EXDENSUR- depemokimab injection, solution
Exdensur by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Exdensur by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by GlaxoSmithKline LLC. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use EXDENSUR safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for EXDENSUR.
EXDENSUR (depemokimab-ulaa) injection, for subcutaneous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2025INDICATIONS AND USAGE
EXDENSUR is an interleukin‑5 (IL-5) antagonist, a monoclonal antibody (humanized immunoglobulin G [IgG]1 kappa) indicated for add-on maintenance treatment of severe asthma characterized by an eosinophilic phenotype in adult and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older. (1)
Limitations of Use: Not for relief of acute bronchospasm or status asthmaticus. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, can occur after administration of EXDENSUR. If a hypersensitivity reaction occurs, discontinue EXDENSUR and initiate appropriate therapy. (5.1)
- Do not abruptly discontinue systemic or inhaled corticosteroids upon initiation of therapy with EXDENSUR. Reduce corticosteroid dose gradually, if appropriate. (5.3)
- Treat pre-existing helminth infections before initiating therapy with EXDENSUR. If patients become infected while receiving treatment with EXDENSUR and do not respond to anti‑helminth treatment, discontinue EXDENSUR until the parasitic infection resolves. (5.4)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥4%) are upper respiratory tract infection, allergic rhinitis, influenza, arthralgia, and pharyngitis. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact GlaxoSmithKline at 1-888-825-5249 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy: EXDENSUR can cross the placenta during pregnancy and the presence of the YTE modification may prolong and increase exposure to the infant exposed in utero. The impact of EXDENSUR transmission to the fetus should be considered. (8.1)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 12/2025
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage
2.2 Preparation and Administration Instructions for EXDENSUR
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
5.2 Acute Asthma Symptoms or Deteriorating Disease
5.3 Risk Associated with Abrupt Reduction of Corticosteroid Dosage
5.4 Parasitic (Helminth) Infection
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
12.6 Immunogenicity
13 NON-CLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
EXDENSUR is indicated for the add‑on maintenance treatment of severe asthma characterized by an eosinophilic phenotype in adult and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older.
Limitations of Use
EXDENSUR is not indicated for the relief of acute bronchospasm or status asthmaticus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage is 100 mg once every 6 months administered by subcutaneous (SC) injection into the upper arm, thigh, or abdomen avoiding 2 inches (5 cm) around the navel [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Missed Dose(s)
If a dose is missed, administer the missed dose as soon as possible and resume the once every 6‑month injection schedule from the date of when the missed dose was given.
2.2 Preparation and Administration Instructions for EXDENSUR
- EXDENSUR is for subcutaneous (SC) use only.
-
EXDENSUR should be administered by a healthcare provider.
Do not use EXDENSUR prefilled pen or syringe if the security seal on the carton has been broken.
Do not use EXDENSUR prefilled pen or syringe if it has been dropped or damaged.
Preparation Instructions
- 1. Remove the prefilled pen or prefilled syringe from the refrigerator. Holding the middle of the prefilled pen or prefilled syringe, take it out from the tray and allow it to sit at room temperature for 30 minutes prior to injection. Do not warm EXDENSUR injection in any other way. Do not remove the needle cap until you are ready to inject. Do not use the pen or syringe if it has been left out of the carton for more than 8 hours.
- 2. Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit. EXDENSUR should be colorless to yellow to brown, clear to opalescent in color. Do not use EXDENSUR if the product exhibits discoloration, cloudiness, or particulate matter. It is normal to see an air bubble. Do not expel the air bubble prior to administration. Do not shake the device.
- 3.
Choose the Injection Site
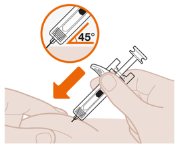
Administer the injection into upper arm, thigh, or abdomen, avoiding the 2 inches (5 cm) around the navel.
Do not give injections into areas where the skin is tender, bruised, red, or hard.
