GINTUIT- allogeneic cultured keratinocytes and fibroblasts in bovine collagen cellular sheet
GINTUIT by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
GINTUIT by is a Other medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Organogenesis, Inc, Organogenesis, Inc . Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use GINTUIT safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for GINTUIT.
GINTUIT (Allogeneic Cultured Keratinocytes and Fibroblasts in Bovine Collagen)
Cellular Sheet for Topical Oral Application
Initial U.S. Approval: 2012INDICATIONS AND USAGE
GINTUIT (Allogeneic Cultured Keratinocytes and Fibroblasts in Bovine Collagen) is an allogeneic cellularized scaffold product indicated for topical (non-submerged) application to a surgically created vascular wound bed in the treatment of mucogingival conditions in adults. (1)
GINTUIT is not intended to provide root coverage. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For topical application in the oral cavity only
GINTUIT is used as one application over a surgically created vascular wound bed in the oral cavity. The size of GINTUIT is adjusted for the size of the wound bed. (2.1)
For single patient use only.
The safety and efficacy of repeat application(s) of GINTUIT have not been established. (2.1) (6.1) (14)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
GINTUIT is available as a ready-to-use circular cellular sheet, 75 millimeter (mm) in diameter and approximately 0.75 mm thick, consisting of human keratinocyte and fibroblast cells, human extracellular matrix proteins, and bovine collagen. Approximately 4 million cells are initially used to manufacture the product. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Oral infection
- Allergy to bovine collagen
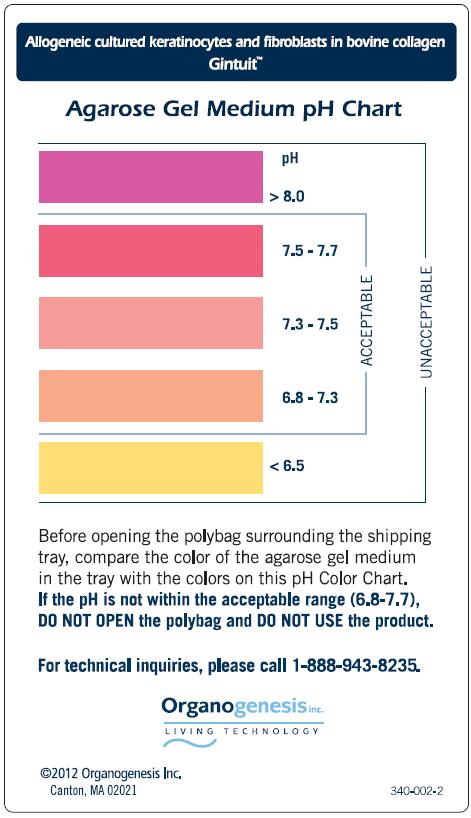
GINTUIT is contraindicated for use on clinically infected wounds and in patients with known allergies to bovine collagen or hypersensitivity to the components of the gel medium (agarose). (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions observed in the clinical trials (≥1%) included sinusitis, nasopharyngitis, respiratory tract infection, aphthous stomatitis, and the local effects of oral surgery. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Organogenesis Inc. at 1-888-943-8235 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Topical cytotoxic antiseptics can degrade GINTUIT.
Exposure to topical cytotoxic antibiotics reduces GINTUIT cell viability. (7)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy: No human or animal data are available. Use only if clearly needed. (8)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 3/2012
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosage
2.2 Preparation
2.3 Application
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Hypersensitivity Reactions
5.2 Wound Infection
5.3 Malignancies
5.4 Transmission of Infectious Diseases
5.5 Sterility Testing
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
GINTUIT (Allogeneic Cultured Keratinocytes and Fibroblasts in Bovine Collagen) is an allogeneic cellularized scaffold product indicated for topical (non-submerged) application to a surgically created vascular wound bed in the treatment of mucogingival conditions in adults.
GINTUIT is not intended to provide root coverage.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For topical application in the oral cavity only
2.1 Dosage
For single patient use only.
