These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Hydrocodone Bitratrate, Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride, and Chlorpheniramine Maleate safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Hydrocodone Bitratrate, Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride, and Chlorpheniramine Maleate. Hydrocodone Bitratrate, Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride, and Chlorpheniramine Maleate oral solution, CIIInitial U.S. Approval: 2011
Hydrocodone Bitartrate, Chlorpheniramine Maleate, and Pseudoephedrine HCl by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Hydrocodone Bitartrate, Chlorpheniramine Maleate, and Pseudoephedrine HCl by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Cypress Pharmaceutical, Inc., Woodfield Pharmaceutical, LLC. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
HYDROCODONE BITARTRATE, CHLORPHENIRAMINE MALEATE, AND PSEUDOEPHEDRINE HCL- hydrocodone bitartrate, chlorpheniramine maleate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride solution
Cypress Pharmaceutical, Inc.
----------
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use Hydrocodone Bitratrate, Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride, and Chlorpheniramine Maleate safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Hydrocodone Bitratrate, Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride, and Chlorpheniramine Maleate.
Hydrocodone Bitratrate, Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride, and Chlorpheniramine Maleate oral solution, CII Initial U.S. Approval: 2011 WARNING: ADDICTION, ABUSE, AND MISUSE; LIFE-THREATENING RESPIRATORY DEPRESSION; ACCIDENTAL INGESTION; MEDICATION ERRORS; CYTOCHROME P450 3A4 INTERACTION; CONCOMITANT USE WITH BENZODIAZEPINES OR OTHER CNS DEPRESSANTS; INTERACTION WITH ALCOHOL; NEONATAL OPIOID WITHDRAWAL SYNDROMESee full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
RECENT MAJOR CHANGESINDICATIONS AND USAGEHydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate is a combination of hydrocodone, an opioid agonist; chlorpheniramine, a histamine-1 (H1) receptor antagonist; and pseudoephedrine, an alpha adrenergic agonist, indicated for temporary relief of cough and upper respiratory symptoms, including nasal congestion, associated with allergies or the common cold in patients 18 years of age and older. (1) Important Limitations of Use (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHSOral solution: Each 5 mL contains hydrocodone bitartrate 5 mg; chlorpheniramine maleate 4 mg; and pseudoephedrine hydrochloride 60 mg. (3) CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONSSee Boxed WARNINGS
ADVERSE REACTIONSCommon adverse reactions include: Sedation (somnolence, mental clouding, lethargy), impaired mental and physical performance, lightheadedness, dizziness, headache, dry mouth, nausea, vomiting, constipation, tachycardia, arrhythmias including premature ventricular contractions, CNS stimulation including anxiety, restlessness, nervousness, tremor, and irritability. (6) To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Hawthorn Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-800-793-2145 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. DRUG INTERACTIONS
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONSSee 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide. Revised: 6/2018 |
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
WARNING: ADDICTION, ABUSE, AND MISUSE; LIFE-THREATENING RESPIRATORY DEPRESSION; ACCIDENTAL INGESTION; MEDICATION ERRORS; CYTOCHROME P450 3A4 INTERACTION; CONCOMITANT USE WITH BENZODIAZEPINES OR OTHER CNS DEPRESSANTS; INTERACTION WITH ALCOHOL; NEONATAL OPIOID WITHDRAWAL SYNDROME
Addiction, Abuse, and Misuse
Hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate exposes patients and other users to the risks of opioid addiction, abuse, and misuse, which can lead to overdose and death. Reserve hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate for use in adult patients for whom the benefits of cough suppression are expected to outweigh the risks, and in whom an adequate assessment of the etiology of the cough has been made. Assess each patient's risk prior to prescribing hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate, prescribe hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate for the shortest duration that is consistent with individual patient treatment goals, monitor all patients regularly for the development of addition or abuse, and refill only after reevaluation of the need for continued treatment. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
Life-Threatening Respiratory Depression
Serious, life-threatening, or fatal respiratory depression may occur with use of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate. Monitor for respiratory depression, especially during initiation of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate therapy or when used in patients at higher risk [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Accidental Ingestion
Accidental ingestion of even one dose of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate, especially by children, can result in a fatal overdose of hydrocodone [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Risk of Medication Errors
Ensure accuracy when prescribing, dispensing, and administering hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate. Dosing errors can result in accidental overdose and death. Always use an accurate milliliter measuring device when measuring and administering hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate [see Dosage and Administration (2.1), Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Cytochrome P450 3A4 Interaction
The concomitant use of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate with all cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibitors may result in an increase in hydrocodone plasma concentrations, which could increase or prolong adverse drug effects and may cause potentially fatal respiratory depression. In addition, discontinuation of a concomitantly used cytochrome P450 3A4 inducer may result in an increase in hydrocodone plasma concentration. Avoid the use of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate in patients taking a CYP3A4 inhibitor or inducer [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7), Drug Interactions (7.2, 7.3)].
Risks from Concomitant Use with Benzodiazepines or Other CNS Depressants
Concomitant use of opioids with benzodiazepines or other central nervous system (CNS) depressants, including alcohol, may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death. Avoid the use of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate in patients taking benzodiazepines, other CNS depressants, or alcohol. [see Warning and Precautions (5.8), Drug Interactions (7.5)]
Interaction with Alcohol
Instruct patients not to consume alcoholic beverages or use prescription or non-prescription products that contain alcohol while taking hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate. The co-ingestion of alcohol with hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate may result in increased plasma levels and a potentially fatal overdose of hydrocodone [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) and Drug Interactions (7.1].
Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome
Hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate is not recommended for use in pregnant women [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]. Prolonged use of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate during pregnancy can result in neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome, which may be life-threatening if not recognized and treated, and requires management according to protocols developed by neonatology experts. If hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate is used for a prolonged period in a pregnant woman, advise the patient of the risk of neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome and ensure that appropriate treatment will be available [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14)]
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate is indicated for the temporary relief of cough and upper respiratory symptoms, including nasal congestion, associated with allergy or the common cold in patients 18 years of age and older.
Important Limitations of Use
- Not indicated for pediatric patients under 18 years of age [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
- Contraindicated in pediatric patients less than 6 years of age [see Contraindications (4)].
- Because of the risks of addiction, abuse, and misuse with opioids, even at recommended doses [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)], reserve hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate for use in adult patients for whom the benefits of cough suppression are expected to outweigh the risks, and in whom an adequate assessment of the etiology of the cough has been made.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Dosage and Administration Instructions
Administer hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate by the oral route only.
Always use an accurate milliliter measuring device when administering hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate to ensure that the dose is measured and administered accurately. A household teaspoon is not an accurate measuring device and could lead to overdosage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]. For prescriptions where a measuring device is not provided, a pharmacist can provide an appropriate measuring device and can provide instructions for measuring the correct dose. Do not overfill. Rinse the measuring device with water after each use.
Advise patients not to increase the dose or dosing frequency of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate because serious adverse events such as respiratory depression may occur with overdosage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Overdosage (10)]. The dosage of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate should not be increased if cough fails to respond; an unresponsive cough should be reevaluated for possible underlying pathology [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
2.3 Monitoring, Maintenance, and Discontinuation of Therapy
Prescribe hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate for the shortest duration that is consistent with individual patient treatment goals [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Monitor patients closely for respiratory depression, especially within the first 24-72 hours of initiating therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Reevaluate patients with unresponsive cough in 5 days or sooner for possible underlying pathology, such as foreign body or lower respiratory tract disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]. If a patient requires a refill, reevaluate the cause of the cough and assess the need for continued treatment with hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate, the relative incidence of adverse reactions, and the development of addiction, abuse, or misuse [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Do not abruptly discontinue hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate in a physically-dependent patient [see Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.3)]. When a patient who has been taking hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate regularly and may be physically dependent no longer requires therapy with hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate, taper the dose gradually, by 25% to 50% every 2 to 4 days, while monitoring carefully for signs and symptoms of withdrawal. If the patient develops these signs or symptoms, raise the dose to the previous level and taper more slowly, either by increasing the interval between decreases, decreasing the amount of change in dose, or both.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Oral solution: Each 5 mL contains: hydrocodone bitartrate, USP, 5 mg; chlorpheniramine maleate, USP, 4 mg; and pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, USP, 60 mg. Hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate is a clear, colorless to light yellow, grape-flavored liquid. [see Description (11)]
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate is contraindicated for:
- All children younger than 6 years of age [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
Hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate is also contraindicated in patients with:
- Significant respiratory depression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Acute or severe bronchial asthma in an unmonitored setting or in the absence of resuscitative equipment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
- Known or suspected gastrointestinal obstruction, including paralytic ileus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
- Narrow angle glaucoma, urinary retention, severe hypertension, or severe coronary artery disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)].