Administration Instructions for Single‑Dose Prefilled Pen
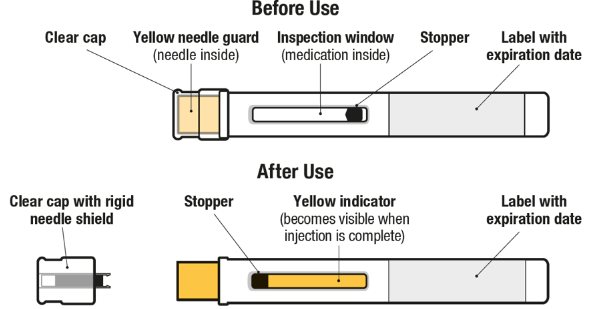
Figure 1. EXDENSUR Prefilled Pen Components
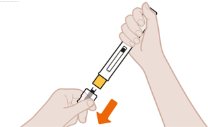
- 1. Pull Off the Clear Cap
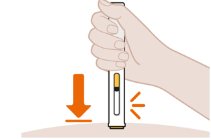
- 2. Position the Pen at the Injection Site and Press Firmly to Start the Injection
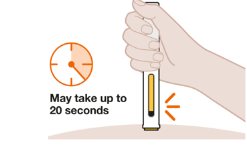
- 3. Continue to Hold Down
- 4. Lift Pen After Injection Completes
- 5. Throw Away
Dispose of used pen and clear cap according to local health and safety laws.
Administration Instructions for Single‑Dose Prefilled Syringe
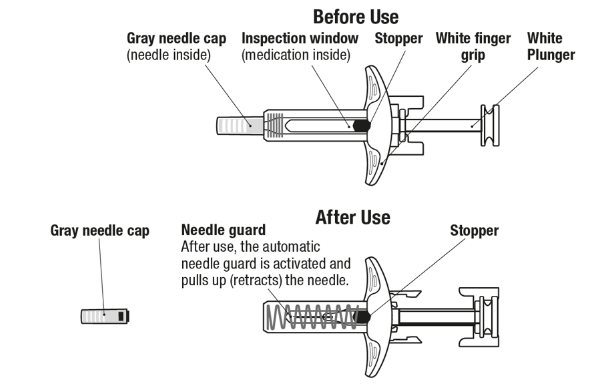
Figure 2. EXDENSUR Prefilled Syringe Components
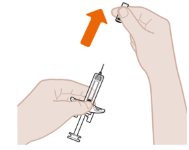
- 1. Pull Off the Gray Needle Cap
- 2. Position the Syringe at the Injection Site
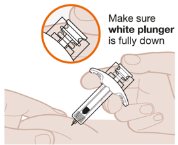
- 3. Start the Injection and Fully Press the White Plunger
- 4. Slowly Lift Thumb After Injection Completes
- 5. Throw Away
Dispose of used syringe according to local health and safety laws.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, can occur following administration of EXDENSUR. If a hypersensitivity reaction occurs, discontinue EXDENSUR and initiate appropriate therapy.
5.2 Acute Asthma Symptoms or Deteriorating Disease
EXDENSUR should not be used to treat acute asthma symptoms or acute exacerbations. Do not use EXDENSUR to treat acute bronchospasm or status asthmaticus. Patients should seek medical advice if their asthma remains uncontrolled or worsens after initiation of treatment with EXDENSUR.
5.3 Risk Associated with Abrupt Reduction of Corticosteroid Dosage
Reduction in corticosteroid dose may be associated with systemic withdrawal symptoms and/or unmask conditions previously suppressed by systemic corticosteroid therapy. Do not abruptly discontinue systemic or inhaled corticosteroids upon initiation of EXDENSUR therapy. Reductions in corticosteroid dose, if appropriate, should be gradual and performed under the supervision of a healthcare provider.
5.4 Parasitic (Helminth) Infection
Eosinophils may be involved in the immunological response to some helminth infections. Patients with pre‑existing helminth infections were excluded from participation in the clinical trials. It is unknown if EXDENSUR will influence a patient’s response against parasitic infections. Patients with pre‑existing helminth infections should be treated for their infection prior to initiation of EXDENSUR therapy. If patients become infected while receiving treatment with EXDENSUR and do not respond to anti‑helminth treatment, discontinue treatment with EXDENSUR until the infection resolves.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of EXDENSUR was based on a pooled safety population from 2 replicate, randomized, double‑blind, parallel‑group, placebo‑controlled, multicenter clinical trials (SWIFT‑1 and SWIFT‑2) of 52 weeks duration. The 2 trials included 762 adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older with asthma, who received either EXDENSUR 100 mg or placebo administered subcutaneously once every 6 months in addition to their existing background medications for asthma [see Clinical Studies (14)]. A total of 475 patients received 2 doses of EXDENSUR 100 mg in these trials.
Adverse reactions with EXDENSUR with incidence of ≥4% are shown in Table 1.
