FESOTERODINE FUMARATE tablet, film coated, extended release
fesoterodine fumarate by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
fesoterodine fumarate by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Zydus Lifesciences Limited. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use fesoterodine fumarate safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for fesoterodine fumarate.
FESOTERODINE fumarate extended-release tablets for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2008
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets are a muscarinic antagonist indicated for the treatment of overactive bladder with symptoms of urge urinary incontinence, urgency, and frequency. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The recommended starting dose of fesoterodine fumarate is 4 mg once daily. Based upon individual response and tolerability, the dose may be increased to 8 mg once daily. (2)
The daily dose of fesoterodine fumarate should not exceed 4 mg in the following populations:
- Patients with severe renal impairment (CLCR < 30 mL/min) (2)
- Patients taking potent CYP3A4 inhibitors, such as ketoconazole, itraconazole, and clarithromycin. (2)
Fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets are not recommended for use in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C). (2)
Fesoterodine fumarate should be taken with liquid and swallowed whole. Fesoterodine fumarate can be administered with or without food, and should not be chewed, divided, or crushed. (2)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- Fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets, 4 mg are light yellow, beveled edge, oval shape, film-coated tablets debossed with "479" on one side and plain on the other side. (3)
- Fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets, 8 mg are white to off-white, beveled edge, oval shape, film-coated tablets debossed with "480" on one side and plain on the other side. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets are contraindicated in patients with urinary retention, gastric retention, or uncontrolled narrow-angle glaucoma. Fesoterodine fumarate is also contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to the drug or its ingredients or to tolterodine tartrate tablets or tolterodine tartrate extended-release capsules. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Angioedema of the face, lips, tongue, and/or larynx has been reported with fesoterodine. (5.1).
- Fesoterodine fumarate should be administered with caution to patients with clinically significant bladder outlet obstruction because of the risk of urinary retention. (5.2)
- Fesoterodine fumarate, like other antimuscarinic drugs, should be used with caution in patients with decreased gastrointestinal motility, such as those with severe constipation. (5.3)
- Fesoterodine fumarate should be used with caution in patients being treated for narrow-angle glaucoma, and only where the potential benefits outweigh the risks (5.4)
- Central Nervous System Effects: Somnolence has been reported with fesoterodine fumarate. Advise patients not to drive or operate heavy machinery until they know how fesoterodine fumarate affects them (5.5)
- Fesoterodine fumarate should be used with caution in patients with myasthenia gravis, a disease characterized by decreased cholinergic activity at the neuromuscular junction. (5.9)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most frequently reported adverse events ( ≥ 4%) for fesoterodine fumarate were: dry mouth (placebo, 7%; fesoterodine fumarate 4 mg, 19%; fesoterodine fumarate 8 mg, 35%) and constipation (placebo, 2%; fesoterodine fumarate 4 mg, 4%; fesoterodine fumarate 8 mg, 6%). (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Zydus Pharmaceuticals (USA) Inc. at 1-877-993-8779 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Pregnancy and Nursing Mothers: fesoterodine fumarate should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit outweighs the potential risk to the fetus. (8.1) fesoterodine fumarate should not be administered during nursing unless the potential benefit outweighs the potential risk to the neonate. (8.3)
- Pediatric Use: The safety and effectiveness of fesoterodine fumarate in pediatric patients have not been established. (8.4)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Pediatric Use: The safety and effectiveness of fesoterodine fumarate in pediatric patients have not been established. (8.4)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 12/2017
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Angioedema
5.2 Bladder Outlet Obstruction
5.3 Decreased Gastrointestinal Motility
5.4 Controlled Narrow-Angle Glaucoma
5.5 Central Nervous System Effects
5.6 Hepatic Impairment
5.7 Renal Impairment
5.8 Concomitant Administration with CYP3A4 Inhibitors
5.9 Myasthenia Gravis
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience:
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Antimuscarinic Drugs
7.2 CYP3A4 Inhibitors
7.3 CYP3A4 Inducers
7.4 CYP2D6 Inhibitors
7.5 Drugs Metabolized by Cytochrome P450 Isoenzymes
7.6 Oral Contraceptives
7.7 Warfarin
7.8 Drug-Laboratory Test Interactions
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
8.8 Gender
8.9 Race
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The recommended starting dose of fesoterodine fumarate is 4 mg once daily. Based upon individual response and tolerability, the dose may be increased to 8 mg once daily.
The daily dose of Fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets should not exceed 4 mg in the following populations:
- Patients with severe renal impairment (CLCR < 30 mL/min).
- Patients taking potent CYP3A4 inhibitors, such as ketoconazole, itraconazole, and clarithromycin.
Fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets are not recommended for use in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6, 5.8, 5.9); Use in Specific Populations (8.6, 8.7); and Drug Interactions (7.2)].
Fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets should be taken with liquid and swallowed whole. Fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets can be administered with or without food, and should not be chewed, divided, or crushed.
-
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- Fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets, 4 mg are light yellow, beveled edge, oval shape, film-coated tablets debossed with "479" on one side and plain on the other side.
- Fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets, 8 mg are white to off-white, beveled edge, oval shape, film-coated tablets debossed with "480" on one side and plain on the other side.
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets are contraindicated in patients with urinary retention, gastric retention, or uncontrolled narrow-angle glaucoma. Fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets are also contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to the drug or its ingredients, or to tolterodine tartrate tablets or tolterodine tartrate extended-release capsules [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)].
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Angioedema
Angioedema of the face, lips, tongue, and/or larynx has been reported with fesoterodine. In some cases angioedema occurred after the first dose. Angioedema associated with upper airway swelling may be life-threatening. If involvement of the tongue, hypopharynx, or larynx occurs, fesoterodine should be promptly discontinued and appropriate therapy and/or measures to ensure a patent airway should be promptly provided.
5.2 Bladder Outlet Obstruction
Fesoterodine fumarate should be administered with caution to patients with clinically significant bladder outlet obstruction because of the risk of urinary retention [see Contraindications (4)].
5.3 Decreased Gastrointestinal Motility
Fesoterodine fumarate, like other antimuscarinic drugs, should be used with caution in patients with decreased gastrointestinal motility, such as those with severe constipation.
5.4 Controlled Narrow-Angle Glaucoma
Fesoterodine fumarate should be used with caution in patients being treated for narrow-angle glaucoma, and only where the potential benefits outweigh the risks [see Contraindications (4)].
