Bromfenac by Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc. BROMFENAC solution
Bromfenac by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Bromfenac by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use BROMFENAC OPHTHALMIC SOLUTION, 0.09% safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for BROMFENAC OPHTHALMIC SOLUTION, 0.09%.
BROMFENAC ophthalmic solution, 0.09%
Initial U.S. Approval: 1997INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Bromfenac ophthalmic solution, 0.09% is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) indicated for the treatment of postoperative inflammation and reduction of ocular pain in patients who have undergone cataract extraction (1).
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Instill one drop into the affected eye once daily beginning 1 day prior to surgery, continued on the day of surgery and through the first 14 days post-surgery (2.1).
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Topical ophthalmic solution: bromfenac 0.09% (3)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most commonly reported adverse reactions in 2 to 7% of patients were abnormal sensation in eye, conjunctival hyperemia and eye irritation (including burning/stinging) (6.1).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-800-399-2561 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 11/2025
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosing
2.2 Use with Other Topical Ophthalmic Medications
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Sulfite Allergic Reactions
5.2 Slow or Delayed Healing
5.3 Potential for Cross-Sensitivity
5.4 Increased Bleeding Time
5.5 Keratitis and Corneal Reactions
5.6 Contact Lens Wear
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
6.2 Post-Marketing Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis and Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Ocular Inflammation and Pain
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
17.1 Slowed or Delayed Healing
17.2 Sterility of Dropper Tip
17.3 Concomitant Use of Contact Lenses
17.4 Concomitant Topical Ocular Therapy
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosing
For the treatment of postoperative inflammation in patients who have undergone cataract extraction, one drop of bromfenac ophthalmic solution should be applied to the affected eye once daily beginning 1 day prior to cataract surgery, continued on the day of surgery, and through the first 14 days of the postoperative period.
2.2 Use with Other Topical Ophthalmic Medications
Bromfenac ophthalmic solution may be administered in conjunction with other topical ophthalmic medications such as alpha-agonists, beta-blockers, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, cycloplegics, and mydriatics. Drops should be administered at least 5 minutes apart.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Sulfite Allergic Reactions
Contains sodium sulfite, a sulfite that may cause allergic-type reactions including anaphylactic symptoms and life-threatening or less severe asthmatic episodes in certain susceptible people. The overall prevalence of sulfite sensitivity in the general population is unknown and probably low. Sulfite sensitivity is seen more frequently in asthmatic than in non-asthmatic people.
5.2 Slow or Delayed Healing
All topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may slow or delay healing. Topical corticosteroids are also known to slow or delay healing. Concomitant use of topical NSAIDs and topical steroids may increase the potential for healing problems.
5.3 Potential for Cross-Sensitivity
There is the potential for cross-sensitivity to acetylsalicylic acid, phenylacetic acid derivatives, and other NSAIDs. Therefore, caution should be used when treating individuals who have previously exhibited sensitivities to these drugs.
5.4 Increased Bleeding Time
With some NSAIDs, there exists the potential for increased bleeding time due to interference with platelet aggregation. There have been reports that ocularly applied NSAIDs may cause increased bleeding of ocular tissues (including hyphemas) in conjunction with ocular surgery.
It is recommended that bromfenac ophthalmic solution be used with caution in patients with known bleeding tendencies or who are receiving other medications which may prolong bleeding time.
5.5 Keratitis and Corneal Reactions
Use of topical NSAIDs may result in keratitis. In some susceptible patients, continued use of topical NSAIDs may result in epithelial breakdown, corneal thinning, corneal erosion, corneal ulceration or corneal perforation. These events may be sight threatening. Patients with evidence of corneal epithelial breakdown should immediately discontinue use of topical NSAIDs and should be closely monitored for corneal health.