GINTUIT is used as one application over a surgically created vascular wound bed in the oral cavity. The size of GINTUIT is adjusted for the size of the wound bed.
The safety and efficacy of repeat application(s) of GINTUIT have not been established.
2.2 Preparation
Preparation of the Surgical Site
Following local anesthesia, surgically create a vascular wound bed with viable wound edges and establish adequate hemostasis.
Preparation of GINTUIT
- Examine the sealed polybag for any leaks or evidence of damage or contamination.
- Verify the expiration date of GINTUIT. The product expires at 11:59 PM ET on the date of expiration.
- Verify that the product pH (6.8-7.7) is within the acceptable range, using the agarose gel medium pH Color Chart.
- Do not open the polybag until the surgical site has been prepared.
- Use GINTUIT within 15 minutes of opening the sealed polybag.
2.3 Application
- Always handle GINTUIT aseptically.
- Do not use GINTUIT if there is evidence of contamination, visible particulates, or pungent odor.
- GINTUIT, as supplied, is not a biohazardous material; however, follow your local (e.g., institutional or private practice) guidelines for disposal of any remaining GINTUIT.
- Lift off the tray lid and place it on a surgical sterile field with the outer lid surface facing down. GINTUIT is packaged with the upper layer (containing keratinocytes that appear dull, with a matte finish) facing up and the lower layer (containing fibroblasts in extracellular matrix that appears glossy) facing down, resting on the polycarbonate base attached to the plastic insert (see Figure 1)

Figure 1:
GINTUIT, as supplied
- Using a sterile blunt instrument, gently tease approximately 0.5 inches (1.3 centimeters) of GINTUIT away from the wall of the plastic insert (see Figure 2). Be careful not to perforate or lift the polycarbonate base beneath GINTUIT. The polycarbonate base should remain attached to the plastic insert.

Figure 2:
Teasing GINTUIT away from the wall of the plastic insert
- With sterile gloved hands, insert either one index finger or a sterile blunt instrument under the released section of GINTUIT (see Figure 3). Use another finger or sterile blunt instrument to grasp GINTUIT in a second spot along the edge. Holding GINTUIT in two places, lift the entire GINTUIT out of the plastic insert using a smooth, even motion to prevent GINTUIT from bending and folding over onto itself.
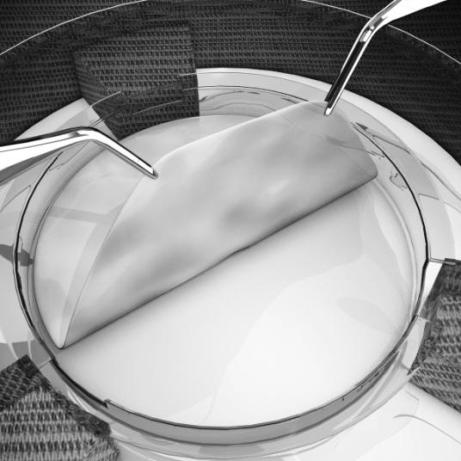

Figure 3:
GINTUIT being lifted off the polycarbonate base - Place GINTUIT on the inner surface of the tray lid, maintaining the proper orientation (upper layer facing up) (see Figure 4). Handle GINTUIT by its edge to minimize damage.
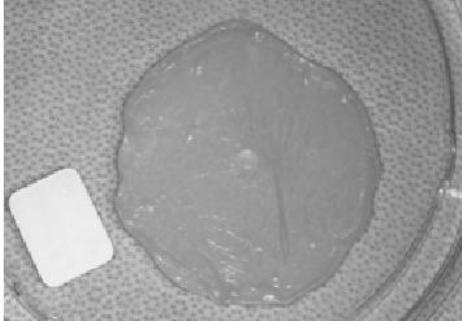
Figure 4:
GINTUIT placed in the inner surface of the upper tray lid
- Following removal of GINTUIT from the plastic insert, lift the plastic insert that contains the polycarbonate base from the bottom tray to ensure that this base is intact (see Figure 5a - intact polycarbonate base, and Figure 5b - torn polycarbonate base). Verify that pieces of this base are not removed and accidently applied to the patient.
