MARQIBO- vincristine sulfate kit
Marqibo by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Marqibo by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Acrotech Biopharma LLC, Hospira Australia Pty Ltd. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use MARQIBO safely and effectively. See Full Prescribing Information for MARQIBO.
Marqibo® (vinCRIStine sulfate LIPOSOME injection) for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2012
WARNING
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- For Intravenous Use Only – Fatal if Given by Other Routes (5.1)
- Death has occurred with intrathecal use
- Marqibo (vinCRIStine sulfate LIPOSOME injection) has different dosage recommendations than vinCRIStine sulfate injection. Verify drug name and dose prior to preparation and administration to avoid overdosage.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Marqibo is a vinca alkaloid indicated for the treatment of adult patients with Philadelphia chromosome-negative (Ph-) acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) in second or greater relapse or whose disease has progressed following two or more anti-leukemia therapies. This indication is based on overall response rate. Clinical benefit such as improvement in overall survival has not been verified (1.1).
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Intravenous use only. Do not administer by any other route (2)
Administer Marqibo at a dose of 2.25 mg/m2 intravenously over 1 hour once every 7 days (2.1).
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
The final drug product is prepared on site from the components in the Marqibo Kit. After preparation, each single-dose vial of Marqibo (vinCRIStine sulfate LIPOSOME injection) contains 5 mg/31 mL (0.16 mg/mL) vincristine sulfate (2.3.2).
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Marqibo is contraindicated in patients with demyelinating conditions including Charcot-Marie-Tooth syndrome (4)
Marqibo is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to vincristine sulfate or any of the other components of Marqibo (vinCRIStine sulfate LIPOSOME injection) (4)
Marqibo is contraindicated for intrathecal administration (4)WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Intrathecal administration is fatal (5.1)
- Extravasation causes tissue injury (5.2)
- Neurologic toxicity: Monitor patients for peripheral motor and sensory, central and autonomic neuropathy, and reduce, interrupt, or discontinue dosing. Patients with preexisting severe neuropathy should be treated with Marqibo only after careful risk-benefit assessment (2.2, 5.3)
- Myelosuppression: Monitor blood counts prior to each dose of Marqibo. Neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, or anemia may occur; consider Marqibo dose reduction or interruption and supportive care measures (5.4)
- Tumor lysis syndrome: Anticipate, monitor for, and manage (5.5)
- Constipation, bowel obstruction, and/or paralytic ileus: Institute a prophylactic bowel regimen to prevent potential constipation, bowel obstruction, and/or paralytic ileus (5.6)
- Fatigue: Severe fatigue can occur (5.7)
- Hepatic toxicity: Monitor liver function and modify or interrupt dosing (5.8)
- Embryofetal toxicity: Can cause fetal harm. Advise women of potential risk to the fetus (5.9, 8.1)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most commonly reported adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 30%) in clinical studies include constipation, nausea, pyrexia, fatigue, peripheral neuropathy, febrile neutropenia, diarrhea, anemia, decreased appetite, and insomnia (6.1).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Acrotech Biopharma LLC at 1-888 292 9617 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.DRUG INTERACTIONS
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pediatric Use: The safety and effectiveness of Marqibo in pediatric patients has not been established (8.4)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 1/2020
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING: FOR INTRAVENOUS USE ONLY
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Adult ALL in Second or Greater Relapse
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage
2.2 Dose modifications: Peripheral Neuropathy
2.3 Preparation and Handling
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 For Intravenous Use Only
5.2 Extravasation Tissue Injury
5.3 Neurologic Toxicity
5.4 Myelosuppression
5.5 Tumor Lysis Syndrome
5.6 Constipation and Bowel Obstruction
5.7 Fatigue
5.8 Hepatic Toxicity
5.9 Embryofetal Toxicity
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 CYP3A Interactions
7.2 P-glycoprotein Interactions
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
15 REFERENCES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 Storage
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING: FOR INTRAVENOUS USE ONLY
- For Intravenous Use Only – Fatal if Given by Other Routes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Death has occurred with intrathecal administration.
- Marqibo (vinCRIStine sulfate LIPOSOME injection) has different dosage recommendations than vinCRIStine sulfate injection. Verify drug name and dose prior to preparation and administration to avoid overdosage.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Adult ALL in Second or Greater Relapse
Marqibo® is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with Philadelphia chromosome-negative (Ph-) acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) in second or greater relapse or whose disease has progressed following two or more anti-leukemia therapies. This indication is based on overall response rate. Clinical benefit such as improvement in overall survival has not been verified.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For Intravenous Use Only. Fatal if Given by Other Routes.
Marqibo (vinCRIStine sulfate LIPOSOME injection) has different dosage recommendations than vincristine sulfate injection. Verify drug name and dose prior to preparation and administration to avoid overdosage.
2.1 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dose of Marqibo is 2.25 mg/m2 intravenously over 1 hour once every 7 days.
Marqibo is liposome-encapsulated vincristine.
2.2 Dose modifications: Peripheral Neuropathy
Marqibo is contraindicated in patients with demyelinating conditions including Charcot-Marie-Tooth syndrome [see Contraindications (4) ]. Patients with preexisting severe neuropathy should be treated with Marqibo only after careful risk-benefit assessment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]. For dose or schedule modifications guidelines for patients who experience peripheral neuropathy, see Table 1 .
