MICARDIS ®HCT (telmisartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets), for oral use
Micardis HCT by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Micardis HCT by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Praxis, LLC. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
MICARDIS HCT- telmisartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablet
Praxis, LLC
----------
MICARDIS ®HCT (telmisartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets), for oral use
10 OVERDOSAGE
Telmisartan
Limited data are available with regard to overdosage of telmisartan in humans. The most likely manifestations of overdosage with telmisartan are hypotension, dizziness, and tachycardia; bradycardia could occur from parasympathetic (vagal) stimulation. If symptomatic hypotension should occur, supportive treatment should be instituted. Telmisartan is not removed by hemofiltration and is not dialyzable.
Hydrochlorothiazide
The most common signs and symptoms observed in patients with a hydrochlorothiazide overdose are those caused by electrolyte depletion (hypokalemia, hypochloremia, hyponatremia) and dehydration resulting from excessive diuresis. If digitalis has also been administered, hypokalemia may accentuate cardiac arrhythmias. The degree to which hydrochlorothiazide is removed by hemodialysis has not been established. The oral LD 50of hydrochlorothiazide is greater than 10 g/kg in both mice and rats.
11 DESCRIPTION
MICARDIS HCT tablets are a combination of telmisartan, an orally active angiotensin II antagonist acting on the AT 1receptor subtype, and hydrochlorothiazide, a thiazide diuretic.
Telmisartan, a non-peptide molecule, is chemically described as 4'-[(1,4'-dimethyl-2'-propyl[2,6'-bi-1H-benzimidazol]-1'-yl)methyl]-[1,1'-biphenyl]-2-carboxylic acid. Its empirical formula is C 33H 30N 4O 2, its molecular weight is 514.63, and its structural formula is:
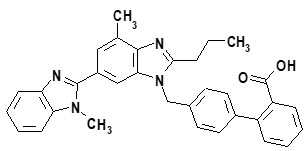
Telmisartan is a white to slightly yellowish solid. It is practically insoluble in water and in the pH range of 3 to 9, sparingly soluble in strong acid (except insoluble in hydrochloric acid), and soluble in strong base.
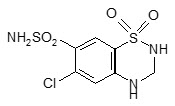
Hydrochlorothiazide is a white, or practically white, practically odorless, crystalline powder with a molecular weight of 297.74. It is slightly soluble in water, and freely soluble in sodium hydroxide solution. Hydrochlorothiazide is chemically described as 6-chloro-3,4-dihydro-2 H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide. Its empirical formula is C 7H 8ClN 3O 4S 2, and its structural formula is:
MICARDIS HCT tablets are formulated for oral administration in three combinations of 40 mg/12.5 mg, 80 mg/12.5 mg, and 80 mg/25 mg telmisartan and hydrochlorothiazide, respectively. The tablets contain the following inactive ingredients: sodium hydroxide, meglumine, povidone, sorbitol, magnesium stearate, lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, maize starch, and sodium starch glycolate. As coloring agents, the 40 mg/12.5 mg and 80 mg/12.5 mg tablets contain ferric oxide red, and the 80 mg/25 mg tablets contain ferric oxide yellow. MICARDIS HCT tablets are hygroscopic and require protection from moisture.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
MICARDIS HCT
MICARDIS HCT is a combination of two drugs with antihypertensive properties: a thiazide diuretic, hydrochlorothiazide, and an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB), telmisartan.
Telmisartan
Angiotensin II is formed from angiotensin I in a reaction catalyzed by angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE, kininase II). Angiotensin II is the principal pressor agent of the renin-angiotensin system, with effects that include vasoconstriction, stimulation of synthesis and release of aldosterone, cardiac stimulation, and renal reabsorption of sodium. Telmisartan blocks the vasoconstrictor and aldosterone-secreting effects of angiotensin II by selectively blocking the binding of angiotensin II to the AT 1receptor in many tissues, such as vascular smooth muscle and the adrenal gland. Its action is therefore independent of the pathways for angiotensin II synthesis.
