NITAZOXANIDE- nitazoxanide tablet, film coated
Nitazoxanide by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Nitazoxanide by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Camber Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Annora Pharma Private Limited. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use NITAZOXANIDE TABLETS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for NITAZOXANIDE TABLETS.
NITAZOXANIDE tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2002INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Nitazoxanide tablets are antiprotozoal indicated for the treatment of diarrhea caused by Giardia lambliaor Cryptosporidium parvum (1).
Limitations of Use:
Nitazoxanide tablets have not been shown to be effective for the treatment of diarrhea caused by C. parvumin HIV-infected or immunodeficient patients (1).DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Nitazoxanide tablets: 500 mg ( 3).
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Hypersensitivity ( 4.1)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions in ≥2% of patients were abdominal pain, headache, chromaturia, and nausea ( 6.1).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Annora Pharma Private Limited at 1-866-495-1995 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.DRUG INTERACTIONS
Competition for binding sites may occur when administered concurrently with other highly plasma protein-bound drugs with narrow therapeutic indices. Monitor for adverse reactions ( 7).
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 12/2025
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage and Important Administration Instructions
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
3.1 Nitazoxanide Tablets (500 mg)
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
4.1 Hypersensitivity
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Highly Protein Bound Drugs with Narrow Therapeutic Indices
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal and Hepatic Impairment
8.7 HIV-Infected or Immunodeficient Patients
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
12.4 Microbiology
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Diarrhea Caused by G. lamblia
14.2 Diarrhea Caused by C. parvum
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 Nitazoxanide Tablets (500 mg)
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Diarrhea caused by Giardia lambliaor Cryptosporidium parvum:
Nitazoxanide tablets (patients 12 years and older) are indicated for the treatment of diarrhea caused by Giardia lambliaor Cryptosporidium parvum.
Limitations of Use
Nitazoxanide tablets have not been shown to be effective for the treatment of diarrhea caused by Cryptosporidium parvumin HIV-infected or immunodeficient patients [see Clinical Studies (14.2)] .
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage and Important Administration Instructions
Important Administration Instructions for Pediatric Patients 11 years of Age or Younger:
Nitazoxanide tablets should not be administered to pediatric patients 11 years of age or younger because a single tablet contains a greater amount of nitazoxanide than the recommended dosing in this pediatric age group.
Table 1. Recommended Dosage
Age
Dosage
Duration
12 years and older
One 500 mg nitazoxanide tablet taken orally every 12 hours with food
3 days
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of nitazoxanide was evaluated in 2177 HIV-uninfected subjects 12 months of age and older who received nitazoxanide tablets or Alina for oral suspension at the recommended dose for at least three days. In pooled controlled clinical trials involving 536 HIV-uninfected subjects treated with nitazoxanide tablets or Alina for oral suspension, the most common adverse reactions were abdominal pain, headache, chromaturia and nausea (≥2%).
Safety data were analyzed separately for 280 HIV-uninfected subjects ≥12 years of age receiving nitazoxanide at the recommended dose for at least three days in 5 placebo-controlled clinical trials and for 256 HIV-uninfected subjects 1 through 11 years of age in 7 controlled clinical trials. There were no differences between the adverse reactions reported for nitazoxanide-treated subjects based upon age.6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of nitazoxanide. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. The following is a list of adverse reactions spontaneously reported with nitazoxanide tablets which were not included in clinical trial listings:
Gastrointestinal disorders:diarrhea, gastroesophageal reflux disease
Nervous System disorders:dizziness
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders:dyspnea
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders:rash, urticaria
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Highly Protein Bound Drugs with Narrow Therapeutic Indices
Tizoxanide (the active metabolite of nitazoxanide) is highly bound to plasma protein (>99.9%). Therefore, monitor for adverse reactions when administering nitazoxanide concurrently with other highly plasma protein-bound drugs with narrow therapeutic indices, as competition for binding sites may occur (e.g., warfarin).
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no data with nitazoxanide in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk. No teratogenicity or fetotoxicity was observed in animal reproduction studies with administration of nitazoxanide to pregnant rats and rabbits during organogenesis at exposures 30 and 2 times, respectively, the exposure at the maximum recommended human dose of 500 mg twice daily based on body surface area (BSA).
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
Nitazoxanide was administered orally to pregnant rats at doses of 0, 200, 800 or 3200 mg/kg/day on gestation days 6 to 15. Nitazoxanide produced no evidence of systemic maternal toxicity when administered once daily via oral gavage to pregnant female rats at levels up to 3200 mg/kg/day during the period of organogenesis.