Post-marketing experience with topical NSAIDs suggests that patients with complicated ocular surgeries, corneal denervation, corneal epithelial defects, diabetes mellitus, ocular surface diseases (e.g., dry eye syndrome), rheumatoid arthritis, or repeat ocular surgeries within a short period of time may be at increased risk for corneal adverse events which may become sight threatening. Topical NSAIDs should be used with caution in these patients.
Post-marketing experience with topical NSAIDs also suggests that use more than 24 hours prior to surgery or use beyond 14 days post surgery may increase patient risk for the occurrence and severity of corneal adverse events.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
The most commonly reported adverse experiences reported following use of bromfenac after cataract surgery include: abnormal sensation in eye, conjunctival hyperemia, eye irritation (including burning/stinging), eye pain, eye pruritus, eye redness, headache, and iritis. These events were reported in 2 to 7% of patients.
6.2 Post-Marketing Experience
The following events have been identified during post-marketing use of bromfenac ophthalmic solution, 0.09% in clinical practice. Because they are reported voluntarily from a population of unknown size, estimates of frequency cannot be made. The events, which have been chosen for inclusion due to either their seriousness, frequency of reporting, possible causal connection to topical bromfenac ophthalmic solution, 0.09% or a combination of these factors, include corneal erosion, corneal perforation, corneal thinning, and epithelial breakdown [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5)]
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C:
Reproduction studies performed in rats at oral doses up to 0.9 mg/kg/day (1300 times the recommended human ophthalmic dose [RHOD]) and in rabbits at oral doses up to 7.5 mg/kg/day (11,000 times RHOD) revealed no evidence of teratogenicity due to bromfenac. However, 0.9 mg/kg/day in rats caused embryo-fetal lethality, increased neonatal mortality, and reduced postnatal growth. Pregnant rabbits treated with 7.5 mg/kg/day caused increased post-implantation loss.
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Nonteratogenic Effects
Because of the known effects of prostaglandin biosynthesis-inhibiting drugs on the fetal cardiovascular system (closure of ductus arteriosus), the use of bromfenac ophthalmic solution during late pregnancy should be avoided.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Caution should be exercised when bromfenac ophthalmic solution is administered to a nursing woman.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Bromfenac ophthalmic solution, 0.09% is a sterile, topical, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) for ophthalmic use. Each mL of bromfenac ophthalmic solution, 0.09% contains 1.035 mg bromfenac sodium (equivalent to 0.9 mg bromfenac free acid). Bromfenac sodium is designated chemically as sodium 2-amino-3-(4-bromobenzoyl) phenylacetate sesquihydrate, with a molecular formula of C15H11BrNNaO3. 1½ H2O. The structural structure for bromfenac sodium is:
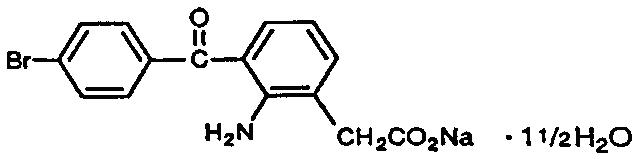
Bromfenac sodium is a yellow to orange crystalline powder. The molecular weight of bromfenac sodium is 383.17. Bromfenac ophthalmic solution is supplied as a sterile aqueous 0.09% solution, with a pH of 8.3. The osmolality of bromfenac ophthalmic solution is approximately 300 mOsmol/kg.
Each mL of bromfenac ophthalmic solution contains:
Active: bromfenac sodium hydrate 0.1035% (1.035 mg)
Preservative: benzalkonium chloride NF (0.05 mg/mL)
Inactives: boric acid, edetate disodium dihydrate (0.2 mg/mL), polysorbate 80 (1.5 mg/mL), povidone (20 mg/mL), sodium borate, sodium sulfite anhydrous (2 mg/mL), sodium hydroxide to adjust pH and water for injection.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Bromfenac is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that has anti-inflammatory activity. The mechanism of its action is thought to be due to its ability to block prostaglandin synthesis by inhibiting cyclooxygenase 1 and 2.