There is also an AT 2receptor found in many tissues, but AT 2is not known to be associated with cardiovascular homeostasis. Telmisartan has much greater affinity (>3,000-fold) for the AT 1receptor than for the AT 2receptor.
Telmisartan does not inhibit ACE (kininase II) nor does it bind to or block other hormone receptors or ion channels known to be important in cardiovascular regulation.
Blockade of the angiotensin II receptor inhibits the negative regulatory feedback of angiotensin II on renin secretion, but the resulting increased plasma renin activity and angiotensin II circulating levels do not overcome the effect of telmisartan on blood pressure.
Hydrochlorothiazide
Hydrochlorothiazide is a thiazide diuretic. Thiazides affect the renal tubular mechanisms of electrolyte reabsorption, directly increasing excretion of sodium salt and chloride in approximately equivalent amounts. Indirectly, the diuretic action of hydrochlorothiazide reduces plasma volume, with consequent increases in plasma renin activity, increases in aldosterone secretion, increases in urinary potassium loss, and decreases in serum potassium. The renin-aldosterone link is mediated by angiotensin II, so co-administration of an ARB tends to reverse the potassium loss associated with these diuretics. The mechanism of the antihypertensive effect of thiazides is not fully understood.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Telmisartan
In normal volunteers, a dose of telmisartan 80 mg inhibited the pressor response to an intravenous infusion of angiotensin II by approximately 90% at peak plasma concentrations with approximately 40% inhibition persisting for 24 hours.
Plasma concentration of angiotensin II and plasma renin activity increased in a dose-dependent manner after single administration of telmisartan to healthy subjects and repeated administration to hypertensive patients. The once-daily administration of up to 80 mg telmisartan to healthy subjects did not influence plasma aldosterone concentrations. In multiple dose studies with hypertensive patients, there were no clinically significant changes in electrolytes (serum potassium or sodium) or in metabolic function (including serum levels of cholesterol, triglycerides, HDL, LDL, glucose, or uric acid).
The antihypertensive effects of telmisartan have been studied in six placebo-controlled clinical trials including a total of 1773 patients with mild to moderate hypertension (diastolic blood pressure of 95 to 114 mmHg), 1031 of whom were treated with telmisartan. Following once-daily administration of telmisartan, the magnitude of blood pressure reduction from baseline after placebo subtraction was approximately (SBP/DBP) 6-8/6 mmHg for 20 mg, 9-13/6-8 mmHg for 40 mg, and 12-13/7-8 mmHg for 80 mg. Larger doses (up to 160 mg) did not appear to cause a further decrease in blood pressure.
The onset of antihypertensive activity occurs within 3 hours, with a maximal reduction by approximately 4 weeks. At doses of 20, 40, and 80 mg, the antihypertensive effect of once-daily administration of telmisartan was maintained for the full 24-hour dose interval.
In 30 hypertensive patients with normal renal function treated for 8 weeks with telmisartan 80 mg or telmisartan 80 mg in combination with hydrochlorothiazide 12.5 mg, there were no clinically significant changes from baseline in renal blood flow, glomerular filtration rate, filtration fraction, renovascular resistance, or creatinine clearance.
Hydrochlorothiazide
After oral administration of hydrochlorothiazide, diuresis begins within 2 hours, peaks in about 4 hours, and lasts approximately 6 to 12 hours.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Telmisartan
Absorption:
Following oral administration, peak concentrations (C max) of telmisartan are reached in 0.5 to 1 hour after dosing. Food slightly reduces the bioavailability of telmisartan, with a reduction in the area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC) of approximately 6% with 40 mg and approximately 20% after a 160 mg dose. MICARDIS HCT can be administered with or without food. The absolute bioavailability of telmisartan is dose dependent. At 40 mg and 160 mg, the bioavailability was 42% and 58%, respectively. The pharmacokinetics of telmisartan with orally administered MICARDIS are nonlinear over the dose range 20 mg to 160 mg, with greater than proportional increases of plasma concentrations (C maxand AUC) with increasing doses. Telmisartan shows bi-exponential decay kinetics with a terminal elimination half-life of approximately 24 hours. Trough plasma concentrations of telmisartan with once-daily dosing are approximately 10% to 25% of peak plasma concentrations. Telmisartan has an accumulation index in plasma of 1.5 to 2.0 upon repeated once-daily dosing.
