HALOPERIDOL DECANOATE injection
Haloperidol Decanoate by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Haloperidol Decanoate by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC , Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING
Increased Mortality in Elderly Patients with Dementia-Related Psychosis - Elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with antipsychotic drugs are at an increased risk of death. Analyses of seventeen placebo-controlled trials (modal duration of 10 weeks), largely in patients taking atypical antipsychotic drugs, revealed a risk of death in drug-treated patients of between 1.6 to 1.7 times the risk of death in placebo-treated patients. Over the course of a typical 10-week controlled trial, the rate of death in drug-treated patients was about 4.5%, compared to a rate of about 2.6% in the placebo group. Although the causes of death were varied, most of the deaths appeared to be either cardiovascular (e.g., heart failure, sudden death) or infectious (e.g., pneumonia) in nature. Observational studies suggest that, similar to atypical antipsychotic drugs, treatment with conventional antipsychotic drugs may increase mortality. The extent to which the findings of increased mortality in observational studies may be attributed to the antipsychotic drug as opposed to some characteristic(s) of the patients is not clear. Haloperidol decanoate injection is not approved for the treatment of patients with dementia-related psychosis (see WARNINGS).
-
DESCRIPTION:
Haloperidol decanoate is the decanoate ester of the butyrophenone, haloperidol. It has a markedly extended duration of effect. It is available as a colorless/pink to yellow amber solution in sesame oil in sterile form for intramuscular (IM) injection. The structural formula of haloperidol decanoate, 4-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-[4-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-oxobutyl]-4 piperidinyl decanoate, is:
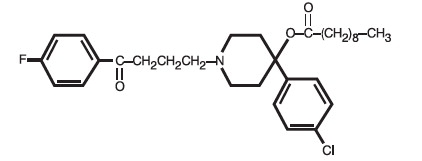
C31H41ClFNO3 M.W. 530.12
Haloperidol decanoate is almost insoluble in water (0.01 mg/mL), but is soluble in most organic solvents.
Each mL of haloperidol decanoate injection, 100 mg/mL, contains 100 mg haloperidol (present as haloperidol decanoate 141.04 mg) in a sesame oil vehicle, with 1.2% (w/v) benzyl alcohol as a preservative.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY:
Haloperidol decanoate is the long-acting form of haloperidol. The basic effects of haloperidol decanoate are no different from those of haloperidol with the exception of duration of action. Haloperidol blocks the effects of dopamine and increases its turnover rate; however, the precise mechanism of action is unknown.
Administration of haloperidol decanoate in sesame oil results in slow and sustained release of haloperidol. The plasma concentrations of haloperidol gradually rise, reaching a peak at about 6 days after the injection, and falling thereafter, with an apparent half-life of about 3 weeks. Steady-state plasma concentrations are achieved after the third or fourth dose. The relationship between dose of haloperidol decanoate and plasma haloperidol concentration is roughly linear for doses below 450 mg. It should be noted, however, that the pharmacokinetics of haloperidol decanoate following intramuscular injections can be quite variable between subjects.
- INDICATIONS AND USAGE:
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
Since the pharmacologic and clinical actions of haloperidol decanoate are attributed to haloperidol as the active medication, CONTRAINDICATIONS, WARNINGS, and additional information are those of haloperidol, modified only to reflect the prolonged action.
Haloperidol is contraindicated in severe toxic central nervous system depression or comatose states from any cause and in individuals who are hypersensitive to this drug or have Parkinson’s disease.
-
WARNINGS:
Increased Mortality in Elderly Patients with Dementia-Related Psychosis
Elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with antipsychotic drugs are at an increased risk of death. Haloperidol decanoate injection is not approved for the treatment of patients with dementia-related psychosis (see BOXED WARNING).
