TRIPTODUR- triptorelin kit
TRIPTODUR by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
TRIPTODUR by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Praxis, LLC. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Drug-Drug Interactions
Results of in vitrostudies show that drug-drug interactions with triptorelin are unlikely [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. However, in the absence of relevant data and as a precaution, hyperprolactinemic drugs should not be used concomitantly with triptorelin since hyperprolactinemia reduces the number of pituitary GnRH receptors.
7.2 Drug-Laboratory Test Interactions
Administration of TRIPTODUR results in suppression of the pituitary-gonadal system.
The effect of TRIPTODUR on pituitary and gonadal function is expected to disappear within six to twelve months after treatment discontinuation. Therefore, diagnostic tests of pituitary gonadotropic and gonadal functions conducted during treatment or after discontinuation of treatment may be affected.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
TRIPTODUR is contraindicated in women who are pregnant [see Contraindications (4)] since expected hormonal changes that occur with TRIPTODUR treatment increase the risk for pregnancy loss. Available data with triptorelin use in pregnant women are insufficient to determine a drug-associated risk of adverse developmental outcomes. Based on mechanism of action in humans and findings of increased pregnancy loss in animal studies, TRIPTODUR may cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the US general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% - 4% and 15% -20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In pregnant rats administered triptorelin at doses of 2, 10, and 100 mcg/kg/day during the period of organogenesis, maternal toxicity (decrease in body weight) and embryo-fetal toxicities (pre-implantation loss, increased resorption, and reduced number of viable fetuses) were observed at 100 mcg/kg, approximately 4 times the clinical dose based on body surface area. No embryonic and fetal developmental toxicities were observed in mice at doses up to 4 times the clinical dose. Teratogenic effects were not observed in viable fetuses in rats or mice.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of triptorelin in human milk, or the effects of the drug on the breastfed infant, or on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for TRIPTODUR and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from TRIPTODUR or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of TRIPTODUR have been established in pediatric patients 2 years of age and older based on a single-arm open-label study of 44 children 2-9 years of age with CPP [see Clinical Studies (14)] . The safety and effectiveness of TRIPTODUR have not been established in pediatric patients less than 2 years old.
8.6 Renal Impairment
TRIPTODUR has not been studied in children with renal impairment. Adult subjects with renal impairment had higher exposure than young healthy adult males [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
TRIPTODUR has not been studied in children with hepatic impairment. Adult subjects with hepatic impairment had higher exposure than young healthy adult males [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Following the first administration, there is a transient surge in circulating levels of LH, FSH, testosterone, and estradiol [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] . After chronic and continuous administration, by 4 weeks after initiation of therapy, a sustained decrease in LH and FSH secretion and marked reduction in sex steroids are observed.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
After an initial intramuscular TRIPTODUR 22.5 mg injection and a second 22.5 mg intramuscular injection 24 weeks later in children 2 to 9 years old with CPP, triptorelin peaked 4 hours postdose with a geometric mean C maxof 39.9 and 36.5 ng/mL, respectively. No apparent accumulation of triptorelin occurred after the second injection. Absorption occurred in two phases, a burst phase followed by a maintenance release phase. In children with CPP, following the burst phase after the first 22.5 mg injection, geometric mean serum triptorelin levels were 0.11, 0.17, 0.05 and 0.03 ng/mL at Months 1, 2, 3, and 6, respectively.
Distribution
There is no evidence that triptorelin, at clinically relevant concentrations, binds to plasma proteins.
Elimination
Metabolism
The metabolism of triptorelin in humans is unknown, but is unlikely to involve hepatic microsomal enzymes (cytochrome P450). Thus far no metabolites of triptorelin have been identified. Pharmacokinetic data suggest that C-terminal fragments produced by tissue degradation are either completely degraded in the tissues, or rapidly degraded in plasma, or cleared by the kidneys.
Excretion
Triptorelin is eliminated by both the liver and the kidneys. Following intravenous administration of 0.5 mg triptorelin peptide to six healthy male volunteers with a creatinine clearance of 149.9 mL/min, 41.7% of the dose was excreted in urine as intact peptide with a total triptorelin clearance of 211.9 mL/min. This percentage increased to 62.3% in patients with liver disease who have a lower creatinine clearance (89.9 mL/min). It has also been observed that the nonrenal clearance of triptorelin (patient anuric, Cl creat= 0) was 76.2 mL/min, thus indicating that the nonrenal elimination of triptorelin is mainly dependent on the liver.
Specific Populations
Renal Impairment
After intravenous bolus injection of 0.5 mg triptorelin in adults, the two distribution half-lives were unaffected by renal impairment. However, renal insufficiency led to a decrease in total triptorelin clearance proportional to the decrease in creatinine clearance as well as increases in volume of distribution and consequently, an increase in the elimination half-life. Adult male subjects with moderate or severe renal impairment had approximately 2-fold higher exposure (AUC values) than young healthy adult males (see Table 1) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Hepatic Impairment
After intravenous bolus injection of 0.5 mg triptorelin in adults, the two distribution half-lives were unaffected by hepatic impairment. In adult males with hepatic insufficiency, triptorelin clearance was reduced and exposure (AUC) was increased 3.7-fold compared to young healthy adult males (Table 2) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)] .