Distribution:
Telmisartan is highly bound to plasma proteins (>99.5%), mainly albumin and α 1-acid glycoprotein. Plasma protein binding is constant over the concentration range achieved with recommended doses. The volume of distribution for telmisartan is approximately 500 liters, indicating additional tissue binding.
Metabolism:
Telmisartan is metabolized by conjugation to form a pharmacologically inactive acyl glucuronide; the glucuronide of the parent compound is the only metabolite that has been identified in human plasma and urine. After a single dose, the glucuronide represents approximately 11% of the measured radioactivity in plasma. The cytochrome P450 isoenzymes are not involved in the metabolism of telmisartan.
Elimination:
Following either intravenous or oral administration of 14C-labeled telmisartan, most of the administered dose (>97%) was eliminated unchanged in feces via biliary excretion; only minute amounts were found in the urine (0.91% and 0.49% of total radioactivity, respectively).
Total plasma clearance of telmisartan is >800 mL/min. Terminal half-life and total clearance appear to be independent of dose.
Hydrochlorothiazide
Hydrochlorothiazide is not metabolized but is eliminated rapidly by the kidney. When plasma levels have been followed for at least 24 hours, the plasma half-life has been observed to vary between 5.6 and 14.8 hours. At least 61% of the oral dose is eliminated unchanged within 24 hours. Hydrochlorothiazide crosses the placental but not the blood-brain barrier and is excreted in breast milk.
Specific Populations
Telmisartan
Renal Insufficiency:Telmisartan is not removed from blood by hemofiltration and is not dialyzable [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)and Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
Hepatic Insufficiency:In patients with hepatic insufficiency, plasma concentrations of telmisartan are increased, and absolute bioavailability approaches 100% [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Drug Interaction Studies
Telmisartan
Ramipril:Co-administration of telmisartan 80 mg once daily and ramipril 10 mg once daily to healthy subjects increases steady-state C maxand AUC of ramipril 2.3- and 2.1-fold, respectively, and C maxand AUC of ramiprilat 2.4- and 1.5-fold, respectively. In contrast, C maxand AUC of telmisartan decrease by 31% and 16%, respectively. When co-administering telmisartan and ramipril, the response may be greater because of the possibly additive pharmacodynamic effects of the combined drugs, and also because of the increased exposure to ramipril and ramiprilat in the presence of telmisartan.
Other Drugs:Co-administration of telmisartan did not result in a clinically significant interaction with acetaminophen, amlodipine, glyburide, simvastatin, hydrochlorothiazide, warfarin, or ibuprofen. Telmisartan is not metabolized by the cytochrome P450 system and had no effects in vitroon cytochrome P450 enzymes, except for some inhibition of CYP2C19. Telmisartan is not expected to interact with drugs that inhibit cytochrome P450 enzymes; it is also not expected to interact with drugs metabolized by cytochrome P450 enzymes, except for possible inhibition of the metabolism of drugs metabolized by CYP2C19.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Telmisartan and Hydrochlorothiazide
No carcinogenicity, mutagenicity, or fertility studies have been conducted with the combination of telmisartan and hydrochlorothiazide.
Telmisartan
There was no evidence of carcinogenicity when telmisartan was administered in the diet to mice and rats for up to 2 years. The highest doses administered to mice (1000 mg/kg/day) and rats (100 mg/kg/day) are, on a mg/m 2basis, about 59 and 13 times, respectively, the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of telmisartan. These same doses have been shown to provide average systemic exposures to telmisartan >100 times and >25 times, respectively, the systemic exposure in humans receiving the MRHD of telmisartan (80 mg/day).