- Hypersensitivity to hydrocodone, chlorpheniramine, pseudoephedrine, or any of the inactive ingredients in hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Addiction, Abuse, and Misuse
Hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate contains hydrocodone, a Schedule II controlled substance. As an opioid, hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate exposes users to the risks of addiction, abuse, and misuse [see Drug Abuse and Dependence (9)], which can lead to overdose and death [see Overdosage (10)]. Reserve hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate for use in adult patients for whom the benefits of cough suppression are expected to outweigh the risks, and in whom an adequate assessment of the etiology of the cough has been made. Assess each patient's risk prior to prescribing hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate, prescribe hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate for the shortest duration that is consistent with individual patient treatment goals, monitor all patients regularly for the development of addiction or abuse, and refill only after reevaluation of the need for continued treatment.
Although the risk of addiction in any individual is unknown, it can occur in patients appropriately prescribed hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate. Addiction can occur at recommended dosages and if the drug is misused or abused. Risks are increased in patients with a personal or family history of substance abuse (including drug or alcohol abuse or addiction) or mental illness (e.g., major depression).
Opioids are sought by drug abusers and people with addiction disorders and are subject to criminal diversion. Consider these risks when prescribing or dispensing hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate. Strategies to reduce these risks include prescribing the drug in the smallest appropriate quantity and advising the patient on the proper disposal of unused drug [see Patient Counseling Information (17)]. Contact local state professional licensing board or state controlled substances authority for information on how to prevent and detect abuse or diversion of this product.
5.2 Life-Threatening Respiratory Depression
Serious, life-threatening, or fatal respiratory depression has been reported with the use of opioids, including hydrocodone, one of the active ingredients in hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate. Hydrocodone produces dose-related respiratory depression by directly acting on the brain stem respiratory center that controls respiratory rhythm and may produce irregular and periodic breathing. Respiratory depression, if not immediately recognized and treated, may lead to respiratory arrest and death. Management of respiratory depression includes discontinuation of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate, close observation, supportive measures, and use of opioid antagonists (e.g. naloxone), depending on the patient's clinical status [see Overdosage (10)]. Carbon dioxide (CO2) retention from opioid-induced respiratory depression can exacerbate the sedating effects of opioids.
While serious, life-threatening, or fatal respiratory depression can occur at any time during the use of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate, the risk is greatest during the initiation of therapy, when hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate is used concomitantly with other drugs that may cause respiratory depression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)], in patients with chronic pulmonary disease or decreased respiratory reserve, and in patients with altered pharmacokinetics or altered clearance (e.g. elderly, cachectic, or debilitated patients) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
To reduce the risk of respiratory depression, proper dosing of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate is essential [see Dosage and Administration (2.1), Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]. Monitor patients closely, especially within the first 24-72 hours of initiating therapy or when used in patients at higher risk.
Overdose of hydrocodone in adults has been associated with fatal respiratory depression, and the use of hydrocodone in children younger than 6 years of age has been associated with fatal respiratory depression when used as recommended. Accidental ingestion of even one dose of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate, especially by children, can result in respiratory depression and death.
5.3 Risks with Use in Pediatric Populations
Children are particularly sensitive to the respiratory depressant effects of hydrocodone [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Because of the risk of life-threatening respiratory depression and death, hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate is contraindicated in children less than 6 years of age [see Contraindications (4)].
Use of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate in children also exposes them to the risks of addiction, abuse, and misuse [see Drug Abuse and Dependence (9)], which can lead to overdose and death [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Overdosage (10)]. Because the benefits of symptomatic treatment of cough associated with allergies or the common cold do not outweigh the risks of use of hydrocodone in pediatric patients, hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate is not indicated for use in patients younger than 18 years of age [see Indications (1), Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
5.4 Risks with Use in Other At-Risk Populations
Unresponsive Cough
The dosage of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate should not be increased if cough fails to respond; an unresponsive cough should be reevaluated in 5 days or sooner for possible underlying pathology, such as foreign body or lower respiratory tract disease [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Asthma and Other Pulmonary Disease
The use of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate in patients with acute or severe bronchial asthma in an unmonitored setting or in the absence of resuscitative equipment is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4)].
Opioid analgesics and antitussives, including hydrocodone, one of the active ingredients in hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate, should not be used in patients with acute febrile illness associated with productive cough or in patients with chronic respiratory disease where interference with ability to clear the tracheobronchial tree of secretions would have a deleterious effect on the patient's respiratory function.
Hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate -treated patients with significant chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or cor pulmonale, and those with a substantially decreased respiratory reserve, hypoxia, hypercapnia, or pre-existing respiratory depression are at increased risk of decreased respiratory drive including apnea, even at recommended dosages of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Elderly, Cachectic, or Debilitated Patients: Life-threatening respiratory depression is more likely to occur in elderly, cachectic, or debilitated patients because they may have altered pharmacokinetics or altered clearance compared to younger, healthier patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Because of the risk of respiratory depression, avoid the use of opioid antitussives, including hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate in patients with compromised respiratory function, patients at risk of respiratory failure, and in elderly, cachectic, or debilitated patients. If hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate is prescribed, monitor such patients closely, particularly when initiating hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate and when hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate is given concomitantly with other drugs that depress respiration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
5.5 Risk of Accidental Overdose and Death due to Medication Errors
Dosing errors can result in accidental overdose and death. To reduce the risk of overdose and respiratory depression, ensure that the dose of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate is communicated clearly and dispensed accurately [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Advise patients to always use an accurate milliliter measuring device when measuring and administering hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate. Inform patients that household teaspoon is not an accurate measuring device and such use could lead to overdosage and serious adverse reactions [see Overdosage (10)]. For prescriptions where a measuring device is not provided, a pharmacist can provide an appropriate calibrated measuring device and can provide instructions for measuring the correct dose.
5.6 Activities Requiring Mental Alertness: Risks of Driving and Operating Machinery
Hydrocodone and chlorpheniramine, two of the active ingredients in hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate, may produce marked drowsiness and impair the mental and/or physical abilities required for the performance of potentially hazardous tasks such as driving a car or operating machinery. Advise patients to avoid engaging in hazardous tasks requiring mental alertness and motor coordination after ingestion of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate. Avoid concurrent use of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate with alcohol or other central nervous system depressants because additional impairment of central nervous system performance may occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
5.7 Risks from Concomitant Use or Discontinuation of Cytochrome P450 3A4 Inhibitors and Inducers
Concomitant use of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate with a CYP3A4 inhibitor, such as macrolide antibiotics (e.g., erythromycin), azole-antifungal agents (e.g., ketoconazole), and protease inhibitors (e.g., ritonavir), may increase plasma concentrations of hydrocodone and prolong opioid adverse reactions, which may cause potentially fatal respiratory depression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)], particularly when an inhibitor is added after a stable dose of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate is achieved. Similarly, discontinuation of a CYP3A4 inducer, such as rifampin, carbamazepine, and phenytoin, in hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate -treated patients may increase hydrocodone plasma concentrations and prolong opioid adverse reactions.
Concomitant use of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate with CYP3A4 inducers or discontinuation of an CYP3A4 inhibitor could decrease hydrocodone plasma concentrations, decrease opioid efficacy or, possibly, lead to a withdrawal syndrome in a patient who had developed physical dependence to hydrocodone.
Avoid the use of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate in patients who are taking a CYP3A4 inhibitor or inducer. If concomitant use of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate with a CYP3A4 inhibitor or inducer is necessary, monitor patients for signs and symptoms that may reflect opioid toxicity and opioid withdrawal [see Drug Interactions (7.2, 7.3)].
5.8 Risks from Concomitant Use with Benzodiazepines or other CNS Depressants
Concomitant use of opioids, including hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate, with benzodiazepines, or other CNS depressants, including alcohol, may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death. Because of these risks, avoid use of opioid cough medications in patients taking benzodiazepines, other CNS depressants, or alcohol [see Drug Interactions (7.5)].