In rabbits, nitazoxanide was administered at doses of 0, 25, 50, or 100 mg/kg/day on gestation days 7 to 20. Oral treatment of pregnant rabbits with nitazoxanide during organogenesis resulted in minimal maternal toxicity and no external fetal anomalies.8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
No information regarding the presence of nitazoxanide in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production is available. The development and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for nitazoxanide and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from nitazoxanide or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and efficacy of nitazoxanide tablets for the treatment of diarrhea caused by G. lambliaor C. parvumin pediatric patients 12 to 17 years of age has been established based on three (3) randomized controlled studies with 47 pediatric subjects treated with nitazoxanide tablets 500 mg.
A single nitazoxanide tablet contains a greater amount of nitazoxanide than is recommended for use in pediatric patients 11 years or younger. [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.1)] .8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of nitazoxanide tablets did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. In general, the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy in elderly patients should be considered when prescribing nitazoxanide tablets.
8.6 Renal and Hepatic Impairment
The pharmacokinetics of nitazoxanide in patients with compromised renal or hepatic function has not been studied.
8.7 HIV-Infected or Immunodeficient Patients
Nitazoxanide tablets have not been studied for the treatment of diarrhea caused by G. lambliain HIV-infected or immunodeficient patients. Nitazoxanide tablets have not been shown to be superior to placebo for the treatment of diarrhea caused by C. parvumin HIV-infected or immunodeficient patients [see Clinical Studies ( 14)] .
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
Limited information on nitazoxanide overdosage is available. In the event of overdose, gastric lavage may be appropriate soon after oral administration. Patients should be observed and given symptomatic and supportive treatment. There is no specific antidote for overdose with nitazoxanide. Because tizoxanide is highly protein bound (>99.9%), dialysis is unlikely to significantly reduce plasma concentrations of the drug.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
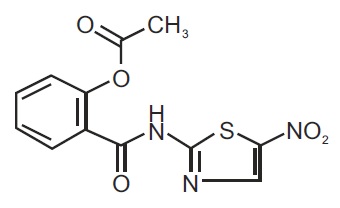
Nitazoxanide tablets contain the active ingredient, nitazoxanide, a synthetic antiprotozoal for oral administration. Nitazoxanide is off-white to yellow powder. It is practically insoluble in ethanol, water and soluble in N, N-dimethylacetamide. Chemically, nitazoxanide is 2-((5-Nitrothiazol-2-yl) carbamoyl) phenyl acetate. The molecular formula is C 12H 9N 3O 5S and the molecular weight is 307.28. The structural formula is:
Nitazoxanide tablets contain 500 mg of nitazoxanide and the following inactive ingredients: corn starch, D&C yellow #10 aluminum lake, FD&C blue #2, FD&C yellow #6, hypromellose, lecithin (soya), magnesium stearate, polyvinyl alcohol, pregelatinized starch, sodium starch glycolate, talc, titanium dioxide and xanthan gum. -
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Single Dosing:
Following oral administration of nitazoxanide tablets, the parent drug, nitazoxanide, is not detected in plasma. The pharmacokinetic parameters of the metabolites, tizoxanide and tizoxanide glucuronide are shown in Tables 2 and 3 below.
Table 2. Mean (± SD) plasma pharmacokinetic parameters of tizoxanide and tizoxanide glucuronide following administration of a single dose of one 500 mg nitazoxanide tablet with food to subjects ≥12 years of age
Tizoxanide
Tizoxanide Glucuronide
Age
C max(mcg/mL)
*T max
(hr)
AUC τ
(mcghr/mL)
C max
(mcg/mL)
*T max
(hr)
AUC τ
(mcghr/mL)
12 to 7 years
9.1 (6.1)
4.0 (1 to 4)
39.5 (24.2)
7.3 (1.9)
4.0 (2 to 8)
46.5 (18.2)
≥18 years
10.6 (2.0)
3.0 (2 to 4)
41.9 (6.0)
10.5 (1.4)
4.5 (4 to 6)
63.0 (12.3)
*T maxis given as a Mean (Range)
Multiple dosing:
Following oral administration of a single nitazoxanide tablet every 12 hours for 7 consecutive days, there was no significant accumulation of nitazoxanide metabolites tizoxanide or tizoxanide glucuronide detected in plasma.
Bioavailability:
Alina for oral suspension is not bioequivalent to nitazoxanide tablets. The relative bioavailability of the suspension compared to the tablet was 70%.
When nitazoxanide tablets are administered with food, the AUC τof tizoxanide and tizoxanide glucuronide in plasma is increased almost two-fold and the C maxis increased by almost 50%.
