(EUA) Alfa 0.9% Sodium Chloride
ALFA 0.9% SODIUM CHLORIDE by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
ALFA 0.9% SODIUM CHLORIDE by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Laboratorios Alfa SRL. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
ALFA 0.9% SODIUM CHLORIDE- sodium chloride injection, solution
Laboratorios Alfa SRL
Disclaimer: This drug has not been found by FDA to be safe and effective, and this labeling has not been approved by FDA. For further information about unapproved drugs, click here.
----------
(EUA) Alfa 0.9% Sodium Chloride
DESCRIPTION
0.9% SODIUM CHLORIDE ALFA, USP is a sterile, non-pyrogenic solution for fluid replenishment in single-dose containers for intravenous administration. Discard unused portions. It contains no antimicrobial agents.
| Table 1: SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.9% ALFA, USP, FOR INJECTION | |||||
| Size (mL) | Composition (mg/ 100mL) | pH | Ionic Concentration (mEq/L) | ||
| Sodium Chloride, USP (NaCl) | Osmolarity (mOsmol/L)
(Calculated) | Sodium |
Chloride |
||
| 100 | 900 | 308 | 4.5-7.0 | 154 | 154 |
| 250 | |||||
| 500 | |||||
| 1000 | |||||
The Plastic container, 100, 250, 500, 1000mL, Polypropylene (PP) bag with printed literature, injection point, and yellow butterfly port. Protected by a formed, transparent Nylon + PEBDT pouch envelope. Packed in corrugated boxes for 24 units, identified with a white label with the corresponding information.
The Plastic container, 100, 250, 500, 1000mL, Polypropylene (PP) bag with printed literature, SFC port, and a yellow lid. Protected by a formed, transparent Nylon + PEBDT pouch envelope. Packed in corrugated boxes for 24 units, identified with a white label with the corresponding information.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Sodium chloride 0.9% Alfa, USP, for injection is an intravenous solution containing sodium chloride, indicated for parenteral replenishment of fluid and sodium chloride as required by the clinical condition of the patient.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Sodium chloride 0.9% Alfa, USP, for injection is contraindicated in patients with clinically significant hypersensitivity to any of its components. Contraindicated in patients with hypernatremia, hyperchloremia, both arterial and intracranial hypertension. Sodium intake should be carefully monitored in patients with heart disease and chronic renal insufficiency.
WARNINGS
0.9% Sodium chloride Alfa, USP, for injection, should be used with great care, if at all, in patients with congestive heart failure, severe renal insufficiency, and in clinical states in which there exists edema with sodium retention.
The intravenous administration of Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, can cause fluid and/or solute overloading resulting in dilution of serum electrolyte concentrations,
overhydration, congested states, or pulmonary edema.
The risk of dilutive states is inversely proportional to the electrolyte concentration of the injections. The risk of solute overload causing congested states with peripheral and pulmonary edema is directly proportional to the electrolyte concentrations of the
injections.
In patients with diminished renal function, administration of Sodium Chloride Injection, USP may result in sodium retention.
Discard if turbidity or sedimentation is present. Discard if the container is damaged.
PRECAUTIONS
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Caution must be exercised in the administration of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Alfa, USP solution for Injection to patients receiving corticosteroids or corticotrophin.
Pregnancy:
Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy Category C
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with Sodium Chloride Injection, USP. It is also not known whether Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Labor and Delivery
Studies have not been conducted to evaluate the effects of Sodium Chloride Injection, USP on labor and delivery. Caution should be exercised when administering this drug during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, is administered to a nursing mother.
Pediatric Use
The use of Sodium Chloride Injection (USP in pediatric patients is based on clinical practice. Plasma electrolyte concentrations should be closely monitored in the pediatric population as this population may have impaired ability to regulate fluids and electrolytes.
Geriatric Use
In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function and of concomitant disease or drug therapy.
This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function.
Do not administer unless the solution is clear and the container is undamaged. Discard unused portion
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
When administered intravenously, the solution provides a source of water and electrolytes.
Solutions that provide combinations of hypotonic or isotonic concentrations of sodium chloride are suitable for parenteral maintenance or replacement of water and electrolyte requirements.