Cardiovascular Effects
Cases of sudden death, QT-prolongation, and Torsades de Pointes have been reported in patients receiving haloperidol. Higher than recommended doses of any formulation and intravenous administration of haloperidol appear to be associated with a higher risk of QT-prolongation and Torsades de Pointes. Although cases have been reported even in the absence of predisposing factors, particular caution is advised in treating patients with other QT-prolonging conditions (including electrolyte imbalance [particularly hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia], drugs known to prolong QT, underlying cardiac abnormalities, hypothyroidism, and familial long QT-syndrome). HALOPERIDOL DECANOATE INJECTION MUST NOT BE ADMINISTERED INTRAVENOUSLY.
Tardive Dyskinesia
A syndrome consisting of potentially irreversible, involuntary, dyskinetic movements may develop in patients treated with antipsychotic drugs. Although the prevalence of the syndrome appears to be highest among the elderly, especially elderly women, it is impossible to rely upon prevalence estimates to predict, at the inception of antipsychotic treatment, which patients are likely to develop the syndrome. Whether antipsychotic drug products differ in their potential to cause tardive dyskinesia is unknown.
Both the risk of developing tardive dyskinesia and the likelihood that it will become irreversible are believed to increase as the duration of treatment and the total cumulative dose of antipsychotic drugs administered to the patient increase. However, the syndrome can develop, although much less commonly, after relatively brief treatment periods at low doses.
There is no known treatment for established cases of tardive dyskinesia, although the syndrome may remit, partially or completely, if antipsychotic treatment is withdrawn. Antipsychotic treatment, itself, however, may suppress (or partially suppress) the signs and symptoms of the syndrome and thereby may possibly mask the underlying process. The effect that symptomatic suppression has upon the long-term course of the syndrome is unknown.
Given these considerations, antipsychotic drugs should be prescribed in a manner that is most likely to minimize the occurrence of tardive dyskinesia. Chronic antipsychotic treatment should generally be reserved for patients who suffer from a chronic illness that 1) is known to respond to antipsychotic drugs, and 2) for whom alternative, equally effective, but potentially less harmful treatments are not available or appropriate. In patients who do require chronic treatment, the smallest dose and the shortest duration of treatment producing a satisfactory clinical response should be sought. The need for continued treatment should be reassessed periodically.
If signs and symptoms of tardive dyskinesia appear in a patient on antipsychotics, drug discontinuation should be considered. However, some patients may require treatment despite the presence of the syndrome. (For further information about the description of tardive dyskinesia and its clinical detection, please refer to ADVERSE REACTIONS.)
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS)
A potentially fatal symptom complex sometimes referred to as Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS) has been reported in association with antipsychotic drugs. Clinical manifestations of NMS are hyperpyrexia, muscle rigidity, altered mental status (including catatonic signs) and evidence of autonomic instability (irregular pulse or blood pressure, tachycardia, diaphoresis, and cardiac dysrhythmias). Additional signs may include elevated creatine phosphokinase, myoglobinuria (rhabdomyolysis) and acute renal failure.
The diagnostic evaluation of patients with this syndrome is complicated. In arriving at a diagnosis, it is important to identify cases where the clinical presentation includes both serious medical illness (e.g., pneumonia, systemic infection, etc.) and untreated or inadequately treated extrapyramidal signs and symptoms (EPS). Other important considerations in the differential diagnosis include central anticholinergic toxicity, heat stroke, drug fever and primary central nervous system (CNS) pathology.
The management of NMS should include 1) immediate discontinuation of antipsychotic drugs and other drugs not essential to concurrent therapy, 2) intensive symptomatic treatment and medical monitoring, and 3) treatment of any concomitant serious medical problems for which specific treatments are available. There is no general agreement about specific pharmacological treatment regimens for uncomplicated NMS.
If a patient requires antipsychotic drug treatment after recovery from NMS, the potential reintroduction of drug therapy should be carefully considered. The patient should be carefully monitored, since recurrences of NMS have been reported.
Hyperpyrexia and heat stroke, not associated with the above symptom complex, have also been reported with haloperidol.