Observational studies have demonstrated that concomitant use of opioid analgesics and benzodiazepines increases the risk of drug-related mortality compared to use of opioids alone. Because of similar pharmacologic properties, it is reasonable to expect similar risk with concomitant use of opioid cough medications and benzodiazepines, other CNS depressants, or alcohol.
Advise both patients and caregivers about the risks of respiratory depression and sedation if hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate is used with benzodiazepines, alcohol, or other CNS depressants [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
Patients must not consume alcoholic beverages, or prescription or non-prescription products containing alcohol, while on hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate therapy. The co-ingestion of alcohol with hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate may result in increased plasma levels and a potentially fatal overdose of hydrocodone [see Drug Interactions (7.1, 7.5)].
5.9 Risks of Use in Patients with Gastrointestinal Conditions
Hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate is contraindicated in patients with known or suspected gastrointestinal obstruction, including paralytic ileus [see Contraindications (4)]. The use of hydrocodone in hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate may obscure the diagnosis or clinical course of patients with acute abdominal conditions.
The concurrent use of anticholinergics with hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate may produce paralytic ileus [see Drug Interactions (7.10)].
The hydrocodone in hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate may result in constipation or obstructive bowel disease, especially in patients with underlying intestinal motility disorders. Use with caution in patients with underlying intestinal motility disorders.
The hydrocodone in hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate may cause spasm of the sphincter of Oddi, resulting in an increase in biliary tract pressure. Opioids may cause increases in serum amylase [see Warnings and Precautions (5.16)]. Monitor patients with biliary tract disease, including acute pancreatitis for worsening symptoms.
5.10 Risks of Use in Patients with Head Injury, Impaired Consciousness, Increased Intracranial Pressure, or Brain Tumors
Avoid the use of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate in patients with head injury, intracranial lesions, or a pre-existing increase in intracranial pressure. In patients who may be susceptible to the intracranial effects of CO2 retention (e.g., those with evidence of increased intracranial pressure or brain tumors), hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate may reduce respiratory drive, and the resultant CO2 retention can further increase intracranial pressure. Furthermore, opioids produce adverse reactions that may obscure the clinical course of patients with head injuries.
5.11 Cardiovascular and Central Nervous System Effects
The pseudoephedrine contained in hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate can produce cardiovascular and central nervous system effects in some patients such as, insomnia, dizziness, weakness, tremor, transient elevations in blood pressure, or arrhythmias. In addition, central nervous system stimulation with convulsions or cardiovascular collapse with accompanying hypotension has been reported. Therefore, hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate is contraindicated in patients with severe hypertension or coronary artery disease [see Contraindications (4)], and should, be used with caution in patients with other cardiovascular disorders.
5.12 Increased Risk of Seizures in Patients with Seizure Disorders
The hydrocodone and chlorpheniramine in hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate may increase the frequency of seizures in patients with seizure disorders, and may increase the risk of seizures occurring in other clinical settings associated with seizures. Monitor patients with a history of seizure disorders for worsened seizure control during hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate therapy.
5.13 Severe Hypotension
Hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate may cause severe hypotension including orthostatic hypotension and syncope in ambulatory patients. There is increased risk in patients whose ability to maintain blood pressure has already been compromised by a reduced blood volume or concurrent administration of certain CNS depressant drugs (e.g., phenothiazines or general anesthetics) [see Drug Interactions (7.5)]. Monitor these patients for signs of hypotension after initiating hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate.
In patients with circulatory shock, hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate may cause vasodilation that can further reduce cardiac output and blood pressure. Avoid the use of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate in patients with circulatory shock.
5.14 Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome
Hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate is not recommended for use in pregnant women. Prolonged use of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate during pregnancy can result in withdrawal in the neonate. Neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome, unlike opioid withdrawal syndrome in adults, may be life-threatening if not recognized and treated, and requires management according to protocols developed by neonatology experts. Observe newborns for signs of neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome and manage accordingly. Advise pregnant women using opioids for a prolonged period of the risk of neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome and ensure that appropriate treatment will be available. [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1), Patient Counseling Information (17)]
5.15 Adrenal Insufficiency
Cases of adrenal insufficiency have been reported with opioid use, more often following greater than one month of use. Presentation of adrenal insufficiency may include non-specific symptoms and signs including nausea, vomiting, anorexia, fatigue, weakness, dizziness, and low blood pressure. If adrenal insufficiency is suspected, confirm the diagnosis with diagnostic testing as soon as possible. If adrenal insufficiency is diagnosed, treat with physiologic replacement doses of corticosteroids. Wean the patient off of the opioid to allow adrenal function to recover and continue corticosteroid treatment until adrenal function recovers. Other opioids may be tried as some cases reported use of a different opioid without recurrence of adrenal insufficiency. The information available does not identify any particular opioids as being more likely to be associated with adrenal insufficiency.
5.16 Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
Because opioid agonists may increase biliary tract pressure, with resultant increase in plasma amylase or lipase levels, determination of these enzyme levels may be unreliable for 24 hours after administration of a dose of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are described, or described in greater detail, in other sections:
- Addiction, abuse, and misuse [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.3)]
- Life-threatening respiratory depression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3, 5.4, 5.8), Overdosage (10)]
- Accidental overdose and death due to medication errors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Decreased mental alertness with impaired mental and/or physical abilities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Interactions with benzodiazepines and other CNS depressants [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8), Drug Interactions (7.1, 7.5)]
- Paralytic ileus, gastrointestinal adverse reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Increased intracranial pressure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
- Obscured clinical course in patients with head injuries [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
- Cardiovascular and CNS effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
- Seizures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]
- Severe hypotension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)]
- Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14)]
- Adrenal insufficiency [see Warnings and Precautions (5.15)]
The following adverse reactions have been identified during clinical studies, in the literature, or during post-approval use of hydrocodone, chlorpheniramine, and/or pseudoephedrine. Because these reactions may be reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
The most common adverse reactions to hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate include: Sedation (somnolence, mental clouding, lethargy), impaired mental and physical performance, lightheadedness, dizziness, headache, dry mouth, nausea, vomiting, constipation tachycardia, arrhythmias including premature ventricular contractions, CNS stimulation including anxiety, restlessness, nervousness, tremor, and irritability.
Other reactions include:
Anaphylaxis: Anaphylaxis has been reported with hydrocodone, one of the ingredients in hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate.
Body as a whole: Coma, death, fatigue, falling injuries, lethargy, weakness, hyperthermia, ataxia, vertigo.
Cardiovascular: Peripheral edema, increased blood pressure, decreased blood pressure, tachycardia, chest pain, palpitation, syncope, orthostatic hypotension, prolonged QT interval, hot flush, atrial fibrillation, myocardial infarction.
Central Nervous System: Facial dyskinesia, insomnia, migraine, increased intracranial pressure, seizure, tremor.
Dermatologic: Flushing, hyperhidrosis, pruritus, rash. Cases of severe skin reactions such as acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) have been reported with pseudoephedrine-containing products.
Endocrine/Metabolic: Cases of serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition, have been reported during concomitant use of opioids with serotonergic drugs. Cases of adrenal insufficiency have been reported with opioid use, more often following greater than one month of use. Cases of androgen deficiency have occurred with chronic use of opioids [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
Gastrointestinal: Abdominal pain, bowel obstruction, decreased appetite, diarrhea, difficulty swallowing, dry mouth, GERD, indigestion, pancreatitis, paralytic ileus, biliary tract spasm (spasm of the sphincter of Oddi), dysgeusia, ischemic colitis.
Genitourinary: Urinary tract infection, ureteral spasm, spasm of vesicle sphincters, urinary retention.
Hematologic: Agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, and thrombocytopenia have been reported.
Laboratory: Increases in serum amylase.
Musculoskeletal: Arthralgia, backache, muscle spasm.
Ophthalmic: Miosis (constricted pupils), visual disturbances, mydriasis (dilated pupils), blurred vision, diplopia.
Psychiatric: Agitation, anxiety, confusion, fear, dysphoria, depression, hyperactivity, ataxia, confusion, hallucinations, hyperexcitability.
Reproductive: Hypogonadism, infertility.
Respiratory: Bronchitis, cough, dyspnea, nasal congestion, nasopharyngitis, respiratory depression, sinusitis, upper respiratory tract infection, thickening of bronchial secretions, tightness of chest and wheezing, dry nose, dry throat, tinnitus.
Other: Drug abuse, drug dependence, opioid withdrawal syndrome.
