Total 2.4 4.3 1.8 1.9 The relative risk for suicidal thoughts or behavior was higher in clinical trials for epilepsy than in clinical trials for psychiatric or other conditions, but the absolute risk differences were similar for the epilepsy and psychiatric indications.
Anyone considering prescribing phenytoin or any other AED must balance the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior with the risk of untreated illness. Epilepsy and many other illnesses for which AEDs are prescribed are themselves associated with morbidity and mortality and an increased risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior. Should suicidal thoughts and behavior emerge during treatment, the prescriber needs to consider whether the emergence of these symptoms in any given patient may be related to the illness being treated.
Patients, their caregivers, and families should be informed that AEDs increase the risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior and should be advised of the need to be alert for the emergence or worsening of the signs and symptoms of depression, any unusual changes in mood or behavior, or the emergence of suicidal thoughts, behavior, or thoughts about self-harm. Behaviors of concern should be reported immediately to healthcare providers.
Lymphadenopathy
There have been a number of reports suggesting a relationship between phenytoin and the development of lymphadenopathy (local or generalized) including benign lymph node hyperplasia, pseudolymphoma, lymphoma, and Hodgkin's disease. Although a cause and effect relationship has not been established, the occurrence of lymphadenopathy indicates the need to differentiate such a condition from other types of lymph node pathology. Lymph node involvement may occur with or without symptoms and signs resembling serum sickness e.g., fever, rash, and liver involvement.
In all cases of lymphadenopathy, follow-up observation for an extended period is indicated and every effort should be made to achieve seizure control using alternative antiepileptic drugs.
Effects of Alcohol Use on Phenytoin Serum Levels
Accute alcoholic intake may increase phenytoin serum levels, while chronic alcoholic use may decrease serum levels.
Exacerbation of Porphyria
In view of isolated reports associating phenytoin with exacerbation of porphyria, caution should be exercised in using this medication in patients suffering from this disease.
Usage in Pregnancy
Clinical:
- An increase in seizure frequency may occur during pregnancy because of altered phenytoin pharmacokinetics. Periodic measurement of plasma phenytoin concentrations may be valuable in the management of pregnant women as a guide to appropriate adjustment of dosage (see ). However, postpartum restoration of the original dosage will probably be indicated. Risks to Mother.PRECAUTIONS, Laboratory Tests
- If this drug is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking the drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential harm to the fetus. Prenatal exposure to phenytoin may increase the risks for congenital malformations and other adverse developmental outcomes. Increased frequencies of major malformations (such as orofacial clefts and cardiac defects), minor anomalies (dysmorphic facial features, nail and digit hypoplasia), growth abnormalities (including microcephaly), and mental deficiency have been reported among children born to epileptic women who took phenytoin alone or in combination with other antiepileptic drugs during pregnancy. There have also been several reported cases of malignancies, including neuroblastoma, in children whose mothers received phenytoin during pregnancy. The overall incidence of malformations for children of epileptic women treated with antiepileptic drugs (phenytoin and/or others) during pregnancy is about 10%, or two- to three-fold that in the general population. However, the relative contributions of antiepileptic drugs and other factors associated with epilepsy to this increased risk are uncertain and in most cases it has not been possible to attribute specific developmental abnormalities to particular antiepileptic drugs. Patients should consult with their physicians to weigh the risks and benefits of phenytoin during pregnancy.
Risks to the Fetus.
- A potentially life-threatening bleeding disorder related to decreased levels of vitamin K-dependent clotting factors may occur in newborns exposed to phenytoin This drug-induced condition can be prevented with vitamin K administration to the mother before delivery and to the neonate after birth. Postpartum Period.in utero.
-
PRECAUTIONS
General
The liver is the chief site of biotransformation of phenytoin; patients with impaired liver function, elderly patients, or those who are gravely ill may show early signs of toxicity.
A small percentage of individuals who have been treated with phenytoin have been shown to metabolize the drug slowly. Slow metabolism may be due to limited enzyme availability and lack of induction; it appears to be genetically determined.
Phenytoin should be discontinued if a skin rash appears (see section regarding drug discontinuation). If the rash is exfoliative, purpuric, or bullous or if lupus erythematosus, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, or toxic epidermal necrolysis is suspected, use of this drug should not be resumed and alternative therapy should be considered (see section). If the rash is of a milder type (measles-like or scarlatiniform), therapy may be resumed after the rash has completely disappeared. If the rash recurs upon reinstitution of therapy, further phenytoin medication is contraindicated. WARNINGSADVERSE REACTIONS
Phenytoin and other hydantoins are contraindicated in patients who have experienced phenytoin hypersensitivity (see ). Additionally, caution should be exercised if using structurally similar (e.g., barbiturates, succinamides, oxazolidinediones and other related compounds) in these same patients. Hyperglycemia, resulting from the drug's inhibitory effects on insulin release, has been reported. Phenytoin may also raise the serum glucose level in diabetic patients. CONTRAINDICATIONS
Osteomalacia has been associated with phenytoin therapy and is considered to be due to phenytoin's interference with Vitamin D metabolism.
