LIDOTHOL- lidocaine, menthol patch
LIDOTHOL by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
LIDOTHOL by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Terrain Pharmaceuticals. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
PATIENT MEDICATION INFORMATION
Lidothol (Lidocaine 4.5% / Menthol 5% Patch)
For Topical Use Only
Do not use:
- On the face or rashes
- On wounds, damaged, or infected skin
- In the eyes, mouth or other mucous membranes
- On genitals
- With a heating pad
Ask a doctor before use if:
- You are allergic to topical products or any ingredients in this product
- You are pregnant or breast feeding
- You are under age 18
When using this product:
- Wash hands after applying or removing patch
- Avoid contact with eyes
- If eye contact occurs, rinse thoroughly with water
Stop use and consult your physician if:
- Rash, irritation, or itching develops
- Condition worsens Keep out of reach of children
Lidothol Patient Information.
Before you begin using this medication: read this entire patient information sheet. If you have any questions, please consult your physician or pharmacist. Inform your physician if your condition does not improve or if it worsens.
This information may not include all of the details needed to use Lidothol safely and effectively. Discuss use with your doctor or pharmacist.
What is Lidothol?
A topical pain relief patch consisting of the local anesthetic Lidocaine (4.5%) and the topical analgesic Menthol (5%).
What is Lidothol used for?
The patch assists patients in the management of mild to moderate acute pain or mild to moderate aches. Lidothol is applied to the skin at the specific region experiencing these pain symptoms. The synthesis of Lidocaine and Menthol is a highly effective combination of pain relievers working to alleviate discomfort while the root cause is being managed and treated by your healthcare providers.
DO NOT USE:
- If you are allergic to any of the ingredients in this product
- On wounds or damaged skin
- With a heating pad
- If you are pregnant, planning to become pregnant, or breastfeeding
What are the possible side effects with Lidothol?
- Common: itching or redness of the skin following application
- NOTE: The majority of patients experience no significant adverse events following patch application. Serious side effects, are, in general, related to accidental toxicity of medication by applying considerably more than directed by your doctor or pharmacist or by ingesting the contents of the patch.
- Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take. This includes prescription and nonprescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
- Avoid excessive alcohol usage, since it may increase the potential for Central Nervous System (CNS) effects such as dizziness, confusion, lightheadedness and orthostatic hypotension.
This is not a complete list of the possible side effects. For more information, talk with your doctor or pharmacist. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-‐800-‐FDA-‐1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch
KEEP OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN Rx ONLY
DIRECTIONS FOR USE
Adults and children 12 years and over:
Apply 1 to 2 patches to the affected area of intact skin. Lidothol should be removed after 12 hours of continuous use and remain off for at least 12 hours.
- Determine area of patch application. If the pain area is smaller than the patch, patches may be cut into smaller sizes with scissors. Safely discard the remaining unused pieces of cut patches where children and pets cannot reach.
- Remove the transparent protective film (clear plastic barrier) before application of patches to the skin. Apply immediately after removing the protective film.
- Apply 1 patch to the affected area so that the patch covers all or most of the painful area.
- Remove patch if irritation occurs.
Children under 12 years of age: Consult a doctor
WARNINGS
- Do not use:
- On wounds, cuts, damaged or infected skin
- On eyes, mouth, genitals, or other mucous membranes
2. Consult physician for children under 12 years of age
3. Stop and consult your prescriber if pain worsens
Call your healthcare provider right away if you experience any of the following warning signs or any other unusual symptoms of concern:
- Shortness of breath
- Swelling or numbness of the tongue or throat
- Severe headache or vomiting
- Dizziness or faintness
- Changes in vision or speech
General information for safe and effective use of Lidothol
Do not use this product for another indication. Do not give this drug to anyone else, even if they have the same condition. This product is intended for use as prescribed by a physician.
How should I store Lidothol?
