ORBAX- orbifloxacin tablet, coated
Orbax by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Orbax by is a Animal medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., Bimeda, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION: Orbifloxacin is a synthetic broad-spectrum antibacterial agent from the class of fluoroquinolone carboxylic acid derivatives. Orbifloxacin is the international nonproprietary name for 1-cyclopropyl-5,6,8-trifluoro-1,4-dihydro-7-(cis-3,5-dimethyl- 1-piperazinyl)-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid. The chemical formula for orbifloxacin is C19H20F3N3O3 and its molecular weight is 395.38. The compound is slightly soluble in water; however, solubility increases in both acidic and alkaline conditions. The compound has two dissociation constants (pKa's): 5.95 and 9.01.
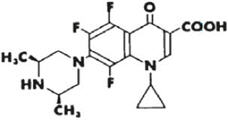
Figure 1. Chemical structure of orbifloxacin.
- INDICATIONS & USAGE
-
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
EFFICACY CONFIRMATION: Clinical efficacy was established in skin and soft tissue infections (wounds and abscesses) in the dog and cat, and urinary tract infections (cystitis) in the dog, associated with bacteria susceptible to orbifloxacin. Specific bacterial pathogens isolated in clinical field trials are listed in the MICROBIOLOGY section.
-
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION: For routine out-patient treatment of infection caused by a susceptible organism, in an otherwise healthy dog or cat, the dose of ORBAX® (orbifloxacin) Tablets is 2.5 to 7.5 mg/kg of body weight administered once daily. (See DRUG INTERACTIONS and TARGET ANIMAL SAFETY). In the cat, ORBAX® (orbifloxacin) Tablets and ORBAX® (orbifloxacin) Oral Suspension are not bioequivalent. On a mg/kg basis, ORBAX® (orbifloxacin) Oral Suspension provides lower and more variable plasma levels of orbifloxacin than ORBAX® (orbifloxacin) Tablets. The determination of dosage for any particular patient must take into consideration such factors as the severity and nature of the infection, the susceptibility of the causative organism, and the integrity of the patient's host-defense mechanisms. Antibiotic susceptibility of the pathogenic organism(s) should be determined prior to use of this preparation. Therapy with ORBAX® (orbifloxacin) Tablets may be initiated before results of these tests are known. Once results become available, continue with appropriate therapy.
For the treatment of skin and associated soft tissue infections, ORBAX® (orbifloxacin) Tablets should be given for two (2) to three (3) days beyond the cessation of clinical signs to a maximum of 30 days. For the treatment of urinary tract infections, ORBAX® (orbifloxacin) Tablets should be administered for at least 10 consecutive days. If no improvement is seen within five (5) days, the diagnosis should be re-evaluated and a different course of therapy considered.
To administer a total daily dose of 2.5 mg/kg, ORBAX® (orbifloxacin) Tablets may be dispensed as indicated in Table 1.
Table 1: Dose Table for ORBAX® (orbifloxacin) Tablets (2.5 mg/kg total daily dose) WEIGHT OF DOG/CAT (lbs) 5 10 20 30 40 50 60 90 120 No. of 22.7 mg tablets ½ 1 1½ 2 2½ No. of 68 mg tablets ½ 1 1½ 2 -
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Pharmacokinetics in healthy adult beagle dogs and healthy adult cats: In fasted animals, orbifloxacin is rapidly and almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract following oral administration. Absorption of orally administered orbifloxacin increases proportionately with dose (exhibits linear pharmacokinetics) up to 37.5 mg/kg when given daily for 30 days. The absolute bioavailability (F) of an oral dose is approximately 100%. Peak plasma concentrations are usually attained within 1 hour of administration. The effects of concomitant feeding on the absorption of orbifloxacin have not been studied. Divalent cations are generally known to diminish the absorption of fluoroquinolones. (See DRUG INTERACTIONS.) The relatively large volume of distribution at steady state (Vss) is indicative of a widespread distribution and penetration into body tissues. Within 24 hours of administration, approximately 40% of an oral dose was excreted into the urine unchanged in dogs with normal renal function. This supports the efficacy of orbifloxacin in the treatment of urinary tract infections. Based on the plasma elimination half-life and the dosing interval, negligible drug accumulation is expected with multiple dosing. Pharmacokinetic parameters estimated in a randomized two-period, two-sequence crossover study using single intravenous and oral doses are summarized in Tables 2 and 3 and Figures 2 and 3.
