TRIAMCINOLONE ACETONIDE spray, metered
Triamcinolone Acetonide by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Triamcinolone Acetonide by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by MedVantx, Inc., TEVA Pharmaceuticals USA Inc, Blenheim Pharmacal, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Triamcinolone Acetonide Nasal Spray safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Triamcinolone Acetonide Nasal Spray.
Triamcinolone Acetonide Nasal Spray
For intranasal use only. Shake Well Before Using.
Initial U.S. Approval: 1957INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- Triamcinolone Acetonide Nasal Spray is a corticosteroid indicated for treatment of nasal symptoms of seasonal and perennial allergic rhinitis in adults and children 6 years of age and older. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Adults and adolescents ≥12 years: Starting and maximum dose is 220 mcg/day (two sprays in each nostril once daily). (2.1)
- Children 6 to 12 years of age: Starting dose is 110 mcg/day (one spray in each nostril once daily). Maximum dose is 220 mcg/day (two sprays per nostril once daily). (2.2)
- Priming/Use: Shake well before each use. Before using for the first time, release 5 sprays into the air away from the face. If the product is not used for more than 2 weeks, release 1 spray into the air before using. (2.3)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- Nasal Spray: 55 mcg triamcinolone acetonide in each spray. Supplied in 16.5 g bottle containing 120 actuations. Each 120 actuation bottle contains 9.075 mg triamcinolone acetonide. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Do not administer to patients with history of hypersensitivity to triamcinolone acetonide or any ingredients of this product. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Epistaxis, nasal septal perforation, Candida albicans infection, impaired wound healing. Monitor patients periodically for signs of adverse effects on the nasal mucosa. Avoid use in patients with recent nasal septal ulcers, nasal surgery, or trauma. (5.1)
- Development of glaucoma or posterior subcapsular cataracts. Monitor patients closely with a change in vision or with a history of increased intraocular pressure, glaucoma, and/or cataracts. (5.2)
- Potential worsening of existing tuberculosis; fungal, bacterial, viral, or parasitic infections; or ocular herpes simplex. More serious or even fatal course of chickenpox or measles in susceptible patients. Use caution in patient with the above because of the potential for worsening of these infections. (5.3)
- Hypercorticism and adrenal suppression with very high dosages or at the regular dosage in susceptible individuals. If such changes occur, discontinue triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray slowly. (5.4)
- Potential reduction in growth velocity in children. Monitor growth routinely in pediatric patients receiving triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray. (5.5, 8.4)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
- Most common adverse reactions (>2% incidence) were pharyngitis, epistaxis, flu syndrome, cough increased, bronchitis, dyspepsia, tooth disorder, headache, pharyngolaryngeal pain, nasopharyngitis, abdominal upper pain, diarrhea, and excoriation. (6.1)
- Other adverse reactions, including serious adverse reactions, have been reported. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact TEVA USA, PHARMACOVIGILANCE at 1-888-838-2872 X6351 ordrug.safety@tevausa.com or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Triamcinolone acetonide should be used during pregnancy only if potential benefit justifies potential risk to fetus. (8.1)
Labeling describing use of triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray in pediatric patients 2 to 5 years of age is approved for Sanofi-Aventis U.S. Inc.’s Nasacort® AQ Nasal Spray. However, due to Sanofi-Aventis U.S. Inc.’s marketing exclusivity rights, a description of that use is not approved for this triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray labeling.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 8/2009
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Adults and Adolescents 12 Years of Age and Older
2.2 Children 6 to 12 Years of Age
2.3 Administration Information
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Local Nasal Effects
5.2 Glaucoma and Cataracts
5.3 Immunosuppression
5.4 Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis Effects
5.5 Effect on Growth
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Post-Marketing Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
16.2 Storage
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
17.1 Local Nasal Effects
17.2 Cataracts and Glaucoma
17.3 Immunosuppression
17.4 Use Daily for Best Effect
17.5 Keep Spray Out of Eyes
17.6 Patient Package Information
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Triamcinolone Acetonide Nasal Spray is indicated for the treatment of the nasal symptoms of seasonal and perennial allergic rhinitis in adults and children 6 years of age and older.
Labeling describing use of triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray in pediatric patients 2 to 5 years of age is approved for Sanofi-Aventis U.S. Inc.’s Nasacort® AQ Nasal Spray. However, due to Sanofi-Aventis U.S. Inc.’s marketing exclusivity rights, a description of that use is not approved for this triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray labeling.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Administer Triamcinolone Acetonide Nasal Spray by the intranasal route only. Shake Triamcinolone Acetonide Nasal Spray well before each use.
2.1 Adults and Adolescents 12 Years of Age and Older
The recommended starting and maximum dose is 220 mcg per day as two sprays in each nostril once daily. Titrate an individual patient to the minimum effective dose to reduce the possibility of side effects. When the maximum benefit has been achieved and symptoms have been controlled, reducing the dose to 110 mcg per day (one spray in each nostril once a day) has been shown to be effective in maintaining control of the allergic rhinitis symptoms.