Genotoxicity assays did not reveal any telmisartan-related effects at either the gene or chromosome level. These assays included bacterial mutagenicity tests with Salmonellaand E. coli(Ames), a gene mutation test with Chinese hamster V79 cells, a cytogenetic test with human lymphocytes, and a mouse micronucleus test.
No drug-related effects on the reproductive performance of male and female rats were noted at 100 mg/kg/day (the highest dose administered), about 13 times, on a mg/m 2basis, the MRHD of telmisartan. This dose in the rat resulted in an average systemic exposure (telmisartan AUC as determined on day 6 of pregnancy) at least 50 times the average systemic exposure in humans at the MRHD (80 mg/day).
Hydrochlorothiazide
Two-year feeding studies in mice and rats conducted under the auspices of the National Toxicology Program (NTP) uncovered no evidence of a carcinogenic potential of hydrochlorothiazide in female mice (at doses of up to approximately 600 mg/kg/day) or in male and female rats (at doses of up to approximately 100 mg/kg/day). The NTP, however, found equivocal evidence for hepatocarcinogenicity in male mice.
Hydrochlorothiazide was not genotoxic in vitroin the Ames mutagenicity assay of Salmonella typhimuriumstrains TA 98, TA 100, TA 1535, TA 1537, and TA 1538 and in the Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) test for chromosomal aberrations, or in vivoin assays using mouse germinal cell chromosomes, Chinese hamster bone marrow chromosomes, and the Drosophilasex-linked recessive lethal trait gene. Positive test results were obtained in the in vitroCHO Sister Chromatid Exchange (clastogenicity) assay, in the Mouse Lymphoma Cell (mutagenicity) assay, and in the Aspergillus nidulansnon-disjunction assay.
Hydrochlorothiazide had no adverse effects on the fertility of mice and rats of either sex in studies wherein these species were exposed, via their diet, to doses of up to 100 and 4 mg/kg, respectively, prior to mating and throughout gestation.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Telmisartan and Hydrochlorothiazide
In controlled clinical trials with more than 2500 hypertensive patients, 1017 patients were exposed to telmisartan (20 mg to 160 mg) and concomitant hydrochlorothiazide (6.25 mg to 25 mg). These trials included one factorial trial (Study 1) with combinations of telmisartan (20 mg, 40 mg, 80 mg, 160 mg, or placebo) and hydrochlorothiazide (6.25 mg, 12.5 mg, 25 mg, and placebo). The factorial trial randomized 818 patients, including 493 (60%) males; 596 (73%) Non-Black and 222 (27%) Blacks; and 143 (18%) ≥65 years of age (median age was 53 years old). The mean supine blood pressure at baseline for the total population was 154/101 mmHg.
The combination of telmisartan and hydrochlorothiazide resulted in additive placebo-adjusted decreases in systolic and diastolic blood pressures at trough of 16-21/9-11 mmHg for doses between 40 mg/12.5 mg and 80 mg/25 mg, compared with 9-13/7-8 mmHg for telmisartan 40 mg to 80 mg monotherapy and 4/4 mmHg for hydrochlorothiazide 12.5 mg monotherapy. The antihypertensive effect was independent of age or gender. There was essentially no change in heart rate in patients treated with the combination of telmisartan and hydrochlorothiazide in the placebo-controlled trial.