Falls
Motor instability, somnolence, and orthostatic hypotension have been reported with the use of antipsychotics, including haloperidol decanoate, which may lead to falls and, consequently, fractures or other fall-related injuries. For patients, particularly the elderly, with diseases, conditions, or medications that could exacerbate these effects, assess the risk of falls when initiating antipsychotic treatment and recurrently during treatment.
Combined Use of Haloperidol and Lithium
An encephalopathic syndrome (characterized by weakness, lethargy, fever, tremulousness and confusion, extrapyramidal symptoms, leukocytosis, elevated serum enzymes, BUN, and fasting blood sugar) followed by irreversible brain damage has occurred in a few patients treated with lithium plus haloperidol. A causal relationship between these events and the concomitant administration of lithium and haloperidol has not been established; however, patients receiving such combined therapy should be monitored closely for early evidence of neurological toxicity and treatment discontinued promptly if such signs appear.
General
A number of cases of bronchopneumonia, some fatal, have followed the use of antipsychotic drugs, including haloperidol. It has been postulated that lethargy and decreased sensation of thirst due to central inhibition may lead to dehydration, hemoconcentration and reduced pulmonary ventilation. Therefore, if the above signs and symptoms appear, especially in the elderly, the physician should institute remedial therapy promptly.
Although not reported with haloperidol, decreased serum cholesterol and/or cutaneous and ocular changes have been reported in patients receiving chemically-related drugs.
-
PRECAUTIONS:
Leukopenia, Neutropenia, and Agranulocytosis
Class Effect: In clinical trial and/or postmarketing experience, events of leukopenia/neutropenia have been reported temporally related to antipsychotic agents, including haloperidol decanoate. Agranulocytosis has also been reported.
Possible risk factors for leukopenia/neutropenia include pre-existing low white blood cell count (WBC) and history of drug-induced leukopenia/neutropenia. Patients with a history of a clinically significant low WBC or a drug-induced leukopenia/neutropenia should have their complete blood count (CBC) monitored frequently during the first few months of therapy and discontinuation of haloperidol decanoate should be considered at the first sign of a clinically significant decline in WBC in the absence of other causative factors.
Patients with clinically significant neutropenia should be carefully monitored for fever or other symptoms or signs of infection and treated promptly if such symptoms or signs occur. Patients with severe neutropenia (absolute neutrophil count <1,000/mm3) should discontinue haloperidol decanoate and have their WBC followed until recovery.
Other
Haloperidol decanoate should be administered cautiously to patients:
- with severe cardiovascular disorders, because of the possibility of transient hypotension and/or precipitation of anginal pain. Should hypotension occur and a vasopressor be required, epinephrine should not be used since haloperidol may block its vasopressor activity, and paradoxical further lowering of the blood pressure may occur. Instead, metaraminol, phenylephrine or norepinephrine should be used.
- receiving anticonvulsant medications, with a history of seizures, or with EEG abnormalities, because haloperidol may lower the convulsive threshold. If indicated, adequate anticonvulsant therapy should be concomitantly maintained.
- with known allergies, or with a history of allergic reactions to drugs.
- receiving anticoagulants, since an isolated instance of interference occurred with the effects of one anticoagulant (phenindione).
If concomitant antiparkinson medication is required, it may have to be continued after haloperidol decanoate is discontinued because of the prolonged action of haloperidol decanoate. If both drugs are discontinued simultaneously, extrapyramidal symptoms may occur. The physician should keep in mind the possible increase in intraocular pressure when anticholinergic drugs, including antiparkinson agents, are administered concomitantly with haloperidol decanoate.
When haloperidol decanoate is used to control mania in cyclic disorders, there may be a rapid mood swing to depression.
Severe neurotoxicity (rigidity, inability to walk or talk) may occur in patients with thyrotoxicosis who are also receiving antipsychotic medication, including haloperidol.
Information for Patients
Haloperidol decanoate may impair the mental and/or physical abilities required for the performance of hazardous tasks such as operating machinery or driving a motor vehicle. The ambulatory patient should be warned accordingly.