2.2 Children 6 to 12 Years of Age
Children 6 to 12 years of Age
The recommended starting dose is 110 mcg per day given as one spray in each nostril once daily. Children not responding adequately to 110 mcg per day may use 220 mcg (2 sprays in each nostril) once daily. Once symptoms have been controlled, the dosage may be decreased to 110 mcg once daily.
Labeling describing additional dosing of triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray in pediatric patients 2 to 5 years of age is approved for Sanofi-Aventis U.S. Inc.’s Nasacort® AQ Nasal Spray. However, due to Sanofi-Aventis U.S. Inc.’s marketing exclusivity rights, a description of that dosing is not approved for this triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray labeling.
Triamcinolone Acetonide Nasal Spray is not recommended for children under 2 years of age.
2.3 Administration Information
Priming
Prime Triamcinolone Acetonide Nasal Spray before using for the first time by shaking the contents well and releasing 5 sprays into the air away from the face. It will remain adequately primed for two weeks. If the product is not used for more than 2 weeks, then it can be adequately reprimed with one spray. Shake Triamcinolone Acetonide Nasal Spray well before each use.
If adequate relief of symptoms has not been obtained after 3 weeks of treatment, Triamcinolone Acetonide Nasal Spray should be discontinued. [see Warnings and Precautions (5), Patient Counseling Information (17), and Adverse Reactions (6)]
-
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray is a metered-dose pump spray containing the active ingredient triamcinolone acetonide. Each actuation delivers 55 mcg triamcinolone acetonide from the nasal actuator after an initial priming of 5 sprays. Each 16.5 gram bottle (120 actuations) contains 9.075 mg of triamcinolone acetonide. The bottle should be discarded when the labeled- number of actuations have been reached even though the bottle is not completely empty.
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Local Nasal Effects
Epistaxis
In clinical studies of 2 to 12 weeks duration, epistaxis was observed more frequently in patients treated with triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray than those who received placebo [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
Nasal Septal Perforation
In clinical trials, nasal septum perforation was reported in one adult patient treated with triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray.
Candida Infection
In clinical studies with triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray, the development of localized infections of the nose and pharynx with Candida albicans has rarely occurred. When such an infection develops it may require treatment with appropriate local or systemic therapy and discontinuation of triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray. Therefore, patients using triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray over several months or longer should be examined periodically for evidence of Candida infection or other signs of adverse effects on the nasal mucosa.
5.2 Glaucoma and Cataracts
Nasal and inhaled corticosteroids may result in the development of glaucoma and/or cataracts. Therefore, close monitoring is warranted in patients with a change in vision or with a history of increased intraocular pressure, glaucoma and/or cataracts.
5.3 Immunosuppression
Persons who are using drugs that suppress the immune system are more susceptible to infections than healthy individuals. Chickenpox and measles, for example, can have a more serious or even fatal course in susceptible children or adults using corticosteroids. In children or adults who have not had these diseases or have not been properly immunized, particular care should be taken to avoid exposure. How the dose, route, and duration of corticosteroid administration affect the risk of developing a disseminated infection is not known. The contribution of the underlying disease and/or prior corticosteroid treatment to the risk is also not known. If exposed to chickenpox, prophylaxis with varicella zoster immune globulin (VZIG) may be indicated. If exposed to measles, prophylaxis with pooled intramuscular immunoglobulin (IG) may be indicated. (see the respective package inserts for complete VZIG and IG prescribing information.) If chickenpox develops, treatment with antiviral agents may be considered.
Corticosteroids should be used with caution, if at all, in patients with active or quiescent tuberculosis infections of the respiratory tract; untreated local or systemic fungal or bacterial infections; systemic viral or parasitic infections, or ocular herpes simplex because of the potential for worsening of these infections.
5.4 Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis Effects
Hypercorticism and Adrenal Suppression
When intranasal steroids are used at higher than recommended dosages or in susceptible individuals at recommended dosages, systemic corticosteroid effects such as hypercorticism and adrenal suppression may appear. If such changes occur, the dosage of triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray should be discontinued slowly, consistent with accepted procedures for discontinuing oral corticosteroid therapy. The replacement of a systemic corticosteroid with a topical corticosteroid can be accompanied by signs of adrenal insufficiency. In addition, some patients may experience symptoms of corticosteroid withdrawal, e.g., joint and/or muscular pain, lassitude, and depression. Patients previously treated for prolonged periods with systemic corticosteroids and transferred to topical corticosteroids should be carefully monitored for acute adrenal insufficiency in response to stress. In those patients who have asthma or other clinical conditions requiring long-term systemic corticosteroid treatment, rapid decreases in systemic corticosteroid dosages may cause a severe exacerbation of their symptoms.