5.5 Central Nervous System Effects
Fesoterodine fumarate is associated with anticholinergic central nervous sytem (CNS) effects [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]. A variety of CNS anticholinergic effects have been reported, including headache, dizziness, and somnolence. Patients should be monitored for signs of anticholinergic CNS effects, particularly after beginning treatment or increasing the dose. Advise patients not to drive or operate heavy machinery until they know how fesoterodine fumarate affects them. If a patient experiences anticholinergic CNS effects, dose reduction or drug discontinuation should be considered.
5.6 Hepatic Impairment
Fesoterodine fumarate has not been studied in patients with severe hepatic impairment and therefore is not recommended for use in this patient population [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7) and Dosage and Administration (2)].
5.7 Renal Impairment
Doses of fesoterodine fumarate greater than 4 mg are not recommended in patients with severe renal impairment [see Use In Specific Populations (8.6) and Dosage and Administration (2)].
5.8 Concomitant Administration with CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Doses of fesoterodine fumarate greater than 4 mg are not recommended in patients taking a potent CYP3A4 inhibitor (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole, clarithromycin).
No dosing adjustments are recommended in the presence of moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., erythromycin, fluconazole, diltiazem, verapamil and grapefruit juice).
While the effect of weak CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., cimetidine) was not examined by clinical study, some pharmacokinetic interaction is expected, albeit less than that observed with moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors [see Drug Interactions (7.2) and Dosage and Administration (2)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience:
The safety of fesoterodine fumarate was evaluated in Phase 2 and 3 controlled trials in a total of 2859 patients with overactive bladder, of which 2288 were treated with fesoterodine. Of this total, 782 received fesoterodine fumarate 4 mg/day, and 785 received fesoterodine fumarate 8 mg/day in Phase 2 or 3 studies with treatment periods of 8 or 12 weeks. Approximately 80% of these patients had > 10 weeks exposure to fesoterodine fumarate in these trials.
A total of 1964 patients participated in two 12 week, Phase 3 efficacy and safety studies and subsequent open-label extension studies. In these two studies combined, 554 patients received fesoterodine fumarate 4 mg/day and 566 patients received fesoterodine fumarate 8 mg/day.
In Phase 2 and 3 placebo-controlled trials combined, the incidences of serious adverse events in patients receiving placebo, fesoterodine fumarate 4 mg, and fesoterodine fumarate 8 mg were 1.9%, 3.5%, and 2.9%, respectively. All serious adverse events were judged to be not related or unlikely to be related to study medication by the investigator, except for four patients receiving fesoterodine fumarate who reported one serious adverse event each: angina, chest pain, gastroenteritis, and QT prolongation on ECG.
The most commonly reported adverse event in patients treated with fesoterodine fumarate was dry mouth. The incidence of dry mouth was higher in those taking 8 mg/day (35%) and in those taking 4 mg/day (19%), as compared to placebo (7%). Dry mouth led to discontinuation in 0.4%, 0.4%, and 0.8% of patients receiving placebo, fesoterodine fumarate 4 mg, and fesoterodine fumarate 8 mg, respectively. For those patients who reported dry mouth, most had their first occurrence of the event within the first month of treatment.
The second most commonly reported adverse event was constipation. The incidence of constipation was 2% in those taking placebo, 4% in those taking 4 mg/day, and 6% in those taking 8 mg/day.
Table 1 lists adverse events, regardless of causality, that were reported in the combined Phase 3, randomized, placebo-controlled trials at an incidence greater than placebo and in 1% or more of patients treated with fesoterodine fumarate 4 or 8 mg once daily for up to 12 weeks.
Table1 Adverse events with an incidence exceeding the placebo rate and reported by ≥ 1 % of patients from double-blind, placebo-controlled Phase 3 trials of 12 weeks treatment duration ALT = alanine aminotransferase; GGT = gamma glutamyltransferase
System organ class/Preferred term
Placebo
N=554 %
Fesoterodine fumarate
4 mg/day
N=554 %
Fesoterodine fumarate
8 mg/day
N=566 %
Gastrointestinal disorders
Dry mouth
Constipation
Dyspepsia
Nausea
7
2
0.5
1.3
18.8
4.2
1.6
0.7
34.6
6
2.3
1.9
Abdominal pain upper
0.5
1.1
0.5
Infections
Urinary tract infection
3.1
3.2
4.2
Upper respiratory tract infection
2.2
2.5
1.8
Eye disorders
Dry eyes
0
1.4
3.7
Renal and urinary disorders
Dysuria
Urinary retention
0.7
0.2
1.3
1.1
1.6
1.4
Respiratory disorders
Cough
Dry throat
0.5
0.4
1.6
0.9
0.9
2.3
General disorders
Edema peripheral
0.7
0.7
1.2
Musculoskeletal disorders
Back pain
0.4
2
0.9
Psychiatric disorders
Insomnia
0.5
1.3
0.4
Investigations
ALT increased
GGT increased
0.9
0.4
0.5
0.4
1.2
1.2
Skin disorders
Rash
0.5
0.7
1.1
Patients also received fesoterodine fumarate for up to three years in open-label extension phases of one Phase 2 and two Phase 3 controlled trials. In all open-label trials combined, 857, 701, 529, and 105 patients received fesoterodine fumarate for at least 6 months, 1 year, 2 years, and 3 years, respectively. The adverse events observed during long-term, open-label studies were similar to those observed in the 12 week, placebo-controlled studies, and included dry mouth, constipation, dry eyes, dyspepsia, and abdominal pain. Similar to the controlled studies, most adverse events of dry mouth and constipation were mild to moderate in intensity. Serious adverse events, judged to be at least possibly related to study medication by the investigator and reported more than once during the open-label treatment period of up to 3 years, included urinary retention (3 cases), diverticulitis (3 cases), constipation (2 cases), irritable bowel syndrome (2 cases), and electrocardiogram QT corrected interval prolongation (2 cases).
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following events have been reported in association with fesoterodine use in worldwide postmarketing experience:
Eye disorders
Blurred vision;
Cardiac disorders
Palpitations;
General disorders and administrative site conditions
Hypersensitivity reactions, including angioedema with airway obstruction, face edema;
Central nervous system disorders
Dizziness, headache, somnolence;
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Urticaria, pruritus
Because these spontaneously reported events are from the worldwide postmarketing experience, the frequency of events and the role of fesoterodine in their causation cannot be reliably determined.