Table 1 Recommended Dose Modifications for Marqibo-related Peripheral NeuropathySeverity of Peripheral Neuropathy Signs and Symptoms a Modification of Dose and Regimen If the patient develops Grade 3(severe symptoms; limiting self-care activities of daily living [ADL]b)or persistent Grade 2(moderate symptoms; limiting instrumental ADLc) peripheral neuropathy:
Interrupt Marqibo. If the peripheral neuropathy remains at Grade 3 or 4, discontinue Marqibo.If the peripheral neuropathy recovers to Grade 1 or 2, reduce the Marqibo dose to 2 mg/m2.
If the patient has persistent Grade 2 peripheral neuropathy after the first dose reduction to 2 mg/m2:
Interrupt Marqibo for up to 7 days. If the peripheral neuropathy increases to Grade 3 or 4, discontinue Marqibo. If peripheral neuropathy recovers to Grade 1, reduce the Marqibo dose to 1.825 mg/m2. If the patient has persistent Grade 2 peripheral neuropathy after the second dose reduction to 1.825 mg/m2:
Interrupt Marqibo for up to 7 days. If the peripheral neuropathy increases to Grade 3 or 4, discontinue Marqibo. If the toxicity recovers to Grade 1, reduce the Marqibo dose to 1.5 mg/m2 a Grading based on the National Cancer Institute (NCI) Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) v3.0.
b Self careADL: refers to bathing, dressing and undressing, feeding self, using the toilet, taking medications, and not bedridden.
c InstrumentalADL: refers to preparing meals, shopping for groceries and clothes, using telephone, managing money, etc.
2.3 Preparation and Handling
2.3.1 Items Required by the Pharmacy to Prepare Marqibo
Marqibo Kit
Water batha
Calibrated thermometera (0°C to 100°C)
Calibrated electronic timera
Sterile venting needle or other suitable device equipped with a sterile 0.2 micron filter
1 mL or 3 mL sterile syringe with needle, and
5 mL sterile syringe with needle.
a The manufacturer will provide the water bath, calibrated thermometer, and calibrated electronic timer to the medical facility at the initial order of Marqibo and will
replace them every 2 years.
b The manufacturer will provide the block heater to the medical facility at the initial order of Marqibo. The block heater will be replaced every 5 years.
c The manufacturer will provide tongs to the medical facility at the initial order of Marqibo.2.3.2 Preparation Instructions for Marqibo (vinCRIStine sulfate LIPOSOME injection), 5 mg/31 mL (0.16 mg/mL)
Procedures for handling and disposal of anticancer drugs should be followed [see References (15)].Call [1 888 292 9617] if you have questions about the preparation of Marqibo. Marqibo takes approximately 60 to 90 minutes to prepare. The preparer should have dedicated uninterrupted time to prepare Marqibo due to the extensive monitoring of temperature and time required for the preparation.
Aseptic technique must be strictly observed since no preservative or bacteriostatic agent is present in Marqibo. The preparation steps of Marqibo that involve mixing the Sodium Phosphate Injection, Sphingomyelin/Cholesterol Liposome Injection, and VinCRIStine Sulfate Injection must be done in a biological safety cabinet or by established pharmacy safety procedures for the preparation of sterile injectable formulations and hazardous drugs. However, the preparation steps that involve placement of the vial in the water bath must be done outside of the sterile area.
Do not use with in-line filters. Do not mix with other drugs.
Water bath process:
- 1. Fill a water bath with water to a level of at least 8 cm (3.2 inches) measured from the bottom and maintain this minimum water level throughout the procedure. The water bath must remain outside of the sterile area.
- 2. Place a calibrated thermometer in the water bath to monitor water temperature and leave it in the water bath until the procedure has been completed.
- 3. Preheat water bath to 63°C to 67°C. Maintain this water temperature until completion of the procedure using the calibrated thermometer.
- 4. Visually inspect each vial in the Marqibo Kit for particulate matter and discoloration prior to preparation, whenever solution and container permit. Do not use if a precipitate or foreign matter is present.
- 5. Remove all the caps on the vials and swab the vials with sterile alcohol pads.
- 6. Vent the Sodium Phosphate Injection vial with a sterile venting needle equipped with a sterile 0.2 micron filter or other suitable venting device in the biological safety cabinet. Always position venting needle point well above liquid level before adding Sphingomyelin/Cholesterol Liposome Injection and VinCRIStine Sulfate Injection.
- 7. Withdraw 1 mL of Sphingomyelin/Cholesterol Liposome Injection.
- 8. Inject 1 mL of Sphingomyelin/Cholesterol Liposome Injection into the Sodium Phosphate Injection vial.
- 9. Withdraw 5 mL of VinCRIStine Sulfate Injection.
- 10. Inject 5 mL of VinCRIStine Sulfate Injection into the Sodium Phosphate Injection vial.
- 11. Remove the venting needle and gently invert the Sodium Phosphate Injection vial 5 times to mix. DO NOT SHAKE.
- 12. Fit Flotation Ring around the neck of the Sodium Phosphate Injection vial.
- 13. Confirm that the water bath temperature is at 63°C to 67°C using the calibrated thermometer. Remove the Sodium Phosphate Injection vial containing VinCRIStine Sulfate Injection, Sphingomyelin/Cholesterol Liposome Injection, and Sodium Phosphate Injection from the biological safety cabinet and place into the water bath for 10 minutes using the calibrated electronic timer. Monitor the temperature to ensure the temperature is maintained at 63°C to 67°C.