Table 1. Adverse Reactions with EXDENSUR with an Incidence ≥4% and More Common than Placebo in Patients with Asthma Adverse Reaction
EXDENSUR
(N = 501)
n (%)
Placebo
(N = 261)
n (%)
Upper respiratory tract infection
46 (9)
20 (8)
Allergic rhinitis
29 (6)
7 (3)
Influenza
24 (5)
11 (4)
Arthralgia
19 (4)
8 (3)
Pharyngitis
18 (4)
3 (1)
Specific Adverse Reactions
Injection Site Reactions: In the pooled safety population (SWIFT‑1 and SWIFT‑2), in which EXDENSUR was administered by a healthcare provider, injection site reactions (e.g., erythema, swelling, and itching) occurred in 7 (1%) and 2 (<1%) patients receiving EXDENSUR and placebo, respectively.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Available data from clinical trials with EXDENSUR use in pregnant women are insufficient to identify a drug‑associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. There are risks to the mother and fetus associated with asthma in pregnancy (see Clinical Considerations).
Transport of endogenous IgG antibodies and monoclonal antibodies, such as depemokimab-ulaa, across the placenta increases as pregnancy progresses and peaks during the third trimester. The impact of the YTE modification on placental transfer is uncertain [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)]; however, the presence of the YTE modification may lead to prolonged and increased exposure of the infant exposed in utero, and the potential of clinical impact is unknown and should be considered. No treatment-related effects on embryofetal or postnatal development have been shown in animal studies targeting IL‑5 signaling pathways (see Data).
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population(s) is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Pregnant women exposed to EXDENSUR, or their healthcare providers, should report EXDENSUR exposure by calling 1‑888‑825‑5249.
Clinical Considerations
Disease‑Associated Maternal and/or Embryofetal Risk: In women with poorly or moderately controlled asthma, evidence demonstrates that there is an increased risk of preeclampsia in the mother, and prematurity, low birth weight, and small for gestational age in the neonate. The level of asthma control should be closely monitored in pregnant women and treatment adjusted as necessary to maintain optimal control.
Data
Animal Data: Reproductive toxicology studies have not been conducted with depemokimab‑ulaa. In animal studies targeting the IL‑5 signaling pathway with a related biologic product without the YTE modification, there were no developmental effects observed [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13)]. Embryofetal development of IL‑5 deficient mice has been reported to be generally unaffected relative to wild‑type mice.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of depemokimab‑ulaa in either human or animal milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. However, depemokimab‑ulaa is a humanized monoclonal antibody (immunoglobulin G1 [IgG1] kappa), and maternal IgG is present in human milk in small amounts. The effects of local gastrointestinal exposure and the extent of systemic exposure in the breastfed infant to EXDENSUR are unknown.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for EXDENSUR, and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from EXDENSUR or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Asthma
The safety and effectiveness of EXDENSUR for add‑on maintenance treatment of severe asthma characterized by an eosinophilic phenotype have been established in pediatric patients aged 12 years and older.
Use of EXDENSUR for this indication is supported by evidence from adequate and well‑controlled trials (SWIFT‑1 and SWIFT‑2) in adults and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older, and pharmacokinetic data in pediatric patients aged 12 years and older. A total of 30 pediatric patients aged 12 to 17 years with asthma were enrolled in the SWIFT‑1 and SWIFT‑2 trials, of whom 15 received EXDENSUR 100 mg. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic data have demonstrated no clinically significant differences in systemic exposure of depemokimab‑ulaa and reduction in blood eosinophil counts in pediatric patients aged 12 years and older compared to that observed in adults following administration of the recommended dosage of EXDENSUR. The safety of EXDENSUR in pediatric patients aged 12 years and older was generally similar to that of the adult population in SWIFT‑1 and SWIFT‑2 [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), Clinical Studies (14)].
The safety and effectiveness of EXDENSUR have not been established in pediatric patients younger than 12 years of age.
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Depemokimab‑ulaa is an interleukin‑5 (IL‑5) antagonist monoclonal antibody (humanized Immunoglobulin G1 [IgG1] kappa). Depemokimab‑ulaa is produced by recombinant DNA technology in Chinese hamster ovary cells. The estimated molecular weight of depemokimab‑ulaa is 149 kDa.
EXDENSUR (depemokimab‑ulaa) injection is a sterile, preservative‑free, colorless, yellow to brown, clear to opalescent solution for subcutaneous (SC) use.