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Antimuscarinic Drugs
Coadministration of fesoterodine fumarate with other antimuscarinic agents that produce dry mouth, constipation, urinary retention, and other anticholinergic pharmacological effects may increase the frequency and/or severity of such effects. Anticholinergic agents may potentially alter the absorption of some concomitantly administered drugs due to anticholinergic effects on gastrointestinal motility.
7.2 CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Doses of fesoterodine fumarate greater than 4 mg are not recommended in patients taking potent CYP3A4 inhibitors, such as ketoconazole, itraconazole, and clarithromycin. Coadministration of the potent CYP3A4 inhibitor ketoconazole with fesoterodine led to approximately a doubling of the maximum concentration (Cmax) and area under the concentration versus time curve (AUC) of 5-hydroxymethyl tolterodine (5-HMT), the active metabolite of fesoterodine. Compared with CYP2D6 extensive metabolizers not taking ketoconazole, further increases in the exposure to 5-HMT were observed in subjects who were CYP2D6 poor metabolizers taking ketoconazole [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), Warnings and Precautions (5.8), and Dosage and Administration (2)].
There is no clinically relevant effect of moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors on the pharmacokinetics of fesoterodine. Following blockade of CYP3A4 by coadministration of the moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor fluconazole 200 mg twice a day for 2 days, the average (90% confidence interval) increase in Cmax and AUC of the active metabolite of fesoterodine was approximately 19% (11% to 28%) and 27% (18% to 36%) respectively. No dosing adjustments are recommended in the presence of moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., erythromycin, fluconazole, diltiazem, verapamil and grapefruit juice).
The effect of weak CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., cimetidine) was not examined; it is not expected to be in excess of the effect of moderate inhibitors [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), Warnings and Precautions (5.8), and Dosage and Administration (2)].
7.3 CYP3A4 Inducers
No dosing adjustments are recommended in the presence of CYP3A4 inducers, such as rifampin and carbamazepine. Following induction of CYP3A4 by coadministration of rifampin 600 mg once a day, Cmax and AUC of the active metabolite of fesoterodine decreased by approximately 70% and 75%, respectively, after oral administration of fesoterodine fumarate 8 mg. The terminal half-life of the active metabolite was not changed.
7.4 CYP2D6 Inhibitors
The interaction with CYP2D6 inhibitors was not tested clinically. In poor metabolizers for CYP2D6, representing a maximum CYP2D6 inhibition, Cmax and AUC of the active metabolite are increased 1.7- and 2-fold, respectively.
No dosing adjustments are recommended in the presence of CYP2D6 inhibitors.
7.5 Drugs Metabolized by Cytochrome P450 Isoenzymes
In vitro data indicate that at therapeutic concentrations, the active metabolite of fesoterodine does not have the potential to inhibit or induce Cytochrome P450 enzyme systems [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.6 Oral Contraceptives
In the presence of fesoterodine, there are no clinically significant changes in the plasma concentrations of combined oral contraceptives containing ethinyl estradiol and levonorgestrel [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.7 Warfarin
A clinical study has shown that fesoterodine 8 mg once daily has no significant effect on the pharmacokinetics or the anticoagulant activity (PT/INR) of warfarin 25 mg. Standard therapeutic monitoring for warfarin should be continued [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
There are no data with the use of fesoterodine fumarate in pregnant women to inform a drug associated risk for birth defects or miscarriage. In animal reproduction studies, oral administration of fesoterodine to pregnant mice and rabbits during organogenesis resulted in fetotoxicity at maternal exposures that were 6 and 3 times, respectively, the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 8 mg/day based on AUC (see Data). The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population are unknown. However, in the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
No dose-related teratogenicity was observed in reproduction studies performed in mice and rabbits. In mice at 6 to 27 times the expected exposure at the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 8 mg based on AUC (75 mg/kg/day, oral), increased resorptions and decreased live fetuses were observed. One fetus with cleft palate was observed at each dose (15, 45, and 75 mg/kg/day), at an incidence within the background historical range. In rabbits treated at 3 to 11 times the MRHD (27 mg/kg/day, oral), incompletely ossified sternebrae (retardation of bone development) and reduced survival were observed in fetuses. In rabbits at 9 to 11 times the MRHD (4.5 mg/kg/day, subcutaneous), maternal toxicity and incompletely ossified sternebrae were observed in fetuses (at an incidence within the background historical range). In rabbits at 3 times the MRHD (1.5 mg/kg/day, subcutaneous), decreased maternal food consumption in the absence of any fetal effects was observed. Oral administration of 30 mg/kg/day fesoterodine to mice in a pre-and post-natal development study resulted in decreased body weight of the dams and delayed ear opening of the pups. No effects were noted on mating and reproduction of the F1 dams or on the F2 offspring.
8.2 Lactation
There is no information on the presence of fesoterodine in human milk, the effects on the breastfed child, or the effects on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for fesoterodine fumarate and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from fesoterodine fumarate or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The pharmacokinetics of fesoterodine have not been evaluated in pediatric patients. The safety and effectiveness of fesoterodine fumarate in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
No dose adjustment is recommended for the elderly. The pharmacokinetics of fesoterodine are not significantly influenced by age.
Of 1567 patients who received fesoterodine fumarate 4 mg/day or 8 mg/day in the Phase 2 and 3, placebo-controlled, efficacy and safety studies, 515 (33%) were 65 years of age or older, and 140 (9%) were 75 years of age or older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between patients younger than 65 years of age and those 65 years of age or older in these studies; however, the incidence of antimuscarinic adverse events, including dry mouth, constipation, dyspepsia, increase in residual urine, dizziness (at 8 mg only) and urinary tract infection, was higher in patients 75 years of age and older as compared to younger patients [see Clinical Studies (14) and Adverse Reactions (6)].
8.6 Renal Impairment
In patients with severe renal impairment (CLCR < 30 mL/min), Cmax and AUC are increased 2.0- and 2.3-fold, respectively. Doses of fesoterodine fumarate greater than 4 mg are not recommended in patients with severe renal impairment. In patients with mild or moderate renal impairment (CLCR ranging from 30 to 80 mL/min), Cmax and AUC of the active metabolite are increased up to 1.5- and 1.8-fold, respectively, as compared to healthy subjects. No dose adjustment is recommended in patients with mild or moderate renal impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) and Dosage and Administration (2)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
Patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C) have not been studied; therefore fesoterodine fumarate is not recommended for use in these patients. In patients with moderate (Child-Pugh B) hepatic impairment, Cmax and AUC of the active metabolite are increased 1.4- and 2.1-fold, respectively, as compared to healthy subjects. No dose adjustment is recommended in patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) and Dosage and Administration (2)].