The use of alcohol with this drug should be avoided due to possible additive effects and hypotension.
Drug Interactions
Drug-drug interactions can be pharmacodynamic (combined pharmacologic effects) or pharmacokinetic (alteration of plasma levels). The risks of using haloperidol in combination with other drugs have been evaluated as described below.
Pharmacodynamic Interactions
Since QT-prolongation has been observed during haloperidol treatment, caution is advised when prescribing to patient with QT-prolongation conditions (long QT-syndrome, hypokalemia, electrolyte imbalance) or to patients receiving medications known to prolong the QT-interval or known to cause electrolyte imbalance.
As with other antipsychotic agents, it should be noted that haloperidol may be capable of potentiating CNS depressants such as anesthetics, opiates and alcohol.
Ketoconazole is a potent inhibitor of CYP3A4. Increases in QTc have been observed when haloperidol was given in combination with the metabolic inhibitors ketoconazole (400 mg/day) and paroxetine (20 mg/day). It may be necessary to reduce the haloperidol dosage.
Pharmacokinetic Interactions
The Effect of Other Drugs on Haloperidol Decanoate
Haloperidol is metabolized by several routes, including the glucuronidation and the cytochrome P450 enzyme system. Inhibition of these routes of metabolism by another drug may result in increased haloperidol concentrations and potentially increase the risk of certain adverse events, including QT-prolongation.
Drugs Characterized as Substrates, Inhibitors or Inducers of CYP3A4, CYP2D6 or Glucuronidation
In pharmacokinetic studies, mild to moderately increased haloperidol concentrations have been reported when haloperidol was given concomitantly with drugs characterized as substrates or inhibitors of CYP3A4 or CYP2D6 isoenzymes, such as itraconazole, nefazodone, buspirone, venlafaxine, alprazolam, fluvoxamine, quinidine, fluoxetine, sertraline, chlorpromazine, and promethazine.
When prolonged treatment (1 to 2 weeks) with enzyme-inducing drugs such as rifampin or carbamazepine is added to haloperidol therapy, this results in a significant reduction of haloperidol plasma levels.
Rifampin
In a study of 12 schizophrenic patients coadministered oral haloperidol and rifampin, plasma haloperidol levels were decreased by a mean of 70% and mean scores on the Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale were increased from baseline. In 5 other schizophrenic patients treated with oral haloperidol and rifampin, discontinuation of rifampin produced a mean 3.3-fold increase in haloperidol concentrations.
Carbamazepine
In a study in 11 schizophrenic patients co-administered haloperidol and increasing doses of carbamazepine, haloperidol plasma concentrations decreased linearly with increasing carbamazepine concentrations.
Thus, careful monitoring of clinical status is warranted when enzyme inducing drugs such as rifampin or carbamazepine are administered or discontinued in haloperidol-treated patients. During combination treatment, the haloperidol dose should be adjusted, when necessary. After discontinuation of such drugs, it may be necessary to reduce the dosage of haloperidol.
Valproate
Sodium valproate, a drug known to inhibit glucuronidation, does not affect haloperidol plasma concentrations.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No mutagenic potential of haloperidol decanoate was found in the Ames Salmonella microsomal activation assay. Negative or inconsistent positive findings have been obtained in in vitro and in vivo studies of effects of short-acting haloperidol on chromosome structure and number. The available cytogenetic evidence is considered too inconsistent to be conclusive at this time.
Carcinogenicity studies using oral haloperidol were conducted in Wistar rats (dosed at up to 5 mg/kg daily for 24 months) and in Albino Swiss mice (dosed at up to 5 mg/kg daily for 18 months). In the rat study survival was less than optimal in all dose groups, reducing the number of rats at risk for developing tumors. However, although a relatively greater number of rats survived to the end of the study in high-dose male and female groups, these animals did not have a greater incidence of tumors than control animals. Therefore, although not optimal, this study does suggest the absence of a haloperidol-related increase in the incidence of neoplasia in rats at doses up to 20 times the usual daily human dose for chronic or resistant patients.