EXDENSUR injection is supplied in a single‑dose, 1‑mL, prefilled pen with a fixed 29‑gauge, half‑inch needle or in a single‑dose, 1‑mL, prefilled syringe with a fixed 29‑gauge, half‑inch needle with a needle guard. Each 1 mL delivers 100 mg depemokimab‑ulaa, (8.43 mg) arginine HCl, (0.017 mg) edetate disodium, (1.41 mg) histidine, (2.29 mg) L‑histidine HCl monohydrate, (0.20 mg) polysorbate 80, (61.6 mg) trehalose, and Water for Injection with a pH of 6.0.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Depemokimab‑ulaa is an IL‑5 antagonist (humanized IgG1 kappa monoclonal antibody), which binds to IL‑5 with a dissociation constant of 10.5 pM, inhibiting the bioactivity of IL‑5 with in vitro IC50 value of 4 pM by blocking its binding to the alpha chain of the IL‑5 receptor complex expressed on the cell surface. Depemokimab‑ulaa contains a triple amino acid substitution (YTE) in the fragment crystallizable (Fc) region which increases binding to the neonatal Fc receptor and thereby extends the elimination half‑life. These properties support the dosing interval of every 6 months.
IL‑5 is the major cytokine responsible for the growth and differentiation, recruitment, activation, and survival of eosinophils. Inflammation is an important component in the pathogenesis of asthma. Multiple cell types (e.g., mast cells, eosinophils, neutrophils, macrophages, lymphocytes) and mediators (e.g., histamine, eicosanoids, leukotrienes, cytokines) are involved in inflammation. Depemokimab‑ulaa, by inhibiting IL‑5 signaling, reduced the production and survival of eosinophils; however, the mechanism of depemokimab‑ulaa action in asthma has not been definitively established.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
In placebo‑controlled studies involving adult and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with asthma, a 100 mg dose of EXDENSUR administered SC every 6 months for 52 weeks reduced blood eosinophils to a geometric mean count of 57 cells/mcL (95% CI: 51, 63) at Week 52. This corresponded to a geometric mean reduction of 79% (95% CI: 75.8, 81.8) compared to placebo. This magnitude of blood eosinophil reduction was observed within 2 weeks of treatment (at the first assessment) and was maintained throughout the treatment period.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of depemokimab‑ulaa were approximately dose‑proportional in patients with asthma following SC administration over a dose range of 0.1‑times the recommended dose to 3‑times the recommended dose. After SC administration of 100 mg of EXDENSUR every 6 months in patients with severe asthma, the mean (SD) model-based estimated trough concentration of depemokimab‑ulaa at Week 26 was approximately 1.30 (0.44) mcg/mL. The mean (SD) model-based estimated average steady‑state plasma concentration over a single dosing interval was 6.16 (1.62) mcg/mL.
Absorption
Depemokimab‑ulaa median Tmax was approximately 14 days. There was no accumulation following repeat SC administration once every 6 months.
Distribution
The estimated typical apparent volume of distribution is 6.3 L.
Elimination
The estimated mean (SD) elimination half‑life was 48 (4.7) days following SC administration of EXDENSUR. The estimated typical apparent clearance was 0.092 L/day.
Metabolism: Depemokimab‑ulaa is a monoclonal antibody which is expected to be metabolized into small peptides and amino acids by catabolic pathways.
Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of depemokimab‑ulaa were observed based on age (12 to 93 years), sex, race (73% White, 7% Black, 19% Asian), body weight (34.6 to 161 kg), renal impairment (eGFR ≥90 mL/min/1.73 m2 [normal, N = 548]; eGFR 60 to <90 mL/min/1.73 m2 [mild, N = 380]; eGFR 30 to <60 mL/min/1.73 m2 [moderate, N = 31], and eGFR ≤30 mL/min/1.73 m2 [severe, N = 2]), or baseline hepatic function biomarkers (alanine aminotransferase [ALT; 5 to 153 IU/L], aspartate aminotransferase [AST; 9 to 115 IU/L], and bilirubin [1.7 to 42 micromol/L]).
Pediatric Patients: There are limited pharmacokinetic data available in the pediatric population. The pharmacokinetics of depemokimab‑ulaa in pediatric patients aged 12 to 17 years were consistent with adults. The pharmacokinetics of depemokimab‑ulaa have not been studied in pediatric patients aged less than 12 years.
Drug Interaction Studies
No drug interaction studies have been conducted.