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablet contains fesoterodine fumarate. Fesoterodine is rapidly de-esterified to its active metabolite (R)-2-(3-diisopropylamino-1-phenylpropyl)-4-hydroxymethyl-phenol, or 5-hydroxymethyl tolterodine, which is a muscarinic receptor antagonist.
Chemically, fesoterodine fumarate is designated as isobutyric acid 2-((R)-3-diisopropylammonium-1-phenylpropyl)-4-(hydroxymethyl) phenyl ester hydrogen fumarate. The molecular formula is C30H41NO7 and its molecular weight is 527.66. The structural formula is:
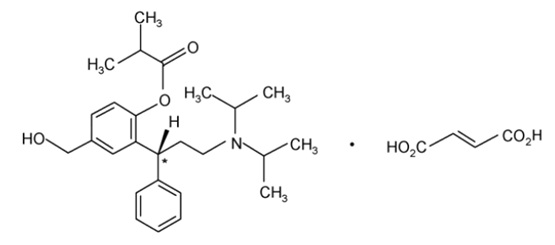
The asterisk (*) indicates the chiral carbon.
Fesoterodine fumarate is a white to off-white powder which is freely soluble in water and methanol.
Each fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablet contains either 4 mg or 8 mg of fesoterodine fumarate and the following inactive ingredients: corn starch, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, lecithin, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyvinyl alcohol, povidone, talc, titanium dioxide and xanthan gum. Additionally each 4 mg tablets contain iron oxide yellow.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Fesoterodine is a competitive muscarinic receptor antagonist. After oral administration, fesoterodine is rapidly and extensively hydrolyzed by nonspecific esterases to its active metabolite, 5-hydroxymethyl tolterodine, which is responsible for the antimuscarinic activity of fesoterodine and is also one of the active moieties of tolterodine tartrate tablets and tolterodine tartrate extended-release capsules.
Muscarinic receptors play a role in contractions of urinary bladder smooth muscle and stimulation of salivary secretion. Inhibition of these receptors in the bladder is presumed to be the mechanism by which fesoterodine produces its effects.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
In a urodynamic study involving patients with involuntary detrusor contractions, the effects after the administration of fesoterodine on the volume at first detrusor contraction and bladder capacity were assessed. Administration of fesoterodine increased the volume at first detrusor contraction and bladder capacity in a dose-dependent manner. These findings are consistent with an antimuscarinic effect on the bladder.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
The effect of fesoterodine 4 mg and 28 mg on the QT interval was evaluated in a double-blind, randomized, placebo- and positive-controlled (moxifloxacin 400 mg once a day) parallel trial with once-daily treatment over a period of 3 days in 261 male and female subjects aged 44 to 65 years. Electrocardiographic parameters were measured over a 24 hour period at pre-dose, after the first administration, and after the third administration of study medication. Fesoterodine 28 mg was chosen because this dose, when administered to CYP2D6 extensive metabolizers, results in an exposure to the active metabolite that is similar to the exposure in a CYP2D6 poor metabolizer receiving fesoterodine 8 mg together with CYP3A4 blockade. Corrected QT intervals (QTc) were calculated using Fridericia's correction and a linear individual correction method. Analyses of 24 hour average QTc, time-matched baseline-corrected QTc, and time-matched placebo-subtracted QTc intervals indicate that fesoterodine at doses of 4 and 28 mg/day did not prolong the QT interval. The sensitivity of the study was confirmed by positive QTc prolongation by moxifloxacin.
Fesoterodine fumarate is associated with an increase in heart rate that correlates with increasing dose. In the study described above, when compared to placebo, the mean increase in heart rate associated with a dose of 4 mg/day and 28 mg/day of fesoterodine was 3 beats/minute and 11 beats/minute, respectively.
In the two, phase 3, placebo-controlled studies in patients with overactive bladder, the mean increase in heart rate compared to placebo was approximately 3 to 4 beats/minute in the 4 mg/day group and 3 to 5 beats/minute in the 8 mg/day group.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
After oral administration, fesoterodine is well absorbed. Due to rapid and extensive hydrolysis by nonspecific esterases to its active metabolite 5-hydroxymethyl tolterodine, fesoterodine cannot be detected in plasma. Bioavailability of the active metabolite is 52%. After single or multiple-dose oral administration of fesoterodine in doses from 4 mg to 28 mg, plasma concentrations of the active metabolite are proportional to the dose. Maximum plasma levels are reached after approximately 5 hours. No accumulation occurs after multiple-dose administration.
A summary of pharmacokinetic parameters for the active metabolite after a single dose of fesoterodine fumarate 4 mg and 8 mg in extensive and poor metabolizers of CYP2D6 is provided in Table 2.
Table2 Summary of geometric mean [CV] pharmacokinetic parameters for the active metabolite after a single dose of fesoterodine fumarate 4 mg and 8 mg in extensive and poor CYP2D6 metabolizers EM = extensive CYP2D6 metabolizer, PM = poor CYP2D6 metabolizer, CV = coefficient of variation
Cmax = maximum plasma concentration, AUC0-tz = area under the concentration time curve from zero up to the last measurable plasma concentration, tmax = time to reach Cmax, t½ = terminal half-life
a Data presented as median (range)
Fesoterodine fumarate
4 mg
Fesoterodine fumarate
8 mg
Parameter
EM (n=16)
PM (n=8)
EM (n=16)
PM (n=8)
Cmax (ng/mL)
1.89 [43%]
3.45 [54%]
3.98 [28%]
6.90 [39%]
AUC0-tz
21.2 [38%]
40.5 [31%]
45.3 [32%]
88.7 [36%]
(ng*h/mL)
tmax (h)a
5 [2 to 6]
5 [5 to 6]
5 [3 to 6]
5 [5 to 6]
t½ (h)
7.31 [27%]
7.31 [30%]
8.59 [41%]
7.66 [21%]
There is no clinically relevant effect of food on the pharmacokinetics of fesoterodine. In a study of the effects of food on the pharmacokinetics of fesoterodine in 16 healthy male volunteers, concomitant food intake increased the active metabolite of fesoterodine AUC by approximately 19% and Cmax by 18% [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
Distribution
Plasma protein binding of the active metabolite is low (approximately 50%) and is primarily bound to albumin and alpha-1-acid glycoprotein. The mean steady-state volume of distribution following intravenous infusion of the active metabolite is 169 L.