5.5 Effect on Growth
Corticosteroids may cause a reduction in growth velocity when administered to pediatric patients. Monitor the growth routinely of pediatric patients receiving triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray. To minimize the systemic effects of intranasal corticosteroids, including triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray, titrate each patient’s dose to the lowest dosage that effectively controls his/her symptoms [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
Systemic and local corticosteroid use may result in the following:
- Epistaxis, Candida albicans infection, nasal septal perforation, impaired wound healing [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Glaucoma and Cataracts [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Immunosuppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis effects, including growth reduction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4, 5.5), Use in Specific Populations (8.4)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
In placebo-controlled, double-blind, and open-label clinical studies, 1483 adults and children 12 years and older received treatment with triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray. These patients were treated for an average duration of 51 days. In the controlled trials (2-5 weeks duration) from which the following adverse reaction data are derived, 1394 patients were treated with triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray for an average of 19 days. In a long-term, open-label study, 172 patients received treatment for an average duration of 286 days. Adverse reactions from 12 studies in adults and adolescent patients 12 to 17 years of age receiving triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray 27.5 mcg to 440 mcg once daily are summarized in Table 1.
In clinical trials, nasal septum perforation was reported in one adult patient who received triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray.
Table 1 - Adverse drug reactions > 2% and greater than placebo with triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray 220 mcg treatment in studies in adults and adolescents 12 years and older Coding dictionary for adverse events is Coding Symbols for Thesaurus of Adverse Reaction Terms (COSTART). Placebo
(N=962)Triamcinolone Acetonide
220 mcg
(N=857)Adverse reaction % % Pharyngitis 3.6 5.1 Epistaxis 0.8 2.7 Cough increased 1.5 2.1 A total of 602 children 6 to 12 years of age were studied in 3 double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials. Of these, 172 received 110 mcg/day and 207 received 220 mcg/day of triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray for two, six, or twelve weeks. The longest average durations of treatment for patients receiving 110 mcg/day and 220 mcg/day were 76 days and 80 days, respectively. One percent of patients treated with triamcinolone acetonide were discontinued due to adverse experiences. No patient receiving 110 mcg/day and one patient receiving 220 mcg/day discontinued due to a serious adverse event. A similar adverse reaction profile was observed in pediatric patients 6 to 12 years of age as compared to adolescents and adults with the exception of epistaxis which occurred in less than 2% of the children studied. Adverse reactions from 2 studies in children 4 to 12 years of age receiving triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray 110 mcg once daily are summarized in Table 2.
Table 2 - Adverse drug reactions > 2% and greater than placebo with triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray 110 mcg treatment in US studies in patients 4 to 12 years of age Coding dictionary for adverse events is Coding Symbols for Thesaurus of Adverse Reaction Terms (COSTART). Placebo
(N=202)Triamcinolone Acetonide
110 mcg
(N=179)Adverse reaction % % Flu syndrome 7.4 8.9 Cough increased 6.4 8.4 Pharyngitis 6.4 7.8 Bronchitis 1 3.4 Dyspepsia 1 3.4 Tooth disorder 1 3.4 Labeling describing adverse events of triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray in pediatric patients 2 to 5 years of age is approved for Sanofi-Aventis U.S. Inc.’s Nasacort® AQ Nasal Spray. However, due to Sanofi-Aventis U.S. Inc.’s marketing exclusivity rights, a description of those adverse events is not approved for this triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray labeling.
In the event of accidental overdose, an increased potential for these adverse experiences may be expected, but acute systemic adverse experiences are unlikely. [see Overdosage (10)]
6.2 Post-Marketing Experience
In addition to the adverse drug reactions reported during clinical studies and listed above, the following adverse events have been identified during post-approval use of triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray. Because these events are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. Events that have been reported during post-marketing experience include: nasal discomfort and congestion, sneezing, alterations of taste and smell, nausea, insomnia, dizziness, fatigue, dyspnea, decreased blood cortisol, cataract, glaucoma, increased ocular pressure, pruritus, rash, and hypersensitivity.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects: Pregnancy Category C
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray in pregnant women. Triamcinolone acetonide was teratogenic in rats, rabbits, and monkeys. Triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray, like other corticosteroids, should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. Since their introduction, experience with oral corticosteroids in pharmacologic as opposed to physiologic doses suggests that rodents are more prone to teratogenic effects from corticosteroids than humans. In addition, because there is a natural increase in glucocorticoid production during pregnancy, most women will require a lower exogenous corticosteroid dose and many will not need corticosteroid treatment during pregnancy.