Table 2: Mean Pharmacokinetic Parameters Estimated in 12 Adult Beagle Dogs and 12 Adult Cats After a Single IV Bolus of Orbifloxacin at 2.5 mg/kg Pharmacokinetic Parameter Dog Estimate (SD) Cat Estimate (SD) Total body clearance, mL/min/kg 2.9 ± 0.2 4.09 ± 0.7 Volume of distribution at steady state, Vss (L/kg) 1.2 ± 0.2 1.3 ± 0.13 AUC 0 - ∞(µg∙h/mL) 14.3 ± 0.9 10.6 ± 2.4 Terminal plasma elimination half-life, t½ (hrs) 5.4 ± 1.1 4.5 ± 1.8 Table 3: Mean Pharmacokinetic Parameters Estimated in 12 Adult Beagle Dogs and 12 Adult Cats After a Single Oral Dose of Orbifloxacin at 2.5 mg/kg Pharmacokinetic Parameter Dog Estimate (SD) Cat Estimate (SD) Total body clearance/F, mL/min/kg 3.0 ± 0.2 3.98 ± 0.8 Maximum concentration, Cmax (µg/mL) 2.3 ± 0.3 2.06 ± 0.6 Time of maximum concentration, Tmax (minutes) 46 ± 27 60 ± 27 AUC 0 - ∞(µg∙h/mL) 14.3 ± 1.4 10.82 ± 2.6 Terminal plasma elimination half-life, t½ (hrs) 5.6 ± 1.1 5.52 ± 2.66 Plasma Concentration of Orbifloxacin vs. Time in Dogs
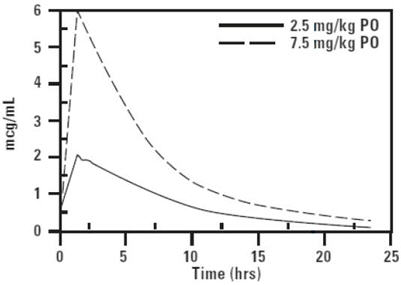
Figure 2. Mean plasma concentration of orbifloxacin vs. time in dogs (2.5 mg/kg = observed values, 7.5 mg/kg = extrapolated values).
Plasma Concentration of Orbifloxacin vs. Time in Cats
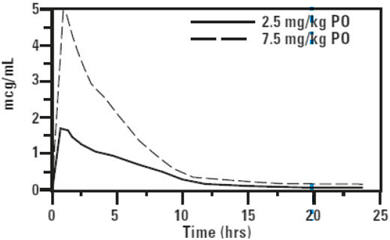
Figure 3. Mean plasma concentration of orbifloxacin vs. time in cats (2.5 mg/kg = normalized from an actual mean dose of 3.32 mg/kg; 7.5 mg/kg = extrapolated values).
MICROBIOLOGY: Orbifloxacin is bactericidal against a wide range of gram-negative and gram-positive organisms and exerts its antibacterial effect through interference with the bacterial enzyme DNA gyrase which is needed for the maintenance and synthesis of bacterial DNA. The minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of pathogens with the oral tablets isolated in multicentered clinical field trials performed in the United States were determined using Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) guidelines and are shown in Tables 4, 5, and 6.
Table 4: MIC Values* (µg/mL) of Orbifloxacin Against Urinary Pathogens Isolated Between 1994 and 1996 From Clinical Infections in Dogs Bacteria Name Number of Isolates MIC50 MIC90 MIC Range - * The correlation between the in vitro susceptibility data (MIC Values) and clinical response has not been determined.