Prostaglandins have been shown in many animal models to be mediators of certain kinds of intraocular inflammation. In studies performed in animal eyes, prostaglandins have been shown to produce disruption of the blood-aqueous humor barrier, vasodilation, increased vascular permeability, leukocytosis, and increased intraocular pressure.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The plasma concentration of bromfenac following ocular administration of bromfenac ophthalmic solution, 0.09% in humans is unknown. Based on the maximum proposed dose of one drop to the eye (0.045 mg) and PK information from other routes of administration, the systemic concentration of bromfenac is estimated to be below the limit of quantification (50 ng/mL) at steady-state in humans.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis and Impairment of Fertility
Long-term carcinogenicity studies in rats and mice given oral doses of bromfenac up to 0.6 mg/kg/day (900 times the recommended human ophthalmic dose [RHOD] of 1.67 mcg/kg in 60 kg person on a mg/kg/basis, assuming 100% absorbed) and 5 mg/kg/day (7500 times RHOD), respectively revealed no significant increases in tumor incidence.
Bromfenac did not show mutagenic potential in various mutagenicity studies, including the reverse mutation, chromosomal aberration, and micronucleus tests.
Bromfenac did not impair fertility when administered orally to male and female rats at doses up to 0.9 mg/kg/day and 0.3 mg/kg/day, respectively (1300 and 450 times RHOD, respectively).
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Ocular Inflammation and Pain
Clinical efficacy was evaluated in three randomized, double-masked, placebo-controlled trials in which subjects requiring cataract surgery were assigned to bromfenac ophthalmic solution or placebo. Patients were dosed with one drop per eye starting the day before surgery and continuing for 14 days. The primary endpoint was clearing of ocular inflammation by day 15. An additional efficacy endpoint was the number of patients who were pain free on day 1 after cataract surgery.
In 2 of the 3 studies, bromfenac ophthalmic solution had statistically significant higher incidence of completely clearing inflammation (46 to 47% vs. 25 to 29%) and also had a statistically significant higher incidence of subjects that were pain free at day 1 post cataract surgery (83 to 89% vs. 51 to 71%).
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Bromfenac Ophthalmic Solution, 0.09% is supplied in a sterile 5 mL white low density polyethylene bottle fitted with a white low density polyethylene nozzle and sealed with gray colored high density polyethylene cap as follows:
1.7 mL in 5 mL bottle (NDC: 68180-436-01)
Storage
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15 to 30°C (59 to 86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
17.1 Slowed or Delayed Healing
Patients should be advised of the possibility that slow or delayed healing may occur while using NSAIDs.
17.2 Sterility of Dropper Tip
Patients should be advised to not touch dropper tip to any surface, as this may contaminate the contents.
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
BROMFENAC
bromfenac solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 68180-436 Route of Administration OPHTHALMIC Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength BROMFENAC SODIUM (UNII: 8ECV571Y37) (BROMFENAC - UNII:864P0921DW) BROMFENAC 0.9 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength BENZALKONIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: F5UM2KM3W7) 0.05 mg in 1 mL BORIC ACID (UNII: R57ZHV85D4) EDETATE DISODIUM (UNII: 7FLD91C86K) 0.2 mg in 1 mL POLYSORBATE 80 (UNII: 6OZP39ZG8H) 1.5 mg in 1 mL POVIDONE (UNII: FZ989GH94E) 20 mg in 1 mL SODIUM BORATE (UNII: 91MBZ8H3QO) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) SODIUM SULFITE (UNII: VTK01UQK3G) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Product Characteristics Color YELLOW (Yellow Colored Clear Transparent) Score Shape Size Flavor Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 68180-436-01 1 in 1 CARTON 02/02/2024 1 1.7 mL in 1 BOTTLE; Type 2: Prefilled Drug Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA202903 02/02/2024 Labeler - Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (089153071)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.
 are registered trademarks of Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
are registered trademarks of Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
