BRUKINSA- zanubrutinib capsule, gelatin coated
BRUKINSA by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
BRUKINSA by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by BEIGENE USA, INC., AndersonBrecon Inc., Changzhou SynTheAll Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd, Catalent CTS, LLC, Beigene (Suzhou) Co.,Ltd. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use BRUKINSA safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for BRUKINSA.
BRUKINSA™ (zanubrutinib) capsules, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2019INDICATIONS AND USAGE
BRUKINSA is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of adult patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) who have received at least one prior therapy. (1)
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on overall response rate. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Recommended dose: 160 mg orally twice daily or 320 mg orally once daily; swallow whole with water and with or without food. (2.1)
- Reduce BRUKINSA dose in patients with severe hepatic impairment. (2.2, 8.7)
- Advise patients not to open, break, or chew capsules. (2.1)
- Manage toxicity using treatment interruption, dose reduction, or discontinuation. (2.4)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Capsules: 80 mg. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Hemorrhage: Monitor for bleeding and manage appropriately. (5.1)
Infections: Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of infection, including opportunistic infections, and treat as needed. (5.2)
Cytopenias: Monitor complete blood counts during treatment. (5.3)
Second Primary Malignancies: Other malignancies have occurred in patients including skin cancers. Advise patients to use sun protection. (5.4)
Cardiac Arrhythmias: Monitor for atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter and manage appropriately. (5.5)
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Can cause fetal harm. Advise women of the potential risk to a fetus and to avoid pregnancy. (5.6)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (≥ 20%) included neutrophil count decreased, platelet count decreased, upper respiratory tract infection, white blood cell count decreased, hemoglobin decreased, rash, bruising, diarrhea and cough. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact BeiGene at 1-877-828-5596 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 11/2019
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage
2.2 Dosage Modification for Use in Hepatic Impairment
2.3 Dosage Modifications for Drug Interactions
2.4 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hemorrhage
5.2 Infections
5.3 Cytopenias
5.4 Second Primary Malignancies
5.5 Cardiac Arrhythmias
5.6 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effect of Other Drugs on BRUKINSA
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Mantle Cell Lymphoma
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
BRUKINSA is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) who have received at least one prior therapy.
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on overall response rate [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dose of BRUKINSA is 160 mg taken orally twice daily or 320 mg taken orally once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
BRUKINSA can be taken with or without food. Advise patients to swallow capsules whole with water. Advise patients not to open, break, or chew the capsules. If a dose of BRUKINSA is missed, it should be taken as soon as possible on the same day with a return to the normal schedule the following day.
2.2 Dosage Modification for Use in Hepatic Impairment
The recommended dose of BRUKINSA for patients with severe hepatic impairment is 80 mg orally twice daily [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.3 Dosage Modifications for Drug Interactions
Recommended dose modifications of BRUKINSA for drug interactions are provided in Table 1 [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Table 1: Dose Modifications for Use With CYP3A Inhibitors or Inducers Co-administered Drug Recommended BRUKINSA Dose Strong CYP3A inhibitor 80 mg once daily Interrupt dose as recommended for adverse reactions [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)]. Moderate CYP3A inhibitor 80 mg twice daily Modify dose as recommended for adverse reactions [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)]. Moderate or strong CYP3A inducer Avoid concomitant use. After discontinuation of a CYP3A inhibitor, resume previous dose of BRUKINSA [see Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.2) and Drug Interactions (7.1)].