In female mice at 5 and 20 times the highest initial daily dose for chronic or resistant patients, there was a statistically significant increase in mammary gland neoplasia and total tumor incidence; at 20 times the same daily dose there was a statistically significant increase in pituitary gland neoplasia. In male mice, no statistically significant differences in incidences of total tumors or specific tumor types were noted.
Antipsychotic drugs elevate prolactin levels; the elevation persists during chronic administration. Tissue culture experiments indicate that approximately one-third of human breast cancers are prolactin dependent in vitro, a factor of potential importance if the prescription of these drugs is contemplated in a patient with a previously detected breast cancer. Although disturbances such as galactorrhea, amenorrhea, gynecomastia, and impotence have been reported, the clinical significance of elevated serum prolactin levels is unknown for most patients.
An increase in mammary neoplasms has been found in rodents after chronic administration of antipsychotic drugs. Neither clinical studies nor epidemiologic studies conducted to date, however, have shown an association between chronic administration of these drugs and mammary tumorigenesis; the available evidence is considered too limited to be conclusive at this time.
Usage in Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C
Rodents given up to 3 times the usual maximum human dose of haloperidol decanoate showed an increase in incidence of resorption, fetal mortality, and pup mortality. No fetal abnormalities were observed.
Cleft palate has been observed in mice given oral haloperidol at 15 times the usual maximum human dose. Cleft palate in mice appears to be a non-specific response to stress or nutritional imbalance as well as to a variety of drugs, and there is no evidence to relate this phenomenon to predictable human risk for most of these agents.
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. There are reports, however, of cases of limb malformations observed following maternal use of haloperidol along with other drugs which have suspected teratogenic potential during the first trimester of pregnancy. Causal relationships were not established with these cases. Since such experience does not exclude the possibility of fetal damage due to haloperidol, haloperidol decanoate should be used during pregnancy or in women likely to become pregnant only if the benefit clearly justifies a potential risk to the fetus.
Nonteratogenic Effects
Neonates exposed to antipsychotic drugs (including haloperidol) during the third trimester of pregnancy are at risk for extrapyramidal and/or withdrawal symptoms following delivery. There have been reports of agitation, hypertonia, hypotonia, tremor, somnolence, respiratory distress, and feeding disorder in these neonates. These complications have varied in severity; while in some cases symptoms have been self-limited, in other cases neonates have required intensive care unit support and prolonged hospitalization.
Haloperidol decanoate should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Nursing Mothers
Since haloperidol is excreted in human breast milk, infants should not be nursed during drug treatment with haloperidol decanoate.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of haloperidol decanoate in children have not been established.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of haloperidol did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not consistently identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. However, the prevalence of tardive dyskinesia appears to be highest among the elderly, especially elderly women (see WARNINGS, Tardive Dyskinesia). Also, the pharmacokinetics of haloperidol in geriatric patients generally warrants the use of lower doses (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS:
Adverse reactions following the administration of haloperidol decanoate are those of haloperidol. Since vast experience has accumulated with haloperidol, the adverse reactions are reported for that compound as well as for haloperidol decanoate. As with all injectable medications, local tissue reactions have been reported with haloperidol decanoate.
Cardiovascular Effects
Tachycardia, hypotension, and hypertension have been reported. QT-prolongation and/or ventricular arrhythmias have also been reported, in addition to ECG pattern changes compatible with the polymorphous configuration of Torsades de Pointes, and may occur more frequently with high doses and in predisposed patients (see WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS).
Cases of sudden and unexpected death have been reported in association with the administration of haloperidol decanoate. The nature of the evidence makes it impossible to determine definitively what role, if any, haloperidol decanoate played in the outcome of the reported cases. The possibility that haloperidol decanoate caused death cannot, of course, be excluded, but it is to be kept in mind that sudden and unexpected death may occur in psychotic patients when they go untreated or when they are treated with other antipsychotic drugs.