- 14. IMMEDIATELY after placing the Sodium Phosphate Injection vial into the water bath, record the constitution start time and water temperature on the Marqibo Overlabel.
- 15. At the end of the 10 minutes using the water bath, confirm that the water temperature is 63°C to 67°C using the calibrated thermometer. Remove the vial from the water bath (use tongs to prevent burns) and remove the Flotation Ring.
- 16. Record the final constitution time and the water temperature on the Marqibo Overlabel.
- 17. Dry the exterior of the Sodium Phosphate Injection vial with a clean paper towel, affix Marqibo (vinCRIStine sulfate LIPOSOME injection) Overlabel, and gently invert 5 times to mix. DO NOT SHAKE.
- 18. Permit the constituted vial contents to equilibrate for at least 30 minutes to controlled room temperature (15°C to 30°C, 59°F to 86°F).
- 19. Marqibo (vinCRIStine sulfate LIPOSOME injection) contains 5 mg/31 mL (0.16 mg/mL) vincristine sulfate. ONCE PREPARED, STORE AT CONTROLLED ROOM TEMPERATURE (15°C to 30°C, 59°F to 86°F) FOR NO MORE THAN 12 HOURS.
- 20. Swab the top of the vial now containing Marqibo with a sterile alcohol pad and return the vial back into the biological safety cabinet.
- 21. Calculate the patient's Marqibo dose based on the patient's actual body surface area (BSA) and remove the volume corresponding to the patient's Marqibo dose from an infusion bag containing 100 mL of 5% Dextrose Injection or 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection.
- 22. Inject the dose of Marqibo into the infusion bag to result in a final volume of 100 mL.
- 23. Complete the information required on the Infusion Bag Label and apply to the infusion bag.
- 24. Finish administration of the diluted product within 12 hours of the initiation of Marqibo preparation.
- 25. Empty, clean, and dry the water bath after each use.
- 26. Deviations in temperature, time, and preparation procedures may fail to ensure proper encapsulation of vincristine sulfate into the liposomes. In the event that the preparation deviates from the instructions in the above steps, the components of the kit should be discarded and a new kit should be used to prepare the dose.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. Do not use if a precipitate or foreign matter is present.
Block heater process:
Note: Do NOT use water with the block heater preparation process.
Note: The flotation ring included with the Marqibo kit is not required for the block heater application.
- 1. Arrange the three heater blocks in the block heater such that the block holding the constitution vial is centered between the two other blank heater blocks. (See the illustration below.)

- 2. Place a calibrated thermometer in the block opening adjacent to the vial well to monitor the temperature. Leave the thermometer in the block opening until the procedure has been completed.
- 3. Turn on the block heater and set the controller to 75°C. Verify the block temperature by checking that the thermometer inserted in the block reads 75 ±2°C. Equilibrate the heating block at 75 ±2°C for 15 minutes. Maintain this block temperature until completion of the procedure using the calibrated thermometer.
- 4. Visually inspect each vial in the Marqibo Kit for particulate matter and discoloration prior to preparation, whenever solution and container permit. Do not use if a precipitate or foreign matter is present.
- 5. Remove all the caps on the vials and swab the vials with sterile alcohol pads.
- 6. Vent the Sodium Phosphate Injection vial with a sterile venting needle equipped with a sterile 0.2 micron filter or other suitable venting device in the biological safety cabinet. Always position venting needle point well above liquid level before adding Sphingomyelin/Cholesterol Liposome Injection and VinCRIStine Sulfate Injection.
- 7. Withdraw 1 mL of Sphingomyelin/Cholesterol Liposome Injection.
- 8. Inject 1 mL of Sphingomyelin/Cholesterol Liposome Injection into the Sodium Phosphate Injection vial.
- 9. Withdraw 5 mL of VinCRIStine Sulfate Injection.
- 10. Inject 5 mL of VinCRIStine Sulfate Injection into the Sodium Phosphate Injection vial.
- 11. Remove the venting needle and gently invert the Sodium Phosphate Injection vial 5 times to mix. DO NOT SHAKE.
- 12. Confirm that the block heater temperature is at 73°C to 77°C using the calibrated thermometer. Remove the Sodium Phosphate Injection vial containing VinCRIStine Sulfate Injection, Sphingomyelin/Cholesterol Liposome Injection, and Sodium Phosphate Injection from the biological safety cabinet and place into the block heater for 18 minutes using the calibrated electronic timer. Monitor the temperature to ensure the temperature is maintained at 73°C to 77°C.
- 13. IMMEDIATELY after placing the Sodium Phosphate Injection vial into the block heater, record the constitution start time and block heater temperature on the Marqibo Overlabel. Use only the calibrated thermometer inserted in the block to monitor temperature.
- 14. At the end of the 18 minutes using the block heater, confirm that the block heater temperature is 73°C to 77°C using the calibrated thermometer. Remove the vial from the block heater (use tongs to prevent burns).
- 15. Record the final constitution time and the block heater temperature on the Marqibo Overlabel.
- 16. Affix Marqibo (vinCRIStine sulfate LIPOSOME injection) Overlabel, and gently invert 5 times to mix. DO NOT SHAKE.
- 17. Permit the constituted vial contents to equilibrate for at least 30 minutes to controlled room temperature (15°C to 30°C, 59°F to 86°F).