2.4 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
Recommended dose modifications of BRUKINSA for Grade 3 or higher adverse reactions are provided in Table 2:
Table 2: Recommended Dose Modification for Adverse Reaction Event Adverse Reaction Occurrence Dose Modification (Starting Dose: 160 mg twice daily or 320 mg once daily) Grade 3 or higher non-hematological toxicities
Grade 3 febrile neutropenia
Grade 3 thrombocytopenia with significant bleeding
Grade 4 neutropenia (lasting more than 10 consecutive days)
Grade 4 thrombocytopenia (lasting more than 10 consecutive days)First Interrupt BRUKINSA Once toxicity has resolved to recovery to Grade 1 or lower or baseline: Resume at 160 mg twice daily or 320 mg once daily Second Interrupt BRUKINSA Once toxicity has resolved to recovery to Grade 1 or lower or baseline: Resume at 80 mg twice daily or 160 mg once daily Third Interrupt BRUKINSA Once toxicity has resolved to recovery to Grade 1 or lower or baseline: Resume at 80 mg once daily Fourth Discontinue BRUKINSA Asymptomatic lymphocytosis should not be regarded as an adverse reaction, and these patients should continue taking BRUKINSA.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hemorrhage
Fatal and serious hemorrhagic events have occurred in patients with hematological malignancies treated with BRUKINSA monotherapy. Grade 3 or higher bleeding events including intracranial and gastrointestinal hemorrhage, hematuria, and hemothorax have been reported in 2% of patients treated with BRUKINSA monotherapy. Bleeding events of any grade, including purpura and petechiae, occurred in 50% of patients treated with BRUKINSA monotherapy.
Bleeding events have occurred in patients with and without concomitant antiplatelet or anticoagulation therapy. Co-administration of BRUKINSA with antiplatelet or anticoagulant medications may further increase the risk of hemorrhage.
Monitor for signs and symptoms of bleeding. Discontinue BRUKINSA if intracranial hemorrhage of any grade occurs. Consider the benefit-risk of withholding BRUKINSA for 3-7 days pre- and post-surgery depending upon the type of surgery and the risk of bleeding.
5.2 Infections
Fatal and serious infections (including bacterial, viral, or fungal) and opportunistic infections have occurred in patients with hematological malignancies treated with BRUKINSA monotherapy. Grade 3 or higher infections occurred in 23% of patients treated with BRUKINSA monotherapy. The most common Grade 3 or higher infection was pneumonia. Infections due to hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation have occurred.
Consider prophylaxis for herpes simplex virus, pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia, and other infections according to standard of care in patients who are at increased risk for infections. Monitor and evaluate patients for fever or other signs and symptoms of infection and treat appropriately.
5.3 Cytopenias
Grade 3 or 4 cytopenias, including neutropenia (27%), thrombocytopenia (10%), and anemia (8%) based on laboratory measurements, were reported in patients treated with BRUKINSA monotherapy.
Monitor complete blood counts during treatment and treat using growth factor or transfusions, as needed.
5.4 Second Primary Malignancies
Second primary malignancies, including non-skin carcinoma, have occurred in 9% of patients treated with BRUKINSA monotherapy. The most frequent second primary malignancy was skin cancer (basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of skin), reported in 6% of patients. Advise patients to use sun protection.
5.5 Cardiac Arrhythmias
Atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter have occurred in 2% of patients treated with BRUKINSA monotherapy. Patients with cardiac risk factors, hypertension, and acute infections may be at increased risk. Grade 3 or higher events were reported in 0.6% of patients treated with BRUKINSA monotherapy. Monitor signs and symptoms for atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter and manage as appropriate.
5.6 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings in animals, BRUKINSA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Administration of zanubrutinib to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis caused embryo-fetal toxicity, including malformations at exposures that were 5 times higher than those reported in patients at the recommended dose of 160 mg twice daily. Advise women to avoid becoming pregnant while taking BRUKINSA and for at least 1 week after the last dose. Advise men to avoid fathering a child during treatment and for at least 1 week after the last dose. If this drug is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to a fetus [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are discussed in more detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Hemorrhage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Cytopenias [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Second Primary Malignancies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Cardiac Arrhythmias [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data in the WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS reflect exposure to BRUKINSA as a single agent at 160 mg twice daily in 524 patients in clinical trials BGB-3111-AU-003, BGB-3111-206, BGB-3111-205, BGB-3111-210, and BGB-3111-1002 and to BRUKINSA at 320 mg once daily in 105 patients in trials BGB-3111-AU-003 and BGB-3111-1002. Among 629 patients receiving BRUKINSA, 79% were exposed for 6 months or longer and 61% were exposed for greater than one year.
In this pooled safety population, the most common adverse reactions in > 10% of patients who received BRUKINSA were neutrophil count decreased (53%), platelet count decreased (39%), upper respiratory tract infection (38%), white blood cell count decreased (30%), hemoglobin decreased (29%), rash (25%), bruising (23%), diarrhea (20%), cough (20%), musculoskeletal pain (19%), pneumonia (18%), urinary tract infection (13%), hematuria (12%), fatigue (11%), constipation (11%), and hemorrhage (10%).
Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL)
The safety of BRUKINSA was evaluated in 118 patients with MCL who received at least one prior therapy in two single-arm clinical trials, BGB-3111-206 [NCT03206970] and BGB-3111-AU-003 [NCT02343120] [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. The median age of patients who received BRUKINSA in studies BGB-3111-206 and BGB-3111-AU-003 was 62 years (range: 34 to 86), 75% were male, 75% were Asian, 21% were White, and 94% had an ECOG performance status of 0 to 1. Patients had a median of 2 prior lines of therapy (range: 1 to 4). The BGB-3111-206 trial required a platelet count ≥ 75 × 109/L and an absolute neutrophil count ≥ 1 × 109/L independent of growth factor support, hepatic enzymes ≤ 2.5 × upper limit of normal, total bilirubin ≤ 1.5 × ULN. The BGB-3111-AU-003 trial required a platelet count ≥ 50 × 109/L and an absolute neutrophil count ≥ 1 × 109/L independent of growth factor support, hepatic enzymes ≤ 3 × upper limit of normal, total bilirubin ≤ 1.5 × ULN. Both trials required a CLcr ≥ 30 mL/min. Both trials excluded patients with prior allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant, exposure to a BTK inhibitor, known infection with HIV, and serologic evidence of active hepatitis B or hepatitis C infection and patients requiring strong CYP3A inhibitors or strong CYP3A inducers. Patients received BRUKINSA 160 mg twice daily or 320 mg once daily. Among patients receiving BRUKINSA, 79% were exposed for 6 months or longer and 68% were exposed for greater than one year.
Fatal events within 30 days of the last dose of BRUKINSA occurred in 8 (7%) of 118 patients with MCL. Fatal cases included pneumonia in 2 patients and cerebral hemorrhage in one patient.
Serious adverse reactions were reported in 36 patients (31%). The most frequent serious adverse reactions that occurred were pneumonia (11%), and hemorrhage (5%).
Of the 118 patients with MCL treated with BRUKINSA, 8 (7%) patients discontinued treatment due to adverse reactions in the trials. The most frequent adverse reaction leading to treatment discontinuation was pneumonia (3.4%). One (0.8%) patient experienced an adverse reaction leading to dose reduction (hepatitis B).
Table 3 summarizes the adverse reactions in BGB-3111-206 and BGB-3111-AU-003.
Table 3: Adverse Reactions (≥ 10%) in Patients Receiving BRUKINSA in BGB-3111-206 and BGB-3111-AU-003 Trials Body System Adverse Reaction Percent of Patients (N=118) All Grades
%Grade 3 or Higher % - * Upper respiratory tract infection includes upper respiratory tract infection, upper respiratory tract infection viral
- † Pneumonia includes pneumonia, pneumonia fungal, pneumonia cryptococcal, pneumonia streptococcal, atypical pneumonia, lung infection, lower respiratory tract infection, lower respiratory tract infection bacterial, lower respiratory tract infection viral
- ‡ Includes fatal adverse reaction
- § Rash includes all related terms containing rash
- ¶ Bruising includes all related terms containing bruise, bruising, contusion, ecchymosis
- # Hemorrhage includes all related terms containing hemorrhage, hematoma
- Þ Musculoskeletal pain includes musculoskeletal pain, musculoskeletal discomfort, myalgia, back pain, arthralgia, arthritis
Blood and lymphatic system disorders Neutropenia and Neutrophil count decreased 38 15 Thrombocytopenia and Platelet count decreased 27 5 Leukopenia and White blood count decreased 25 5 Anemia and Hemoglobin decreased 14 8 Infections and infestations Upper respiratory tract infection * 39 0 Pneumonia † 15 10‡ Urinary tract infection 11 0.8 Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders Rash § 36 0 Bruising ¶ 14 0 Gastrointestinal disorders Diarrhea 23 0.8 Constipation 13 0 Vascular disorders Hypertension 12 3.4 Hemorrhage # 11 3.4‡ Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders Musculoskeletal pain Þ 14 3.4 Metabolism and nutrition disorders Hypokalemia 14 1.7 Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders Cough 12 0 Other clinically significant adverse reactions that occurred in < 10% of patients with mantle cell lymphoma include major hemorrhage (defined as ≥ Grade 3 hemorrhage or CNS hemorrhage of any grade) (5%), hyperuricemia (6%) and headache (4.2%).