Metabolism
After oral administration, fesoterodine is rapidly and extensively hydrolyzed to its active metabolite. The active metabolite is further metabolized in the liver to its carboxy, carboxy-N-desisopropyl, and N-desisopropyl metabolites via two major pathways involving CYP2D6 and CYP3A4. None of these metabolites contribute significantly to the antimuscarinic activity of fesoterodine.
Variability in CYP2D6 Metabolism
A subset of individuals (approximately 7% of Caucasians and approximately 2% of African Americans) are poor metabolizers for CYP2D6. Cmax and AUC of the active metabolite are increased 1.7- and 2-fold, respectively, in CYP2D6 poor metabolizers, as compared to extensive metabolizers.
Excretion
Hepatic metabolism and renal excretion contribute significantly to the elimination of the active metabolite. After oral administration of fesoterodine, approximately 70% of the administered dose was recovered in urine as the active metabolite (16%), carboxy metabolite (34%), carboxy-N-desisopropyl metabolite (18%), or N-desisopropyl metabolite (1%), and a smaller amount (7%) was recovered in feces.
The terminal half-life of the active metabolite is approximately 4 hours following an intravenous administration. The apparent terminal half-life following oral administration is approximately 7 hours.
Pharmacokinetics in Specific Populations
Geriatric Patients
Following a single 8 mg oral dose of fesoterodine, the mean (±SD) AUC and Cmax for the active metabolite 5-hydroxymethyl tolterodine in 12 elderly men (mean age 67 years) were 51.8 ± 26.1 h*ng/mL and 3.8 ± 1.7 ng/mL, respectively. In the same study, the mean (±SD) AUC and Cmax in 12 young men (mean age 30 years) were 52 ± 31.5 h*ng/mL and 4.1 ± 2.1 ng/mL, respectively. The pharmacokinetics of fesoterodine were not significantly influenced by age [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
Pediatric Patients
The pharmacokinetics of fesoterodine have not been evaluated in pediatric patients [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
Gender
Following a single 8 mg oral dose of fesoterodine, the mean (±SD) AUC and Cmax for the active metabolite 5-hydroxymethyl tolterodine in 12 elderly men (mean age 67 years) were 51.8 ± 26.1 h*ng/mL and 3.8 ± 1.7 ng/mL, respectively. In the same study, the mean (±SD) AUC and Cmax in 12 elderly women (mean age 68 years) were 56.0 ± 28.8 h*ng/mL and 4.6 ± 2.3 ng/mL, respectively. The pharmacokinetics of fesoterodine were not significantly influenced by gender [see Use in Specific Populations (8.8)].
Race
The effects of Caucasian or Black race on the pharmacokinetics of fesoterodine were examined in a study of 12 Caucasian and 12 Black African young male volunteers. Each subject received a single oral dose of 8 mg fesoterodine. The mean (±SD) AUC and Cmax for the active metabolite 5-hydroxymethyl tolterodine in Caucasian males were 73.0 ± 27.8 h*ng/mL and 6.1 ± 2.7 ng/mL, respectively. The mean (±SD) AUC and Cmax in Black males were 65.8 ± 23.2 h*ng/mL and 5.5 ± 1.9 ng/mL, respectively. The pharmacokinetics of fesoterodine were not significantly influenced by race [see Use in Specific Populations (8.9)].
Renal Impairment
In patients with mild or moderate renal impairment (CLCR ranging from 30 to 80 mL/min), Cmax and AUC of the active metabolite are increased up to 1.5- and 1.8-fold, respectively, as compared to healthy subjects. In patients with severe renal impairment (CLCR < 30 mL/min), Cmax and AUC are increased 2- and 2.3-fold, respectively. [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6), Warnings and Precautions (5.7), and Dosage and Administration (2)].
Hepatic Impairment
In patients with moderate (Child-Pugh B) hepatic impairment, Cmax and AUC of the active metabolite are increased 1.4- and 2.1-fold, respectively, as compared to healthy subjects.
Subjects with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C) have not been studied [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7), Warnings and Precautions (5.6), and Dosage and Administration (2)].
Drug-Drug Interactions
Drugs Metabolized by Cytochrome P450
At therapeutic concentrations, the active metabolite of fesoterodine does not inhibit CYP1A2, 2B6, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, 2E1, or 3A4, or induce CYP1A2, 2B6, 2C9, 2C19, or 3A4 in vitro [see Drug Interactions (7.5)].
CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Following blockade of CYP3A4 by coadministration of the potent CYP3A4 inhibitor ketoconazole 200 mg twice a day for 5 days, Cmax and AUC of the active metabolite of fesoterodine increased 2- and 2.3-fold, respectively, after oral administration of fesoterodine fumarate 8 mg to CYP2D6 extensive metabolizers. In CYP2D6 poor metabolizers, Cmax and AUC of the active metabolite of fesoterodine increased 2.1- and 2.5-fold, respectively, during coadministration of ketoconazole 200 mg twice a day for 5 days. Cmax and AUC were 4.5- and 5.7-fold higher, respectively, in subjects who were CYP2D6 poor metabolizers and taking ketoconazole compared to subjects who were CYP2D6 extensive metabolizers and not taking ketoconazole. In a separate study coadministering fesoterodine with ketoconazole 200 mg once a day for 5 days, the Cmax and AUC values of the active metabolite of fesoterodine were increased 2.2-fold in CYP2D6 extensive metabolizers and 1.5- and 1.9-fold, respectively, in CYP2D6 poor metabolizers. Cmax and AUC were 3.4-and 4.2-fold higher, respectively, in subjects who were CYP2D6 poor metabolizers and taking ketoconazole compared to subjects who were CYP2D6 extensive metabolizers and not taking ketoconazole.
There is no clinically relevant effect of moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors on the pharmacokinetics of fesoterodine. In a drug-drug interaction study evaluating the coadministration of the moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor fluconazole 200 mg twice a day for 2 days, a single 8 mg dose of fesoterodine was administered 1 hour following the first dose of fluconazole on day 1 of the study. The average (90% confidence interval) for the increase in Cmax and AUC of the active metabolite of fesoterodine was approximately 19% (11% to 28%) and 27% (18% to 36%) respectively.
The effect of weak CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., cimetidine) was not examined; it is not expected to be in excess of the effect of moderate inhibitors [see Drug Interactions (7.2)], Warnings and Precautions (5.8), and Dosage and Administration (2)].