In reproduction studies in rats and rabbits, triamcinolone acetonide administered by inhalation produced cleft palate and/or internal hydrocephaly and axial skeletal defects at exposures less than and 2 times, respectively, the maximum recommended daily intranasal dose in adults on a mcg/m2 basis. In a monkey reproduction study, triamcinolone acetonide administered by inhalation produced cranial malformations at an exposure approximately 37 times the maximum recommended daily intranasal dose in adults on a mcg/m2 basis.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether triamcinolone acetonide is excreted in human milk. Because other corticosteroids are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray is administered to nursing women.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray has been evaluated in 518 children 6 to 12 years of age, and 176 adolescents 12 to 17 years of age [see Clinical Studies (14)]. The safety and effectiveness of triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray in children below 2 years of age have not been established.
Labeling describing use of triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray in pediatric patients 2 to 5 years of age is approved for Sanofi-Aventis U.S. Inc.’s Nasacort® AQ Nasal Spray. However, due to Sanofi-Aventis U.S. Inc.’s marketing exclusivity rights, a description of that use is not approved for this triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray labeling.
Controlled clinical studies have shown that intranasal corticosteroids may cause a reduction in growth velocity in pediatric patients. This effect has been observed in the absence of laboratory evidence of HPA axis suppression, suggesting that growth velocity is a more sensitive indicator of systemic corticosteroid exposure in pediatric patients than some commonly used tests of HPA axis function. The long-term effects of reduction in growth velocity associated with intranasal corticosteroids, including the impact of final adult height are unknown. The potential for “catch-up” growth following discontinuation of treatment with intranasal corticosteroids has not been adequately studied. The growth of pediatric patients receiving intranasal corticosteroids, including triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray, should be monitored routinely (e.g., via stadiometry). The potential growth effects of prolonged treatment should be weighed against the clinical benefits obtained and the risks/benefits of treatment alternatives. To minimize the systemic effects of intranasal corticosteroids, including triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray, each patient’s dose should be titrated to the lowest dosage that effectively controls his/her symptoms.
The potential for triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray to cause growth suppression in susceptible patients and when given at higher than recommended dosages cannot be ruled out.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of triamcinolone acetonide did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
Chronic overdosage may result in signs/symptoms of hypercorticism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]. There are no data on the effects of acute or chronic overdosage with triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray. Because of low systemic bioavailability and an absence of acute drug-related systemic findings in clinical studies overdose is unlikely to require any therapy other than observation.
Acute overdosing with the intranasal dosage form is unlikely in view of the total amount of active ingredient present and low bioavailability of triamcinolone acetonide. In the event that the entire contents of the bottle were administered all at once, via either oral or nasal application, clinically significant systemic adverse events would most likely not result.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Triamcinolone acetonide, USP, the active ingredient in Triamcinolone Acetonide Nasal Spray, is a corticosteroid with the chemical designation 9-Fluoro-11ß,16α,17,21-tetrahydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione cyclic 16,17-acetal with acetone.
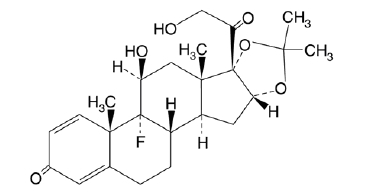
C24H31FO6 M.W. 434.51
Triamcinolone Acetonide Nasal Spray is a thixotropic, water-based, metered-dose pump spray formulation unit containing a microcrystalline suspension of triamcinolone acetonide in an aqueous medium. Inactive ingredients are benzalkonium chloride, carboxymethylcellulose sodium, dextrose anhydrous, edetate disodium dihydrate, microcrystalline cellulose and polysorbate 80. Hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide may be added to adjust the pH to a target of 5.0 within a range of 4.5 and 6.0.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Triamcinolone acetonide is a synthetic fluorinated corticosteroid with approximately 8 times the potency of prednisone in animal models of inflammation.
Although the precise mechanism of corticosteroid antiallergic action is unknown, corticosteroids have been shown to have a wide range of actions on multiple cell types (e.g., mast cells, eosinophils, neutrophils, macrophages, lymphocytes) and mediators (e.g., histamine, eicosanoids, leukotrienes, cytokines) involved in inflammation.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
In order to determine if systemic absorption plays a role in the effect of triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray on allergic rhinitis symptoms, a two week double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study was conducted comparing triamcinolone acetonide, orally ingested triamcinolone acetonide, and placebo in 297 adult patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis. The study demonstrated that the therapeutic efficacy of triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray can be attributed to the topical effects of triamcinolone acetonide.
Adrenal Function
In order to evaluate the effects of systemic absorption on the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal (HPA) axis, 3 clinical studies, one each in adults and in children 6 to 12 years of age and 2 to 5 years of age, were conducted.