Store product at room temperature at 65˚F to 75˚F (18˚C to 24˚C). Keep away from heat or sunlight. Protect from excessive moisture. Safely discard product after expiration date posted on the product label. Discard patches away from small children or animals.
DO NOT use the product after the expiration date printed on the box.
This insert provides the most important information about Lidothol. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider or pharmacist. There is additional information in the following sections intended for healthcare professionals.
What are the active ingredients in Lidothol?
The patch consists of 4.5% Lidocaine and 5% Menthol.
What are the inactive Ingredients in Lidothol?
Alcohol, Carboxymethylcellulose Sodium, Dihydroxyaluminum Aminoacetate, Glycerine, Kaolin, Partially Neutralized Polyacrylate, Phenoxyethanol, Polysorbate 80, Polyvinyl Pyrrolidone, Tartaric Acid, Tetrasodium EDTA, Water
-
DESCRIPTION:
Lidothol is a prescription topical patch, packaged with 15 medicated patches: 5 re-‐sealable pouches containing 3 patches each. Lidocaine is present in a 4.5% concentration (w/w). It is chemically designated as 2-‐(diethylamino)-‐N-‐(2,6-‐ dimethylphenyl) acetamide and has an empirical formula of C14H22N2O. The molecular weight of Lidocaine is 234.34 g/mol. Menthol is present in a 5% concentration (w/w). The chemical name is (1R,2S,5R)-‐2-‐isopropyl-‐5-‐methylcyclohexanol. The empirical formula for Menthol is C10H20O with a molecular weight of 156.27 g/mol.
Lidothol (Lidocaine 4.5% / Menthol 5% Patch) consists of an adhesive hydrogel containing Lidocaine 4.5% and Menthol 5%, applied to flexible woven polyester backing and protected by a plastic film. The protective film is removed prior to application to the skin. The size of the patch is 12cm x 8cm.
Lidocaine is chemically designated as 2-‐(diethylamino)-‐N-‐(2,6-‐dimethylphenyl), has an octanol: water partition ration of 43 at pH 7.4, and has the following structure:
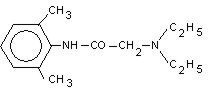
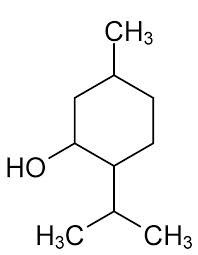
Menthol is chemically designated as 2-‐Isopropyl-‐5-‐methylcyclohexanol. It contains colorless, hexagonal crystals, usually needle-‐like; fused masses or crystalline powder with a pleasant, peppermint-‐like odor. It has a melting point between 31°C to 36° C. Menthol has the following structure:
Each adhesive patch contains 76.5mg of Lidocaine and 85mg of Menthol. It also contains the following inactive ingredients: Alcohol, Carboxymethylcellulose Sodium, Dihydroxyaluminum Aminoacetate, Glycerine, Kaolin, Partially Neutralized Polyacrylate, Phenoxyethanol, Polysorbate 80, Polyvinyl Pyrrolidone, Tartaric Acid, Tetrasodium EDTA, Water
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY:
Lidocaine is a topical anesthetic and stabilizes the neuronal membrane by inhibiting the ionic fluxes required for the initiation and conduction of impulses, thereby effecting local anesthetic action.
Menthol has local anesthetic and counterirritant qualities. It also acts as a weak kappa (ĸ) opioid receptor agonist. Menthol chemically triggers the cold-‐sensitive TRPM-‐8 receptors in the skin, which are responsible for the well-‐documented cooling sensation that occurs when applied to the skin. Menthol’s analgesic properties are not fully understood; however, they are mediated through a selective activation of ĸ-‐opioid receptors. Menthol also blocks voltage-‐sensitive sodium channels, reducing neural activity that may stimulate muscle tissue.