CNS Effects
Extrapyramidal Symptoms (EPS)
EPS during the administration of haloperidol have been reported frequently, often during the first few days of treatment. EPS can be categorized generally as Parkinson-like symptoms, akathisia, or dystonia (including opisthotonos and oculogyric crisis). While all can occur at relatively low doses, they occur more frequently and with greater severity at higher doses. The symptoms may be controlled with dose reductions or administration of antiparkinson drugs such as benztropine mesylate or trihexyphenidyl hydrochloride. It should be noted that persistent EPS have been reported; the drug may have to be discontinued in such cases.
Dystonia
Class Effect: Symptoms of dystonia, prolonged abnormal contractions of muscle groups, may occur in susceptible individuals during the first few days of treatment. Dystonic symptoms include: spasm of the neck muscles, sometimes progressing to tightness of the throat, swallowing difficulty, difficulty breathing, and/or protrusion of the tongue. While these symptoms can occur at low doses, they occur more frequently and with greater severity with high potency and at higher doses of first generation antipsychotic drugs. An elevated risk of acute dystonia is observed in males and younger age groups.
Withdrawal Emergent Neurological Signs
Generally, patients receiving short-term therapy experience no problems with abrupt discontinuation of antipsychotic drugs. However, some patients on maintenance treatment experience transient dyskinetic signs after abrupt withdrawal. In certain of these cases the dyskinetic movements are indistinguishable from the syndrome described below under “Tardive Dyskinesia” except for duration. Although the long-acting properties of haloperidol decanoate provide gradual withdrawal, it is not known whether gradual withdrawal of antipsychotic drugs will reduce the rate of occurrence of withdrawal emergent neurological signs.
Tardive Dyskinesia
As with all antipsychotic agents haloperidol has been associated with persistent dyskinesias. Tardive dyskinesia, a syndrome consisting of potentially irreversible, involuntary, dyskinetic movements, may appear in some patients on long-term therapy with haloperidol decanoate or may occur after drug therapy has been discontinued. The risk appears to be greater in elderly patients on high-dose therapy, especially females. The symptoms are persistent and in some patients appear irreversible. The syndrome is characterized by rhythmical involuntary movements of tongue, face, mouth, or jaw (e.g., protrusion of tongue, puffing of cheeks, puckering of mouth, chewing movements). Sometimes these may be accompanied by involuntary movements of extremities and the trunk.
There is no known effective treatment for tardive dyskinesia; antiparkinson agents usually do not alleviate the symptoms of this syndrome. It is suggested that all antipsychotic agents be discontinued if these symptoms appear. Should it be necessary to reinstitute treatment, or increase the dosage of the agent, or switch to a different antipsychotic agent, this syndrome may be masked.
It has been reported that fine vermicular movement of the tongue may be an early sign of tardive dyskinesia and if the medication is stopped at that time the full syndrome may not develop.
Tardive Dystonia
Tardive dystonia, not associated with the above syndrome, has also been reported. Tardive dystonia is characterized by delayed onset of choreic or dystonic movements, is often persistent, and has the potential of becoming irreversible.
Other CNS Effects
Insomnia, restlessness, anxiety, euphoria, agitation, drowsiness, depression, lethargy, headache, confusion, vertigo, grand mal seizures, exacerbation of psychotic symptoms including hallucinations, and catatonic-like behavioral states which may be responsive to drug withdrawal and/or treatment with anticholinergic drugs.
Body as a Whole
Neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS), hyperpyrexia and heat stroke have been reported with haloperidol (see WARNINGS for further information concerning NMS).
Hematologic Effects
Reports have appeared citing the occurrence of mild and usually transient leukopenia and leukocytosis, minimal decreases in red blood cell counts, anemia, or a tendency toward lymphomonocytosis. Agranulocytosis has rarely been reported to have occurred with the use of haloperidol, and then only in association with other medication (see PRECAUTIONS, Leukopenia, Neutropenia, and Agranulocytosis).
Liver Effects
Impaired liver function and/or jaundice have been reported.