The adult clinical study compared 220 mcg or 440 mcg triamcinolone acetonide per day, or 10 mg prednisone per day with placebo for 42 days. Adrenal response to a six-hour 250 mcg cosyntropin stimulation test showed that triamcinolone acetonide administered at doses of 220 mcg and 440 mcg had no statistically significant effect on HPA activity versus placebo. Conversely, oral prednisone at 10 mg/day significantly reduced the response to ACTH.
A study evaluating plasma cortisol response thirty and sixty minutes after 250 mcg cosyntropin stimulation in 80 pediatric patients 6 to 12 years of age who received 220 mcg or 440 mcg (twice the maximum recommended daily dose) daily for six weeks was conducted. No abnormal response to cosyntropin infusion (peak serum cortisol <18 mcg/dL) was observed in any pediatric patient after six weeks of dosing with triamcinolone acetonide at 440 mcg per day.
In pediatric patients 2 to 5 years of age, HPA axis assessment was performed; however, the results were inconclusive and an effect of triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray on adrenal function in children 2 to 5 years of age cannot be ruled out.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Based upon intravenous dosing of triamcinolone acetonide phosphate ester in adults, the half-life of triamcinolone acetonide was reported to be 88 minutes. The volume of distribution (Vd) reported was 99.5 L (SD ± 27.5) and clearance was 45.2 L/hour (SD ± 9.1) for triamcinolone acetonide. The plasma half-life of corticosteroids does not correlate well with the biologic half-life.
Pharmacokinetic characterization of the triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray formulation was determined in both normal adult subjects and patients with allergic rhinitis. Single dose intranasal administration of 220 mcg of triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray in normal adult subjects and patients demonstrated minimal absorption of triamcinolone acetonide. The mean peak plasma concentration was approximately 0.5 ng/mL (range: 0.1 to 1 ng/mL) and occurred at 1.5 hours post dose. The mean plasma drug concentration was less than 0.06 ng/mL at 12 hours, and below the assay detection limit (the minimum LOQ of the assay was 0.025 ng/mL) at 24 hours. The average terminal half-life was 3.1 hours. The range of mean AUC0–∞ values was 1.4 nghr/mL to 4.7 nghr/mL between doses of 110 mcg to 440 mcg in both patients and healthy volunteers. Dose proportionality was demonstrated in both normal adult subjects and in allergic rhinitis patients following single intranasal doses of 110 mcg or 220 mcg triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray. The Cmax and AUC0-∞ of the 440 mcg dose increased less than proportionally when compared to 110 and 220 mcg doses.
Following multiple dose administration of triamcinolone acetonide 440 mcg once daily in pediatric patients 6 to 12 years of age, plasma drug concentrations, AUC0-∞, Cmax and Tmax were similar to those values observed in adult patients receiving the same dose.
Labeling describing additional pharmacokinetics in pediatric patients 2 to 5 years of age treated with triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray is approved for Sanofi-Aventis U.S. Inc.’s Nasacort® AQ Nasal Spray. However, due to Sanofi-Aventis U.S. Inc.’s marketing exclusivity rights, a description of that pharmacokinetic information is not approved for this triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray labeling.
In animal studies using rats and dogs, three metabolites of triamcinolone acetonide have been identified. They are 6β-hydroxytriamcinolone acetonide, 21-carboxytriamcinolone acetonide and 21-carboxy-6β-hydroxytriamcinolone acetonide. All three metabolites are expected to be substantially less active than the parent compound due to (a) the dependence of anti-inflammatory activity on the presence of a 21-hydroxyl group, (b) the decreased activity observed upon 6-hydroxylation, and (c) the markedly increased water solubility favoring rapid elimination. There appeared to be some quantitative differences in the metabolites among species. No differences were detected in metabolic pattern as a function of route of administration.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In a two-year study in rats, triamcinolone acetonide caused no treatment-related carcinogenicity at oral doses up to 1 mcg/kg (less than the maximum recommended daily intranasal dose in adults and children on a mcg/m2 basis, respectively). In a two-year study in mice, triamcinolone acetonide caused no treatment-related carcinogenicity at oral doses up to 3 mcg/kg (less than the maximum recommended daily intranasal dose in adults and children on a mcg/m2 basis, respectively).
No evidence of mutagenicity was detected from in vitro tests (a reverse mutation test in Salmonella bacteria and a forward mutation test in Chinese hamster ovary cells) conducted with triamcinolone acetonide.