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
No specific drug interaction studies have been conducted with hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate.
7.1 Alcohol
Concomitant use of alcohol with hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate can result in an increase of hydrocodone plasma levels and potentially fatal overdose of hydrocodone. Instruct patients not to consume alcoholic beverages or use prescription or nonprescription products containing alcohol while on hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.2 Inhibitors of CYP3A4 and CYP2D6
The concomitant use of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate and CYP3A4 inhibitors, such as macrolide antibiotics (e.g., erythromycin), azole-antifungal agents (e.g. ketoconazole), or protease inhibitors (e.g., ritonavir), can increase the plasma concentration of hydrocodone, resulting in increased or prolonged opioid effects. These effects could be more pronounced with concomitant use of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate and CYP2D6 and CYP3A4 inhibitors, particularly when an inhibitor is added after a stable dose of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate is achieved [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]. After stopping a CYP3A4 inhibitor, as the effects of the inhibitor decline, the hydrocodone plasma concentration will decrease [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], resulting in decreased opioid efficacy or a withdrawal syndrome in patients who had developed physical dependence to hydrocodone.
Avoid the use of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate while taking a CYP3A4 or CYP2D6 inhibitor. If concomitant use is necessary, monitor patients for respiratory depression and sedation at frequent intervals.
7.3 CYP3A4 Inducers
The concomitant use of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate and CYP3A4 inducers such as rifampin, carbamazepine, or phenytoin, can decrease the plasma concentration of hydrocodone [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], resulting in decreased efficacy or onset of a withdrawal syndrome in patients who have developed physical dependence to hydrocodone [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]. After stopping a CYP3A4 inducer, as the effects of the inducer decline, the hydrocodone plasma concentration will increase [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which could increase or prolong both the therapeutic effects and adverse reactions, and may cause serious respiratory depression.
Avoid the use of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate in patients who are taking CYP3A4 inducers. If concomitant use of a CYP3A4 inducer is necessary, follow the patient for reduced efficacy.
7.4 Phenytoin
Adverse event reports in the literature suggest a possible drug interaction involving increased serum phenytoin levels and phenytoin toxicity when chlorpheniramine and phenytoin are co-administered. The exact mechanism for this interaction is not known, however it is believed that chlorpheniramine may inhibit the hepatic metabolism of phenytoin. Avoid the use of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate in patients who are taking phenytoin.
7.5 Benzodiazepines, and Other CNS Depressants
Due to additive pharmacologic effect, the concomitant use of benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants, including alcohol, other sedatives/hypnotics, anxiolytics, tranquilizers, muscle relaxants, general anesthetics, antipsychotics, and other opioids, can increase the risk of hypotension, respiratory depression, profound sedation, coma, and death. Avoid the use of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate in patients who are taking benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)], and instruct patients to avoid consumption of alcohol while on hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate [see Drug Interactions (7.1), Patient Counseling Information (17)].
7.6 Serotonergic Drugs
The concomitant use of opioids with other drugs that affect the serotonergic neurotransmitter system has resulted in serotonin syndrome. If concomitant use is warranted, carefully observe the patient, particularly during treatment initiation. Discontinue hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate if serotonin syndrome is suspected.
7.7 Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
Avoid the use of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate in patients who are taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) or have taken MAOIs within 14 days. The use of MAOIs or tricyclic antidepressants with hydrocodone, one of the active ingredients in hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate, may increase the effect of either the antidepressant or hydrocodone. MAOI interactions with opioids may manifest as serotonin syndrome or opioid toxicity (e.g., respiratory depression, coma). An increase in blood pressure or hypertensive crisis may also occur when pseudoephedrine containing preparations are used with MAOIs.
7.8 Muscle Relaxants
Hydrocodone may enhance the neuromuscular blocking action of skeletal muscle relaxants and produce an increased degree of respiratory depression. Avoid the use of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate in patients taking muscle relaxants. If concomitant use is necessary, monitor patients for signs of respiratory depression that may be greater than otherwise expected.
7.9 Diuretics
Opioids can reduce the efficacy of diuretics by inducing the release of antidiuretic hormone. Monitor patients for signs of diminished diuresis and/or effects on blood pressure and increase the dosage of the diuretic as needed.
7.10 Anticholinergic Drugs
The concomitant use of anticholinergic drugs with hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate may increase risk of urinary retention and/or severe constipation, which may lead to paralytic ileus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]. Monitor patients for signs of urinary retention or reduced gastric motility when hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate is used concomitantly with anticholinergic drugs.
Additive adverse effects resulting from cholinergic blockade (e.g., xerostomia, blurred vision, or constipation) may occur when anticholinergic drugs are administered with chlorpheniramine.
7.11 Antihypertensive drugs
Due to the antagonistic pharmacologic effects of pseudoephedrine, one of the active ingredients in hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate, the concomitant use of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate with antihypertensive drugs which interfere with sympathetic activity (e.g., methyldopa, mecamylamine, and reserpine) may reduce their antihypertensive effects. Use hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate with caution in patients who are taking antihypertensive drugs.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate is not recommended for use in pregnant women, including during or immediately prior to labor.
Prolonged use of opioids during pregnancy may cause neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13), Clinical Considerations].
There are no available data with hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate use in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk for adverse developmental outcomes. Published studies with hydrocodone have reported inconsistent findings and have important methodological limitations (see Data).
Reproductive toxicity studies have not been conducted with hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate; however, studies are available with individual active ingredients or related active ingredients (see Data).
In animal reproduction studies, hydrocodone administered by the subcutaneous route to pregnant hamsters during the period of organogenesis produced a teratogenic effect at a dose approximately 70 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) (see Data).
Chlorpheniramine administered by the oral route to mice throughout pregnancy was embryolethal at a dose approximately 9 times the MRHD and decreased postnatal survival when dosing was continued after parturition. Chlorpheniramine administered by the oral route to male and female rats prior to mating produced embryolethality at a dose approximately 9 times the MRHD (see Data).
Based on the animal data, advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reactions
Prolonged use of opioid analgesics during pregnancy for medical or nonmedical purposes can result in physical dependence in the neonate and neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome shortly after birth.
Neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome presents as irritability, hyperactivity and abnormal sleep pattern, high pitched cry, tremor, vomiting, diarrhea and failure to gain weight. The onset, duration, and severity of neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome vary based on the specific opioid used, duration of use, timing and amount of last maternal use, and rate of elimination of the drug by the newborn. Observe newborns for symptoms of neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome and manage accordingly [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14)].
Maternal use of pseudoephedrine can cause fetal tachycardia.
Labor or Delivery
Opioids cross the placenta and may produce respiratory depression and psycho-physiologic effects in neonates. An opioid antagonist, such as naloxone, must be available for reversal of opioid-induced respiratory depression in the neonate. Opioids, including hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate, can prolong labor through actions which temporarily reduce the strength, duration, and frequency of uterine contractions. However, this effect is not consistent and may be offset by an increased rate of cervical dilation, which tends to shorten labor. Monitor neonates exposed to opioids during labor for signs of excess sedation and respiratory depression.
Data
Human Data
Hydrocodone
A limited number of pregnancies have been reported in published observational studies and postmarketing reports describing hydrocodone use during pregnancy. However, these data cannot definitely establish or exclude any drug-associated risk during pregnancy. Methodological limitations of these observational studies include small sample size and lack of details regarding dose, duration and timing of exposure.
Chlorpheniramine
The majority of studies examining the use of chlorpheniramine in pregnancy did not find an association with an increased risk of congenital anomalies. In the few studies reporting an association, there was no consistent pattern of malformations noted.
Pseudoephedrine
The majority of studies examining the use of pseudoephedrine in pregnancy did not find an association with an increased risk of congenital anomalies. Some studies reported an association with an increased risk of gastroschisis. However, several similar studies did not find a statistically significant association. Methodological limitations of these studies included small sample size, recall bias and lack of information regarding dose and timing of exposure.
Animal Data
Reproductive toxicity studies have not been conducted with hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate; however, studies are available with individual active ingredients or related active ingredients.