- 18. Marqibo (vinCRIStine sulfate LIPOSOME injection) contains 5 mg/31 mL (0.16 mg/mL) vincristine sulfate. ONCE PREPARED, STORE AT CONTROLLED ROOM TEMPERATURE (15°C to 30°C, 59°F to 86°F) FOR NO MORE THAN 12 HOURS.
- 19. Swab the top of the vial now containing Marqibo with a sterile alcohol pad and return the vial back into the biological safety cabinet.
- 20. Calculate the patient’s Marqibo dose based on the patient’s actual body surface area (BSA) and remove the volume corresponding to the patient’s Marqibo dose from an infusion bag containing 100 mL of 5% Dextrose Injection or 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection.
- 21. Inject the dose of Marqibo into the infusion bag to result in a final volume of 100 mL.
- 22. Complete the information required on the Infusion Bag Label and apply to the infusion bag.
- 23. Finish administration of the diluted product within 12 hours of the initiation of Marqibo preparation.
- 24. Deviations in temperature, time, and preparation procedures may fail to ensure proper encapsulation of vincristine sulfate into the liposomes. In the event that the preparation deviates from the instructions in the above steps, the components of the kit should be discarded and a new kit should be used to prepare the dose.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. Do not use if a precipitate or foreign matter is present.
-
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Marqibo is prepared from the components in the Marqibo Kit. Following the preparation procedure according to section 2.3.2, each single-dose vial of Marqibo (vinCRIStine sulfate LIPOSOME injection)contains 5 mg/31 mL (0.16 mg/mL) vincristine sulfate.
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Marqibo is contraindicated in patients with demyelinating conditions including Charcot Marie Tooth syndrome.
Marqibo is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to vincristine sulfate or any of the other components of Marqibo (vinCRIStine sulfate LIPOSOME injection).
Marqibo is contraindicated for intrathecal administration. -
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 For Intravenous Use Only
Fatal if Given by Other Routes. Death has occurred with intrathecal use.
5.2 Extravasation Tissue Injury
Only administer through a secure and free-flowing venous access line. If extravasation is suspected, discontinue infusion immediately and consider local treatment measures.
5.3 Neurologic Toxicity
Sensory and motor neuropathies are common and are cumulative. Monitor patients for symptoms of neuropathy, such as hypoesthesia, hyperesthesia, paresthesia, hyporeflexia, areflexia, neuralgia, jaw pain, decreased vibratory sense, cranial neuropathy, ileus, burning sensation, arthralgia, myalgia, muscle spasm, or weakness, both before and during treatment. Orthostatic hypotension may occur. The risk of neurologic toxicity is greater if Marqibo is administered to patients with preexisting neuromuscular disorders or when other drugs with risk of neurologic toxicity are being given. In the studies of relapsed and/or refractory adult ALL patients, Grade ≥ 3 neuropathy events occurred in 32.5% of patients. Worsening neuropathy requires dose delay, reduction, or discontinuation of Marqibo [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
5.4 Myelosuppression
Monitor complete blood counts prior to each dose of Marqibo. If Grade 3 or 4 neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, or anemia develops, consider Marqibo dose modification or reduction as well as supportive care measures.
5.5 Tumor Lysis Syndrome
Tumor lysis syndrome (TLS) may occur in patients with ALL receiving Marqibo. Anticipate, monitor for, and manage.
5.6 Constipation and Bowel Obstruction
Ileus, bowel obstruction, and colonic pseudo-obstruction have occurred. Marqibo can cause constipation [see Adverse Reactions (6)]. Institute a prophylactic bowel regimen to mitigate potential constipation, bowel obstruction, and/or paralytic ileus, considering adequate dietary fiber intake, hydration, and routine use of stool softeners, such as docusate. Additional treatments, such as senna, bisacodyl, milk of magnesia, magnesium citrate, and lactulose may be considered.
5.7 Fatigue
Marqibo can cause severe fatigue. Marqibo dose delay, reduction, or discontinuation may be necessary.
5.8 Hepatic Toxicity
Fatal liver toxicity and elevated levels of aspartate aminotransferase have occurred. Elevated levels of aspartate aminotransferase of Grade ≥3 occurred in 6-11% of patients in clinical trials. Monitor hepatic function tests. Reduce or interrupt Marqibo for hepatic toxicity.
5.9 Embryofetal Toxicity
Marqibo can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Vincristine sulfate liposome injection was teratogenic or caused embryo-fetal death in animals. Women of childbearing potential should avoid becoming pregnant while being treated with Marqibo. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of Marqibo in pregnant women and there were no reports of pregnancy in any of the clinical studies in the Marqibo clinical development program. If this drug is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to a fetus [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are also discussed in other sections of the labeling:
- For intravenous use only [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Extravasation tissue injury [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Peripheral Neuropathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Myelosuppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Tumor lysis syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Constipation and bowel obstruction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Fatigue [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Hepatic toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
Integrated Summary of Safety in Relapsed and/or Refractory Ph- Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Marqibo, at a dose of 2.25 mg/m2 weekly, was studied in a total of 83 patients in two trials: study 1 and study 2. Adverse reactions were observed in 100% of patients. The most common adverse reactions (>30%) were constipation (57%), nausea (52%), pyrexia (43%), fatigue (41%), peripheral neuropathy (39%), febrile neutropenia (38%), diarrhea (37%), anemia (34%), decreased appetite (33%), and insomnia (32%).