Phenytoin is not indicated for seizures due to hypoglycemic or other metabolic causes. Appropriate diagnostic procedures should be performed as indicated.
Phenytoin is not effective for absence (petit mal) seizures. If tonic-clonic (grand mal) and absence (petit mal) seizures are present, combined drug therapy is needed.
Serum levels of phenytoin sustained above the optimal range may produce confusional states referred to as "delirium,""psychosis," or "encephalopathy," or rarely irreversible cerebellar dysfunction. Accordingly, at the first sign of acute toxicity, plasma levels are recommended. Dose reduction of phenytoin therapy is indicated if plasma levels are excessive; if symptoms persist, termination is recommended (see section). WARNINGS
Information for Patients
Patients taking phenytoin should be advised of the importance of adhering strictly to the prescribed dosage regimen, and of informing the physician of any clinical condition in which it is not possible to take the drug orally as prescribed, e.g., surgery, etc.
Patients should be instructed to use an accurately calibrated measuring device when using this medication to ensure accurate dosing.
Patients should also be cautioned on the use of other drugs or alcoholic beverages without first seeking the physician's advice.
Patients should be instructed to call their physician if skin rash develops.
The importance of good dental hygiene should be stressed in order to minimize the development of gingival hyperplasia and its complications.
Patients, their caregivers, and families should be counseled that AEDs, including phenytoin, may increase the risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior and should be advised of the need to be alert for the emergence or worsening of symptoms of depression, any unusual changes in mood or behavior, or the emergence of suicidal thoughts, behavior, or thoughts about self-harm. Behaviors of concern should be reported immediately to healthcare providers.
Patients should be encouraged to enroll in the North American Antiepileptic Drug (NAAED) Pregnancy Registry if they become pregnant. This registry is collecting information about the safety of antiepileptic drugs during pregnancy. To enroll, patients can call the toll free number 1-888-233-2334 (see section). PRECAUTIONS: Pregnancy
Laboratory Tests
Phenytoin serum level determinations may be necessary to achieve optimal dosage adjustments.
Drug Interactions
There are many drugs which may increase or decrease phenytoin levels or which phenytoin may affect. Serum level determinations for phenytoin are especially helpful when possible drug interactions are suspected. The most commonly occurring drug interactions are:
- Drugs which may increase phenytoin serum levels include: acute alcohol intake, amiodarone, chloramphenicol, chlordiazepoxide, cimetidine, diazepam, dicumarol, disulfiram, estrogens, ethosuximide, fluoxetine, H -antagonists, halothane, isoniazid, methylphenidate, phenothiazines, phenylbutazone, salicylates, succinimides, sulfonamides, ticlopidine, tolbutamide, trazodone. 2
- Drugs which may decrease phenytoin levels include: carbamazepine, chronic alcohol abuse, reserpine, and sucralfate. Moban brand of molindone hydrochloride contains calcium ions which interfere with the absorption of phenytoin. Ingestion times of phenytoin and antacid preparations containing calcium should be staggered in patients with low serum phenytoin levels to prevent absorption problems. 1®
- Drugs which may either increase or decrease phenytoin serum levels include: phenobarbital, sodium valproate, and valproic acid. Similarly, the effect of phenytoin on phenobarbital, valproic acid, and sodium valproate serum levels is unpredictable.
- Although not a true drug interaction, tricyclic antidepressants may precipitate seizures in susceptible patients and phenytoin dosage may need to be adjusted.
- Drugs whose efficacy is impaired by phenytoin include: corticosteroids, coumarin anticoagulants, digitoxin, doxycycline, estrogens, furosemide, oral contraceptives, paroxetine, quinidine, rifampin, theophylline, vitamin D.
- 1 (Moban is a registered trademark of Endo Pharmaceuticals, Inc.) ®
Drug Enteral Feeding/Nutritional Preparations Interaction
Literature reports suggest that patients who have received enteral feeding preparations and/or related nutritional supplements have lower than expected phenytoin plasma levels. It is therefore suggested that phenytoin not be administered concomitantly with an enteral feeding preparation. More frequent serum phenytoin level monitoring may be necessary in these patients.
Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
Phenytoin may decrease serum concentrations of T4. It may also produce lower than normal values for dexamethasone or metyrapone tests. Phenytoin may cause increased serum levels of glucose, alkaline phosphatase, and gamma glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT).