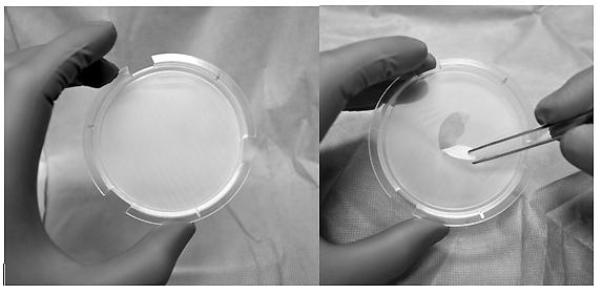
Figure 5:
(a) Intact polycarbonate base and (b) torn polycarbonate base
- Fold GINTUIT into a “z-fold” resulting in the upper layer exposed on the top side and the bottom layer exposed at the bottom side using either sterile gloved hands or sterile blunt instruments (see Figure 6).
Note: Do not allow GINTUIT to fold or wrinkle upon itself. If needed, add sterile saline or another physiological salt solution to GINTUIT in the tray lid to facilitate folding. Do not use water.
Figure 6: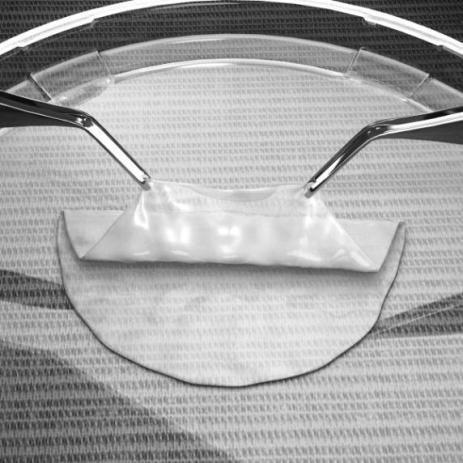
Folding GINTUIT
- Trim GINTUIT with surgical scissors to the size needed for the surgical site. Use a sterile periodontal probe or other blunt instrument to stabilize the “z-folded” GINTUIT while trimming (see Figure 7).
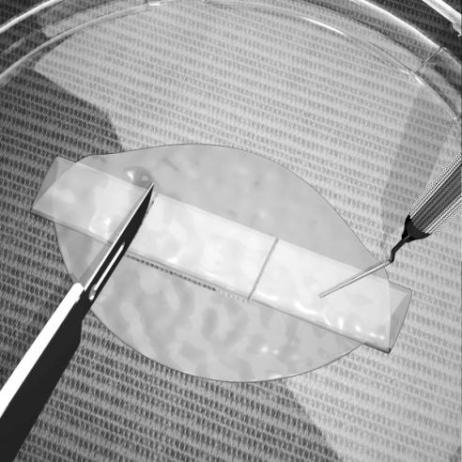

Figure 7:
Trimming GINTUIT
- Place the lower layer (i.e., fibroblast/extracellular matrix side) of GINTUIT in direct contact with the surgical site so that there are no pockets or wrinkled edges (see Figure 8). If needed, use saline to smooth wrinkles.
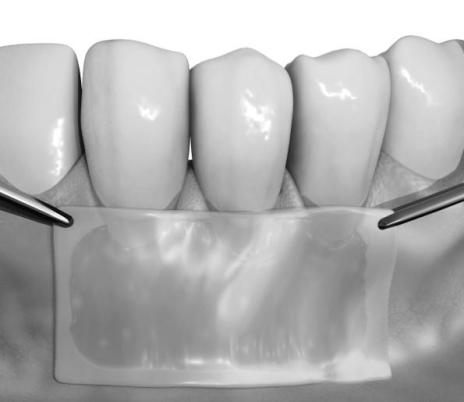
Figure 8:
Placement of GINTUIT on the surgical wound bed
- Immobilize and attach GINTUIT to the surgical mucosal defect with sutures placed at the papillae and apically at each corner. If necessary, add a central suture at the apical margin or lateral margins. Use a crisscross (i.e., suspensory or sling) suture over GINTUIT to enhance stability and help maintain direct contact with the wound bed. GINTUIT must not move during mucosal or muscle traction. Tension may cause GINTUIT to tear.