Adverse reactions of Grade 3 or greater were reported in 96% of patients. Adverse reactions of Grade 3 or greater and occurring in ≥ 5% of patients are summarized in Table 2 .
Table 2 Most Commonly Reported (> 5%) Gradea 3 or Greater Adverse Reactions among 83 Patients Receiving the Clinical Dosing Regimen Adverse Reactions Grade ≥ 3
Study 1 and 2
(N=83)
n (%)
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders
47 (56.6)
Febrile Neutropenia
26 (31.3)
Neutropenia
15 (18.1)
Anemia
14 (16.9)
Thrombocytopenia
14 (16.9)
Infections
33 (39.8)
Pneumonia
7 (8.4)
Septic Shock
5 (6.0)
Staphylococcal Bacteremia
5 (6.0)
Neuropathyb
27 (32.5)
Peripheral Sensory and Motor Neuropathy
14 (16.7)
Constipation
4 (4.8)
Ileus, Colonic Pseudo-Obstruction
5 (6.0)
Asthenia
4 (4.8)
Muscular Weakness
1 (1.2)
Respiratory Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders
17 (20.5)
Respiratory Distress
5 (6.0)
Respiratory Failure
4 (4.8)
General Disorders and Administration Site Condition
31 (37.3)
Pyrexia
12 (14.5)
Fatigue
10 (12.0)
Pain
7 (8.4)
Gastrointestinal Disorders
21 (25.3)
Abdominal Pain
7 (8.4)
Investigations
20 (24.1)
Aspartate Aminotransferase Increased
6 (7.2)
Vascular Disorders
8 (9.6)
Hypotension
5 (6.0)
Psychiatric Disorders
9 (10.8)
Mental Status Changes
3 (3.6)
Cardiac Disorders
9 (10.8)
Cardiac Arrest
5 (6.0)
Renal and Urinary Disorders
6 (7.2)
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders
7 (8.4)
a National Cancer Institute (NCI) Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) v3.0.
b Including neuropathy-associated adverse reactions.
A total of 75.9% of patients experienced serious adverse events (SAEs) during the studies. The most commonly reported SAEs included febrile neutropenia (20.5%), pyrexia (13.3%), hypotension (7.2%), respiratory distress (6.0%), and cardiac arrest (6.0%).Dose reduction, delay, or omission occurred in 53% of patients during the treatment.
Twenty-eight percent of patients experienced adverse reactions leading to treatment discontinuation. The most common adverse reactions that caused treatment discontinuation were peripheral neuropathy (10%), leukemia-related (7%), and tumor lysis syndrome (2%).
Adverse reactions related to neuropathy and leading to treatment discontinuation were decreased vibratory sense, facial palsy, hyporeflexia, constipation, asthenia, fatigue, and musculoskeletal pain, each reported in at least 1 patient.
Deaths occurred in 23% of patients in study 1. The non-leukemia related causes of deaths were brain infarct (1), intracerebral hemorrhage (2), liver failure (1), multi system organ failure (2), pneumonia and septic shock (3), respiratory failure (4), pulmonary hemorrhage (1), and sudden cardiac death (1).
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
No formal drug interaction studies have been conducted with Marqibo. Marqibo is expected to interact with drugs known to interact with non-liposomal vincristine sulfate.
Simultaneous oral or intravenous administration of phenytoin and antineoplastic chemotherapy combinations that included non-liposomal vincristine sulfate have been reported to reduce blood levels of phenytoin and to increase seizure activity.
7.1 CYP3A Interactions
Vincristine sulfate, the active agent in Marqibo, is a substrate for cytochrome P450 3A isozymes (CYP3A); therefore, the concomitant use of strong CYP3A inhibitors should be avoided (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole, voriconazole, posaconazole, clarithromycin, atazanavir, indinavir, nefazodone, nelfinavir, ritonavir, saquinavir, telithromycin). Similarly, the concomitant use of strong CYP3A inducers should be avoided (e.g., dexamethasone, phenytoin, carbamazepine, rifampin, rifabutin, rifapentine, phenobarbital, St. John's Wort).
7.2 P-glycoprotein Interactions
Vincristine sulfate, the active agent in Marqibo, is also a substrate for P-glycoprotein (P-gp). The effect of concomitant use of potent P-gp inhibitors or inducers has not been investigated; it is likely that these agents will alter the pharmacokinetics or pharmacodynamics of Marqibo. Therefore the concomitant use of potent P-gp inhibitors or inducers should be avoided.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Based on its mechanism of action and findings from animal studies, Marqibo can cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
If this drug is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to a fetus. In an embryofetal developmental study, pregnant rats were administered vincristine sulfate liposome injection intravenously during the period of organogenesis at vincristine sulfate doses of 0.022 to 0.09 mg/kg/day. Drug related adverse effects included fetal malformations (skeletal and visceral), decreases in fetal weights, increased numbers of early resorptions and post implantation losses, and decreased maternal body weights. Malformations were observed at doses ≥ 0.044 mg/kg/day in animals at systemic exposures approximately 20 40% of those reported in patients at the recommended dose.8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or discontinue the drug taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of Marqibo in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in elderly individuals have not been established. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
8.6 Renal Impairment
The influence of renal impairment on the safety, efficacy, and pharmacokinetics of Marqibo has not been evaluated.