Table 4: Selected Laboratory Abnormalities* (> 20%) in Patients with MCL in Studies BGB-3111-206 and BGB-3111-AU-003 Laboratory Parameter Percent of Patients (N=118) All Grades (%) Grade 3 or 4 (%) - * Based on laboratory measurements.
- † Asymptomatic lymphocytosis is a known effect of BTK inhibition.
Neutrophils decreased 45 20 Platelets decreased 40 7 Hemoglobin decreased 27 6 Lymphocytosis † 41 16 Chemistry abnormalities Blood uric acid increased 29 2.6 ALT increased 28 0.9 Bilirubin increased 24 0.9 -
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effect of Other Drugs on BRUKINSA
Table 5: Drug Interactions that Affect Zanubrutinib Moderate and Strong CYP3A Inhibitors Clinical Impact - Co-administration with a moderate or strong CYP3A inhibitor increases zanubrutinib Cmax and AUC [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] which may increase the risk of BRUKINSA toxicities.
Prevention or management - Reduce BRUKINSA dosage when co-administered with moderate or strong CYP3A inhibitors [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Moderate and Strong CYP3A Inducers Clinical Impact - Co-administration with a moderate or strong CYP3A inducer decreases zanubrutinib Cmax and AUC [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] which may reduce BRUKINSA efficacy.
Prevention or management - Avoid co-administration of BRUKINSA with moderate or strong CYP3A inducers [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings in animals, BRUKINSA can cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women. There are no available data on BRUKINSA use in pregnant women to evaluate for a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. In animal reproduction studies, oral administration of zanubrutinib to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis was associated with fetal heart malformation at approximately 5-fold human exposures (see Data). Women should be advised to avoid pregnancy while taking BRUKINSA. If BRUKINSA is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking BRUKINSA, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
Embryo-fetal development toxicity studies were conducted in both rats and rabbits. Zanubrutinib was administered orally to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis at doses of 30, 75, and 150 mg/kg/day. Malformations in the heart (2- or 3-chambered hearts) were noted at all dose levels in the absence of maternal toxicity. The dose of 30 mg/kg/day is approximately 5 times the exposure (AUC) in patients receiving the recommended dose of 160 mg twice daily.
Administration of zanubrutinib to pregnant rabbits during the period of organogenesis at 30, 70, and 150 mg/kg/day resulted in post-implantation loss at the highest dose. The dose of 150 mg/kg is approximately 32 times the exposure (AUC) in patients at the recommended dose and was associated with maternal toxicity.
In a pre- and post-natal developmental toxicity study, zanubrutinib was administered orally to rats at doses of 30, 75, and 150 mg/kg/day from implantation through weaning. The offspring from the middle and high dose groups had decreased body weights preweaning, and all dose groups had adverse ocular findings (e.g. cataract, protruding eye). The dose of 30 mg/kg/day is approximately 5 times the AUC in patients receiving the recommended dose.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of zanubrutinib or its metabolites in human milk, the effects on the breastfed child, or the effects on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions from BRUKINSA in a breastfed child, advise lactating women not to breastfeed during treatment with BRUKINSA and for at least two weeks following the last dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Pregnancy Testing
Pregnancy testing is recommended for females of reproductive potential prior to initiating BRUKINSA therapy.
Contraception
Females
BRUKINSA can cause embryo-fetal harm when administered to pregnant women [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]. Advise female patients of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with BRUKINSA and for at least 1 week following the last dose of BRUKINSA. If this drug is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be informed of the potential hazard to a fetus.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 641 patients in clinical studies with BRUKINSA, 49% were ≥ 65 years of age, while 16% were ≥ 75 years of age. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between younger and older patients.