12.6 Immunogenicity
The observed incidence of anti‑drug antibodies is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Differences in assay methods preclude meaningful comparisons of the incidence of anti‑drug antibodies (ADA) in the studies described below with the incidence of ADA in other studies, including those of EXDENSUR or of other depemokimab products.
In adults and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with asthma, the incidence of ADA to depemokimab in patients treated with EXDENSUR 100 mg once every 6 months in SWIFT‑1, SWIFT‑2, and an open‑label extension was 10% (66/691). Among ADA‑positive patients, 6% (4/66) developed neutralizing antibodies.
There was no identified clinically significant effect of ADA on the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety, or efficacy of EXDENSUR.
-
13 NON-CLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No genotoxicity or carcinogenicity studies have been conducted.
Male and female fertility were unaffected based upon no adverse histopathological findings in the reproductive organs from cynomolgus monkeys receiving SC dosages up to 100 mg/kg depemokimab‑ulaa for 6 months. Mating and reproductive performance were unaffected in male and female CD‑1 mice receiving an analogous antibody, which inhibits the activity of murine IL‑5.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of EXDENSUR for the add‑on maintenance treatment of severe asthma characterized by an eosinophilic phenotype was evaluated in 2 replicate, randomized (2:1 to EXDENSUR or placebo), double‑blind, parallel‑group, placebo‑controlled, multicenter clinical trials (SWIFT‑1 [NCT04719832] and SWIFT‑2 [NCT04718103]) of 52 weeks duration. The trials enrolled adult and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with asthma characterized by an eosinophilic phenotype, defined as a blood eosinophil count ≥150 cells/mcL at screening or ≥300 cells/mcL documented in the year prior to study entry. Patients were required to have 2 or more asthma exacerbations requiring treatment with systemic corticosteroids (SCS) in the prior year while on background asthma therapy consisting of a medium‑ to high‑dose ICS plus at least one additional asthma controller with or without maintenance oral corticosteroids (OCS). Patients were also required to have reduced lung function at baseline (pre‑bronchodilator forced expiratory volume in 1 second [FEV1] <80% predicted normal in adults; FEV1 <90% or FEV1 to forced vital capacity ratio <0.8 in pediatric patients aged 12 years and older). Patients were enrolled without requiring a minimum baseline Asthma Control Questionnaire‑5 (ACQ‑5) score. In these trials, EXDENSUR 100 mg was administered SC once every 6 months for a total of 2 doses in addition to background asthma therapy. The efficacy population consisted of 762 patients who received at least 1 dose of EXDENSUR 100 mg or placebo in SWIFT‑1 (N = 382) and SWIFT‑2 (N = 380).
The demographics and baseline characteristics of the efficacy population in SWIFT‑1 and SWIFT‑2 are provided in Table 2.
Table 2. Demographics and Baseline Characteristics of Adult and Pediatric Patients Aged 12 Years and Older with Severe Asthma in SWIFT-1 and SWIFT-2 FEV1 = forced expiratory volume in 1 second; ICS = inhaled corticosteroid; IgE = immunoglobulin E; LABA = long‑acting beta agonist; LAMA = long‑acting muscarinic antagonist; mcL = microliter; N = number of patients in the efficacy population; n = number of patients in the respective group; OCS = oral corticosteroid; SD = standard deviation; U = units. a Medium ICS dose = 440 mcg fluticasone propionate (FP) daily or equivalent; High ICS dose >440 mcg FP daily or equivalent. SWIFT‑1
N = 382
SWIFT‑2
N = 380
Age (years), n (%)
12‑17
8 (2)
22 (6)
18‑64
276 (72)
262 (69)
≥65
98 (26)
96 (25)
Mean (SD)
54 (14.2)
53 (16.2)
Female, n (%)
223 (58)
241 (63)
Race, n (%)
White
316 (83)
272 (72)
Asian
58 (15)
75 (20)
Black or African American
8 (2)
28 (7)
Other
0
5 (1)
Hispanic or Latino, n (%)
23 (6)
65 (17)
Never smoked, n (%)
288 (75)
294 (77)
Duration of asthma (years), mean (SD)
22 (16.2)
25 (18.5)
Pre‑bronchodilator % predicted FEV1, mean (SD)
62 (15.2)
62 (15.9)
% reversibility, mean (SD)
17 (15.3)
18 (17.4)
Eosinophil count (cells/mcL), median (min; max)
310
(20; 2,360)
340
(10; 4,440)
Exacerbations in previous year, mean (SD)
2.2 (0.7)
2.7 (1.9)
High‑dose ICS use, n (%)a
203 (53)
226 (59)
ICS + LABA + LAMA use, n (%)
95 (25)
127 (33)
Maintenance OCS use, n (%)
21 (5)
19 (5)
Total IgE (U/mcL),
median (min; max)
185
(2; 12,142)
180
(2; 16,199)
Exacerbations
The primary efficacy endpoint for SWIFT‑1 and SWIFT‑2 was the annualized rate of clinically significant exacerbations over the 52‑week treatment period. A clinically significant exacerbation was defined as worsening of asthma requiring use of SCS such as intravenous (IV) or oral steroids for at least 3 days or a single intramuscular (IM) corticosteroid dose and/or hospitalization and/or Emergency Department visit. For patients on maintenance SCS, at least double the existing maintenance dose for at least 3 days was required. All patients experiencing an exacerbation were treated with SCS.