Dermatologic Reactions
Maculopapular and acneiform skin reactions and isolated cases of photosensitivity and loss of hair.
Endocrine Disorders
Lactation, breast engorgement, mastalgia, menstrual irregularities, gynecomastia, impotence, increased libido, hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia and hyponatremia.
Gastrointestinal Effects
Anorexia, constipation, diarrhea, hypersalivation, dyspepsia, nausea and vomiting.
Autonomic Reactions
Dry mouth, blurred vision, urinary retention, diaphoresis and priapism.
Respiratory Effects
Laryngospasm, bronchospasm and increased depth of respiration.
Special Senses
Cataracts, retinopathy and visual disturbances.
Postmarketing Events
Hyperammonemia has been reported in a 5½ year old child with citrullinemia, an inherited disorder of ammonia excretion, following treatment with haloperidol.
Rhabdomyolysis has been reported. -
OVERDOSAGE:
While overdosage is less likely to occur with a parenteral than with an oral medication, information pertaining to haloperidol is presented, modified only to reflect the extended duration of action of haloperidol decanoate.
Manifestations
In general, the symptoms of overdosage would be an exaggeration of known pharmacologic effects and adverse reactions, the most prominent of which would be: 1) severe extrapyramidal reactions, 2) hypotension, or 3) sedation. The patient would appear comatose with respiratory depression and hypotension which could be severe enough to produce a shock-like state. The extrapyramidal reactions would be manifested by muscular weakness or rigidity and a generalized or localized tremor, as demonstrated by the akinetic or agitans types, respectively. With accidental overdosage, hypertension rather than hypotension occurred in a two-year old child. The risk of ECG changes associated with Torsades de Pointes should be considered.
(For further information regarding Torsades de Pointes, please refer to ADVERSE REACTIONS.)
Treatment
Since there is no specific antidote, treatment is primarily supportive. A patent airway must be established by use of an oropharyngeal airway or endotracheal tube or, in prolonged cases of coma, by tracheostomy. Respiratory depression may be counteracted by artificial respiration and mechanical respirators. Hypotension and circulatory collapse may be counteracted by use of intravenous fluids, plasma, or concentrated albumin, and vasopressor agents such as metaraminol, phenylephrine and norepinephrine. Epinephrine should not be used. In case of severe extrapyramidal reactions, antiparkinson medication should be administered, and should be continued for several weeks, and then withdrawn gradually as extrapyramidal symptoms may emerge. ECG and vital signs should be monitored especially for signs of QT-prolongation or dysrhythmias and monitoring should continue until the ECG is normal. Severe arrhythmias should be treated with appropriate anti-arrhythmic measures.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION:
Haloperidol decanoate injection should be administered by deep intramuscular injection. A 21 gauge needle is recommended. The maximum volume per injection site should not exceed 3 mL. DO NOT ADMINISTER INTRAVENOUSLY.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
Haloperidol decanoate injection is intended for use in schizophrenic patients who require prolonged parenteral antipsychotic therapy. These patients should be previously stabilized on antipsychotic medication before considering a conversion to haloperidol decanoate. Furthermore, it is recommended that patients being considered for haloperidol decanoate therapy have been treated with, and tolerate well, short-acting haloperidol in order to reduce the possibility of an unexpected adverse sensitivity to haloperidol. Close clinical supervision is required during the initial period of dose adjustment in order to minimize the risk of overdosage or reappearance of psychotic symptoms before the next injection. During dose adjustment or episodes of exacerbation of symptoms of schizophrenia, haloperidol decanoate therapy can be supplemented with short-acting forms of haloperidol.
The dose of haloperidol decanoate should be expressed in terms of its haloperidol content. The starting dose of haloperidol decanoate should be based on the patient’s age, clinical history, physical condition, and response to previous antipsychotic therapy. The preferred approach to determining the minimum effective dose is to begin with lower initial doses and to adjust the dose upward as needed. For patients previously maintained on low doses of antipsychotics (e.g., up to the equivalent of 10 mg/day oral haloperidol), it is recommended that the initial dose of haloperidol decanoate be 10 to 15 times the previous daily dose in oral haloperidol equivalents; limited clinical experience suggests that lower initial doses may be adequate.