CYP3A4 Inducers
Following induction of CYP3A4 by coadministration of rifampicin 600 mg once a day, Cmax and AUC of the active metabolite of fesoterodine decreased by approximately 70% and 75%, respectively, after oral administration of fesoterodine fumarate 8 mg. The terminal half-life of the active metabolite was not changed.
Induction of CYP3A4 may lead to reduced plasma levels. No dosing adjustments are recommended in the presence of CYP3A4 inducers [see Drug Interactions (7.3)].
CYP2D6 Inhibitors
The interaction with CYP2D6 inhibitors was not studied. In poor metabolizers for CYP2D6, representing a maximum CYP2D6 inhibition, Cmax and AUC of the active metabolite are increased 1.7- and 2-fold, respectively. [see Drug Interactions (7.4)].
Oral Contraceptives
Thirty healthy female subjects taking an oral contraceptive containing 0.03 mg ethinyl estradiol and 0.15 mg levonorgestrel were evaluated in a 2-period crossover study. Each subject was randomized to receive concomitant administration of either placebo or fesoterodine 8 mg once daily on days 1 to 14 of hormone cycle for 2 consecutive cycles. Pharmacokinetics of ethinyl estradiol and levonorgestrel were assessed on day 13 of each cycle. Fesoterodine increased the AUC and Cmax of ethinyl estradiol by 1 to 3% and decreased the AUC and Cmax of levonorgestrel by 11 to 13% [see Drug Interactions (7.6)].
Warfarin
In a cross-over study in 14 healthy male volunteers (18 to 55 years), a single oral dose of warfarin 25 mg was given either alone or on day 3 of once daily dosing for 9 days with fesoterodine 8 mg. Compared to warfarin alone dosing, the Cmax and AUC of S-warfarin were lower by ~ 4 %, while the Cmax and AUC of R-warfarin were lower by approximately 8 % and 6% for the coadministration, suggesting absence of a significant pharmacokinetic interaction.
There were no statistically significant changes in the measured pharmacodynamic parameters for anti-coagulant activity of warfarin (INRmax, AUCINR), with only a small decrease noted in INRmax of ~ 3 % with the coadministration relative to warfarin alone. INR versus time profiles across individual subjects in the study suggested some differences following coadministration with fesoterodine, although there was no definite trend with regard to the changes noted [see Drug Interactions (7.7)].
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No evidence of drug-related carcinogenicity was found in 24 month studies with oral administration to mice and rats. The highest tolerated doses in mice (females 45 to 60 mg/kg/day, males 30 to 45 mg/kg/day) correspond to 11 to 19 times (females) and 4 to 9 times (males) the estimated human AUC values reached with fesoterodine 8 mg, which is the Maximum Recommended Human Dose (MRHD). In rats, the highest tolerated dose (45 to 60 mg/kg/day) corresponds to 3 to 8 times (females) and 3 to 14 times (males) the estimated human AUC at the MRHD.
Fesoterodine was not mutagenic or genotoxic in vitro (Ames tests, chromosome aberration tests) or in vivo (mouse micronucleus test).
Fesoterodine had no effect on male reproductive function or fertility at doses up to 45 mg/kg/day in mice. At 45 mg/kg/day, a lower number of corpora lutea, implantation sites and viable fetuses was observed in female mice administered fesoterodine for 2 weeks prior to mating and continuing through day 7 of gestation. The maternal No-Observed-Effect Level (NOEL) and the NOEL for effects on reproduction and early embryonic development were both 15 mg/kg/day. At the NOEL, , the systemic exposure, based on AUC, was 0.6 to 1.5 times higher in mice than in humans at the MRHD, whereas based on peak plasma concentrations, the exposure in mice was 5 to 9 times higher.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets were evaluated in two, Phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 12 week studies for the treatment of overactive bladder with symptoms of urge urinary incontinence, urgency, and urinary frequency. Entry criteria required that patients have symptoms of overactive bladder for ≥ 6 months duration, at least 8 micturitions per day, and at least 6 urinary urgency episodes or 3 urge incontinence episodes per 3 day diary period. Patients were randomized to a fixed dose of fesoterodine fumarate 4 or 8 mg/day or placebo. In one of these studies, 290 patients were randomized to an active control arm (an oral antimuscarinic agent). For the combined studies, a total of 554 patients received placebo, 554 patients received fesoterodine fumarate 4 mg/day, and 566 patients received fesoterodine fumarate 8 mg/day. The majority of patients were Caucasian (91%) and female (79%) with a mean age of 58 years (range 19 to 91 years).
The primary efficacy endpoints were the mean change in the number of urge urinary incontinence episodes per 24 hours and the mean change in the number of micturitions (frequency) per 24 hours. An important secondary endpoint was the mean change in the voided volume per micturition.
Results for the primary endpoints and for mean change in voided volume per micturition from the two 12 week clinical studies of fesoterodine fumarate are reported in Table 3.
Table3 MeanbaselineandchangefrombaselinetoWeek12forurgeurinaryincontinenceepisodes , numberofmicturitions , andvolumevoidedpermicturition vs. = versus
a Only those patients who were urge incontinent at baseline were included for the analysis of number of urge incontinence episodes per 24 hours: In Study 1, the number of these patients was 211, 199, and 223 in the placebo, fesoterodine fumarate 4 mg/day and fesoterodine fumarate 8 mg/day groups, respectively. In Study 2, the number of these patients was 205, 228, and 218, respectively.
Study 1
Study 2
Parameter
Placebo N=279
Fesoterodine fumarate
4 mg/day N=265
Fesoterodine fumarate
8 mg/day N=276
Placebo N=266
Fesoterodine fumarate
4 mg/day N=267
Fesoterodine fumarate
8 mg/day N=267
Number of urge incontinence episodes per 24 hoursa
Baseline
3.7
3.8
3.7
3.7
3.9
3.9
Change from baseline
-1.20
-2.06
-2.27
-1
-1.77
-2.42
p-value vs. placebo
-
0.001
< 0.001
-
< 0.003
< 0.001
Number of micturitions per 24 hours
Baseline
12
11.6
11.9
12.2
12.9
12
Change from baseline
-1.02
-1.74
-1.94
-1.02
-1.86
-1.94
p-value vs. placebo
-
< 0.001
< 0.001
-
0.032
< 0.001
Voided volume per micturition (mL)
Baseline
150
160
154
159
152
156
Change from baseline
10
27
33
8
17
33
p-value vs. placebo
-
< 0.001
< 0.001
-
0.150
< 0.001
Figures 1-4: The following figures show change from baseline over time in number of micturitions and urge urinary incontinence episodes per 24 h in the two studies.