In male and female rats, triamcinolone acetonide caused no change in pregnancy rate at oral doses up to 15 mcg/kg (less than the maximum recommended daily intranasal dose in adults on a mcg/m2 basis). Triamcinolone acetonide caused increased fetal resorptions and stillbirths and decreases in pup weight and survival at doses of 5 mcg/kg and above (less than the maximum recommended daily intranasal dose in adults on a mcg/m2 basis). At 1 mcg/kg (less than the maximum recommended daily intranasal dose in adults on a mcg/m2 basis), it did not induce the above mentioned effects.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Triamcinolone acetonide was teratogenic in rats, rabbits, and monkeys. In rats, triamcinolone acetonide was teratogenic at inhalation doses of 20 mcg/kg and above (approximately 7/10 of the maximum recommended daily intranasal dose in adults on a mcg/m2 basis). In rabbits, triamcinolone acetonide was teratogenic at inhalation doses of 20 mcg/kg and above (approximately 2 times the maximum recommended daily intranasal dose in adults on a mcg/m2 basis). In monkeys, triamcinolone acetonide was teratogenic at an inhalation dose of 500 mcg/kg (approximately 37 times the maximum recommended daily intranasal dose in adults on a mcg/m2 basis). Dose-related teratogenic effects in rats and rabbits included cleft palate and/or internal hydrocephaly and axial skeletal defects, whereas the effects observed in the monkey were cranial malformations.
Hypoadrenalism may occur in infants born of mothers receiving corticosteroids during pregnancy. Such infants should be carefully observed.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The safety and efficacy of triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray have been evaluated in 10 double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical studies of two- to four-weeks duration in adults and children 12 years and older with seasonal or perennial allergic rhinitis. The number of patients treated with triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray in these studies was 1266; of these patients, 675 were males and 591 were females.
Overall, the results of these clinical studies in adults and children 12 years and older demonstrated that triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray 220 mcg once daily (2 sprays in each nostril), when compared to placebo, provides statistically significant relief of nasal symptoms of seasonal or perennial allergic rhinitis including sneezing, stuffiness, discharge, and itching.
The safety and efficacy of triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray, at doses of 110 mcg or 220 mcg once daily, have also been adequately studied in two double-blind, placebo-controlled studies of two- and twelve-weeks duration in children ages 6 through 12 years with seasonal and perennial allergic rhinitis. These studies included 341 males and 177 females. Triamcinolone acetonide administered at either dose resulted in statistically significant reductions in the severity of nasal symptoms of allergic rhinitis.
Labeling describing additional clinical studies of triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray in pediatric patients 2 to 5 years of age is approved for Sanofi-Aventis U.S. Inc.’s Nasacort® AQ Nasal Spray. However, due to Sanofi-Aventis U.S. Inc.’s marketing exclusivity rights, a description of those clinical studies is not approved for this triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray labeling.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
Triamcinolone Acetonide Nasal Spray, 55 mcg per spray, is supplied in a white high-density polyethylene container with a metered-dose pump unit, white nasal adapter, and patient instructions.
The contents of one 16.5 gram bottle provide 120 actuations. After 120 actuations, the amount of triamcinolone acetonide delivered per actuation may not be consistent and the unit should be discarded. Each actuation delivers 55 mcg triamcinolone acetonide from the nasal actuator after an initial priming of 5 sprays [see Administration Information (2.3)].
In the Patient Package Information, patients are provided with a check-off form to track usage [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
WARNING: KEEP THIS AND ALL MEDICATIONS OUT OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN.
Rx only
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-Approved Patient Labeling accompanying the product.
17.1 Local Nasal Effects
Patients should be informed that treatment with triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray may lead to adverse reactions, which include epistaxis and nasal ulceration. Candida infection may also occur with treatment with triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray. In addition, nasal corticosteroids are associated with nasal septal perforation and impaired wound healing. Patients who have experienced recent nasal ulcers, nasal surgery, or nasal trauma should not use triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray until healing has occurred [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
17.2 Cataracts and Glaucoma
Patients should be informed that glaucoma and cataracts are associated with nasal and inhaled corticosteroid use. Patients should inform his/her healthcare provider if a change in vision is noted while using triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
17.3 Immunosuppression
Patients who are on immunosuppressant doses of corticosteroids should be warned to avoid exposure to chickenpox or measles and, if exposed, to consult their physician without delay. Patients should be informed of potential worsening of existing tuberculosis, fungal, bacterial, viral or parasitic infections, or ocular herpes simplex [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
17.4 Use Daily for Best Effect
Patients should use triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray on a regular once-daily basis for optimal effect. It is also important to shake the bottle well before each use. Do not blow your nose for 15 minutes after using the spray. Triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray, like other corticosteroids, does not have an immediate effect on rhinitis symptoms. Although improvement in some patient symptoms may be seen within the first day of treatment, maximum benefit may not be reached for up to one week. The patient should not increase the prescribed dosage but should contact the physician if symptoms do not improve or if the condition worsens.
17.5 Keep Spray Out of Eyes
Patients should be informed to avoid spraying triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray in their eyes.
17.6 Patient Package Information
IMPORTANT: Please read these instructions carefully before using your triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray.
Manufactured In Israel By:
Perrigo Israel Pharmaceuticals Ltd.