Four other studies of hypertensive patients of at least six months' duration allowed add-on of hydrochlorothiazide for patients who either were not adequately controlled on the randomized telmisartan monotherapy dose or had not achieved adequate blood pressure response after completing the up-titration of telmisartan. In active-controlled studies, the addition of 12.5 mg hydrochlorothiazide to titrated doses of telmisartan in patients who did not achieve or maintain adequate response with telmisartan monotherapy further reduced systolic and diastolic blood pressures.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
MICARDIS HCT is available in three strengths as biconvex two-layered, oblong-shaped, uncoated tablets containing telmisartan and hydrochlorothiazide:
- 40 mg/12.5 mg tablet:red and white (may contain red specks) marked with the Boehringer Ingelheim company symbol and "H4"; individually blister-sealed in cartons of 30 tablets as 3 × 10 cards (NDC: 0597-0043-37)
- 80 mg/12.5 mg tablet:red and white (may contain red specks) marked with the Boehringer Ingelheim company symbol and "H8"; individually blister-sealed in cartons of 30 tablets as 3 × 10 cards (NDC: 0597-0044-37)
- 80 mg/25 mg tablet:yellow and white (may contain yellow specks) marked with the Boehringer Ingelheim company symbol and "H9"; individually blister-sealed in cartons of 30 tablets as 3 × 10 cards (NDC: 0597-0042-37)
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Pregnancy
Advise female patients of childbearing age about the consequences of exposure to MICARDIS HCT during pregnancy. Discuss treatment options with women planning to become pregnant. Tell patients to report pregnancies to their physicians as soon as possible [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)and Use in Specific Populations (8.1)] .
Lactation
Advise nursing women not to breastfeed during treatment with MICARDIS HCT [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Symptomatic Hypotension and Syncope
Advise patients that lightheadedness can occur, especially during the first days of therapy, and to report it to their healthcare provider. Inform patients that inadequate fluid intake, excessive perspiration, diarrhea, or vomiting can lead to an excessive fall in blood pressure, with the same consequences of lightheadedness and possible syncope. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider if syncope occurs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] .
Potassium Supplements
Advise patients not to use potassium supplements or salt substitutes that contain potassium without consulting the prescribing healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)and Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Acute Myopia and Secondary Angle-Closure Glaucoma
Advise patients to discontinue MICARDIS HCT and seek immediate medical attention if they experience symptoms of Acute Myopia or Secondary Angle-Closure Glaucoma [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)] .
Distributed by:
Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Ridgefield, CT 06877 USA
Licensed from:
Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH
Ingelheim, Germany
Copyright © 2022 Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH
ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
MICARDIS ®is a registered trademark of and used under license from Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH.
Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. either owns or uses the ONTARGET ®trademark under license.
The other brands listed are trademarks of their respective owners and are not trademarks of Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
COL10674AL272022
SPL10694A
Patient Information
MICARDIS® HCT (my-CAR-dis HCT)
(telmisartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets)
Read this Patient Information before you start taking MICARDIS HCT tablets and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your doctor about your medical condition or your treatment.
What is the most important information I should know about MICARDIS HCT tablets?
MICARDIS HCT can cause harm or death to an unborn baby. Talk to your doctor about other ways to lower your blood pressure if you plan to become pregnant. If you get pregnant while taking MICARDIS HCT, tell your doctor right away.
What is MICARDIS HCT?
MICARDIS HCT is a prescription medicine used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension). MICARDIS HCT contains:
- telmisartan, an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB)
- hydrochlorothiazide, a water pill or diuretic
Your doctor may prescribe other medicines for you to take along with MICARDIS HCT to treat your high blood pressure.
It is not known if MICARDIS HCT is safe and effective in children.
Do not take MICARDIS HCT tablets if you:
- have low or no urine output
- are allergic (hypersensitive) to the active ingredients (telmisartan or hydrochlorothiazide) or any of the other ingredients listed at the end of this leaflet
What should I tell my doctor before using MICARDIS HCT tablets?
Before you take MICARDIS HCT tablets, tell your doctor if you:
- are pregnant or are planning to become pregnant. See " What is the most important information I should know about MICARDIS HCT tablets?"
- are breast-feeding or plan to breast-feed. MICARDIS HCT can pass into your breast milk and may harm your baby. You and your doctor should decide if you will take MICARDIS HCT or breast-feed. You should not do both. Talk with your doctor about the best way to feed your baby if you take MICARDIS HCT tablets.