Figure 1: Change in Number of Micturitions per 24 h (Study 1)
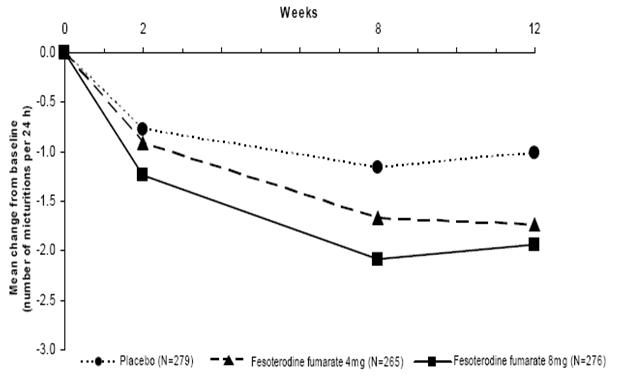
Figure 2: Change in Urge Incontinence Episodes per 24 h (Study 1)
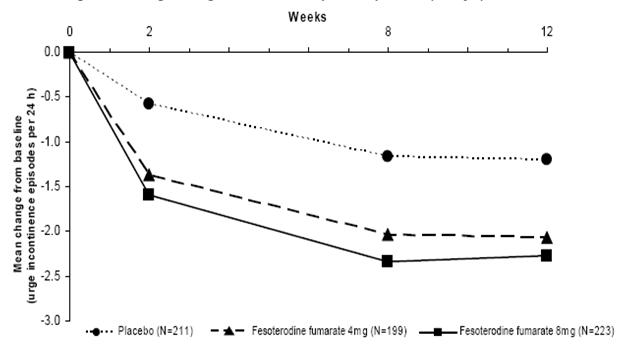
Figure 3: Change in Number of Micturitions per 24 h (Study 2)
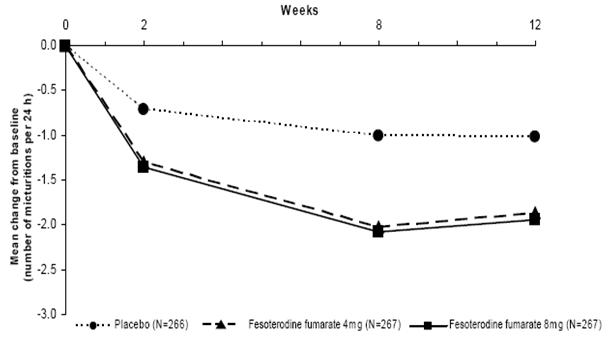
Figure 4: Change in Urge Incontinence Episodes per 24 h (Study 2) Weeks
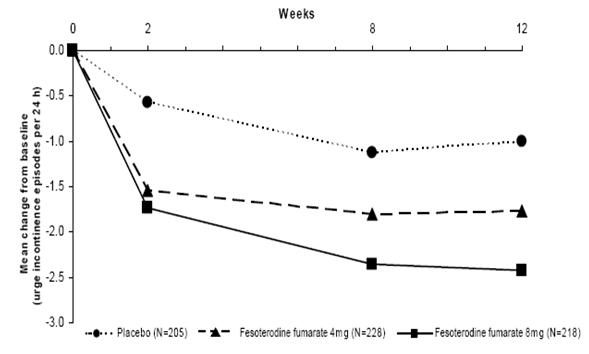
A reduction in number of urge urinary incontinence episodes per 24 hours was observed for both doses as compared to placebo as early as two weeks after starting fesoterodine fumarate therapy.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Fesoterodine Fumarate Extended-release Tablets, 4 mg are light yellow, beveled edge, oval shape, film-coated tablets debossed with "479" on one side and plain on the other side and are supplied as follows:
NDC: 70771-1168-3 in bottle of 30 tablets
NDC: 70771-1168-9 in bottle of 90 tablets
NDC: 70771-1168-4 in cartons of 100 (10 x 10) unit-dose tablets
Fesoterodine Fumarate Extended-release Tablets, 8 mg are white to off-white, beveled edge, oval shape, film-coated tablets debossed with "480" on one side and plain on the other side are supplied as follows:
NDC: 70771-1169-3 in bottle of 30 tablets
NDC: 70771-1169-9 in bottle of 90 tablets
NDC: 70771-1169-4 in cartons of 100 (10 x 10) unit-dose tablets
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-Approved Patient Labeling (Patient Information)
Patients should be informed that fesoterodine may produce angioedema, which could result in life-threatening airway obstruction. Patients should be advised to promptly discontinue fesoterodine therapy and seek immediate medical attention if they experience edema of the tongue or laryngopharynx, or difficult breathing.
Antimuscarinic Effects
Patients should be informed that fesoterodine fumarate, like other antimuscarinic agents, may produce clinically significant adverse effects related to antimuscarinic pharmacological activity including constipation and urinary retention. Fesoterodine fumarate, like other antimuscarinics, may be associated with blurred vision, therefore, patients should be advised to exercise caution in decisions to engage in potentially dangerous activities until the drug's effects on the patient have been determined. Heat prostration (due to decreased sweating) can occur when fesoterodine fumarate, like other antimuscarinic drugs, is used in a hot environment.
Alcohol
Patients should also be informed that alcohol may enhance the drowsiness caused by fesoterodine fumarate, like other anticholinergic agents. Patients should read the patient leaflet entitled "Patient Information Fesoterodine Fumarate" before starting therapy with fesoterodine fumarate.
Manufactured by:
Cadila Healthcare Limited
Ahmedabad, India.
Rev.: 12/17
-
SPL PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
Fesoterodine Fumarate
(FES-oh-TER-oh-deen FUE-ma-rate)
Extended-release Tablets
Read the Patient Information that comes with fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets before you start taking it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your medical condition or your treatment.
What are fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets?
Fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets are a prescription medicine used in adults to treat symptoms of a condition called overactive bladder, including:
- Urge urinary incontinence--leaking or wetting accidents due to a strong need to urinate,
- Urinary urgency--having a strong need to urinate right away,
- Urinary frequency--having to urinate too often.
Fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets have not been studied in children.
Who should not take fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets?