Hydrocodone
In an embryofetal development study in pregnant hamsters dosed on gestation day 8 during the period of organogenesis, hydrocodone induced cranioschisis, a malformation, at approximately 70 times the MRHD (on a mg/m2 basis with a maternal subcutaneous dose of 102 mg/kg). Reproductive toxicology studies were also conducted with codeine, an opiate related to hydrocodone. In an embryofetal development study in pregnant rats dosed throughout the period of organogenesis, codeine increased resorptions and decreased fetal weights at a dose approximately 95 times the MRHD of hydrocodone (on a mg/m2 basis with a maternal oral dose of codeine at 120 mg/kg/day); however, these effects occurred in the presence of maternal toxicity. In embryofetal development studies with pregnant rabbits and mice dosed throughout the period of organogenesis, codeine produced no adverse developmental effects at doses approximately 50 and 240 times, respectively, the MRHD of hydrocodone (on a mg/m2 basis with maternal oral doses of codeine at 30 mg/kg/day in rabbits and 600 mg/kg/day in mice).
Chlorpheniramine
In embryofetal development studies with pregnant rats and rabbits dosed throughout the period of organogenesis, chlorpheniramine produced no adverse developmental effects at oral doses up to approximately 35 and 45 times, respectively, the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis. However, in a reproduction study with pregnant mice dosed throughout pregnancy, chlorpheniramine produced embryolethality at a dose approximately 9 times the MRHD (on a mg/m2 basis with a maternal oral dose of 20 mg/kg/day) and decreased postnatal survival when dosing was continued after parturition. In a fertility and reproduction study with male and female rats dosed prior to mating, chlorpheniramine produced embryolethality at a dose approximately 9 times the MRHD (on a mg/m2 basis with an oral parental dose of 10 mg/kg/day).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions, including excess sedation, respiratory depression, and death in a breastfed infant, advise patients that breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate.
There are no data on the presence of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate in human milk, the effects of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate on the breastfed infant, or the effects of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate on milk production; however, data are available with hydrocodone, chlorpheniramine, and pseudoephedrine.
Hydrocodone
Hydrocodone is present in breast milk. Published cases report variable concentrations of hydrocodone and hydromorphone (an active metabolite) in breast milk with administration of immediate-release hydrocodone to nursing mothers in the early post-partum period with relative infant doses of hydrocodone ranging between 1.4 and 3.7%. There are case reports of excessive sedation and respiratory depression in breastfed infants exposed to hydrocodone. No information is available on the effects of hydrocodone on milk production.
Chlorpheniramine
Chlorpheniramine is present in human milk. Chlorpheniramine has not been reported to cause effects on the breastfed infant. The published literature suggests that chlorpheniramine may decrease milk production based on its anticholinergic effects. (see Clinical Considerations)
Pseudoephedrine
Pseudoephedrine is present in human milk. Pseudoephedrine has been reported to decrease milk production (see Data). Pseudoephedrine has been reported to cause "irritability" in a breastfed infant (see Clinical Considerations and Data).
Clinical Considerations
Infants exposed to hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate through breast milk should be monitored for excess sedation, respiratory depression, and irritability. Withdrawal symptoms can occur in breastfed infants when maternal administration of an opioid is stopped, or when breastfeeding is stopped.
Data
Pseudoephedrine
In a study of eight lactating women, who were 8 to 76 weeks postpartum and received a single dose of 60 mg of pseudoephedrine, the mean 24-hour milk production was reduced by 24%. In the same study, the estimated mean relative infant dose from breast milk (assuming mean milk consumption of 150 ml/kg/day and a maternal dosing regimen of 60 mg pseudoephedrine four times per day) was calculated to be 4.3% of the weight-adjusted maternal dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Infertility
Chronic use of opioids, such as hydrocodone, a component of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate, may cause reduced fertility in females and males of reproductive potential. It is not known whether these effects on fertility are reversible [see Adverse Reactions (6), Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
Hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate is not indicated for use in patients younger than 18 years of age because the benefits of symptomatic treatment of cough associated with allergies or the common cold do not outweigh the risks for use of hydrocodone in these patients [see Indications (1), Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Life-threatening respiratory depression and death have occurred in children who received hydrocodone [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Because of the risk of life-threatening respiratory depression and death, hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate is contraindicated in children less than 6 years of age [see Contraindications (4)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies have not been conducted with hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate in geriatric populations.
Use caution when considering the use of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate in patients 65 years of age or older. Elderly patients may have increased sensitivity to hydrocodone; greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function; or concomitant disease or other drug therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Respiratory depression is the chief risk for elderly patients treated with opioids, including hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate. Respiratory depression has occurred after large initial doses of opioids were administered to patients who were not opioid-tolerant or when opioids were co-administered with other agents that depress respiration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4, 5.8)].
Hydrocodone is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of adverse reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, monitor these patients closely for respiratory depression, sedation, and hypotension.
8.6 Renal Impairment
The pharmacokinetics of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate has not been characterized in patients with renal impairment. Patients with renal impairment may have higher plasma concentrations than those with normal function [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Chlorpheniramine maleate is cleared substantially by the kidney. As such, impaired renal function could potentially lead to the risk of decreased clearance and thereby increased retention or systemic levels of chlorpheniramine. Pseudoephedrine is primarily excreted unchanged in the urine. Therefore, pseudoephedrine may accumulate in patients with renal impairment. Hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate should be used with caution in patients with severe impairment of renal function, and patients should be monitored closely for signs of hydrocodone toxicity (respiratory depression, sedation, and hypotension), chlorpheniramine toxicity and pseudoephedrine toxicity.
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
The pharmacokinetics of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate has not been characterized in patients with hepatic impairment. Patients with severe hepatic impairment may have higher plasma concentrations than those with normal hepatic function [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Chlorpheniramine is extensively metabolized by liver before elimination from the body. As such, impaired hepatic function could potentially lead to the risk of decreased metabolism and thereby increased systemic levels of chlorpheniramine. Therefore, hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate should be used with caution in patients with severe impairment of hepatic function, and patients should be monitored closely for signs of hydrocodone toxicity (respiratory depression, sedation, and hypotension) and chlorpheniramine toxicity.
9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
9.1 Controlled Substance
Hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate contains hydrocodone, a Schedule II controlled substance.
9.2 Abuse
Hydrocodone
Hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate contains hydrocodone, a substance with a high potential for abuse similar to other opioids including morphine and codeine. Hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate can be abused and is subject to misuse, addiction, and criminal diversion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
All patients treated with opioids require careful monitoring for signs of abuse and addiction, since use of opioid analgesic and antitussive products carries the risk of addiction even under appropriate medical use.
Prescription drug abuse is the intentional non-therapeutic use of a prescription drug, even once, for its rewarding psychological or physiological effects.
Drug addiction is a cluster of behavioral, cognitive, and physiological phenomena that develop after repeated substance use and includes: a strong desire to take the drug, difficulties in controlling its use, persisting in its use despite harmful consequences, a higher priority given to drug use than to other activities and obligations, increased tolerance, and sometimes a physical withdrawal.
"Drug-seeking" behavior is very common in persons with substance use disorders. Drug-seeking tactics include emergency calls or visits near the end of office hours, refusal to undergo appropriate examination, testing, or referral, repeated "loss" of prescriptions, tampering with prescriptions, and reluctance to provide prior medical records or contact information for other treating health care provider(s). "Doctor shopping" (visiting multiple prescribers to obtain additional prescriptions) is common among drug abusers and people suffering from untreated addiction. Preoccupation with achieving adequate pain relief can be appropriate behavior in a patient with poor pain control.
Abuse and addiction are separate and distinct from physical dependence and tolerance. Health care providers should be aware that addiction may not be accompanied by concurrent tolerance and symptoms of physical dependence in all addicts. In addition, abuse of opioids can occur in the absence of true addiction.
Hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate, like other opioids, can be diverted for non-medical use into illicit channels of distribution. Careful record-keeping of prescribing information, including quantity, frequency, and renewal requests, as required by state and federal law, is strongly advised.
Proper assessment of the patient, proper prescribing practices, periodic re-evaluation of therapy, and proper dispensing and storage are appropriate measures that help to limit abuse of opioid drugs.
Risks Specific to Abuse of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate
Hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate O is for oral use only. Abuse of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate poses a risk of overdose and death. The risk is increased with concurrent use of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate with alcohol and other central nervous system depressants [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8), Drug Interactions (7.1, 7.5)].
Parenteral drug abuse is commonly associated with transmission of infectious diseases such as hepatitis and HIV.