Pharmacodynamics
Menthol works by targeting the k-‐opiod receptor on the TRPM8 neuron. The TRPM8 neuron is normally activated at temperatures between (8° -‐ 28° C). Menthol causes the neuron to fire at temperatures above normal activation, which triggers the characteristic cooling sensation. Also because of Menthol's specific targeting of the k-‐opioid receptor, it is endowed with analgesic properties.
Lidocaine is an amide-‐type local anesthetic agent and is suggested to stabilize neuronal membranes by inhibiting the ionic fluxes required for the initiation and conduction of impulses.
The penetration of Lidocaine into intact skin after application of patch is sufficient to produce an analgesic effect, but less than the amount necessary to produce a complete sensory block.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption:
The amount of Lidocaine and Menthol systemically absorbed is directly related to both the duration of application and the surface area over which it is applied.
In a pharmacokinetic study, three Lidocaine 5% patches were applied over an area of 420 cm2 of intact skin on the back of
normal volunteers for 12 hours. Blood samples were withdrawn for a determination of Lidocaine concentration during the application and for 12 hours after removal of patches. The results are summarized in table 1.
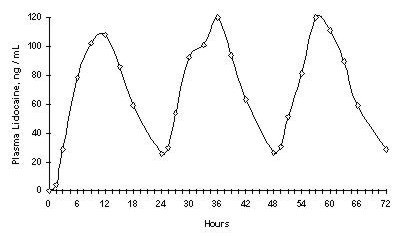
Repeated application of three days indicated that the Lidocaine concentration does not increase with daily use. The mean plasma pharmacokinetic profile for the 15 healthy volunteers is shown in Figure 1.When Lidocaine 5% patch is used according to the recommended dosing instructions, only 3 ± 2% of the dose applied is expected to be absorbed. At least 95% (665 mg) of Lidocaine will remain in a used patch. Mean peak blood concentration of Lidocaine is about 0.13 µg/mL (about 1/10 of the therapeutic concentration required to treat cardiac arrhythmias).Figure 1
Mean Lidocaine blood concentrations after three consecutive daily applications of three Lidocaine 5% patches simultaneously for 12 hours per day in healthy volunteers (n = 15).
Distribution:
When Lidocaine is administered intravenously to healthy volunteers, the volume of distribution is 0.7 to 2.7 L/kg (mean 1.5
± 0.6 SD, n = 15). At concentrations produced by application of Lidocaine Patch 5%, Lidocaine is approximately 70% bound to plasma proteins, primarily alpha-‐1-‐acid glycoprotein. At much higher plasma concentrations (1 to 4 µg/mL of free base), the plasma protein binding of Lidocaine is concentration dependent. Lidocaine crosses the placental and blood brain barriers, presumably by passive diffusion.
Metabolism:
It is not known if Lidocaine is metabolized in the skin. Lidocaine is metabolized rapidly by the liver to a number of metabolites, including menoethylglycinexylidie (MEGX) and glycinexylidide (GX), both of which have pharmacologic activity similar to, but less potent than that of Lidocaine. A minor metabolite, 2,6-‐xylidine, has unknown pharmacologic activity but is carcinogenic in rats. The blood concentration of this metabolite is negligible following application of Lidocaine Patch 5%.
Following intravenous administration, MEGX and GX concentrations in serum range from 11% to 36% and from 5% to 11% of Lidocaine concentrations, respectively.
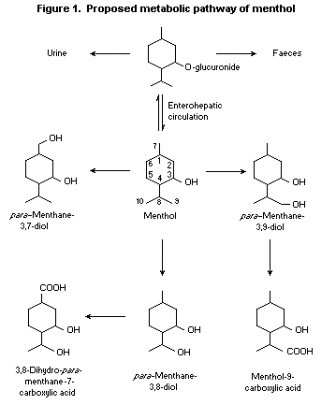
Humans rapidly metabolize Menthols primarily in the liver by the microsomes, using the enzyme CYP2A6. Cytochrome P450-‐mediated oxidation occurs in humans, yielding various alcohol and hydroxy acid derivatives. These are eliminated in the urine unchanged or conjugated with glucuronic acid.