Isotonic concentrations of sodium chloride are suitable for parenteral replacement of chloride losses that exceed or equal the sodium loss. Hypotonic concentrations of sodium chloride are suited for parenteral maintenance of water requirements when only small quantities of salt are desired. A hypertonic concentration of sodium chloride may be used to repair severe salt depletion syndrome.
Sodium chloride in water dissociates to provide sodium (Na +) and chloride (Cl -) ions. Sodium (Na +) is the principal cation of the extracellular fluid and plays a large part in the therapy of fluid and electrolyte disturbances. Chloride (Cl -) has an integral role in buffering action when oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange occurs in the red blood cells. The distribution and excretion of sodium (Na +) and chloride (Cl -) are largely under the control of the kidney, which maintains a balance between intake and output.
Water is an essential constituent of all body tissues and accounts for approximately 70% of total body weight. Average normal adult daily requirements range from two to three liters (1.0 to 1.5 liters each for insensible water loss by perspiration and urine production).
Water balance is maintained by various regulatory mechanisms. Water distribution depends primarily on the concentration of electrolytes in the body compartments, and sodium (Na +) plays a major role in maintaining physiologic equilibrium.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Reactions that may occur because of the solution or the technique of administration include febrile response, infection at the site of injection, venous thrombosis or phlebitis extending from the site of injection, extravasation, and hypervolemia.
If an adverse reaction does occur, discontinue the infusion, evaluate the patient, institute appropriate therapeutic countermeasures, and save the remainder of the fluid for examination if deemed necessary.
OVERDOSAGE
In the event of overhydration or solute overload, re-evaluate the patient and institute appropriate corrective measures (see WARNINGS, PRECAUTIONS, and ADVERSE REACTIONS).
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
As directed by a doctor. Dosage is dependent upon the age, weight, and clinical condition of the patient, as well as laboratory determinations.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit (see PRECAUTIONS ).
Additives may be incompatible. Consult with a pharmacist if available. When introducing additives, use the aseptic technique, mix thoroughly, and do not store.
Administer intravenously using a strict aseptic technique. Discard the unused portion. Single-use container.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Check for leaks by squeezing the solution container firmly. If leaks are found, discard the solution, as sterility may be impaired. If supplemental medication is desired, follow the directions below before preparing for administration. Check the flexible container solution composition, lot number, and expiry date.
To Open:
- Turn the solution container over so that the text is face down. Using the pre-cut corner tabs, peel open the overwrap and remove the solution container.
- Check the solution container for leaks by squeezing it firmly. If leaks are found or if the seal is not intact, discard the solution.
- Do not use it if the solution is cloudy or a precipitate is present.
NOTE: Before use, perform the following checks:
Inspect each container and read the label before use. Ensure the solution is the one ordered and is within the expiration date.
Invert the container and carefully inspect the solution in good light for cloudiness, haze, or particulate matter. Any container that fails inspection should not be used. Use only if the solution is clear and the container and seals are intact.
Preparation for Administration:
- Remove the plastic protector from the sterile set port at the bottom of the container.
- Attach the administration set. Refer to complete directions accompanying the set.
To Add Medication:
Warning: Some additives may be incompatible.
To Add Medication Before Solution Administration:
Prepare the medication site by removing the additive port closure. Swab the exposed medication site before puncturing.
Using a syringe with 18-22 Ga. needle, puncture medication port and inner diaphragm and inject.
Squeeze and tap ports while ports are upright and mix solution and medication thoroughly.
To Add Medication During Solution Administration:
- Close the clamp on the set.
- Prepare the medication site by removing the additive port closure. Swab the exposed medication site before puncturing.
- Using a syringe with 18-22 Ga. needle of appropriate length (at least 5/8 inch), puncture resealable medication port and inner diaphragm and inject.
- Remove the container from the IV pole and/or turn to an upright position.
- Evacuate both ports by tapping and squeezing them while the container is in the upright position.
- Mix the solution and medication thoroughly.
- Return the container to the in-use position and continue administration.
NOTE: See full directions accompanying the administration set.
WARNING: Do not use a flexible container in series connections.