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
Non-liposomal vincristine sulfate is excreted primarily by the liver. The influence of severe hepatic impairment on the safety and efficacy of Marqibo has not been evaluated.
The pharmacokinetics of Marqibo was evaluated in patients with moderate hepatic dysfunction (Child-Pugh B) secondary to melanoma liver metastases. The dose-adjusted maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) and area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) of Marqibo in patients with moderate hepatic impairment was comparable to the Cmax and AUC of patients with ALL who had otherwise normal hepatic function.
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
When Marqibo (vinCRIStine sulfate LIPOSOME injection) was administered at a dose of 2.4 mg/m2, severe toxicities including motor neuropathy of Grade 3, grand mal seizure of Grade 4, and elevated aspartate aminotransferase and hyperbilirubinemia of Grade 4 were reported in 1 patient each. There is no known antidote for overdosage.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Marqibo (vinCRIStine sulfate LIPOSOME injection) is vincristine encapsulated in sphingomyelin/cholesterol liposomes for intravenous administration.
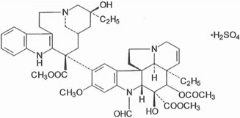
The active ingredient in Marqibo is vincristine sulfate. Vincristine sulfate is a vinca alkaloid isolated as a 1:1 sulfate salt from the periwinkle plant (Catharanthus roseus). It is a hygroscopic, white to slightly yellowish crystalline powder that is soluble in water. It has a molecular weight of 923.04 (salt form) / 824.98 (base form) and a molecular formula of C46H56N4O10 H2SO4. The chemical name for vincristine sulfate is 22-oxovincaleukoblastine and it has the following chemical structure:
Vincristine is encapsulated in a Sphingomyelin/Cholesterol liposome. The lipid components in the liposome are sphingomyelin and cholesterol at a molar ratio of approximately 60:40 (mol:mol).
After preparation, each vial of Marqibo contains 5 mg vincristine sulfate, 500 mg mannitol, 73.5 mg sphingomyelin, 29.5 mg cholesterol, 36 mg sodium citrate, 38 mg citric acid, 355 mg sodium phosphate, and 225 mg sodium chloride.
Marqibo (vinCRIStine sulfate LIPOSOME injection) appears as a white to off-white, translucent suspension, essentially free of visible foreign matter and aggregates, comprised of sphingomyelin/cholesterol liposomes, with an approximate liposome mean diameter of 100 nm. Greater than 95% of the drug is encapsulated in the liposomes.
The Marqibo Kit component vials for the preparation of Marqibo (vinCRIStine sulfate LIPOSOME injection) include:
- VinCRIStine Sulfate Injection, USP (5 mg/5 mL). Each VinCRIStine Sulfate Injection vial consists of 5 mg/5 mL vincristine sulfate (which is equivalent to 4.5 mg/5 mL vincristine free base) and 500 mg/5 mL mannitol.
- Sphingomyelin/Cholesterol Liposome Injection (103 mg/mL). Each Sphingomyelin/Cholesterol Liposome Injection vial consists of 73.5 mg/mL sphingomyelin, 29.5 mg/mL cholesterol, 33.6 mg/mL citric acid, 35.4 mg/mL sodium citrate, and not more than 0.1% ethanol.
- Sodium Phosphate Injection (355 mg/25 mL). Each Sodium Phosphate Injection vial consists of 355 mg/25 mL dibasic sodium phosphate and 225 mg/25 mL sodium chloride.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Marqibo is a sphingomyelin/cholesterol liposome-encapsulated formulation of vincristine sulfate. Non-liposomal vincristine sulfate binds to tubulin, altering the tubulin polymerization equilibrium, resulting in altered microtubule structure and function. Non-liposomal vincristine sulfate stabilizes the spindle apparatus, preventing chromosome segregation, triggering metaphase arrest and inhibition of mitosis.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The plasma pharmacokinetics of Marqibo was investigated in 13 adult patients with relapsed ALL who received a Marqibo dose of 2.25 mg/m2 administered as a 1 hour intravenous infusion. The calculated pharmacokinetic parameters for total plasma vincristine sulfate are given in Table 3 . The vincristine sulfate levels reported in Table 3 reflect liposome encapsulated drug that may not be immediately bioavailable and may not be directly comparable to plasma levels of vincristine sulfate after administration of non liposomal vincristine sulfate, which is immediately bioavailable.
Table 3. Pharmacokinetic Parameters from Patients with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Treated with 2.25 mg/m2 Marqiboa
Variable N Mean SE Median Range AUC∞ (hng/mL) 13 14566 1766 13680 7036-26074 CL (mL/h) 12 345 100 302 148-783 Cmax (ng/mL) 13 1220 64 1230 919-1720 a Dose was administered as a 1 hour infusion.
The plasma clearance (CL) of Marqibo is slow, 345 mL/h, at a dose of 2.25 mg/m2. This is in comparison to the rapid clearance of non liposomal vincristine sulfate at 189 mL/min/m2 (11,340 mL/h). The slow clearance of Marqibo contributes to a much higher AUC for Marqibo relative to non liposomal vincristine sulfate.