Nitazoxanide tablets were administered with food in clinical trials and hence they are recommended to be administered with food [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.1)] .
Distribution
In plasma, more than 99% of tizoxanide is bound to proteins.
Elimination
Metabolism
Following oral administration in humans, nitazoxanide is rapidly hydrolyzed to an active metabolite, tizoxanide (desacetyl-nitazoxanide). Tizoxanide then undergoes conjugation, primarily by glucuronidation.
Excretion
Tizoxanide is excreted in the urine, bile and feces, and tizoxanide glucuronide is excreted in urine and bile. Approximately two-thirds of the oral dose of nitazoxanide is excreted in the feces and one-third in the urine.
Specific Populations
Pediatric Patients
The pharmacokinetics of tizoxanide and tizoxanide glucuronide following administration of nitazoxanide tablets in pediatric patients 12 to 17 years of age are provided above in Table 2. Mean (±SD) plasma pharmacokinetic parameters of tizoxanide and tizoxanide glcuronide following administration of a single dose of one 500 mg nitazoxanide tablet with food to subject ≥12 years of age.
Drug Interaction Studies
In vitrostudies demonstrated that tizoxanide has no significant inhibitory effect on cytochrome P450 enzymes.12.4 Microbiology
Mechanism of Action
The antiprotozoal activity of nitazoxanide is believed to be due to interference with the pyruvate:ferredoxin oxidoreductase (PFOR) enzyme-dependent electron transfer reaction which is essential to anaerobic energy metabolism. Studies have shown that the PFOR enzyme from G. lambliadirectly reduces nitazoxanide by transfer of electrons in the absence of ferredoxin. The DNA-derived PFOR protein sequence of C. parvumappears to be similar to that of G. lamblia. Interference with the PFOR enzyme-dependent electron transfer reaction may not be the only pathway by which nitazoxanide exhibits antiprotozoal activity.
Resistance
A potential for development of resistance by C. parvumor G. lambliato nitazoxanide has not been examined.
Antimicrobial Activity
Nitazoxanide and its metabolite, tizoxanide, are active in vitroin inhibiting the growth of (i) sporozoites and oocysts of C. parvumand (ii) trophozoites of G. lamblia.
Susceptibility Test Methods
For protozoa such as C. parvumand G. lamblia, standardized tests for use in clinical microbiology laboratories are not available. -
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Long-term carcinogenicity studies have not been conducted.
Mutagenesis
Nitazoxanide was not genotoxic in the Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell chromosomal aberration assay or the mouse micronucleus assay. Nitazoxanide was genotoxic in one tester strain (TA 100) in the Ames bacterial mutation assay.
Impairment of Fertility
Nitazoxanide did not adversely affect male or female fertility in the rat at 2400 mg/kg/day (approximately 20 times the clinical adult dose adjusted for body surface area). -
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Diarrhea Caused by G. lamblia
Diarrhea caused by G. lambliain adults and adolescents 12 years of age or older:
In a double-blind, controlled trial (Study 1) conducted in Peru and Egypt in adults and adolescents with diarrhea and with one or more enteric symptoms (e.g., abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, fever, abdominal distention, loss of appetite, flatulence) caused by G. lamblia, a three-day course of treatment with nitazoxanide tablets administered 500 mg twice daily was compared with a placebo tablet for 3 days. A second double-blind, controlled trial (Study 2) conducted in Egypt in adults and adolescents with diarrhea and with or without enteric symptoms (e.g., abdominal colic, abdominal tenderness, abdominal cramps, abdominal distention, fever, bloody stool) caused by G. lambliacompared nitazoxanide tablets administered 500 mg twice daily for 3 days to a placebo tablet. For both of these studies, clinical response was evaluated 4 to 7 days following the end of treatment. A clinical response of ‘well’ was defined as ‘no symptoms, no watery stools and no more than 2 soft stools with no hematochezia within the past 24 hours’ or ‘no symptoms and no unformed stools within the past 48 hours.’ The following clinical response rates were obtained:
Table 4. Adult and Adolescent Patients with Diarrhea Caused by G. lamblia Clinical Response Rates* 4 to 7 Days Post-therapy % (Number of Successes/Total)
Nitazoxanide Tablets
Placebo Tablets
Study 1
85% (46/54) ¶ §
44% (12/27)
Study 2
100% (8/8)
30% (3/10)
*Includes all patients randomized with G. lambliaas the sole pathogen. Patients failing to complete the studies were treated as failures.
¶Clinical response rates statistically significantly higher when compared to placebo.
§The 95% confidence interval of the difference in response rates for the tablet and suspension is (-14%, 17%).