In SWIFT‑1 and SWIFT‑2, the annualized rate of asthma exacerbations was significantly lower in patients receiving EXDENSUR compared to placebo (Table 3). During the 52‑week treatment period, fewer patients experienced exacerbations in the EXDENSUR group (32% and 32%) compared to the placebo group (46% and 50%) in SWIFT‑1 and SWIFT‑2, respectively.
Table 3. Annualized Rate of Clinically Significant Asthma Exacerbations Over 52 Weeks in SWIFT-1 and SWIFT-2 N = number of patients in the efficacy population. Note: Results obtained from a negative binomial model with an offset term for years in study and fixed effects for treatment group, asthma exacerbation history, baseline ICS dose, geographical region, and baseline pre‑bronchodilator % predicted FEV1. SWIFT‑1
SWIFT‑2
EXDENSUR
N = 250
Placebo
N = 132
EXDENSUR
N = 252
Placebo
N = 128
Annualized rate of clinically significant asthma exacerbations
0.46
1.11
0.56
1.08
Rate ratio (95% CI)
0.42 (0.30, 0.59)
0.52 (0.36, 0.73)
P‑value
<0.001
<0.001
The percentage of patients with exacerbations requiring hospitalization and/or Emergency Department visit was numerically lower for patients treated with EXDENSUR (1% and 4%) compared with placebo (8% and 10%) in SWIFT‑1 and SWIFT‑2, respectively.
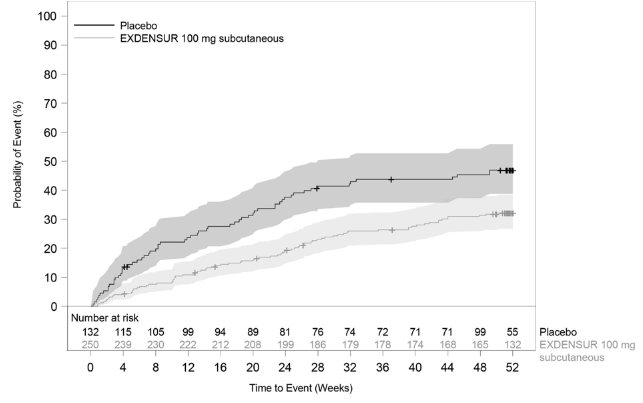
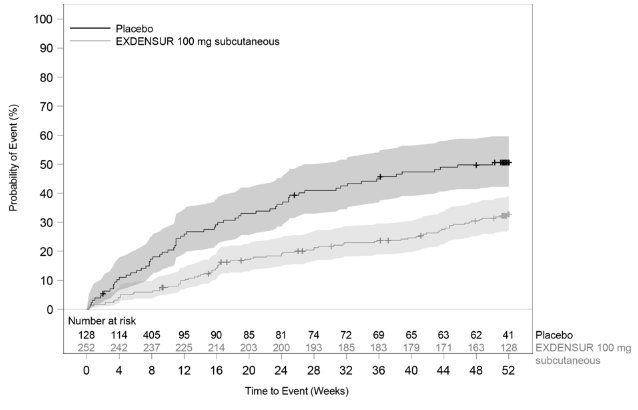
In SWIFT‑1 and SWIFT‑2, the time to first clinically significant exacerbation was longer for EXDENSUR compared to placebo (Figures 3 and 4).
Figure 3. Kaplan Meier Curve for Time to First Clinically Significant Exacerbation (SWIFT‑1)
Shaded areas represent 95% confidence intervals.