8.6 Renal Impairment
No dosage modification is recommended in patients with mild to moderate renal impairment (CLcr ≥ 30 mL/min, estimated by Cockcroft-Gault). Monitor for BRUKINSA adverse reactions in patients with severe renal impairment (CLcr < 30 mL/min) or on dialysis [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
Dosage modification of BRUKINSA is recommended in patients with severe hepatic impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. The safety of BRUKINSA has not been evaluated in patients with severe hepatic impairment. No dosage modification is recommended in patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment. Monitor for BRUKINSA adverse reactions in patients with hepatic impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
11 DESCRIPTION
BRUKINSA (zanubrutinib) is a Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor. The empirical formula of zanubrutinib is C27H29N5O3 and the chemical name is (S)-7-(1-acryloylpiperidin-4-yl)-2-(4-phenoxyphenyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydropyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-3-carboxamide. Zanubrutinib is a white to off-white powder, with a pH of 7.8 in saturated solution. The aqueous solubility of zanubrutinib is pH dependent, from very slightly soluble to practically insoluble.
The molecular weight of zanubrutinib is 471.55 Daltons.
Zanubrutinib has the following structure:
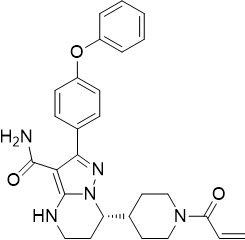
Each BRUKINSA capsule for oral administration contains 80 mg zanubrutinib and the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and sodium lauryl sulfate. The capsule shell contains edible black ink, gelatin, and titanium dioxide.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Zanubrutinib is a small-molecule inhibitor of BTK. Zanubrutinib forms a covalent bond with a cysteine residue in the BTK active site, leading to inhibition of BTK activity. BTK is a signaling molecule of the B-cell antigen receptor (BCR) and cytokine receptor pathways. In B-cells, BTK signaling results in activation of pathways necessary for B-cell proliferation, trafficking, chemotaxis, and adhesion. In nonclinical studies, zanubrutinib inhibited malignant B-cell proliferation and reduced tumor growth.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
BTK Occupancy in PBMCs and Lymph Nodes
The median steady-state BTK occupancy in peripheral blood mononuclear cells was maintained at 100% over 24 hours at a total daily dose of 320 mg in patients with B-cell malignancies. The median steady-state BTK occupancy in lymph nodes was 94% to 100% following the approved recommended dosage.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Zanubrutinib maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) and area under the plasma drug concentration over time curve (AUC) increase proportionally over a dosage range from 40 mg to 320 mg (0.13 to 1 time the recommended total daily dose). Limited systemic accumulation of zanubrutinib was observed following repeated administration.
The geometric mean (%CV) zanubrutinib steady-state daily AUC is 2,295 (37%) ng∙h/mL following 160 mg twice daily and 2,180 (41%) ng∙h/mL following 320 mg once daily. The geometric mean (%CV) zanubrutinib steady-state Cmax is 314 (46%) ng/mL following 160 mg twice daily and 543 (51%) ng/mL following 320 mg once daily.
Distribution
The geometric mean (%CV) apparent steady-state volume of distribution of zanubrutinib is 881 (95%) L. The plasma protein binding of zanubrutinib is approximately 94% and the blood-to-plasma ratio is 0.7 to 0.8.
Elimination
The mean half-life (t½) of zanubrutinib is approximately 2 to 4 hours following a single oral zanubrutinib dose of 160 mg or 320 mg. The geometric mean (%CV) apparent oral clearance (CL/F) of zanubrutinib is 182 (37%) L/h.
Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of zanubrutinib were observed based on age (19 to 90 years), sex, race (Asian, Caucasian, and Other), body weight (36 to 140 kg), or mild or moderate renal impairment (creatinine clearance [CLcr] ≥ 30 mL/min as estimated by Cockcroft-Gault). The effect of severe renal impairment (CLcr < 30 mL/min) and dialysis on zanubrutinib pharmacokinetics is unknown.
Hepatic Impairment
The total AUC of zanubrutinib increased by 11% in subjects with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class A), by 21% in subjects with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class B), and by 60% in subjects with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class C) relative to subjects with normal liver function. The unbound AUC of zanubrutinib increased by 23% in subjects with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class A), by 43% in subjects with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class B), and by 194% in subjects with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class C) relative to subjects with normal liver function.