Table 2: Pharmacokinetic Parameters (Mean ± SD) in Healthy Adults, Adults with Renal Impairment, and Adults with Hepatic Impairment Following an I.V. Bolus of 0.5 mg Triptorelin in Solution Group C max
(ng/mL)AUC inf
(h∙ng/mL)Cl p
(mL/min)Cl renal
(mL/min)t 1/2(h) Cl creat
(mL/min)6 healthy male volunteers 48.2 ±11.8 36.1 ±5.8 211.9 ±31.6 90.6 ±35.3 2.81 ±1.21 149.9 ±7.3 6 males with moderate renal impairment 45.6 ±20.5 69.9 ±24.6 120.0 ±45.0 23.3 ±17.6 6.56 ±1.25 39.7 ±22.5 6 males with severe renal impairment 46.5 ±14.0 88.0 ±18.4 88.6 ±19.7 4.3 ±2.9 7.65 ±1.25 8.9 ±6.0 6 males with liver disease 54.1 ±5.3 131.9 ±18.1 57.8 ±8.0 35.9 ±5.0 7.58 ±1.17 89.9 ±15.1 Drug-Drug Interactions
In Vitro Assessment of Drug Interactions
Drug Metabolizing Enzyme Inhibition
Triptorelin did not inhibit CYP1A2, 2B6, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19 or 2D6, or CYP 3A4/5 at clinically relevant concentrations.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis was evaluated in an 18-month study in mice and a 24-month study in rats. In rats, triptorelin doses of 120, 600, and 3000 mcg/kg given every 28 days (approximately 0.2, 0.8, and 4 times the estimated human monthly dose based on body surface area) resulted in increased mortality with a drug treatment period of 13 to 19 months. The incidences of benign and malignant pituitary tumors and histosarcomas were increased in a dose-related manner. There were no treatment-related tumors in mice at exposure up to 4-fold higher than the estimated human monthly dose based on body surface area.
Mutagenicity studies performed with triptorelin using bacterial and mammalian systems ( in vitroAmes test and chromosomal aberration test in CHO cells and an in vivomouse micronucleus test) provided no evidence of mutagenic potential.
After 60 days of subcutaneous treatment followed by a minimum of four estrus cycles prior to mating, triptorelin at doses of 2, 20, and 200 mcg/kg (approximately 0.07, 0.7, and 7 times the estimated human daily dose based on body surface area) or two monthly injections as slow release microspheres (~20 mcg/kg/day) had no effect on the fertility or general reproductive function of female rats.
No studies were conducted to assess the effect of triptorelin on male fertility.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Each TRIPTODUR 22.5 mg single-use kit (NDC: 24338-150-20) contains:
- One single-dose vial of TRIPTODUR 22.5 mg (NDC: 24338-150-01) with a Flip-Off seal containing sterile lyophilized white to slightly yellow powder cake
- One sterile, glass syringe with Luer Lock prefilled with 2 mL of Sterile Water for Injection (NDC: 24338-150-02)
- Two sterile 21 gauge, 1½" needles ( thin-wall) with safety cover
- One Package Insert
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Medication Guide).
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Inform caregivers that anaphylactic shock, hypersensitivity, and angioedema have been reported with triptorelin use and to immediately seek medical attention if any hypersensitivity reaction occurs.
Symptoms after Initial TRIPTODUR Administration
Inform caregivers that during the first weeks after the first TRIPTODUR injection, signs of puberty may occur such as vaginal bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)and Adverse Reactions (6.1)] . Caregivers should notify the physician if these symptoms continue beyond the second month after TRIPTODUR administration.
Psychiatric Events
Inform caregivers that symptoms of emotional lability, such as crying, irritability, impatience, anger, and aggression have been observed in patients receiving GnRH agonists, including triptorelin. Alert caregivers to the possibility of development or worsening of psychiatric symptoms, including depression, during treatment with TRIPTODUR [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)and Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
Convulsions
Inform caregivers that reports of convulsions have been observed in patients receiving GnRH agonists, including triptorelin. Patients with a history of seizures, epilepsy, cerebrovascular disorders, central nervous system anomalies or tumors, and patients on concomitant medications that have been associated with convulsions may be at increased risk [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Pseudotumor Cerebri (Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension)
Inform patients and caregivers that reports of pseudotumor cerebri (idiopathic intracranial hypertension) have been observed in pediatric patients receiving GnRH agonists, including triptorelin. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of pseudotumor cerebri, including headache, and vision issues such as blurred vision, double vision, loss of vision, pain behind the eye or pain with eye movement, ringing in the ears, dizziness, and nausea. Advise patients and caregivers to contact their healthcare provider if the patient develops any of these symptoms. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] .