Excretion:
Lidocaine and its metabolites are excreted by the kidneys. Less than 10% of Lidocaine is excreted unchanged. The half-‐life of Lidocaine elimination from plasma following IV administration is 81 to 149 minutes (mean 107 ± 22 SD, n=15). The systemic clearance is 0.33 to 0.90 L/min (mean 0.64 ± 0.18 SD, n=15).
Menthols are largely eliminated as glucuronides. In an experiment, 79% of a 1g (Quick, 1928) and 78% of a 10-‐20mg (Atzl et al., 1972) oral dose of Menthol was eliminated as the glucuronic acid conjugate within 6 h after administration to volunteers. Of a dose of 47 mg/kg bw [3-‐3H]-‐(-‐)-‐Menthol, 82% was eliminated in the urine 17 hours after administration.
Smaller amounts were distributed in the feces and ileum; only 1% of the activity remained in the liver (Clegg et al., 1982).
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE:
Lidothol is a formulation used to assist patients in the treatment of mild to moderate acute or chronic aches or pain. Muscle or joint pain can be due to muscle or ligament strains, simple backache, tendonitis, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, peripheral neuropathies such as diabetic neuropathy or post herpetic neuralgia, and other complex regional pains. It can also be used to help with certain types of headaches, but use with caution when applying in order to avoid eye contact.
Other uses may be considered if deemed clinically relevant.
- CONTRAINDICATIONS:
-
WARNINGS:
Excessive dosage or short interval between doses can result in high plasma levels and serious adverse effects. Patients should be instructed to strictly adhere to the recommended dosage and administration guidelines set forth in this literature and on your prescription label. The management of serious adverse reactions may require the use of resuscitative equipment, oxygen or other resuscitative drugs.
Accidental Exposure in Children
Even a used Lidothol patch contains a large amount of Lidocaine. The potential exists for a small child or a pet to suffer serious adverse effects from chewing or ingesting a new or used Lidothol patch, although the risk with this formulation has not been evaluated. It is important for patients to store and dispose of Lidothol beyond the reach of children, pets and others. (See HANDLING AND DISPOSAL)
Excessive Dosing
Excessive dosing by applying Lidothol to larger areas for longer than the recommended wearing time could result in increased absorption of Lidocaine and high blood concentrations, leading to serious adverse effects. Lidocaine toxicity could be expected at Lidocaine blood concentrations above 5 µg/mL. The blood concentration of Lidocaine is determined by the rate of systemic absorption and elimination. Longer duration of application, application of more than the recommended number of patches, smaller patients, or impaired elimination may all contribute to increasing the blood concentration of Lidocaine. With recommended dosing of Lidothol, the average blood concentration is about 0.13 µg/mL, but concentration higher than 0.25 µg/mL have been observed in some patients.
-
PRECAUTIONS:
Because of the possibility of sedation, patients should be cautioned regarding the use of heavy machinery or automobiles, also any activities made hazardous by decreased alertness.
Hepatic Disease
Patients with severe hepatic disease are at greater risk of developing toxic blood concentrations of Lidocaine, because of their inability to metabolize Lidocaine normally.
Allergic Reactions
Patients allergic to para-‐aminobenzoic acid derivatives (procaine, tetracaine, benzocaine, etc.) have not shown cross sensitivity to Lidocaine. However, Lidothol should be used with caution in patients with a history of drug sensitivities, especially if the etiologic agent is uncertain.
Non-intact Skin
Application to broken or inflamed skin, although not tested, may result in higher blood concentrations of Lidocaine from increased absorption. Lidothol is only recommended for use on intact skin.
Eye Exposure
The contact of Lidothol with eyes, although not studied, should be avoided based on the findings of severe eye irritations with the use of similar products in animals. If eye contact occurs, immediately wash out the eye with water or saline and protect the eye until sensation returns.