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies and Model-Informed Approaches
CYP3A Inhibitors: Co-administration of multiple doses of CYP3A inhibitors increases zanubrutinib Cmax and AUC (Table 6).
Table 6: Observed or Predicted Increase in Zanubrutinib Exposure After Co-Administration of CYP3A Inhibitors Co-administered CYP3A Inhibitor Increase in Zanubrutinib Cmax Increase in Zanubrutinib AUC Observed Itraconazole (200 mg once daily) 157% 278% Predicted Clarithromycin (250 mg twice daily) 175% 183% Diltiazem (60 mg three times daily) 151% 157% Erythromycin (500 mg four times daily) 284% 317% Fluconazole (200 mg once daily) 179% 177% Fluconazole (400 mg once daily) 270% 284% CYP3A Inducers: Co-administration of multiple doses of rifampin (strong CYP3A inducer) decreased the zanubrutinib Cmax by 92% and AUC by 93%.
Co-administration of multiple doses of efavirenz (moderate CYP3A inducer) is predicted to decrease zanubrutinib Cmax by 58% and AUC by 60%.
CYP3A Substrates: Co-administration of multiple doses of zanubrutinib decreased midazolam (CYP3A substrate) Cmax by 30% and AUC by 47%.
CYP2C19 Substrates: Co-administration of multiple doses of zanubrutinib decreased omeprazole (CYP2C19 substrate) Cmax by 20% and AUC by 36%.
Other CYP Substrates: No clinically significant differences were observed with warfarin (CYP2C9 substrate) pharmacokinetics or predicted with rosiglitazone (CYP2C8 substrate) pharmacokinetics when co-administered with zanubrutinib.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies have not been conducted with zanubrutinib.
Zanubrutinib was not mutagenic in a bacterial mutagenicity (Ames) assay, was not clastogenic in a chromosome aberration assay in mammalian (CHO) cells, nor was it clastogenic in an in vivo bone marrow micronucleus assay in rats.
A combined male and female fertility and early embryonic development study was conducted in rats at oral zanubrutinib doses of 30 to 300 mg/kg/day. Male rats were dosed 4 weeks prior to mating and through mating and female rats were dosed 2 weeks prior to mating and to gestation day 7. No effect on male or female fertility was noted but at the highest dose tested, morphological abnormalities in sperm and increased post-implantation loss were noted. The high dose of 300 mg/kg/day is approximately 10 times the human recommended dose, based on body surface area.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Mantle Cell Lymphoma
The efficacy of BRUKINSA was assessed in BGB-3111-206 [NCT03206970], a Phase 2, open-label, multicenter, single-arm trial of 86 previously treated patients with MCL who had received at least one prior therapy. BRUKINSA was given orally at a dose of 160 mg twice daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
The median age of patients was 60.5 years (range: 34 to 75) and the majority were male (78%). The median time since diagnosis to study entry was 30 months (range: 3 to 102) and the median number of prior therapies was 2 (range: 1 to 4). The most common prior regimens were CHOP-based (91%) followed by rituximab-based (74%). The majority of patients had extranodal involvement (71%) and refractory disease (52%). Blastoid variant of MCL was present in 14% of patients. The MIPI score was low in 58%, intermediate in 29%, and high risk in 13%.
The efficacy of BRUKINSA was also assessed in BGB-3111-AU-003 [NCT02343120], a Phase 1/2, open-label, dose-escalation, global, multicenter, single-arm trial of B-cell malignancies including 32 previously treated MCL patients treated with BRUKINSA. BRUKINSA was given orally at doses of 160 mg twice daily or 320 mg daily. The median age of patients with previously treated MCL was 70 years (range: 42 to 86), and 38% of patients were ≥ 75 years old. Most patients were male (69%) and Caucasian (78%). The MIPI score was low in 28%, intermediate in 41%, and high risk in 31%.
Tumor response was according to the 2014 Lugano Classification for both studies, and the primary efficacy endpoint was overall response rate as assessed by an Independent Review Committee.