- If possible, to help protect GINTUIT, place an additional layer of GINTUIT, extending laterally beyond the defect margins over the “z-folded” GINTUIT, and suture at the four corners. The bottom side (i.e., fibroblast/collagen side) of this additional layer should be in contact with the previously applied “z-folded” GINTUIT.
- Place a non-occlusive protective dressing over the treated site.
-
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
GINTUIT is available as a circular cellular sheet, 75 millimeters (mm) in diameter and approximately 0.75 mm thick, consisting of human keratinocyte and fibroblast cells, human extracellular matrix proteins, and bovine collagen. Approximately 4 million cells are initially used to manufacture the product.
GINTUIT is stored on a semi-permeable polycarbonate base within a plastic insert, which separates the product from an agarose gel medium in a sterile transparent shipping tray.
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Hypersensitivity Reactions
There is a potential for hypersensitivity reactions to occur with GINTUIT.
Monitor for both early and later signs of hypersensitivity reaction following GINTUIT application. Evaluate and treat signs and symptoms of potential allergic reactions according to standard practice. If necessary, remove GINTUIT as part of the treatment for the allergic reaction.
5.2 Wound Infection
Monitor for signs and symptoms of wound infection. Signs of surgical site infection may include pain, edema, erythema, drainage, odor, warmth, or fever. The diagnosis of wound infection may be complicated by the white or yellow appearance of GINTUIT after it becomes hydrated with wound fluid.
5.3 Malignancies
The safety of this product for oral administration has not been evaluated beyond six months. The long-term potential for oral mucosal cancers to arise from, or in response to, this product is unknown.
5.4 Transmission of Infectious Diseases
Transmission of infectious diseases by known or unknown infectious agents may occur with GINTUIT.
GINTUIT contains cells derived from donated human newborn foreskin tissue. The foreskin donor’s mother was tested and found negative for human pathogens, including antibodies to human immunodeficiency virus types 1 and 2 (HIV-1 and HIV-2), human T-lymphotropic virus types 1 and 2 (HTLV-1 and HTLV-2), hepatitis A virus (HAV), hepatitis B virus (HBV), hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg), hepatitis C virus (HCV), West Nile virus (WNV), Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), cytomegalovirus (CMV), and syphilis. GINTUIT cells are tested for human and animal viruses, retroviruses, bacteria, fungi, yeast, and mycoplasma.
Product manufacture also includes reagents derived from animal materials, including bovine pituitary extract (BPE). All animal-derived reagents are tested for viruses, retroviruses, bacteria, fungi, yeast, and mycoplasma before use. Bovine materials are sourced to minimize bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE), the cause of a rare fatal condition in humans called variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD). vCJD has never been attributed to use of any medical product manufactured with BPE, but the theoretical possibility cannot be dismissed.
These measures do not totally eliminate the risk of transmitting these or other transmissible infectious diseases and disease agents. Report the occurrence of a transmitted infection to Organogenesis Inc. at 1-888-943-8235.
5.5 Sterility Testing
GINTUIT is shipped after passing primary test results from in-process microbial tests. A final sterility test is initiated prior to shipping, but the result will not be available for up to 14 days. If microbial contamination is detected after the product has been shipped, Organogenesis will notify health care providers and recommend appropriate actions.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions observed in the clinical trials (≥1%) included sinusitis, nasopharyngitis, respiratory tract infections, aphthous stomatitis, and the local effects of oral surgery.