Some patients with ‘well’ clinical responses had G. lambliacysts in their stool samples 4 to 7 days following the end of treatment. The relevance of stool examination results in these patients is unknown. Patients should be managed based upon clinical response to treatment.14.2 Diarrhea Caused by C. parvum
Diarrhea caused by C. parvumin adults and adolescents 12 years of age or older:
In a double-blind, controlled trial conducted in Egypt in adults and adolescents with diarrhea and with or without enteric symptoms (e.g., abdominal pain/cramps, nausea, vomiting) caused by C. parvum, a three-day course of treatment with nitazoxanide tablets administered 500 mg twice daily was compared with a placebo tablet for 3 days. Clinical response was evaluated 4 to 7 days following the end of treatment. A clinical response of ‘well’ was defined as ‘no symptoms, no watery stools and no more than 2 soft stools within the past 24 hours’ or ‘no symptoms and no unformed stools within the past 48 hours.’ The following clinical response rates were obtained:
Table 6. Clinical Response Rates in Adult and Adolescent Patients 4 to 7 Days Post-therapy % (Number of Successes/Total)
Nitazoxanide Tablets
Placebo Tablets
Intent-to-treat analysis *
96% (27/28) ¶ §
41% (11/27)
*Includes all patients randomized with C. parvumas the sole pathogen. Patients failing to complete the study were treated as failures.
¶Clinical response rates statistically significantly higher when compared to placebo.
§The 95% confidence interval of the difference in response rates for the tablet and suspension is (-10%, 28%).
In a second double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of nitazoxanide tablets conducted in Egypt in adults and adolescents with diarrhea and with or without enteric symptoms (e.g., abdominal colic, abdominal cramps, epigastric pain) caused by C. parvumas the sole pathogen, clinical and parasitological response rates showed a similar trend to the first study. Clinical response rates, evaluated 2 to 6 days following the end of treatment, were 71% (15/21) in the nitazoxanide group and 42.9% (9/21) in the placebo group.
Some patients with ‘well’ clinical responses had C. parvumoocysts in their stool samples 4 to 7 days following the end of treatment. The relevance of stool examination results in these patients is unknown. Patients should be managed based upon clinical response to treatment. -
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 Nitazoxanide Tablets (500 mg)
Nitazoxanide tablets 500 mg are green colored, round biconvex film-coated tablets debossed with “V1” on one side and “1” on the other side. Each tablet contains 500 mg of nitazoxanide. The tablets are packaged in HDPE bottles of 6, 12 and 30 tablets.
Bottles of 12 tablets NDC: 31722-100-31
Bottles of 30 tablets NDC 31722-100-30
Bottles of 6 tablets NDC: 31722-100-32
Store the tablets at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature] -
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise patients and parents/caregivers of pediatric patients taking nitazoxanide tablets of the following information:
Dosage and Administration:
Nitazoxanide tablets should be taken with food.
Drug-drug Interactions:
Avoid concurrent warfarin use.

Manufactured for:
Camber Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Piscataway, NJ 08854
By: Annora Pharma Pvt. Ltd.
Sangareddy - 502313, Telangana, India.
Revised: 05/2025
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
NITAZOXANIDE
nitazoxanide tablet, film coatedProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 31722-100 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength NITAZOXANIDE (UNII: SOA12P041N) (NITAZOXANIDE - UNII:SOA12P041N) NITAZOXANIDE 500 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength STARCH, CORN (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) D&C YELLOW NO. 10 ALUMINUM LAKE (UNII: CQ3XH3DET6) FD&C BLUE NO. 2 (UNII: L06K8R7DQK) FD&C YELLOW NO. 6 (UNII: H77VEI93A8) HYPROMELLOSE 2910 (15 MPA.S) (UNII: 36SFW2JZ0W) SOYBEAN LECITHIN (UNII: 1DI56QDM62) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) POLYVINYL ALCOHOL, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 532B59J990) SODIUM STARCH GLYCOLATE TYPE A POTATO (UNII: 5856J3G2A2) TALC (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) XANTHAN GUM (UNII: TTV12P4NEE) Product Characteristics Color green Score no score Shape ROUND (biconvex) Size 13mm Flavor Imprint Code V1;1 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 31722-100-31 1 in 1 CARTON 04/15/2025 1 12 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 31722-100-30 1 in 1 CARTON 04/15/2025 2 30 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 3 NDC: 31722-100-32 1 in 1 CARTON 04/15/2025 3 6 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA218701 04/15/2025 Labeler - Camber Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (826774775) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Annora Pharma Private Limited 650980746 manufacture(31722-100)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.