9.3 Dependence
Psychological dependence, physical dependence, and tolerance may develop upon repeated administration of opioids; therefore, hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate should be prescribed and administered for the shortest duration that is consistent with individual patient treatment goals and patients should be reevaluated prior to refills [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Physical dependence, the condition in which continued administration of the drug is required to prevent the appearance of a withdrawal syndrome, assumes clinically significant proportions only after several weeks of continued oral opioid use, although some mild degree of physical dependence may develop after a few days of opioid therapy.
If hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate is abruptly discontinued in a physically-dependent patient, a withdrawal syndrome may occur. Withdrawal also may be precipitated through the administration of drugs with opioid antagonist activity (e.g., naloxone, nalmefene), mixed agonist/antagonist analgesics (e.g., pentazocine, butorphanol, nalbuphine), or partial agonists (e.g., buprenorphine). Some or all of the following can characterize this syndrome: restlessness, lacrimation, rhinorrhea, yawning, perspiration, chills, myalgia, and mydriasis. Other signs and symptoms also may develop, including irritability, anxiety, backache, joint pain, weakness, abdominal cramps, insomnia, nausea, anorexia, vomiting, diarrhea, or increased blood pressure, respiratory rate, or heart rate.
Infants born to mothers physically dependent on opioids will also be physically dependent and may exhibit respiratory difficulties and withdrawal signs [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
10 OVERDOSAGE
Clinical Presentation
Hydrocodone
Acute overdose with hydrocodone is characterized by respiratory depression (a decrease in respiratory rate and/or tidal volume, Cheyne-Stokes respiration, cyanosis), extreme somnolence progressing to stupor or coma, skeletal muscle flaccidity, cold and clammy skin, constricted pupils, and, in some cases, pulmonary edema, bradycardia, partial or complete airway obstruction, atypical snoring, hypotension, circulatory collapse, cardiac arrest, and death.
Hydrocodone may cause miosis, even in total darkness. Pinpoint pupils are a sign of opioid overdose but are not pathognomonic (e.g., pontine lesions of hemorrhagic or ischemic origin may produce similar findings). Marked mydriasis rather than miosis may be seen with hypoxia in overdose situations [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
Chlorpheniramine
Signs and symptoms of chlorpheniramine overdosage may vary from central nervous system depression to stimulation. Central toxic effects are characterized by agitation, anxiety, delirium, disorientation, hallucinations, hyperactivity, sedation, and seizures. Severe overdosage may produce coma, medullary paralysis, and death. Peripheral toxicity includes hypertension, tachycardia, dysrhythmias, vasodilation, hyperpyrexia, mydriasis, urinary retention, and diminished gastrointestinal motility. Atropine-like signs and symptoms (dry mouth, fixed dilated pupils, flushing, tachycardia, hallucinations, gastrointestinal symptoms, convulsions, urinary retention, cardiac arrhythmias and coma) may be observed.
Impaired secretion from sweat glands following toxic doses of drugs with anticholinergic side effects may predispose to hyperthermia.
Toxic psychosis, a possible class effect from overdose of sedating antihistamines, has been reported.
Pseudoephedrine
Overdosage with sympathomimetics such as pseudoephedrine can cause excessive CNS stimulation resulting in nervousness, anxiety, tremor, restlessness and insomnia. Other effects may include headache, tachycardia, palpitations, precordial pain, hypertension, pallor, mydriasis, nausea, vomiting, sweating, thirst, urinary retention (difficulty in micturition), muscle weakness and tenseness, giddiness, anxiety, restlessness, hyperglycemia, and insomnia. Many patients can present a toxic psychosis with delusion and hallucinations. Severe overdosage may cause tachypnea or hyperpnea, hallucinations, convulsions, delirium, or coma, but in some individuals there may be CNS depression with somnolence, stupor, respiratory depression, or respiratory failure. Arrhythmias (including ventricular fibrillation) may lead to hypotension and circulatory collapse. Severe hypokalemia can occur, probably due to compartmental shift rather than depletion of potassium.
Treatment of Overdose
Treatment of overdosage is driven by the overall clinical presentation, and consists of discontinuation of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate together with institution of appropriate therapy. Give primary attention to the reestablishment of adequate respiratory exchange through provision of a patent and protected airway and the institution of assisted or controlled ventilation. Employ other supportive measures (including oxygen and vasopressors) in the management of circulatory shock and pulmonary edema as indicated. Cardiac arrest or arrhythmias will require advanced life-support techniques. Gastric emptying may be useful in removing unabsorbed drug.
The opioid antagonists, naloxone and nalmefene, are specific antidotes for respiratory depression resulting from opioid overdose. For clinically significant respiratory or circulatory depression secondary to hydrocodone overdose, administer an opioid antagonist. An antagonist should not be administered in the absence of clinically significant respiratory depression. Because the duration of opioid reversal is expected to be less than the duration of action of hydrocodone in hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate, carefully monitor the patient until spontaneous respiration is reliably reestablished. If the response to an opioid antagonist is suboptimal or only brief in nature, administer additional antagonist as directed by the product's prescribing information.
Hemodialysis is not routinely used to enhance the elimination of hydrocodone, chlorpheniramine, or pseudoephedrine from the body.
Urinary excretion of chlorpheniramine is increased when the pH of the urine is acidic; however, acid diuresis is NOT recommended to enhance elimination in overdose, as the risks of acidemia and acute tubular necrosis in patients with rhabdomyolysis far outweigh any potential benefits.
Adrenergic receptor blocking agents (beta-blockers), such as propranolol, may be used for the treatment of cardiac toxicity due to pseudoephedrine.
11 DESCRIPTION
Hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution contains hydrocodone an opioid agonist; chlorpheniramine a histamine-1 (H1) receptor antagonist; and pseudoephedrine an alpha-adrenergic agonist.
Each 5 mL of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate contains 5 mg of hydrocodone bitartrate, 4 mg of chlorpheniramine maleate, and 60 mg of pseudoephedrine hydrochloride for oral administration.
Hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate also contains the following inactive ingredients: citric acid anhydrous, glycerin, grape flavor, methylparaben, propylene glycol, propylparaben, purified water, sodium citrate, sodium saccharin, and sucrose.
Hydrocodone Bitartrate
The chemical name for hydrocodone bitartrate is morphinan-6-one, 4,5-epoxy-3-methoxy-17-methyl-, (5α)-, [R-(R*,R*)]-2,3-dihydroxybutanedioate (1:1), hydrate (2:5). It is also known as 4,5α-Epoxy-3-methoxy-17-methylmorphinan-6-one tartrate (1:1) hydrate (2:5). It occurs as a fine white crystal or crystalline powder, which is derived from the opium alkaloid, thebaine; and it has the following chemical structure:
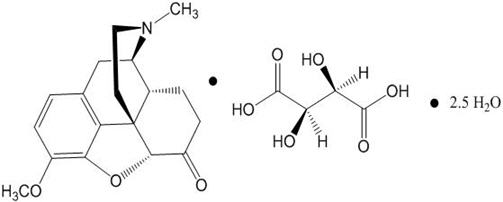 |
|
| Hydrocodone Bitartrate C18H21NO3 ∙ C4H6O6 ∙ 2.5 H2O Molecular weight = 494.5 |
|
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Hydrocodone
Hydrocodone is an opioid agonist with relative selectivity for the mu-opioid receptor, although it can interact with other opioid receptors at higher doses. The precise mechanism of action of hydrocodone and other opiates is not known; however, hydrocodone is believed to act centrally on the cough center. In excessive doses, hydrocodone will depress respiration.
Chlorpheniramine
Chlorpheniramine is a propylamine derivative antihistamine (H1-receptor antagonist) of the alkylamine class that also possesses anticholinergic and sedative activity. It prevents released histamine from dilating capillaries and causing edema of the respiratory mucosa.
Pseudoephedrine
Pseudoephedrine is a sympathomimetic amine that exerts a decongestant action on the nasal mucosa via alpha adrenergic activity. Pseudoephedrine produces peripheral effects similar to those of ephedrine and central effects similar to, but less intense than, amphetamines. It has the potential for excitatory side effects.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Hydrocodone
Effects on the Central Nervous System
Hydrocodone produces respiratory depression by direct action on brain stem respiratory centers. The respiratory depression involves a reduction in the responsiveness of the brain stem respiratory centers to both increases in carbon dioxide tension and to electrical stimulation.
Hydrocodone causes miosis, even in total darkness. Pinpoint pupils are a sign of opioid overdose but are not pathognomonic (e.g., pontine lesions of hemorrhagic or ischemic origins may produce similar findings). Marked mydriasis rather than miosis may be seen due to hypoxia in overdose situations.