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of GINTUIT cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another product and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
GINTUIT has been studied in two randomized, within-subject controlled (i.e., each subject received both GINTUIT and control treatment) clinical studies. The control treatment was a free gingival graft (FGG), using donor graft tissue from the subject’s palate. The duration of the studies was six months following GINTUIT application. Study One was a single-center study (n=25) to evaluate the safety and efficacy of GINTUIT in establishing a zone of attached gingiva. Study Two was a multicenter study (n=96) to evaluate the safety and efficacy of GINTUIT in establishing keratinized tissue (KT) in a similar study population.
Overall, 34% of subjects reported at least one adverse reaction. Table 1 lists all reported adverse reactions that occurred at an incidence of 1% or greater.
Table 1: Adverse Reactions Reported at a Frequency of ≥1% (n=121)* Reported Adverse Reaction (MedDRA Preferred Term) Subject
n (%)Events
nOVERALL 41 (34%) 65 Sinusitis 5 (4%) 6 Nasopharyngitis 2 (2%) 2 Respiratory Tract Infection 2 (2%) 2 Upper Respiratory Tract Infection 2 (2%) 2 Aphthous Stomatitis 2 (2%) 2 Oral Pain 2 (2%) 2 Mouth Injury 2 (2%) 2 Hypoaesthesia Facial 2 (2%) 2 * Study One (n=25); Study Two (n=96) In Studies One and Two, local (occurring at the site of GINTUIT application) adverse reactions included gingival pain, gingival injury (due to inadvertent failure to remove a polycarbonate base from GINTUIT before application), and ulceration.
In another study (n=15), in which the placement of GINTUIT was under a mucosal flap, local (occurring at the site of GINTUIT application) adverse reactions included impaired healing and suture-related complications.
The safety of GINTUIT beyond six months was not evaluated in the clinical trials.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
GINTUIT is manufactured using a similar process as Apligraf, an FDA-approved medical device. Localized allergic reaction, skin inflammation and erosion, skin blistering, localized wound infection, and cellulitis have been reported during post-approval use of Apligraf for the treatment of chronic cutaneous wounds. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily by a population of uncertain size, and because there are no controls, it is not possible to determine their frequency in the exposed population or establish a causal relationship to exposure to Apligraf. It is uncertain whether information obtained from the postmarketing safety database from use of Apligraf in chronic cutaneous wounds can be extrapolated to use of GINTUIT in the oral environment.
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Exposure to topical antiseptics, such as povidone-iodine solution and chlorhexidine (concentrations greater than 0.12%), has been shown to degrade GINTUIT during in vitro and in vivo histological studies.
Exposure to topical antibiotics such as polymyxin/nystatin also reduces GINTUIT cell viability.
If cytotoxic topical antiseptics or antibiotics, including those listed above, have been used, then irrigate the wound thoroughly with saline and allow a suitable wash-out period to elapse before applying GINTUIT.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with GINTUIT. It is also unknown whether GINTUIT can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. GINTUIT should be used in a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
GINTUIT, Allogeneic Cultured Keratinocytes and Fibroblasts in Bovine Collagen, is a cellular sheet that contains allogeneic human cells, human extracellular matrix proteins, and bovine collagen for topical application in the oral cavity. GINTUIT appears off-white in color and is comprised of two main layers: an upper cornified layer formed by keratinocytes, and a lower layer constructed of bovine-derived collagen, human extracellular matrix proteins, and dermal fibroblasts. These components interact and produce the final bilayered structure. GINTUIT does not contain Langerhans cells, melanocytes, macrophages, lymphocytes, blood vessels, or hair follicles.
The active ingredients of GINTUIT are the allogeneic keratinocytes, allogeneic dermal fibroblasts, and bovine Type I collagen. In vitro studies have shown that GINTUIT secretes human growth factors and cytokines, and contains extracellular matrix proteins. Growth factors, cytokines, and extracellular matrix proteins are known to be involved in wound repair and regeneration.