- † There were an insufficient number of isolates to calculate the MIC50 or MIC90.
Staphylococcus pseudintermedius 5 † † 0.0975 - 0.39 Proteus mirabilis 19 0.78 1.56 0.048 - 1.56 Escherichia coli 35 0.0975 0.39 0.024 - ≥25 Enterococcus faecalis 5 † † 0.003 - 3.12 Table 5: MIC Values* (µg/mL) of Orbifloxacin Against Dermal Pathogens Isolated Between 1994 and 1996 From Clinical Infections of Dogs Bacteria Name Number of Isolates MIC50 MIC90 MIC Range - * The correlation between the in vitro susceptibility data (MIC Values) and clinical response has not been determined.
- † There were an insufficient number of isolates to calculate the MIC50 or MIC90.
Staphylococcus pseudintermedius 51 0.195 0.39 0.003 - 1.56 Staphylococcus aureus 8 † † 0.195 - ≥25 Coagulase +ve staphylococci 59 0.195 0.39 0.003 - ≥25 Pasteurella multocida 5 † 0 0.003 - 0.78 Proteus mirabilis 7 † † 0.39 - 1.56 Pseudomonas aeruginosa 14 3.125 12.5 0.39 - ≥25 Pseudomonas spp. 18 3.125 12.5 0.02 - ≥25 Klebsiella pneumonia 9 † † 0.0975 - 0.195 Escherichia coli 28 0.0975 0.39 0.012 - 6.25 Enterobacter spp. 24 0.0975 0.39 0.012 - 6.25 Citrobacter spp. 4 † † 0.024 - 0.0975 Enterococcus faecalis 11 † † 0.3 - ≥25 ß-hemolytic streptococci (Group G) 22 0.39 1.56 0.006 - 3.12 Streptococcus equisimilis 10 † † 0.003 - 0.78 Table 6: MIC Values* (µg/mL) of Orbifloxacin Against Dermal Pathogens Isolated Between 1994 and 1996 From Clinical Infections of Cats Bacteria Name Number of Isolates MIC50 MIC90 MIC Range - * The correlation between the in vitro susceptibility data (MIC Values) and clinical response has not been determined.
- † There were an insufficient number of isolates to calculate the MIC50 or MIC90.
Staphylococcus pseudintermedius 25 0.39 0.39 0.024 - 3.125 Staphylococcus aureus 7 † † 0.195 - 0.39 Coagulase +ve staphylococci 32 0.39 0.39 0.024 - 3.125 Pasteurella multocida 47 0.012 0.048 0.003 - 0.195 Pseudomonas aeruginosa 3 † † 0.39 - 3.125 Pseudomonas spp. 10 † † 0.195 - 6.25 Escherichia coli 17 0.048 0.195 0.024 - 25 Enterobacter spp. 12 † † 0.024 - 0.78 Enterococcus faecalis 10 † † 1.56 - 3.125 ß-hemolytic streptococci (Group G) 14 † † 0.006 - 1.56 -
DRUG INTERACTIONS
DRUG INTERACTIONS: Compounds (eg, sucralfate, antacids, and multivitamins) containing divalent and trivalent cations (eg, iron, aluminum, calcium, magnesium, and zinc) may substantially interfere with the absorption of quinolones resulting in a decrease in product bioavailability. Therefore, the concomitant oral administration of quinolones with foods, supplements, or other preparations containing these compounds should be avoided. The dosage of theophylline should be reduced when used concurrently with fluoroquinolones. Cimetidine has been shown to interfere with the metabolism of fluoroquinolones and should be used with care when used concurrently. Concurrent use of fluoroquinolones with oral cyclosporine is contraindicated. Concurrent administration of fluoroquinolones may increase the action of oral anticoagulants.