Care should be taken when using immunoanalytical methods to measure plasma phenytoin concentrations.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category D; See section. WARNINGS
To provide information regarding the effects of exposure to phenytoin, physicians are advised to recommend that pregnant patients taking phenytoin enroll in the NAAED Pregnancy Registry. This can be done by calling the toll free number 1-888-233-2334, and must be done by patients themselves. Information on the registry can also be found at the website http://www.aedpregnancyregistry.org/. in utero
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Central Nervous System
The most common manifestations encountered with phenytoin therapy are referable to this system and are usually dose-related. These include nystagmus, ataxia, slurred speech, decreased coordination, and mental confusion. Dizziness, insomnia, transient nervousness, motor twitchings, and headaches have also been observed. There have also been rare reports of phenytoin-induced dyskinesias, including chorea, dystonia, tremor and asterixis, similar to those induced by phenothiazine and other neuroleptic drugs.
A predominantly sensory peripheral polyneuropathy has been observed in patients receiving long-term phenytoin therapy.
Integumentary System
Dermatological manifestations sometimes accompanied by fever have included scarlatiniform or morbilliform rashes. A morbilliform rash (measles-like) is the most common; other types of dermatitis are seen more rarely. Other more serious forms which may be fatal have included bullous, exfoliative or purpuric dermatitis, lupus erythematosus, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and toxic epidermal necrolysis (see section). PRECAUTIONS
Hemopoietic System
Hemopoietic complications, some fatal, have occasionally been reported in association with administration of phenytoin. These have included thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, granulocytopenia, agranulocytosis, and pancytopenia with or without bone marrow suppression. While macrocytosis and megaloblastic anemia have occurred, these conditions usually respond to folic acid therapy. Lymphadenopathy including benign lymph node hyperplasia, pseudolymphoma, lymphoma, and Hodgkin's disease have been reported (see section). WARNINGS
-
OVERDOSAGE
The lethal dose in pediatric patients is not known. The lethal dose in adults is estimated to be 2 to 5 grams. The initial symptoms are nystagmus, ataxia, and dysarthria. Other signs are tremor, hyperreflexia, lethargy, slurred speech, nausea, vomiting. The patient may become comatose and hypotensive. Death is due to respiratory and circulatory depression.
There are marked variations among individuals with respect to phenytoin plasma levels where toxicity may occur. Nystagmus, on lateral gaze, usually appears at 20 mcg/mL, ataxia at 30 mcg/mL; dysarthria and lethargy appear when the plasma concentration is over 40 mcg/mL, but as high a concentration as 50 mcg/mL has been reported without evidence of toxicity. As much as 25 times the therapeutic dose has been taken to result in a serum concentration over 100 mcg/mL with complete recovery.
Treatment
Treatment is nonspecific since there is no known antidote.
The adequacy of the respiratory and circulatory systems should be carefully observed and appropriate supportive measures employed. Hemodialysis can be considered since phenytoin is not completely bound to plasma proteins. Total exchange transfusion has been used in the treatment of severe intoxication in pediatric patients.
In acute overdosage the possibility of other CNS depressants, including alcohol, should be borne in mind.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION – (NOT FOR PARENTERAL USE)
Serum concentrations should be monitored and care should be taken when switching a patient from the sodium salt to the free acid form. The free acid form of phenytoin is used in Phenytoin Oral Suspension. Because there is approximately an 8% increase in drug content with the free acid form over that of the sodium salt, dosage adjustments and serum level monitoring may be necessary when switching from a product formulated with the free acid to a product formulated with the sodium salt and vice versa.
General
Dosage should be individualized to provide maximum benefit. In some cases serum blood level determinations may be necessary for optimal dosage adjustments—the clinically effective serum level is usually 10–20 mcg/mL. With recommended dosage, a period of seven to ten days may be required to achieve steady-state blood levels with phenytoin and changes in dosage (increase or decrease) should not be carried out at intervals shorter than seven to ten days.
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
- PHENYTOIN SUSPENSION
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
PHENYTOIN
phenytoin suspensionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 17856-0067(NDC:60432-131) Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Phenytoin (UNII: 6158TKW0C5) (Phenytoin - UNII:6158TKW0C5) Phenytoin 125 mg in 5 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength magnesium aluminum silicate (UNII: 6M3P64V0NC) glycerin (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) carboxymethylcellulose sodium (UNII: K679OBS311) anhydrous citric acid (UNII: XF417D3PSL) trisodium citrate dihydrate (UNII: B22547B95K) sodium benzoate (UNII: OJ245FE5EU) raw sugar (UNII: 8M707QY5GH) polysorbate 40 (UNII: STI11B5A2X) water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) FD&C Yellow No. 6 (UNII: H77VEI93A8) Alcohol (UNII: 3K9958V90M) vanillin (UNII: CHI530446X) Sodium Citrate (UNII: 1Q73Q2JULR) Citric Acid Monohydrate (UNII: 2968PHW8QP) Product Characteristics Color Score Shape Size Flavor ORANGE (Orange-Vanilla) Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 17856-0067-3 4 mL in 1 CUP Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA040420 06/24/2002 Labeler - Atlantic Biologicals Corps (047437707) Registrant - Atlantic Biologicals Corps (047437707) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Atlantic Biologicals Corps 047437707 RELABEL, REPACK
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.