Effects on the Gastrointestinal Tract and Other Smooth Muscle
Hydrocodone causes a reduction in motility associated with an increase in smooth muscle tone in the antrum of the stomach and duodenum. Digestion of food in the small intestine is delayed and propulsive contractions are decreased. Propulsive peristaltic waves in the colon are decreased, while tone may be increased to the point of spasm resulting in constipation. Other opioid-induced effects may include a reduction in biliary and pancreatic secretions, spasm of sphincter of Oddi, and transient elevations in serum amylase.
Effects on the Cardiovascular System
Hydrocodone produces peripheral vasodilation which may result in orthostatic hypotension or syncope. Manifestations of histamine release and/or peripheral vasodilation may include pruritus, flushing, red eyes and sweating and/or orthostatic hypotension.
Effects on the Endocrine System
Opioids inhibit the secretion of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), cortisol, and luteinizing hormone (LH) in humans [see Adverse Reactions (6)]. They also stimulate prolactin, growth hormone (GH) secretion, and pancreatic secretion of insulin and glucagon.
Chronic use of opioids may influence the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis, leading to androgen deficiency that may manifest as low libido, impotence, erectile dysfunction, amenorrhea, or infertility. The causal role of opioids in the clinical syndrome of hypogonadism is unknown because the various medical, physical, lifestyle, and psychological stressors that may influence gonadal hormone levels have not been adequately controlled for in studies conducted to date [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
Effects on the Immune System
Opioids have been shown to have a variety of effects on components of the immune system in in vitro and animal models. The clinical significance of these findings is unknown. Overall, the effects of opioids appear to be modestly immunosuppressive.
Concentration–Adverse Reaction Relationships
There is a relationship between increasing hydrocodone plasma concentration and increasing frequency of dose-related opioid adverse reactions such as nausea, vomiting, CNS effects, and respiratory depression. In opioid-tolerant patients, the situation may be altered by the development of tolerance to opioid-related adverse reactions.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
After oral administration, hydrocodone had mean (SD) peak plasma concentration of 10.6 (2.63) ng/mL at 1.4 (0.55) hours. Chlorpheniramine had a mean (SD) plasma peak concentration of 7.20 (1.98) ng/mL at 3.5 (1.6) hours. Pseudoephedrine had a mean (SD) peak plasma concentration of 212 (46.2) ng/mL at 1.8 (0.56) hours.
Food has no significant effect on the extent of absorption of hydrocodone.
Distribution
Although the extent of protein binding of hydrocodone in human plasma has not been definitively determined, structural similarities to related opioid analgesics suggest that hydrocodone is not extensively protein bound. As most agents in the 5-ring morphinan group of semi-synthetic opioids bind plasma protein to a similar degree (range 19% [hydromorphone] to 45% [oxycodone]), hydrocodone is expected to fall within this range.
Chlorpheniramine is widely distributed throughout the tissues of the body, including the central nervous system. It reportedly has an apparent steady-state volume of distribution of approximately 3.2 L/kg in adults and children and is about 70% bound to plasma proteins. Chlorpheniramine and its metabolites likely cross the placental barrier and are excreted into human breast milk.
Pseudoephedrine hydrochloride is extensively distributed into extravascular sites. The apparent volume of distribution (V/F) of pseudoephedrine ranged between 2.6 and 3.5 L/kg.
Elimination
Metabolism
Hydrocodone exhibits a complex pattern of metabolism, including N-demethylation, O-demethylation, and 6keto reduction to the corresponding 6-α-and 6-β-hydroxy metabolites. CYP3A4 mediated N-demethylation to norhydrocodone is the primary metabolic pathway of hydrocodone with a lower contribution from CYP2D6 mediated O-demethylation to hydromorphone. Hydromorphone is formed from the O-demethylation of hydrocodone and may contribute to the total analgesic effect of hydrocodone. Therefore, the formation of these and related metabolites can, in theory, be affected by other drugs [see Drug Interactions (7)]. Published in vitro studies have shown that N-demethylation of hydrocodone to form norhydrocodone can be attributed to CYP3A4 while O-demethylation of hydrocodone to hydromorphone is predominantly catalyzed by CYP2D6 and to a lesser extent by an unknown low affinity CYP enzyme.
Chlorpheniramine is rapidly and extensively metabolized via demethylation in the liver, forming mono-and didesmethyl derivatives. Oxidative metabolism of chlorpheniramine is catalyzed by cytochrome P-450 2D6.
Excretion
Hydrocodone and its metabolites are eliminated primarily in the kidneys. The mean plasma half-life of hydrocodone is approximately 4 hours.
Chlorpheniramine and its metabolites are primarily excreted through the kidneys, with large individual variation. Urinary excretion depends on urine pH and flow rate. The mean plasma half-life of chlorpheniramine is approximately 21-24 hours.
About 43-96% of an administered dose of pseudoephedrine is excreted unchanged in the urine. The remainder is apparently metabolized in the liver to inactive compounds by N-demethylation, parahydroxylation and oxidative deamination.
Pseudoephedrine has been shown to have a mean elimination half-life of 4–6 hours which is dependent on urine pH. The elimination half-life is decreased at urine pH lower than 6 and may be increased at urine pH higher than 8.
Specific Populations
Renal Impairment
No data are available on the pharmacokinetics of pseudoephedrine in renally-impaired subjects. Pseudoephedrine is primarily excreted unchanged in the urine. A decrease in renal function is, therefore, likely to decrease the clearance of pseudoephedrine, prolonging the half-life and resulting in accumulation. Therefore, pseudoephedrine may accumulate in patients with renal impairment.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity, mutagenicity, and fertility studies have not been conducted with hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate; however, published information is available for the individual active ingredients or related active ingredients.
Hydrocodone
Carcinogenicity studies were conducted with codeine, an opiate related to hydrocodone. Two-year studies in F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice were conducted to assess the carcinogenic potential of codeine. No evidence of tumorigenicity was observed in male and female rats at codeine dietary doses up to 70 and 80 mg/kg/day (approximately equivalent to 55 and 65 times the MRHD of hydrocodone on a mg/m2 basis, respectively). No evidence of tumorigenicity was observed in male and female mice at codeine dietary doses up to 400 mg/kg/day (approximately equivalent to 160 times the MRHD of hydrocodone on a mg/m2 basis).
Mutagenicity studies with hydrocodone have not been conducted.
Fertility studies with hydrocodone have not been conducted.
Chlorpheniramine
Carcinogenicity studies were conducted with chlorpheniramine maleate. Two-year studies in F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice were conducted to assess the carcinogenic potential of chlorpheniramine. No evidence of tumorigenicity was observed in male and female rats at chlorpheniramine oral doses up to 30 and 60 mg/kg/day for 5 days/week (approximately equivalent to 25 and 50 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis, respectively). No evidence of tumorigenicity was observed in male and female mice at chlorpheniramine oral doses up to 50 and 200 mg/kg/day for 5 days/week (approximately equivalent to 20 and 85 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis, respectively).
Chlorpheniramine maleate was not mutagenic in the in vitro bacterial reverse mutation assay or the in vitro mouse lymphoma forward mutation assay. Chlorpheniramine maleate was clastogenic in the in vitro Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell chromosomal aberration assay.
Chlorpheniramine maleate had no effects on fertility in rats and rabbits at oral doses approximately 35 and 45 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis, respectively.
Pseudoephedrine
Carcinogenicity studies were conducted with ephedrine sulfate, a structurally related drug. Two-year studies in F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice were conducted to assess the carcinogenic potential of ephedrine sulfate. No evidence of tumorigenicity was observed in male and female rats at ephedrine sulfate dietary doses up to 9 and 11 mg/kg/day (approximately equivalent to 0.4 and 0.5 times the MRHD of pseudoephedrine on a mg/m2 basis, respectively). No evidence of tumorigenicity was observed in male and female mice at ephedrine sulfate dietary doses up to 29 and 25 mg/kg/day (approximately equivalent to 0.7 and 0.6 times the MRHD of pseudoephedrine on a mg/m2 basis, respectively).
Mutagenicity studies with pseudoephedrine have not been conducted.
Fertility studies with pseudoephedrine have not been conducted.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate oral solution is suppled as a clear, colorless to light yellow, grape-flavored liquid containing 5 mg of hydrocodone bitartrate, 4 mg of chlorpheniramine maleate, and 60 mg of pseudoephedrine hydrochloride. It is available in:
| NDC: 60258-876-16 | One pint (480 mL) |
Store solution at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F). [USP Controlled Room Temperature.]