Following intravenous administration of Marqibo, urinary excretion was a minor route of elimination for vincristine sulfate and its metabolite. Less than 8% of the administered Marqibo dose was eliminated in urine over a 96 hour observation period, which is similar to the urinary excretion of non liposomal vincristine sulfate. Following non liposomal vincristine sulfate infusion, the main route of vincristine sulfate excretion was the fecal route, accounting for 69% of the administered dose over 72 hours.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No carcinogenicity studies have been conducted with Marqibo or non-liposomal vincristine sulfate. Based on the mechanism of action and genotoxicity findings in nonclinical studies conducted with non-liposomal vincristine sulfate, Marqibo may be carcinogenic.
No genotoxicity studies have been conducted with Marqibo. Non-liposomal vincristine was genotoxic in some in vitro and in vivo studies.
The single- and repeat-dose animal toxicology study results indicate that Marqibo can impair male fertility, consistent with the literature on non-liposomal vincristine sulfate. Administration of vincristine liposome injection causes testicular degeneration and atrophy, and epididymal aspermia in rats.
Gonadal dysfunction has been reported in both male and female post-pubertal patients who received multi-agent chemotherapy including non-liposomal vincristine sulfate. The degree to which testicular or ovarian functions are affected is age-, dose-, and agent-dependent. Recovery may occur in some but not all patients.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
In a repeat-dose comparative toxicology study in rats, vincristine sulfate liposome injection or non-liposomal vincristine sulfate was administered to animals intravenously once per week for 6 weeks. Clinical signs of toxicity consistent with neurotoxicity were greater with vincristine sulfate liposome injection than with non-liposomal vincristine sulfate at equal vincristine sulfate doses of 2 mg/m2/week and included uncoordinated movements, weakness, reduced muscle tone, and limited usage of the limbs. Neurological testing indicated drug-induced peripheral neurotoxicity with both drugs. Based on the histopathology examination after 6 weekly doses, vincristine sulfate liposome injection induced greater peripheral neurotoxicity (nerve fiber degeneration) and secondary skeletal muscle atrophy than the equal dose of non-liposomal vincristine sulfate. In a separate tissue distribution study in rats, administration of 2 mg/m2 of intravenous liposomal or non-liposomal vincristine sulfate showed greater accumulation of vincristine sulfate in sciatic and tibial nerves (as well as the lymph nodes, spleen, and bone marrow) of the animals following vincristine sulfate liposome injection.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Marqibo was studied in an international, open-label, multi-center, single-arm trial (Study 1). Eligible patients were 18 years of age or older with Philadelphia chromosome negative ALL in second or greater relapse or whose disease progressed after two or greater treatment lines of anti-leukemia therapy. Patients had to have achieved a complete remission (CR) to at least one prior anti-leukemia chemotherapy, defined by a leukemia-free interval of equal or more than 90 days. Patients were not eligible for immediate hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) at the time of screening and enrollment.
Patients received intravenous Marqibo monotherapy at 2.25 mg/m2 over 60 minutes every 7 days. Concomitant corticosteroids were not permitted beyond Day 5.
The treated population included 65 patients who received at least 1 dose of Marqibo. All of the treated patients had received prior vincristine sulfate and 80% had evidence of residual neuropathy at study baseline. Among treated patients, 51% were male, 86% were white, 45% were under 30 years of age, 11% were age 65 or older, 48% had undergone prior HSCT, 51% had received 3 or more prior therapies, and 45% were refractory to their immediate prior therapy. Disease characteristics were 85% precursor B-cell ALL and 15% precursor T-cell ALL. In addition, 22 of 65 (34%) treated patients did not receive asparaginase products prior to enrollment. Efficacy results are shown in Table 4.
Table 4. Study 1 ResultsStudy 1(N=65) n (%)
Complete remission (CR)
3 (4.6)
CR with incomplete blood count recovery (CRi)
7 (10.8)
CR + CRi
10 (15.4)
(95% CIa )
(7.6 – 26.5)
MEDIAN DURATION of CR or CRi:
Days (95% CI)
Based on the first date of CR or CRi to the date of the last available histologic assessment of the same response(n=8)
28 (7, 36)
Based on the first date of CR or CRi to date of documented relapse, death, or subsequent chemotherapies including hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) (n=10)
56(9,65)
a CI = Confidence interval (Clopper-Pearson).
-
15 REFERENCES
- 1. NIOSH Alert: Preventing occupational exposure to antineoplastic and other hazardous drugs in healthcare settings. 2004. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, DHHS (NIOSH) Publication No. 2004-165.
- 2. OSHA Technical Manual, TED 1-0.15A, Section VI: Chapter 2. Controlling Occupational Exposure to Hazardous Drugs. OSHA, 1999. http://www.osha.gov/dts/osta/otm/otm_vi/otm_vi_2.html
- 3. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. ASHP guidelines on handling hazardous drugs. Am J Health-Syst Pharm. (2006) 63:1172-1193.
- 4. Polovich M, White JM, Kelleher LO (eds.) 2005. Chemotherapy and biotherapy guidelines and recommendations for practice (2nd. ed.) Pittsburgh, PA: Oncology Nursing Society.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
The Marqibo Kit (NDC # 72893-008-03) contains:
- Vial containing VinCRIStine Sulfate Injection, USP 5 mg/5 mL (1 mg/mL) – NDC # 72893-012-05
- Vial containing Sphingomyelin/Cholesterol Liposome Injection 103 mg/mL – NDC # 72893-011-05
- Vial containing Sodium Phosphate Injection 355 mg/25 mL (14.2 mg/mL) – NDC # 72893-010-05
- Flotation Ring
- Overlabel for Sodium Phosphate Injection vial containing constituted Marqibo (vinCRIStine sulfate LIPOSOME injection), 5 mg/31 mL (0.16 mg/mL)
- Infusion Bag Label
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Physicians are advised to discuss the following with patients prior to treatment with Marqibo:
Extravasation Tissue Injury: Advise patients to report immediately any burning or local irritation during or after the infusion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Ability to Drive or Operate Machinery or Impairment of Mental Ability: Marqibo may cause fatigue and symptoms of peripheral neuropathy. Advise patients not to drive or operate machinery if they experience any of these symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3, 5.7)].