Figure 4 Kaplan Meier Curve for Time to First Clinically Significant Exacerbation (SWIFT‑2)
Shaded areas represent 95% confidence intervals.
Lung Function
In SWIFT‑1 and SWIFT‑2, the mean change from baseline in pre‑bronchodilator FEV1 for EXDENSUR was 160 mL and 240 mL, respectively, compared to 160 mL and 184 mL for placebo. The treatment difference in SWIFT‑1 and SWIFT‑2 relative to placebo was -1 mL (95% CI: -89, 88) and 56 mL (95% CI: -43, 154), respectively.
Patient-Reported Outcome
In SWIFT‑1 and SWIFT‑2, the proportion of ACQ‑5 responders (clinically meaningful improvement defined as a decrease in score of 0.5 or more) at Week 52 was 54% for EXDENSUR in both studies compared to 55% and 53%, respectively, for placebo.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
EXDENSUR (depemokimab‑ulaa) injection is a sterile, preservative‑free, colorless, yellow to brown, clear to opalescent solution for subcutaneous (SC) use. The pens and syringes are not made with natural rubber latex. EXDENSUR injection is supplied as described in Table 4.
Table 4. EXDENSUR Injection Package Configuration Package Configuration Strength NDC 1 single‑dose, prefilled pen with attached 29‑gauge, half‑inch needle in a carton
100 mg/mL
0173‑0927‑31
1 single‑dose, prefilled syringe with attached 29‑gauge, half‑inch needle with needle guard in a carton
100 mg/mL
0173‑0927‑42
Storage and Handling
Store refrigerated at 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C) in the original carton to protect from light.
Do not freeze. Do not shake. Avoid exposure to heat.
The prefilled pen and prefilled syringe can be removed from the refrigerator and kept in the unopened carton, protected from light for up to 7 days at room temperature up to 86°F (30°C). Discard if left out of the refrigerator for more than 7 days.
The prefilled pen or prefilled syringe must be administered within 8 hours once removed from the carton. Discard if not administered within 8 hours.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA‑approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Inform patients of hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, that can occur following administration of EXDENSUR. Instruct patients to contact their healthcare provider if they experience symptoms of a hypersensitivity reaction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Acute Asthma Symptoms or Deteriorating Disease
Inform patients that EXDENSUR does not treat acute asthma symptoms or acute exacerbations. Advise patients to seek medical advice if their asthma remains uncontrolled or worsens after initiation of treatment with EXDENSUR [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Risk Associated with Abrupt Reduction of Corticosteroid Dosage
Advise patients to not abruptly discontinue systemic or inhaled corticosteroids after initiation of EXDENSUR therapy. Inform patients that reduction in corticosteroid dose may be associated with systemic withdrawal symptoms and/or unmask conditions previously suppressed by systemic corticosteroid therapy. Inform patients that reductions in corticosteroid dose, if appropriate, should be gradual and performed under the supervision of a healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
EXDENSUR Exposure to Fetus or Infants During Pregnancy
Advise patients that the potential clinical impact of prolonged and increased EXDENSUR exposure in infants that were exposed in utero is unknown. Inform providers of infants exposed to EXDENSUR in utero of the potential for the infant to be exposed to elevated levels of EXDENSUR for a prolonged period [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Advise patients who are exposed to EXDENSUR during pregnancy to contact GlaxoSmithKline at 1‑888‑825‑5249.
Trademarks are owned by or licensed to the GSK group of companies.
Manufactured by
GlaxoSmithKline LLC
2929 Walnut Street, Suite 1700
Philadelphia, PA 19104
U.S. License No. 1727Distributed by
GlaxoSmithKline
Durham, NC 27701©2025 GSK group of companies or its licensor.
EXD:1PI
-
PATIENT INFORMATION
EXDENSUR [Ex‑DEN‑shur]
(depemokimab‑ulaa)
injection, for subcutaneous use
What is EXDENSUR?
-
EXDENSUR is a prescription medicine:
- o for the add‑on maintenance treatment of severe asthma in people 12 years and older whose asthma is not controlled with their current medicines.
- ▪ EXDENSUR helps prevent severe asthma attacks (exacerbations).
- ▪ EXDENSUR is not used to treat sudden breathing problems that occur with asthma. Tell your healthcare provider if your asthma does not get better or if it gets worse after you start treatment with EXDENSUR.