External Heat Sources
Placement of external heat sources, such as heating pads or electric blankets, over patches is not recommended as this has not been evaluated and may increase plasma Lidocaine levels.
Drug Interactions: Antiarrhythmic Drugs
Lidothol should be used with caution in patients receiving Class 1 antiarrhythmic drugs (such as tocainide and mexiletine) since the toxic effects are additive and potentially synergistic.
Local Anesthetics
When Lidothol is used concurrently with other products containing local anesthetic agents the amount absorbed from all formulations must be considered.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility Carcinogenesis
A minor metabolite, 2,6-‐xylidine, has been found to be carcinogenic in rats. The blood concentration of this metabolite is negligible following application of Lidothol
Mutagenesis
Lidocaine is not mutagenic in Salmonella/mammalian microsome test nor clastogenic in chromosome aberration assay with human lymphocytes and mouse micronucleus test.
Impairment of Fertility
The effect of Lidothol on fertility has not been studied.
PREGNANCY:
The safety of Lidothol has not been established during pregnancy. There are no well-‐controlled studies in pregnant women. Lidothol should not be used during pregnancy unless absolutely needed. Discuss with physician prior to using Lidothol during pregnancy.
NURSING MOTHERS:
The effect of Lidothol on the nursing infant has not been evaluated. Lidothol has not been studied in nursing mothers. Caution should be exercised when Lidothol is administered to a nursing mother.
PEDIATRIC/GERIATRIC USE:
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric and geriatric patients have not been established.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS:
The most common adverse reactions occur at the application site, including dermatitis, itching or scaling. These tend to be dose-‐limiting and diminish with time.
Serious adverse experiences following the administration of Lidothol are similar in nature to those observed in other amide anesthetic-‐containing agents. These adverse experiences are, in general, dose-‐related and may result from high plasma levels caused by excessive dosage, rapid absorption, or may result from hypersensitivity, idiosyncrasy, or a diminished tolerance on the part of the patient. Serious adverse experiences are generally systemic in nature. During or immediately after treatment with Lidothol, the skin at the site of application may develop redness, blisters, bruising, burning sensation, depigmentation, dermatitis, or mild irritation.
Allergic Reactions
Allergic and anaphylactoid reactions associated with Lidocaine, although rare, can occur. They are characterized by angioedema, bronchospasm, dermatitis, dyspnea, hypersensitivity, laryngospasm, pruritus, shock, and urticaria. If they occur, consult your doctor.
-
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Methemoglobinemia
Cases of methemoglobinemia have been reported in association with local anesthetic use. Although all patients are at risk for methemoglobinemia, patients with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, congenital or idiopathic methemoglobinemia, cardiac or pulmonary compromise, infants under 6 months of age, and concurrent exposure to oxidizing agents or their metabolites are more susceptible to developing clinical manifestations of the condition. If local anesthetics must be used in these patients, close monitoring for symptoms and signs of methemoglobinemia is recommended.
Signs and symptoms of methemoglobinemia may occur immediately or may be delayed some hours after exposure and are characterized by a cyanotic skin discoloration and abnormal coloration of the blood. Methemoglobin levels may continue to rise; therefore, immediate treatment is required to avert more serious central nervous system and cardiovascular adverse effects, including seizures, coma, arrhythmias, and death. Discontinue Lidothol and any other oxidizing agents. Depending on the severity of the symptoms, patients may respond to supportive care, i.e., oxygen therapy, hydration. More severe symptoms may require treatment with methylene blue, exchange transfusion, or hyperbaric oxygen.