Gastrointestinal/Constipation: Patients receiving Marqibo may experience constipation. Advise patients how to avoid constipation by a diet high in bulk fiber, fruits and vegetables, and adequate fluid intake as well as use of a stool softener, such as docusate. Instruct patients to seek medical advice if they experience symptoms of constipation such bowel movement infrequency, abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, nausea, or vomiting [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Pregnancy/Nursing: Advise patients to use effective contraceptive measures to prevent pregnancy during treatment with Marqibo [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]. Instruct patients to report pregnancy to their physicians immediately. Advise patients that they should not receive Marqibo while pregnant or breastfeeding. If a patient wishes to re-start breastfeeding after treatment, she should be advised to discuss the appropriate timing with her physician [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Concomitant Medications: Advise patients to speak with their physicians about any other medication they are currently taking [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Peripheral Neuropathy: Advise patients to contact their physicians if they experience new or worsening symptoms of peripheral neuropathy such as tingling, numbness, pain, a burning feeling in the feet or hands, or weakness in the feet or hands [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Other: Instruct patients to notify their physicians if they experience fever, productive cough, or decreased appetite [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL

Vial Label
NDC: 72893-012-05
VinCRIStine Sulfate Injection, USP
5 mg/5 mL (1 mg/mL)
for use only in the preparation of Marqibo®
Single Use Vial -
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL

Vial Label
NDC: 72893-011-05
Sphingomyelin-Cholesterol Liposome Injection
103 mg/mL
for use only in the preparation of Marqibo®
Single Use Vial -
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL

Vial Label
NDC: 72893-010-05
Sodium Phosphate Injection
355 mg/25 mL (14.2 mg/mL)
for use only in the preparation of Marqibo®
Single Use Vial -
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL

Kit Label
NDC: 72893-008-03
Marqibo® (vinCRIStine sulfate LIPOSOME injection)
Marqibo Kit Contents:- Sodium Phosphate Injection Vial 355 mg/25 mL (14.2 mg/mL)
- Sphingomyelin-Cholesterol Liposome Injection Vial 103 mg/mL
- VinCRIStine Sulfate Injection, USP Vial 5 mg/5 mL (1 mg/mL)
- Floatation Ring
- Overlabel and Infusion Bag Label
- Package Insert
Single Use Vials
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
MARQIBO
vincristine sulfate kitProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 72893-008 Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 72893-008-03 1 in 1 CARTON; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 01/14/2013 Quantity of Parts Part # Package Quantity Total Product Quantity Part 1 1 VIAL, GLASS 5 mL Part 2 1 VIAL, GLASS 1 mL Part 3 1 VIAL, GLASS 25 mL Part 1 of 3 VINCRISTINE SULFATE
vincristine sulfate injection, solutionProduct Information Item Code (Source) NDC: 72893-012 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Vincristine Sulfate (UNII: T5IRO3534A) (Vincristine - UNII:5J49Q6B70F) Vincristine Sulfate 5 mg in 5 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Mannitol (UNII: 3OWL53L36A) 500 mg in 5 mL Sodium Hydroxide (UNII: 55X04QC32I) Sulfuric Acid (UNII: O40UQP6WCF) Water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 72893-012-05 5 mL in 1 VIAL, GLASS; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA202497 01/14/2013 Part 2 of 3 SPHINGOMYELIN CHOLESTEROL
cholesterol, citric acid monohydrate, sodium citrate, alcohol, and water injection, suspension, liposomalProduct Information Item Code (Source) NDC: 72893-011 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Cholesterol (UNII: 97C5T2UQ7J) Citric Acid Monohydrate (UNII: 2968PHW8QP) SODIUM CITRATE, UNSPECIFIED FORM (UNII: 1Q73Q2JULR) Alcohol (UNII: 3K9958V90M) Water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 72893-011-05 1 mL in 1 VIAL, GLASS; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA202497 01/14/2013 Part 3 of 3 SODIUM PHOSPHATE
sodium phosphate, dibasic, heptahydrate, sodium chloride, and water injection, solutionProduct Information Item Code (Source) NDC: 72893-010 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Sodium Phosphate, Dibasic, Heptahydrate (UNII: 70WT22SF4B) 14.2 mg in 1 mL Sodium Chloride (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) Water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 72893-010-05 25 mL in 1 VIAL, GLASS; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA202497 01/14/2013 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA202497 01/14/2013 Labeler - Acrotech Biopharma LLC (116965616) Registrant - Acrotech Biopharma LLC (116965616) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Hospira Australia Pty Ltd 758967652 MANUFACTURE(72893-008)
Trademark Results [Marqibo]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 MARQIBO 78243740 2869431 Live/Registered |
ACROTECH BIOPHARMA LLC 2003-04-30 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.