- have been told that you have abnormal body salt (electrolytes) levels in your blood
- have liver problems
- have asthma or history of asthma
- have lupus
- have diabetes
- have kidney problems
- have any other medical conditions
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take,including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Also, tell your doctor if you drink alcohol.
MICARDIS HCT may affect the way other medicines work, and other medicines may affect how MICARDIS HCT works. Especially tell your doctor if you take:
- aliskiren
- digoxin (Lanoxin ®)
- lithium (Lithobid ®, lithium carbonate, lithium citrate)
- other medicines used to treat your high blood pressure or a heart problem
- water pills (diuretic)
- aspirin or other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- potassium supplements or a salt substitute containing potassium
- medicine used to treat diabetes, including insulin
- narcotic pain medicines
- sleeping pills
- steroid medicine or Adrenocorticotrophic Hormone (ACTH)
- barbiturates
- certain cholesterol lowering medicines (resins that are used for cholesterol reduction, e.g., cholestyramine and colestipol resins)
Ask your doctor if you are not sure if you are taking one of the medicines listed above.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them and show it to your doctor or pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I take MICARDIS HCT tablets?
- Take MICARDIS HCT tablets exactly as your doctor tells you to take it.
- Your doctor will tell you how much MICARDIS HCT to take and when to take it.
- Do not change your dose unless your doctor tells you to.
- Take MICARDIS HCT once each day.
- Take MICARDIS HCT tablets with or without food.
- If you take too much MICARDIS HCT, call your doctor, or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
- Read the "How to open the blister"at the end of this leaflet before you use MICARDIS HCT. Talk with your doctor if you do not understand the instructions.
What are the possible side effects of MICARDIS HCT tablets?
MICARDIS HCT tablets may cause serious side effects,including:
- Injury or death to your unborn baby.See " What is the most important information I should know about MICARDIS HCT tablets?"
-
Low blood pressure (hypotension)is most likely to happen if you also:
- take water pills (diuretics)
- are on a low-salt diet
- get dialysis treatments
- have heart problems
- get sick with vomiting or diarrhea
- do not drink enough fluids
- sweat a lot
-
Kidney problems,which may get worse if you already have kidney disease. You may have changes in your kidney test results, and you may need a lower dose of MICARDIS HCT tablets. Call your doctor if you get:
- swelling in your feet, ankles, or hands
- unexplained weight gain
- Liver problems,which may get worse in people who already have liver problems and take MICARDIS HCT.
-
Eye problems. One of the medicines in MICARDIS HCT can cause eye problems that may lead to vision loss. Symptoms of eye problems can happen within hours to weeks of starting MICARDIS HCT. Tell your doctor right away if you have:
- decrease in vision
- eye pain
-
Allergic reactions.Tell your doctor right away if you get any of these symptoms:
- swelling of the face, tongue, throat
- difficulty breathing
- Worsening of lupus.Tell your doctor if your lupus gets worse or becomes active while taking MICARDIS HCT.
- Change in body salts (electrolytes) level in your blood and fluid problems.Your doctor may do tests to check your blood. Call your doctor right away if you have:
|
|
- Skin Cancer.One of the medicines in MICARDIS HCT may increase your risk of getting non-melanoma skin cancer. Protect your skin from the sun and undergo regular skin cancer screening when taking MICARDIS HCT.
The most common side effects of MICARDIS HCT tablets include:
- upper respiratory tract infections, including sinus pain/congestion and sore throat
- dizziness
- feeling tired
- flu-like symptoms
- back pain
- diarrhea
- nausea
These are not all the possible side effects with MICARDIS HCT tablets. Tell your doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store MICARDIS HCT tablets?
- Store MICARDIS HCT tablets at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Do not remove MICARDIS HCT tablets from blisters until right before you take them.