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS
CONTRAINDICATIONS: Orbifloxacin and other quinolones have been shown to cause arthropathy in immature animals of most species tested, the dog being particularly sensitive to this side effect. Orbifloxacin is contraindicated in immature dogs during the rapid growth phase (between 2 and 8 months of age in small and medium-sized breeds, and up to 18 months of age in large and giant breeds). Orbifloxacin is contraindicated in dogs and cats known to be hypersensitive to quinolones.
-
PRECAUTIONS
PRECAUTIONS: Prescribing antibacterial drugs in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection is unlikely to provide benefit to treated animals and may increase the risk of the development of drug-resistant animal pathogens.
The use of fluoroquinolones in cats has been reported to adversely affect the retina. Such products should be used with caution in cats. Blindness has also been reported post-approval in cats. In some cases, blindness has been temporary. DO NOT EXCEED 3.4 mg/lb (7.5 mg/kg) BODY WEIGHT PER DAY IN CATS.
Quinolones should be used with caution in animals with known or suspected central nervous system (CNS) disorders. In such animals, quinolones have, in rare instances, been associated with CNS stimulation which may lead to convulsive seizures. Quinolones have been shown to produce erosions of cartilage of weight-bearing joints and other signs of arthropathy in immature animals of various species.
Administer orbifloxacin with caution in the presence of hepatic insufficiency/ impairment. The safety of orbifloxacin in animals that are used for breeding or that are pregnant and/or lactating has not been demonstrated.
-
WARNINGS
WARNINGS: For use in animals only. Do not exceed 7.5 mg/kg body weight per day in cats. Keep out of the reach of children.
Avoid contact with eyes. In case of contact, immediately flush eyes with copious amounts of water for 15 minutes. In case of dermal contact, wash skin with soap and water. Consult a physician if irritation persists following ocular or dermal exposure. Individuals with a history of hypersensitivity to quinolones should avoid this product. In humans, there is a risk of user photosensitization within a few hours after excessive exposure to quinolones. If excessive accidental exposure occurs, avoid direct sunlight.
-
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
TARGET ANIMAL SAFETY: Orbifloxacin administered to young, clinically healthy, adult dogs and cats at doses of 7.5 mg/kg, 22.5 mg/kg, and 37.5 mg/kg for 30 consecutive days was well tolerated. At the exaggerated doses of 22.5 and 37.5 mg/kg/day, orbifloxacin caused mild gastrointestinal effects (soft feces) in both male and female cats. Emesis (males only), diarrhea (males only), reduced food consumption with subsequent reduced body weight were evident in cats administered ORBAX® (orbitfloxacin) Tablets at 75 mg/kg/day for 10 days. Orbifloxacin and other quinolones have been shown to cause arthropathy in immature animals of most species tested, the dog being particularly sensitive to this side effect. In 8- to 10-week-old beagle puppies dosed daily with orbifloxacin for 30 days, microscopic lesions consistent with fluoroquinolone-induced arthropathy of the articular cartilage was seen in only one of eight dogs dosed at 12.5 mg/kg, and in all eight dogs dosed at 25 mg/kg. (See CONTRAINDICATIONS.) No arthropathy was noted in 12-week-old kittens administered orbifloxacin at doses as high as 25 mg/kg for 1 month.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONS: In clinical trials, when the drug was administered at 2.5 mg/ kg/day, no drug-related adverse reactions were reported.
Post Approval Experience with ORBAX® (orbifloxacin) Tablets (Rev. 2010): The following adverse events are based on postapproval adverse drug experience reporting with ORBAX® (orbifloxacin) Tablets. Not all adverse reactions are reported to FDA CVM. It is not always possible to reliably estimate the adverse event frequency or establish a causal relationship to product exposure using this data. The following adverse events are listed in decreasing order of reporting frequency:
CAT: Blindness, mydriasis, anorexia, ataxia, depression/lethargy, vomiting, convulsions, abnormal retina, hypersalivation. In some cases, blindness has been temporary.
DOG: Vomiting, convulsions, depression/lethargy, anorexia.