Industrial Zone, Yeruham 80500, Israel
Manufactured For:
TEVA PHARMACEUTICALS USA
Sellersville, PA 18960
Iss. 10/2010
TRIAMCINOLONE ACETONIDE
Nasal SprayPatient Information
These instructions provide important information about triamcinolone acetonide. Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist if you have any questions.
Important: For use as a nasal spray only.
What is Triamcinolone Acetonide?
Triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray is a prescription medicine called a corticosteroid used to treat nasal symptoms of seasonal and year around allergies in adults and children 6 years of age and older. When triamcinolone acetonide is sprayed in your nose, this medicine helps to lessen the symptoms of sneezing, runny nose, nasal itching and stuffy nose.
Triamcinolone acetonide is not for children under the age of 2 years.
Who should use Triamcinolone Acetonide?
Do not use triamcinolone acetonide if you have had a reaction to triamcinolone acetonide or to any of the other ingredients in triamcinolone acetonide. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in triamcinolone acetonide.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before using Triamcinolone Acetonide?
Tell your healthcare provider if you are:
- pregnant or planning to become pregnant
- breast-feeding
- exposed to chickenpox or measles
- feeling unwell or have any symptoms that you do not understand
Tell your healthcare provider about all of the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
How do I use Triamcinolone Acetonide?
- Use triamcinolone acetonide exactly as your healthcare provider tells you.
- You will get the best results if you use triamcinolone acetonide regularly and without missing a dose. Do not take extra doses.
- Triamcinolone acetonide should be used as a nasal spray only. Do not spray it in your eyes or mouth.
- Your healthcare provider will tell you how and when to use triamcinolone acetonide. Do not use more triamcinolone acetonide or take it more often than your healthcare provider tells you.
- The prescription label will usually tell you how many sprays to take and how often. If it does not or if you are unsure, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
- For people aged 12 years and older, the usual dose is 2 sprays in each nostril, one time each day.
- For children aged 6 to 12 years, the usual dose is 1 spray in each nostril, one time each day. Your healthcare provider may tell you to take 2 sprays in each nostril one time each day.
- An adult should help a young child use this medicine.
Do not stop taking triamcinolone acetonide without telling your healthcare provider. Before you throw away triamcinolone acetonide, talk to your healthcare provider to see if you need another prescription. If your healthcare provider tells you to continue using triamcinolone acetonide, throw away the empty or expired bottle and use a new bottle of triamcinolone acetonide.
- For detailed instructions, see the “Patient Instructions for Use” at the end of this leaflet.
- Some symptoms may get better on the first day of treatment. It generally takes one week of use to feel the most benefit.
- Protect your eyes from the spray. If you get the spray in your eyes, rinse your eyes well with water.
- If your symptoms do not improve, or if they become worse, contact your healthcare provider.
- Tell your healthcare provider if you have irritation, burning or stinging inside your nose that does not go away when using triamcinolone acetonide.
What are the possible side effects of Triamcinolone Acetonide?
Common side effects of triamcinolone acetonide include:
Sore throat, headache, and nosebleeds. If you have an increase in nosebleeds after using triamcinolone acetonide or the inside of your nose hurts, contact your healthcare provider.
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
Patient Instructions for Use
Read these instructions carefully before using your triamcinolone acetonide.
Before using the spray pump bottle:
- Pull the cover and the clip off the spray pump unit. See figure A.
If the top part of the spray pump comes off of the bottle when removing the cover, then re-insert the stem back into the pump.
-
Figure A
- Shake the spray pump bottle before each use.
Priming the Spray Pump Bottle - Before using the spray pump bottle for the first time, it must be primed. To prime, put your thumb on the bottom of the bottle and your index and middle fingers on the “shoulders” of the bottle, and hold it upright. See figure B.
-

Figure B
- Point the bottle away from your eyes. Push the bottle up with your thumb and against your two fingers firmly and quickly until a fine spray appears. Do this pumping action 5 times.
Now your spray pump bottle is primed and ready for use.
A fine mist can only be made by a rapid and firm pumping action. - Repeat priming the pump, if it has not been used for more than 2 weeks. To reprime, shake the spray pump bottle and pump it just one time. Now the spray pump bottle is reprimed.
Using the spray: - Gently blow your nose to clear it, if needed. For small children, be sure to help them gently blow their nose, as much as possible.
- Pull off the cover and clip as shown in figure C. Shake the spray pump well.
-
Figure C
- Hold the spray pump firmly, with the index and middle finger on either side of the spray tip. Place your thumb on the bottom of the bottle. Be careful so that your fingers will not slip off the spray pump as you spray inside your nose. See figure D.
-
Figure D
- Put the spray tip into one side of your nose. The tip should not reach far into the nose. Rest the side of your index finger against your upper lip. Tip your head back a little and aim the spray toward the back of your nose. See figure E.