Table 7: Efficacy Results in Patients with MCL by Independent Review Committee Study BGB-3111-206
(N=86)Study BGB-3111-AU-003
(N=32)ORR: overall response rate, CR: complete response, PR: partial response, DoR: duration of response, CI: confidence interval, NE: not estimable - * FDG-PET scans were not required for response assessment
ORR (95% CI) 84% (74, 91) 84% (67, 95) CR 59% 22%* PR 24% 62% Median DoR in months (95% CI) 19.5 (16.6, NE) 18.5 (12.6, NE) - 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise patients to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Hemorrhage
Inform patients to report signs or symptoms of severe bleeding. Inform patients that BRUKINSA may need to be interrupted for major surgeries or procedures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Infections
Inform patients to report signs or symptoms suggestive of infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Cytopenias
Inform patients that they will need periodic blood tests to check blood counts during treatment with BRUKINSA [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Second Primary Malignancies
Inform patients that other malignancies have been reported in patients who have been treated with BRUKINSA, including skin cancer. Advise patients to use sun protection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Cardiac Arrhythmias
Counsel patients to report any signs of palpitations, lightheadedness, dizziness, fainting, shortness of breath, and chest discomfort [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Advise women of the potential hazard to a fetus and to avoid becoming pregnant during treatment and for at least 1 week after the last dose of BRUKINSA [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Advise males with female sexual partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during BRUKINSA treatment and for at least 1 week after the last dose of BRUKINSA [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Lactation
Advise females not to breastfeed during treatment with BRUKINSA and for at least 2 weeks after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Administration Instructions
BRUKINSA may be taken with or without food. Advise patients that BRUKINSA capsules should be swallowed whole with a glass of water, without being opened, broken, or chewed [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Missed Dose
Advise patients that if they miss a dose of BRUKINSA, they may still take it as soon as possible on the same day with a return to the normal schedule the following day [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Drug Interactions
Advise patients to inform their healthcare providers of all concomitant medications, including over-the-counter medications, vitamins, and herbal products [see Drug Interactions (7)].
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
PATIENT INFORMATION
BRUKINSA™ (BROO-kin-sah)
(zanubrutinib)
capsulesThis Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Issued: 11/2019 What is BRUKINSA? BRUKINSA is a prescription medicine used to treat adults with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) who have received at least one prior treatment for their cancer. It is not known if BRUKINSA is safe and effective in children. Before taking BRUKINSA, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you: - have bleeding problems.
- have had recent surgery or plan to have surgery. Your healthcare provider may stop BRUKINSA for any planned medical, surgical, or dental procedure.
- have an infection.
- have or had heart rhythm problems.
- have high blood pressure.
- have liver problems, including a history of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. BRUKINSA can harm your unborn baby. If you are able to become pregnant, your healthcare provider may do a pregnancy test before starting treatment with BRUKINSA.
- Females should not become pregnant during treatment and for at least 1 week after the last dose of BRUKINSA. You should use effective birth control (contraception) during treatment and for at least 1 week after the last dose of BRUKINSA.
- Males should avoid getting female partners pregnant during treatment and for at least 1 week after the last dose of BRUKINSA. You should use effective birth control (contraception) during treatment and for at least 1 week after the last dose of BRUKINSA.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if BRUKINSA passes into your breast milk. Do not breastfeed during treatment with BRUKINSA and for at least 2 weeks after your last dose of BRUKINSA.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Taking BRUKINSA with certain other medications may affect how BRUKINSA works and can cause side effects. How should I take BRUKINSA? - Take BRUKINSA exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to take it.
- Do not change your dose or stop taking BRUKINSA unless your healthcare provider tells you to.
- Your healthcare provider may tell you to decrease your dose, temporarily stop, or completely stop taking BRUKINSA if you develop certain side effects.
- Take BRUKINSA with or without food.
- Swallow BRUKINSA capsules whole with a glass of water. Do not open, break, or chew the capsules.
- If you miss a dose of BRUKINSA, take it as soon as you remember on the same day. Return to your normal schedule the next day.