-
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Patients that are administered local anesthetics may be at increased risk of developing methemoglobinemia when concurrently exposed to the following oxidizing agents
Class
Nitrates/Nitrites
Local Anesthetics
Antineoplastic agents
Antibiotics
Antimalarials
Anticonvulsants
Other drugs
Examples
nitroglycerin, nitroprusside, nitric oxide, nitrous oxide
benzocaine, lidocaine, bupivacaine, mepivacaine, tetracaine, prilocaine, procaine, articaine, ropivacaine
cyclophosphamide, flutamide, rasburicase, ifosfamide, hydroxyurea
dapsone, sulfonamides, nitrofurantoin, para-aminosalicyclic acid
chloroquine, primaquine
phenytoin, sodium valproate, phenobarbital
acetaminophen, metoclopramide, sulfa drugs (i.e., sulfasalazine), quinine
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION:
Apply Lidothol to intact skin to cover the most painful area. Apply no more than four patches per day. Each patch should not be applied for more than 12 hours in a given 24-‐ hour period. Patches may be cut into smaller sizes with scissors prior to removal of the protective film. Clothing may be worn over the area of application. Smaller areas of treatment are recommended in a debilitated patient, or a patient with impaired elimination.
If irritation or a burning sensation occurs during application, remove the patch and do not reapply until the irritation subsides.
When Lidothol is used concurrently with other products containing local anesthetic agents, the amount absorbed from all formulations must be considered.
Lidothol may not stick if it gets wet. Avoid contact with water, such as bathing, swimming or showering.
- OVERDOSAGE:
- HOW SUPPLIED:
-
STORAGE AND HANDLING
HANDLING AND DISPOSAL:
Wash hands immediately after applying or removing Lidothol. Eye contact with Lidothol should be avoided. Do not store patch outside the sealed envelope. Apply immediately after removal from the protective envelope. Fold used patches so the adhesive side sticks to itself, then safely discard used patches or pieces of cut patches where children and pets cannot access them. Lidothol should be kept out of reach of children.
STORAGE:
Store at room temperature of 65˚F to 75˚F (18˚C to 24˚C). Keep away from heat or sunlight. Protect from excessive moisture. The product can be considered safe and effective to use when maintained under these recommended conditions within the posted expiration date.
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
LIDOTHOL
lidocaine, menthol patchProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 53225-1025 Route of Administration TOPICAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength MENTHOL (UNII: L7T10EIP3A) (MENTHOL - UNII:L7T10EIP3A) MENTHOL 5 g LIDOCAINE (UNII: 98PI200987) (LIDOCAINE - UNII:98PI200987) LIDOCAINE 4.5 g Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength DITETRACYCLINE TETRASODIUM EDETATE (UNII: WX0A0IT7K5) DIHYDROXYALUMINUM AMINOACETATE (UNII: DO250MG0W6) KAOLIN (UNII: 24H4NWX5CO) PHENOXYETHANOL (UNII: HIE492ZZ3T) CARBOXYMETHYLCELLULOSE SODIUM (0.7 CARBOXYMETHYL SUBSTITUTION PER SACCHARIDE; 100-200 MPA.S AT 1%) (UNII: 99H65D77XY) GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) POLYSORBATE 80 (UNII: 6OZP39ZG8H) TARTARIC ACID (UNII: W4888I119H) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) .ALPHA.-ISOBUTYLPHENETHYL ALCOHOL (UNII: 2SBL0E1I0N) SODIUM POLYACRYLATE (8000 MW) (UNII: 285CYO341L) VINYLPYRROLIDONE/HEXADECENE COPOLYMER (UNII: KFR5QEN0N9) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 53225-1025-1 15 in 1 BOX 06/16/2015 1 1 in 1 PATCH; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date unapproved drug other 06/16/2015 Labeler - Terrain Pharmaceuticals (078358750)
Trademark Results [LIDOTHOL]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 LIDOTHOL 98736029 not registered Live/Pending |
Clinic Pharmaceuticals, LLC 2024-09-05 |
 LIDOTHOL 97332176 not registered Live/Pending |
Terrain Pharmaceuticals 2022-03-26 |
 LIDOTHOL 86664422 not registered Dead/Abandoned |
Terrain Pharmaceuticals LLC 2015-06-16 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.