Do not take fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets if you:
- Are not able to empty your bladder (urinary retention)
- Have delayed or slow emptying of your stomach (gastric retention)
- Have an eye problem called "uncontrolled narrow-angle glaucoma"
- Are allergic to fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets or any of its ingredients. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients
- Are allergic to Detrol®# or Detrol®# LA, which contains tolterodine.
What should I tell my doctor before starting fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets?
Before starting fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets, tell your doctor about all of your medical and other conditions that may affect the use of fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets, including:
- Stomach or intestinal problems or problems with constipation
- Problems emptying your bladder or if you have a weak urine stream
- Treatment for an eye problem called narrow-angle glaucoma
- Kidney problems
- Liver problems
- A condition called myasthenia gravis
- If you are pregnant or trying to become pregnant. It is not known if fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets can harm your unborn baby.
- If you are breastfeeding. It is not known if fesoterodine fumarate passes into breast milk or if it can harm your baby. Talk to your doctor about the best way to feed your baby if you take fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets.
Before starting on fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets, tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and nonprescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal products. Fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets may affect the way other medicines work, and other medicines may affect how fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets work. Especially tell your doctor if you are taking antibiotics or antifungal medicines.
Know all the medicines you take. Keep a list of them with you to show your doctor and pharmacist each time you get a new medicine.
How should I take fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets?
- Take fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets exactly as your doctor tells you to take it.
- Your doctor may give you the lower 4 mg dose of fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets if you have certain medical conditions, such as severe kidney problems.
- Take fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets with liquid and swallow the tablet whole. Do not chew, divide, or crush the tablet.
- You can take fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets with or without food.
- If you miss a dose of fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets, begin taking fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets again the next day. Do not take 2 doses of fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets in the same day.
If you take too much fesoterodine fumarate, call your doctor or go to an emergency department right away.
What are the possible side effects of fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets?
Fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets may cause allergic reactions that may be serious. Symptoms of a serious allergic reaction may include swelling of the face, lips, throat or tongue. If you experience these symptoms, you should stop taking fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets and get emergency medical help right away.
The most common side effects of fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets are:
- Dry mouth
- Constipation
Fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets may cause other less common side effects, including:
- Dry eyes
- Trouble emptying the bladder
Tell your doctor if you have any side effects that bother you or that do not go away.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
These are not all of the possible side effects of fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets. For a complete list, ask your doctor.
What else should I keep in mind while taking fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets?
- Do not drive, operate machinery, or do other dangerous activities until you know how fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets affect you. Blurred vision, dizziness, and drowsiness are possible side effects of medicines such as fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets.
- Use caution in hot environments. Decreased sweating and severe heat illness can occur when medicines such as fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets are used in a hot environment.
- Drinking alcohol while taking medicines such as fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets may cause increased drowsiness.
How should I store fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets?
- Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
- Protect the medicine from moisture by keeping the bottle closed tightly.
- Safely throw away fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets those are out of date or no longer needed.
Keep fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for conditions that are not mentioned in patient information leaflets. Only use fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets the way your doctor tells you. Do not give fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
This leaflet summarizes the most important information about fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your doctor for information about fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets that is written for healthcare professionals.
Please address medical inquiries to, (MedicalAffairs@zydususa.com) or Tel.: 1-877-993-8779.
What are the ingredients in fesoterodine fumarate extended-release tablets?
Active ingredient: fesoterodine fumarate
Inactive ingredients: corn starch, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, lecithin, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyvinyl alcohol, povidone, talc, titanium dioxide and xanthan gum. Additionally each 4 mg tablet contains iron oxide yellow.
#The brand names motioned are the registered trademarks of their respective owner.
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
This product's package insert may have been updated. For current package insert, please visit www.zydususa.com.
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC: 68382-479-16 in bottle of 90 tablets
Fesoterodine Fumarate Extended-release Tablets, 4 mg
Rx only
90 tablets
ZYDUS

NDC: 68382-480-16 in bottle of 90 tablets
Fesoterodine Fumarate Extended-release Tablets, 8 mg
Rx only
90 tablets
ZYDUS

-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
FESOTERODINE FUMARATE
fesoterodine fumarate tablet, film coated, extended releaseProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 70771-1168 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength FESOTERODINE FUMARATE (UNII: EOS72165S7) (FESOTERODINE - UNII:621G617227) FESOTERODINE FUMARATE 4 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength STARCH, CORN (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) HYPROMELLOSES (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) LECITHIN, SOYBEAN (UNII: 1DI56QDM62) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) POVIDONE (UNII: FZ989GH94E) TALC (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) XANTHAN GUM (UNII: TTV12P4NEE) FERRIC OXIDE YELLOW (UNII: EX438O2MRT) POLYVINYL ALCOHOL, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 532B59J990) Product Characteristics Color YELLOW (Light Yellow) Score no score Shape OVAL (Oval) Size 13mm Flavor Imprint Code 479 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 70771-1168-3 30 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 12/07/2017 2 NDC: 70771-1168-9 90 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 12/07/2017 3 NDC: 70771-1168-4 10 in 1 CARTON 12/07/2017 3 NDC: 70771-1168-2 10 in 1 BLISTER PACK; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA204946 12/07/2017 FESOTERODINE FUMARATE
fesoterodine fumarate tablet, film coated, extended releaseProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 70771-1169 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength FESOTERODINE FUMARATE (UNII: EOS72165S7) (FESOTERODINE - UNII:621G617227) FESOTERODINE FUMARATE 8 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength STARCH, CORN (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) HYPROMELLOSES (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) LECITHIN, SOYBEAN (UNII: 1DI56QDM62) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) POVIDONE (UNII: FZ989GH94E) TALC (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) XANTHAN GUM (UNII: TTV12P4NEE) POLYVINYL ALCOHOL, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 532B59J990) Product Characteristics Color WHITE (White to Off-White) Score no score Shape OVAL (Oval) Size 13mm Flavor Imprint Code 480 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 70771-1169-3 30 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 12/07/2017 2 NDC: 70771-1169-9 90 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 12/07/2017 3 NDC: 70771-1169-4 10 in 1 CARTON 12/07/2017 3 NDC: 70771-1169-2 10 in 1 BLISTER PACK; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA204946 12/07/2017 Labeler - Cadila Healthcare Limited (918596198) Registrant - Cadila Healthcare Limited (918596198) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Cadila Healthcare Limited 918596198 ANALYSIS(70771-1168, 70771-1169) , MANUFACTURE(70771-1168, 70771-1169)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.