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
HOW SUPPLIED
HOW SUPPLIED: ORBAX® (orbifloxacin) Tablets are available in the following presentations:
22.7 mg: Bottles of 250 green, E-Z Break, single-scored tablets NDC: 0061-1141-01 68 mg: Bottles of 100 blue, E-Z Break, single-scored tablets NDC: 0061-1174-01 -
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
For technical assistance or to report a suspected adverse reaction call 1-800-224-5318.
Made in USA
Intervet Inc (d/b/a Merck Animal Health)
Summit, NJ 07901© 1997, 2010, 2014 Intervet Inc. a subsidiary of Merck & Co.
All rights reserved.For patent information:
http://www.merck.com/product/patent/home.html. -
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL- 22.7 mg Tablet Bottle Label
250 Tablets 22.7 mg
NDC 0061-1141-01
ORBAX®
(orbifloxacin)Tablets for Dogs and Cats Only
Caution: Federal law restricts this drug to use
by or on the order of a licensed veterinarian.Federal law prohibits the extra label use
of this drug in food-producing animals.NADA #141-081, Approved by FDA.
MERCK
Animal Health
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL- 68 mg Tablet Bottle Label
100 Tablets 68 mg
NDC 0061-1174-01
ORBAX®
(orbifloxacin)Tablets for Dogs and Cats Only
Caution: Federal law restricts this drug to use
by or on the order of a licensed veterinarian.Federal law prohibits the extra label use
of this drug in food-producing animals.NADA #141-081, Approved by FDA.
MERCK
Animal Health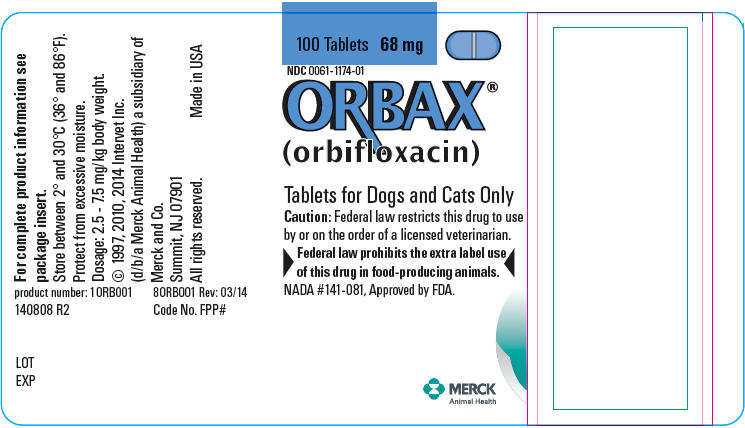
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
ORBAX
orbifloxacin tablet, coatedProduct Information Product Type PRESCRIPTION ANIMAL DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0061-1141 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Orbifloxacin (UNII: 660932TPY6) (Orbifloxacin - UNII:660932TPY6) Orbifloxacin 22.7 mg Product Characteristics Color GREEN Score 2 pieces Shape OVAL Size 14mm Flavor Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0061-1141-01 250 in 1 BOTTLE Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NADA NADA141081 04/22/1997 ORBAX
orbifloxacin tablet, coatedProduct Information Product Type PRESCRIPTION ANIMAL DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0061-1174 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Orbifloxacin (UNII: 660932TPY6) (Orbifloxacin - UNII:660932TPY6) Orbifloxacin 68 mg Product Characteristics Color BLUE Score 2 pieces Shape OVAL Size 20mm Flavor Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0061-1174-01 100 in 1 BOTTLE Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NADA NADA141081 04/22/1997 Labeler - Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. (001317601) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Bimeda, Inc. 060492923 MANUFACTURE
Trademark Results [Orbax]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 ORBAX 75070881 2164405 Live/Registered |
INTERVET INC. 1996-03-11 |
 ORBAX 73392839 1256727 Dead/Cancelled |
Maivald; Olga 1982-09-29 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.