- EXDENSUR works by targeting inflammation that plays a major role in severe asthma. EXDENSUR reduces blood eosinophils. Eosinophils are a type of white blood cells that may contribute to your disease.
It is not known if EXDENSUR is safe and effective in children with asthma under 12 years of age.
Before using EXDENSUR, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- are taking systemic or inhaled corticosteroid medicines. Do not change or stop taking your corticosteroid medicines unless instructed by your healthcare provider. This may cause other symptoms that were controlled by the corticosteroid medicine to come back.
- have a parasitic (helminth) infection.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. Babies exposed to EXDENSUR before birth may have higher and longer‑lasting levels of the medicine in their bodies. It is not known if EXDENSUR may harm your unborn baby. If you become pregnant while taking EXDENSUR contact GlaxoSmithKline at 1‑888‑825‑5249.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. You and your healthcare provider should decide if you will use EXDENSUR and breastfeed. You should not do both without talking with your healthcare provider first.
- Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over‑the‑counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
- Do not change or stop taking your other medicines unless instructed to do so by your healthcare provider.
How EXDENSUR is given:
A healthcare provider will inject EXDENSUR under your skin (subcutaneously) every 6 months. If you miss a dose of EXDENSUR, contact your healthcare provider to get your next dose as soon as you can.
What are the possible side effects of EXDENSUR?
EXDENSUR can cause serious side effects including:
- allergic (hypersensitivity) reactions, including anaphylaxis. Serious allergic reactions can happen after you get your EXDENSUR injection. Contact your healthcare provider or get emergency help right away if you have any of the following symptoms of an allergic reaction:
- o swelling of your face, mouth, and tongue
- o fainting, dizziness, feeling lightheaded (low blood pressure)
- o hives
- o breathing problems
- o rash
The most common side effects of EXDENSUR include:
- upper respiratory tract infection (common cold, sinus infection)
- sneezing, nasal congestion, runny nose, and nasal itching (allergic rhinitis)
- flu or flu‑like symptoms
- joint pain
- sore throat (pharyngitis)
These are not all of the possible side effects of EXDENSUR.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1‑800‑FDA‑1088.
General information about the safe and effective use of EXDENSUR.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet.
You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about EXDENSUR that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in EXDENSUR?
Active ingredients: depemokimab‑ulaa
Inactive ingredients: arginine HCl, edetate disodium, histidine, L‑histidine HCl monohydrate, polysorbate 80, trehalose, Water for Injection.
For more information about EXDENSUR, call 1‑833‑EXDENSUR or visit our website at EXDENSUR.com.
Trademarks are owned by or licensed to the GSK group of companies.
Manufactured by:
GlaxoSmithKline LLC, Philadelphia, PA 19104, U.S. License No. 1727
Distributed by:
GlaxoSmithKline, Durham, NC 27701
©2025 GSK group of companies or its licensor.
EXD:1PIL
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Issued: December 2025
-
EXDENSUR is a prescription medicine:
-
PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC: 0173-0927-42
EXDENSUR
(depemokimab-ulaa)
Injection
Rx Only
GSK
100 mg/mL
For subcutaneous use
Prefilled Syringe
Contents:
- 1 Single-Dose 1-mL Prefilled Syringe
- Prescribing Information
- Patient Information
©2025 GSK group of companies or its licensor.
Rev. 12/25
62000000099386
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
EXDENSUR
depemokimab injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0173-0927 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength DEPEMOKIMAB (UNII: D16EQP0KKH) (DEPEMOKIMAB - UNII:D16EQP0KKH) DEPEMOKIMAB 100 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength ARGININE HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: F7LTH1E20Y) EDETATE DISODIUM (UNII: 7FLD91C86K) HISTIDINE (UNII: 4QD397987E) HISTIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: 1D5Q932XM6) POLYSORBATE 80 (UNII: 6OZP39ZG8H) TREHALOSE DIHYDRATE (UNII: 7YIN7J07X4) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0173-0927-31 1 in 1 CARTON 12/16/2025 12/16/2025 1 1 mL in 1 SYRINGE; Type 2: Prefilled Drug Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) 2 NDC: 0173-0927-42 1 in 1 CARTON 12/16/2025 2 1 mL in 1 SYRINGE; Type 2: Prefilled Drug Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA761458 12/16/2025 Labeler - GlaxoSmithKline LLC (167380711)
Trademark Results [Exdensur]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 EXDENSUR 97160260 not registered Live/Pending |
Glaxo Group Limited 2021-12-07 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.