The cells are isolated from donated human newborn foreskin tissue and are multiplied into cell banks used in large-scale manufacturing. The donor’s mother is tested and found negative for human pathogens, and the cell banks are extensively tested for microbiological safety [See Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Product manufacture also uses reagents derived from animal materials including bovine collagen and bovine pituitary extract (BPE). These reagents are tested for viruses, retroviruses, bacteria, fungi, yeast, and mycoplasma before use.
GINTUIT is shipped in an agarose gel medium to maintain product potency and therefore may contain low amounts of inactive components present from the media. These include agarose Type IV HI EEO, L-glutamine, hydrocortisone, full-chain human recombinant insulin, ethanolamine, O-phosphorylethanolamine, adenine, selenious acid, Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) nutrients, Ham’s F-12 nutrients, sodium bicarbonate, calcium chloride, and water for injection.
A final sterility test is initiated prior to shipping, but the result will not be available for up to 14 days. Passing results from in-process microbial tests are required for release of GINTUIT for shipping.
- 12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy analysis of GINTUIT was based on two six-month, prospective, randomized, within subject controlled (matched for teeth and gingival condition), treatment comparison clinical trials. A total of 107 subjects from the two trials were included in the efficacy analysis. Each subject received GINTUIT and a free gingival graft (FGG) taken from the subject’s palate (control), with placement sites randomized to two non-adjacent teeth on contralateral sides of the jaw. Treatment of the underlying disease was not addressed in the studies. All subjects completed all study visits in both trials. Subjects in Study One (n=22) were predominantly White (86%) and female (68%), with a mean age of 50 years (range, 31-70). Subjects in Study Two (n=85) were predominantly White (91%) and female (54%), with a mean age of 47 years (range, 18-71).
Study One was a non-inferiority study, conducted at a single center (n=25). The three subjects who participated as training subjects were not included in the efficacy analysis (n=22 for efficacy analysis). The study was designed to rule out a greater than 1 mm decrease in the change in attached gingiva for GINTUIT relative to control. In addition, the amount of keratinized tissue (KT) at the application site was measured. For inclusion, subjects had an insufficient zone of attached gingiva (≤ mm) that required soft tissue grafting. At six months, 14/22 (63.6%) GINTUIT sites and 21/22 (95%) control sites showed an increase in attached gingiva. The mean increase in the amount of attached gingiva was 0.85 mm (95% CI 0.48, 1.21) for GINTUIT and 2.43 mm (95% CI 2.06, 2.79) for control. At least 2 mm of KT width was established in 18/22 (81.8 %) of GINTUIT sites and in 22/22 (100%) of control sites. The mean increase in KT width was 1.37 mm (95% CI 0.97, 1.77) at GINTUIT sites and 3.33 mm (95% CI 2.93, 3.74) at control sites.
Study Two was a multi-center study conducted at four sites in the United States (n = 96). Eleven subjects participated as training subjects and were not included in the efficacy analysis (n=85 for efficacy analysis). The study was designed to determine the percentage of sites with ≥2 mm KT at six months. Eighty-one of the 85 subjects (95.3%) demonstrated ≥2 mm KT at the GINTUIT site (See Table 2). All 96 subjects demonstrated ≥2 mm KT at the control site.
Table 2: Keratinized Tissue ≥2 mm at the GINTUIT site at 6 Months Month 6 Statistics GINTUIT Subjects with KT width ≥2 mm
KT width (mm)n
n (%)
95% CI
p- value*
Mean (SD)
Median
Min., Max85
81 (95.3%)
(88.4, 98.7)
<0.001*
3.21 (1.14)
3.0
1.0, 6.0* Comparison to a pre-defined standard of 50% of subjects with KT width ≥2 mm
In Study Two, GINTUIT sites exhibited superiority for color matching and texture matching (p< 0.0001) and subject preference (p<0.0001) when compared to control.