What are the possible side effects of BRUKINSA? BRUKINSA may cause serious side effects, including: - Bleeding problems (hemorrhage) that can be serious and may lead to death. Your risk of bleeding may increase if you are also taking a blood thinner medicine. Tell your healthcare provider if you have any signs or symptoms of bleeding, including:
- blood in your stools or black stools (looks like tar)
- pink or brown urine
- unexpected bleeding, or bleeding that is severe or you cannot control
- vomit blood or vomit that looks like coffee grounds
- cough up blood or blood clots
- increased bruising
- dizziness
- weakness
- confusion
- changes in speech
- headache that lasts a long time
- Infections that can be serious and may lead to death. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have fever, chills, or flu-like symptoms.
- Decrease in blood cell counts. Decreased blood counts (white blood cells, platelets, and red blood cells) are common with BRUKINSA, but can also be severe. Your healthcare provider should do blood tests during treatment with BRUKINSA to check your blood counts.
- Second primary cancers. New cancers have happened in people during treatment with BRUKINSA, including cancers of the skin. Use sun protection when you are outside in sunlight.
- Heart rhythm problems (atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter). Tell your healthcare provider if you have any of the following signs or symptoms:
- your heartbeat is fast or irregular
- feel lightheaded or dizzy
- pass out (faint)
- shortness of breath
- chest discomfort
The most common side effects of BRUKINSA include: - decreased white blood cells
- decreased platelet count
- rash
- diarrhea
- upper respiratory infection
- decreased red blood cells (anemia)
- bruising
- cough
These are not all the possible side effects of BRUKINSA. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. How should I store BRUKINSA? - Store BRUKINSA capsules at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- BRUKINSA comes in a bottle with a child-resistant cap.
Keep BRUKINSA and all medicines out of the reach of children. General information about the safe and effective use of BRUKINSA. Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use BRUKINSA for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give BRUKINSA to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for more information about BRUKINSA that is written for healthcare professionals. What are the ingredients in BRUKINSA? Active ingredient: zanubrutinib Inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and sodium lauryl sulfate. Capsule shell contains edible black ink, gelatin, and titanium dioxide. Distributed and Marketed by: BeiGene USA, Inc. San Mateo, CA 94403
BRUKINSA™ is a trademark owned by BeiGene, Ltd.
© BeiGene, Ltd. 2019
For more information, go to www.BRUKINSA.com or call 1-833-969-2463. -
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 80 mg Capsule Bottle Label
NDC: 72579-011-02
Rx onlyBrukinsa™
zanubrutinib
capsules80 mg
Do not open, break or
chew the capsules120 Capsules

-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
BRUKINSA
zanubrutinib capsule, gelatin coatedProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 72579-011 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength ZANUBRUTINIB (UNII: AG9MHG098Z) (ZANUBRUTINIB - UNII:AG9MHG098Z) ZANUBRUTINIB 80 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) CROSCARMELLOSE SODIUM (UNII: M28OL1HH48) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) MICROCRYSTALLINE CELLULOSE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) SODIUM LAURYL SULFATE (UNII: 368GB5141J) GELATIN, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 2G86QN327L) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) Product Characteristics Color WHITE (white) Score no score Shape CAPSULE Size 22mm Flavor Imprint Code Zanu;80 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 72579-011-02 120 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 11/18/2019 2 NDC: 72579-011-01 60 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 11/18/2019 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA213217 11/18/2019 Labeler - Beigene Usa, Inc. (081210042)
Trademark Results [BRUKINSA]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 BRUKINSA 88129427 not registered Live/Pending |
BeiGene, Ltd. 2018-09-24 |
 BRUKINSA 88129424 not registered Live/Pending |
BeiGene, Ltd. 2018-09-24 |
 BRUKINSA 88129422 not registered Live/Pending |
BeiGene, Ltd. 2018-09-24 |
 BRUKINSA 88129418 not registered Live/Pending |
BeiGene, Ltd. 2018-09-24 |
 BRUKINSA 88124611 not registered Live/Pending |
BeiGene, Ltd. 2018-09-20 |
 BRUKINSA 88124607 not registered Live/Pending |
BeiGene, Ltd. 2018-09-20 |
 BRUKINSA 88104646 not registered Live/Pending |
BeiGene, Ltd. 2018-09-05 |
 BRUKINSA 88104645 not registered Live/Pending |
BeiGene, Ltd. 2018-09-05 |
 BRUKINSA 87609614 not registered Live/Pending |
BeiGene, Ltd. 2017-09-15 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.