-

Figure E
- Press against the other side of your nose with your finger so the nostril is closed. Pump the spray bottle by pushing on the bottom of the bottle with your thumb firmly and quickly for the full dose of medicine. Sniff gently at the same time to help the medicine get to the back of your nose. See figure F. Repeat this step for the other side.
-
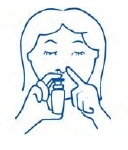
Figure F
- Repeat steps 8, 9 and 10 if your healthcare provider tells you to use more than one spray in each nostril.
- Do not blow your nose for 15 minutes after using the spray.
- After use, wipe the nozzle on the spray bottle with a clean tissue, and replace the blue cover.
- Keep the cover and the clip on the spray pump bottle when not in use.
Cleaning the spray pump bottle: - To clean the spray pump bottle, remove the cover and the spray nozzle only. Soak the cover and spray nozzle in warm water for a few minutes, and then rinse under cold water. See figure G.
-
Figure G
- Shake or tap off the excess water and allow to air dry. Once the cap and spray nozzle are dry, put the nozzle back onto the bottle, and prime the bottle as necessary until a fine mist is made. Use the spray as directed by your healthcare provider.
If the spray bottle does not work:
The hole in the tip of the nozzle may be blocked. Never try to unblock the spray hole or enlarge it with a pin or other sharp object. This will make the spray mechanism not work correctly. Changing the size of the opening can change the amount of medicine you or your child will receive. This could cause an overdose of the medicine. To clean nasal spray pump bottle, refer to Step 15.
Important information
Repriming the spray pump is only necessary when it has not been used for more than 2 weeks. To reprime, shake the bottle and only pump the spray bottle one time. Do not reprime if you use the spray more often than every two weeks.
Each triamcinolone acetonide bottle contains 120 doses of medicine plus a little extra for priming the pump. A check-off chart is included with your triamcinolone acetonide to help you keep track of the number of sprays. This will help make sure that you receive 120 sprays of triamcinolone acetonide.
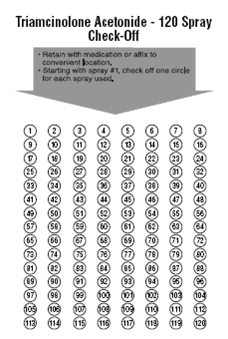
How should I store Triamcinolone Acetonide?
- Store triamcinolone acetonide between 68° to 77°F (20° to 25° C).
- After using 120 sprays, throw the medicine away, as directed by your healthcare provider, even if the bottle is not empty. You may not get enough medicine if you use the bottle after 120 sprays.
Keep triamcinolone acetonide and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of triamcinolone acetonide.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for conditions that are not mentioned in patient information. Do not use triamcinolone acetonide for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give triamcinolone acetonide to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
This leaflet summarizes the most important information about triamcinolone acetonide. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about triamcinolone acetonide that is written for health professionals.
For more information, call 1-800-227-7522.
What are the ingredients in Triamcinolone Acetonide Nasal Spray?
Active ingredient: triamcinolone acetonide
Inactive ingredients: benzalkonium chloride, carboxymethylcellulose sodium, dextrose anhydrous, edetate disodium dihydrate, microcrystalline cellulose and polysorbate 80. Hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide may be added to adjust the pH to a target of 5.0 within a range of 4.5 and 6.0.
Labeling describing the use of triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray in pediatric patients 2 to 5 years of age is approved for Sanofi-Aventis U.S. Inc.’s Nasacort® AQ Nasal Spray. However, due to Sanofi-Aventis U.S. Inc.’s marketing exclusivity rights, a description of that use is not approved for this triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray labeling.
Manufactured In Israel By:
Perrigo Israel Pharmaceuticals Ltd.
Industrial Zone, Yeruham 80500, Israel
Manufactured For:
TEVA PHARMACEUTICALS USA
Sellersville, PA 18960
Iss. 10/2010
11001739
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
TRIAMCINOLONE ACETONIDE
triamcinolone acetonide spray, meteredProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 66116-471(NDC: 0093-2085) Route of Administration NASAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength TRIAMCINOLONE ACETONIDE (UNII: F446C597KA) (TRIAMCINOLONE - UNII:1ZK20VI6TY) TRIAMCINOLONE ACETONIDE 55 ug Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength BENZALKONIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: F5UM2KM3W7) CARBOXYMETHYLCELLULOSE SODIUM (UNII: K679OBS311) ANHYDROUS DEXTROSE (UNII: 5SL0G7R0OK) EDETATE DISODIUM (UNII: 7FLD91C86K) CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) POLYSORBATE 80 (UNII: 6OZP39ZG8H) HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 66116-471-55 1 in 1 CARTON 1 120 in 1 BOTTLE, SPRAY Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA078104 04/06/2011 Labeler - MedVantx, Inc. (806427725) Registrant - TEVA Pharmaceuticals USA Inc (118234421) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Blenheim Pharmacal, Inc. 171434587 REPACK
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.