Keep MICARDIS HCT tablets and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about MICARDIS HCT tablets:
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use MICARDIS HCT tablets for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give MICARDIS HCT tablets to other people, even if they have the same condition you have. It may harm them.
This Patient Information leaflet summarizes the most important information about MICARDIS HCT tablets. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your pharmacist or doctor for information about MICARDIS HCT tablets that is written for health professionals.
For current prescribing information, scan the code or call Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-800-542-6257.

What are the ingredients in MICARDIS HCT tablets?
Active Ingredients: telmisartan and hydrochlorothiazide
Inactive Ingredients: sodium hydroxide, meglumine, povidone, sorbitol, magnesium stearate, lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, maize starch, and sodium starch glycolate
The 40 mg/12.5 mg and 80 mg/12.5 mg tablets also contain: ferric oxide red.
The 80 mg/25 mg tablets also contain: ferric oxide yellow.
What is high blood pressure (hypertension)?
Blood pressure is the force in your blood vessels when your heart beats and when your heart rests. You have high blood pressure when the force is too much. Medicines that lower your blood pressure lower your chance of having a stroke or heart attack.
High blood pressure makes the heart work harder to pump blood through the body and causes damage to the blood vessels. MICARDIS HCT tablets can help your blood vessels relax so your blood pressure is lower.
How to open the blister:
- Tear (You may also use scissors to tear the blister apart)
- Peel (Peel off the paper layer from the aluminum foil)
- Push (Push the tablet through the aluminum foil)
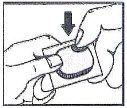
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Distributed by:
Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Ridgefield, CT 06877 USA
Licensed from:
Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH
Ingelheim, Germany
Copyright © 2022 Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH
ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
MICARDIS ®is a registered trademark of and used under license from Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH.
Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. either owns or uses the ONTARGET ®trademark under license.
The other brands listed are trademarks of their respective owners and are not trademarks of Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Revised: December 2022
COL10674AL272022
SPL10694A
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 40 mg/12.5 mg Tablet Blister Card Carton
NDC: 0597-0043-37
Micardis
®HCT
(telmisartan/
hydrochlorothiazide tablets)
40 mg/12.5 mg
Rx only
30 tablets - 3 blister cards of 10 tablets each.
Each tablet contains 40 mg of telmisartan and 12.5 mg of
hydrochlorothiazide.
Dosage: Read accompanying prescribing information.
Keep out of reach of children.
Important: Moisture sensitive tablets - do not remove
from blisters until immediately before administration.
Boehringer
Ingelheim
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 80 mg/12.5 mg Tablet Blister Card Carton
NDC: 0597-0044-37
Micardis
®HCT
(telmisartan/
hydrochlorothiazide tablets)
80 mg/12.5 mg
Rx only
30 tablets - 3 blister cards of 10 tablets each.
Each tablet contains 80 mg of telmisartan and 12.5 mg of
hydrochlorothiazide.
Dosage: Read accompanying prescribing information.
Keep out of reach of children.
Important: Moisture sensitive tablets - do not remove
from blisters until immediately before administration.
Boehringer
Ingelheim
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 80 mg/25 mg Tablet Blister Card Carton
NDC: 0597-0042-37
Micardis
®HCT
(telmisartan/
hydrochlorothiazide tablets)
80 mg/25 mg
Rx only
30 tablets - 3 blister cards of 10 tablets each.
Each tablet contains 80 mg of telmisartan and 25 mg of
hydrochlorothiazide.
Dosage: Read accompanying prescribing information.
Keep out of reach of children.
Important: Moisture sensitive tablets - do not remove
from blisters until immediately before administration.
Boehringer
Ingelheim
| MICARDIS HCT
telmisartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablet |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| MICARDIS HCT
telmisartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablet |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Praxis, LLC (016329513) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Praxis, LLC | 016329513 | pack(59368-385, 59368-386) , label(59368-385, 59368-386) , manufacture(59368-385, 59368-386) | |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.