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container, as defined in the USP, with a child resistant closure.
Ensure that patients have an oral dosing dispenser that measures the appropriate volume in milliliters. Counsel patients on how to utilize an oral dosing dispenser and correctly measure the oral suspension as prescribed.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Addiction, Abuse, and Misuse
Inform patients that the use of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate, even when taken as recommended, can result in addiction, abuse, and misuse, which can lead to overdose and death [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Instruct patients not to share hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate with others and to take steps to protect hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate from theft or misuse.
Important Dosing and Administration Instructions
Instruct patients how to measure and take the correct dose of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate. Advise patients to measure hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate with an accurate milliliter measuring device. Patients should be informed that a household teaspoon is not an accurate measuring device and could lead to overdosage. Advise patients to ask their pharmacist to recommend an appropriate measuring device and for instructions for measuring the correct dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.1), Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]. Advise patients not to increase the dose or dosing frequency of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate because serious adverse events such as respiratory depression may occur with overdosage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Overdosage (10)].
Life-Threatening Respiratory Depression
Inform patients of the risk of life-threatening respiratory depression, including information that the risk is greatest when starting hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate and that it can occur even at recommended dosages [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Advise patients how to recognize respiratory depression and to seek medical attention if breathing difficulties develop.
Accidental Ingestion
Inform patients that accidental ingestion, especially by children, may result in respiratory depression or death [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Instruct patients to take steps to store hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate securely and to properly dispose of unused hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate in accordance with the local state guidelines and/or regulations.
Activities Requiring Mental Alertness
Advise patients to avoid engaging in hazardous tasks that require mental alertness and motor coordination such as operating machinery or driving a motor vehicle as hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate may produce marked drowsiness [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Interactions with Benzodiazepines and Other Central Nervous System Depressants, Including Alcohol
Inform patients and caregivers that potentially fatal additive effects may occur if hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate is used with benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants, including alcohol. Advise patients to avoid concomitant use of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate with benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants and instruct patients not to consume alcoholic beverages, as well as prescription and over-the-counter products that contain alcohol, during treatment with hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8), Drug Interactions (7.5)].
Constipation
Advise patients of the potential for severe constipation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9), Adverse Reactions (6)].
Cardiovascular and CNS Effects
Inform patients that the pseudoephedrine contained in hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate can produce cardiovascular and central nervous system effects in some patients such as, insomnia, dizziness, weakness, tremor, transient elevations in blood pressure, or arrhythmias.
Anaphylaxis
Inform patients that anaphylaxis has been reported with ingredients contained in hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate. Advise patients how to recognize such a reaction and when to seek medical attention [see Contraindications (4), Adverse Reactions (6)].
MAOI Interaction
Inform patients not to take hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate while using or within 14 days of stopping any drugs that inhibit monoamine oxidase. Patients should not start MAOIs while taking hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate [see Drug Interactions (7.7)].
Hypotension
Inform patients that hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate may cause orthostatic hypotension and syncope. Instruct patients how to recognize symptoms of low blood pressure and how to reduce the risk of serious consequences should hypotension occur (e.g., sit or lie down, carefully rise from a sitting or lying position) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)].
Pregnancy
Advise patients that use of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate is not recommended during pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome
Inform female patients of reproductive potential that use of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate during pregnancy can result in neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome, which may be life-threatening if not recognized and treated [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14), Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Inform female patients of reproductive potential that hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate can cause fetal harm and to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Lactation
Advise women that breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Infertility
Inform patients that chronic use of opioids, such as hydrocodone, a component of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate, may cause reduced fertility. It is not known whether these effects on fertility are reversible [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Adrenal Insufficiency
Inform patients that hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate could cause adrenal insufficiency, a potentially life-threatening condition. Adrenal insufficiency may present with non-specific symptoms and signs such as nausea, vomiting, anorexia, fatigue, weakness, dizziness, and low blood pressure. Advise patients to seek medical attention if they experience a constellation of these symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.15)].
Serotonin Syndrome
Inform patients that hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate could cause a rare but potentially life-threatening condition resulting from concomitant administration of serotonergic drugs. Warn patients of the symptoms of serotonin syndrome and to seek medical attention right away if symptoms develop. Instruct patients to inform their physicians if they are taking, or plan to take serotonergic medications. [see Adverse Reactions (6), Drug Interactions (7.6)].
Disposal of Unused hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate
Advise patients to properly dispose of unused hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate. Advise patients to throw the drug in the household trash following these steps. 1) Remove them from their original containers and mix them with an undesirable substance, such as used coffee grounds or kitty litter (this makes the drug less appealing to children and pets, and unrecognizable to people who may intentionally go through the trash seeking drugs). 2) Place the mixture in a sealable bag, empty can, or other container to prevent the drug from leaking or breaking out of a garbage bag, or to dispose of in accordance with local state guidelines and/or regulations.
| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | I392 Revised: 06 2018 | ||||
| MEDICATION GUIDE Hydrocodone Bitartrate, Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride and Chlorpheniramine Maleate Oral Solution, C-II |
|||||
| What is the most important information I should know about hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate? Hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate is not for children under 18 years of age. Hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate can cause serious side effects, including:
|
|||||
|
|
||||
| Keep hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate in a safe place away from children. Accidental use of even 1 dose of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate, especially by a child, is a medical emergency and can cause breathing problems (respiratory depression) which can lead to death. If a child accidentally takes hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate, get emergency medical help right away. | |||||
|
|||||
What is Hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate?
|
|||||
| Who should not take hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate? Hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate is not for children under 18 years of age. See "What is the most important information I should know about hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate?" Do not take hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate if you:
|
|||||
| Before you take hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you: | |||||
|
|
||||
Taking hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate with certain other medicines can cause side effects or affect how well hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate or the other medicines work. Do not start or stop taking other medicines without talking to your healthcare provider. Especially tell your healthcare provider if you:
|
|||||
How should I take hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate?
|
|||||
What should I avoid while taking hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate?
|
|||||
| What are the possible side effects of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate? Hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate can cause serious side effects, including:
|
|||||
|
| ||||
| The most common side effects of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate include: | |||||
|
|
||||
| These are not all the possible side effects of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
|||||
How should I store hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate?
|
|||||
| How should I dispose of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate?
Remove unused hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate from the container and mix it with an undesirable, non-toxic substance such as cat litter or used coffee grounds to make it less appealing to children and pets. Place the mixture in a container such as a sealed plastic bag and throw it away in the household trash. You can also follow your state or local guidelines on how to safely throw away hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate. |
|||||
| General information about the safe and effective use of hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate that is written for health professionals. |
|||||
| What are the ingredients in hydrocodone bitartrate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and chlorpheniramine maleate? Active ingredients: hydrocodone bitartrate, chlorpheniramine maleate, and pseudoephedrine hydrochloride Inactive ingredients: citric acid anhydrous, glycerin, grape flavor, methylparaben, propylene glycol, propylparaben, purified water, sodium citrate, sodium saccharin, and sucrose. Manufactured for: Cypress Pharmaceutical, Inc., Morristown, NJ 07960. For more information, call 1-800-793-2145. |
|||||
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 480 mL Bottle Label
NDC: 60258-876-16
Hydrocodone Bitartrate,
Chlorpheniramine Maleate,
and Pseudoephedrine HCl
Oral Solution
5 mg/4 mg/60 mg per 5 mL
Contains:
Hydrocodone
Bitartrate
5 mg/5 mL
WARNING: May be habit forming.
Chlorpheniramine
Maleate
4 mg/5 mL
Pseudoephedrine
Hydrochloride
60 mg/5 mL
PHARMACIST: Dispense the enclosed
Medication Guide to each patient.
Rx Only
CYPRESS
PHARMACEUTICAL, INC.
16 fl oz (480 mL)

| HYDROCODONE BITARTRATE, CHLORPHENIRAMINE MALEATE, AND PSEUDOEPHEDRINE HCL
hydrocodone bitartrate, chlorpheniramine maleate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride solution |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Cypress Pharmaceutical, Inc. (790248942) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Woodfield Pharmaceutical, LLC | 079398730 | MANUFACTURE(60258-876) , PACK(60258-876) , LABEL(60258-876) | |