Initial Therapy
Conversion from oral haloperidol to haloperidol decanoate can be achieved by using an initial dose of haloperidol decanoate that is 10 to 20 times the previous daily dose in oral haloperidol equivalents.
In patients who are elderly, debilitated, or stable on low doses of oral haloperidol (e.g., up to the equivalent of 10 mg/day oral haloperidol), a range of 10 to 15 times the previous daily dose in oral haloperidol equivalents is appropriate for initial conversion.
In patients previously maintained on higher doses of antipsychotics for whom a low dose approach risks recurrence of psychiatric decompensation and in patients whose long-term use of haloperidol has resulted in a tolerance to the drug, 20 times the previous daily dose in oral haloperidol equivalents should be considered for initial conversion, with downward titration on succeeding injections.
The initial dose of haloperidol decanoate should not exceed 100 mg regardless of previous antipsychotic dose requirements. If, therefore, conversion requires more than 100 mg of haloperidol decanoate as an initial dose, that dose should be administered in two injections, i.e., a maximum of 100 mg initially followed by the balance in 3 to 7 days.
Maintenance Therapy
The maintenance dosage of haloperidol decanoate must be individualized with titration upward or downward based on therapeutic response. The usual maintenance range is 10 to 15 times the previous daily dose in oral haloperidol equivalents dependent on the clinical response of the patient.
HALOPERIDOL DECANOATE DOSING RECOMMENDATIONS
Patients
Monthly
1st Month
Maintenance
Stabilized on low daily oral doses (up to 10 mg/day)
10 to 15 x Daily
Oral Dose
10 to 15 x Previous Daily
Oral Dose
Elderly or Debilitated
High dose
20 x Daily
Oral Dose
10 to 15 x Previous Daily
Oral Dose
Risk of relapse
Tolerant to oral haloperidol
Close clinical supervision is required during initiation and stabilization of haloperidol decanoate therapy. Haloperidol decanoate is usually administered monthly or every 4 weeks. However, variation in patient response may dictate a need for adjustment of the dosing interval as well as the dose (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY).
Clinical experience with haloperidol decanoate at doses greater than 450 mg per month has been limited.
-
HOW SUPPLIED:
Haloperidol decanoate injection is supplied as:
Product Code Unit of Sale Strength
PRX437101
NDC: 63323-471-41
One 1mL fill in a
2 mL flip-top vial100 mg* per mL
*as haloperidol
The above product is packaged individually.Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Do not refrigerate or freeze.
PROTECT FROM LIGHT.
Keep in carton until empty.
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY - Haloperidol Decanoate Injection 1 mL Vial Label
NDC: 63323-471-41 PRX437101
Haloperidol
Decanoate
Injection100 mg* per mL
Intramuscular Use Only
1 mL Rx only
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY - Haloperidol Decanoate Injection 1 mL Vial Carton Panel
NDC: 63323-471-41 PRX437101
Haloperidol
Decanoate
Injection100 mg* per mL
*as haloperidol
Intramuscular Use Only
1 mL
Rx only
Sterile
Keep in carton until empty

-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
HALOPERIDOL DECANOATE
haloperidol decanoate injectionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 63323-471 Route of Administration INTRAMUSCULAR Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength HALOPERIDOL DECANOATE (UNII: AC20PJ4101) (HALOPERIDOL - UNII:J6292F8L3D) HALOPERIDOL 100 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SESAME OIL (UNII: QX10HYY4QV) BENZYL ALCOHOL (UNII: LKG8494WBH) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 63323-471-41 1 in 1 CARTON 07/12/2000 1 1 mL in 1 VIAL; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA074893 07/12/2000 Labeler - Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC (608775388) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC 023648251 MANUFACTURE(63323-471)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.