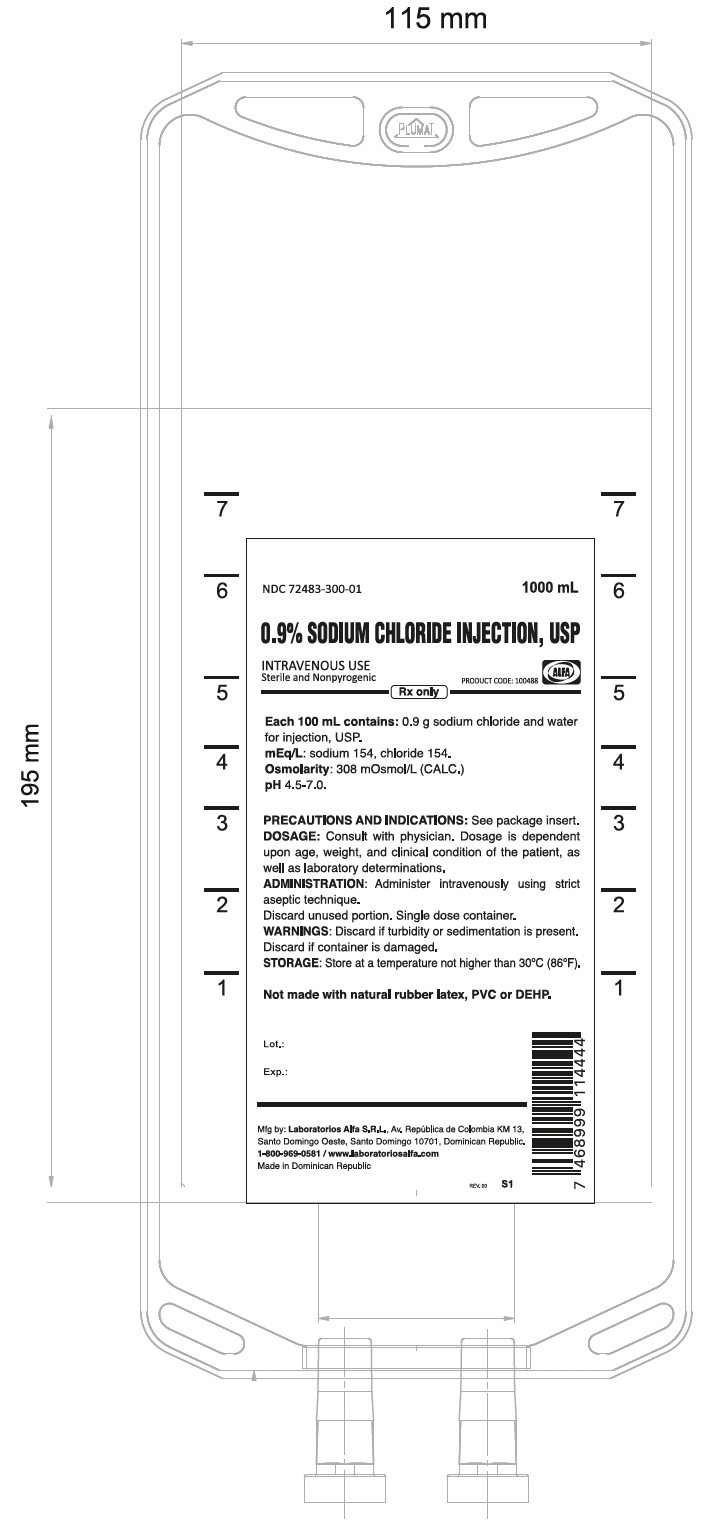
HOW SUPPLIED
| Product Code | Master case (Unit of Sale) | Strength |
Each |
| 100488 | NDC: 72483-300-02
Package of 12 | 0.9% ( 9,000 mg per 1000 mL) (9 mg per mL) | NDC: 72483-300-01
1000 mL bag |
| 100487 | NDC: 72483-301-02
Package of 24 | 0.9% ( 4,500 mg per 500 mL) (9 mg per mL) | NDC: 72483-301-01
500 mL bag |
| 100496 | NDC: 72483-302-02
Package of 24 | 0.9% ( 2,250 mg per 250 mL) (9 mg per mL) | NDC: 72483-302-01
250 mL bag |
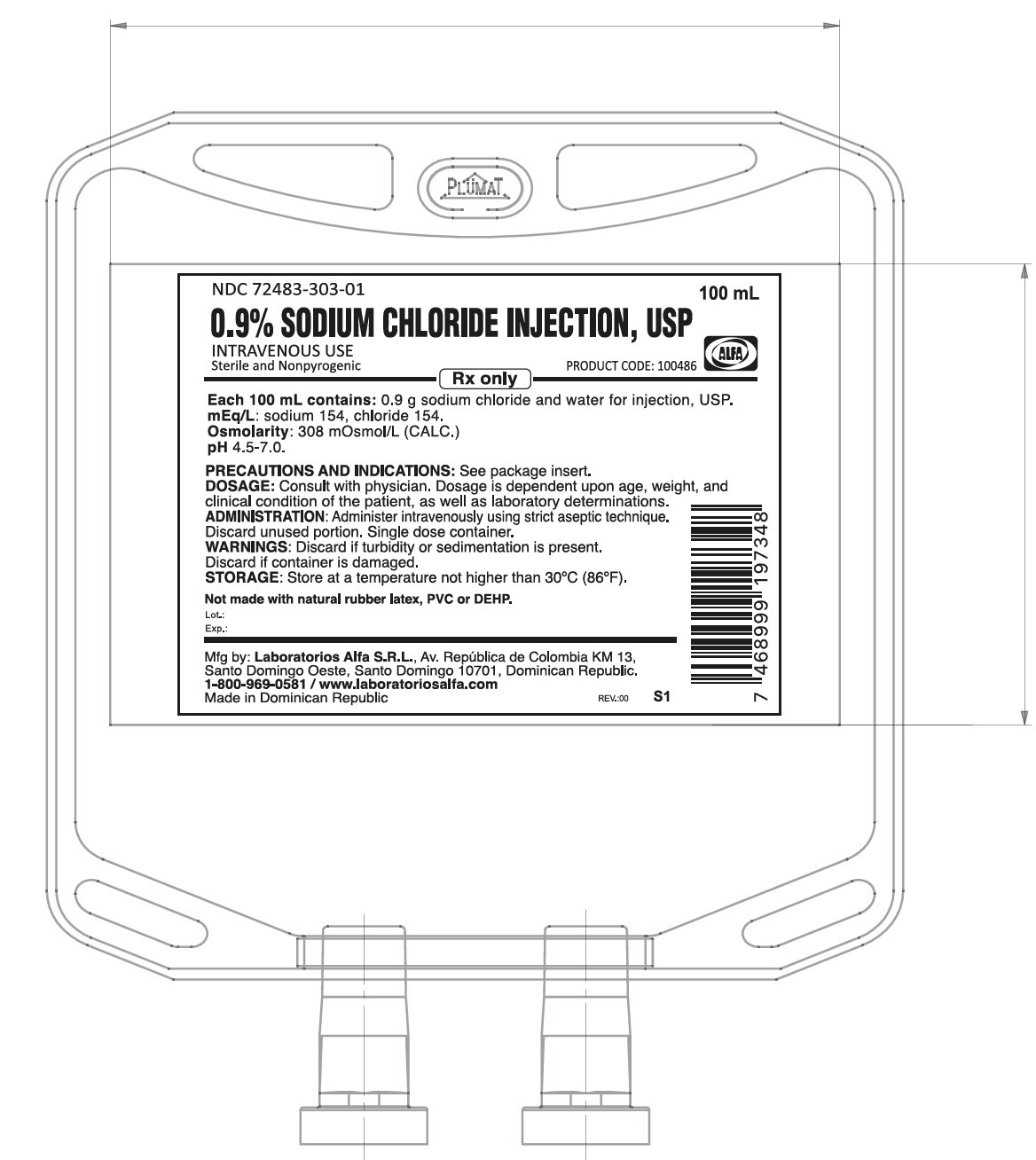
| 100486 | NDC: 72483-303-02
Package of 48 | 0.9% ( 900 mg per 100 mL) (9 mg per mL) | NDC: 72483-303-01
100 mL bag |
| ALFA 0.9% SODIUM CHLORIDE
sodium chloride injection, solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| ALFA 0.9% SODIUM CHLORIDE
sodium chloride injection, solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| ALFA 0.9% SODIUM CHLORIDE
sodium chloride injection, solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| ALFA 0.9% SODIUM CHLORIDE
sodium chloride injection, solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Laboratorios Alfa SRL (815941244) |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.