Pregnancy is Contraindicated
TRIPTODUR is contraindicated in pregnancy. If the patient becomes pregnant while taking the drug, the patient should be informed of the potential risk to fetus [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
-
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
Manufactured for:
Azurity Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Woburn, MA 01801Manufactured by:
Debiopharm Research & Manufacturing SA
CH-1920 Martigny, SwitzerlandTRIPTODUR is a registered trademark of Debiopharm International SA.
Patent: https://azurity.com/patents_and_trademarks/
This product's labeling may have been updated. For current Full Prescribing Information, please visit www.triptodur.com
TRIP-PI-08 Rev. NOV 2023
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Kit Carton
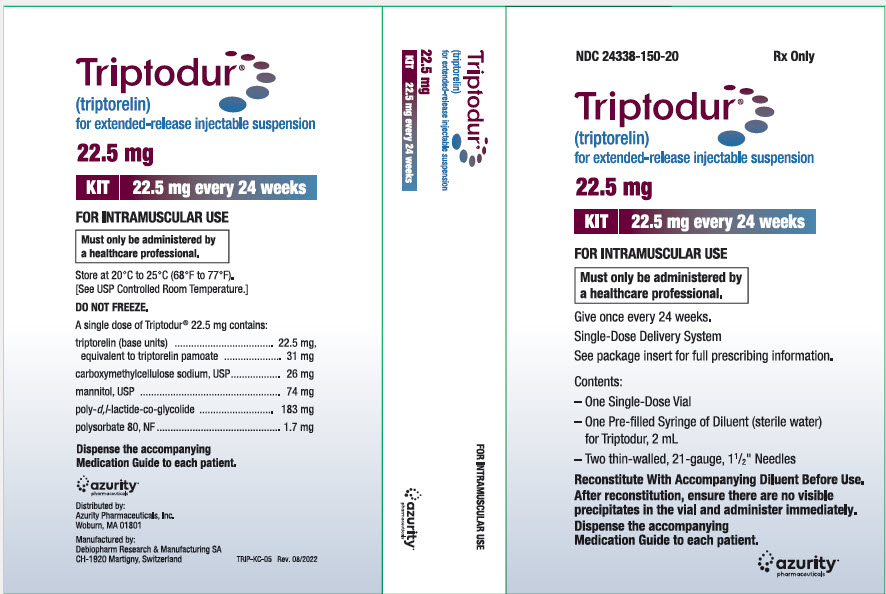 NDC: 24338-150-20
NDC: 24338-150-20
Rx OnlyTriptodur ®
(triptorelin)
for extended-release injectable suspension22.5 mg
KIT
22.5 mg every 24 weeksFOR INTRAMUSCULAR USE
Must only be administered by
a healthcare professional.Give once every 24 weeks.
Single-Dose Delivery System
See package insert for full prescribing information.Contents:
–One Single-Dose Vial
–One Pre-filled Syringe of Diluent (sterile water)
for Triptodur, 2 mL–Two thin-walled, 21-gauge, 1½" Needles
Reconstitute With Accompanying Diluent Before Use.
After reconstitution, ensure there are no visible
precipitates in the vial and administer immediately.Dispense the accompanying
Medication Guide to each patient.azurity ®
pharmaceuticals -
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
TRIPTODUR
triptorelin kitProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 59368-404 Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 59368-404-01 1 in 1 CARTON 09/08/2017 Quantity of Parts Part # Package Quantity Total Product Quantity Part 1 1 VIAL 2 mL Part 2 1 SYRINGE, GLASS 2 mL Part 1 of 2 TRIPTODUR
triptorelin injection, powder, lyophilized, for suspensionProduct Information Route of Administration INTRAMUSCULAR Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength TRIPTORELIN (UNII: 9081Y98W2V) (TRIPTORELIN - UNII:9081Y98W2V) TRIPTORELIN 22.5 mg in 2 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength POLY(DL-LACTIC-CO-GLYCOLIC ACID), (50:50; 12000 MW) (UNII: WE369X5600) MANNITOL (UNII: 3OWL53L36A) CARBOXYMETHYLCELLULOSE SODIUM, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: K679OBS311) POLYSORBATE 80 (UNII: 6OZP39ZG8H) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 2 mL in 1 VIAL; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA208956 09/08/2017 Part 2 of 2 DILUENT
sterile water injectionProduct Information Route of Administration INTRAMUSCULAR Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 2 mL in 1 SYRINGE, GLASS; Type 2: Prefilled Drug Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA208956 09/08/2017 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA208956 09/08/2017 Labeler - Praxis, LLC (016329513) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Praxis, LLC 016329513 manufacture(59368-404) , label(59368-404) , pack(59368-404)
Trademark Results [TRIPTODUR]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 TRIPTODUR 87000131 5351344 Live/Registered |
Debiopharm International SA 2016-04-13 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.