The effectiveness of GINTUIT beyond six months or with repeat administration was not evaluated in the clinical trials.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
GINTUIT is supplied ready for use as a cellular sheet approximately 75 mm in diameter and 0.75 mm thick, in a sealed heavy-gauge polyethylene bag (polybag) with a 10% CO2/air atmosphere. GINTUIT is stored on a semi-permeable polycarbonate base within a plastic insert, which separates the product from the agarose gel medium in a sterile transparent shipping tray.
(NDC: 42606-044-01)Storage and Handling
- To maintain cell viability, store GINTUIT in the sealed polybag at 68°F to 73°F (20°C to 23°C) in its shipping box with all insulating components intact until use.
- DO NOT FREEZE OR REFRIGERATE, sterilize, or incubate GINTUIT.
- Inspect the packaging for damage. DO NOT USE GINTUIT if the packaging or seal is damaged.
- Use GINTUIT prior to 11:59 PM ET on the date of expiration printed on the package.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Prior to application of GINTUIT, the healthcare provider should
- Discuss the procedure and ask the patient to report any persistent symptoms that occur following the surgical procedure.
- Ask the patient about history of allergy to bovine collagen.
Following application of GINTUIT, provide post-procedure instructions, including the following
- Expect mild to moderate redness, swelling, bruising, or pain following the surgery.
- Do not disturb or disrupt the surgical dressing or GINTUIT. Contact the dental care provider if GINTUIT is dislodged. Leave the post-procedure surgical dressing in place until it falls off on its own, or as instructed by the dental care provider.
- If the dental care provider prescribes a mouth rinse, use it as prescribed and directed. Avoid aggressive rinsing while the dressing is in place.
- Do not brush teeth for the first two weeks after the procedure. After two weeks, resume gentle brushing as directed by the dental care provider. Avoid directly brushing the surgically treated area until instructed by the dental care provider to resume normal brushing.
- Avoid eating hard or rough foods or chewing food on the treated side of the mouth until evaluated by the dental care provider.
- Avoid touching the surgical dressing or treated areas or pulling on the lips or cheek for the first four weeks.
- When directed by the dental care provider, stop using the prescribed rinse and gradually resume normal tooth brushing and flossing.
- Contact the dental care provider if any persistent or unexpected side effects occur.
- Label
- pH color chart
- Instruction
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
GINTUIT
allogeneic cultured keratinocytes and fibroblasts in bovine collagen cellular sheetProduct Information Product Type CELLULAR THERAPY Item Code (Source) NDC: 42606-004 Route of Administration TOPICAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength FORESKIN FIBROBLAST (NEONATAL) (UNII: T34C307W5N) (FORESKIN FIBROBLAST (NEONATAL) - UNII:T34C307W5N) FORESKIN FIBROBLAST (NEONATAL) BOVINE TYPE I COLLAGEN (UNII: FHJ3ATL51C) (BOVINE TYPE I COLLAGEN - UNII:FHJ3ATL51C) BOVINE TYPE I COLLAGEN FORESKIN KERATINOCYTE (NEONATAL) (UNII: ZJO8CP3Q2A) (FORESKIN KERATINOCYTE (NEONATAL) - UNII:ZJO8CP3Q2A) FORESKIN KERATINOCYTE (NEONATAL) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 42606-004-01 44.2 cm2 in 1 TRAY Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA125400 03/15/2012 Labeler - Organogenesis, Inc (152165817) Registrant - Organogenesis, Inc (152165817) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Organogenesis, Inc 152165817 manufacture, analysis, pack, label
Trademark Results [GINTUIT]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 GINTUIT 98171634 not registered Live/Pending |
Organogenesis Inc. 2023-09-08 |
 GINTUIT 88714232 not registered Live/Pending |
Organogenesis Inc. 2019-12-04 |
 GINTUIT 85556369 4463271 Live/Registered |
Organogenesis Inc. 2012-02-29 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.